ALPHAWAVE SEMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ALPHAWAVE SEMI Bundle
ALPHAWAVE SEMI operates in a dynamic semiconductor landscape, where intense competition and evolving technological demands shape its market. Understanding the subtle interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this competitive arena. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ALPHAWAVE SEMI’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, empowering you to make informed decisions.
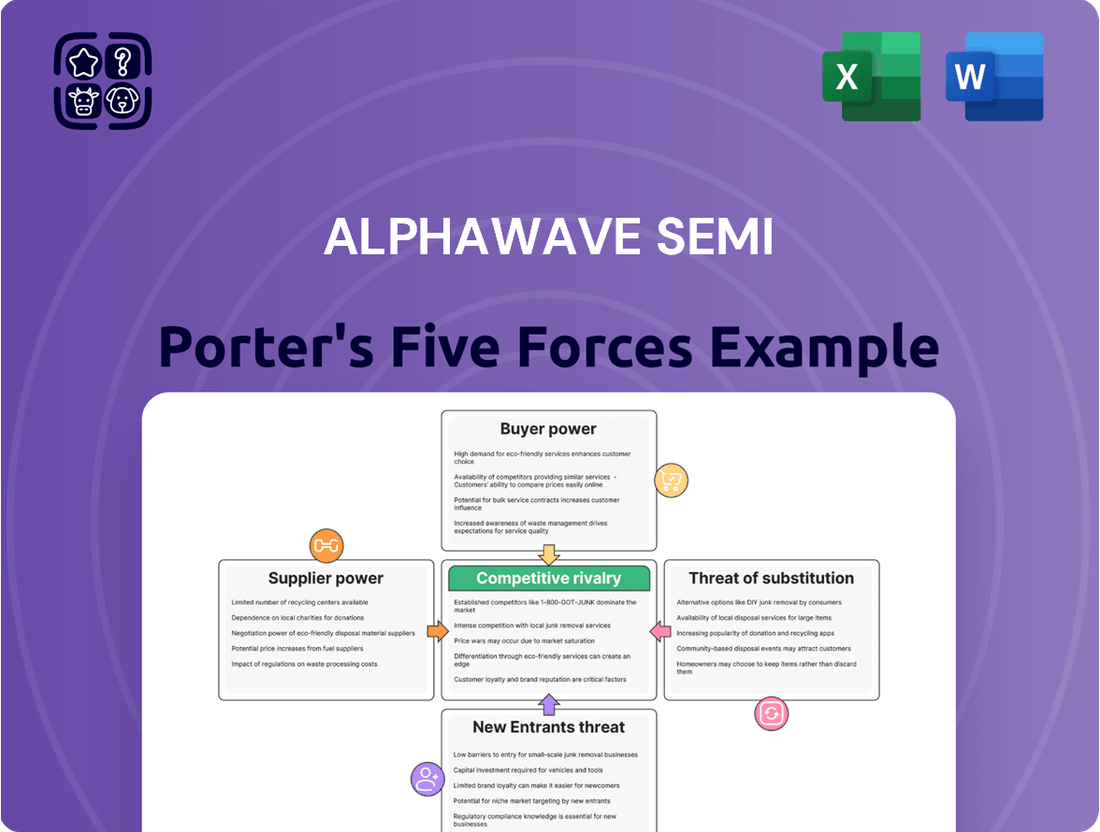
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Alphawave Semi's reliance on a concentrated group of advanced silicon IP and chiplet manufacturers, such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. These foundries represent a limited pool of highly specialized and capital-intensive facilities, making them indispensable for cutting-edge semiconductor production.
The immense investment required for advanced fabrication, often in the tens of billions of dollars, creates high barriers to entry, consolidating power in the hands of a few dominant players. For instance, TSMC alone accounted for over 60% of the global foundry market share in 2023, highlighting its substantial leverage over its customers.
This concentration means that any capacity constraints, pricing adjustments, or strategic shifts by these key suppliers can directly impact Alphawave Semi's production schedules, costs, and overall time-to-market for its advanced connectivity solutions.
Alphawave Semi's reliance on highly specialized silicon IP and chiplets, particularly for advanced AI and data center applications, grants its suppliers significant bargaining power. These unique inputs often involve proprietary technologies and materials with few readily available substitutes. For instance, the development of cutting-edge high-speed SerDes (Serializer/Deserializer) IP, a core offering for Alphawave Semi, necessitates specialized fabrication processes and advanced materials that only a select group of suppliers can provide. This limited supplier pool, coupled with the critical nature of these components for Alphawave Semi's product performance, allows suppliers to command premium pricing and dictate favorable terms.
Alphawave Semi faces significant switching costs when changing foundries or key intellectual property (IP) providers. These costs include the substantial time and resources required for re-design, extensive verification, and rigorous re-qualification of their advanced semiconductor designs. For instance, a shift in fabrication partners could necessitate millions in upfront investment and months of delay.
These high switching costs effectively create a lock-in effect, binding Alphawave Semi to its current supplier relationships. This dependency diminishes the company's leverage during price negotiations and contract renewals, as the cost and complexity of transitioning away are prohibitive.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, particularly large foundries or intellectual property (IP) providers, could impact Alphawave Semi's bargaining power. These entities might choose to move into designing or offering more comprehensive connectivity solutions, thereby directly competing with Alphawave Semi. For instance, a major chip manufacturer with significant foundry capacity could leverage its existing infrastructure to develop its own integrated connectivity IP, potentially undercutting Alphawave Semi's offerings.
While not an immediate or prevalent concern, the *potential* for such a strategic shift by dominant suppliers warrants consideration. If a key supplier, like TSMC, were to expand its services beyond pure manufacturing to include advanced chip design and integration for connectivity applications, it would fundamentally alter the competitive landscape. This would grant them greater leverage in negotiations, as they could dictate terms or even capture a larger share of the value chain.
- Potential for Foundries to Offer Integrated Connectivity IP: Large foundries possess the technical expertise and capital to develop their own connectivity solutions, moving beyond mere manufacturing.
- Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power: If suppliers integrate forward, they gain more control over the value chain, potentially increasing their leverage over companies like Alphawave Semi.
- Competitive Threat to Alphawave Semi: Direct competition from powerful suppliers could dilute Alphawave Semi's market share and affect its pricing power.
Importance of Alphawave Semi to Suppliers
Alphawave Semi's substantial bookings, including multi-year agreements and design wins in cutting-edge semiconductor nodes, highlight its significance as a customer for its suppliers. This strong demand positions Alphawave Semi favorably, potentially reducing the leverage suppliers hold over the company.
The company's ongoing collaboration with key foundries like Samsung Foundry, and its recognition as TSMC's OIP Partner of the Year, underscore a symbiotic relationship. These partnerships suggest a mutual dependence that can help moderate the bargaining power of suppliers, as Alphawave Semi is a valued and strategic client.
- Significant Bookings: Alphawave Semi's multi-year deals and advanced node design wins demonstrate its importance to suppliers.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with Samsung Foundry and recognition from TSMC indicate a mutually beneficial supplier relationship.
- Tempered Supplier Power: The company's value as a customer can mitigate the extent to which suppliers can dictate terms.
Alphawave Semi's suppliers, particularly advanced foundries like TSMC and Samsung, wield considerable bargaining power due to the capital-intensive nature of semiconductor manufacturing and the limited number of advanced fabrication facilities. TSMC, for instance, held over 60% of the global foundry market share in 2023, giving it significant leverage. This concentration means that Alphawave Semi faces high switching costs, estimated in the millions of dollars, for redesign and re-qualification if it were to change fabrication partners, effectively locking it into existing relationships and limiting its negotiation flexibility.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Alphawave Semi | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Advanced Foundries | High supplier bargaining power | TSMC Global Foundry Market Share: >60% |
| Capital Intensity of Fabrication | High barriers to entry, fewer suppliers | Estimated cost for new advanced fab: $10-$20 billion+ |
| Switching Costs for Alphawave Semi | Supplier lock-in, reduced negotiation leverage | Estimated switching cost: Millions of dollars, months of delay |
| Criticality of Specialized IP/Chiplets | Suppliers can command premium pricing | N/A (Proprietary technology) |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to ALPHAWAVE SEMI's semiconductor industry position.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive spider chart, turning complex Porter's Five Forces data into actionable strategic insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Alphawave Semi's customer base is concentrated, with major hyperscalers and tier-one semiconductor companies in AI, data centers, and 5G forming its core. In 2024, the company recognized revenue from 103 end-customers, yet a significant portion, 36%, came from its top five clients. This reliance on a few large customers grants them considerable bargaining power.
For Alphawave Semi's customers, the integration of its high-speed connectivity IP and chiplets into their intricate system designs represents a significant undertaking. This process demands extensive design, rigorous verification, and thorough qualification, all of which contribute to substantial switching costs.
These elevated switching costs, stemming from the deep integration of Alphawave Semi's core technology, grant customers considerable bargaining power. Once a customer has invested heavily in a particular design using Alphawave Semi's solutions, the effort and expense required to transition to a different provider become a major deterrent, effectively locking them in.
Customers in the data center and AI sectors are acutely aware of costs, particularly when undertaking large-scale infrastructure projects. For instance, data center capital expenditure globally is projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant investment involved and the inherent pressure to manage expenses.
While Alphawave Semi provides cutting-edge, high-performance connectivity solutions, clients will inevitably compare pricing. This competitive landscape means Alphawave Semi must balance its innovation with cost-effectiveness to maintain market share and avoid margin erosion.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers of Alphawave Semi face a significant bargaining power due to the availability of substitute products. While Alphawave Semi offers specialized high-speed connectivity and chiplet solutions, clients can explore developing their own in-house designs or adopting alternative interconnect technologies. This creates a competitive landscape where customers can leverage other options if Alphawave Semi's offerings do not meet their price or performance expectations.
The market for advanced semiconductor solutions is dynamic, with ongoing innovation. The emergence of new industry standards or novel technological approaches can further broaden customer choices. For instance, advancements in optical interconnects or different serializing/deserializing technologies could present viable alternatives, thereby enhancing customer leverage against Alphawave Semi.
Consider the impact of custom silicon development. Major tech companies, often Alphawave Semi's clients, possess the resources and expertise to design their own custom connectivity solutions. This capability directly challenges Alphawave Semi's market position, as these large customers can choose to internalize design and manufacturing rather than relying solely on external providers. For example, in 2024, hyperscalers continued to invest heavily in custom silicon for their data centers, aiming for greater control and optimization of their infrastructure.
- In-house Development: Large customers like hyperscalers and cloud providers can leverage their significant R&D budgets to develop proprietary interconnect solutions, reducing reliance on third-party vendors.
- Alternative Technologies: The semiconductor industry is constantly evolving, with new interconnect standards and architectures emerging, offering customers a wider array of choices beyond current offerings.
- Standardization Impact: The adoption of new industry standards can democratize access to advanced connectivity, potentially lowering barriers to entry for alternative solutions and increasing customer bargaining power.
Volume of Purchases
Alphawave Semi's customers, particularly hyperscalers, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes. The company has secured multi-year deals and large bookings, demonstrating the scale of these commitments. This high-volume purchasing behavior inherently grants these clients greater leverage in negotiations.
For instance, in 2023, Alphawave Semi reported a substantial increase in its design wins, many of which are tied to long-term supply agreements with major players in the data center and networking industries. These agreements often include volume commitments that provide customers with considerable influence over pricing and terms.
- High Volume Commitments: Customers like hyperscalers often commit to purchasing millions of units over several years.
- Economies of Scale for Buyers: Large order volumes allow these customers to negotiate better unit prices, leveraging their own economies of scale.
- Switching Costs for Suppliers: While customers face switching costs, suppliers like Alphawave Semi also face significant costs to onboard and qualify new high-volume clients, making them keen to retain existing ones.
- Market Influence: The sheer size of their orders means these customers can significantly impact a supplier's revenue and production planning.
Alphawave Semi's customers, especially hyperscalers, hold substantial bargaining power due to their significant order volumes and the high integration costs of its technology.
The company's reliance on a few key clients, who represent a large portion of its revenue, further amplifies this customer leverage.
Customers can also explore in-house development or alternative interconnect technologies, especially as custom silicon investments in data centers continue to grow, with global data center CapEx projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024.
This dynamic forces Alphawave Semi to balance innovation with competitive pricing to retain its crucial customer relationships.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Alphawave Semi |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperscalers & AI Companies | High purchase volume, significant switching costs for Alphawave Semi, custom silicon development capabilities. | Strong negotiation leverage on pricing and terms; potential for reduced reliance on third-party IP. |
| Tier-one Semiconductor Companies | Integration complexity, potential for alternative interconnect technologies, price sensitivity in large infrastructure projects. | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear value proposition; need to manage customer expectations regarding cost-effectiveness. |
Same Document Delivered
ALPHAWAVE SEMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ALPHAWAVE SEMI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the semiconductor industry. You're looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The high-speed connectivity and chiplet market is a crowded space, featuring a diverse array of competitors. This includes major semiconductor players with broad portfolios as well as niche companies focusing on specific intellectual property (IP) or solutions. For instance, Alphawave Semi finds itself in direct competition with firms such as Availink, Zilog, and Netronome, each bringing their own distinct connectivity technologies to the table.
Alphawave Semi operates in markets like AI, data centers, and 5G, all experiencing robust expansion. For instance, the global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, with some estimates reaching over $1.8 trillion by 2030. This rapid growth creates a less intense competitive environment, as there's ample room for multiple companies to capture market share without solely relying on taking it from rivals.
Alphawave Semi distinguishes itself through a strong focus on cutting-edge connectivity and chiplet technology. They offer advanced solutions like 224G and UCIe IP, crucial for demanding AI, High-Performance Computing, and networking sectors.
Their proprietary WidEye™ DSP architecture and EyeQ™ diagnostics are key differentiators, designed to deliver enhanced performance and reduced power usage compared to competitors.
Switching Costs for Customers in the Industry
Alphawave Semi's customers experience significant switching costs once their technology is integrated into a product. This integration creates a strong lock-in effect, making it difficult and expensive to switch to a competitor. For instance, the extensive validation and testing required for semiconductor components means that once a design is finalized, changing suppliers can delay product launches and incur substantial re-engineering expenses.
This high switching cost environment intensifies competition among rivals, as each company strives to win initial design engagements. Securing these early design wins is crucial for establishing a sticky customer relationship and building a defensible market position. The race to be embedded in next-generation products drives aggressive sales and R&D efforts from all players.
The competitive dynamic is further shaped by the fact that rivals are also focused on creating similar high switching costs for their own customer bases. This leads to a continuous battle for market share and technological leadership, where the ability to offer superior performance and seamless integration becomes paramount. For example, in the data center interconnect market, companies like Broadcom and Marvell also invest heavily in developing proprietary solutions that foster deep customer integration.
- High Integration Costs: Once Alphawave Semi's silicon is designed into a customer's system, the cost and complexity of re-designing and re-validating for a new vendor can be prohibitive, often running into millions of dollars and months of development time.
- Rivalry for Design Wins: The industry sees intense competition to secure initial design wins, as these early engagements create long-term customer relationships due to the aforementioned switching costs.
- Technological Lock-in: Competitors also aim to create high switching costs by offering advanced, often proprietary, technological solutions that are deeply embedded in customer product architectures.
Exit Barriers
The semiconductor industry, including companies like Alphawave Semi, faces significant exit barriers due to substantial investments. High fixed costs are tied to research and development, the need for highly specialized talent, and the intricate nature of manufacturing processes. These considerable upfront and ongoing expenses make it difficult and financially risky for companies to leave the market.
These high exit barriers mean that even when market conditions are unfavorable or profitability is low, semiconductor firms may continue to operate. This persistence, driven by the inability to easily recoup sunk costs, directly contributes to intensified competition. Companies are compelled to stay in the game, potentially leading to prolonged periods of intense rivalry as they strive to maintain market share and recover their investments.
- High R&D Investment: Semiconductor R&D spending can reach billions annually; for instance, Intel projected around $25 billion in capital expenditures for 2024, highlighting the scale of investment.
- Specialized Workforce Costs: The demand for highly skilled engineers and technicians drives up labor costs, with average salaries for semiconductor engineers often exceeding $120,000 annually in the US.
- Complex Manufacturing Infrastructure: Building and maintaining advanced fabrication plants (fabs) can cost tens of billions of dollars, with TSMC’s new Arizona fab representing a $40 billion investment.
Alphawave Semi faces intense competition from established semiconductor giants and specialized IP providers alike. The market for high-speed connectivity solutions is characterized by a constant drive for technological advancement, with rivals aggressively pursuing design wins to leverage significant customer switching costs. This rivalry is further fueled by high exit barriers in the semiconductor industry, compelling companies to remain active even in challenging conditions.
The competitive landscape is fierce, with companies like Broadcom and Marvell also investing heavily in proprietary technologies to foster customer integration. This creates a continuous battle for technological leadership and market share, where superior performance and seamless integration are paramount. For example, the race to embed advanced connectivity IP into next-generation AI and data center hardware drives substantial R&D and sales efforts across the board.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Key Competitive Factor |
| Broad Semiconductor Players | Broadcom, Marvell | Established market presence, integrated solutions, strong customer relationships |
| Specialized IP Providers | Availink, Zilog, Netronome | Niche technology focus, specific connectivity IP |
| Internal Development | In-house chip design teams at large tech companies (e.g., Google, Amazon) | Customization, control over supply chain, strategic integration |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Alphawave Semi's core business in silicon IP and chiplets for high-speed connectivity faces potential threats from alternative technologies. For instance, advancements in optical interconnects, which offer higher bandwidth and longer reach, could become more cost-effective and widely adopted.
Furthermore, innovations in traditional copper-based interconnects, driven by miniaturization and improved signal integrity, might offer competitive solutions for certain applications. The market for data transfer is constantly evolving, with new approaches emerging regularly, posing a continuous challenge to existing technologies.
The threat of substitutes for AlphaWave Semi's products hinges on whether these alternatives can deliver comparable performance at a more appealing price. For demanding, data-intensive applications, performance and unwavering reliability are paramount, making direct, lower-cost replacements challenging.
However, if emerging, less expensive solutions can adequately meet the core functional needs of certain market segments, they could indeed siphon off demand. For instance, in less critical processing tasks, a substitute offering 80% of the performance at 50% of the cost would present a significant competitive pressure.
Customers' willingness to switch to substitute technologies for AlphaWave Semi's products hinges on several factors. The ease with which a new solution can be integrated into existing systems plays a crucial role. For instance, if a competitor offers a chip that requires minimal redesign of a customer's product, it lowers the switching barrier. Perceived risk associated with adopting new, unproven technology also influences decisions. If a substitute provides substantial benefits, such as a 15% reduction in power consumption or a 10% cost saving, as seen in some emerging semiconductor solutions in late 2024, customers are more likely to overcome integration hurdles and perceived risks.
Evolution of Industry Standards
The threat of substitutes for Alphawave Semi is significantly influenced by the rapid evolution of industry standards in high-speed connectivity. For instance, the ongoing development of standards like PCIe 6.0, which offers double the bandwidth of PCIe 5.0, presents a potential substitute if it gains widespread adoption and outperforms existing solutions. Similarly, advancements in Ethernet speeds, such as the increasing prevalence of 400GbE and the development of 800GbE, could offer alternative connectivity methods.
The emergence of new interconnect standards, such as the Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe), also poses a substitution threat. While Alphawave Semi is actively involved in shaping these standards, a disruptive new architecture that offers superior performance or cost-effectiveness could displace current technologies. For example, if UCIe enables a more modular and efficient chip design approach, it might reduce the reliance on traditional integrated solutions that Alphawave Semi specializes in.
The market is constantly seeking more efficient and faster ways to transfer data. This drive creates an environment where entirely new approaches to interconnectivity could emerge, potentially rendering current technologies obsolete. The success of these evolving standards is often tied to their ability to deliver tangible benefits in terms of speed, power efficiency, and cost, making them direct substitutes for Alphawave Semi's offerings if they prove superior.
- PCIe 6.0: Offers a theoretical bandwidth of 64 GT/s per lane, a significant increase over PCIe 5.0's 32 GT/s.
- Ethernet Advancements: 400GbE is becoming more common, with 800GbE actively being developed and tested.
- UCIe: Aims to standardize chiplet interconnects, potentially altering how complex systems are built and connected.
In-house Development by Customers
Large technology firms and hyperscalers possess substantial research and development resources. This enables them to engineer their own advanced high-speed connectivity intellectual property and chiplet solutions internally, bypassing the need for external suppliers like Alphawave Semi. This in-house development represents a potent substitute, particularly for their most crucial infrastructure components.
For instance, in 2024, major cloud providers continued to invest heavily in custom silicon. Microsoft's Maia AI Accelerator and Amazon's Trainium and Inferentia chips exemplify this trend, showcasing their commitment to vertical integration and control over core technology. This strategic move directly diminishes the market for Alphawave Semi's offerings in these specific areas.
- Significant R&D Investment: Major tech players allocate billions annually to R&D, enabling in-house chip design capabilities.
- Customization and Control: Developing internally allows for tailored solutions optimized for specific workloads and greater control over the supply chain.
- Strategic Independence: Reducing reliance on external vendors enhances strategic flexibility and potentially lowers long-term costs for critical components.
The threat of substitutes for Alphawave Semi is amplified by the ongoing advancements in alternative connectivity technologies and evolving industry standards. For example, the increasing adoption of PCIe 6.0, offering double the bandwidth of PCIe 5.0, and the push towards 800GbE in Ethernet present significant competitive alternatives. Furthermore, the development of open standards like UCIe could foster more modular chip designs, potentially reducing reliance on integrated solutions.
Large technology firms and hyperscalers are increasingly developing their own proprietary high-speed connectivity solutions, representing a direct substitute for Alphawave Semi's IP and chiplets. This trend, driven by a desire for customization and strategic independence, was evident in 2024 with major cloud providers continuing substantial investments in custom silicon for their AI and data processing needs.
| Technology | Key Benefit | Potential Impact on Alphawave Semi |
| PCIe 6.0 | 64 GT/s per lane bandwidth | Offers higher performance alternative for data transfer |
| 800GbE | Increased Ethernet speeds | Provides alternative high-speed networking solutions |
| In-house Custom Silicon | Tailored performance, cost control | Reduces demand for external IP and chiplet providers |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor industry, particularly for advanced connectivity IP and chiplets, demands enormous upfront capital. Companies need significant investment for research and development, sophisticated design software, and securing access to leading-edge fabrication facilities. For instance, setting up a new advanced semiconductor fabrication plant, or fab, can cost tens of billions of dollars, with TSMC’s new Arizona fab reportedly costing over $40 billion.
This immense financial barrier naturally discourages many potential new players from entering the market. The sheer scale of investment required means only well-funded entities or those with strong backing can realistically consider competing. In 2024, the ongoing global demand for advanced chips continues to drive up the cost of R&D and manufacturing, further solidifying this barrier.
Alphawave Semi's robust portfolio of silicon intellectual property (IP), particularly in high-speed SerDes, PCIe, Ethernet, and UCIe technologies, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. The company's extensive patent filings and deep-seated expertise in complex, high-speed chip design require substantial upfront investment and specialized knowledge, making it challenging for competitors to replicate their offerings. This technological moat, backed by a strong IP strategy, effectively deters potential new players from entering the market.
Established players like Alphawave Semi leverage significant economies of scale in crucial areas such as chip design, verification processes, and customer support. New entrants would find it incredibly difficult to replicate these cost advantages, as they would need to invest heavily to achieve comparable operational efficiencies. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for advanced semiconductor design and verification can run into tens of millions of dollars.
Furthermore, the deep well of accumulated experience within incumbent firms in navigating the complexities of high-speed connectivity solutions presents a formidable barrier. This accumulated knowledge translates into faster product development cycles and a better understanding of market needs, which are intangible assets that new companies would take years to build.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
The semiconductor industry, particularly for advanced chips, is characterized by deeply entrenched relationships between established players and key customers like hyperscalers and major semiconductor companies. For new entrants, gaining access to these critical distribution channels and forging comparable customer relationships presents a significant hurdle. Incumbents have spent years, even decades, building trust and securing design wins, making it difficult for newcomers to displace them.
Securing the initial design wins is paramount for any new entrant aiming to penetrate the semiconductor market. This process often involves extensive collaboration and validation with tier-one customers. For example, in 2024, the lead times for qualifying new chip designs with major automotive or cloud computing clients can extend beyond 18 months, a substantial barrier for companies lacking established credibility and a proven track record.
- Customer Loyalty: Established semiconductor firms benefit from strong, long-standing relationships with major clients, making it challenging for new entrants to secure initial design wins.
- Switching Costs: For hyperscalers and large semiconductor companies, the cost and complexity associated with qualifying and integrating new chip suppliers are substantial, favoring incumbents.
- Distribution Network: Access to established sales channels and support networks is vital for reaching key customers, a resource that new entrants typically lack.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The semiconductor industry, particularly for advanced technologies and critical infrastructure, is encumbered by intricate regulatory and compliance requirements. For instance, the US CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, while aiming to boost domestic production, also introduces stringent conditions for recipients of its funding, impacting how new entrants might operate and scale. These complexities can represent a substantial barrier, demanding significant investment in legal, compliance, and R&D resources before a new player can even begin to compete effectively.
Navigating these regulatory landscapes is a significant challenge for new companies aiming to enter the semiconductor market. Consider the export control regulations imposed by various governments, which can restrict the sale of certain technologies to specific countries. For example, in 2023, the US government expanded its export controls on advanced AI chips and manufacturing equipment to China, creating a more complex environment for any new entrant seeking to serve global markets.
- Complex Licensing: Obtaining necessary licenses for manufacturing, design, and intellectual property can be a lengthy and costly process.
- Geopolitical Restrictions: Trade policies and national security concerns often lead to export controls and import restrictions, limiting market access for newcomers.
- Environmental Standards: Semiconductor manufacturing involves chemicals and processes that are subject to strict environmental regulations, requiring substantial compliance infrastructure.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Governments are increasingly scrutinizing semiconductor supply chains for security and ethical reasons, adding another layer of complexity for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the advanced connectivity IP and chiplet market, where Alphawave Semi operates, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements. Setting up advanced semiconductor fabrication facilities alone can cost upwards of $40 billion, as seen with TSMC's Arizona fab. These financial hurdles, coupled with the escalating costs of R&D and manufacturing in 2024, create a substantial barrier.
Alphawave Semi's established technological expertise and extensive patent portfolio further deter new players. Replicating their complex, high-speed chip designs requires significant upfront investment and specialized knowledge, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. The company's deep-seated experience in areas like high-speed SerDes and UCIe technologies represents an intangible asset that takes years to build.
Entrenched customer relationships and high switching costs also limit the threat of new entrants. Major customers, such as hyperscalers, have invested heavily in qualifying and integrating existing suppliers, making it challenging for new companies to secure crucial design wins. For instance, the lead time for qualifying new chip designs with major clients can exceed 18 months in 2024, a significant barrier for unproven entities.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our ALPHAWAVE SEMI Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific data, including market research reports from leading firms, financial disclosures from publicly traded companies, and relevant trade publications.
We leverage data from semiconductor industry associations, government economic indicators, and competitor annual reports to gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
