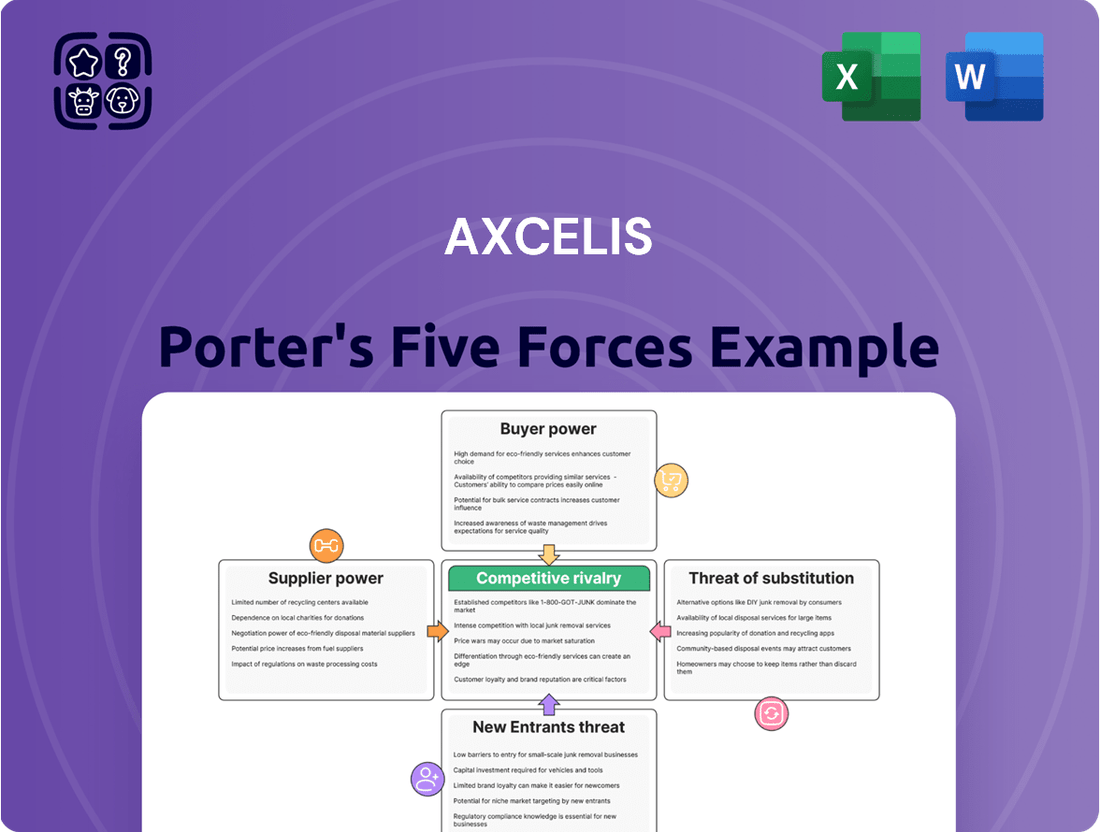
Axcelis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Axcelis Bundle
Axcelis operates in a dynamic semiconductor equipment market, facing intense rivalry and significant buyer power from major chip manufacturers. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any strategic evaluation.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Axcelis’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The semiconductor equipment sector often depends on a small group of suppliers for highly specialized components and materials. This scarcity of alternative sources grants these suppliers considerable leverage, potentially impacting Axcelis's procurement costs and supply chain stability. For instance, in 2023, the lead times for certain advanced semiconductor fabrication equipment components could extend significantly, reflecting this concentrated supplier power.
Suppliers offering unique or proprietary components, particularly those essential for ion beam technology and vacuum systems, hold considerable bargaining power. Axcelis's dependence on these specialized inputs for its advanced ion implanters allows these suppliers to dictate higher prices or enforce more stringent contract terms. The highly specialized nature of these critical inputs significantly limits the ability to find readily available substitutes.
Axcelis faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to high switching costs. When Axcelis needs to change suppliers for highly integrated or customized components, the expenses associated with redesigning, re-qualifying, and the potential for production delays are substantial. This situation inherently limits Axcelis's maneuverability and bolsters the leverage of its current suppliers.
The rigorous testing and validation processes that Axcelis must undertake to approve new suppliers further solidify the entrenched relationships with existing ones. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor equipment industry, where Axcelis operates, continued to see complex supply chains with specialized parts, making supplier diversification a lengthy and costly endeavor.
Talent Shortages in the Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry is grappling with a significant shortage of skilled talent, particularly engineers and technicians crucial for equipment design, manufacturing, and maintenance. This scarcity directly bolsters the bargaining power of these specialized professionals. For instance, a 2024 report indicated a projected deficit of over 100,000 semiconductor professionals globally by 2030, underscoring the intensity of this issue.
This talent crunch translates into increased labor costs and difficulties in filling essential positions for companies like Axcelis. Such staffing challenges can hinder operational efficiency and slow down the pace of innovation, as companies compete fiercely for a limited pool of qualified individuals.
- Persistent Global Talent Deficit: A shortage of specialized engineers and technicians in semiconductor equipment design, manufacturing, and servicing.
- Increased Labor Costs: The scarcity of skilled professionals drives up wages and benefits, impacting operational expenses.
- Operational and Innovation Challenges: Difficulty in staffing critical roles can impede production schedules and the development of new technologies.
- Supplier Power Amplified: Talent scarcity empowers specialized labor as a key supplier, giving them leverage in negotiations.
Geopolitical Factors and Raw Material Restrictions
Geopolitical tensions, particularly those affecting access to critical raw materials, significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. For instance, export restrictions on materials like gallium and germanium, essential for semiconductor manufacturing, can create scarcity and drive up costs for companies like Axcelis. This forces them to contend with a more concentrated supplier base, increasing the leverage of those who can still provide these vital inputs.
These external pressures necessitate careful navigation of international trade dynamics. Companies may face increased costs or delays in securing necessary components, potentially impacting production schedules and profitability. The need to find alternative, perhaps more expensive, sources further amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers who remain accessible.
- Disruptions: Geopolitical events can lead to sudden restrictions on key raw materials, directly impacting supply chain stability.
- Cost Increases: Limited availability and trade barriers often translate into higher input costs for manufacturers.
- Supplier Leverage: When fewer suppliers can provide critical materials, their ability to dictate terms and prices increases.
- Strategic Sourcing: Companies must develop robust strategies to mitigate these risks, including diversifying suppliers and exploring alternative materials.
Axcelis's suppliers wield significant bargaining power due to the highly specialized nature of components and the limited number of qualified manufacturers. This concentration means suppliers can often dictate terms, impacting Axcelis's costs and production timelines. The industry's reliance on proprietary technologies further entrenches this supplier leverage.
In 2024, the semiconductor equipment sector continued to experience extended lead times for critical components, a direct reflection of concentrated supplier power. For instance, specialized vacuum pumps and advanced wafer handling systems often come from a few select providers, giving them considerable pricing influence.
High switching costs also amplify supplier power. The intricate integration of components into Axcelis's ion implanters, coupled with rigorous qualification processes, makes changing suppliers a costly and time-consuming undertaking. This inertia benefits existing suppliers, solidifying their advantageous market position.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Axcelis | Supporting Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | Increased procurement costs, potential supply chain disruptions | Extended lead times for advanced vacuum systems and ion sources |
| Limited Supplier Base | Reduced negotiation leverage for Axcelis | Concentration in suppliers for critical semiconductor processing materials |
| High Switching Costs | Entrenched supplier relationships, limited flexibility | Lengthy qualification and integration periods for new component suppliers |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the semiconductor equipment industry's competitive landscape for Axcelis, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrant threats, substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities with a comprehensive, visual breakdown of each force, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Axcelis's customer base is highly concentrated, featuring a limited number of major global semiconductor manufacturers. These industry titans, such as Intel, TSMC, and Samsung, represent a significant portion of Axcelis's sales. Their substantial order volumes translate directly into considerable bargaining power.
The sheer scale of these semiconductor giants allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2023, the top 10 semiconductor companies accounted for a substantial percentage of global semiconductor sales, highlighting their market dominance and influence over suppliers like Axcelis.
This concentration means that losing even one major customer can have a material impact on Axcelis's revenue. Consequently, these customers can leverage their purchasing power to demand better pricing, customized solutions, and extended warranties, thereby influencing Axcelis's profitability.
The semiconductor industry's significant capital expenditure, with fab constructions often costing billions, means customers like Intel or TSMC meticulously vet equipment suppliers. This substantial investment amplifies their bargaining power, as they demand robust performance guarantees and highly competitive pricing from companies like Axcelis Technologies.
For instance, a new advanced semiconductor fabrication plant can easily exceed $10 billion in construction costs. This immense financial commitment naturally leads customers to exert considerable pressure on their equipment vendors, seeking the best possible terms and ensuring minimal risk.
Moreover, the inherent cyclicality of semiconductor capital spending, characterized by periods of intense investment followed by 'digestion periods,' further empowers customers. During these slower investment cycles, chipmakers can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate more favorable contracts and pricing for essential manufacturing equipment.
Customers in the semiconductor industry consistently demand equipment that can manufacture chips at increasingly advanced process nodes, such as 5nm and even 3nm. This relentless pursuit of smaller, faster, and more power-efficient chips directly translates into significant bargaining power for these customers.
This demand for cutting-edge technology allows customers to exert leverage, pushing suppliers like Axcelis for specific performance metrics, tailored customization, and a continuous stream of innovation. For instance, major chip manufacturers often have stringent requirements for yield and throughput, directly influencing their purchasing decisions and the terms they negotiate.
Axcelis's ability to meet these evolving technical requirements is paramount for retaining its customer base. In 2024, the semiconductor industry saw continued investment in advanced manufacturing, with companies like TSMC and Samsung heavily focused on next-generation nodes, underscoring the critical nature of technological capability in customer relationships.
Criticality of Equipment and Aftermarket Support
The criticality of ion implantation equipment for semiconductor manufacturers means that any downtime directly impacts their production output and revenue. This reliance gives customers significant bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, semiconductor fabrication plants operate with extremely tight schedules, where even a few hours of unplanned downtime can cost millions in lost production. Axcelis's customers, therefore, demand and expect highly reliable equipment and readily available aftermarket support to ensure continuous operation.
Customers' need for uninterrupted production lines translates into strong leverage over service contracts and the availability of spare parts. They can negotiate favorable terms for maintenance, technical assistance, and parts delivery, as the cost of equipment failure is exceptionally high. This bargaining power directly influences Axcelis's ability to secure and maintain recurring revenue from these essential services.
- Criticality of Equipment: Ion implanters are essential for semiconductor manufacturing, making their uptime crucial for customer production.
- Customer Demands: Buyers require robust post-sales service, technical support, and prompt spare parts availability.
- Leverage through Downtime Costs: The high cost of production line stoppages gives customers significant power in negotiating service agreements and support levels.
- Impact on Recurring Revenue: This customer leverage can affect the profitability and predictability of Axcelis's service and support revenue streams.
Customer's Ability to Delay or Consolidate Purchases
The semiconductor equipment industry, including players like Axcelis Technologies, sees customers with significant bargaining power due to their ability to delay or consolidate purchases. The lengthy timelines for building and equipping semiconductor fabrication plants, often stretching over several years, grant these customers considerable flexibility. This means they can strategically postpone or bundle their equipment orders in response to shifts in market demand or their own internal strategic realignments.
This flexibility directly translates into leverage for customers, particularly when the semiconductor market experiences downturns. During periods of subdued demand, customers can effectively apply pressure on pricing and delivery schedules for essential equipment. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor industry faced a cyclical slowdown, impacting capital expenditure plans for many foundries, thereby increasing their negotiating power with equipment suppliers.
- Delayed Purchases: Customers can postpone equipment orders, especially during market downturns, reducing immediate demand for suppliers.
- Consolidated Orders: Bundling multiple equipment purchases into larger, less frequent orders can give customers greater leverage in price negotiations.
- Market Sensitivity: Fluctuations in end-market demand for semiconductors directly influence customer willingness and ability to commit to large capital expenditures.
- Fab Construction Timelines: The multi-year nature of new fab construction provides a long window during which purchasing decisions can be deferred or adjusted.
The bargaining power of customers in the semiconductor equipment sector, including Axcelis's clientele, is substantial. These major chip manufacturers, such as TSMC and Intel, represent a concentrated customer base, meaning losing even one can significantly impact Axcelis's revenue. In 2023, the top 10 semiconductor companies commanded a significant share of global sales, underscoring their influence.
The immense capital investment required for semiconductor fabrication plants, often exceeding $10 billion, compels these customers to meticulously vet suppliers and demand highly competitive pricing and performance guarantees. This financial commitment amplifies their leverage, particularly during cyclical downturns in semiconductor capital spending, as seen in 2023, when many foundries adjusted their expenditure plans.
Customers' relentless pursuit of advanced process nodes, like 3nm and below, means they dictate technological requirements, pushing suppliers for innovation and customization. In 2024, the industry's focus on next-generation nodes highlights the critical nature of technological capability in customer relationships. Furthermore, the high cost of production downtime, with even hours costing millions, grants customers significant power in negotiating service contracts and spare parts availability, impacting Axcelis's recurring revenue.
| Key Factor | Impact on Axcelis | Customer Leverage Example (2023-2024) |
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on major clients | Top 10 semiconductor firms' sales dominance |
| Capital Expenditure Scale | Demand for competitive pricing & performance | $10B+ fab costs drive stringent supplier vetting |
| Technological Demands | Need for innovation and customization | Focus on 3nm nodes necessitates supplier R&D |
| Production Downtime Costs | Leverage in service & support negotiations | Millions lost per hour of downtime increase service contract power |
What You See Is What You Get
Axcelis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Axcelis Porter's Five Forces analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the ion implantation equipment industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of existing rivalry. No surprises, no placeholders—just a comprehensive and ready-to-use strategic document.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The ion implantation equipment market is a highly concentrated space, dominated by a few key players. Applied Materials and Axcelis Technologies are the primary forces, with Axcelis holding the second-largest global market share. This duopoly fuels intense competition as both companies battle for dominance in this specialized technology sector.
Competitive rivalry in the ion implant equipment sector is fierce, largely fueled by an unceasing drive for innovation in equipment performance, precision, throughput, and overall cost of ownership. Both Axcelis and its primary rivals pour significant resources into research and development, consistently aiming to launch cutting-edge products and refine existing ones. This relentless pursuit of technological differentiation is crucial for market leadership, particularly in specialized areas like power devices and advanced logic manufacturing.
Competitors in the semiconductor equipment sector operate globally, necessitating robust sales, service, and support networks to cater to manufacturers across different regions. This geographical reach is a critical differentiator.
The intensity of rivalry is amplified by the need for timely and localized customer support, driving companies to continually expand and refine their global operational footprints. For instance, in 2024, major players like Applied Materials and ASML continued to invest heavily in their international service centers to ensure rapid response times for their sophisticated equipment.
Maintaining strong, localized customer relationships is paramount, and a widespread, efficient support infrastructure directly contributes to customer loyalty and market share. This global presence is not just about sales but about providing end-to-end solutions.
Emergence of Domestic Chinese Competitors
China's ambitious drive for semiconductor independence is fueling the rise of domestic ion implanter manufacturers. Companies like Kingstone Semiconductor and CETC Electronics Equipment Group are emerging as significant players, particularly within the vast Chinese market. This burgeoning domestic competition presents a tangible threat to established international firms, including Axcelis, potentially impacting market share and pricing dynamics.
The competitive landscape is intensifying as these Chinese companies develop their capabilities. While still in earlier stages of technological maturity compared to global leaders, their rapid advancement and government backing cannot be overlooked. For instance, China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has set aggressive targets for domestic equipment production, aiming to significantly reduce reliance on foreign suppliers by 2025. This strategic focus translates into direct competition for market share, especially as these domestic firms gain traction with local foundries and chipmakers.
- Kingstone Semiconductor: A key emerging Chinese player in ion implantation technology.
- CETC Electronics Equipment Group: Another significant domestic competitor backed by state investment.
- Market Share Erosion: Potential for international players like Axcelis to see reduced market share in China due to domestic alternatives.
- Strategic Importance: China's national strategy prioritizes self-sufficiency in semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
Cyclical Nature of the Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry's inherent cyclicality significantly fuels competitive rivalry. During industry downturns, often referred to as 'digestion periods,' companies like Axcelis face a shrinking demand, forcing them to compete more fiercely for fewer orders. This intensified competition can lead to considerable pricing pressure.
This cyclical nature means that periods of high demand are often followed by periods of oversupply and reduced orders, which in turn escalates competition. For instance, while the semiconductor market saw robust growth in prior years, projections for 2025 indicate a more cautious environment, where market share preservation and cost efficiency become paramount. Companies may delay or scale back expansion plans to navigate these leaner times.
- Intensified Competition: Downturns force companies to vie more aggressively for a smaller customer base.
- Pricing Pressure: Reduced demand often leads to price cuts to secure orders.
- Focus on Efficiency: Companies prioritize cost management and operational improvements to survive lean periods.
- Market Share Preservation: The goal shifts from aggressive growth to maintaining existing market positions.
The ion implantation market is characterized by intense rivalry, driven by a few dominant global players and the emergence of new domestic competitors, particularly in China. This competition centers on technological innovation, global service capabilities, and navigating the industry's inherent cyclicality, all of which pressure companies like Axcelis to maintain a competitive edge.
The fierce competition is further intensified by the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry, where periods of high demand are followed by downturns, leading to increased price pressure and a greater focus on market share preservation. For example, while the semiconductor capital equipment market experienced strong growth in preceding years, analysts projected a more moderate growth rate for 2024 and 2025, emphasizing the need for operational efficiency and strategic market positioning.
| Company | Primary Focus | Estimated Market Share (Ion Implantation) |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Materials | Broad semiconductor equipment portfolio, leading in ion implantation. | 40-50% (estimated) |
| Axcelis Technologies | Specialized in ion implantation, strong in specific market segments. | 20-30% (estimated) |
| Kingstone Semiconductor | Emerging Chinese player, focusing on domestic market needs. | <5% (estimated, growing) |
| CETC Electronics Equipment Group | State-backed Chinese entity, expanding its semiconductor equipment offerings. | <5% (estimated, growing) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Ion implantation is a cornerstone of semiconductor manufacturing, enabling precise control over the electrical characteristics of chips. There isn't a readily available, cost-effective alternative that matches its accuracy and versatility across the board.
This fundamental role means that for many critical applications, especially in advanced logic and memory devices, direct substitution is not feasible. The industry relies on this process for creating the intricate circuitry that powers modern electronics.
While research into alternative doping methods continues, no other technology has emerged to displace ion implantation's dominance in achieving the required precision and performance for a vast array of semiconductor products manufactured globally.
While ion implantation remains the cornerstone of semiconductor doping, research into alternative methods like gas-phase doping and diffusion continues. These techniques might present viable options for highly specialized or niche applications where the extreme precision of ion implantation isn't paramount.
However, for the vast majority of semiconductor manufacturing, these alternatives fall short. They generally lack the fine-tuned control and broad applicability that ion implantation offers, particularly in high-volume, advanced node production. For instance, in 2024, ion implantation equipment sales continued to dominate the doping market, reflecting its established superiority in mainstream applications.
The emergence of new materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), alongside evolving chip architectures like 3D ICs and advanced packaging, presents a dynamic landscape for ion implantation. These innovations can shift the demand for specific types of ion implanters, for instance, increasing the need for high-energy systems for power device fabrication. However, these advancements are more likely to redefine the application of ion implantation rather than render it obsolete, meaning substitutes for the core process are not yet a significant threat.
Integration of Functions into Multi-Process Tools
The integration of multiple processing functions into single, highly automated tools presents a potential threat of substitutes for standalone ion implanters. This trend could lead to a reduced demand for separate ion implantation equipment if these multi-process tools can effectively perform the implantation step alongside other critical fabrication processes.
However, this development is more accurately characterized as a evolution in equipment design and functionality rather than a true substitution of the core ion implantation technology. The fundamental need for precise ion implantation in semiconductor manufacturing remains, meaning the underlying process is not being replaced.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry continued its push for greater manufacturing efficiency and reduced wafer handling. Companies are investing heavily in advanced process control and integrated systems to streamline production lines. This focus on consolidation means that while the form factor of equipment might change, the necessity of ion implantation as a fabrication step is enduring.
- Technological Evolution: The threat lies in integrated systems performing implantation, not replacing the need for implantation itself.
- Efficiency Drive: Semiconductor manufacturers are prioritizing consolidated, automated tools for cost and throughput improvements.
- Market Adaptability: Equipment manufacturers like Axcelis are likely to adapt by offering integrated solutions or enhancing the capabilities of their standalone tools to remain competitive.
Software-Driven Process Optimization
Advances in software, particularly AI and machine learning, offer significant potential for process optimization within semiconductor manufacturing. These technologies can refine existing ion implantation processes, potentially extending the useful life of current equipment and reducing the need for frequent upgrades or new purchases. For instance, predictive maintenance software can minimize downtime, and AI-driven process control can improve yield, making existing tools more efficient.
While these software-driven optimizations enhance the performance and longevity of ion implantation equipment, they do not represent a direct substitute for the physical ion implantation process itself. The core function of introducing ions into a substrate remains a hardware-intensive operation that cannot be replicated by software alone. Therefore, the threat of substitutes from this area is considered moderate, as it impacts the *demand cycle* for new equipment rather than eliminating the need for it.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing technologies, with software and AI playing a crucial role in improving operational efficiency. Companies are increasingly leveraging data analytics and machine learning to fine-tune their fabrication processes. For example, a report from Gartner in late 2023 projected that AI in semiconductor manufacturing could lead to a 10-15% improvement in operational efficiency by 2025, primarily through process optimization and yield enhancement.
- Software-driven process optimization, including AI and machine learning, enhances the efficiency and lifespan of existing ion implantation equipment.
- These technological advancements do not, however, eliminate the fundamental need for physical ion implantation processes.
- The threat of substitution is therefore moderate, impacting the frequency of new equipment acquisition rather than the core demand for the technology.
The threat of substitutes for ion implantation in semiconductor manufacturing is generally low, as no readily available, cost-effective alternative offers the same precision and versatility. While research into methods like gas-phase doping continues, these are typically suited for niche applications rather than mainstream, high-volume production where ion implantation reigns supreme.
For example, in 2024, sales of ion implantation equipment continued to dominate the doping market, underscoring its established position. Emerging technologies like SiC and GaN, while demanding specific ion implanter types, are more likely to evolve the application of ion implantation rather than replace the core process itself.
Furthermore, advancements in software, including AI and machine learning, enhance the efficiency and lifespan of existing ion implantation equipment through process optimization and predictive maintenance. While these software improvements impact the demand cycle for new equipment, they do not substitute the fundamental need for physical ion implantation processes.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the semiconductor equipment manufacturing market, especially for sophisticated ion implanters, requires enormous initial capital for R&D and advanced production sites. The sheer cost of establishing a modern fabrication facility can easily fall between $10 billion and $20 billion, presenting a significant financial hurdle for any newcomers.
Developing ion implantation technology demands profound scientific understanding, advanced engineering skills, and consistent, significant investment in research and development to align with swift semiconductor process evolution. This deep technical knowledge and the need for substantial R&D spending create a formidable barrier for any potential new competitor seeking to enter the market.
For example, the U.S. semiconductor industry alone poured $62.7 billion into R&D in 2024, highlighting the capital-intensive nature of innovation in this sector. New entrants would face the monumental task of either cultivating this specialized expertise internally or acquiring it, both of which represent substantial hurdles to market entry.
Established customer relationships and trust are significant barriers to entry in the semiconductor equipment market. Semiconductor manufacturers rely on their equipment suppliers for critical tools and ongoing, dependable support throughout the equipment's operational life. Dislodging established players like Axcelis, who have cultivated decades of trust and demonstrated reliability with their customer base, presents a formidable challenge for any newcomer.
Intellectual Property and Patent Barriers
The threat of new entrants in the ion implantation sector is significantly dampened by substantial intellectual property and patent barriers. Leading companies, such as Axcelis Technologies, boast extensive patent portfolios that protect their core ion implantation technologies. For instance, as of early 2024, Axcelis holds a robust portfolio of patents covering various aspects of their ion implanter designs and processes.
These intellectual property rights create a formidable legal and technological hurdle for any potential new competitor. Developing competitive ion implantation equipment without infringing on these existing patents requires either substantial investment in circumventing existing technology or the creation of entirely novel, proprietary solutions. This high barrier to entry makes it economically challenging and legally risky for new players to establish a foothold in the market.
The cost and complexity associated with navigating and potentially challenging these patent landscapes are significant deterrents. New entrants would need to invest heavily in research and development to create non-infringing technologies, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive, further limiting the threat of new competition.
- Extensive Patent Portfolios: Leading firms like Axcelis and Applied Materials possess vast collections of patents safeguarding their ion implantation innovations.
- Legal and Technological Barriers: These patents make it difficult for newcomers to design and market comparable products without infringing existing IP.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants must commit significant resources to develop alternative technologies or face legal challenges.
- Market Entry Costs: The combined legal and technological hurdles translate into substantial upfront costs for aspiring competitors.
Need for Global Service and Support Infrastructure
The semiconductor equipment industry demands a robust global service and support network. This includes offering comprehensive installation, ongoing maintenance, and rapid troubleshooting across various international locations. For instance, leading companies like Applied Materials and ASML maintain extensive networks of field service engineers and spare parts depots worldwide to support their complex machinery.
Building and maintaining this worldwide infrastructure requires significant capital investment in skilled personnel, specialized training programs, and sophisticated logistics. The cost and complexity associated with establishing such capabilities present a substantial barrier for any new entrant looking to compete effectively against established players who already possess this critical advantage.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a global service and support infrastructure requires substantial upfront investment in facilities, inventory, and trained personnel.
- Skilled Workforce Requirement: The industry needs highly specialized engineers capable of handling complex equipment installation, maintenance, and repair globally.
- Logistical Complexity: Managing spare parts inventory and ensuring timely delivery across different continents is a significant logistical challenge.
- Customer Expectations: Semiconductor manufacturers expect immediate and reliable support, making a well-established global network a non-negotiable requirement.
The threat of new entrants in the ion implanter market is low due to immense capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, with fab construction alone costing billions. Furthermore, deep technical expertise and substantial, ongoing R&D investment, exemplified by the $62.7 billion poured into U.S. semiconductor R&D in 2024, create significant hurdles.
Established customer relationships built on trust and reliable support are difficult for newcomers to replicate. Extensive patent portfolios held by incumbents like Axcelis Technologies also present a formidable legal and technological barrier, requiring significant investment to circumvent or develop non-infringing technologies.
A global service and support network, crucial for semiconductor equipment, demands massive capital investment in skilled personnel and logistics, making it challenging for new players to compete with established firms.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost for R&D and advanced production facilities. | Semiconductor fab construction: $10-$20 billion. |
| Technical Expertise & R&D | Need for deep scientific understanding and continuous investment. | U.S. semiconductor R&D spending in 2024: $62.7 billion. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protect core technologies. | Axcelis Technologies' robust patent portfolio as of early 2024. |
| Service & Support Network | Requirement for a global infrastructure of skilled engineers and parts. | Need for worldwide field service and spare parts depots. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Axcelis Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also leverage data from reputable financial databases and trade publications to capture the nuances of competitive dynamics.
