Ball Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ball Bundle
Ball's position in the beverage can industry is shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this competitive landscape.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Ball dives deep into each of these pressures, revealing the nuances of supplier relationships and the barriers to new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The aluminum packaging industry, where Ball Corporation operates, is significantly dependent on a limited number of primary raw material suppliers, predominantly aluminum producers. This concentration means that if a few large entities control the aluminum supply, they gain substantial leverage over Ball, influencing pricing and availability.
For instance, in 2023, the global primary aluminum production was dominated by China, followed by India and Russia, indicating a degree of supplier concentration. Fluctuations in global aluminum prices, driven by factors like energy costs and geopolitical events, directly translate into changes in Ball Corporation's cost of goods sold, impacting its profitability margins.
The availability of substitutes for aluminum in can production presents a nuanced picture for Ball Corporation. While other materials like glass or plastic exist for beverage packaging, aluminum remains dominant due to its recyclability and lightweight properties, limiting direct substitutes for its core function in Ball's primary products.
However, Ball's ability to source aluminum from different regions or suppliers can mitigate the bargaining power of any single aluminum supplier. For instance, in 2023, global aluminum production was approximately 70 million metric tons, with major producing regions including China, India, and Russia, offering Ball a degree of flexibility in its sourcing strategies.
Ball Corporation's substantial global demand for aluminum significantly influences its suppliers. As one of the largest purchasers of this commodity, Ball's purchasing power can dictate terms, potentially limiting suppliers' ability to negotiate favorable prices or contract conditions. In 2023, Ball Corporation reported purchasing approximately 1.1 million metric tons of aluminum, underscoring its immense scale in the market.
Switching Costs for Ball Corporation
Ball Corporation faces considerable bargaining power from its aluminum suppliers, largely due to the substantial switching costs involved. Shifting to a new aluminum supplier could necessitate extensive contract renegotiations, significant adjustments to Ball's intricate logistics network, and rigorous revalidation processes to ensure the consistent quality of aluminum that is critical for their beverage can production. These hurdles make it challenging and expensive for Ball to change suppliers frequently.
The high switching costs directly empower Ball's existing aluminum suppliers. For instance, in 2023, aluminum prices saw volatility, with the London Metal Exchange (LME) aluminum price fluctuating. Ball's reliance on a stable and predictable aluminum supply chain means that suppliers who can guarantee quality and delivery terms often hold a stronger negotiating position. Ball Corporation's significant scale means even small disruptions or quality variations can have a large impact on their operations.
- High Switching Costs: Ball Corporation incurs significant expenses and operational disruptions when changing aluminum suppliers, including contract renegotiations and logistics adjustments.
- Supplier Leverage: These switching costs enhance the bargaining power of Ball's current aluminum suppliers, allowing them to potentially command more favorable terms.
- Aluminum Price Volatility: Fluctuations in global aluminum prices, such as those observed in 2023, can further amplify supplier power if Ball is locked into less advantageous contracts.
- Operational Dependence: Ball's reliance on consistent, high-quality aluminum for its beverage can manufacturing makes it difficult to absorb supplier-driven changes without impacting production and product integrity.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by aluminum suppliers is generally low for can manufacturers like Ball. This is because entering the can manufacturing business requires significant capital investment and specialized expertise, creating a substantial barrier to entry for suppliers. For instance, establishing a modern aluminum can production facility can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a sum that most raw material suppliers may not readily commit.
If aluminum suppliers were to integrate forward and begin manufacturing packaging themselves, they would become direct competitors to Ball. This would fundamentally alter the supply chain dynamics, potentially leading to price wars and reduced margins for existing players. However, the high capital expenditure and the need for established distribution networks and customer relationships make this a less probable scenario for most suppliers.
- Low Likelihood: The specialized nature of can manufacturing and the substantial capital investment required act as significant deterrents for aluminum suppliers considering forward integration.
- High Capital Requirements: Building a can production facility involves costs in the hundreds of millions of dollars, making it a risky proposition for many suppliers.
- Competitive Landscape: Ball Corporation operates in a competitive market, and suppliers would face established players with strong brand recognition and market share if they chose to enter directly.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the aluminum industry, a key input for Ball Corporation, is significant. This stems from the concentrated nature of aluminum production and the high switching costs for can manufacturers. Suppliers can leverage these factors to influence pricing and contract terms, impacting Ball's profitability.
In 2023, Ball Corporation's substantial demand, approximately 1.1 million metric tons of aluminum, gives it considerable purchasing power. However, this is counterbalanced by the specialized nature of aluminum supply and the difficulty Ball faces in switching suppliers due to logistical and quality validation hurdles, which were estimated to cost millions in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Ball Corporation | 2023 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited suppliers can exert more control over pricing and availability. | Major aluminum production concentrated in China, India, and Russia. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to change suppliers limit Ball's flexibility. | Millions of dollars in potential costs for logistics and revalidation. |
| Ball's Purchasing Power | Large volume provides some leverage in negotiations. | Ball purchased ~1.1 million metric tons of aluminum in 2023. |
| Aluminum Price Volatility | Fluctuations can amplify supplier leverage if Ball is on unfavorable contracts. | LME aluminum prices showed significant movement throughout 2023. |
What is included in the product
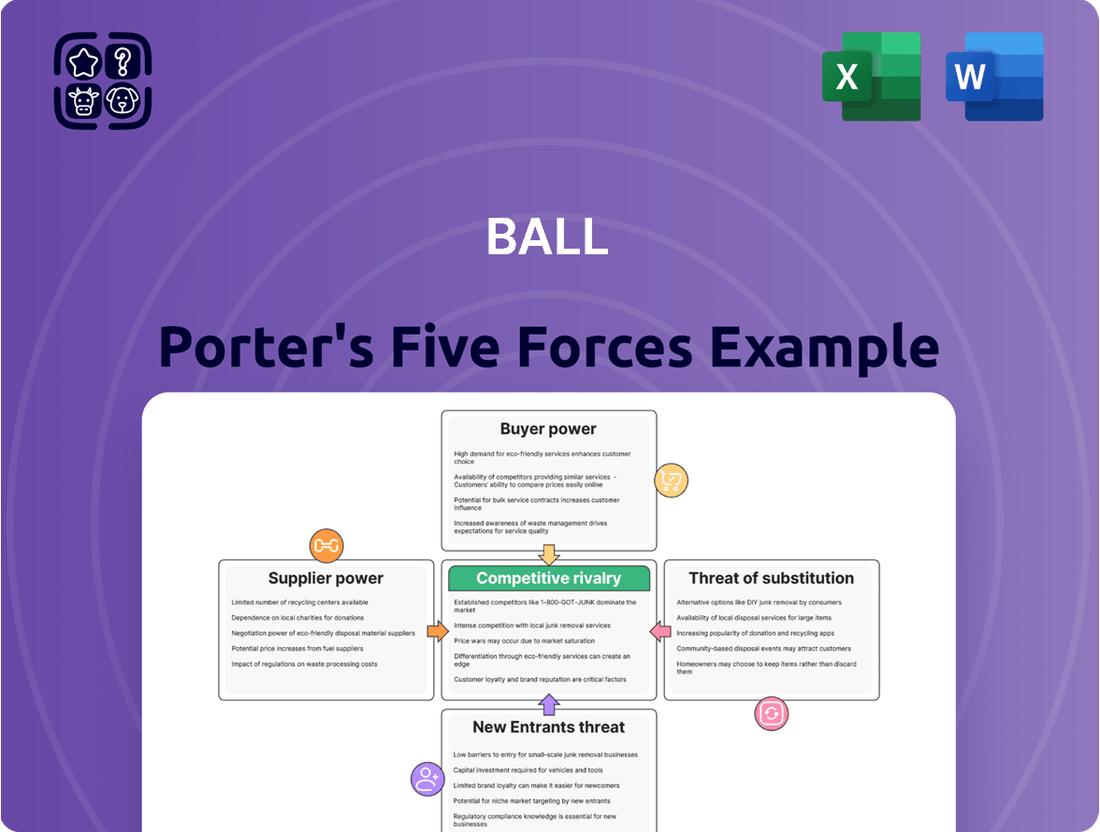
Ball Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within Ball's operating industries by examining rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Easily identify and address competitive pressures with a visual breakdown of each force, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ball Corporation's customer base is heavily concentrated among major players in the beverage, personal care, and household product industries. These large-volume buyers, such as Coca-Cola or Procter & Gamble, possess significant leverage. For instance, in 2023, Ball's top five customers accounted for approximately 29% of its net sales, highlighting the substantial influence these entities can wield.
For major beverage and consumer goods firms, changing packaging suppliers isn't a simple switch. It often means substantial investments in retooling production lines and redesigning packaging. For example, in 2024, a major beverage company might face costs of $500,000 to $2 million to adapt its bottling and labeling machinery for new packaging formats.
These significant upfront expenses create a barrier, effectively lowering the bargaining power of these customers. They are less likely to demand price concessions or favorable terms from their current supplier if the cost and disruption of switching are prohibitively high.
Customers for beverage packaging have a range of choices beyond aluminum cans, including plastic bottles and glass containers. This availability of substitutes directly impacts Ball Corporation's pricing power.
While sustainability trends in 2024 have seen a growing preference for aluminum, especially over certain plastics, the cost-effectiveness and lighter weight of plastic packaging continue to make it a competitive option for some beverage producers. For instance, the global plastic packaging market was valued at over $1 trillion in 2023, showcasing its significant market presence.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in the beverage and consumer goods sectors often exhibit high price sensitivity. This is largely driven by the intense competition they face within their own industries, compelling them to seek competitive pricing from suppliers like Ball, particularly for standardized products such as basic aluminum cans.
This price sensitivity translates directly into significant bargaining power for customers. For instance, in 2024, the global beverage market continued to be characterized by aggressive pricing strategies among major players, directly impacting their procurement decisions for packaging materials.
- Intense Competition: Competitors in the beverage and consumer goods markets often engage in price wars, pushing customers to demand lower costs from their suppliers.
- Commoditized Products: Standard beverage cans are largely undifferentiated, making price a primary factor in purchasing decisions.
- Volume Purchasing: Large beverage companies purchase massive volumes of cans, giving them considerable leverage to negotiate favorable pricing.
- Market Trends: Shifts in consumer preferences or economic downturns can further amplify customer demands for lower prices on packaging.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large beverage manufacturers, like Coca-Cola or PepsiCo, possess the financial clout to consider backward integration into can production. This move, while demanding significant capital expenditure, represents a potent bargaining lever for these major buyers. For instance, the global beverage market is projected to reach over $1.7 trillion by 2027, highlighting the immense purchasing power of leading companies within it.
The threat of backward integration is particularly relevant for can manufacturers serving a concentrated customer base. If a few key clients represent a substantial portion of a can producer's revenue, those clients can exert considerable pressure on pricing and terms. This potential for customers to become competitors directly impacts the bargaining power they hold.
- Capital Intensive Nature: Establishing a can manufacturing facility requires billions in investment for machinery, raw materials, and skilled labor.
- Scale Economies: Existing can producers often benefit from economies of scale that new entrants, including beverage companies, might struggle to match initially.
- Customer Concentration: The bargaining power of customers is amplified when a small number of large customers account for a significant percentage of a can manufacturer's sales.
Ball Corporation's customers possess considerable bargaining power, primarily due to their substantial purchase volumes and the availability of alternative packaging solutions. These large buyers, often major beverage and consumer goods companies, can exert pressure on pricing and terms. For example, in 2023, Ball's top five customers represented nearly 30% of its net sales, underscoring their influence.
| Factor | Impact on Ball Corporation | Supporting Data/Example (2023-2024) |
| Customer Concentration | High | Top 5 customers accounted for 29% of net sales in 2023. |
| Switching Costs | Low to Moderate | Retooling costs for new packaging can range from $500,000 to $2 million for major beverage firms in 2024. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate | Plastic and glass packaging remain competitive alternatives, with the global plastic packaging market exceeding $1 trillion in 2023. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Intense competition in the beverage market in 2024 drives demand for lower packaging costs. |
What You See Is What You Get
Ball Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ball Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You can confidently expect this comprehensive report, ready for immediate use and application to your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The aluminum beverage can industry is dominated by a few major global players, including Ball Corporation, Crown Holdings, and Ardagh Group. These companies collectively hold a substantial portion of the market share, meaning there are relatively few direct, large-scale competitors. This concentration means that any new entrant would face significant hurdles in matching the scale and established relationships of these industry giants.
The aluminum can industry is experiencing a moderate growth rate, particularly in developed markets. For instance, the U.S. beverage can market saw a 2.1% increase in shipments in 2023, reaching approximately 100 billion cans. This steady expansion, however, is tempered by the mature nature of some key segments.
Emerging markets present a more dynamic growth picture for aluminum cans, driven by rising disposable incomes and a preference for convenient packaging. Furthermore, the global push for sustainable packaging solutions is a significant tailwind. The aluminum industry, as a whole, reported a 3% year-over-year increase in global primary aluminum production in the first half of 2024, indicating broader industrial demand and potential for can sector growth.
Innovation, such as the introduction of aluminum cups for events and concessions, is also contributing to market expansion. These new product formats, alongside the ongoing demand for traditional beverage cans, create opportunities that can influence competitive intensity as companies vie for market share in these evolving segments.
Aluminum cans, the primary product for companies like Ball Corporation, are largely commoditized. This means there's very little customers can do to tell one can apart from another, beyond basic attributes like size, shape, and the printing on them. This lack of distinctiveness forces competition to focus heavily on price and operational efficiency.
In 2024, the intense competition in the aluminum can market means that even small price differences can sway major beverage producers. Ball Corporation, like its competitors, must constantly optimize its manufacturing processes to maintain cost leadership. For instance, improvements in energy efficiency in production can directly translate into a competitive edge on price, a critical factor for large-volume buyers.
Exit Barriers
High capital investments are a major hurdle for companies looking to leave the aluminum packaging sector. Think about the massive costs associated with setting up factories and buying specialized machinery. These sunk costs make it incredibly difficult to just walk away, even when times are tough.
Because exiting is so costly, companies often stay in the market longer than they might otherwise. This can mean more players competing, even with slim profits, which naturally cranks up the intensity of the rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the global aluminum packaging market, while growing, still saw companies heavily invested in production capacity, making divestment a complex financial decision.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for manufacturing plants and specialized equipment.
- Sunk Costs: Investments that cannot be recovered, discouraging market exit.
- Persistent Competition: Competitors remain active even in low-profitability periods, intensifying rivalry.
Strategic Commitments of Competitors
Major players in the industry are significantly increasing their production capabilities. For instance, in 2024, several leading companies announced plans for new facilities or expansions, aiming to capture a larger market share.
These strategic moves, including substantial investments in sustainable technologies and process automation, signal a deep commitment to long-term market presence. Companies are prioritizing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors, with many reporting increased capital allocation towards green initiatives in their 2024 financial disclosures.
This heightened dedication to market growth and operational improvement fuels a robust and enduring competitive rivalry. The ongoing investments in efficiency and capacity suggest a market where competitors are actively vying for dominance, making it challenging for new entrants.
- Capacity Expansion: Competitors are investing in new plants and upgrading existing ones, with significant capital expenditure announcements in 2024.
- Sustainable Practices: A growing trend shows increased spending on eco-friendly technologies and processes, reflecting a long-term strategic focus.
- Operational Efficiencies: Investments in automation and streamlining operations are common, aiming to reduce costs and improve output.
- Sustained Rivalry: These commitments indicate a highly competitive landscape where companies are dedicated to outperforming each other over the long haul.
Competitive rivalry in the aluminum beverage can industry is intense, driven by a few dominant global players like Ball Corporation, Crown Holdings, and Ardagh Group. The commoditized nature of aluminum cans means competition centers heavily on price and operational efficiency, with little product differentiation beyond basic attributes. For instance, in 2024, companies focused on optimizing manufacturing to gain a price advantage, as even minor cost differences could sway large beverage clients.
The market is characterized by high capital investment and significant sunk costs in manufacturing facilities, which discourages companies from exiting. This persistence means competitors remain active even during periods of lower profitability, further intensifying the rivalry. Capacity expansions and investments in sustainable technologies, with many companies increasing capital allocation to green initiatives in 2024, signal a deep commitment to market share and long-term presence, fueling ongoing competition.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Dominated by a few large global players. | High rivalry due to established market share and scale. |
| Product Commoditization | Little differentiation between cans from different manufacturers. | Intensifies price-based competition and focus on cost efficiency. |
| Capital Intensity & Sunk Costs | High investment in manufacturing plants and specialized equipment. | Discourages exit, leading to persistent competition even in tough times. |
| Capacity Expansion & Investment | Companies actively investing in new facilities and technology (e.g., sustainability). | Signals commitment to market growth and a drive to outmaneuver competitors. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for aluminum cans, like those produced by Ball Corporation, are plastic bottles and glass containers. While aluminum excels in recyclability and providing excellent barrier properties to protect beverages, plastic often presents a more cost-effective and lighter alternative. For instance, the global plastic packaging market was valued at approximately $1 trillion in 2023, highlighting its significant presence.
Glass containers, on the other hand, can offer a premium perception for certain beverages, appealing to a different consumer segment. Despite aluminum's strong environmental credentials, the price sensitivity of some beverage producers and the established infrastructure for plastic and glass packaging represent a considerable threat.
The price of aluminum compared to plastic and glass is a major factor in how appealing substitute materials are. For instance, in 2024, while aluminum prices saw some volatility, the cost of certain plastics remained relatively stable, making them a more attractive option for some packaging applications purely on a per-unit cost basis.
Even though aluminum often offers superior performance, such as better barrier properties or recyclability, significant price jumps can erode this advantage. If the cost of aluminum rises substantially, businesses might find it more economical to switch to plastic or glass, even if those materials require design compromises or have a larger environmental footprint.
Customer propensity to substitute is influenced by a growing preference for sustainable packaging. For instance, aluminum's infinite recyclability makes it an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers, a trend that saw a significant uptick in 2024 with many brands highlighting their eco-friendly packaging initiatives.
However, this preference is often balanced against practical considerations. The convenience of certain materials, like flexible plastics for on-the-go consumption, or the lower cost of glass for specific beverage segments, can still sway consumer choices.
In 2024, the cost of raw materials played a crucial role; fluctuations in aluminum prices, for example, could make alternatives like steel or even certain bioplastics more appealing to manufacturers and, subsequently, consumers if the price difference is passed on.
Switching Costs for End-Users and Customers
While Ball Corporation's direct customers, like beverage manufacturers, might incur some costs when switching packaging suppliers, the real pressure comes from the end-user. Consumers have virtually no switching costs when deciding between different beverage brands or types, and by extension, the packaging they come in.
This low switching cost for consumers means they can easily opt for a beverage in a different container if it's more convenient, appealing, or readily available. This directly influences demand for Ball's aluminum cans and other packaging solutions.
- Consumer Preference Shifts: If consumers increasingly favor beverages packaged in glass or cartons due to perceived environmental benefits or aesthetic appeal, demand for aluminum cans could decline.
- Brand Loyalty vs. Packaging: While brand loyalty exists, a significant shift in packaging preference by a major beverage producer could force Ball's customers to adapt, impacting Ball's market share.
- Example: In 2023, the global beverage packaging market saw continued innovation, with a growing emphasis on sustainability, potentially influencing consumer choices and, consequently, demand for specific packaging materials like aluminum.
Innovation in Substitute Products
Ongoing innovations in packaging materials, such as lighter and more resilient plastics with enhanced barrier properties, alongside advancements in glass manufacturing, present a persistent threat of substitution for aluminum. The emergence of novel packaging formats, like advanced flexible pouches or biodegradable alternatives, could also divert market share. For instance, the global flexible packaging market is projected to reach $393.3 billion by 2028, indicating significant growth in competing formats.
However, the aluminum industry is not standing still. Innovations in can design, including new shapes and improved structural integrity, and advancements in printing and coating technologies are enhancing aluminum's appeal and functionality. These developments aim to maintain aluminum's competitive edge against evolving substitutes.
The threat of substitutes is further influenced by consumer preferences and regulatory landscapes. For example, a growing consumer demand for sustainable packaging solutions could favor materials perceived as more environmentally friendly, although aluminum's high recyclability rate is a strong counter-argument. In 2023, the aluminum recycling rate in the US beverage can market remained high, exceeding 45%.
- Plastic Innovations: Development of thinner, stronger films and improved barrier coatings for food and beverage packaging.
- Glass Advancements: Lightweighting techniques and enhanced durability in glass bottle production.
- New Formats: Growth in the market for stand-up pouches, aseptic packaging, and compostable materials.
- Aluminum Counter-Innovations: Novel can shapes, advanced printing for branding, and improved recyclability technologies.
The threat of substitutes for aluminum cans, such as plastic bottles and glass containers, remains a significant factor. While aluminum offers excellent recyclability and barrier properties, plastic's cost-effectiveness and lighter weight, coupled with glass's premium perception, pose challenges. In 2024, aluminum's price volatility compared to more stable plastic costs directly influences manufacturers' choices, impacting Ball Corporation's market position.
| Substitute Material | Key Advantages | Key Disadvantages for Ball's Customers | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Bottles | Lower cost, lighter weight, flexibility | Lower recyclability rates, potential for taste/odor transfer, environmental concerns | Global plastic packaging market valued at approx. $1 trillion in 2023; price stability in 2024 |
| Glass Containers | Premium perception, inertness, recyclability | Heavier, breakable, higher transportation costs | Appeals to specific beverage segments; lightweighting innovations continue |
| Other Alternatives (e.g., Cartons, Pouches) | Sustainability perception, convenience | Varying barrier properties, different filling/sealing infrastructure needs | Flexible packaging market projected for significant growth; innovations in aseptic and compostable formats |
Entrants Threaten
The aluminum can manufacturing sector demands significant upfront capital. Building and equipping a modern production facility can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, encompassing specialized machinery, automated systems, and robust infrastructure. This immense financial hurdle deters many aspiring competitors from entering the market.
Established players in the aluminum packaging industry, such as Ball Corporation, benefit immensely from economies of scale. This means they can produce cans and other packaging at a substantially lower cost per unit due to their massive production volumes. In 2023, Ball Corporation reported net sales of $13.0 billion, a testament to their extensive operational capacity.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. To achieve comparable per-unit costs, a new company would need to invest heavily to reach similar production volumes, a daunting prospect given the capital-intensive nature of the industry and the established market share of incumbents.
Ball Corporation, a leader in the packaging industry, benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with major beverage companies. These long-standing partnerships and existing contracts create significant barriers for new entrants seeking to establish their own distribution networks.
Securing shelf space and access to retailers globally is a monumental task for any newcomer. Ball's established global distribution network, built over decades, provides a competitive advantage that is difficult and costly to replicate, especially for emerging players in the 2024 market.
Proprietary Technology and Know-How
While some innovations might be quickly copied, the deep operational efficiencies and manufacturing expertise built by established players over many years act as a significant barrier. Newcomers would struggle to match this proprietary know-how without substantial investment and time. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, companies like TSMC have decades of experience in advanced process technology, making it incredibly difficult for a new entrant to achieve comparable yields and quality.
This accumulated knowledge isn't easily codified or transferred, giving incumbents a distinct advantage. Consider the automotive sector, where established manufacturers possess intricate supply chain management systems and specialized production techniques honed over decades. A new electric vehicle startup, despite having innovative battery technology, still faces the challenge of building a comparable manufacturing and distribution network. In 2024, the capital expenditure required to set up a state-of-the-art semiconductor fabrication plant, for example, can easily exceed $20 billion, highlighting the immense financial and technical hurdle for new entrants.
- Proprietary Know-How: Decades of operational and manufacturing experience are difficult to replicate.
- Incumbent Advantage: Established firms possess unique efficiencies and expertise.
- High Entry Costs: Acquiring or developing similar capabilities requires substantial investment and time.
- Industry Examples: Semiconductor manufacturing and advanced automotive production showcase these barriers.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly influence the threat of new entrants in the packaging sector. Stringent environmental regulations, for instance, can impose substantial compliance costs and operational complexities on newcomers, making it harder to enter the market. These requirements, often related to recycling, waste reduction, and material sourcing, necessitate upfront investment in new technologies and processes.
Tariffs on key raw materials like imported aluminum also serve as a considerable barrier. For example, in 2024, fluctuations in global aluminum prices, exacerbated by trade policies, directly impacted the cost structure for packaging manufacturers. New entrants, lacking established supply chains and bulk purchasing power, are particularly vulnerable to these cost increases, hindering their ability to compete on price.
- Environmental Regulations: Increased compliance costs for new packaging companies due to sustainability mandates.
- Tariffs: Higher raw material costs for new entrants, particularly on imported aluminum, impacting price competitiveness.
- Licensing and Permits: Government-issued licenses and permits can add time and expense to market entry.
The threat of new entrants in the aluminum can manufacturing sector is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements and established economies of scale. Ball Corporation's 2023 net sales of $13.0 billion highlight the immense production capacity and cost efficiencies that new players must overcome. Furthermore, deep-seated customer relationships and extensive global distribution networks built over decades by incumbents like Ball create significant barriers to entry for aspiring competitors in 2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building a modern aluminum can plant costs hundreds of millions of dollars. | Deters many potential competitors due to the immense upfront investment needed. |
| Economies of Scale | Incumbents like Ball achieve lower per-unit costs through high production volumes. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies without massive initial investment. |
| Customer Relationships & Distribution | Established players have long-standing contracts and global networks. | Newcomers face difficulty securing customers and replicating distribution reach. |
| Proprietary Know-How | Decades of operational expertise and manufacturing techniques are hard to replicate. | New entrants need significant time and investment to develop comparable efficiency and quality. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and publicly available trade association data to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
