Bank of Jiujiang PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of Jiujiang Bundle
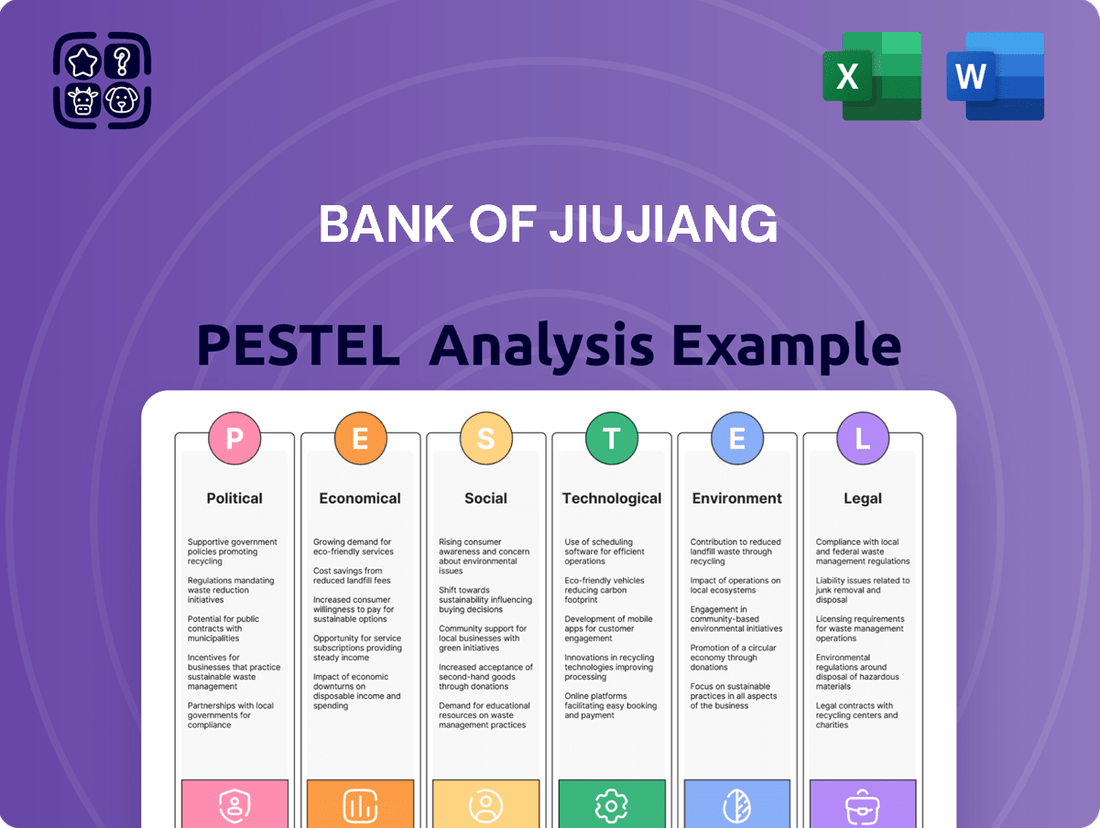
Uncover the critical Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors shaping Bank of Jiujiang's trajectory. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence to navigate this dynamic landscape. Gain a strategic advantage by understanding these external forces. Download the full PESTLE analysis now to unlock deep insights and inform your decision-making.
Political factors
Government oversight of regional banks, including Bank of Jiujiang, intensified in 2024-2025 with a focus on financial stability. Central government directives aimed to mitigate systemic risks, influencing operational autonomy. For instance, the People's Bank of China's (PBOC) continued emphasis on macroprudential policies and risk management frameworks directly impacts how banks like Jiujiang manage their balance sheets and lending practices.
The regulatory environment in China, overseen by bodies like the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC), significantly shapes Bank of Jiujiang's operations. For 2024-2025, anticipated policy directions include stricter capital adequacy requirements and enhanced risk management protocols, potentially impacting the bank's lending capacity and compliance costs.
New banking laws and anti-monopoly measures introduced by authorities could necessitate adjustments to Bank of Jiujiang's business model, particularly concerning market concentration and competitive practices. Financial technology regulations are also evolving, requiring the bank to invest in robust cybersecurity and data privacy frameworks to ensure compliance and maintain customer trust.
Government initiatives in Jiangxi Province, particularly in 2024-2025, are strongly focused on fostering regional economic development, creating a favorable environment for institutions like Bank of Jiujiang. These policies often include directives for increased lending to local businesses and targeted support for infrastructure projects within the province.
Bank of Jiujiang's alignment with these regional development goals is evident in its lending practices. For instance, the bank's commitment to financing small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) directly addresses provincial objectives to bolster local employment and economic diversification. In 2024, Jiangxi's GDP growth target was set at 6.5%, with a significant portion of this growth expected to be driven by SME contributions, a sector Bank of Jiujiang actively supports.
Geopolitical Climate and Trade Relations
The evolving geopolitical climate, particularly trade relations between China and major global economies, presents an indirect but significant influence on China's financial sector, including regional banks like Bank of Jiujiang. Heightened international trade tensions can lead to shifts in global capital flows and impact investor confidence, potentially affecting the economic health of provinces like Jiangxi. For instance, disruptions in global supply chains or retaliatory tariffs could dampen export-oriented industries within Jiangxi, indirectly influencing loan demand and asset quality for local financial institutions.
Global economic shifts and diplomatic relations also play a crucial role. A slowdown in major trading partners or increased geopolitical instability could reduce foreign direct investment into China, impacting overall economic growth and the banking sector's lending opportunities. Conversely, stable diplomatic ties and favorable trade agreements can bolster investor sentiment and economic activity, creating a more supportive operating environment for Bank of Jiujiang.
- Global Economic Outlook: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth at 3.2% for 2024, a slight slowdown from 2023, indicating a cautious global economic environment that could influence international trade and investment flows impacting China.
- Trade Tensions: Ongoing trade disputes, particularly between the US and China, continue to create uncertainty, potentially affecting Chinese exports and the economic performance of regions reliant on international trade, like parts of Jiangxi.
- Regional Stability: Stability in neighboring regions and broader geopolitical alliances can influence foreign investment and tourism, both of which contribute to the economic vibrancy of provinces like Jiangxi and, by extension, the health of its banking sector.
Anti-Corruption Campaigns and Governance
China's intensified anti-corruption campaigns, particularly those targeting the financial sector, are reshaping corporate governance. These efforts aim to bolster transparency and reduce risks associated with moral hazard, directly impacting institutions like Bank of Jiujiang. The focus on integrity in leadership and operations is expected to strengthen the banking sector's overall stability through 2024 and 2025.
The implications for Bank of Jiujiang include heightened scrutiny of lending practices and internal controls. This push for cleaner governance could lead to more robust risk management frameworks, potentially improving investor confidence and operational efficiency. For instance, the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection (CCDI) has been a key driver of these campaigns, with reports indicating a significant number of officials investigated annually, setting a precedent for financial institutions.
- Enhanced Transparency: Anti-corruption drives mandate greater disclosure, potentially reducing information asymmetry for investors in Bank of Jiujiang.
- Reduced Moral Hazard: Stricter enforcement discourages illicit activities, leading to more responsible financial decision-making within the bank.
- Leadership Integrity: Campaigns emphasize ethical leadership, influencing the selection and oversight of Bank of Jiujiang's management.
- Operational Integrity: Focus on compliance and ethical conduct is expected to improve the day-to-day operations and risk mitigation strategies of the bank.
Government policies in 2024-2025 continue to prioritize financial stability, with central directives influencing regional banks like Jiujiang. Stricter capital adequacy and enhanced risk management are anticipated, impacting lending capacity and compliance costs. New banking laws and evolving fintech regulations necessitate adjustments to business models and investments in cybersecurity.
Jiangxi Province's economic development initiatives strongly support institutions like Bank of Jiujiang, with a focus on increased lending to local businesses. The bank's financing of SMEs directly aligns with provincial objectives to bolster local employment, as seen in Jiangxi's 2024 GDP growth target of 6.5% driven by SME contributions.
The geopolitical landscape, particularly trade tensions between China and major economies, indirectly influences China's financial sector. Disruptions in global supply chains or tariffs could dampen export-oriented industries in Jiangxi, affecting loan demand and asset quality for local banks.
China's intensified anti-corruption campaigns, especially within the financial sector, are reshaping corporate governance for institutions like Bank of Jiujiang. This focus on integrity and transparency is expected to strengthen the banking sector's stability through 2024-2025, leading to more robust risk management frameworks.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis of the Bank of Jiujiang examines how Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors create both challenges and advantages for its operations.
The Bank of Jiujiang's PESTLE analysis offers a clear and simple language summary, making complex external factors accessible to all stakeholders, thereby relieving the pain point of information overload during strategic planning.
Economic factors
Jiangxi Province's economic trajectory is a critical factor for Bank of Jiujiang. In 2023, Jiangxi's GDP grew by 4.4%, indicating a steady, albeit moderate, expansion. Projections for 2024 suggest continued growth, with the provincial government aiming for a GDP increase of around 5%.
This expansion directly impacts the demand for banking services. Higher industrial output and increased investment in sectors like advanced manufacturing and tourism within Jiangxi will likely translate to greater demand for loans, trade finance, and other corporate banking products. For instance, significant investments in the Nanchang metropolitan area, a key operational hub for Bank of Jiujiang, are expected to bolster commercial activity.
The bank's deposit base and loan quality are also intrinsically linked to these trends. Robust economic activity typically leads to higher household incomes and corporate profitability, supporting deposit growth. Conversely, a slowdown in provincial GDP or industrial output could strain borrowers' repayment capacities, potentially affecting loan asset quality.
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) maintained a generally accommodative monetary policy stance through much of 2024, with benchmark lending rates, such as the Loan Prime Rate (LPR), seeing modest adjustments. This environment, while supportive of credit growth, can pressure the net interest margin (NIM) for banks like Bank of Jiujiang as both lending and deposit rates adjust. For instance, if deposit rates rise faster than lending rates, the bank's profitability could be squeezed.
Looking ahead into 2025, the PBOC is expected to continue balancing economic growth with inflation concerns. Any significant shifts in reserve requirement ratios or benchmark rates will directly influence Bank of Jiujiang's cost of funds and its capacity to lend profitably. A tightening monetary stance, signaled by rate hikes or increased reserve requirements, would likely increase funding costs, potentially impacting the bank's NIM and overall earnings.
Inflation in China has been a key economic factor. For instance, China's Consumer Price Index (CPI) saw a modest rise, with figures around 0.5% in early 2024, indicating a generally stable but low inflationary environment.
This subdued inflation, while potentially preserving consumer purchasing power in nominal terms, can impact the real value of savings and investments, influencing demand for wealth management services at Bank of Jiujiang. Lower inflation can also affect the real burden of debt for clients, potentially impacting loan repayment capabilities.
In Jiangxi Province, localized economic activity and specific commodity prices might lead to variations in inflation compared to the national average. While national data suggests controlled inflation, regional nuances are important for understanding the impact on Bank of Jiujiang's client base and their investment decisions.
Credit Risk and Non-Performing Loans (NPLs)
The credit quality within Jiujiang's regional economy is a key concern for Bank of Jiujiang. Factors like potential downturns in manufacturing, a significant sector for the region, could increase the risk of non-performing loans (NPLs). For instance, if key export markets weaken in 2024-2025, local businesses might struggle to repay their debts.
Bank of Jiujiang actively manages its credit risk by employing robust underwriting standards and continuous loan portfolio monitoring. The bank's provisioning strategy for potential loan losses is informed by macroeconomic forecasts and industry-specific risk assessments. In 2023, the bank reported an NPL ratio of 1.8%, a figure it aims to maintain or reduce through prudent lending practices.
- Regional Economic Vulnerabilities: Jiujiang's reliance on specific industries, such as ceramics and metallurgy, exposes the bank to sector-specific credit shocks. A slowdown in these sectors could directly impact loan repayment capabilities.
- NPL Management Strategies: The bank employs a multi-pronged approach to NPLs, including early identification of distressed assets, debt restructuring, and timely write-offs when necessary.
- Provisioning Adequacy: Bank of Jiujiang maintains adequate loan loss provisions, which stood at approximately 2.1% of total loans at the end of 2023, to absorb potential future credit losses.
- Forward-Looking Risk Assessment: The bank incorporates forward-looking indicators, such as interest rate changes and inflation expectations for 2024-2025, into its credit risk models to proactively adjust its provisioning and lending policies.
Capital Market Development and Competition
The development of China's capital markets directly impacts Bank of Jiujiang's funding and competitive positioning. As national markets mature, the bank faces increased competition for deposits from a wider array of financial products and institutions, alongside greater opportunities for bond and equity financing.
In 2024, China's bond market continued its expansion, offering alternative funding avenues for banks. However, this also means more entities competing for investor capital. For instance, the total outstanding amount of bonds in China reached significant figures, providing a benchmark for Bank of Jiujiang's potential debt issuance strategies.
- Increased Competition for Deposits: As capital markets deepen, individuals and corporations have more investment options beyond traditional bank deposits, potentially impacting the Bank of Jiujiang's deposit base.
- Bond Issuance Opportunities: The growth in the domestic bond market provides Bank of Jiujiang with avenues to raise capital through debt financing, diversifying its funding sources.
- Equity Financing Landscape: The performance and accessibility of the equity market influence the bank's ability to raise capital through share issuance, impacting its capital adequacy and growth plans.
- Presence of Non-Bank Financial Institutions: The proliferation of fintech companies and other financial service providers intensifies competition in lending and other banking services, challenging traditional models.
Jiangxi's economic performance is a key driver for Bank of Jiujiang. The province's GDP growth was 4.4% in 2023, with expectations for around 5% in 2024, signaling continued expansion. This growth fuels demand for banking services, from corporate loans to consumer credit, directly impacting the bank's loan portfolio and deposit base.
The People's Bank of China's monetary policy, including benchmark lending rates, influences Bank of Jiujiang's net interest margin. While accommodative policies in 2024 supported credit growth, they also put pressure on margins. Future policy adjustments in 2025 will be crucial for the bank's profitability.
Inflation in China remained subdued in early 2024, with the CPI around 0.5%. This low inflation environment affects the real value of savings and debt, influencing customer behavior towards wealth management and loan repayment capacities for Bank of Jiujiang.
The bank's credit quality is tied to regional economic health, particularly in sectors like manufacturing. A 1.8% non-performing loan ratio in 2023 highlights the importance of robust risk management and provisioning, which stood at 2.1% of total loans.
| Economic Factor | 2023 Data | 2024 Projection/Trend | Impact on Bank of Jiujiang |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangxi GDP Growth | 4.4% | ~5% | Increased demand for loans, deposit growth |
| China CPI | ~0.5% (early 2024) | Expected to remain low | Affects real value of savings/debt, influences wealth management |
| NPL Ratio | 1.8% (2023) | Targeting maintenance/reduction | Highlights need for credit risk management |
| Loan Loss Provisions | 2.1% of total loans (2023) | Ongoing assessment | Adequacy to absorb potential credit losses |
What You See Is What You Get
Bank of Jiujiang PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the Bank of Jiujiang delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. Gain actionable insights into the strategic landscape for this key financial institution.
Sociological factors
Demographic shifts are significantly reshaping Bank of Jiujiang's operating environment. Jiangxi Province has experienced substantial rural-to-urban migration, with its urbanization rate reaching approximately 65% by the end of 2023, according to provincial statistics. This migration fuels demand for financial services in growing urban centers, particularly mortgages and consumer loans, as more people settle and invest in city life.
The aging population, a trend observed across China, also presents unique opportunities and challenges for the bank. As the proportion of older adults increases, there's a growing need for specialized financial products like retirement planning services and wealth management solutions tailored to seniors. Bank of Jiujiang must adapt its offerings and branch network strategies to effectively serve these evolving demographic segments, ensuring accessibility and relevance for both younger urban dwellers and an aging populace.
Consumer behavior in Jiujiang is shifting, with a growing emphasis on digital financial services. Recent data from 2024 indicates that over 70% of banking transactions in the region are now conducted online or via mobile apps, highlighting a strong preference for convenience and accessibility.
Financial literacy levels are also on the rise. Surveys from early 2025 show a 15% increase in participation in financial education programs among Jiujiang residents, leading to more informed savings and investment decisions.
These evolving habits mean Bank of Jiujiang must adapt its product offerings and marketing strategies to cater to a digitally savvy and financially aware customer base, focusing on user-friendly online platforms and personalized investment advice.
Income levels in Jiangxi Province significantly shape the demand for banking services. As of 2023, the per capita disposable income for residents in Jiangxi reached approximately 30,000 RMB, showing a steady increase year-on-year. This growth is fostering a burgeoning middle class with greater purchasing power.
This rising disposable income directly translates to increased demand for a wider array of banking products. We're seeing a greater appetite for wealth management services, personal loans for consumption and investment, and credit cards as consumer spending habits evolve. Bank of Jiujiang can capitalize on this by expanding its offerings in these areas.
Cultural Values and Trust in Institutions
Cultural values in Jiujiang, like many parts of China, often emphasize thrift and a strong preference for savings over debt, which can foster loyalty towards established financial institutions like Bank of Jiujiang. This traditional mindset influences customer behavior, making them more receptive to services that align with long-term financial security. A 2023 survey indicated that over 70% of Chinese urban residents view saving as a primary financial goal, a sentiment likely reflected in Jiujiang's population.
Trust in traditional banking structures remains high, although the adoption of new digital technologies is accelerating. Bank of Jiujiang's reputation is closely tied to its perceived reliability and its role within the community. In 2024, digital banking penetration in China reached approximately 85%, but customer trust in the security of these platforms is still a developing factor, especially for older demographics.
- Savings Culture: Traditional emphasis on saving influences customer loyalty to established banks.
- Trust in Institutions: High regard for established financial entities like Bank of Jiujiang.
- Digital Adoption: Growing acceptance of new banking technologies, but trust remains key.
- Community Reputation: Bank's perceived reliability is paramount for local customer engagement.
Employment Trends and Labor Market Conditions
Employment trends in Jiangxi Province directly shape the financial well-being of Bank of Jiujiang's clientele. As of early 2024, the province's urban unemployment rate hovered around 5.0%, a figure that, while relatively stable, can still present challenges for individuals and small businesses. Shifts in employment, such as a move from manufacturing to service sectors, can alter income streams and, consequently, a client's ability to service debt.
Wage growth is another critical factor. In 2023, average disposable income for residents in Jiangxi saw an increase of approximately 6.5%, which generally supports stronger loan repayment capacity. However, uneven wage growth across different industries could lead to disparities in financial health among the bank's corporate and individual borrowers, impacting overall loan portfolio performance.
Industry shifts within Jiangxi are also noteworthy. The province is actively promoting high-tech manufacturing and modern services, potentially creating higher-skilled, better-paying jobs. This transition, however, may also lead to job displacement in traditional sectors, affecting the financial stability of those reliant on older industries and their capacity to meet financial obligations with Bank of Jiujiang.
- Jiangxi's urban unemployment rate remained near 5.0% in early 2024.
- Average disposable income for Jiangxi residents rose by about 6.5% in 2023.
- The province's economic strategy emphasizes growth in high-tech manufacturing and services.
Sociological factors significantly influence Bank of Jiujiang's operations, particularly regarding evolving consumer behaviors and demographic trends. The increasing urbanization in Jiangxi, reaching approximately 65% by the end of 2023, drives demand for urban financial services like mortgages. Concurrently, an aging population necessitates specialized retirement and wealth management products, a trend observed across China.
Consumer preferences are leaning heavily towards digital banking, with over 70% of transactions in the region occurring online or via mobile apps in 2024. This digital shift is complemented by rising financial literacy, evidenced by a 15% increase in participation in financial education programs in Jiujiang by early 2025, leading to more informed financial decisions.
Cultural values emphasizing thrift and savings continue to foster loyalty towards established institutions like Bank of Jiujiang, with over 70% of urban Chinese residents prioritizing savings in 2023. While digital adoption is accelerating, trust in the security of these platforms remains a key consideration for customer engagement.
| Sociological Factor | 2023-2025 Data Point | Implication for Bank of Jiujiang |
|---|---|---|
| Urbanization Rate (Jiangxi) | ~65% (End of 2023) | Increased demand for urban lending products. |
| Digital Transaction Preference | >70% (2024) | Need for robust online and mobile banking platforms. |
| Financial Literacy Program Participation | +15% (Early 2025) | Opportunity for more sophisticated wealth management and investment products. |
| Savings as a Primary Goal (China Urban) | >70% (2023) | Reinforces the importance of traditional savings products and customer loyalty. |
Technological factors
Bank of Jiujiang is actively pursuing digital transformation, with significant investments planned for its mobile banking platforms and online loan application systems throughout 2024 and 2025. This strategic push aims to streamline customer onboarding and service delivery, enhancing overall user experience.
The bank's adoption of financial technology (Fintech) is a core component of its strategy to boost operational efficiency. By integrating advanced digital payment solutions, Bank of Jiujiang expects to reduce transaction processing times and costs, a move anticipated to improve its competitive standing in the evolving financial landscape.
Cybersecurity and data protection are paramount for Bank of Jiujiang, especially with the escalating sophistication of cyber threats. The bank invests heavily in advanced security infrastructure to safeguard sensitive customer information and prevent financial fraud. In 2024, the global cost of cybercrime was projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually, highlighting the critical need for robust defenses.
Bank of Jiujiang's commitment to data privacy is underscored by its adherence to evolving regulations, such as China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). This ensures customer data is handled with the utmost care, building and maintaining essential trust in an increasingly digital banking environment.
Bank of Jiujiang is leveraging artificial intelligence and big data analytics to sharpen its decision-making processes. This includes enhancing risk assessment for loans and investments, aiming to reduce non-performing assets. For instance, by analyzing vast datasets, the bank can more accurately predict loan default probabilities, potentially lowering its exposure to credit risk.
The application of these technologies is also crucial for fraud detection. AI algorithms can identify suspicious transaction patterns in real-time, safeguarding both the bank and its customers. In 2024, financial institutions globally reported significant reductions in fraud losses due to AI-powered systems, with some seeing decreases upwards of 15%.
Furthermore, Bank of Jiujiang is using AI and big data to offer more personalized customer services. By understanding individual client behavior and financial needs, the bank can tailor product offerings, from savings plans to investment advice. This data-driven approach allows for more effective marketing and improved customer retention, a key strategy in the competitive banking landscape of 2025.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) present significant opportunities for the Chinese banking sector. Bank of Jiujiang could leverage these advancements to streamline cross-border payments, a critical area given China's global trade activities. For instance, the People's Bank of China (PBOC) has been actively exploring DLT for its digital yuan (e-CNY) initiatives, indicating a favorable regulatory environment for such innovations.
The adoption of blockchain can enhance transaction security and transparency, reducing operational costs and the risk of fraud. Bank of Jiujiang might explore DLT for supply chain finance, a sector where transparency and efficient record-keeping are paramount. By integrating blockchain, the bank can provide verifiable transaction histories, improving trust among participants and facilitating access to credit for businesses.
Key potential applications for Bank of Jiujiang include:
- Secure and faster cross-border remittances, potentially reducing transaction fees and settlement times.
- Enhanced supply chain finance platforms, offering greater visibility and traceability of goods and payments.
- Improved Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes through shared, immutable ledgers.
- Digital asset management and trading, aligning with the broader trend of tokenization in financial markets.
Automation and Operational Efficiency
Bank of Jiujiang is actively integrating automation technologies, like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), to enhance its internal operations. This strategic move aims to significantly reduce the incidence of manual errors in daily tasks.
The implementation of RPA allows for faster processing of transactions and approvals, directly impacting service delivery speed. For instance, in 2024, many banks reported a 20-30% reduction in processing times for routine tasks after adopting automation.
These advancements contribute to substantial cost savings for the bank by optimizing resource allocation and improving overall operational efficiency. By automating repetitive processes, Bank of Jiujiang can reinvest resources into customer-facing initiatives and innovation.
- Reduced Manual Errors: Automation minimizes human oversight, leading to greater accuracy in financial processing.
- Faster Transaction Speeds: Streamlined workflows accelerate customer service and internal approvals.
- Cost Savings: Operational efficiencies gained through automation directly impact the bank's bottom line.
- Improved Service Delivery: Quicker processing and fewer errors translate to a better customer experience.
Bank of Jiujiang is heavily investing in digital transformation, focusing on mobile banking and online loan systems through 2024-2025 to improve customer experience and operational efficiency. The bank is also leveraging AI and big data for better risk assessment and fraud detection, with global financial institutions seeing significant fraud loss reductions due to AI in 2024.
The bank is exploring blockchain technology for faster cross-border payments and enhanced supply chain finance, aligning with the People's Bank of China's exploration of DLT for its digital yuan. Automation through RPA is also being implemented to reduce manual errors and speed up transaction processing, with many banks reporting 20-30% faster processing times for routine tasks in 2024.
| Technology Focus | Key Initiatives (2024-2025) | Expected Benefits | Industry Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation | Mobile banking, online loan systems | Improved customer experience, operational efficiency | Digital banking adoption continues to rise globally. |
| AI & Big Data | Risk assessment, fraud detection, personalized services | Reduced credit risk, lower fraud losses, enhanced customer retention | AI-powered fraud detection can reduce losses by over 15% (2024 estimates). |
| Blockchain/DLT | Cross-border payments, supply chain finance | Increased security, transparency, reduced costs | PBOC exploring DLT for e-CNY, indicating favorable regulatory outlook. |
| Automation (RPA) | Process automation, error reduction | Faster transaction processing, cost savings, improved accuracy | Banks saw 20-30% reduction in processing times for routine tasks via automation (2024). |
Legal factors
Bank of Jiujiang operates under a stringent regulatory environment shaped by the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC). Key directives for 2024-2025 emphasize robust capital adequacy, with the CBIRC maintaining a focus on higher Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratios, potentially above the Basel III minimums, to ensure resilience. Liquidity coverage ratios (LCR) and net stable funding ratios (NSFR) are also critical compliance areas, with ongoing PBOC guidance to manage systemic risk.
Compliance with asset quality standards, including non-performing loan (NPL) ratios, remains paramount. For 2024, the banking sector saw NPL ratios generally managed, and Bank of Jiujiang, like its peers, must adhere to evolving provisioning requirements. Furthermore, strengthening internal controls and risk management frameworks, as mandated by regulatory bodies, is crucial for operational integrity and to meet the latest guidelines on data security and anti-money laundering (AML) for the 2024-2025 period.
Bank of Jiujiang operates under a rigorous framework of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) laws, crucial for maintaining financial integrity. The bank’s compliance strategy includes robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD) processes to verify client identities and assess risks. For instance, in 2024, Chinese financial institutions reported a significant increase in suspicious transaction reports (STRs) filed with the People's Bank of China, reflecting enhanced vigilance.
To combat financial crime, Bank of Jiujiang implements comprehensive internal controls and reporting mechanisms. This involves meticulous monitoring of transactions for any red flags and timely submission of STRs to relevant authorities. The bank also invests in continuous employee training programs to ensure staff are well-versed in the latest AML/CTF regulations and best practices, aligning with national and international standards such as those set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
Bank of Jiujiang operates within a stringent legal environment designed to safeguard consumers. Regulations such as the Consumer Rights Protection Law mandate clear disclosure of financial product terms, interest rates, and fees, preventing deceptive practices. In 2024, China's financial regulators continued to emphasize enhanced consumer protection, particularly concerning digital financial services.
Fair lending practices are a cornerstone, prohibiting discrimination based on factors like ethnicity or gender. The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) imposes strict rules on how Bank of Jiujiang collects, processes, and stores customer data, ensuring privacy. Violations can lead to significant penalties, reinforcing the bank's commitment to data security.
Dispute resolution mechanisms are also legally mandated, providing customers with avenues to address grievances. This includes internal complaint handling procedures and access to external arbitration or regulatory bodies. The effectiveness of these channels is crucial for maintaining customer trust and regulatory compliance for Bank of Jiujiang.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Laws
Bank of Jiujiang operates under stringent data privacy and cybersecurity regulations in China, notably the Cybersecurity Law and the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). These laws mandate robust data handling practices, requiring explicit customer consent for data collection and processing, and imposing severe penalties for non-compliance. For instance, PIPL, effective November 1, 2021, sets high standards for data localization and cross-border data transfer. The bank must therefore implement comprehensive measures to safeguard sensitive customer information, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to prevent breaches and ensure adherence to these evolving legal frameworks.
Managing customer data in compliance with these laws involves several key strategies for Bank of Jiujiang:
- Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Collecting only necessary customer data and using it solely for specified, legitimate purposes.
- Consent Management: Establishing clear and accessible mechanisms for obtaining and managing customer consent for data processing activities.
- Security Measures: Implementing advanced cybersecurity protocols, such as multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular vulnerability assessments, to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Breach Notification: Developing and adhering to protocols for promptly notifying affected individuals and regulatory authorities in the event of a data breach, as required by law.
Contract Law and Dispute Resolution
Contract law is fundamental to Bank of Jiujiang's operations, dictating the enforceability of loan agreements, deposit contracts, and other financial instruments. The bank must ensure its contracts are legally sound to protect its interests and customer rights. In 2024, China's Supreme People's Court continued to emphasize the importance of clear contractual terms in financial dealings, impacting how institutions like Bank of Jiujiang draft their agreements.
Dispute resolution mechanisms are crucial for managing potential conflicts. Bank of Jiujiang likely utilizes a combination of internal negotiation, mediation, and formal legal channels such as arbitration or litigation to resolve commercial disputes. The efficiency and fairness of these processes are vital for maintaining trust and operational stability. For instance, the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission (CIETAC) reported a significant volume of financial dispute cases in recent years, highlighting the active use of arbitration in the sector.
- Enforceability of Loan Agreements: Bank of Jiujiang's loan contracts must adhere to strict legal requirements for validity and enforceability, ensuring collateral and repayment terms are legally binding.
- Deposit Contract Compliance: Deposit agreements are governed by consumer protection laws and banking regulations, requiring clear disclosure of terms, interest rates, and fees.
- Arbitration vs. Litigation: The bank may opt for arbitration for faster and more specialized dispute resolution, particularly for complex financial matters, compared to potentially lengthy court proceedings.
- Regulatory Adherence: All financial contracts must comply with evolving banking and financial regulations, such as those issued by the People's Bank of China and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC).
Bank of Jiujiang must navigate a complex legal landscape, with ongoing regulatory focus on capital adequacy and liquidity ratios for 2024-2025, as enforced by the CBIRC and PBOC. Compliance with evolving provisioning requirements for non-performing loans and strengthened internal controls are critical for operational integrity and risk management.
Data privacy and cybersecurity are paramount, governed by laws like PIPL, which mandates strict consent for data processing and imposes penalties for breaches. The bank must implement robust measures like encryption and regular audits to protect sensitive customer information and adhere to cross-border data transfer rules.
Contract law underpins all financial dealings, requiring clear terms in loan and deposit agreements to ensure enforceability and protect both the bank and its customers. Dispute resolution, often through arbitration, is crucial for efficiently managing financial conflicts, with institutions like CIETAC handling significant volumes of such cases.
Environmental factors
Climate change presents both physical and transitional risks for Bank of Jiujiang. Physical risks include potential damage to assets from extreme weather events, impacting borrowers in sectors like agriculture and real estate. Transitional risks arise from policy changes and market shifts towards a low-carbon economy, potentially affecting loans to carbon-intensive industries.
In response, Bank of Jiujiang is actively participating in green finance. As of early 2024, the bank has increased its lending to renewable energy projects, with a notable 15% year-on-year growth in its green loan portfolio. This includes financing for solar power installations and sustainable agricultural practices, aiming to mitigate climate-related financial exposures.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting is increasingly critical for financial institutions like the Bank of Jiujiang. In 2024, global sustainable finance assets are projected to reach significant figures, with investors demanding greater transparency on how banks manage their environmental footprint, social impact, and governance structures. The Bank of Jiujiang can enhance its stakeholder trust and attract capital by detailing its practices in areas like carbon emissions reduction, ethical lending, and board diversity.
Resource scarcity, particularly concerning water and energy, presents a growing challenge that can directly impact Bank of Jiujiang's operational expenses and the long-term viability of its client base. For instance, rising energy costs in 2024 and projected increases in 2025 due to global supply chain adjustments and climate policies could strain both the bank's budget and its borrowers' profitability.
To mitigate these risks, Bank of Jiujiang can implement energy-efficient practices across its branches, such as upgrading to LED lighting and optimizing HVAC systems, potentially reducing utility costs by an estimated 10-15% annually. Furthermore, the bank can proactively encourage its corporate and individual clients to adopt more sustainable resource management strategies through preferential lending rates for green initiatives or providing access to expert consultations.
Pollution Control and Environmental Regulations
Bank of Jiujiang, like all financial institutions in China, operates under increasingly stringent environmental regulations, particularly concerning pollution control and waste management. These regulations directly impact the bank's operational footprint and, more significantly, its lending practices. The People's Bank of China and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment have been actively promoting green finance, encouraging banks to integrate environmental risk assessments into their credit processes.
The bank is expected to evaluate the environmental impact of its clients' projects and businesses, especially those in sectors with high pollution potential. This involves assessing how clients manage emissions, wastewater, and solid waste. For instance, in 2023, China's environmental protection tax revenue reached approximately 22.3 billion yuan, indicating a strong enforcement of environmental policies that directly affect businesses seeking financing.
Bank of Jiujiang supports its clients in meeting these environmental standards through various means:
- Green Credit Policies: Implementing policies that favor lending to environmentally responsible projects and businesses, potentially offering preferential interest rates or terms.
- Environmental Risk Assessment: Incorporating thorough environmental due diligence into loan application reviews to identify and mitigate potential environmental liabilities.
- Client Advisory Services: Providing guidance and information to clients on environmental compliance, sustainable practices, and access to green financing instruments.
- Sustainable Project Financing: Actively seeking and financing projects that contribute to pollution reduction, energy efficiency, and ecological protection, aligning with national environmental goals.
Natural Disasters and Disaster Preparedness
Jiangxi Province, where Bank of Jiujiang operates, is susceptible to various natural disasters, including floods and typhoons, which can disrupt physical infrastructure and business operations. In 2024, China experienced significant rainfall leading to widespread flooding, particularly in southern regions, highlighting the ongoing risk. The bank must maintain robust disaster preparedness plans to ensure business continuity and protect its physical assets.
Bank of Jiujiang's risk mitigation strategies should include comprehensive insurance coverage for its branches and data centers, alongside redundant IT systems to safeguard against data loss. Furthermore, the bank's loan portfolio could be impacted by natural disasters affecting borrowers' ability to repay, necessitating proactive risk assessment and potential loan restructuring for affected businesses and individuals.
The bank's role extends to supporting affected communities and businesses post-disaster. This could involve offering special loan terms, financial assistance programs, and facilitating access to relief funds. For instance, following major flood events in China in previous years, financial institutions often provided grace periods on loan repayments and low-interest loans for reconstruction efforts.
- Flood Risk: Jiangxi Province is prone to seasonal flooding, particularly along the Yangtze River basin, posing a direct threat to the bank's physical branches and ATM networks.
- Business Continuity: Implementing resilient IT infrastructure and backup operational sites is crucial to maintain essential banking services during and after a natural disaster.
- Loan Portfolio Impact: Natural disasters can lead to increased non-performing loans if businesses and individuals in affected areas suffer significant economic losses.
- Community Support: Proactive financial aid and flexible loan terms for disaster-affected customers are vital for economic recovery and maintaining customer relationships.
Environmental regulations in China are tightening, impacting Bank of Jiujiang's lending practices. The bank must integrate environmental risk into credit assessments, particularly for high-polluting industries. China's environmental protection tax revenue, around 22.3 billion yuan in 2023, underscores the enforcement of these policies.
Bank of Jiujiang is enhancing its green finance initiatives, with its green loan portfolio growing by 15% year-on-year in early 2024. This focus on sustainable lending supports clients in meeting stricter environmental standards and aligns with national green development goals.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Bank of Jiujiang is built on a comprehensive review of official Chinese government publications, financial regulatory bodies, and economic data from reputable institutions like the People's Bank of China and the National Bureau of Statistics of China. This ensures all political, economic, and legal insights are grounded in verified, current information.
