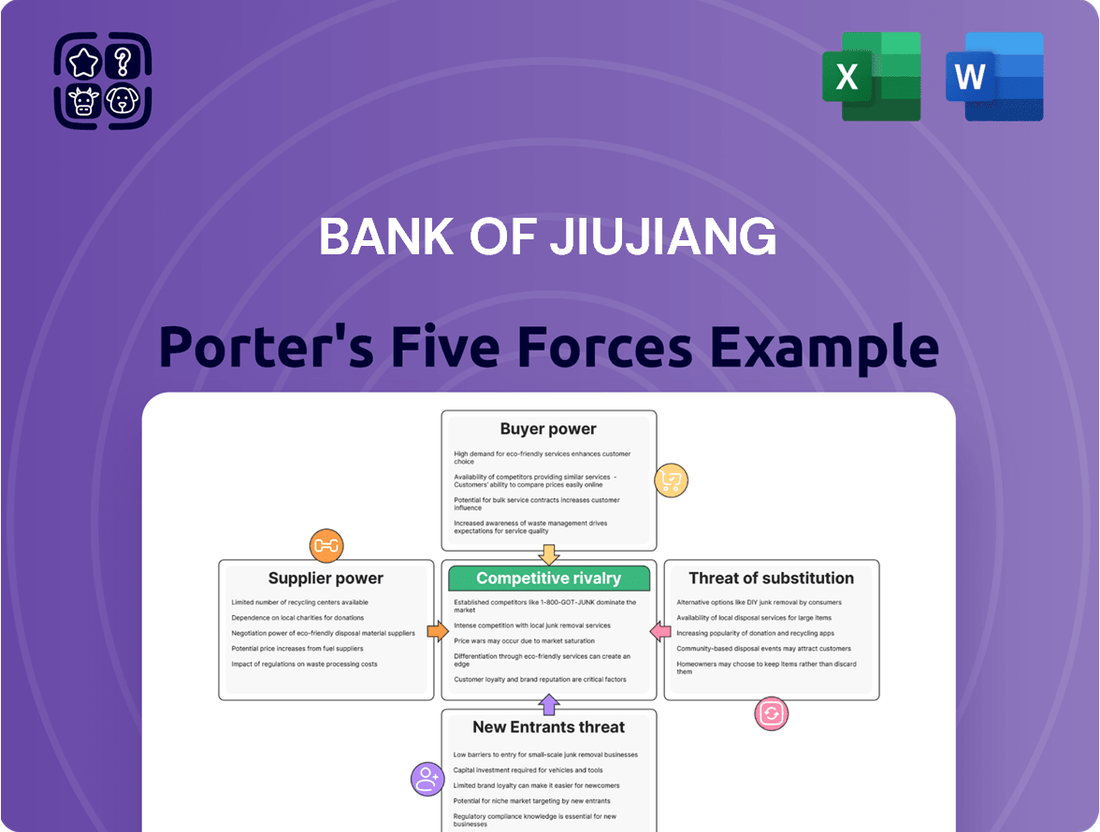
Bank of Jiujiang Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of Jiujiang Bundle
The Bank of Jiujiang faces moderate rivalry from existing competitors, with significant barriers to entry limiting new players. Buyer power is present, as customers can switch banks, but is somewhat mitigated by brand loyalty and specialized services. The threat of substitutes, like online financial platforms, is growing, while supplier power, primarily from technology providers, remains manageable.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Bank of Jiujiang’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the National Financial Regulatory Administration (NFRA) are key suppliers for the Bank of Jiujiang, issuing operational licenses and setting the regulatory landscape. Their directives on capital adequacy, loan-to-deposit ratios, and interest rates directly shape the bank's profitability and operational freedom. For instance, the NFRA's ongoing efforts to manage property sector risks and refine capital management rules in 2024 highlight their substantial influence.
Depositors, both individuals and corporations, hold a generally moderate bargaining power over the Bank of Jiujiang. This is largely due to China's regulated interest rate environment and the inherent trust in the stability of its banking sector. For instance, as of late 2024, deposit growth in China remained robust, indicating a continued reliance on traditional banking channels by many customers.
However, this power can increase, particularly in economic conditions where interest rates are low. When deposit rates offer minimal returns, depositors may be more inclined to explore alternative investment avenues, forcing banks like Jiujiang to offer more competitive terms to retain their funding. Furthermore, the growing popularity of wealth management products in China, which often provide higher yields than standard savings accounts, can reduce the stickiness of traditional deposits.
Other financial institutions in the interbank market are crucial suppliers of liquidity and funding for the Bank of Jiujiang, particularly for short-term operational needs. The interest rates these institutions charge directly reflect their bargaining power, influencing the Bank of Jiujiang's cost of funds. For instance, in early 2024, interbank lending rates for maturities like overnight and one-week saw fluctuations influenced by overall market liquidity conditions.
Accessing capital markets by issuing bonds or other financial instruments offers alternative funding avenues for the Bank of Jiujiang. However, the cost and availability of this capital are heavily dependent on prevailing market conditions and investor confidence. For example, the yield on a new bond issuance by a comparable Chinese bank in late 2023 was influenced by global interest rate trends and investor sentiment towards emerging markets.
Changes in regulatory frameworks, such as updated capital rules that affect risk weights for interbank exposures, directly impact the bargaining power of suppliers. These adjustments can alter the cost of capital and the attractiveness of certain funding sources for banks like Jiujiang, highlighting the dynamic interplay between regulation and supplier influence.
Technology and Fintech Providers
Technology and fintech providers wield significant bargaining power over banks like Bank of Jiujiang, especially as digital transformation becomes a necessity. These firms supply essential software, cloud infrastructure, and cutting-edge solutions for digital banking platforms, robust risk management systems, and advanced data analytics. Their specialized knowledge and unique technological offerings mean banks must invest substantially to stay competitive and streamline operations.
The increasing reliance on these suppliers is evident in the market. For instance, global spending on fintech software and services was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in 2024, highlighting the critical role these providers play. Banks often face limited alternatives for highly specialized fintech solutions, further amplifying supplier leverage.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new core banking systems or fintech solutions involves substantial upfront investment and integration complexities, making it costly for banks to switch providers.
- Proprietary Technology: Many fintech firms possess unique, patented technologies that are difficult for competitors to replicate, giving them a strong negotiating position.
- Concentration of Expertise: Specialized knowledge in areas like AI-driven fraud detection or blockchain for financial transactions is often concentrated among a few key players.
- Demand for Innovation: The constant need for banks to innovate and offer digital-first services drives demand for advanced technology, empowering suppliers who can meet these evolving needs.
Skilled Labor and Talent
The availability of skilled professionals, especially in burgeoning fields like financial technology, robust risk management, and sophisticated wealth management, significantly impacts banking operations. A scarcity of such talent directly amplifies the bargaining power of these skilled individuals, potentially driving up recruitment and retention expenses for institutions like Bank of Jiujiang. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists in finance continued to outstrip supply, with average salaries for these roles seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year in major financial hubs.
Bank of Jiujiang's strategic development hinges on its capacity to attract and retain experienced personnel. The competitive landscape for top financial talent means that banks must offer compelling compensation packages and career advancement opportunities. In 2023, the financial services sector reported a 15% increase in employee turnover for specialized roles, underscoring the challenge of talent retention.
- Talent Scarcity: Shortages in specialized financial skills grant employees greater negotiation leverage.
- Increased Costs: Higher demand for talent leads to elevated recruitment and retention expenses for banks.
- Strategic Importance: Attracting and keeping experienced staff is crucial for a bank's growth and competitive edge.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bank of Jiujiang is multifaceted, with regulators like the PBOC and NFRA holding significant sway through licensing and policy directives, as seen in 2024 property sector risk management efforts. Depositors generally have moderate power due to China's regulated rates, though this can shift with low-interest environments and the rise of wealth management products, which saw continued growth through late 2024. Fintech providers and skilled professionals also exert considerable influence due to specialized technology and talent scarcity, driving up costs for banks needing to innovate and retain expertise.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Assessment | Key Influencing Factors (2024 Focus) | Impact on Bank of Jiujiang |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulators (PBOC, NFRA) | High | Licensing, capital adequacy rules, interest rate policies, property sector risk management | Shapes operational freedom, profitability, and compliance costs |
| Depositors | Moderate (Variable) | Interest rate environment, trust in banking sector, growth of alternative investments | Influences cost of funds, deposit retention strategies |
| Interbank Market Lenders | Moderate to High | Market liquidity conditions, overall economic stability, short-term funding needs | Directly impacts short-term borrowing costs |
| Fintech & Technology Providers | High | Proprietary technology, high switching costs, demand for digital innovation | Drives investment in technology, impacts operational efficiency and costs |
| Skilled Professionals | High | Talent scarcity in specialized financial fields (e.g., AI, risk management) | Increases recruitment and retention expenses, impacts strategic capabilities |
What is included in the product
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to the Bank of Jiujiang, dissecting its competitive environment by examining rivalry, new entrants, buyer power, supplier power, and substitutes.
Understand the competitive landscape of Jiujiang's banking sector with a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making.
Identify and mitigate threats by customizing pressure levels based on new data or evolving market trends in Jiujiang's banking environment.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual retail customers with Bank of Jiujiang is typically low to moderate. This is largely due to the standardized offerings in basic banking products like savings accounts and personal loans, where differentiation is often minimal. While customers can indeed switch providers, the convenience of Bank of Jiujiang's local branches and existing customer relationships can provide a degree of loyalty.
However, the evolving financial landscape, significantly shaped by digital banking advancements and the proliferation of mobile payment solutions, has demonstrably lowered switching costs for consumers. This increased ease of transition empowers individuals to seek better rates or services from competitors, thereby increasing their overall bargaining influence.
Corporate and SME clients, particularly the larger ones, wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial transaction volumes mean they can easily explore financing options from numerous banks or even secure funds directly, putting pressure on banks like Bank of Jiujiang to offer competitive terms. In 2023, the average loan size for SMEs in China saw an increase, reflecting the growing capacity of these businesses to negotiate better rates.
Government agencies and public institutions represent a significant client segment for Bank of Jiujiang, wielding substantial bargaining power. Their large deposit volumes and consistent need for project financing, especially within Jiangxi Province, give them considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, public sector deposits often offer lower cost of funds for banks compared to retail or corporate deposits, allowing these institutions to negotiate more favorable terms on lending rates and fees.
Wealth Management and High-Net-Worth Clients
Customers seeking wealth management services, particularly high-net-worth individuals, often wield significant bargaining power. They expect tailored advice, competitive investment performance, and a broad spectrum of financial products. For instance, in 2024, the global wealth management market saw continued demand for personalized solutions, with many clients switching providers if their expectations for returns and service weren't met. Banks like Bank of Jiujiang must therefore differentiate their offerings and demonstrate superior value to attract and retain this discerning client base.
The ability of these clients to compare offerings across multiple financial institutions intensifies their leverage. They can easily shift their assets to competitors who provide better rates, more innovative investment strategies, or a higher level of personalized attention. This pressure forces institutions to maintain high service standards and competitive pricing. For example, reports from late 2024 indicated that client retention in the private banking sector was heavily influenced by the perceived quality of advisory services and the ability to consistently outperform market benchmarks.
- High-Net-Worth Client Expectations: Demand for bespoke financial planning, access to exclusive investment opportunities, and proactive wealth preservation strategies.
- Competitive Returns: Clients actively compare performance metrics and fee structures across different wealth management providers.
- Service Personalization: A key differentiator, with clients expecting dedicated relationship managers and tailored communication.
- Switching Costs: While some switching costs exist, the potential for higher returns and better service often outweighs them for these clients.
Sensitivity to Interest Rates and Fees
In a low-interest rate climate, Bank of Jiujiang's customers exhibit heightened sensitivity to both loan rates and deposit yields, as well as the fees charged for services. This increased awareness directly translates into greater collective bargaining power for consumers and businesses alike.
This heightened sensitivity compels Bank of Jiujiang to maintain competitive pricing and clear, understandable fee structures to win and keep customers. For instance, as of early 2024, many regional banks in China were adjusting their deposit rates to remain competitive amidst fluctuating market conditions, reflecting this customer pressure.
- Customer Sensitivity: Low interest rates amplify customer focus on fees and deposit/loan yields.
- Bargaining Power: This sensitivity boosts customers' ability to negotiate better terms.
- Competitive Pressure: Banks like Bank of Jiujiang must offer attractive pricing and transparent fees.
- Market Example: Regional banks in China adjusted deposit rates in early 2024 to stay competitive, demonstrating this trend.
The bargaining power of Bank of Jiujiang's customers is a significant force, especially for larger corporate and government clients who can leverage substantial transaction volumes and deposit balances to negotiate favorable terms. Even individual wealth management clients wield considerable influence due to their demand for personalized service and competitive returns, often switching providers if expectations aren't met. This collective customer power is amplified in environments with low interest rates, forcing banks to maintain competitive pricing and transparent fee structures.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Drivers of Power | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Low to Moderate | Standardized products, convenience, digital access | Switching costs reduced by digital banking adoption. |
| SME Clients | Moderate to High | Transaction volume, access to alternative financing | Average SME loan size increased in China in 2023. |
| Corporate & Government | High | Large deposits, consistent financing needs, public sector benefits | Public sector deposits often offer lower funding costs for banks. |
| Wealth Management Clients | High | Demand for tailored advice, competitive returns, service quality | Client retention in private banking linked to advisory quality and performance (late 2024 reports). |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Bank of Jiujiang Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Bank of Jiujiang Porter's Five Forces Analysis, meticulously detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the institution. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate value. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Bank of Jiujiang contends with formidable competition from major state-owned commercial banks. Institutions like the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), Agricultural Bank of China (ABC), Bank of China (BOC), and China Construction Bank (CCB) command vast branch networks and deep financial reserves, extending their reach throughout China, including Jiujiang's home province of Jiangxi.
These giants leverage their scale to offer highly competitive interest rates on loans and deposits, alongside a comprehensive suite of financial products and digital services. For instance, as of the first half of 2024, the aggregate assets of the top four state-owned banks exceeded 100 trillion RMB, dwarfing regional banks and enabling them to absorb costs and invest heavily in technology and customer acquisition, directly challenging smaller players like Bank of Jiujiang.
Joint-stock commercial banks present a significant competitive force against regional players like the Bank of Jiujiang. These larger institutions, operating across the nation, vie directly for both corporate and retail clientele, especially in bustling urban areas. Their extensive branch networks and established brand recognition give them a considerable edge.
Furthermore, these nationwide banks often boast superior digital infrastructure and a broader array of financial products. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, major joint-stock commercial banks in China reported average digital transaction growth rates exceeding 15%, a pace that can be challenging for smaller regional banks to match. This technological advantage and product diversification intensify the battle for market share.
Bank of Jiujiang faces significant rivalry from other city and rural commercial banks within Jiangxi Province. These institutions, like Jiangxi Bank, also concentrate on serving local economies and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), leading to intense competition. This rivalry often hinges on established local relationships, the quality of customer service, and a deep understanding of the specific needs within these regional markets.
Product and Service Homogenization
Many core banking products, like savings accounts and basic loans, are virtually identical across institutions. This product and service homogenization means competition often boils down to price, squeezing profit margins. For instance, in 2024, the average net interest margin for regional banks in China remained under pressure, hovering around 1.8% to 2.2%, reflecting this commoditization.
To combat this, banks like Bank of Jiujiang must invest heavily in differentiating factors. This includes enhancing customer service, developing user-friendly digital platforms, and creating niche financial solutions. The intense rivalry compels banks to constantly innovate, making the competitive landscape more dynamic.
- Commoditized Products: Traditional banking offerings face significant price-based competition.
- Narrower Margins: Homogenization leads to reduced net interest margins across the sector.
- Differentiation Imperative: Banks must stand out through service, digital offerings, and specialization.
- Intensified Rivalry: The need for differentiation makes competition more acute.
Intensified Digital Transformation and Fintech Competition
The competitive rivalry within the Chinese banking sector is intensifying, largely driven by a rapid digital transformation. Banks are increasingly vying for market share based on their fintech prowess, focusing on areas like advanced mobile banking platforms, streamlined online lending processes, and sophisticated smart risk control systems.
Bank of Jiujiang faces a significant challenge to maintain its competitive edge. To keep pace with rivals and enhance both customer experience and operational efficiency, the bank must commit to ongoing, substantial investments in cutting-edge technology.
- Fintech Investment: Chinese banks collectively invested over RMB 1.5 trillion in technology during 2023, highlighting the scale of digital competition.
- Mobile Banking Adoption: As of late 2024, over 90% of retail banking transactions in China are conducted via mobile channels, underscoring the importance of robust digital offerings.
- Online Lending Growth: The online lending market in China experienced a growth of approximately 15% year-over-year in early 2024, indicating a strong demand for digital credit solutions.
- Customer Experience Focus: Banks prioritizing digital channels reported a 10% higher customer satisfaction rate compared to those with less developed digital capabilities in recent industry surveys.
Competitive rivalry for Bank of Jiujiang is intense, marked by the dominance of large state-owned and joint-stock commercial banks. These giants offer competitive pricing and a wide array of digital services, often supported by assets exceeding 100 trillion RMB for the top four state-owned banks as of mid-2024.
Regional banks, including those in Jiangxi like Jiangxi Bank, also present a strong challenge by focusing on local relationships and SME needs, leading to commoditized products and squeezed net interest margins, which averaged between 1.8% and 2.2% for regional banks in 2024.
The sector's rapid digital transformation, with over 90% of retail transactions occurring via mobile channels by late 2024, forces banks like Bank of Jiujiang to invest heavily in fintech to differentiate and enhance customer experience, as demonstrated by the collective RMB 1.5 trillion invested in technology by Chinese banks in 2023.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech platforms and digital payment solutions presents a substantial threat to traditional banks like Bank of Jiujiang. Companies such as Alipay and WeChat Pay, along with numerous online lending platforms, are increasingly offering financial services that bypass conventional banking infrastructure. These alternatives provide users with enhanced convenience and often reduced transaction fees, which has led to a rapid adoption rate among consumers. For instance, by the end of 2023, China's mobile payment market, dominated by Alipay and WeChat Pay, processed trillions of dollars in transactions, demonstrating the sheer scale of this shift away from traditional banking methods.
Shadow banking and non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Bank of Jiujiang. These entities, including investment funds, hedge funds, and peer-to-peer lenders, offer alternative financing and investment avenues that can siphon off customers and capital. For instance, in 2024, the global NBFI sector continued its expansion, managing trillions in assets, providing competitive yields and more flexible terms for certain borrowers and investors compared to conventional bank offerings.
These alternative providers can attract business by offering specialized products or catering to market segments that traditional banks may find less attractive or slower to adapt to. While regulatory scrutiny has grown, the inherent agility of NBFIs allows them to innovate and provide attractive options, especially in areas like specialized lending or wealth management, thereby posing a persistent substitute threat to Bank of Jiujiang's core business.
Larger corporations increasingly bypass traditional bank lending by directly accessing capital markets. In 2023, China's corporate bond issuance reached approximately 15.5 trillion yuan, a significant increase from previous years, demonstrating a clear shift away from bank financing for many established entities.
This direct financing route, through issuing equity or bonds, acts as a potent substitute for the corporate banking services Bank of Jiujiang offers. As China's capital markets continue to deepen and mature, this trend is expected to accelerate, presenting a significant competitive pressure.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending and Crowdfunding
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and crowdfunding platforms, while facing increased regulatory scrutiny and industry consolidation, historically presented a significant threat to traditional banking models. These platforms provided alternative channels for both borrowers seeking capital and investors looking for returns, particularly impacting smaller loan segments. For instance, in 2023, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $60 billion, demonstrating its substantial reach as an alternative to bank loans.
The accessibility and often faster processing times offered by P2P and crowdfunding platforms attracted individuals and small businesses who might find traditional bank processes cumbersome or less accommodating. This competition directly challenged banks like Bank of Jiujiang by diverting loan origination volume and deposit flows. By 2024, while the P2P sector has matured, its legacy impact continues to shape customer expectations regarding financial service speed and convenience.
- Market Disruption: P2P and crowdfunding platforms offered alternatives to traditional bank lending, especially for small business loans and personal loans.
- Customer Acquisition: These platforms attracted customers seeking faster approvals and potentially more flexible terms than conventional banks.
- Regulatory Evolution: Increased regulation and consolidation in the P2P space have somewhat tempered the immediate threat, but the underlying competitive pressure remains.
- Impact on Deposits: Alternative investment avenues can draw funds away from traditional bank deposits, affecting a bank's funding base.
Internal Corporate Finance Departments
Large corporations increasingly leverage sophisticated internal finance departments, diminishing their reliance on external banking services for core functions. These departments can effectively manage cash flow, execute investment strategies, and even facilitate inter-company lending, acting as direct substitutes for some traditional bank offerings.
For instance, companies with strong treasury functions might bypass commercial paper markets for short-term funding, managing it internally. In 2024, many large enterprises continued to invest in advanced financial technology and talent, further enhancing their in-house capabilities. This trend directly impacts the demand for certain transactional and lending services from banks.
- Internal Cash Management: Corporations can manage their own liquidity, reducing the need for banks' treasury services.
- In-house Investment: Sophisticated firms can directly manage their investment portfolios, bypassing bank advisory or asset management.
- Inter-company Lending: Large conglomerates can fund subsidiaries internally, substituting for external credit facilities.
The threat of substitutes for Bank of Jiujiang is substantial, driven by evolving financial technologies and alternative financial providers. Fintech platforms and digital payment systems offer convenience and lower fees, rapidly gaining consumer traction. For example, China's mobile payment market, led by Alipay and WeChat Pay, processed trillions of dollars in transactions by the end of 2023, illustrating a significant shift away from traditional banking.
Shadow banking entities and non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) also present a strong substitute threat by offering specialized financing and investment avenues. In 2024, the global NBFI sector continued its growth, managing trillions in assets and providing competitive terms that attract both borrowers and investors. These agile players can innovate faster than traditional banks, particularly in niche markets like specialized lending.
Furthermore, larger corporations increasingly bypass banks by directly accessing capital markets through bond and equity issuance. China's corporate bond issuance reached approximately 15.5 trillion yuan in 2023, indicating a growing preference for direct financing. This trend, fueled by deepening capital markets, directly competes with Bank of Jiujiang's corporate banking services.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) | Impact on Bank of Jiujiang |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Digital Payments | Convenience, lower fees, rapid adoption | Trillions processed by Alipay/WeChat Pay (end of 2023) | Loss of transaction volume and customer base |
| Shadow Banking/NBFIs | Specialized services, competitive yields, flexibility | Global NBFI asset management in trillions (2024) | Siphoning of capital and customers |
| Capital Markets Access | Direct financing for corporations | 15.5 trillion yuan in China corporate bond issuance (2023) | Reduced demand for corporate lending |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector in China, including institutions like Bank of Jiujiang, faces significant barriers to entry due to substantial capital requirements and complex regulatory frameworks. New entrants must meet stringent capital adequacy ratios, such as the Basel III standards, which demand significant financial resources. For instance, as of early 2024, Chinese banks were generally required to maintain a Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio above 7.5%, with many operating at higher levels to ensure stability.
Navigating the intricate licensing and approval processes mandated by the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) also presents a formidable challenge. These hurdles, coupled with evolving capital management rules that further reinforce prudential standards, effectively limit the number of new players that can realistically enter the market and compete with established banks.
Established brand loyalty and trust are significant barriers for new entrants in the banking sector. Existing institutions, such as Bank of Jiujiang, leverage decades of operation to cultivate deep customer relationships and a reputation for reliability. For instance, in 2023, the top five largest banks in China held approximately 37% of the total banking assets, indicating a strong concentration of market share built on established trust.
Bank of Jiujiang's extensive branch network and ATM infrastructure present a significant barrier to new entrants. While digital banking is on the rise, a robust physical presence remains crucial for customer trust and accessibility, particularly in regional markets. Building such an infrastructure demands considerable capital and time, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established banks like Bank of Jiujiang leverage significant economies of scale, which translates into lower per-unit costs for operations, technology, and risk management. This cost advantage allows them to offer more competitive pricing and a broader array of services than a new player could easily replicate.
For instance, in 2023, major Chinese banks reported substantial operational efficiencies driven by large-scale digital transformation initiatives. A new entrant would face immense difficulty matching these entrenched cost structures and service offerings from the outset, creating a substantial barrier.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbent banks benefit from lower average costs due to high-volume operations.
- Technology Infrastructure: Existing banks have already invested heavily in robust and efficient IT systems.
- Risk Management: Larger institutions have more sophisticated and cost-effective risk management frameworks.
- Competitive Pricing: Scale allows incumbents to offer more attractive rates and fees to customers.
Government Influence and Market Protection
The Chinese government exerts considerable control over its banking sector, often acting to ensure stability and favor established institutions, including state-owned and regional banks. This governmental stance can present a formidable barrier for potential new entrants, as securing necessary regulatory approvals and policy backing is paramount for market entry and success.
In 2024, China's financial regulatory landscape continued to emphasize stability, with authorities closely monitoring capital requirements and operational risks for all financial institutions. For instance, the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) have consistently enforced stringent licensing procedures and capital adequacy ratios, making it challenging for new, undercapitalized entities to gain a foothold.
This environment can be seen in the limited number of new banking licenses issued in recent years, particularly for purely digital or fintech-driven banks, which often face stricter scrutiny compared to traditional players. The government's focus remains on managing systemic risk, which inherently favors institutions with proven track records and robust capital bases, thus deterring many potential disruptors.
- Government Prioritization of Stability: Chinese regulators consistently aim to maintain financial system stability, often at the expense of rapid new market entrants.
- Regulatory Hurdles for New Banks: Obtaining licenses and approvals in China's banking sector is a rigorous process, demanding substantial capital and adherence to strict operational guidelines.
- Support for Existing Institutions: Policy and regulatory support often lean towards established state-owned and regional banks, creating an uneven playing field for newcomers.
- Capital Requirements in 2024: As of 2024, minimum capital requirements for new banks remained high, with a particular emphasis on robust risk management frameworks, deterring less capitalized entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Bank of Jiujiang is generally low due to significant hurdles. High capital requirements, stringent regulatory approvals from bodies like the CBIRC, and the need for substantial technology infrastructure investment deter many potential competitors. For instance, new banks in China typically need to demonstrate significant initial capital, often in the hundreds of millions of USD, before even applying for a license.
Established players benefit from strong brand loyalty and extensive physical networks, as evidenced by the market concentration where the top five banks held roughly 37% of assets in 2023. Furthermore, government policies in 2024 continue to prioritize financial stability, favoring incumbents with proven track records and robust capital bases, making it difficult for less established entities to gain a foothold.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High minimum capital needed, e.g., hundreds of millions of USD for new licenses. | Significant financial barrier. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and approval processes by CBIRC. | Time-consuming and uncertain market entry. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established banks like Bank of Jiujiang have long-standing customer relationships. | Difficult for newcomers to attract and retain customers. |
| Economies of Scale | Incumbents operate at lower per-unit costs. | New entrants struggle to match competitive pricing. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bank of Jiujiang is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, regulatory filings from Chinese banking authorities, and reports from reputable financial data providers. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the bank's competitive environment.
