Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria Bundle
Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria (BBVA) operates within a dynamic financial services landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the underlying forces at play is crucial for navigating this complex market. For instance, the threat of new entrants, while somewhat mitigated by regulatory hurdles, remains a consideration as fintech innovations emerge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BBVA's dependence on technology providers for essential functions like core banking, cybersecurity, and cloud services means these suppliers can wield considerable influence. For instance, specialized software providers or those offering critical IT infrastructure can command higher prices if their expertise is scarce or if switching costs for BBVA are substantial, potentially impacting profitability and operational efficiency.
The bank's strategic focus on digital transformation, a key driver for growth and customer engagement, further amplifies the bargaining power of technology suppliers. As of early 2024, global IT spending by financial institutions was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the significant market for these providers and their leverage in negotiations with major players like BBVA.
Financial institutions such as BBVA rely heavily on data and information providers for critical functions including market intelligence, credit scoring, and anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. The bargaining power of these suppliers is typically moderate. This is because specialized and extensive datasets are often proprietary and indispensable for effective risk management and strategic planning, making them difficult to substitute.
The ability of data providers to command higher prices or favorable terms is influenced by the uniqueness and comprehensiveness of their offerings. For instance, providers of specialized alternative data, such as sentiment analysis from social media or supply chain transaction data, can wield significant influence. BBVA’s ability to access accurate and timely information directly impacts its competitive edge in the market.
While depositors are a bank's main source of funds, BBVA also taps into wholesale markets like interbank lending, bond issuances, and institutional investors. The influence these funding sources wield hinges on market liquidity, prevailing interest rates, and BBVA's own creditworthiness. For instance, a robust credit rating significantly dampens the bargaining power of these wholesale funders, leading to more favorable borrowing costs.
Human Capital and Talent
The bargaining power of suppliers in the context of human capital and talent for BBVA hinges on the availability of specialized skills. For instance, the demand for cybersecurity experts remains exceptionally high. In 2024, the global cybersecurity workforce gap was estimated to be around 3.4 million professionals, meaning organizations like BBVA face intense competition for qualified individuals.
This scarcity translates into increased leverage for these professionals and the institutions that train them. BBVA's ability to innovate and maintain efficient operations, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence and data science, directly depends on securing this talent. The cost of attracting and retaining these individuals significantly influences operational expenditures and the pace of strategic initiatives.
- High demand for specialized skills: Cybersecurity, data science, and AI professionals are in short supply globally.
- Talent gap impact: In 2024, the cybersecurity workforce gap was 3.4 million, driving up talent costs.
- Strategic importance: Access to top talent is critical for BBVA's innovation and operational efficiency.
- Cost implications: Attracting and retaining skilled professionals directly affects operational budgets and strategic execution.
Professional Services
BBVA relies on a diverse range of professional service providers, including legal counsel, audit firms, and management consultants. The bargaining power of these suppliers is often elevated when their services are highly specialized or legally required, particularly for intricate global operations or navigating complex regulatory landscapes. For instance, the demand for specialized legal expertise in cross-border financial regulations can give top-tier law firms significant leverage.
The reputation and demonstrable expertise of these professional service firms are crucial factors in their ability to command higher fees and favorable terms. In 2024, major global consulting firms reported fee increases, reflecting strong demand for specialized advice in areas like digital transformation and ESG compliance, which directly impacts banks like BBVA.
- High Specialization: Services like complex international tax law or specific cybersecurity consulting carry high switching costs for BBVA, granting these suppliers greater power.
- Reputation and Brand: Prestigious law firms or well-regarded auditing companies can leverage their brand name to negotiate better contracts.
- Regulatory Mandates: Certain services, such as mandatory financial audits, create a baseline demand that can empower established suppliers.
- Concentration of Suppliers: In niche areas of financial law or specialized IT security, a limited number of highly capable providers can significantly increase their bargaining leverage.
Suppliers of specialized technology and data are key players in BBVA's operational framework. The increasing reliance on digital transformation and sophisticated data analytics means that providers of cloud services, cybersecurity solutions, and market intelligence can exert significant influence. This is particularly true for those offering unique or difficult-to-replicate capabilities, where switching costs for BBVA are high, potentially impacting cost structures and strategic agility.
The global demand for IT services in banking, projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, underscores the leverage held by technology vendors. Similarly, the critical nature of proprietary data for risk management and competitive advantage empowers specialized data providers. BBVA's need for such indispensable resources grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power, influencing contract terms and pricing, especially for unique alternative data sets crucial for market insights.
| Supplier Type | BBVA's Dependence | Supplier Bargaining Power | Key Factors | Data Point (2024/Early 2024) |
| Technology Providers (Cloud, Cybersecurity, Software) | High (Core Banking, Digital Transformation) | High | Scarcity of specialized skills, high switching costs | Global IT spending by financial institutions projected > $600 billion |
| Data & Information Providers (Market Intelligence, Credit Scoring) | High (Risk Management, Strategic Planning) | Moderate to High | Proprietary and indispensable datasets, uniqueness of alternative data | N/A (Specific data provider market size not readily available) |
| Human Capital (Talent for AI, Data Science, Cybersecurity) | High (Innovation, Operations) | High | Significant global talent gap, high demand for specialized skills | Cybersecurity workforce gap estimated at 3.4 million professionals |
| Professional Services (Legal, Audit, Consulting) | Moderate to High (Regulatory Compliance, Strategy) | Moderate to High | Specialization, reputation, regulatory mandates | Major global consulting firms reported fee increases |
What is included in the product
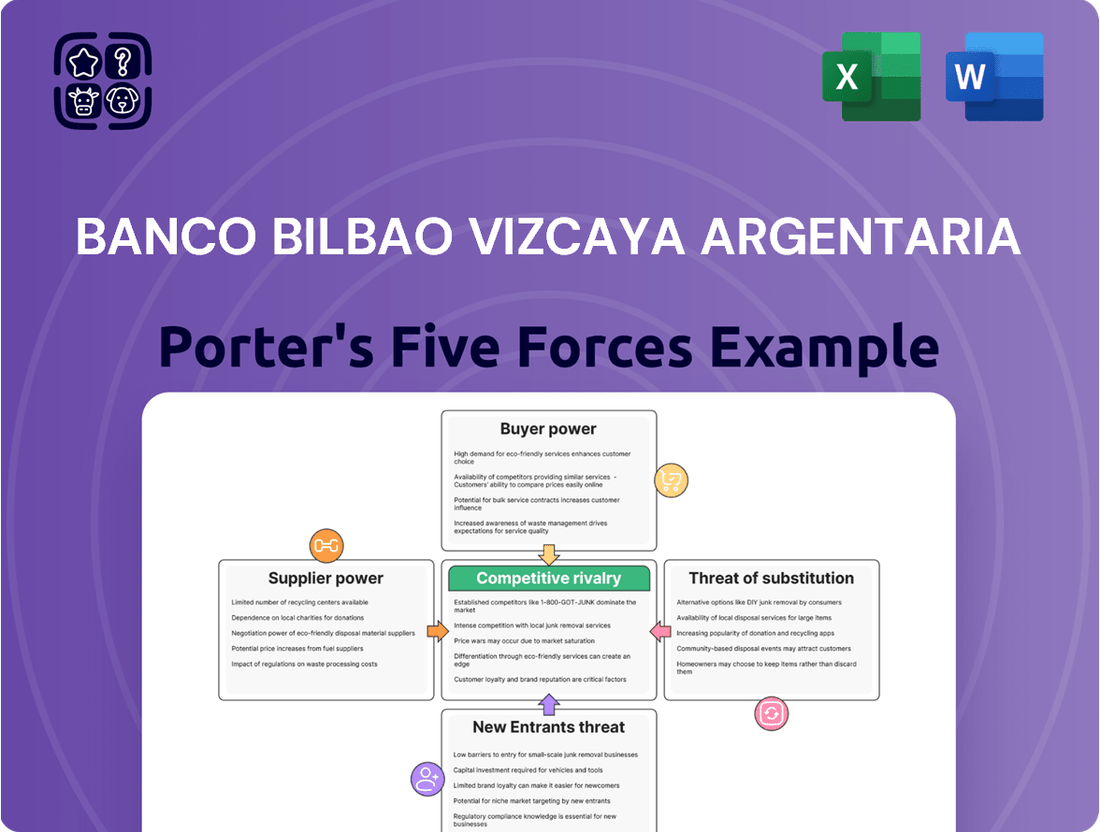
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, examining the intensity of rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes within the financial services sector.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, tailored for BBVA's strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail banking customers typically wield moderate bargaining power. The widespread availability of numerous banking institutions, coupled with decreasing switching costs facilitated by digital onboarding, allows customers to easily move between providers. This ease of switching, especially for commoditized services, can amplify their ability to negotiate better terms or seek out more competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, many banks actively promoted fee-free checking accounts and attractive interest rates on savings, directly responding to customer demand for better value.
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) often possess considerable bargaining power with banks like BBVA. This is especially true for SMEs that represent substantial transaction volumes or have specialized financing requirements. For instance, data from 2024 indicates that SMEs account for a significant portion of the business loan market in many European countries, giving them leverage to negotiate better interest rates and terms on services like loans and payment processing.
These businesses are adept at comparing the offerings of various financial institutions, actively seeking the most favorable conditions. Their financial health and demonstrated growth potential further amplify their negotiating position, enabling them to secure more advantageous terms for their banking relationships. This competitive landscape within business banking means that banks must actively court and retain these valuable clients.
Large corporations and institutional clients wield considerable bargaining power due to their substantial transaction volumes and the complexity of their financial requirements. These sophisticated entities often solicit bids from multiple financial institutions, creating a highly competitive environment for banks like BBVA. For instance, in 2024, major corporations were actively seeking customized treasury management solutions and competitive pricing on large-scale syndicated loans, directly influencing the terms banks could offer.
Their ability to demand tailored financial products and services, coupled with the potential to shift significant business to competitors, forces banks to offer attractive terms and specialized expertise. This dynamic underscores the importance of relationship banking and the development of niche financial solutions to retain and attract these high-value clients.
Digital Channel Customers
Digital channel customers at BBVA, like many in the banking sector, often display heightened price sensitivity. The ease of online comparison means they can quickly assess offerings from various institutions, putting pressure on providers to remain competitive on fees and interest rates. This digital savviness translates to a lower inherent loyalty, as switching providers becomes a less burdensome process.
The convenience offered by digital banking channels significantly boosts customer bargaining power. BBVA’s digital platforms allow customers to access services 24/7, research products, and manage accounts with minimal effort. This accessibility empowers them to actively seek out the best deals and most user-friendly experiences, making them less inclined to stay with a provider if better options are readily available.
Customers interacting primarily through digital channels have a clear demand for seamless and intuitive solutions. They expect a smooth user experience, from account opening to transaction processing. For instance, in 2024, the global average customer satisfaction score for digital banking services reached 78%, indicating a strong preference for efficient and easy-to-use platforms.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: Digital banking customers can easily compare fees and interest rates across multiple providers, leading to a stronger negotiation position.
- Lower Loyalty: The reduced friction in switching providers digitally means customer loyalty is often less entrenched.
- Demand for Seamless Experience: Customers expect intuitive, user-friendly digital interfaces and efficient service delivery.
- Empowerment through Accessibility: 24/7 access and readily available information give digital customers greater control and choice.
Information Access and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information about banking products and services. Digital comparison tools and financial aggregators make it incredibly easy to see how different banks stack up on interest rates, fees, and features. This transparency significantly boosts customer bargaining power, as they can readily identify the best deals available.
This reduction in information asymmetry forces financial institutions, including BBVA, to be more competitive. Banks must offer clearer pricing and more attractive terms to retain customers who can easily switch to a competitor offering better value. For instance, in 2024, the average customer could compare mortgages from over 50 different lenders within minutes online.
The ease of comparison means that customers are less loyal to a single institution based on convenience alone. They are empowered to seek out the most favorable terms, directly impacting a bank's ability to charge premium prices or retain customers through inertia.
- Increased Digital Comparison: Customers can easily compare rates and fees from numerous financial institutions online.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Transparency in pricing and product features empowers customers to make informed choices.
- Enhanced Bargaining Power: Easy access to comparative data allows customers to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
- Competitive Pressure: Banks like BBVA face pressure to offer more transparent and competitive pricing to attract and retain customers.
The bargaining power of BBVA's customers is significant, driven by digital accessibility and increased price sensitivity. Customers can effortlessly compare offerings from numerous financial institutions, putting pressure on banks to provide competitive rates and lower fees. This ease of switching, particularly for standardized banking products, means customers have considerable leverage to negotiate better terms or simply move their business elsewhere.
In 2024, the proliferation of online financial comparison platforms empowered consumers to scrutinize banking services more than ever. For instance, a customer could compare savings account interest rates from dozens of banks within minutes, directly impacting BBVA's ability to retain deposits without offering attractive yields. This transparency reduces information asymmetry, giving customers a stronger hand in negotiations.
This dynamic forces BBVA to focus on offering value-added services and a superior customer experience to maintain loyalty. The ability for customers to easily switch providers means that banks must constantly innovate and remain competitive on price and service quality. Ultimately, informed and digitally savvy customers hold considerable sway in the retail banking landscape.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, exactly as you will receive it immediately after purchase. You'll gain immediate access to this professionally formatted document, detailing the competitive landscape of BBVA. The analysis meticulously covers the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, so what you're previewing is precisely what you get.
Rivalry Among Competitors
BBVA contends with formidable competition from other major domestic and international banks. In Spain, Santander is a significant rival, while in Mexico, Banorte and Citibanamex vie for customers. These established players offer a broad spectrum of financial services, directly challenging BBVA for market share across all customer segments.
This intense rivalry means that strategic initiatives by one bank often trigger reactions from others, creating a dynamic competitive landscape. For instance, if BBVA introduces a new digital banking feature, competitors are likely to respond with similar innovations to retain their customer base. This constant pressure necessitates continuous adaptation and investment in technology and customer service.
The competitive rivalry from digital-only banks and neobanks is a substantial force impacting traditional institutions like BBVA. These agile players, leveraging technology, are particularly strong in the retail and small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) markets.
Neobanks often boast lower operational costs due to their digital-first approach, enabling them to offer more attractive pricing and user-friendly interfaces. For instance, by mid-2024, several prominent neobanks reported exponential user growth, capturing market share previously held by incumbents.
Their focus on seamless digital experiences and innovative features directly appeals to a growing customer base that prefers online banking. This shift in customer preference challenges the traditional branch-centric models of established banks.
The rapid adoption of digital banking solutions, with global digital banking users projected to exceed 2.5 billion by 2025, underscores the intensity of this rivalry. Traditional banks must innovate and enhance their digital offerings to remain competitive.
Fintech companies are intensely competitive rivals for BBVA, particularly in specialized areas like payments, lending, and wealth management. They disaggregate traditional banking services, offering highly focused and user-friendly solutions. For instance, many digital payment platforms saw significant growth in 2024, with transaction volumes increasing by over 20% year-over-year in key markets. This direct competition in niche segments forces BBVA to either innovate rapidly or collaborate with these agile players.
Market Concentration and Regulatory Environment
The intensity of competition for BBVA is shaped by how concentrated its operating markets are and the specific regulatory frameworks in place. In regions where a few dominant banks operate, rivalry might appear less fierce, but strict regulations often act as significant entry barriers, influencing how existing players compete. For instance, in 2023, the European Central Bank (ECB) maintained a prudent approach to banking supervision, with capital requirements like the Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio remaining a crucial factor for competitive positioning. BBVA’s strong capital ratios, often exceeding regulatory minimums, allow for strategic flexibility.
Compliance with diverse and often stringent regulations across its global footprint, including Spain, Turkey, and Mexico, significantly impacts BBVA's operational costs and strategic choices. These regulatory burdens can limit aggressive pricing or product innovation that might otherwise intensify rivalry. For example, in 2024, the implementation of new digital banking regulations in several key markets requires substantial investment in technology and compliance, potentially favouring larger, well-capitalized institutions like BBVA.
- Market Concentration: BBVA operates in markets with varying degrees of concentration. For example, Spain's banking sector has seen consolidation, with the top five banks holding a significant market share.
- Regulatory Impact: Stringent capital adequacy ratios, such as the CET1 requirements set by European authorities, influence how banks like BBVA can deploy capital and compete on price or product offerings.
- Compliance Costs: The cost of adhering to differing regulatory landscapes in countries like Mexico and Turkey adds to operational expenses and can affect competitive dynamics.
- Barriers to Entry: High capital requirements and complex licensing procedures established by regulators act as significant barriers, limiting the number of new entrants and thus influencing the level of rivalry.
Geographic Diversification
BBVA's extensive geographic footprint, spanning Spain, Mexico, South America, and Turkey, exposes it to a spectrum of competitive pressures. This diversification, while a strategic advantage for risk mitigation, necessitates tailored approaches to local market conditions, customer preferences, and regulatory environments. Consequently, the intensity of rivalry can fluctuate considerably across these diverse operating regions, demanding adaptive strategies.
The competitive landscape for BBVA varies significantly by region. For instance, in Mexico, BBVA Mexico is a major player but faces strong competition from banks like Banorte and Citibanamex. In Spain, while BBVA remains a dominant force, it contends with established domestic banks such as Santander and CaixaBank, alongside a growing presence of digital-only banks. South America presents a mosaic of competitive dynamics, with local champions and international banks vying for market share. Turkey, a key market for BBVA, has its own set of robust domestic banking competitors.
- Spain: Intense rivalry among established players like Santander and CaixaBank, plus increasing competition from neobanks.
- Mexico: Strong competition from Banorte and Citibanamex, alongside BBVA Mexico's significant market presence.
- South America: Fragmented markets with competition from both strong local banks and international financial institutions.
- Turkey: A competitive environment dominated by major Turkish banks such as Is Bankasi and Garanti BBVA itself, which BBVA holds a majority stake in.
The competitive rivalry for BBVA is characterized by a dynamic interplay between traditional banking giants and agile digital disruptors across its key markets. Established banks like Santander in Spain and Banorte in Mexico represent significant challenges, forcing BBVA to continually innovate its service offerings to retain customers. This intense competition is further amplified by the rise of neobanks and fintech firms, which are capturing market share, particularly in retail and SME segments, by offering streamlined digital experiences and competitive pricing.
Digital banking's rapid expansion, with global users expected to surpass 2.5 billion by 2025, highlights the pressure on traditional players like BBVA to enhance their digital capabilities. Fintech companies, in particular, are disaggregating banking services, creating direct competition in specialized areas such as payments and lending. For instance, digital payment platforms saw transaction volumes increase by over 20% year-over-year in key markets during 2024, demonstrating their growing influence.
BBVA's strategic positioning is also influenced by market concentration and regulatory environments, with stringent capital requirements like the CET1 ratio impacting competitive strategies. For example, in 2023, the ECB's oversight maintained prudent supervision, underscoring the importance of strong capital ratios for competitive flexibility, which BBVA generally possesses, often exceeding regulatory minimums.
The competitive intensity varies significantly across BBVA's geographic footprint, from mature markets like Spain to emerging economies. In Mexico, BBVA Mexico competes fiercely with Banorte and Citibanamex, while in Spain, Santander and CaixaBank are key rivals, alongside a growing number of neobanks. This regional variation necessitates highly localized strategies to navigate diverse competitive landscapes, from consolidating Spanish markets to fragmented South American territories.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech payment solutions presents a substantial threat of substitutes for BBVA's traditional payment services. Mobile wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, alongside peer-to-peer apps and non-bank payment providers, offer increasingly seamless alternatives for everyday transactions. These platforms often boast lower transaction fees for consumers and businesses, alongside enhanced convenience and speed, directly chipping away at the necessity of relying solely on bank-provided payment infrastructure.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms present a significant threat by offering alternative funding channels that bypass traditional banks like BBVA. These platforms allow individuals and businesses to secure loans or raise capital directly, often with more streamlined processes and potentially more competitive rates for certain segments. For instance, the global P2P lending market was projected to reach over $300 billion by 2025, indicating substantial growth and a direct challenge to traditional lending models.
These digital alternatives can be particularly appealing to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individuals seeking smaller loan amounts, as they may find the application and approval processes quicker and less stringent than those at established banks. Crowdfunding, in particular, has seen tremendous growth, with global crowdfunding volume exceeding $20 billion in recent years, demonstrating its increasing relevance as a substitute for traditional financing for various projects and businesses.
The flexibility and speed offered by P2P and crowdfunding can directly siphon off business and consumer lending opportunities from traditional financial institutions. This disintermediation means that banks like BBVA need to innovate and adapt their offerings to remain competitive in a market increasingly influenced by these agile, technology-driven competitors.
The rise of online brokerage platforms and direct investment apps presents a significant threat of substitutes for BBVA's traditional wealth management services. These digital alternatives, such as Robinhood and Charles Schwab's online offerings, often boast substantially lower fees, attracting cost-conscious investors. For instance, many of these platforms offer commission-free trading for stocks and ETFs, a stark contrast to potentially higher fees associated with traditional bank advisory services.
Robo-advisors, like Betterment and Wealthfront, further intensify this threat by providing automated, algorithm-driven investment advice at a fraction of the cost of human financial advisors. Their accessibility and ease of use appeal to a growing segment of investors, particularly millennials and Gen Z, who are comfortable managing their finances digitally. This directly challenges BBVA's role as a primary investment advisor, as these platforms offer a streamlined, cost-effective pathway to market participation.
In 2024, the digital investment landscape continues to mature, with many fintech companies reporting substantial user growth and asset under management increases. This trend indicates a clear shift in investor preference towards more accessible, lower-cost digital solutions. For example, the robo-advisor market alone was projected to reach hundreds of billions in assets under management by the end of 2023, a figure expected to continue its upward trajectory.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology represent a developing threat to traditional banking services, particularly in areas like cross-border payments and remittances. While mainstream adoption is still evolving, these digital assets offer alternative avenues for financial transactions. For instance, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024, indicating significant and growing interest in these alternatives. BBVA needs to closely track advancements in decentralized finance (DeFi) and consider strategic integrations to maintain its competitive edge.
- Growing Market: The global cryptocurrency market's substantial valuation highlights its increasing relevance as a potential substitute.
- Payment Innovation: Blockchain's potential to streamline cross-border payments offers a faster and potentially cheaper alternative to traditional methods.
- DeFi Disruption: Decentralized finance platforms challenge established financial intermediation models, creating new competitive pressures.
- Strategic Imperative: BBVA must proactively engage with and potentially adopt these emerging technologies to ensure future market position.
Non-Bank Lending and Credit Providers
The threat of substitutes for BBVA's traditional lending products comes from a growing array of non-bank lending and credit providers. These include specialized credit companies, retail financing arms within large corporations, and increasingly, technology giants venturing into credit services. These entities often compete by offering tailored solutions to specific market niches or credit types, sometimes operating with lighter regulatory burdens than traditional banks.
These alternative credit providers directly challenge BBVA by offering financing that can replace bank loans. For instance, the rise of peer-to-peer lending platforms and buy-now-pay-later services directly competes for consumer and small business credit needs. In 2024, the global alternative lending market was projected to continue its robust growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach over $1.5 trillion, indicating a significant and expanding substitute landscape for traditional banking services.
- Specialized Credit Companies: Focus on specific loan types like equipment financing or invoice discounting.
- Retail Financing Arms: Offer point-of-sale credit, such as store cards or financing for durable goods.
- Fintech Platforms: Including peer-to-peer lenders and crowdfunding sites, providing alternative access to capital.
- Large Tech Companies: Increasingly entering the lending space, leveraging their data and customer bases.
The threat of substitutes for BBVA's core banking services is multi-faceted, driven by technological innovation and evolving consumer preferences. Fintech solutions for payments, lending, and wealth management offer increasingly competitive alternatives, often at lower costs and with greater convenience. These substitutes directly challenge BBVA's traditional revenue streams and customer relationships.
Fintech platforms are rapidly gaining traction, particularly among younger demographics, by providing user-friendly digital interfaces and specialized services. This shift necessitates that BBVA continually innovate and adapt its offerings to remain relevant in a dynamic financial landscape. Failing to do so risks ceding market share to more agile, digitally-native competitors.
The increasing adoption of digital payment methods, peer-to-peer lending, and robo-advisory services signifies a clear trend away from traditional banking models. For instance, the global digital payments market is projected to exceed $10 trillion by 2026, demonstrating a significant migration towards alternative transaction channels. Similarly, the alternative lending market's projected growth to over $1.5 trillion in 2024 underscores the competitive pressure on traditional loan products.
| Substitute Category | Key Examples | Impact on BBVA | Market Trend Data (2024/Projected) |
| Payments | Mobile Wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay), P2P Apps | Reduced transaction fees, lower reliance on bank infrastructure | Global digital payments market projected > $10T by 2026 |
| Lending | P2P Lending Platforms, BNPL Services | Disintermediation of loan origination, competition for credit needs | Alternative lending market projected > $1.5T in 2024 |
| Wealth Management | Online Brokerages, Robo-Advisors | Lower fees, increased accessibility for investors | Robo-advisor market AUM in hundreds of billions, growing |
| Investments/Transactions | Cryptocurrencies, Blockchain | Alternative for cross-border payments, evolving DeFi landscape | Global crypto market cap ~$2.5T (early 2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces formidable regulatory hurdles that significantly deter new entrants. Banks must maintain substantial capital reserves, a requirement that can run into billions for major institutions, making it difficult for startups to compete. For instance, in 2024, many jurisdictions continue to enforce Basel III and its evolving extensions, demanding robust capital adequacy ratios that price out smaller, less capitalized operations.
Obtaining the necessary licenses is a lengthy and expensive process, often involving extensive due diligence and proving operational soundness. Furthermore, compliance with intricate anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations demands significant investment in technology and personnel, adding another layer of complexity and cost for any aspiring bank.
These stringent requirements, including ongoing compliance with evolving data privacy laws and cybersecurity mandates, effectively create a high barrier to entry. The sheer cost and time involved in establishing a compliant banking operation in 2024 are often prohibitive, protecting established players like Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria from a flood of new competition.
Establishing a full-service bank requires substantial capital for infrastructure, technology, and regulatory compliance. For instance, in 2024, major banks like BBVA continue to invest billions in digital transformation, a cost prohibitive for many new entrants. Meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios, such as Basel III requirements, demands significant upfront investment, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
Customers often exhibit strong loyalty to their existing banks, particularly for core services like checking accounts and mortgages, due to the perceived trust and convenience. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates in the banking sector remained robust, with many individuals hesitant to switch for minor benefits. This ingrained loyalty creates a substantial hurdle for newcomers aiming to disrupt established players like BBVA.
Building a new brand and earning customer trust in the highly sensitive financial services sector is a significant challenge for new entrants. The financial crisis of 2008, while years ago, still influences consumer behavior, making them wary of unfamiliar institutions. This ingrained caution means new banks must invest heavily in security and transparent communication to even begin to compete with established trust.
BBVA benefits from its established brand reputation and extensive customer base across its markets, reinforcing this barrier. As of early 2025, BBVA reported a significant global customer base, a testament to decades of building relationships and trust. This existing network provides a powerful advantage, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction without a compelling and highly differentiated offering.
Digital-First Entrants and Fintechs
The threat of new entrants, particularly from digital-first banks and agile fintechs, presents a significant challenge to established institutions like BBVA. While traditional banking faces high regulatory and capital barriers, these newer players can carve out profitable niches by focusing on specific services, like payments or specialized lending, often with considerably lower operational overheads. This allows them to sidestep some of the legacy infrastructure costs that burden incumbents.
These digital disruptors leverage technology to offer streamlined, often cheaper, alternatives for consumers. Their agility and capacity for rapid innovation are crucial competitive advantages, enabling them to quickly adapt to market demands and introduce novel products. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at over $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a fertile ground for new entrants targeting lucrative segments within the financial services landscape.
- Targeted Niches: Fintechs often enter by focusing on specific, profitable services, like cross-border payments or peer-to-peer lending, rather than offering a full suite of banking products initially.
- Lower Overheads: Digital-first banks can operate with significantly reduced physical branch networks and legacy IT systems, leading to lower operational costs.
- Agility and Innovation: Their lean structures allow for quicker development cycles and the introduction of user-friendly interfaces and innovative features, attracting tech-savvy customers.
- Market Growth: The substantial growth in the fintech sector, with projections indicating continued expansion, underscores the increasing potential for new players to gain market share.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Established financial institutions like BBVA leverage substantial economies of scale. In 2024, BBVA reported a cost-to-income ratio of 42.7%, demonstrating operational efficiency. This scale allows for competitive pricing and a wide array of services that new entrants find difficult to match immediately.
Network effects also create a significant barrier. BBVA's extensive digital platforms and broad ATM network, utilized by millions of customers, enhance service value. For instance, a large customer base facilitates better data analytics for personalized offerings, a feature nascent competitors can’t replicate overnight.
New entrants face challenges in achieving comparable operational reach and customer adoption. Building a widespread physical or digital presence and cultivating a large, loyal customer base requires substantial time and capital investment, hindering their ability to compete effectively.
- Economies of Scale: BBVA's 2024 cost-to-income ratio of 42.7% highlights operational efficiency derived from scale.
- Network Effects: Millions of active users on BBVA's digital platforms and extensive ATM network increase service value, a hurdle for new entrants.
- Barriers to Entry: New competitors struggle to quickly replicate BBVA's established infrastructure and customer loyalty, making cost-based or reach-based competition difficult.
While high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles form traditional barriers, digital-first banks and agile fintechs are emerging as significant threats. These new entrants often focus on specific, lucrative financial niches, leveraging technology to offer streamlined services with lower overheads. Their ability to innovate quickly and attract tech-savvy customers poses a challenge to incumbents like BBVA.
| Threat Type | Key Differentiator | BBVA's Counter-Strategy |
| Fintechs & Digital Banks | Niche focus, lower costs, agility | Digital transformation, customer experience enhancement |
| Market Entry Strategy | Targeted services (e.g., payments, P2P lending) | Broadening digital service offerings, partnerships |
| Competitive Advantage | User-friendly interfaces, rapid innovation | Investing in AI, data analytics for personalized services |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for BBVA utilizes financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable sources like S&P Global Market Intelligence and Euromonitor to gauge competitive pressures.
