Boise Cascade Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Boise Cascade Bundle
Boise Cascade faces moderate bargaining power from both suppliers and buyers within the competitive lumber and building products industry. The threat of substitutes, while present, is somewhat mitigated by the unique properties of wood products. Intense rivalry among existing players significantly shapes the market landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Boise Cascade’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Boise Cascade's supplier bargaining power is significantly shaped by the concentration of its raw material providers, especially for timber and logs. When there are limited sources for specific, high-quality wood species or essential chemicals for engineered wood products, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Forest Service managed over 193 million acres of national forests, but the availability of specific timber types for Boise Cascade's needs can be geographically concentrated, impacting supplier options.
Boise Cascade's ability to switch between suppliers significantly influences the bargaining power of those suppliers. If the costs associated with changing suppliers are high, existing suppliers gain leverage. For instance, retooling machinery to accommodate different wood dimensions or altering chemical formulations for wood treatment can be costly and time-consuming, making it difficult for Boise Cascade to switch.
In 2023, lumber prices experienced volatility, with some species seeing significant fluctuations. This volatility can increase switching costs if a new supplier offers materials that require adjustments to Boise Cascade's manufacturing processes. For example, if a supplier provides wood with a slightly different moisture content, it might necessitate changes in drying procedures, adding to the expense and complexity of switching.
Conversely, if alternative suppliers offer wood products with identical specifications and minimal integration challenges, Boise Cascade's ability to switch would be easier, thereby reducing supplier power. The availability of a broad market for raw materials with consistent quality and readily adaptable specifications empowers Boise Cascade to negotiate more favorable terms.
Suppliers might threaten Boise Cascade by moving into its core business, like setting up their own wood product manufacturing or distribution networks. This is more likely if suppliers have substantial financial backing, deep industry knowledge, or established relationships with Boise Cascade's customers.
For instance, a large timber supplier might consider acquiring or building its own sawmills or even retail outlets for finished wood products. The significant capital investment required for such forward integration, however, often serves as a substantial barrier, mitigating this particular threat for Boise Cascade.
Importance of Boise Cascade to Suppliers
Boise Cascade's substantial presence in the building products industry means it is a significant customer for many of its suppliers. For instance, in 2023, Boise Cascade reported net sales of $7.1 billion, indicating the sheer volume of materials they procure. This scale means that for many suppliers, Boise Cascade represents a crucial, and potentially large, portion of their overall business.
When a supplier relies heavily on Boise Cascade for a significant percentage of their revenue, their ability to dictate terms or demand higher prices is often diminished. The risk of losing such a valuable client can make them more accommodating to Boise Cascade's pricing and supply demands. This dynamic directly impacts the bargaining power of these suppliers.
Conversely, if Boise Cascade is a relatively small customer for a particular supplier, that supplier might feel more empowered to negotiate more favorable terms. However, given Boise Cascade's market position, it's more common for suppliers to find themselves in a position where Boise Cascade's business is important to them.
- Significant Customer Base: Boise Cascade's $7.1 billion in net sales for 2023 highlights its importance as a buyer in the supply chain.
- Supplier Dependence: Many suppliers may depend on Boise Cascade for a substantial portion of their revenue, reducing their bargaining leverage.
- Reduced Price Pressure: This dependence can lead suppliers to offer more competitive pricing and be less aggressive in price negotiations.
- Strategic Importance: For suppliers, maintaining a strong relationship with a major player like Boise Cascade is often a strategic priority.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly weakens the bargaining power of suppliers for Boise Cascade. If the company can readily source alternative raw materials or components, it reduces its dependence on any single supplier. For instance, the ability to use different wood species or engineered wood products instead of traditional timber gives Boise Cascade more leverage in negotiations with timber suppliers.
This availability of alternatives directly impacts pricing and terms. When substitutes exist, suppliers cannot unilaterally dictate higher prices without risking Boise Cascade switching to a more cost-effective option. This is particularly relevant in the current market, where increased construction and infrastructure projects are boosting demand for raw materials.
In 2024, the demand for lumber and wood products saw a notable increase, driven by residential and commercial construction. Despite this heightened demand, the presence of composite materials and alternative building supplies provides a crucial check on the pricing power of traditional timber suppliers. For example, engineered wood products, which offer comparable structural integrity and aesthetic appeal, can be substituted for solid lumber, thus limiting the leverage of traditional forestry suppliers.
- Availability of Substitute Inputs: The existence of alternative raw materials or components that Boise Cascade can utilize in its production processes directly diminishes the bargaining power of its suppliers.
- Impact on Leverage: If alternative wood species or composite materials can be used to produce similar products, suppliers of traditional timber possess less leverage over pricing and contractual terms.
- Market Dynamics in 2024: The wood products market in 2024 experienced robust growth, with increased construction and infrastructure activities driving demand for raw materials, yet the availability of substitutes continues to moderate supplier influence.
Boise Cascade's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by the concentration of raw material sources and the ease of switching suppliers. High switching costs, like retooling for different wood types, strengthen supplier leverage. Conversely, the availability of alternative materials, such as composite products, reduces supplier power by providing Boise Cascade with more options.
Boise Cascade's significant scale, evidenced by $7.1 billion in net sales in 2023, makes it a crucial customer for many suppliers, thereby limiting their ability to dictate terms. However, if suppliers have unique or specialized inputs, their bargaining power can increase.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context |
| Supplier Concentration | Can be high if few suppliers offer specific wood types or chemicals. | U.S. Forest Service managed 193 million acres in 2023, but specific timber availability is geographically concentrated. |
| Switching Costs | High costs (e.g., retooling, process changes) increase supplier leverage. | Adjusting for different wood moisture content can require process changes. |
| Boise Cascade's Size | Lowers supplier power as Boise Cascade is a significant customer. | 2023 Net Sales: $7.1 billion. Many suppliers depend on Boise Cascade for substantial revenue. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Weakens supplier power by offering alternatives. | Engineered wood products and composite materials can substitute for traditional timber, moderating supplier influence even with 2024 demand growth. |
What is included in the product
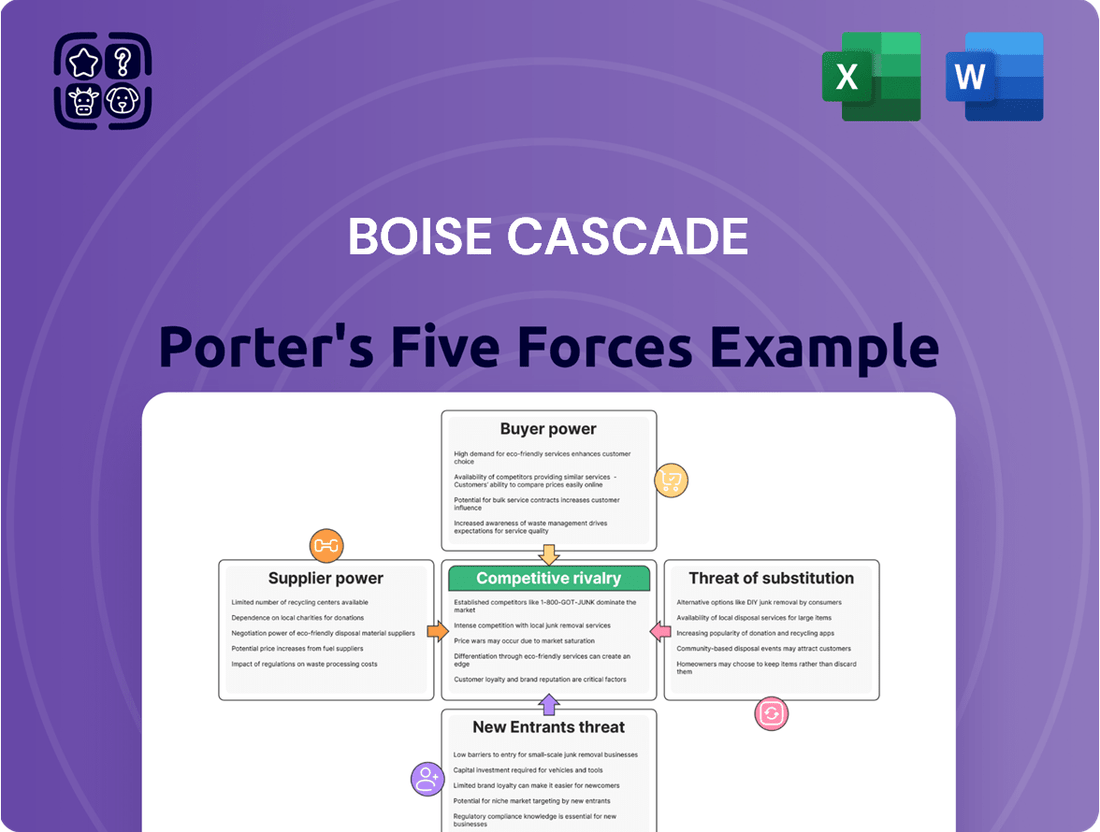
This analysis specifically examines Boise Cascade's competitive environment, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Instantly identify competitive pressures with a clear, visual representation of each force, empowering strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Boise Cascade's customer bargaining power is heavily influenced by customer concentration and the volume of their purchases. Large national builders and industrial clients, who represent substantial purchase volumes, can negotiate more favorable pricing and terms.
For instance, in 2023, Boise Cascade's building materials distribution segment served a diverse customer base, with its top ten customers accounting for approximately 15% of the segment's net sales, indicating a moderate level of customer concentration. This means while individual large customers hold some sway, the overall customer base prevents extreme leverage by any single entity.
The bargaining power of Boise Cascade's customers is significantly influenced by product differentiation and the availability of alternatives. For standard wood products, which often behave like commodities, customers face numerous suppliers. This abundance of choices means they can easily switch providers if prices or terms aren't favorable, giving them substantial leverage. For instance, in the general lumber market, price is often the primary driver, and customers can readily compare offerings from multiple mills.
However, Boise Cascade's position in engineered wood products (EWP) presents a different dynamic. As a leading producer of items like I-joists and laminated veneer lumber (LVL), the company offers more specialized solutions. These products often require specific engineering and performance characteristics that may not be easily replicated by all competitors. In 2023, Boise Cascade reported that its EWP segment continued to be a strong performer, indicating a degree of product uniqueness that can mitigate customer bargaining power in these specific markets.
The costs customers face when moving from Boise Cascade to a competitor directly impact their leverage. For standard lumber or plywood, these switching costs are generally minimal, enabling customers to readily shift to the lowest-priced option. This ease of switching means customers hold significant power in these segments.
However, for Boise Cascade's engineered wood products (EWP) and integrated supply chain solutions, switching can be more complex. Consider the scenario where a builder has designed an entire project around Boise Cascade's specific EWP specifications. Changing suppliers would necessitate redesigns, re-engineering, and potential logistical overhauls, significantly increasing costs and effort. For instance, in 2023, the construction industry saw ongoing supply chain challenges, making the disruption of switching EWP suppliers a considerable risk for many firms, thereby reducing their bargaining power with reliable providers like Boise Cascade.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, such as major home builders or lumber distributors, hold significant bargaining power. They might consider backward integration, meaning they could produce some of their own wood products or bypass Boise Cascade to source raw materials directly. This threat is more pronounced for basic wood products where manufacturing is less complex.
For instance, a large national home builder might explore setting up its own mill for standard dimensional lumber, reducing its reliance on suppliers like Boise Cascade. While the production of engineered wood products, a key area for Boise Cascade, involves more intricate processes making backward integration less feasible, the threat remains for simpler offerings.
- Customer Bargaining Power: Major customers can leverage their size to negotiate better prices or terms.
- Backward Integration Threat: Large builders or distributors may consider producing wood products internally.
- Feasibility Varies: Backward integration is more likely for basic lumber than for complex engineered wood products.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Boise Cascade, particularly given the cyclical nature and commodity-like aspects of the building materials industry. When economic conditions tighten, such as the impact of higher interest rates on residential construction, customers become more hesitant to absorb price increases, thus amplifying their bargaining power.
For instance, Boise Cascade's Wood Products segment experienced a notable decline in sales during 2024. This downturn was primarily attributed to reduced sales prices and lower volumes for key products like engineered wood products (EWP) and plywood, directly reflecting increased customer price sensitivity in the prevailing economic climate.
- Economic Downturns Amplify Price Sensitivity: Higher interest rates in 2024 led to a slowdown in residential construction, making customers more resistant to price hikes.
- Commodity Nature of Products: Many of Boise Cascade's offerings, like plywood, are treated as commodities, allowing customers to easily switch suppliers if prices are not competitive.
- Impact on Sales: The company reported decreased sales in its Wood Products segment for 2024, a direct consequence of both lower sales prices and volumes, underscoring heightened customer price sensitivity.
Boise Cascade's customers, particularly large buyers like national home builders and distributors, wield considerable bargaining power. This is amplified by the commodity nature of many of its products, such as standard lumber, where price is the primary differentiator and switching costs are low.
In 2024, the company's Wood Products segment saw a notable downturn, with sales decreasing due to lower prices and volumes for key items like plywood and EWP. This reflects increased customer price sensitivity, especially as rising interest rates cooled the residential construction market.
While engineered wood products (EWP) offer some differentiation, reducing customer leverage due to higher switching costs associated with project-specific designs, the overall customer power remains a significant force, particularly for more standardized offerings.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Boise Cascade (2024 Data) |
| Large National Builders/Distributors | High volume purchases, commodity nature of some products, potential for backward integration | Reduced pricing flexibility, increased price sensitivity |
| Engineered Wood Product (EWP) Buyers | Project-specific designs, higher switching costs | Moderate bargaining power, mitigated by product specialization |
| Overall Customer Base | Top ten customers accounted for ~15% of segment sales in 2023 (moderate concentration) | Prevents extreme leverage by any single entity, but collective pressure exists |
Preview Before You Purchase
Boise Cascade Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Boise Cascade Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the building materials industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering a complete and actionable strategic overview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The building materials and wood products sectors in North America feature a significant number of large, established companies. Key players like Weyerhaeuser, LP (Louisiana-Pacific), Builders FirstSource, and BlueLinx are substantial competitors, each holding considerable market presence.
This robust competition among major entities creates an intense rivalry, as these companies actively compete for market share and customer loyalty. For instance, in 2023, Builders FirstSource reported net sales of $16.7 billion, highlighting the scale of operations within this competitive landscape.
The pace of industry growth significantly impacts competitive rivalry. In Q1 2025, the housing market experienced constrained demand, leading to lower housing starts, which intensified competition as companies vied for a smaller pool of customers. This environment, characterized by slower growth, typically fuels more aggressive pricing and market share battles.
The level of product differentiation significantly influences competitive rivalry. For basic wood products, which are largely undifferentiated, competition often boils down to price. However, Boise Cascade's strategic emphasis on engineered wood products, like I-joists and glued laminated timber, offers distinct advantages in terms of strength and design flexibility. This focus, coupled with a robust distribution network that ensures reliable supply and customer service, helps foster a degree of brand loyalty, thereby softening the intensity of pure price-based competition.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Boise Cascade operates in industries characterized by substantial fixed costs. For instance, the capital expenditure for a new lumber mill can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting the significant investment in land, machinery, and infrastructure required for wood products manufacturing. Similarly, establishing a widespread distribution network for building materials involves considerable outlay for warehouses, fleets of trucks, and inventory management systems.
These high fixed costs, combined with the specialized nature of assets like sawmills and specialized distribution equipment, create significant exit barriers. Companies are often compelled to continue operations, even in periods of low demand or profitability, to avoid the substantial losses associated with shutting down and liquidating specialized assets. This commitment to remaining in the market, regardless of economic conditions, naturally fuels intense competitive rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Intensity: Wood products manufacturing and building materials distribution demand significant upfront investments in plant, property, and equipment.
- Specialized Assets: The machinery and facilities used are often highly specialized, limiting their resale value and increasing the cost of exiting the market.
- Operational Imperative: Companies must maintain production to cover fixed costs, leading to a willingness to compete aggressively on price during market slumps.
Industry Consolidation and Acquisitions
The building products industry has experienced significant consolidation, with Boise Cascade actively participating through strategic acquisitions. A notable example is their acquisition of BROSCO in late 2023, which aimed to bolster their distribution segment. This type of activity reshapes the competitive arena, often leading to increased market concentration and fewer direct competitors in specific product categories.
- Industry Consolidation: Boise Cascade's acquisition of BROSCO in late 2023 is a prime example of ongoing consolidation within the building products sector.
- Market Concentration: Such acquisitions can lead to fewer, larger players dominating market segments, potentially impacting pricing and product availability.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: Increased market concentration can alter the intensity of rivalry, as remaining companies may face less direct competition but potentially more powerful consolidated entities.
The competitive rivalry within the building materials and wood products sectors is intense, driven by a substantial number of large, established players like Weyerhaeuser and Builders FirstSource. This vigorous competition is further amplified by high fixed costs and specialized assets, which create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain active even during downturns. The industry's growth pace, as seen with constrained housing demand in Q1 2025, directly fuels more aggressive pricing and market share battles as companies vie for a smaller customer base.
Boise Cascade's strategic focus on differentiated products like engineered wood, alongside a strong distribution network, helps mitigate pure price competition. However, the ongoing industry consolidation, exemplified by Boise Cascade's late 2023 acquisition of BROSCO, reshapes the competitive landscape, potentially leading to greater market concentration and altered rivalry dynamics among the remaining, larger entities.
| Company | 2023 Net Sales (USD Billions) | Key Product Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Boise Cascade | 17.5 | Engineered Wood Products, Plywood, Lumber, Building Materials Distribution |
| Builders FirstSource | 16.7 | Building Materials Distribution, Lumber, Millwork, Windows, Doors |
| Weyerhaeuser | 7.5 | Timberland, Lumber, Engineered Wood Products, Pulp, Paper |
| LP (Louisiana-Pacific) | 3.1 | Engineered Wood Products, Siding, OSB |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Boise Cascade's wood products is significant, with materials like steel and concrete being prominent alternatives in the construction industry. These substitutes offer distinct performance advantages, such as superior strength-to-weight ratios for steel or enhanced fire resistance and durability for concrete, which can sway builder preferences. For instance, in 2024, the global steel construction market was valued at approximately $250 billion, highlighting its substantial presence as an alternative building material.
Customers naturally weigh the cost against the benefits when considering alternatives to wood products. If substitute materials offer similar or better performance at a lower price point, the threat of substitution for Boise Cascade's offerings intensifies.
This dynamic is amplified in volatile commodity markets. For instance, fluctuations in lumber prices, which saw significant spikes in 2021 and 2022, can make engineered wood products or even non-wood alternatives like steel framing more attractive to builders and consumers, directly impacting demand for Boise Cascade's core products.
Builders and contractors are increasingly open to alternative materials if they offer cost savings, enhanced performance, or meet new regulations. For instance, the growing adoption of engineered wood products and composite materials signifies a shift, driven by factors like improved durability and design flexibility. The demand for sustainable building practices, a trend gaining significant traction in 2024, further encourages exploration beyond traditional wood framing.
Innovation and Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Ongoing innovation in substitute materials, like advanced steel framing and pre-fabricated concrete, directly heightens their threat to Boise Cascade. These advancements offer easier installation and superior properties, potentially luring customers away from wood products. For instance, the global construction market for engineered wood products is projected to reach over $150 billion by 2027, but advancements in steel and concrete offer competitive alternatives.
These innovations mean that substitutes are not static; they are constantly improving their performance and cost-effectiveness. Consider the rise of cross-laminated timber (CLT) as a wood-based innovation, but also the parallel advancements in modular construction using non-wood materials. The threat isn't just about existing substitutes but the *potential* for new, disruptive ones to emerge due to R&D.
The ease of installation and enhanced properties of substitutes are key drivers of their appeal. For example, some new composite materials can be assembled much faster than traditional wood framing, reducing labor costs on construction sites. This directly impacts Boise Cascade's value proposition.
- Technological advancements in steel framing offer lighter, stronger alternatives to wood.
- Pre-fabricated concrete components can speed up construction timelines, reducing labor costs.
- New composite materials are being developed with improved durability and moisture resistance compared to traditional wood.
- The global market for alternative building materials is expanding, driven by factors like sustainability and cost efficiency.
Regulatory and Environmental Factors
Stricter building codes and environmental regulations are increasingly influencing material choices. For instance, the growing emphasis on green building certifications like LEED can favor alternative materials if they are perceived to offer superior environmental performance or meet specific sustainability benchmarks. While Boise Cascade's products can be sourced sustainably, shifts in regulatory landscapes might inadvertently promote substitutes that are seen as more environmentally friendly or possess unique performance characteristics that align with new standards.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by regulatory and environmental factors. For example, as of early 2024, many regions are tightening regulations around embodied carbon in construction materials. This could lead to increased adoption of materials with lower carbon footprints, potentially impacting demand for traditional wood products if not adequately addressed through sustainable forestry practices and transparent reporting. Boise Cascade's commitment to sustainability, including its 2023 ESG report highlighting progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, is crucial in mitigating this threat.
- Regulatory Shifts Favoring Alternatives: Evolving building codes and environmental mandates, such as those promoting energy efficiency and reduced embodied carbon, can create opportunities for substitute materials.
- Green Building Certifications: The increasing prevalence of certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) encourages the use of materials that meet stringent environmental criteria, potentially benefiting alternatives if wood products do not fully align with specific certification requirements.
- Perception of Environmental Friendliness: Regulatory bodies and consumers may perceive certain substitute materials as inherently more environmentally friendly, even if wood can be a highly sustainable option when managed responsibly.
- Performance-Based Standards: New regulations might focus on specific performance metrics, such as fire resistance or insulation properties, which could favor engineered substitutes or composite materials if they demonstrably outperform traditional wood in these areas.
The threat of substitutes for Boise Cascade's wood products remains a persistent challenge, driven by ongoing innovation in alternative materials like steel, concrete, and engineered composites. These substitutes are continually improving their performance characteristics, such as strength, durability, and ease of installation, making them increasingly competitive. For instance, the global market for engineered wood products, while growing, faces intense competition from advancements in non-wood alternatives. In 2024, the construction industry saw continued investment in research and development for these substitutes, aiming to offer cost-effective and performance-driven solutions.
Cost-competitiveness is a critical factor influencing customer decisions. When substitute materials offer comparable or superior benefits at a lower price point, the threat to Boise Cascade's market share increases. Fluctuations in lumber prices, as seen in recent years, can make alternatives like steel framing more appealing to builders and consumers, directly impacting demand for wood products.
The evolving regulatory landscape and growing emphasis on sustainability also play a significant role. Stricter building codes and green building certifications can favor alternative materials if they are perceived to have a lower environmental impact or meet specific performance standards. For example, as of early 2024, many regions are focusing on reducing embodied carbon in construction, which could influence material choices for projects seeking to meet these new environmental benchmarks.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Market Trend/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Framing | High strength-to-weight ratio, fire resistance, dimensional stability | Global steel construction market valued at approx. $250 billion |
| Concrete | Durability, fire resistance, thermal mass | Significant adoption in infrastructure and commercial projects |
| Engineered Wood Products (e.g., CLT) | Design flexibility, strength, sustainability potential | Projected global market to exceed $150 billion by 2027, but faces competition |
| Composite Materials | Moisture resistance, durability, ease of installation | Growing demand driven by performance improvements and specialized applications |
Entrants Threaten
The wood products manufacturing and building materials distribution sectors demand considerable capital. Establishing and maintaining production facilities, securing timberlands, and developing robust distribution networks require significant upfront investment, acting as a substantial barrier for potential new entrants.
Boise Cascade's own strategic plans underscore this reality. The company has projected substantial capital expenditures for 2025, indicating the ongoing need for significant investment to remain competitive and expand operations within these capital-intensive industries.
Established players in the building materials sector, including Boise Cascade, benefit from substantial economies of scale. This means they can produce and distribute goods at a lower per-unit cost due to their large operational size. For instance, in 2023, Boise Cascade reported net sales of $7.4 billion, indicating a significant volume of operations that drives these cost advantages.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without a comparable scale of operations, they would likely have higher production and procurement costs. This makes it challenging for them to compete effectively on price against established companies that have already amortized their large capital investments over years of high-volume output.
New companies entering the building materials market face a tough challenge in securing access to established distribution channels. Boise Cascade's robust Building Materials Distribution network, a key asset, makes it difficult for newcomers to reach customers efficiently. In 2023, Boise Cascade's Building Materials Distribution segment generated $7.5 billion in revenue, highlighting the scale and importance of its distribution capabilities.
Proprietary Technology and Product Differentiation
While basic wood products are largely commoditized, the engineered wood products (EWP) segment presents a significant barrier to new entrants due to specialized manufacturing processes and proprietary technologies. Boise Cascade, for instance, leverages its expertise in developing and marketing innovative EWP solutions.
The capital investment required for advanced EWP production and the time needed to build brand recognition and customer trust further deter potential competitors. This technological moat, coupled with established supply chain relationships, makes it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold.
- Proprietary EWP Technology: Boise Cascade holds patents and trade secrets related to its engineered wood products, creating a technological advantage.
- R&D Investment: Significant ongoing investment in research and development is necessary for new EWP product innovation, a cost barrier for new entrants.
- Product Differentiation: Boise Cascade's ability to differentiate its EWP offerings through performance, sustainability, and technical support creates customer loyalty, making it harder for new players to compete on product alone.
Government Policy, Regulations, and Raw Material Access
Government policies significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the building materials sector. Regulations concerning forestry management, environmental protection standards, and building codes can erect substantial barriers. For instance, stringent environmental regulations, like those enforced by the EPA, often require significant upfront investment in compliance technology for new players.
Access to raw materials, particularly timber for companies like Boise Cascade, presents another formidable challenge. Securing consistent and cost-effective timber supplies is often dependent on long-term contracts with landowners or outright land ownership, both of which are difficult for new entrants to establish quickly. In 2024, the U.S. Forest Service managed over 191 million acres of national forest land, with timber sales being a crucial component of supply for many companies.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New entrants face compliance costs related to environmental protection, forestry practices, and building codes.
- Raw Material Access: Securing reliable and affordable timber supplies is challenging due to land ownership and long-term contracts.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs and trade agreements can influence the cost and availability of imported materials, affecting new market entrants.
- Capital Investment: Meeting regulatory standards and establishing raw material supply chains often requires substantial initial capital outlay.
The threat of new entrants for Boise Cascade is moderate. The significant capital required for facilities, timberlands, and distribution networks acts as a primary barrier. For example, Boise Cascade's substantial 2025 capital expenditure projections underscore this capital intensity. Furthermore, established economies of scale, as evidenced by their $7.4 billion in net sales in 2023, provide cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. Proprietary engineered wood product technologies and established distribution channels further solidify Boise Cascade's competitive position, making market entry challenging.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for facilities, timberlands, and distribution networks. | Significant barrier, requiring substantial upfront funding. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies, impacting price competitiveness. |
| Distribution Channels | Established, robust networks are difficult to replicate. | New companies face challenges reaching customers efficiently. |
| Proprietary Technology | Specialized processes and patents in engineered wood products. | Creates a technological moat, requiring significant R&D for competitors. |
| Regulatory Environment | Compliance with environmental, forestry, and building codes. | Adds to upfront costs and complexity for new market participants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Boise Cascade leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific trade publications. We also incorporate insights from market research firms and government economic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
