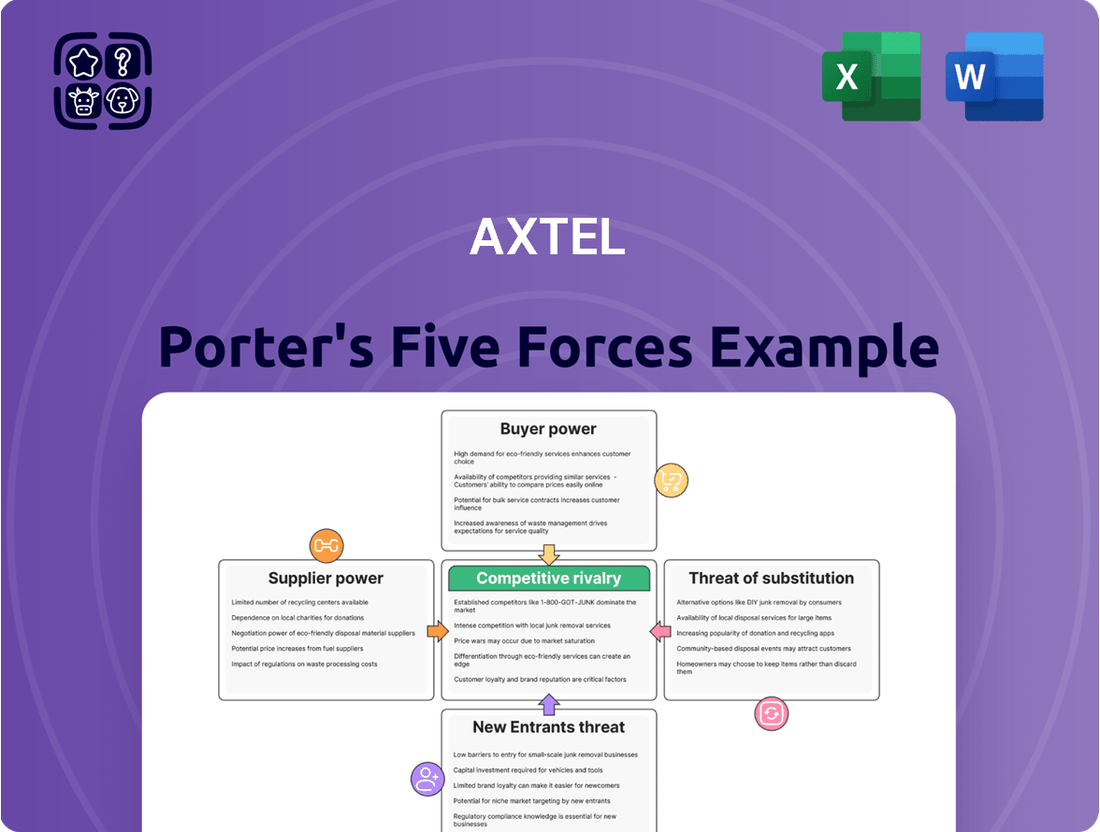
Axtel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Axtel Bundle
Axtel's competitive landscape is shaped by five critical forces: the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic assessment of Axtel's market position. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Axtel’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for Axtel's critical components, such as fiber optic cables and networking equipment, is a key factor in supplier bargaining power. If a few major players dominate the market for these essential inputs, they can exert significant influence over pricing and contract terms. This is particularly true for specialized technologies like 5G infrastructure, where the supplier pool might be more limited.
For instance, in 2024, the global fiber optic cable market saw continued consolidation, with a few large manufacturers holding substantial market share. This concentration means Axtel may face less flexibility in negotiating prices for these vital materials, potentially impacting its cost of network expansion and maintenance. A diverse supplier base, however, would naturally dilute this power, offering Axtel more competitive options.
Axtel's reliance on specialized technology and infrastructure for its ICT services, such as broadband, data centers, and IT security, directly impacts supplier bargaining power. If key suppliers provide unique or proprietary technologies with few alternatives, their leverage grows significantly.
This is especially true for advanced cloud infrastructure or highly specialized IT security solutions, where finding comparable substitutes can be challenging and costly for Axtel.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Axtel is significantly influenced by switching costs. For instance, migrating Axtel's core network infrastructure from one provider to another could incur substantial expenses, estimated in the millions of dollars, along with considerable operational downtime. These high costs make it challenging for Axtel to change suppliers readily, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Axtel's suppliers could significantly bolster their bargaining power. If suppliers possess the capability and a strong incentive to bypass Axtel and directly serve its end customers with comparable Information and Communications Technology (ICT) services, Axtel's competitive position would be challenged.
While this scenario is less prevalent within the typical telecommunications infrastructure and software supply chain, it represents a potential long-term risk. For instance, major technology component manufacturers might choose to enter the services market, directly competing with Axtel. In 2024, the global ICT services market was valued at over $5 trillion, indicating the substantial revenue potential that could incentivize such a move by large suppliers.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers must possess the necessary technological expertise, customer relationships, and operational infrastructure to offer services directly.
- Supplier Incentive: The potential for higher profit margins or increased market share by bypassing intermediaries like Axtel would drive this incentive.
- Market Dynamics: A shift towards more integrated service offerings by technology providers could accelerate this threat.
- Impact on Axtel: Increased supplier bargaining power could lead to higher input costs or reduced service availability for Axtel.
Importance of Axtel to the Supplier
The significance of Axtel's business to its suppliers is a crucial factor in determining the supplier's bargaining power. If Axtel constitutes a significant portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier will likely be more amenable to offering favorable terms and pricing to secure Axtel's continued patronage. This is because losing Axtel as a customer could have a material impact on the supplier's financial performance.
Conversely, if Axtel represents a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, Axtel's leverage would be considerably diminished. In such scenarios, the supplier has less incentive to negotiate aggressively on price or terms, as Axtel's business is not critical to their bottom line. For instance, if a supplier's revenue is primarily derived from a few large clients, a smaller account like Axtel would have limited influence.
- Supplier Dependence: Axtel's revenue contribution to its suppliers directly impacts their willingness to concede on pricing and terms.
- Diversification of Suppliers: Axtel's ability to switch suppliers also influences the bargaining power of its current suppliers.
- Market Share: If Axtel is a major buyer in a specific market, its demand can shape supplier behavior.
- Contractual Agreements: The terms of existing contracts can either strengthen or weaken a supplier's bargaining position with Axtel.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Axtel is elevated due to the concentration of key component providers, particularly for specialized technologies like 5G infrastructure, where the supplier pool is limited. This concentration, evident in the 2024 fiber optic cable market with a few dominant manufacturers, restricts Axtel's negotiation flexibility and can increase input costs.
Axtel's reliance on unique or proprietary technologies, such as advanced cloud infrastructure and specialized IT security solutions, further amplifies supplier leverage, as finding viable substitutes is both challenging and expensive. The substantial switching costs, potentially in the millions of dollars and involving significant operational disruption, also lock Axtel into existing supplier relationships, diminishing its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
The threat of suppliers forward integrating into Axtel's service market, though less common in the ICT sector, remains a potential risk, especially given the global ICT services market's value exceeding $5 trillion in 2024. This could lead to increased supplier bargaining power, higher input costs, or reduced service availability for Axtel.
Axtel's influence over its suppliers is directly tied to its revenue contribution; a larger share of a supplier's business grants Axtel more negotiation power. Conversely, if Axtel is a minor client for a diversified supplier, its leverage is significantly reduced, making it harder to secure favorable pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact on Axtel | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased costs, reduced flexibility | Consolidation in fiber optic cable market |
| Switching Costs | Limited supplier choice, higher costs | Millions of dollars for infrastructure migration |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential direct competition from suppliers | Large ICT services market ($5T+) offers incentive |
| Axtel's Business Significance | Negotiating power dependent on revenue contribution | Minor client status weakens Axtel's leverage |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Axtel's telecommunications and IT services market.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each Porter's Force, transforming complex analysis into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Axtel's customer base is varied, encompassing businesses, government agencies, and individual households. This diversity generally dilutes customer bargaining power.
However, customer concentration can significantly amplify this power. If a few major clients make up a large chunk of Axtel's revenue, their ability to negotiate better terms or switch providers increases, posing a risk.
For instance, in 2020, Axtel's top ten customers represented 27% of its total sales. This highlights a notable level of customer concentration, which could grant these key clients considerable leverage in negotiations.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when numerous alternative providers offer comparable telecommunications and ICT solutions. In Mexico's dynamic telecom landscape, the presence of multiple players for broadband, managed networks, and IT security empowers customers to demand better pricing and service conditions.
The ease or difficulty customers face when switching from Axtel to a competitor significantly influences their bargaining power. For residential customers, switching internet providers can be relatively straightforward, often involving a simple service transfer.
However, for Axtel's business and government clients, switching costs are considerably higher. These costs stem from factors like the integration of Axtel's services into existing IT infrastructure, long-term contractual obligations, and the complex process of migrating critical business operations to a new provider without service disruption.
In 2024, the telecommunications industry saw continued investment in network upgrades, with companies like Telmex and AT&T Mexico enhancing their fiber optic capabilities. This competitive landscape means that while Axtel aims to retain clients through service quality, the potential for customers to leverage competitive offerings can increase their leverage in negotiations, especially for larger enterprise contracts where service continuity is paramount.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers' sensitivity to price directly influences their leverage over Axtel. When consumers are keenly aware of price differences, Axtel might need to reduce its prices or enhance its service offerings to remain competitive, particularly for basic internet and phone services. This is especially true in markets where switching providers is relatively easy.
For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications sector saw continued price competition. Many consumers actively sought out the best deals, leading to a higher churn rate for providers that didn't offer competitive pricing. Axtel, like its peers, had to balance service quality with affordability to retain its customer base.
- Price Sensitivity: High price sensitivity among customers increases their bargaining power.
- Competitive Landscape: In competitive markets, Axtel faces pressure to match or beat competitor pricing.
- Service Differentiation: For standard services, price is a primary decision factor for customers.
- Customer Retention: Lower prices or better value can be crucial for retaining customers in price-sensitive segments.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
The threat of Axtel's customers integrating backward, meaning they'd provide their own Information and Communication Technology (ICT) services, is generally low across most of its client base. This is because developing and maintaining robust ICT infrastructure requires significant capital investment and specialized expertise, which most businesses do not possess or wish to manage internally.
However, for very large enterprises or government organizations, the possibility of building some in-house IT infrastructure or network management capabilities exists. This potential for backward integration, even if partial, can give these larger clients a slight edge in negotiations with Axtel, as they have a credible alternative, albeit a costly one.
- Low Threat of Backward Integration: Most Axtel clients lack the resources and expertise to replicate its comprehensive ICT services.
- Potential for Large Clients: Major enterprises and government bodies may consider limited in-house IT solutions, increasing their bargaining power.
- Cost Barrier: The substantial investment required for independent ICT infrastructure development deters most customers from backward integration.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Businesses generally prefer to outsource ICT to focus on their primary operational activities.
Axtel's customer bargaining power is influenced by several factors, including price sensitivity and the competitive landscape. In 2024, the telecom market saw continued price competition, with customers actively seeking better deals, which pressured providers like Axtel to offer competitive pricing and value to retain them.
The concentration of Axtel's customer base also plays a role; for instance, in 2020, its top ten customers accounted for 27% of sales, indicating that these major clients could wield significant negotiation leverage. While the threat of backward integration is generally low due to high costs and expertise requirements, large enterprises might consider partial in-house solutions, subtly enhancing their bargaining position.
| Factor | Impact on Axtel's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration amplifies power for key clients. | Top 10 customers represented 27% of sales in 2020, indicating potential leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Higher for businesses than residential customers. | Businesses face integration and contractual complexities when switching providers. |
| Competitive Landscape | Intensifies pressure for better pricing and service. | Continued investment in fiber optics by competitors like Telmex and AT&T Mexico empowers customers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Directly influences negotiation leverage. | High price sensitivity in 2024 led to increased churn for less competitive providers. |
What You See Is What You Get
Axtel Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual Axtel Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for the company. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing a comprehensive understanding of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes relevant to Axtel.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Mexican telecommunications and ICT landscape is a crowded arena, with Axtel facing off against formidable rivals. Key competitors include giants like Telmex, a subsidiary of America Movil, AT&T Mexico, and Telefonica Mexico operating under the Movistar brand. Beyond these major carriers, Axtel also contends with significant fixed-line and broadband providers such as Megacable and Totalplay, alongside a host of specialized IT service firms.
The Mexican telecom and ICT markets are booming. The telecom sector is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, the ICT market is expected to expand at an even faster pace, with a CAGR of 10.6% between 2025 and 2030.
While robust industry growth is generally a positive sign, it can paradoxically intensify competitive rivalry. As the market expands, it becomes a more attractive target for existing players and new entrants alike, all vying to secure a significant portion of this increasing demand.
Axtel's competitive edge hinges on differentiating its broadband, managed network, data center, and IT security services. By offering specialized solutions tailored to specific industries or providing exceptional customer support, Axtel can sidestep intense price wars. For instance, Axtel's focus on boosting client productivity and efficiency through its advanced technology solutions serves as a key differentiator in a crowded market.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the telecommunications sector are substantial, significantly impacting competitive rivalry. Companies like Axtel face immense costs associated with divesting specialized assets such as their extensive fiber optic networks, which in Axtel's case, spans over 50,000 kilometers. These high fixed costs, coupled with long-term customer contracts and regulatory requirements, make exiting the market a complex and often financially punitive decision. This reluctance to leave, even in the face of declining profitability, forces companies to remain engaged in intense competition, driving down prices and margins for all players.
The presence of high exit barriers means that even struggling telecommunications firms are likely to persist, intensifying the competitive landscape. This can manifest as aggressive pricing strategies and a continuous push for market share, as companies seek to recover their substantial investments. For instance, the significant capital expenditure required to build and maintain infrastructure like data centers and transmission lines creates a strong incentive to continue operating, regardless of current market conditions. This dynamic directly fuels rivalry, as firms fight to maintain viability within a market where exiting is prohibitively expensive.
- High Capital Investment: Telecommunications companies invest billions in infrastructure, such as fiber optic networks and data centers, creating significant sunk costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with customers and service providers create ongoing obligations that are difficult to terminate prematurely.
- Specialized Assets: The highly specific nature of telecommunications equipment makes it difficult to repurpose or sell, increasing losses upon exit.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Exiting the market often involves complex regulatory approvals and compliance procedures, adding further complexity and cost.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers in the telecommunications sector, particularly for a company like Axtel, are generally quite low. This low barrier means customers can easily switch to a different provider if they find a better deal or service. In 2024, this dynamic forces Axtel to continually focus on competitive pricing and superior customer service to prevent churn.
The ease with which customers can change providers directly fuels intense rivalry. For Axtel, this translates into a constant need to innovate and offer compelling value propositions. For instance, a customer might switch from Axtel to a competitor like Telmex or AT&T Mexico for a slight reduction in their monthly internet bill or a more attractive bundle package.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily migrate between telecom providers, impacting Axtel's customer retention efforts.
- Price Sensitivity: Low switching costs often lead to increased price competition, pressuring Axtel's profit margins.
- Service Quality Focus: Companies like Axtel must prioritize service quality and customer experience to differentiate themselves beyond price.
Axtel operates in a highly competitive Mexican telecommunications market, facing pressure from major players like Telmex, AT&T Mexico, and Telefonica. The industry's robust growth, with the telecom sector expected to grow at an 8.2% CAGR from 2024-2029, attracts intense rivalry as companies vie for market share. This competition necessitates Axtel's focus on differentiated services in broadband, data centers, and IT security to avoid price wars.
The intensity of competition is further amplified by high exit barriers, such as Axtel's extensive 50,000+ kilometer fiber optic network, making it costly to leave the market. This forces companies to remain engaged, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies. Additionally, low customer switching costs in 2024 mean Axtel must prioritize service quality and competitive pricing to retain its customer base amidst this fierce landscape.
| Competitor | Market Segment Focus | 2024 Market Share (Est.) |
|---|---|---|
| Telmex (América Móvil) | Fixed-line, Mobile, Broadband | 40-45% |
| AT&T Mexico | Mobile, Broadband | 20-25% |
| Telefonica (Movistar) | Mobile, Broadband | 15-20% |
| Megacable | Broadband, Cable TV | 5-10% |
| Totalplay | Broadband, Pay TV | 5-10% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Axtel's ICT services is significant, primarily due to the increasing availability of alternative technologies that can meet similar customer demands. For example, while Axtel offers robust fixed broadband solutions, the rapid expansion of mobile broadband, particularly 5G networks from competitors such as Telcel, AT&T, and Movistar, presents a viable substitute for many residential and mobile business users seeking connectivity.
Customers constantly weigh the price against the performance offered by substitute products or services. If a competitor's offering delivers similar or superior functionality at a lower price point, the threat of substitution intensifies significantly. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, while traditional landline services remain, the widespread availability and decreasing cost of mobile data plans provide a compelling, often cheaper, alternative for many communication needs.
Customers are more likely to switch to a substitute if they see clear advantages and minimal downsides. For instance, in the realm of basic internet services, price often drives the decision to switch. A 2024 report indicated that over 40% of consumers would consider switching providers solely based on a 10% price reduction for comparable services.
However, when it comes to sophisticated managed network services or critical IT security solutions, the willingness to substitute is significantly lower. This is primarily due to the paramount importance of reliability, security, and the need for specialized, proven expertise. Businesses in 2024 often prioritize long-term partnerships with providers offering robust support and a strong track record, even at a higher cost, rather than risking disruptions or breaches by switching to a less established or less specialized alternative.
Evolution of Cloud and SaaS Services
The growing availability and sophistication of cloud and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions present a substantial threat of substitutes for Axtel's traditional offerings. Businesses can now readily access data storage, application hosting, and even IT security services directly from cloud providers, often at competitive price points. This shift allows them to bypass the need for Axtel's underlying infrastructure and managed services.
For instance, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion in 2024, indicating a massive shift towards these services. Many companies are migrating their operations to platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, which offer scalable and flexible alternatives to on-premises or traditional managed IT solutions. This trend directly impacts Axtel's potential market share for its infrastructure and related services.
- Cloud Adoption Growth: The worldwide public cloud services market is expected to grow by 20.4% in 2024 to total $678.8 billion, up from $569 billion in 2023.
- SaaS Dominance: SaaS continues to be the largest cloud service segment, expected to reach $313.4 billion in 2024.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many cloud solutions offer pay-as-you-go models, which can be more cost-effective for businesses than investing in and maintaining their own infrastructure, making them attractive substitutes.
DIY Solutions and In-house Capabilities
For large corporations and government bodies, developing their own IT and communication infrastructure presents a significant threat of substitution. This in-house capability, though demanding substantial upfront capital, allows these entities to bypass reliance on external providers like Axtel for critical services, potentially leading to cost savings and greater control over their operations.
The increasing availability of advanced technology and skilled personnel makes in-house solutions more feasible. For instance, many large enterprises now possess the internal expertise to manage their own cloud infrastructure, cybersecurity, and network operations, directly competing with the core offerings of telecommunications companies.
Consider these points regarding DIY solutions:
- Significant Capital Investment: Building and maintaining in-house IT and communication networks requires substantial financial outlay for hardware, software, and specialized personnel.
- Reduced Reliance on External Providers: Successful in-house capabilities diminish the need for services offered by companies like Axtel, impacting their market share and revenue streams.
- Control and Customization: Businesses opting for in-house solutions gain greater control over their technology stack and can customize it precisely to their unique operational needs.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: While feasible, attracting and retaining the highly specialized talent required for advanced in-house IT management remains a critical factor for success.
The threat of substitutes for Axtel's services is substantial, driven by the rise of mobile broadband, cloud computing, and the potential for in-house solutions. While Axtel provides robust fixed and managed services, alternatives like 5G mobile networks from competitors offer comparable connectivity for many users. The increasing adoption of cloud platforms like AWS and Azure, with SaaS dominating the market, provides scalable and often cost-effective alternatives to traditional IT infrastructure. For instance, the public cloud services market was projected to exceed $678 billion in 2024.
Customers often evaluate substitutes based on price and performance. A slight price reduction for comparable services can sway over 40% of consumers to switch, according to 2024 data. However, for critical services like IT security or complex network management, reliability and proven expertise are paramount, making customers less likely to opt for substitutes. Businesses prioritize established providers with strong support, even at a premium, over less specialized alternatives.
The capacity for large corporations to develop in-house IT and communication infrastructure also poses a significant threat. While requiring substantial capital, these DIY solutions offer greater control and customization, reducing reliance on external providers. This trend is facilitated by the increasing availability of advanced technology and skilled personnel, making internal management of cloud, cybersecurity, and network operations a viable competitive option.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the telecommunications and ICT services market, particularly with a broad service portfolio like Axtel's, demands immense capital. Significant investments are needed for building and maintaining fiber optic networks, establishing state-of-the-art data centers, and developing robust IT infrastructure. For instance, the global telecommunications infrastructure market was valued at approximately $1.9 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow, highlighting the scale of investment required.
Regulatory barriers significantly deter new entrants in Mexico's telecommunications industry. The sector is heavily regulated, requiring extensive licensing, careful spectrum allocation, and adherence to strict industry standards. For instance, the Federal Institute of Telecommunications (IFT) oversees these processes, and obtaining necessary approvals can be a lengthy and costly endeavor, effectively raising the barrier to entry.
Established players like Axtel leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in their extensive fiber optic network infrastructure. This scale allows for lower per-unit costs in network maintenance, bandwidth provision, and customer service, making it difficult for newcomers to match their pricing competitiveness. For instance, in 2024, the capital expenditure required to build a comparable national telecommunications network easily runs into billions of dollars, a prohibitive barrier for most potential entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
While Axtel operates in a sector where brand loyalty might not be as intensely cultivated as in consumer goods, the company has successfully built strong, long-term relationships with its key business and government clients. These established connections represent a significant hurdle for potential new entrants seeking to capture market share.
New competitors would need to invest considerable resources not only in matching Axtel's service offerings but also in dismantling the existing trust and perceived value that Axtel's clients associate with its brand. This is a substantial barrier to entry that requires more than just a competitive pricing strategy.
Furthermore, customer switching costs for Axtel's clientele are not negligible. These costs encompass several factors:
- Contractual Obligations: Many business and government contracts have lock-in periods, making it financially disadvantageous for clients to switch providers before their current agreements expire.
- Migration Effort: Transitioning services, such as telecommunications, data management, or IT infrastructure, involves technical complexities, potential downtime, and the reallocation of internal resources. This operational disruption acts as a deterrent to switching.
- Integration Costs: New systems need to be integrated with existing business processes, which can incur additional costs and require specialized expertise.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants into Mexico's telecommunications market, like Axtel operates within, often struggle to build out the necessary distribution channels and sales networks. Reaching the diverse customer base, from large enterprises and government bodies to individual households, requires significant investment and established relationships.
Axtel, having been in operation for years, possesses established commercial models and a physical presence across its key segments. This existing infrastructure provides a significant advantage, making it harder for newcomers to gain comparable market access and effectively compete for customers.
- Established Networks: Axtel's existing distribution and sales infrastructure across Mexico presents a substantial barrier to entry.
- Customer Reach: New entrants must invest heavily to replicate Axtel's ability to reach businesses, government, and residential customers.
- Commercial Models: Axtel's proven commercial strategies for different market segments are difficult for new players to quickly emulate.
The threat of new entrants for Axtel remains moderate due to substantial capital requirements for network infrastructure and regulatory hurdles in Mexico's telecommunications sector. Established players benefit from significant economies of scale, with the cost of building a national network in 2024 easily reaching billions of dollars, a prohibitive barrier for most newcomers.
Customer switching costs, including contractual obligations and integration complexities, further solidify Axtel's market position. New entrants must overcome not only these financial and operational barriers but also the established client relationships and brand trust Axtel has cultivated.
The difficulty in replicating Axtel's extensive distribution channels and commercial models also limits the threat. New companies need considerable investment to achieve comparable market access and customer reach across different segments.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building fiber optic networks and data centers requires billions of dollars. | Very High |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Licensing, spectrum allocation, and IFT approvals are complex and costly. | High |
| Economies of Scale | Existing players have lower per-unit costs due to large infrastructure. | High |
| Customer Switching Costs | Contractual lock-ins, migration effort, and integration expenses deter clients. | Moderate |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Established trust with business and government clients is hard to displace. | Moderate |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Axtel Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Axtel's official investor relations communications, public financial filings, and comprehensive industry reports from leading telecommunications research firms. This allows for a precise evaluation of competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
