BCE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BCE Bundle
BCE's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the telecommunications industry effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore BCE’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bell Canada Enterprises (BCE) faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to a concentrated market for specialized network infrastructure. Key suppliers for advanced technologies like 5G equipment and fiber optic cables are few, granting them considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, the global market for 5G infrastructure equipment remained dominated by a handful of major players, limiting BCE's options and negotiation flexibility.
The high switching costs associated with integrating new network technologies further bolster supplier leverage. Replacing complex, deeply embedded systems requires substantial investment in new hardware, software, and retraining, making it economically challenging for BCE to change suppliers frequently. This dependency means suppliers can often dictate terms and pricing, impacting BCE's operational costs and capital expenditures.
BCE's significant investment in proprietary network infrastructure and specialized telecommunications equipment creates substantial switching costs. For instance, upgrading or replacing core network components from a single vendor involves not just the purchase price of new hardware but also the complex and time-consuming process of system integration and employee retraining. This deep integration means that if a supplier were to significantly increase prices or reduce service quality, BCE would face considerable financial and operational hurdles in finding and implementing an alternative solution.
Many critical components and software for telecommunications networks are protected by patents and proprietary technologies held by a few dominant suppliers. This intellectual property significantly strengthens their bargaining position, as BCE often has no viable alternatives for these essential innovations.
For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications equipment market saw continued consolidation, with a handful of companies holding key patents for 5G infrastructure and advanced network management software. This concentration means BCE must negotiate with these specialized providers, who can leverage their exclusive rights to dictate pricing and terms.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The bargaining power of suppliers for BCE can be significantly influenced by their ability to forward integrate. While uncommon in the telecommunications sector, a supplier of critical network technology, such as advanced fiber optic cable or 5G infrastructure components, could theoretically leverage their expertise to offer telecommunication services directly to consumers. This would represent a substantial shift, turning a supplier into a direct competitor.
Such a move, though posing high entry barriers for most equipment manufacturers due to regulatory hurdles and capital requirements, would dramatically increase their leverage. For instance, if a dominant provider of specialized network switching equipment decided to enter the retail service market, BCE would face direct competition from a company intimately familiar with its core infrastructure. This scenario, while hypothetical, underscores the potential for suppliers to gain considerable power by becoming direct service providers.
Consider the implications for BCE's cost structure and competitive positioning. If a key supplier were to integrate forward, they could potentially dictate terms more aggressively, knowing they offer an alternative service. This threat, even if remote, necessitates ongoing monitoring of supplier capabilities and market strategies. For example, in 2024, the telecommunications equipment market saw continued consolidation, with companies like Nokia and Ericsson investing heavily in R&D for future network technologies, hinting at their potential to expand service offerings.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: The potential for a key technology supplier to directly enter the telecommunications service market, thereby becoming a competitor.
- High Entry Barriers: Significant regulatory, capital, and technical challenges generally prevent equipment manufacturers from easily becoming direct service providers.
- Impact on BCE: A supplier's forward integration could lead to increased cost pressure and altered competitive dynamics for BCE.
- Market Trends: Ongoing R&D investments by major equipment suppliers in advanced network technologies in 2024 suggest a continuous evolution of their strategic capabilities.
Importance of Supplier's Input to BCE's Quality
The quality and reliability of BCE's services are intrinsically linked to the performance of the equipment and technology sourced from its suppliers. Any lapse in supplier quality can significantly affect customer satisfaction and network performance, increasing BCE's dependence on these providers to uphold its service standards.
In 2024, BCE continued to invest heavily in network upgrades, with a significant portion of its capital expenditures directed towards acquiring advanced telecommunications equipment. For instance, BCE's 2024 capital expenditure was projected to be around $5.0 billion, with a substantial portion allocated to network modernization, which relies on specialized components from a limited number of global suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: BCE's reliance on a select group of technology providers for its core infrastructure, such as fiber optic cables and advanced network switching equipment, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power.
- Criticality of Inputs: The performance and innovation of BCE's telecommunications services are directly tied to the quality and technological advancement of the components supplied.
- Impact of Disruption: A disruption in the supply chain or a decline in the quality of critical components from key suppliers could lead to significant service degradation, impacting BCE's reputation and revenue.
- Market Concentration: The telecommunications equipment market is characterized by a high degree of concentration, with a few dominant players supplying the most advanced and essential technologies, further amplifying supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bell Canada Enterprises (BCE) is substantial, driven by market concentration and high switching costs for specialized telecommunications equipment. Key suppliers for advanced technologies like 5G infrastructure and fiber optics are limited, giving them significant leverage. For example, in 2024, a few major global players continued to dominate the 5G equipment market, restricting BCE's negotiation options.
BCE's deep integration with proprietary network technologies means switching suppliers is costly and complex, involving hardware, software, and retraining expenses. This dependency allows suppliers to influence pricing and terms, impacting BCE's capital expenditures. In 2024, BCE's capital expenditure was projected at approximately $5.0 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to network modernization, highlighting its reliance on these specialized suppliers.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on BCE | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Limited supplier options, increased leverage | Dominance of a few players in 5G infrastructure |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change vendors, dependency | Complex integration of advanced network components |
| Proprietary Technology | Lack of viable alternatives for key innovations | Patented technologies in network management software |
| Capital Expenditure Dependence | Reliance on suppliers for network upgrades | Significant portion of BCE's $5.0 billion capex for network modernization |
What is included in the product
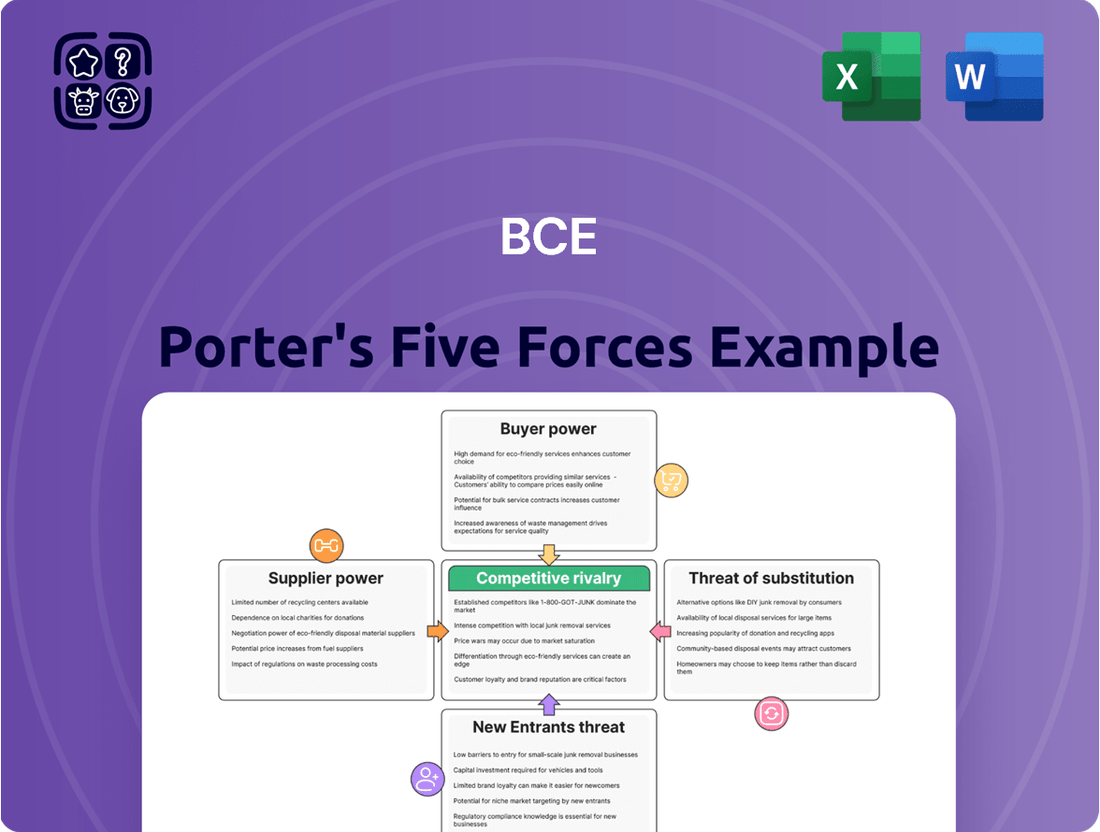
Analyzes the competitive intensity within BCE's telecommunications and media markets by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
In Canada's competitive telecom landscape, customers experience low switching costs for services like wireless, internet, and television. This allows them to easily move between providers, seeking out better pricing and service packages. For instance, in 2024, many providers continued to offer aggressive promotions and contract buyout incentives, making it financially feasible for consumers to change carriers.
Canadian telecom customers, both individuals and businesses, are very mindful of prices. They actively look for deals and respond quickly to special offers. This makes them a powerful force, pushing companies like BCE to compete aggressively on price.
The demand for affordable services means BCE and its rivals frequently run promotions. For instance, in 2024, many telecom providers offered significant discounts on internet and mobile plans to capture market share. This constant promotional activity directly reflects the bargaining power of customers who prioritize value.
Customers today have a significantly wider range of choices than ever before. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, consumers can opt for various broadband providers, impacting companies like BCE. Beyond traditional services, over-the-top (OTT) streaming platforms offer alternatives for entertainment, and numerous communication apps provide substitutes for traditional voice and messaging services.
This abundance of substitutes, encompassing both direct competitors and indirect alternatives, directly enhances customer bargaining power. When customers have many options, they are less reliant on any single provider, giving them the leverage to demand better pricing, service quality, or features from BCE.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, making them more informed than ever. Online platforms provide detailed comparisons of pricing, service plans, and extensive customer reviews, empowering individuals to make educated choices. This heightened transparency directly impacts BCE by increasing the pressure to offer competitive pricing and clear, honest service descriptions.
The ease with which customers can compare BCE's offerings against competitors means they have significant leverage. This allows them to negotiate for better deals and service terms, forcing BCE to continually adapt and maintain a competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications sector saw increased price sensitivity among consumers, with many actively switching providers based on promotional offers and perceived value.
- Informed Consumer Base: Online resources allow customers to easily research and compare BCE's pricing, plans, and service quality against competitors.
- Negotiating Power: Increased transparency empowers customers to negotiate for better terms, discounts, and service packages.
- Competitive Pressure: This customer leverage compels BCE to maintain competitive pricing and transparent operations to retain its market share.
- 2024 Market Trend: The telecommunications market in 2024 showed a strong consumer focus on value, with many customers readily switching providers for better deals.
Consolidated Customer Segments (e.g., large businesses)
While individual consumers collectively hold some sway, BCE's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by large business and wholesale clients. These major customers, by virtue of the sheer volume of services they procure, possess considerable leverage. For instance, in 2023, BCE's enterprise segment, which includes large businesses, contributed substantially to its overall revenue, enabling these clients to negotiate more favorable terms.
These large clients often secure customized contracts and pricing structures. This can directly affect BCE's profit margins and the flexibility of its service agreements, as these contracts are typically long-term and involve significant financial commitments. The ability to negotiate bespoke solutions means these customers can demand specific service levels and pricing, putting pressure on BCE's standard offerings.
- Large Enterprise Contracts: Major corporations can negotiate bulk discounts and tailored service packages, impacting BCE's revenue per user.
- Wholesale Agreements: Partnerships with other telecommunication providers or large resellers involve significant volume, giving these partners considerable bargaining power.
- Customized Service Demands: Large clients often require specific network configurations or service level agreements that deviate from standard offerings, increasing operational complexity and potentially lowering margins.
- Competitive Bidding: For large contracts, BCE often faces competitive bidding processes where customer power is amplified by the availability of alternative service providers.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for BCE, driven by low switching costs and an abundance of choices in the Canadian telecom market. Customers are well-informed, thanks to readily available online comparisons, which empowers them to negotiate better deals. This dynamic forces BCE to maintain competitive pricing and transparent operations to retain its customer base.
In 2024, the telecom sector continued to see aggressive promotions, with companies offering contract buyouts and significant discounts, reflecting the high customer sensitivity to value. This trend underscores the substantial leverage customers wield, compelling providers like BCE to constantly innovate and offer compelling packages to avoid churn.
Large business and wholesale clients represent an even more potent force due to the volume of services they procure. These entities can negotiate customized contracts and pricing, directly impacting BCE's profit margins and operational flexibility. The ability to secure bespoke solutions means these clients can demand specific service levels, putting pressure on BCE's standard offerings.
| Factor | Impact on BCE | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Increases customer mobility, forcing competitive pricing. | Continued aggressive promotions and contract buyouts observed. |
| Informed Consumer Base | Empowers negotiation for better deals and service terms. | Easy online access to price/plan comparisons drives demand for transparency. |
| Abundance of Substitutes | Reduces reliance on single providers, increasing leverage. | OTT platforms and communication apps offer alternatives to traditional services. |
| Large Enterprise Clients | Significant leverage through high-volume contracts and custom needs. | Enterprise segment revenue substantial, enabling strong negotiation power. |
Same Document Delivered
BCE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you see is the exact, professionally crafted Porter's Five Forces Analysis for BCE that you will receive immediately after purchase. This comprehensive document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering no placeholders or sample content. You can be confident that what you are previewing is the complete, high-quality analysis you will download and utilize without any further customization or setup.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Canadian telecommunications landscape is highly concentrated, with BCE, Rogers, and Telus often called the 'Big Three'. This oligopoly means intense rivalry as these giants battle for market share, with each company's strategic moves directly influencing the others. For instance, as of early 2024, BCE reported over 14 million total mobile subscribers, showcasing its substantial presence in this competitive arena.
BCE operates in a market defined by intense price competition, with companies frequently engaging in price wars and offering aggressive promotions across their wireless, internet, and TV services. This strategy is designed to win over new customers and prevent existing ones from switching providers. For instance, in early 2024, major telecom players continued to offer significant discounts on new phone plans and bundled services, often exceeding 20% off for the first year.
This constant promotional activity directly impacts revenue growth and profit margins for all key industry participants, including BCE. The pressure to match competitor pricing can lead to a race to the bottom, eroding profitability. In 2023, Canadian telecom companies saw their average revenue per user (ARPU) growth moderate, partly due to these pricing pressures.
Competitors are relentlessly pouring vast sums into expanding and upgrading their network infrastructure, especially in fiber optic and 5G technologies, all to seize a competitive advantage. This intense investment cycle means BCE, alongside its peers, faces the constant necessity of significant capital expenditures to uphold and improve network quality and reach.
In 2023, for instance, BCE reported capital expenditures of $5.0 billion, a substantial commitment to its network build-out and modernization efforts. This level of investment is crucial for staying competitive in a market where technological advancement and coverage are paramount differentiators.
Product and Service Differentiation through Bundling and Innovation
Competitive rivalry in the telecommunications sector is intense, with companies like BCE focusing on differentiating their offerings. This often involves creating attractive service bundles that combine wireless, internet, television, and home phone services. By packaging these essential services, BCE aims to provide greater value and convenience to customers, thereby reducing the likelihood of them switching to competitors.
Technological innovation and exclusive content are also key battlegrounds. BCE invests in upgrading its network infrastructure and securing premium content, such as sports rights or original programming, to attract and retain subscribers. In 2024, continued investment in 5G network expansion and fiber optic deployment remains crucial for delivering enhanced customer experiences and staying ahead in a rapidly evolving market.
- Bundling Strategy: BCE leverages household bundling across its various services (wireless, internet, TV, home phone) to increase customer stickiness and perceived value.
- Premium Services & Customer Experience: Focus on offering premium services and an enhanced customer experience to differentiate from competitors and mitigate churn.
- Innovation Investment: Continued investment in technological advancements, such as 5G and fiber optics, is vital for competitive advantage.
- Exclusive Content: Securing exclusive content remains a significant factor in attracting and retaining subscribers in the highly competitive media and telecommunications landscape.
Regulatory Environment and its Impact on Competition
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) significantly influences competitive dynamics for BCE. Its policies are designed to foster affordability and increase consumer choice in the telecommunications sector.
Recent CRTC decisions, such as those mandating wholesale high-speed internet access rates, directly alter the competitive landscape. These rulings can empower smaller internet service providers, thereby intensifying competition for established players like BCE.
- CRTC Mandates: In 2024, the CRTC continued to implement policies affecting wholesale access, impacting how competitors connect to BCE's network.
- Affordability Focus: Regulatory pressure to keep prices down for consumers can squeeze profit margins, influencing strategic pricing decisions for BCE and its rivals.
- Consumer Choice Initiatives: CRTC efforts to promote greater consumer choice, for instance, through easier switching processes or mandated service unbundling, can shift market share.
The competitive rivalry within Canada's telecommunications sector, where BCE operates, is exceptionally fierce. This is largely due to the market being dominated by a few major players, often referred to as the 'Big Three', which include BCE, Rogers, and Telus. These companies are constantly vying for market share, making strategic moves that directly impact each other's performance.
Price wars and aggressive promotional offers are commonplace across wireless, internet, and TV services as companies try to attract new customers and retain existing ones. For example, in early 2024, significant discounts, often exceeding 20% for the first year, were observed on new phone plans and bundled services. This intense competition directly affects revenue growth and profit margins, with average revenue per user (ARPU) growth moderating in 2023, partly due to these pricing pressures.
To gain an edge, competitors are heavily investing in network infrastructure, particularly in fiber optic and 5G technologies. BCE itself reported capital expenditures of $5.0 billion in 2023, a substantial commitment to its network modernization. This continuous investment is critical for maintaining service quality and expanding coverage, which are key differentiators in the market.
Differentiation strategies also include bundling services and securing exclusive content, such as sports rights. BCE's bundling strategy, combining wireless, internet, TV, and home phone services, aims to increase customer loyalty and perceived value. Furthermore, the CRTC's policies, which focus on affordability and consumer choice, can further intensify competition by empowering smaller providers and influencing pricing strategies.
| Key Competitors | Market Share Focus | Key Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| BCE | Broadband, Wireless, Media | Network investment (5G, Fiber), Bundling, Content acquisition |
| Rogers Communications | Wireless, Cable, Media | Network expansion, Service bundling, Content and sports rights |
| Telus Corporation | Wireless, Wireline, Health Tech | Network investment, Customer experience, Diversification into health |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of Over-the-Top (OTT) streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime Video presents a substantial threat to BCE's traditional television offerings. These platforms provide consumers with vast content libraries and flexible viewing options, directly challenging the established cable and satellite TV models.
Consumers are increasingly "cutting the cord," a trend that accelerated in 2024 with millions of households worldwide abandoning traditional pay-TV. This shift is driven by the perceived value and convenience of streaming, often at a lower price point, directly impacting BCE's subscriber numbers and revenue streams from its TV division.
The rise of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and messaging apps presents a significant threat to BCE's traditional voice revenue. Services like WhatsApp, FaceTime, and Google Voice offer free or very low-cost voice communication, directly competing with BCE's home and mobile phone plans. This shift means consumers are increasingly relying on internet-based platforms for calls, diminishing the value proposition of standard voice services.
In 2024, the global VoIP market was valued at over $130 billion, with continuous growth projected. This indicates a substantial portion of communication is already migrating to these alternative channels. For example, over 2 billion people use WhatsApp globally, facilitating billions of calls annually, many of which would have previously been revenue-generating for telecom companies like BCE.
The proliferation of public Wi-Fi networks and the increasing reliance on mobile hotspots present a subtle yet significant threat of substitution for traditional fixed-line internet services offered by companies like BCE. While not a perfect replacement, these alternatives can diminish the perceived necessity of a dedicated home internet connection for a segment of consumers, particularly those with modest data consumption habits. This can indeed temper BCE's subscriber growth in specific market niches.
Emerging Technologies (e.g., Satellite Internet)
Emerging technologies such as satellite internet, exemplified by SpaceX's Starlink, present a growing threat of substitutes, especially for customers in rural and underserved regions where traditional broadband infrastructure is less prevalent. These new offerings could provide a viable alternative for connectivity needs, potentially diverting customers from BCE's established fibre and cable networks.
While satellite internet is still developing, its potential to reach areas previously lacking robust connectivity means it could carve out a significant market share. For instance, by late 2023, Starlink reported having over 2.7 million active subscribers globally, demonstrating tangible customer adoption and a growing competitive force.
- Satellite Internet Growth: Starlink's subscriber base surpassed 2.7 million by late 2023, indicating a significant uptake in this substitute technology.
- Geographic Reach: These services are particularly disruptive in rural and remote areas where BCE's terrestrial network coverage is limited.
- Potential Market Share: As satellite technology improves and costs decrease, it could capture a notable portion of the broadband market, impacting BCE's customer acquisition and retention.
Self-Installation and DIY Solutions
The growing trend of self-installation for internet and TV services presents a significant threat of substitutes for BCE. As consumer electronics become more user-friendly and installation guides become readily available, customers are increasingly empowered to set up their own systems, reducing their dependence on professional installation services offered by traditional providers. This DIY approach can lead to lower switching costs for consumers looking for alternative service providers.
This shift is particularly evident in the broadband market. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of new internet service activations were facilitated through self-installation kits, bypassing the need for technician visits. This trend suggests that customers are comfortable managing their own network setups, directly challenging the bundled equipment and installation revenue streams of companies like BCE.
- Self-installation kits are becoming more sophisticated and user-friendly.
- The availability of online tutorials and guides further lowers the barrier to DIY setup.
- This trend can reduce customer reliance on bundled equipment and installation fees from providers like BCE.
- Lower switching costs for consumers may lead to increased competition from alternative service providers.
The threat of substitutes for BCE's traditional services is multifaceted, encompassing streaming, VoIP, and alternative internet solutions. These substitutes offer consumers greater flexibility, lower costs, and enhanced convenience, directly challenging BCE's established revenue models.
The shift towards Over-the-Top (OTT) streaming and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services continues to erode BCE's traditional television and voice revenues. In 2024, the global VoIP market exceeded $130 billion, illustrating a significant migration of communication to internet-based platforms. Furthermore, over 2 billion people use messaging apps like WhatsApp, which facilitate a vast number of calls, directly competing with BCE's voice plans.
Emerging technologies like satellite internet, with over 2.7 million global subscribers for services like Starlink by late 2023, are also becoming viable substitutes, particularly in underserved areas. Coupled with the increasing trend of self-installation for home services, which bypasses traditional installation revenues for providers like BCE, these substitutes collectively heighten competitive pressure.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | Impact on BCE | 2024 Market Data/Trends |
| Video Streaming | Netflix, Disney+, Amazon Prime Video | Declining traditional TV subscriptions, reduced pay-TV revenue | Millions of households worldwide cutting the cord in 2024 |
| Voice Communication | WhatsApp, FaceTime, Google Voice | Erosion of traditional voice revenue | VoIP market > $130 billion (2024), billions of calls via messaging apps annually |
| Internet Connectivity | Satellite Internet (Starlink), Public Wi-Fi | Potential loss of broadband subscribers, especially in rural areas | Starlink > 2.7 million subscribers (late 2023) |
| Service Installation | DIY Self-Installation | Reduced reliance on professional installation, lower switching costs | Increasing adoption of self-installation kits for broadband in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the telecommunications sector, particularly for a comprehensive provider like BCE, demands substantial initial capital for building out network infrastructure, including fiber optics and 5G spectrum. This significant financial hurdle acts as a major deterrent for prospective competitors.
For instance, in 2023, Canadian telecommunications companies collectively invested billions in network upgrades and spectrum acquisition. BCE itself reported significant capital expenditures, underscoring the immense financial commitment needed to establish a competitive presence.
The Canadian telecom sector faces significant barriers to entry due to extensive regulatory hurdles and licensing requirements overseen by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC). New entrants must navigate a complex web of policies, including mandated wholesale access for smaller providers and stringent consumer protection measures. For instance, in 2023, the CRTC continued to emphasize competition and affordability, often through regulatory interventions that favor established players’ compliance burdens, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a foothold without substantial investment in legal and compliance expertise.
Established brand loyalty is a significant barrier for new entrants in the telecommunications sector. Companies like BCE have cultivated decades of brand recognition, fostering deep customer relationships and loyalty programs that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, BCE's extensive network of retail stores and customer service centers further solidifies its connection with millions of Canadians, making it challenging for new players to gain traction.
Economies of Scale and Scope
BCE, as a major player in the Canadian telecommunications market, leverages substantial economies of scale. This allows them to spread the high fixed costs associated with building and maintaining vast network infrastructure, such as fiber optic cables and wireless towers, across a large customer base. For instance, in 2023, BCE reported capital expenditures of $3.1 billion, a significant investment that smaller, new entrants would find incredibly difficult to match.
These scale advantages translate directly into cost efficiencies in areas like customer service centers and content licensing for their media divisions. New companies entering the market would face immense pressure to achieve similar cost per unit, making it challenging to offer competitive pricing or a comparable breadth of services to BCE's integrated offerings in wireless, internet, TV, and media.
The threat of new entrants is therefore somewhat mitigated by these entrenched economies of scale. Potential disruptors would need to overcome substantial capital barriers and achieve rapid customer acquisition to even approach BCE's cost structure. For example, while 5G network deployment is ongoing, the sheer investment required to build a competitive 5G network across Canada is a major hurdle for any new player.
- Economies of Scale: BCE's vast infrastructure and customer base allow for lower per-unit costs in network operation and service delivery.
- Capital Intensity: The telecommunications sector demands massive upfront investment, creating a significant barrier for new entrants.
- Customer Service Efficiency: Large-scale operations enable BCE to achieve greater efficiency in managing customer support, reducing costs.
- Content Acquisition: BCE's size provides leverage in negotiating content rights, a cost advantage not easily replicated by smaller competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels and Spectrum
New companies entering the telecommunications market face significant hurdles in securing essential distribution channels and the necessary radio spectrum. Established players often have locked-in agreements with prime retail locations and exclusive rights to valuable spectrum bands, making it difficult for newcomers to reach customers effectively.
The scarcity and escalating cost of spectrum are particularly daunting. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has conducted numerous spectrum auctions. In a 2023 auction for mid-band spectrum, the winning bids totaled over $27 billion, highlighting the substantial investment required to acquire these vital assets.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: Existing telecommunications providers have built extensive retail networks and partnerships, creating a significant advantage that new entrants struggle to replicate.
- Spectrum Acquisition Costs: The high price of acquiring spectrum licenses, as demonstrated by billions in auction revenue, presents a substantial financial barrier for new companies.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape for spectrum allocation and distribution agreements adds another layer of difficulty for potential new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for BCE remains relatively low due to substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for network infrastructure, complex regulatory requirements from bodies like the CRTC, and the difficulty in overcoming established brand loyalty and distribution channels. Furthermore, securing scarce and expensive radio spectrum presents a significant financial hurdle, making it challenging for new players to compete effectively.
| Barrier Category | Description | Example/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Significant upfront investment needed for network build-out. | BCE's 2023 capital expenditures of $3.1 billion illustrate the scale of investment required. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, compliance, and policy navigation. | CRTC regulations in 2023 emphasized competition, often increasing compliance burdens for newcomers. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established customer relationships and extensive retail presence. | BCE's decades of brand building and numerous retail stores create a strong customer lock-in. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations and infrastructure. | BCE's size allows for lower per-unit costs in network operation and customer service. |
| Spectrum Access | Acquisition of essential radio frequencies. | US mid-band spectrum auctions in 2023 exceeded $27 billion, demonstrating high acquisition costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our BCE Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
