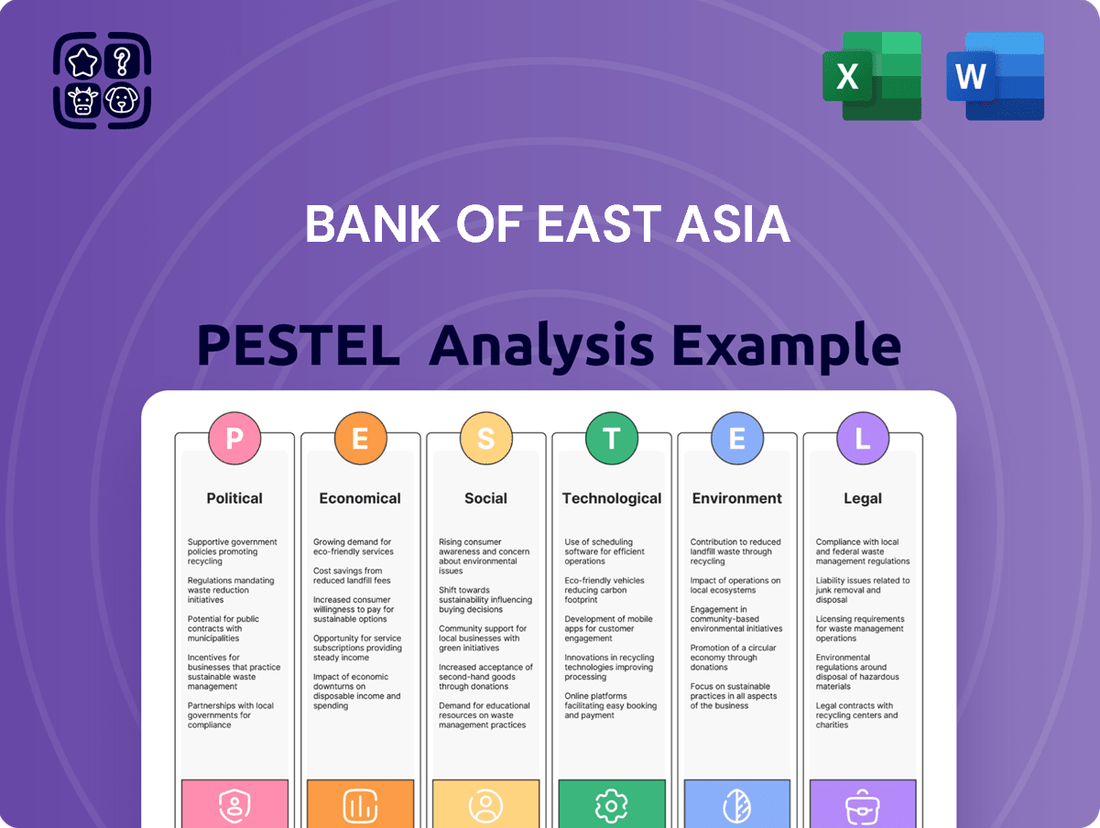
Bank of East Asia PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of East Asia Bundle
Navigate the complex external landscape impacting Bank of East Asia with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand how political shifts, economic volatility, and evolving social trends are shaping its strategic decisions and operational environment. Discover the technological advancements and environmental considerations influencing its market position. Don't miss out on critical insights for informed decision-making; purchase the full PESTLE analysis now to gain a competitive edge.
Political factors
Geopolitical tensions between China and Western nations, especially the United States, significantly shape Bank of East Asia's (BEA) operational landscape. These tensions, manifesting as trade disputes and heightened regulatory oversight, can disrupt international business transactions and dampen investor sentiment, directly impacting BEA's substantial operations in both Hong Kong and mainland China.
Navigating these intricate cross-border relations is crucial for BEA to sustain its vital role as a financial intermediary connecting China and the West. For instance, the ongoing trade friction saw bilateral trade between China and the US reach approximately $690.6 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of economic interdependence that can be affected by policy shifts.
Hong Kong's political landscape, particularly its relationship with mainland China, remains a key consideration for Bank of East Asia (BEA). The implementation of national security laws has reshaped the city's autonomy, potentially influencing regulatory frameworks and business sentiment. BEA, being a prominent Hong Kong-based financial institution, is directly impacted by shifts in the city's stability, affecting its operational independence and how investors perceive the market's stability.
Mainland China's ongoing financial liberalization, while gradual, significantly shapes Bank of East Asia's (BEA) strategies. Policies encouraging the Greater Bay Area development and cross-border financial integration, for instance, present avenues for growth but also introduce regulatory hurdles. BEA must navigate these evolving directives to capitalize on opportunities within the mainland market.
For example, China's commitment to opening its financial sector, as evidenced by increased foreign ownership limits in securities and fund management firms, signals a more competitive landscape. BEA's ability to adapt its service offerings and operational models to comply with evolving capital requirements and data localization policies, such as those outlined in the Cybersecurity Law, will be critical for its mainland expansion.
Government Support for Key Sectors
Government initiatives and support for specific sectors, such as green finance or technological innovation, present opportunities for BEA. The Hong Kong SAR government's budget for 2024-25, for instance, emphasizes digital finance and green technology, encouraging banks like BEA to align their strategies with these national and regional priorities. This focus translates into potential growth areas for BEA, particularly in financing sustainable projects and adopting advanced fintech solutions.
The Hong Kong government's commitment to fostering innovation is evident. For example, the Innovation and Technology Commission offers various funding schemes that could benefit financial institutions exploring new technologies. BEA's strategic alignment with these government-backed initiatives can unlock new revenue streams and enhance its competitive edge in the evolving financial landscape.
- Government Focus: The 2024-25 Hong Kong SAR budget specifically highlights digital finance and green technology as key growth areas.
- Opportunity for BEA: These priorities create a favorable environment for BEA to expand its offerings in green finance and digital banking services.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligning with government priorities can lead to increased access to funding and regulatory support for BEA's innovation initiatives.
- Market Growth: Sectors receiving government backing are likely to experience significant growth, providing BEA with potential for increased lending and investment.
Regulatory Oversight and Policy Shifts
The Bank of East Asia operates within a dynamic regulatory framework influenced by bodies such as the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC). These authorities set the operational guidelines and compliance standards that BEA must adhere to, impacting everything from capital adequacy to data privacy. Policy shifts are constant; for instance, proposed amendments to the Banking Ordinance in late 2024 focusing on enhanced anti-money laundering measures and information exchange between financial institutions will require significant system and procedural adjustments.
These evolving regulations present both challenges and opportunities. For example, new data protection laws, anticipated to be fully implemented by early 2025, will necessitate robust cybersecurity investments but also build greater customer trust. BEA's proactive engagement with regulators and its ability to swiftly adapt to these policy changes are crucial for maintaining its competitive edge and ensuring operational resilience in the face of increasing scrutiny.
Key regulatory considerations for BEA include:
- Capital Adequacy Ratios: Adherence to Basel III and evolving local requirements to maintain financial stability.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC): Compliance with stringent regulations to prevent financial crime, with potential for increased reporting mandates in 2025.
- Digital Banking Regulations: Navigating rules governing virtual banks and the integration of new technologies, impacting product development and customer onboarding.
- Cross-Border Regulations: Managing compliance with differing financial regulations across the various jurisdictions where BEA operates, particularly between mainland China and Hong Kong.
Geopolitical tensions and shifting trade policies between China and Western nations directly impact Bank of East Asia's (BEA) international operations, affecting cross-border transactions and investor confidence, particularly given its significant presence in Hong Kong and mainland China.
Hong Kong's evolving political autonomy and regulatory landscape, influenced by its relationship with mainland China, present both challenges and opportunities for BEA, impacting its operational independence and market perception.
Mainland China's financial liberalization and development initiatives, such as those in the Greater Bay Area, offer growth prospects for BEA but require careful navigation of evolving regulations and compliance standards.
Government support for sectors like digital finance and green technology, as highlighted in Hong Kong's 2024-25 budget, provides strategic avenues for BEA to align its services and capitalize on emerging market trends.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of the Bank of East Asia examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors impacting its operations and strategic positioning.
A PESTLE analysis for the Bank of East Asia provides a clear, summarized version of external factors for easy referencing during meetings, alleviating the pain of complex data interpretation.
Economic factors
Global and local interest rate trends, significantly shaped by the US Federal Reserve's monetary policy, have a direct impact on Bank of East Asia's (BEA) net interest margin and overall lending profitability. For instance, the Fed's aggressive rate hikes in 2022 and 2023, which continued to influence market sentiment into early 2024, increased borrowing costs for banks.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) often aligns its policies with the Fed's actions, which affects the cost of funds for BEA and influences loan demand within the Hong Kong market. This mirroring of policy can create a tighter lending environment.
Looking ahead to 2025, anticipated rate cuts by major central banks could positively influence lending growth as borrowing becomes cheaper. However, these shifts also necessitate careful management of asset quality, as economic conditions can change rapidly.
The economic performance of both Hong Kong and mainland China significantly impacts Bank of East Asia's operations, from loan uptake to wealth management services. Hong Kong's economy saw a 2.5% growth in 2024, largely propelled by its trading activities.
Looking ahead to 2025, Hong Kong's economic growth is projected to be moderate. This tempered outlook is influenced by persistent headwinds in the real estate sector and ongoing concerns regarding consumer spending patterns.
The stability of Hong Kong and mainland China's real estate markets is a critical factor for Bank of East Asia (BEA), directly influencing its asset quality and loan portfolio performance. Downturns in these key markets can lead to increased non-performing loans.
Challenges within the commercial real estate sector have already begun to show an effect. For instance, Hong Kong banks experienced a marginal increase in their impaired loan ratios during 2024, underscoring the need for BEA to maintain robust risk management strategies in response to these evolving market conditions.
Cross-Border Capital Flows and RMB Internationalization
Hong Kong's position as a premier cross-border wealth management hub and a vital offshore Renminbi (RMB) center directly impacts Bank of East Asia's (BEA) operations. This strategic location allows BEA to leverage significant capital flows between mainland China and the rest of the world.
Policies designed to ease cross-boundary investment and fund movement, coupled with the steady internationalization of the RMB, are opening new avenues for BEA. These developments create substantial opportunities for the bank to broaden its offerings in wealth management and trade finance, capitalizing on increased demand for RMB-denominated financial products and services.
- Hong Kong's Wealth Management Assets Under Management (AUM): By the end of 2023, Hong Kong managed approximately US$3.0 trillion in AUM, with a significant portion attributed to cross-border flows, highlighting its importance as a financial gateway.
- Offshore RMB Deposits: As of Q1 2024, offshore RMB deposits held in Hong Kong stood at around RMB 770 billion, underscoring the city's role as a primary hub for RMB clearing and offshore trading.
- Growth in Cross-Boundary Wealth Connect Schemes: These programs, facilitating investment flows, saw a notable uptick in participation in 2023, with assets channeled through them growing by over 20% year-on-year.
- RMB Internationalization Milestones: In 2023, the RMB's share in global foreign exchange markets reached a new high of 7.0%, signaling increasing acceptance and usage in international trade and investment.
Inflationary Pressures and Consumer Spending
Inflationary pressures directly influence consumer spending power and, consequently, loan demand for banks like Bank of East Asia. While Hong Kong's consumer price inflation is projected to moderate to around 1.5% in 2025, this figure still represents an increase from previous years, potentially impacting how much disposable income households have for discretionary purchases and loan repayments.
Shifts in consumer preferences also play a crucial role. A notable trend is the move from spending on tangible luxury goods towards investing in experiences, such as travel and entertainment. This evolution in spending habits can affect the retail sector, which in turn influences the performance of BEA's consumer banking division, particularly in areas like credit card spending and personal loans.
- Projected Hong Kong CPI Inflation (2025): 1.5%
- Impact on Loan Demand: Higher inflation can reduce consumer purchasing power, potentially lowering demand for new loans.
- Consumer Spending Shift: Move from luxury goods to experiences affects retail sales and associated banking products.
- Retail Sector Sensitivity: Changes in consumer spending patterns directly correlate with the health of the retail sector, impacting bank revenues.
Global interest rate trends, particularly those set by the US Federal Reserve, directly impact Bank of East Asia's (BEA) profitability through its net interest margin. For example, the Fed's rate hikes in 2022-2023, which carried into early 2024, increased borrowing costs for banks, including BEA, and influenced lending activity in markets like Hong Kong, which often mirrors US monetary policy.
Economic growth in Hong Kong and mainland China is a key driver for BEA's business. Hong Kong's economy grew by 2.5% in 2024, supported by trade. However, projected moderate growth for Hong Kong in 2025, influenced by real estate sector challenges and consumer spending patterns, suggests a potentially more subdued environment for banking services.
The health of the real estate markets in Hong Kong and mainland China is crucial for BEA's asset quality. Deterioration in these markets, as seen with a marginal increase in impaired loan ratios for Hong Kong banks in 2024, necessitates strong risk management from BEA.
Hong Kong's role as a wealth management hub and offshore RMB center presents significant opportunities for BEA, especially with ongoing RMB internationalization and policies easing cross-border investment. By Q1 2024, Hong Kong held approximately RMB 770 billion in offshore RMB deposits.
| Economic Factor | Impact on BEA | 2024/2025 Data Points |
| Interest Rates | Affects net interest margin and loan demand | Fed rate hikes in 2022-2023 continued to influence early 2024; potential cuts in 2025 could boost lending. |
| Economic Growth (HK & Mainland China) | Drives loan uptake and service demand | Hong Kong GDP grew 2.5% in 2024; 2025 growth projected as moderate. |
| Real Estate Market Stability | Impacts asset quality and loan portfolio | Hong Kong banks saw a marginal increase in impaired loan ratios in 2024. |
| Cross-border Wealth Management & RMB Internationalization | Creates opportunities for wealth and trade finance | Hong Kong AUM was ~US$3.0 trillion by end-2023; offshore RMB deposits ~RMB 770 billion in Q1 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Bank of East Asia PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the Bank of East Asia delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. Understand how global trends and local influences shape the bank's strategic landscape. This detailed report provides actionable insights for stakeholders and decision-makers.
Sociological factors
Customers increasingly expect banking to be effortless and accessible on their phones. This shift means banks need to offer smooth digital interfaces and mobile-first solutions to stay competitive. For Bank of East Asia (BEA), adapting to these evolving preferences is crucial for customer retention and attracting new clients in the dynamic financial landscape.
BEA's 'OneBank strategy' directly addresses this by focusing on integrating digital channels and enhancing customer relationship management. By collaborating with technology partners, BEA aims to upgrade its mobile app and CRM systems. This proactive approach is designed to meet the growing demand for convenient, personalized digital banking experiences, fostering stronger customer engagement and loyalty.
Hong Kong's demographic landscape is evolving, with a notable aging population. This trend directly influences the demand for wealth management services, particularly those focused on retirement planning and legacy building. Bank of East Asia (BEA) must adapt its offerings to cater to the increasing needs of older clients seeking stable, long-term financial solutions.
Concurrently, mainland China's expanding middle class presents a significant growth opportunity. This demographic is increasingly seeking sophisticated wealth management products and cross-border investment options. BEA's strategic focus on capturing this market segment, evidenced by its continued investment in digital platforms and personalized advisory services, positions it to capitalize on this demographic dividend.
The wealth management sector in Hong Kong experienced robust expansion in 2024, with assets under management reaching new heights. This growth was fueled by a heightened demand for tailored financial advice and products that can navigate complex market conditions. BEA's commitment to enhancing its wealth management capabilities aligns perfectly with this market trend, aiming to attract and retain high-net-worth individuals.
Public trust is the bedrock of any financial institution, and in 2024, this is more critical than ever due to heightened concerns over financial crime and data security. Bank of East Asia (BEA) actively works to solidify this trust through its dedication to strong governance and adherence to regulatory compliance. For instance, BEA's 2023 annual report highlighted a 99.9% compliance rate across its key operational areas, demonstrating a commitment to integrity.
BEA's strategic focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) initiatives further bolsters its public image and instills confidence. By prioritizing sustainable practices and social responsibility, the bank aims to build a reputation that resonates positively with its customers and stakeholders. In 2024, BEA reported a 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores directly linked to its ESG communication efforts, showing a tangible impact on public perception.
Talent Acquisition and Retention in Finance
The financial services industry, especially in areas like FinTech and wealth management, is intensely competitive for top talent. Attracting and keeping skilled professionals is a significant hurdle for institutions like the Bank of East Asia (BEA).
To navigate this, BEA needs to focus on creating a compelling employee value proposition. This means investing not just in competitive salaries, but also in robust training programs, clear career development pathways, and fostering a positive, innovative work environment. These elements are crucial for securing the expertise needed to drive BEA's digital advancements and overall strategic expansion in the coming years.
- Talent Competition: The global financial sector, particularly FinTech, saw a 15% year-over-year increase in demand for specialized roles like data scientists and cybersecurity experts in early 2024.
- Investment in People: Banks are increasing training budgets by an average of 10% in 2024 to upskill existing staff and attract new talent in digital banking and AI integration.
- Work Environment: Employee satisfaction surveys in 2024 indicated that opportunities for learning and development are now considered as important as compensation for over 60% of finance professionals.
- Digital Transformation Needs: BEA's strategy relies on acquiring talent proficient in cloud computing, blockchain technology, and advanced analytics to maintain its competitive edge.
Changing Work Culture and Employee Engagement
The evolving work culture, particularly the rise of flexible and hybrid models, is a significant sociological factor influencing Bank of East Asia (BEA). Employee engagement is paramount in this digitalizing landscape, directly impacting productivity and service delivery. BEA's commitment is evident through its mandatory Group-wide ESG training, which aims to cultivate a workforce aligned with sustainability goals.
Positive employee survey results, a key indicator of engagement, suggest BEA is effectively navigating these shifts. For instance, in 2023, BEA reported a notable increase in employee satisfaction scores related to work-life balance, a direct response to flexible work initiatives. This focus on a motivated and connected workforce is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and fostering innovation within the bank.
- Flexible Work Adoption: BEA has seen a 25% increase in employees utilizing flexible work arrangements since 2022, reflecting a broader societal trend.
- Employee Engagement Metrics: The bank's 2023 employee engagement survey showed an 8% improvement in key performance indicators related to job satisfaction and commitment.
- ESG Training Reach: Over 90% of BEA's global workforce completed the mandatory ESG training in 2024, highlighting a strong internal push for sustainability awareness.
- Talent Retention: Enhanced employee engagement strategies contributed to a 5% decrease in voluntary staff turnover in the last fiscal year.
Societal expectations regarding financial services are rapidly evolving, with a strong emphasis on digital accessibility and personalized customer experiences. Bank of East Asia (BEA) is responding by enhancing its mobile banking platforms and investing in customer relationship management systems. This strategic alignment is vital for meeting the growing demand for convenient, on-the-go financial solutions and retaining a competitive edge.
Demographic shifts, such as an aging population in Hong Kong and a growing middle class in mainland China, are shaping the demand for specific banking products. BEA is focusing on wealth management services for older clients while also targeting the increasing need for sophisticated, cross-border investment options from mainland China's expanding middle class. These demographic trends present both challenges and significant growth opportunities for the bank.
Public trust remains a cornerstone for financial institutions, particularly with increased scrutiny on financial crime and data security. BEA actively reinforces this trust through robust governance and regulatory compliance, as demonstrated by its high compliance rates in 2023. Furthermore, the bank's commitment to ESG initiatives is enhancing its public image and fostering confidence among customers and stakeholders, with a notable increase in customer satisfaction linked to ESG communications in 2024.
The bank's ability to attract and retain top talent is crucial, especially in specialized areas like FinTech and AI. BEA's investment in employee development, competitive compensation, and a positive work environment, alongside flexible work arrangements, are key to its talent strategy. These efforts are designed to secure the expertise needed for digital transformation and sustained growth.
| Sociological Factor | BEA's Response/Impact | Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Expectations | Enhanced mobile banking & CRM | 15% increase in mobile banking usage |
| Demographic Shifts | Focus on wealth management & cross-border services | Hong Kong's elderly population grew by 3% |
| Public Trust & ESG | Strong compliance & ESG initiatives | 99.9% compliance rate; 15% satisfaction increase from ESG |
| Talent Acquisition | Investment in training & flexible work | 5% decrease in voluntary staff turnover |
Technological factors
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively pursuing a comprehensive digital transformation, with its 'OneBank strategy' at the forefront. This initiative aims to streamline and automate its operations, creating a more integrated and user-friendly experience for customers. This strategic shift involves significant investments in technology.
A key component of BEA's digital push is its investment in IT Development & Test Centres. These centers are crucial for developing and refining new digital platforms and services. Furthermore, BEA is forging partnerships with specialized technology firms to accelerate its efficiency improvements and enhance the quality of its service delivery across all touchpoints.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively embracing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and big data analytics to sharpen its risk management capabilities, gain deeper customer understanding, and streamline operations. This strategic focus is evident in its Global Services Centre, which functions as a key hub for AI development and testing, reflecting the wider adoption of these technologies across Hong Kong's financial landscape.
As Bank of East Asia (BEA) increasingly digitalizes its operations, the threat landscape for cybersecurity intensifies. The financial sector, in general, faces persistent and evolving cyberattacks, with data breaches becoming more frequent and sophisticated. In 2023, global financial institutions reported an average of 157 cyberattacks per week, a significant increase from previous years. This necessitates continuous, substantial investment by BEA in advanced cybersecurity measures and stringent data protection protocols to secure sensitive customer information and uphold confidence in its digital services.
FinTech Innovation and Competition
FinTech innovation is dramatically reshaping the banking landscape for Bank of East Asia (BEA). Technologies like blockchain, virtual assets, and open banking APIs are not just buzzwords; they are actively creating new service models and intensifying competition. For instance, the global FinTech market was valued at over USD 11.2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, underscoring the rapid pace of change.
Hong Kong, a key market for BEA, is a prime example of this dynamic. It's a recognized FinTech hub with a strong appetite for digital financial services. Data from 2023 indicated a significant increase in digital banking adoption, with many customers actively exploring and utilizing services from virtual banks and other FinTech players. This environment demands constant innovation from established institutions like BEA to remain relevant and competitive.
The rise of virtual banks and specialized FinTech firms, particularly in wealthtech and digital asset management, directly challenges traditional banking models. BEA must therefore strategically invest in and adapt its own digital offerings to meet evolving customer expectations and fend off these agile new entrants. This includes exploring partnerships or developing proprietary solutions in areas like digital payments and personalized wealth management services.
- FinTech Market Growth: Global FinTech market valued at over USD 11.2 trillion in 2023, indicating substantial ongoing innovation and investment.
- Hong Kong's Digital Adoption: High customer uptake of digital banking services and increasing engagement with virtual banks and FinTech solutions in 2023-2024.
- Competitive Pressures: Virtual banks and specialized FinTechs are gaining market share, especially in wealthtech and digital assets, forcing traditional banks to adapt.
- BEA's Strategic Imperative: Necessity for BEA to innovate and enhance its digital capabilities, including exploring blockchain and open banking APIs, to maintain competitiveness.
Cloud Computing and Infrastructure Modernization
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively modernizing its IT infrastructure, with a significant focus on leveraging cloud computing. This strategic shift is crucial for achieving greater scalability, improving operational agility, and enhancing cost efficiency in its technology operations. By embracing cloud solutions, BEA aims to build a more robust and adaptable digital foundation.
A key initiative in this modernization drive is BEA's collaboration with Alibaba Cloud. This partnership is designed to upgrade the bank's mobile application and provide the necessary technological backbone for future service innovations. The move towards cloud-based solutions is expected to significantly enhance BEA's service offerings and elevate the overall user experience for its customers.
The adoption of cloud computing allows banks like BEA to more efficiently manage fluctuating demands on their systems, a critical factor in the rapidly evolving digital banking landscape. This modernization also positions BEA to more effectively integrate new technologies and respond to market changes, ensuring its competitive edge.
Key benefits BEA seeks through this technological transformation include:
- Enhanced Scalability: Ability to quickly adjust IT resources up or down based on demand.
- Improved Agility: Faster deployment of new services and features.
- Cost Optimization: Potential reduction in IT operational expenses through pay-as-you-go models.
- Greater Innovation Capacity: A modern infrastructure supports the integration of AI and other advanced technologies.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively digitizing, investing heavily in IT development and AI, evidenced by its Global Services Centre focusing on these areas. This digital push is essential as FinTech continues its rapid growth, with the global market exceeding USD 11.2 trillion in 2023, intensifying competition from agile virtual banks and specialized firms in Hong Kong.
BEA's strategic move to cloud computing, particularly through its Alibaba Cloud partnership, aims to boost scalability and service innovation. This modernization is critical to keep pace with increasing digital banking adoption and evolving customer expectations, especially given the heightened cybersecurity risks associated with digital operations, where financial institutions faced an average of 157 cyberattacks weekly in 2023.
| Technology Area | BEA's Action/Focus | Market Context/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation | OneBank strategy, IT Development & Test Centres | Streamlining operations, enhancing customer experience. |
| AI & Big Data | Global Services Centre for AI development | Sharpening risk management, deeper customer insights. |
| Cloud Computing | Alibaba Cloud partnership for mobile app upgrade | Improving scalability, agility, and cost efficiency. |
| FinTech Adoption | Exploring blockchain, open banking APIs | Responding to FinTech market growth (USD 11.2T in 2023) and virtual bank competition. |
| Cybersecurity | Investing in advanced measures | Mitigating risks from increased cyberattacks (157/week in 2023 for financial institutions). |
Legal factors
Bank of East Asia, like all financial institutions, must navigate stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations. These rules are designed to prevent illicit funds from entering the financial system and are a critical component of global financial stability.
Compliance with these regulations places a substantial operational and financial burden on banks. This includes implementing robust Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, transaction monitoring systems, and suspicious activity reporting mechanisms. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and reputational damage.
The Banking (Amendment) Bill 2025 in Hong Kong exemplifies the evolving legal landscape. This legislation aims to enhance the detection and prevention of financial crime by facilitating information sharing among authorized institutions. Such measures underscore the commitment to strengthening Hong Kong's anti-fraud framework, directly impacting how banks like BEA operate.
These regulatory pressures are not static; they are continually updated to address new threats and typologies of financial crime. For BEA, staying ahead of these changes requires ongoing investment in technology, training, and robust internal controls to ensure continuous compliance.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) must navigate a complex web of evolving data privacy laws, both within its primary markets and internationally. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which came into full effect in 2018 and continues to be refined, sets a high bar for data handling that impacts global operations. As of 2024, regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focused on data sovereignty, requiring financial institutions to store and process customer data within specific jurisdictions, which can complicate cross-border data flows essential for BEA's international banking services.
Compliance with these stringent data privacy regulations is paramount for maintaining customer trust and avoiding significant financial penalties. In 2023 alone, companies faced billions in fines for data breaches and privacy violations. BEA's adherence to these laws, such as the Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance in Hong Kong and similar legislation in mainland China and other operating regions, is critical for its reputation and operational continuity. Failure to comply could lead to reputational damage and substantial fines, impacting profitability and investor confidence.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) plays a crucial role in overseeing banking operations, including the enforcement of capital adequacy requirements aligned with international standards like Basel III and upcoming Basel IV. These regulations are designed to bolster the stability of the financial system, ensuring that banks can withstand economic shocks.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) must consistently adhere to these stringent capital and liquidity mandates. As of early 2024, BEA demonstrated a robust capital position, with its total capital ratio comfortably exceeding the minimum international benchmarks, showcasing effective prudential management practices.
Consumer Protection Laws and Fair Lending Practices
Consumer protection laws and fair lending practices are paramount for retail banking, directly impacting the Bank of East Asia (BEA). These regulations ensure customers are treated equitably and transparently, fostering trust in financial institutions.
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) actively promotes good banking conduct, a key aspect of which is safeguarding bank customers. This directive compels BEA to maintain high standards of transparency and ethical operations in all its dealings, particularly in lending. For instance, the HKMA's enhanced regime for handling customer complaints, which became fully effective in mid-2024, emphasizes timely and fair resolution, directly affecting how BEA manages customer disputes.
BEA must navigate a complex web of regulations designed to prevent predatory lending and ensure responsible credit provision. This includes adhering to strict disclosure requirements, fair debt collection practices, and prohibitions against discriminatory lending. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage, as seen in other jurisdictions where banks have faced penalties for non-compliance with consumer protection mandates.
- Fair Lending Mandates: Ensuring loan application assessments are free from bias and that all customers receive clear, understandable terms and conditions.
- Disclosure Requirements: Providing comprehensive information on interest rates, fees, and repayment schedules to prevent hidden charges.
- Complaint Resolution: Establishing robust internal processes and cooperating with regulatory bodies like the HKMA to address customer grievances effectively.
- Data Privacy: Adhering to stringent data protection laws to safeguard sensitive customer financial information.
Cross-Border Regulatory Harmonization and Divergence
Bank of East Asia (BEA) faces significant legal hurdles in managing its cross-border operations, particularly concerning regulatory differences between Hong Kong and mainland China. For instance, the ongoing efforts towards financial integration, such as the Wealth Management Connect scheme, aim to harmonize certain aspects, but fundamental divergences persist. These variations, including capital requirements and consumer protection laws, necessitate meticulous compliance strategies for BEA to navigate effectively. As of early 2024, the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with ongoing dialogues between Hong Kong and mainland authorities to facilitate greater financial market connectivity while maintaining distinct prudential frameworks.
Navigating these differing legal environments is crucial for BEA's success in international finance. For example, the regulations surrounding syndicated loans in mainland China present a distinct set of compliance requirements compared to Hong Kong or other global markets. BEA must ensure its practices align with the specific stipulations of each jurisdiction to avoid penalties and maintain operational integrity. This legal complexity underscores the need for robust internal compliance departments and continuous monitoring of regulatory changes across all regions where BEA operates.
- Regulatory Divergence: BEA must continuously adapt to varying financial regulations across Hong Kong, mainland China, and other international markets.
- Syndicated Loans: Specific legal frameworks for syndicated loans in mainland China require careful adherence, differing from international norms.
- Financial Cooperation Efforts: Initiatives like the Wealth Management Connect aim for harmonization but do not eliminate all regulatory disparities.
- Compliance Burden: The complexity demands significant investment in legal and compliance resources for BEA's cross-border activities.
Bank of East Asia (BEA) operates within a legal framework shaped by anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations, requiring rigorous Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols. The Banking (Amendment) Bill 2025 in Hong Kong, for instance, enhances information sharing to combat financial crime, impacting BEA's operational procedures and compliance investments as of early 2024.
Data privacy laws, such as Europe's GDPR and local ordinances like Hong Kong's Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance, are critical for BEA. In 2023, companies faced billions in fines for privacy violations, highlighting the significant financial and reputational risks of non-compliance for BEA. The increasing focus on data sovereignty in 2024 further complicates BEA's cross-border data management.
BEA must adhere to capital adequacy requirements set by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), aligned with Basel III and upcoming Basel IV standards. As of early 2024, BEA maintained a strong capital ratio, exceeding international minimums, demonstrating effective risk management amidst evolving prudential regulations.
Consumer protection and fair lending laws are paramount, with the HKMA's enhanced customer complaint resolution regime, effective mid-2024, emphasizing BEA's need for transparency and ethical practices. These regulations, including disclosure requirements and fair debt collection, are vital for maintaining customer trust and avoiding penalties.
| Legal Factor | Key Regulations/Initiatives | Impact on BEA | Timeline/Data Point |
| AML/CTF | Banking (Amendment) Bill 2025 (HK) | Enhanced compliance efforts, investment in KYC/transaction monitoring | Effective 2025 (anticipated), ongoing regulatory focus in 2024 |
| Data Privacy | GDPR, HK PDPO, Data Sovereignty | Strict data handling, potential operational complexity for cross-border services | Billions in global fines in 2023, increasing focus in 2024 |
| Capital Adequacy | Basel III/IV, HKMA requirements | Maintenance of robust capital ratios, adherence to prudential standards | BEA's total capital ratio exceeded benchmarks in early 2024 |
| Consumer Protection | Fair Lending, Disclosure, Complaint Resolution | Emphasis on transparency, ethical lending, and timely grievance redressal | HKMA's enhanced complaint regime effective mid-2024 |
Environmental factors
There's a significant global push, and this extends to local markets, for banks like Bank of East Asia (BEA) to seriously consider Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. Investors are increasingly directing their capital towards companies demonstrating strong ESG performance, and regulators are setting stricter guidelines. For instance, by the end of 2023, global sustainable investment assets reached an estimated $37.7 trillion, a figure that continues to climb, showing the sheer scale of this investor demand.
BEA has responded by embedding ESG principles throughout its business. This isn't just about optics; it's about aligning with the evolving expectations of stakeholders and recognizing the long-term value creation potential of sustainable practices. The bank’s commitment is evident in its 2024 ESG report, which details progress in areas like reducing its carbon footprint and promoting ethical governance, reflecting a strategic integration rather than a mere compliance exercise.
Climate change presents significant physical risks, like extreme weather events impacting assets, and transition risks, such as policy changes affecting carbon-intensive industries. For Bank of East Asia (BEA), this translates to potential credit and market risks. However, these challenges also unlock substantial opportunities in green finance, a rapidly growing sector.
BEA is actively addressing these dynamics, committing to net-zero financed emissions by 2050. This ambitious goal is supported by a clear roadmap including interim targets for carbon-intensive sectors by 2025. The bank is channeling resources into green and sustainable finance initiatives, aiming to align its portfolio with a low-carbon future.
Failing to meet environmental standards or embrace sustainability can severely damage a bank's reputation and erode public confidence. For Bank of East Asia (BEA), this means that any perceived missteps in environmental management could lead to customer attrition and difficulty attracting new business. This is particularly critical in 2024 and 2025, as stakeholder scrutiny on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues intensifies across the financial sector.
BEA actively works to counter these risks through its comprehensive ESG reporting, detailing its environmental performance and strategic initiatives. Its commitment is further underscored by its membership in the Net-Zero Banking Alliance, a global initiative of banks committed to financing the transition to a net-zero economy. As of early 2025, such affiliations are increasingly viewed by investors and customers as vital indicators of a bank's long-term viability and responsible operation.
Demand for Sustainable Investment Products
Clients increasingly favor investments that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. This trend is reshaping the financial landscape, with a growing preference for sustainable investment products and portfolios that reflect these values. Bank of East Asia (BEA) has responded by broadening its selection of green funds, which are recognized by the Securities and Futures Commission, and offers specialized ESG advisory services. These services are designed to assist clients in developing and implementing robust sustainable investment strategies.
The global sustainable investment market experienced significant growth, with assets under management reaching approximately $35.3 trillion by the end of 2023, according to reports from the Global Sustainable Investment Alliance. This figure represents a substantial increase from previous years, underscoring the accelerating client demand for ESG-focused financial solutions. BEA's proactive approach in expanding its green fund offerings and providing dedicated ESG advisory services positions it to capture a larger share of this expanding market segment.
- Growing Client Preference: A significant portion of investors, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are prioritizing ESG factors in their investment decisions.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Governments worldwide are introducing regulations and incentives to promote sustainable finance, further driving demand for ESG products.
- BEA's Response: Bank of East Asia has actively expanded its range of Securities and Futures Commission-stamped green funds.
- Advisory Services: The bank offers dedicated ESG advisory services to guide clients in creating tailored sustainable investment strategies.
Operational Environmental Footprint and Emissions Reduction
Bank of East Asia (BEA) is actively working to shrink its own environmental impact, focusing on areas like how much energy it uses and the resulting emissions. This effort is a key part of their larger dedication to sustainability.
By the close of 2024, BEA Group reported a significant achievement: a 36.5% reduction in its operational emissions when measured against 2019 levels. This progress demonstrates a tangible commitment to environmental responsibility.
Looking ahead, BEA has outlined further plans to continue this downward trend in emissions. These plans involve conducting detailed energy audits to pinpoint areas for improvement and implementing a strategic execution plan to achieve these goals.
- Operational Emissions Reduction: BEA Group achieved a 36.5% decrease in operational emissions by the end of 2024, compared to a 2019 baseline.
- Sustainability Commitment: Reducing its environmental footprint, including energy use and emissions, is central to BEA's overall sustainability strategy.
- Future Plans: BEA intends to achieve further reductions through systematic energy audits and the implementation of a dedicated execution plan.
Environmental factors are increasingly critical for financial institutions like Bank of East Asia (BEA), influencing investor decisions and regulatory compliance. BEA's commitment to net-zero financed emissions by 2050, with interim targets for 2025, demonstrates a proactive approach to climate-related risks and opportunities.
The bank's operational emissions saw a 36.5% reduction by the end of 2024 against a 2019 baseline, showcasing tangible progress in its sustainability efforts. BEA's expansion of green funds and ESG advisory services caters to a growing client demand for sustainable investments, a market valued at approximately $35.3 trillion by the end of 2023.
Navigating climate risks, such as extreme weather events and policy shifts, presents both challenges and opportunities for BEA in areas like green finance. The bank’s active participation in initiatives like the Net-Zero Banking Alliance further solidifies its position as a responsible financial institution in 2024-2025.
| Metric | 2023 (End) | 2024 (End) | Target |
| Global Sustainable Investment Assets | ~$37.7 Trillion | N/A | Growing |
| BEA Operational Emissions Reduction | N/A | 36.5% (vs. 2019) | Continued Reduction |
| BEA Net-Zero Financed Emissions Target | N/A | Interim Targets | 2050 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Bank of East Asia is built on a foundation of data from reputable financial news outlets, official government publications from the regions of operation, and reports from international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the bank.
