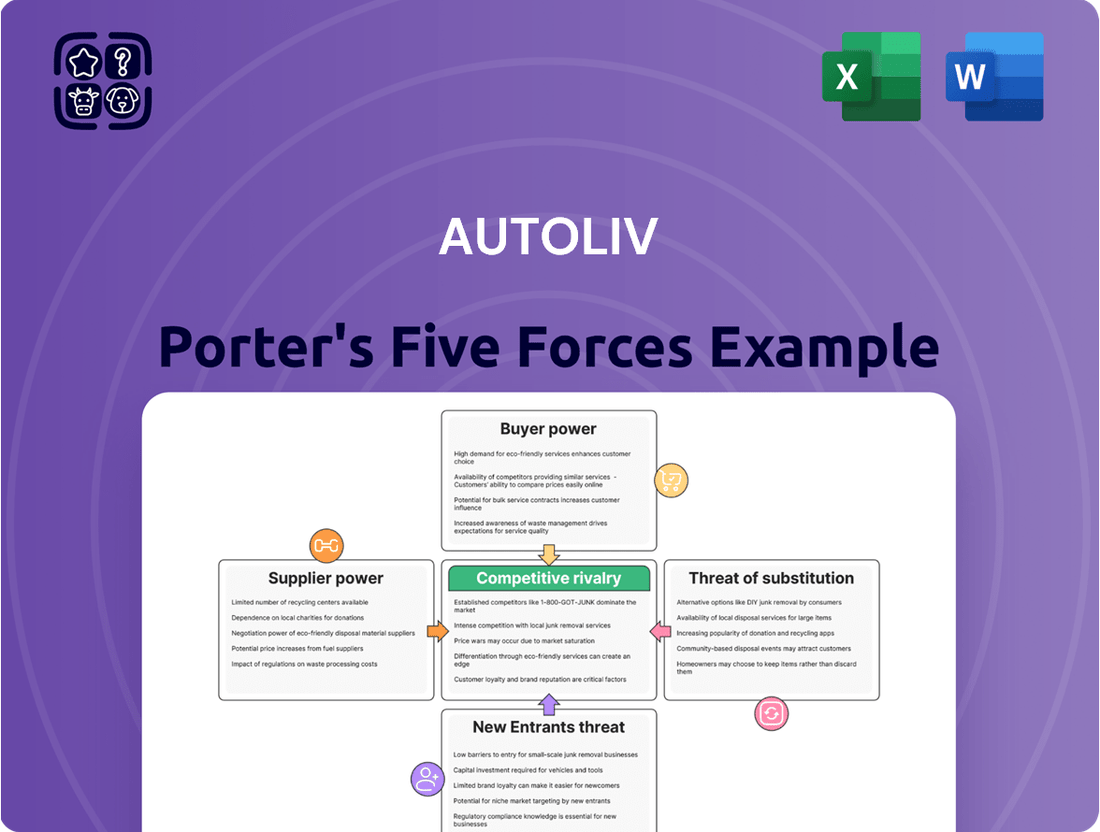
Autoliv Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Autoliv Bundle
Autoliv navigates a complex automotive safety landscape, where the bargaining power of buyers, like major car manufacturers, significantly influences pricing. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing players and the threat of new entrants is crucial for grasping Autoliv's competitive position. The availability of substitute products and the power of suppliers also play pivotal roles in shaping its market dynamics.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Autoliv’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Autoliv's reliance on a concentrated supplier base for critical components, such as advanced sensors, microcontrollers, and specialized textile materials essential for airbags and seatbelts, highlights a significant source of supplier bargaining power. The limited availability of these highly specialized inputs, often with unique or difficult-to-replicate characteristics, allows these suppliers to exert considerable influence over pricing and terms. For instance, in 2023, the automotive industry saw continued supply chain disruptions for semiconductor components, a key area for Autoliv's sensor technology, with lead times extending significantly for certain chips, impacting production schedules and costs for many automotive suppliers.
Autoliv faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the substantial switching costs involved. For automotive safety components, these costs encompass extensive re-validation of parts, re-tooling manufacturing equipment, and rigorous testing and re-certification to meet demanding automotive safety standards and Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) specifications. This complexity and expense limit Autoliv's ability to easily change suppliers, thereby strengthening the suppliers' negotiating leverage, particularly on pricing.
Suppliers who possess proprietary technology or patents for critical automotive safety components, like specialized inflator designs or advanced sensor arrays, wield significant bargaining power. Autoliv's reliance on such unique inputs can restrict its ability to source alternatives, potentially driving up costs for these essential materials. For instance, a supplier holding a patent on a novel airbag inflation system might command premium pricing due to the lack of comparable substitutes.
Integration and Customization Requirements
The bargaining power of suppliers for Autoliv is significantly influenced by the deep integration and customization required for many automotive safety components. Suppliers often become involved in the early stages of vehicle development, crafting bespoke solutions that are not readily available from other sources.
This customization makes it difficult for Autoliv to switch suppliers, as the components are specifically designed for particular vehicle platforms or safety systems. For instance, a supplier providing a highly integrated airbag control module for a specific car model has substantial leverage. In 2023, the automotive industry saw continued trends towards platform standardization, yet the complexity of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicle (EV) safety components necessitates specialized supplier input, reinforcing their strong position.
- High Integration: Many Autoliv components, like advanced sensor modules or complex airbag inflators, are intricately linked to a vehicle's electronic architecture.
- Customization: Suppliers develop unique solutions for specific vehicle models, reducing interchangeability and increasing reliance.
- Early Involvement: Suppliers contributing to R&D and design phases gain critical knowledge and influence over product specifications.
- Limited Alternatives: The specialized nature of these safety-critical parts means few suppliers can meet the stringent quality and performance demands, bolstering their power.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While not a widespread concern, there's a theoretical risk of large, technologically advanced suppliers integrating forward into safety system assembly. If a supplier has substantial R&D and manufacturing capacity, they could potentially become a direct competitor, impacting Autoliv's bargaining power.
The significant complexity and capital investment required for full safety system integration present a substantial barrier to entry for most suppliers. For instance, developing and manufacturing the intricate electronic control units and sensor networks essential for modern automotive safety systems demands specialized expertise and considerable financial resources, making such a move less likely for many.
- Supplier Integration Risk: While rare, major component suppliers with advanced R&D and manufacturing scale could theoretically integrate forward into safety system assembly.
- Competitive Threat: Such forward integration by suppliers could transform them into direct competitors, potentially altering the competitive landscape and Autoliv's negotiating leverage.
- Barriers to Entry: The high complexity and capital intensity of assembling complete safety systems act as a significant deterrent for suppliers considering this strategic move.
Autoliv's suppliers hold considerable bargaining power due to the specialized nature of many automotive safety components, such as advanced sensor technology and unique airbag inflator designs. The high switching costs, involving extensive re-validation and re-tooling for safety-critical parts, further solidify supplier leverage. In 2023, the automotive industry continued to grapple with supply chain constraints, particularly for semiconductors, impacting lead times and costs for key Autoliv inputs, underscoring supplier influence.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Autoliv | Example (2023/2024 Trend) |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized/Proprietary Technology | Increases supplier pricing power; limits alternatives. | Patented airbag inflation systems or advanced sensor algorithms. |
| High Switching Costs | Reduces Autoliv's flexibility; strengthens supplier negotiation. | Re-validation, re-tooling, and recertification for safety components. |
| Deep Integration & Customization | Creates supplier lock-in; difficult to source elsewhere. | Bespoke control modules for specific vehicle platforms. |
| Concentrated Supplier Base | Few alternatives for critical inputs, boosting supplier leverage. | Limited suppliers for advanced microcontrollers used in ADAS. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Autoliv's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive safety industry.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments to mitigate risks.
Customers Bargaining Power
Autoliv's customer base is highly concentrated, primarily consisting of major global automotive manufacturers. These Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) purchase components in massive volumes, giving them considerable leverage.
This concentration means that a few large customers can significantly influence Autoliv's pricing and terms. For example, in 2024, the top five automotive OEMs accounted for a substantial portion of global vehicle production, underscoring their bargaining power.
Their immense purchasing scale allows them to demand competitive pricing, stringent quality standards, and reliable delivery schedules, directly impacting Autoliv's profitability and operational flexibility.
While original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) hold considerable sway, the process for them to switch safety system suppliers like Autoliv is far from simple. It necessitates substantial re-engineering of vehicle platforms, rigorous testing protocols, and obtaining new regulatory approvals for the redesigned safety systems.
This entire undertaking can stretch over several years and involve millions in development costs. For instance, a new airbag system might require re-tooling of assembly lines and extensive crash testing, a process that can easily cost tens of millions of dollars per vehicle model.
Consequently, these high switching costs effectively grant Autoliv a degree of bargaining power. Automakers find it both time-consuming and financially burdensome to sever existing ties with established suppliers, making continuity a more attractive option.
Automotive manufacturers, facing their own intense market competition, are highly sensitive to costs. This pressure translates directly to suppliers like Autoliv, who often face demands for annual price reductions and increased operational efficiency. For instance, in 2023, the automotive industry saw continued efforts by OEMs to manage input costs, a trend that persisted into early 2024, directly impacting supplier pricing negotiations.
Product Standardization and Information Asymmetry
While automotive safety systems are inherently complex, certain fundamental components and basic functionalities can become standardized across the industry, often driven by regulatory mandates. This standardization can empower customers, particularly large automotive manufacturers, by increasing the availability of comparable products and potentially leading to price pressures. For instance, basic airbag modules or seatbelt pretensioners might see less differentiation, making it easier for buyers to switch suppliers.
Customers gain significant bargaining power when they possess comprehensive information regarding supplier costs, manufacturing processes, and the availability of alternative suppliers. In 2024, major automotive OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) likely leveraged their scale and market intelligence to negotiate favorable terms with safety system providers like Autoliv. Access to detailed cost breakdowns and a clear understanding of the competitive landscape allows these customers to challenge pricing and demand greater value.
Autoliv actively combats this by focusing on continuous innovation in advanced safety features, such as sophisticated driver-assistance systems and integrated occupant protection technologies. This differentiation strategy helps to create unique value propositions that are less susceptible to commoditization. For example, Autoliv's advancements in active safety systems, which go beyond basic passive safety, are not easily replicated and command a premium, thereby reducing the impact of customer bargaining power derived from standardization.
- Component Standardization: Regulations can lead to standardization in basic safety components, increasing customer leverage.
- Information Asymmetry Reduction: Well-informed customers, especially large OEMs in 2024, can negotiate better terms.
- Autoliv's Innovation Edge: Continuous development of advanced safety features differentiates Autoliv and mitigates standardization impact.
- Customer Bargaining Power Mitigation: Autoliv's focus on high-tech solutions reduces reliance on standardized, price-sensitive components.
Potential for Backward Integration by OEMs
Major automotive manufacturers, or OEMs, possess the potential to integrate backward and produce certain safety components internally. However, the complex, capital-intensive nature and substantial R&D investment needed for advanced systems like airbags and their associated electronics make complete backward integration by OEMs improbable for most intricate parts.
This strategic limitation significantly curtails the threat of customers directly competing with Autoliv in its primary market. For instance, while an OEM might source basic seatbelt components, the sophisticated pyrotechnic initiators and crash-sensing electronics within an airbag module require specialized expertise that most OEMs do not possess or find economically viable to develop in-house.
- High R&D Costs: Developing cutting-edge automotive safety technology, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) integrated with restraint systems, demands billions in research and development, a barrier for most OEMs considering in-house production.
- Specialized Manufacturing: The production of safety-critical components involves highly specialized manufacturing processes and stringent quality control, often requiring dedicated facilities and expertise that Autoliv has cultivated over decades.
- Economies of Scale: Autoliv, as a global supplier, benefits from significant economies of scale by serving multiple OEMs, making its per-unit cost for complex safety systems generally lower than what an individual OEM could achieve by producing them solely for its own needs.
The bargaining power of customers, primarily major automotive manufacturers (OEMs), is significant due to their concentrated purchasing power and the sheer volume of components they buy. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to emphasize cost efficiency, leading OEMs to exert pressure on suppliers like Autoliv for competitive pricing and improved operational performance. While OEMs can demand favorable terms, the high costs and complexity associated with switching safety system suppliers provide Autoliv with a degree of counter-leverage.
The threat of backward integration by OEMs is limited for complex safety systems due to Autoliv's specialized expertise, high R&D investment, and economies of scale. For instance, the intricate electronics and pyrotechnics in advanced airbag systems are not typically manufactured in-house by automakers. This strategic limitation effectively reduces the direct competitive threat from customers in Autoliv's core business areas.
| Factor | Impact on Autoliv | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major OEMs | Top 5 OEMs dominate global production, increasing their influence. |
| Switching Costs | Mitigates customer power | Re-engineering and regulatory approval for new safety systems can cost tens of millions per model. |
| Cost Sensitivity | Pressure on pricing and margins | OEMs consistently seek annual price reductions and operational efficiencies. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low for complex systems | High R&D and specialized manufacturing requirements deter OEMs from producing advanced safety components internally. |
What You See Is What You Get
Autoliv Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Autoliv Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the automotive safety systems industry. The document you see here is the actual, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into Autoliv's market position. You're looking at the exact document, so rest assured that what you preview is precisely what you'll be able to download and utilize for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The automotive safety systems sector operates as a global oligopoly, dominated by a handful of major companies. This intense competition among these large, established players significantly shapes market dynamics.
Autoliv stands out as a dominant force in passive safety, commanding an estimated global market share of approximately 45% in this segment. This leadership position highlights its significant influence within the industry.
Key rivals challenging Autoliv include ZF Friedrichshafen, Continental AG, Joyson Safety Systems, and Magna International. These companies are actively competing to expand their market presence and capture a larger share of the automotive safety systems market.
The automotive safety industry, where Autoliv operates, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. Companies must invest heavily in research and development (R&D) to create cutting-edge safety technologies, as well as in advanced manufacturing facilities and rigorous testing equipment. For instance, Autoliv's commitment to innovation is evident in its significant R&D expenditures, which are crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
These high upfront investments create a strong incentive for firms to maximize production capacity utilization. Operating at full capacity helps to spread the substantial overhead costs across a larger number of units, thereby lowering the per-unit cost. This drive for volume can lead to intense price competition as companies vie for large contracts to ensure their facilities are running efficiently.
Autoliv, as a leader in the sector, consistently invests in R&D to maintain its technological edge. In 2023, the company reported R&D expenses of approximately $793 million, underscoring the critical role of innovation in this capital-intensive industry. This focus on development is essential for Autoliv to offer advanced solutions and secure its market position.
The automotive safety industry is characterized by intense competition fueled by a relentless pursuit of innovation and product differentiation. Companies like Autoliv are constantly pushing the boundaries to develop more effective and advanced safety features, from sophisticated airbag systems to advanced driver-assistance technologies.
Autoliv's strategy heavily relies on its focus on cutting-edge technology in airbags, seatbelts, and active safety solutions to create a distinct market position. The ability to offer superior performance, utilize lighter materials for improved fuel efficiency, and provide seamlessly integrated safety solutions is paramount for securing and maintaining lucrative contracts with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
In 2024, the demand for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), which often integrate with passive safety features, continued to surge, with projections indicating a significant market expansion. For instance, the global ADAS market was expected to reach over $40 billion in 2024, underscoring the critical need for suppliers to innovate and differentiate their offerings to capture market share and maintain competitiveness.
Industry Growth and Market Development
The automotive safety systems market is a hotbed of activity, fueled by a growing demand for safer vehicles and stricter government mandates. This dynamic environment is projected to see the market expand significantly, moving from an estimated $124.7 billion in 2024 to a substantial $193.73 billion by 2029.
This robust growth trajectory, however, doesn't come without its challenges. It naturally intensifies competitive rivalry as established players and new entrants alike vie for dominance in this expanding sector.
- Driving Forces: Increasing safety regulations and rising consumer expectations are key growth drivers.
- Market Expansion: The global automotive safety systems market is expected to grow from $124.7 billion in 2024 to $193.73 billion by 2029.
- ADAS Impact: The proliferation of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and the advent of autonomous driving technologies further propel market expansion and innovation.
- Competitive Landscape: This rapid market development creates opportunities but also heightens competition among industry participants.
Exit Barriers and Industry Consolidation
High capital investments, specialized assets like advanced testing facilities, and deeply entrenched customer relationships with major automakers create substantial exit barriers in the automotive safety systems industry. These factors make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, potentially leading less profitable firms to persist and intensify competitive pressures through price reductions.
While the sector has experienced some consolidation, the remaining dominant players continue to engage in aggressive competition for new contracts and increased market share. For instance, in 2024, Autoliv itself has been actively managing its portfolio, divesting non-core assets to focus on its primary safety systems business, a move that can reshape competitive dynamics.
- High Capital Intensity: Establishing and maintaining state-of-the-art manufacturing and R&D facilities requires billions of dollars in investment, deterring new entrants and making it costly for existing firms to exit.
- Specialized Assets: Assets such as crash test dummies, simulation software, and proprietary manufacturing equipment are highly specific to the automotive safety sector, limiting their resale value if a company were to exit.
- Customer Lock-in: Long-term contracts and deep integration with vehicle platforms create strong relationships between suppliers and automakers, making it challenging for companies to switch suppliers and for suppliers to exit without significant disruption.
- Ongoing Consolidation: Despite exit barriers, the industry has seen strategic acquisitions and divestitures, with major players like ZF Friedrichshafen and Aptiv continuing to refine their market positions through M&A activity in 2024.
Competitive rivalry within the automotive safety systems sector is intense, driven by a few dominant global players like Autoliv, ZF Friedrichshafen, Continental AG, Joyson Safety Systems, and Magna International. This rivalry is fueled by significant investments in research and development, with Autoliv alone spending approximately $793 million on R&D in 2023 to maintain its technological edge in areas like airbags and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
The market's projected growth, from an estimated $124.7 billion in 2024 to $193.73 billion by 2029, further intensifies competition as companies vie for market share. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous innovation and differentiation, especially as ADAS market growth was expected to exceed $40 billion in 2024, pushing suppliers to develop more advanced solutions.
High capital intensity, specialized assets, and strong customer relationships create significant barriers to exit, meaning less profitable firms may remain, contributing to sustained competitive pressure. Despite this, strategic M&A activity, such as Autoliv's divestitures in 2024, continues to reshape the competitive landscape among established firms.
| Key Competitors | Autoliv's 2023 R&D Spend | 2024 Automotive Safety Market Estimate | Projected 2029 Market Value | ADAS Market 2024 Estimate |
| ZF Friedrichshafen, Continental AG, Joyson Safety Systems, Magna International | $793 million | $124.7 billion | $193.73 billion | >$40 billion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for traditional passive safety systems, like airbags and seatbelts, comes from the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). These active safety technologies are designed to prevent accidents altogether.
Features such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control are becoming increasingly common in new vehicles. The global ADAS market is expected to see substantial growth, with projections indicating it could reach USD 133.8 billion by 2034. This trend suggests a future where crashes are less frequent and less severe, potentially diminishing the long-term demand for passive safety components.
As autonomous driving technologies advance, the focus of automotive safety is evolving. The industry is moving beyond merely reducing injury severity in crashes to actively preventing them. This shift could impact the perceived value of traditional passive safety systems.
For instance, by 2024, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), precursors to full autonomy, are becoming standard on many new vehicles, contributing to accident avoidance. The development of sophisticated sensor suites and AI algorithms aims to eliminate human error, which is a factor in over 90% of road accidents.
Furthermore, the integration of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication and smart infrastructure will create an interconnected ecosystem designed for accident prevention. While passive safety systems like airbags and seatbelts will likely remain regulatory requirements, their role as the primary safety feature might diminish in the eyes of consumers as autonomous systems take over.
The regulatory environment strongly supports Autoliv's business. For instance, in 2024, many regions continued to strengthen mandates for essential passive safety features such as airbags and seatbelts, guaranteeing a consistent demand for Autoliv's foundational offerings.
Furthermore, the relationship between passive and active safety systems is fundamentally complementary, not substitutive. While advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) aim to prevent accidents, passive systems like airbags and seatbelts are crucial for occupant protection when a collision is unavoidable. This synergy means ADAS enhances, rather than replaces, the need for passive safety technologies.
High Cost and Complexity of Full Substitution
Completely replacing passive safety systems like airbags and seatbelts with active ones is currently not a realistic option. Regulatory mandates still require passive safety features, and active systems, while advanced, cannot prevent every conceivable collision scenario.
The financial and technical hurdles in developing active safety systems capable of fully substituting passive ones are immense. The research, development, and implementation costs for such comprehensive active systems remain prohibitively high for widespread adoption across the automotive industry.
Consequently, passive safety systems continue to be an indispensable component of vehicle safety. For instance, in 2024, global automotive safety system market analysis consistently highlights the sustained demand for traditional passive safety components, underscoring their ongoing necessity.
- Regulatory Mandates: Passive safety systems remain legally required in most markets.
- Inherent Limitations of Active Systems: Active systems cannot eliminate all collision risks.
- Prohibitive Development Costs: Creating fully substitutive active systems is economically unfeasible at present.
- Continued Demand for Passive Systems: The market in 2024 shows strong ongoing demand for established passive safety technologies.
Focus on Integrated Safety Solutions
Autoliv actively combats the threat of substitutes by innovating integrated safety solutions. They are developing systems that combine passive safety features, like airbags and seatbelts, with active safety technologies, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). For instance, Autoliv is exploring how pre-crash sensing data from ADAS can dynamically adjust airbag deployment, creating a more comprehensive safety offering.
This strategy directly addresses the potential for alternative safety approaches to emerge. By focusing on the synergy between active and passive systems, Autoliv aims to lead the market in holistic vehicle safety. This proactive integration ensures they are not merely reacting to potential substitutes but are actively shaping the future of automotive safety.
- Integrated Safety Development: Autoliv's R&D investment in 2023 for safety systems reached $1.1 billion, underscoring their commitment to combining passive and active safety.
- ADAS Synergy: The company's work on adaptive airbag deployment, informed by ADAS data, exemplifies their strategy to leverage technological convergence.
- Market Positioning: By offering comprehensive, integrated solutions, Autoliv aims to differentiate itself from single-technology providers and mitigate the threat of simpler, standalone substitutes.
While advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are growing, they don't fully replace passive safety. Regulatory mandates for airbags and seatbelts remain strong, as seen in 2024 vehicle safety standards globally. The cost and complexity of creating active systems that can entirely substitute passive ones are currently prohibitive.
Autoliv is mitigating this threat by integrating passive and active safety, leveraging ADAS data to enhance passive system performance. For example, their 2023 R&D investment of $1.1 billion in safety systems highlights this focus on combined solutions.
| Threat Factor | Description | Impact on Autoliv | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advancement of ADAS | Active systems aim to prevent accidents, potentially reducing the need for passive systems. | Moderate to High | Integration of ADAS with passive systems. |
| Regulatory Mandates | Passive safety features are legally required, ensuring continued demand. | Low | Compliance and continued innovation in mandated areas. |
| Development Costs | High costs for fully substitutive active systems limit their immediate impact. | Low to Moderate | Focus on cost-effective integrated solutions. |
| Consumer Perception | Shift towards proactive safety could de-emphasize passive systems. | Moderate | Educating consumers on the complementary nature of active and passive safety. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive safety industry demands significant upfront capital for specialized manufacturing plants and cutting-edge testing labs. For instance, developing a new airbag system can cost tens of millions of dollars in R&D alone. This substantial financial commitment acts as a major deterrent for potential new competitors.
Stringent regulatory standards and certification requirements pose a significant threat of new entrants in the automotive safety systems market. For instance, compliance with evolving global standards like Euro NCAP's latest protocols, which increasingly emphasize advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and pedestrian protection, demands substantial investment in research, development, and testing. New companies must navigate complex and costly certification processes, often taking years to achieve, which favors incumbents like Autoliv with established compliance infrastructure and expertise. In 2024, the average cost for a new automotive component to achieve full regulatory compliance across major markets like the EU and North America can easily exceed several million dollars, a prohibitive barrier for many aspiring entrants.
Autoliv and its established competitors benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with major automotive manufacturers, often spanning decades. These long-standing partnerships are crucial because OEMs prioritize reliability and proven performance for safety-critical components, making it difficult for newcomers to break in.
The integration into complex global supply chains further solidifies the position of existing players. New entrants would face significant hurdles in replicating this level of integration and trust, which is built over years of consistent delivery and collaboration.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
The automotive safety industry, particularly for components like airbags and seatbelts, is heavily protected by intellectual property. Established companies such as Autoliv hold extensive patent portfolios covering critical technologies, including advanced airbag inflation systems and sophisticated sensor technologies. For instance, Autoliv's significant R&D investment, which reached approximately $900 million in 2023, underpins this technological moat.
This deep well of proprietary technology acts as a substantial barrier to entry. New companies would face immense costs and time to develop comparable innovations or would need to negotiate complex licensing agreements for existing patented technologies. The sheer volume and sophistication of patents held by incumbents make it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete on technological merit without significant upfront investment or strategic partnerships.
- Extensive Patent Portfolios: Companies like Autoliv possess thousands of patents globally, covering core safety technologies.
- High R&D Investment: Significant annual R&D spending, like Autoliv's nearly $1 billion in 2023, fuels continuous innovation and strengthens IP barriers.
- Licensing Challenges: New entrants must either develop entirely novel technologies or secure costly licenses for existing patented solutions.
- Technological Differentiation: Proprietary technologies provide a competitive edge that is difficult and expensive for new players to replicate.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Autoliv, as a leader in automotive safety systems, benefits immensely from economies of scale. This means they can produce components like airbags and seatbelts at a much lower cost per unit than a newcomer could. For instance, in 2023, Autoliv reported net sales of $10.4 billion, reflecting their substantial production volume and efficient supply chain management.
A new entrant would struggle to match these per-unit costs initially, facing higher expenses for raw materials, manufacturing setup, and distribution. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for them to offer competitive pricing against established players like Autoliv.
Furthermore, Autoliv's decades of experience have created a steep learning curve. This translates into optimized production processes, higher quality control, and innovative product development, all of which are difficult for a new company to replicate quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Autoliv's large-scale operations in 2023, generating $10.4 billion in net sales, allow for significant cost reductions in manufacturing and procurement.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Decades of experience have honed Autoliv's production efficiency and product quality, creating a barrier for new entrants.
- Cost Disadvantage for Entrants: New companies face higher initial per-unit costs, hindering their ability to compete on price with established leaders.
The threat of new entrants in the automotive safety sector is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements for specialized manufacturing and R&D, with new airbag system development alone costing tens of millions. Furthermore, stringent global safety regulations, such as evolving Euro NCAP protocols, necessitate substantial investment in compliance and certification, a process that can take years and cost millions, favoring established players like Autoliv with existing infrastructure.
Established relationships with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and deeply integrated global supply chains create formidable barriers. Newcomers struggle to build the trust and proven reliability that OEMs demand for safety-critical components, a hurdle that takes decades of consistent performance to overcome.
Autoliv's extensive patent portfolio, supported by approximately $900 million in R&D spending in 2023, represents a significant technological moat. New entrants face the daunting challenge of either developing entirely novel, non-infringing technologies or incurring substantial costs for licensing existing intellectual property.
Economies of scale, evidenced by Autoliv's $10.4 billion in net sales in 2023, provide a substantial cost advantage. New entrants are burdened with higher initial per-unit costs for materials, manufacturing, and distribution, making it difficult to compete on price with industry leaders.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for specialized facilities and R&D. | New airbag system development: Tens of millions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and costly compliance with global safety standards. | New component certification cost (EU/NA): Millions of dollars (2024 estimate). |
| Customer Relationships | Long-standing partnerships with OEMs prioritizing proven reliability. | Decades of established relationships. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protecting core technologies. | Autoliv's 2023 R&D: ~$900 million; thousands of global patents. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit production costs due to high volume. | Autoliv's 2023 Net Sales: $10.4 billion. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Autoliv Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Autoliv's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit and Mordor Intelligence.
We also incorporate insights from automotive industry trade publications and macroeconomic data from sources such as the World Bank to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
