Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Attica Group Bundle
Attica Group navigates a competitive landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of its customers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the company's strategic positioning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves deeper, revealing the subtle yet powerful influence of suppliers and the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes. Unlock the complete report to gain a comprehensive strategic overview and identify Attica Group's key vulnerabilities and strengths.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Attica Group’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The maritime sector, including ferry operators like Attica Group, is heavily dependent on marine fuel. The global market for specific marine fuel grades can be quite concentrated, with a limited number of major suppliers. This limited supply base, particularly during periods of high demand or geopolitical instability, grants these fuel suppliers considerable bargaining power. For instance, the price of Very Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (VLSFO), a common marine fuel, can see significant fluctuations driven by global crude oil prices and supply chain disruptions.
This concentration directly impacts Attica Group's operational expenses. When fuel suppliers have significant leverage, they can dictate terms and prices, especially when alternative suppliers are scarce or when specific fuel qualities are required. In 2023, the average price of marine fuel saw considerable volatility, directly affecting the profitability of shipping companies. Attica Group's financial performance is therefore intrinsically linked to its ability to manage these fuel costs, which are heavily influenced by the bargaining power of a concentrated supplier base.
The construction and significant maintenance of large passenger ferries demand highly specialized shipyards and engineering firms. Globally, there's a limited pool of facilities possessing the requisite expertise and capacity for such complex projects.
This scarcity translates into substantial switching costs for ferry operators like Attica Group, as finding and onboarding alternative providers can be time-consuming and expensive. For instance, a major refit can cost millions and lead to significant operational downtime, reinforcing the suppliers' leverage.
Port authorities and infrastructure providers wield significant bargaining power over Attica Group, as they control access to essential services like berths and loading facilities. These entities often operate as monopolies or are heavily regulated, meaning Attica Group has limited alternatives for critical port operations. For instance, in 2024, major European ports saw increased operational costs due to infrastructure upgrades and labor agreements, which are often passed on to shipping companies.
Attica Group's reliance on these specific routes and facilities, coupled with the limited number of providers, grants port authorities leverage through fees, regulations, and the allocation of valuable port slots. Favorable agreements with these providers are crucial for Attica Group's operational efficiency and cost management. In 2023, several Greek ports experienced a rise in berthing fees, impacting the profitability of ferry operators.
Limited High-Skilled Maritime Labor Pool
The bargaining power of suppliers for Attica Group is significantly influenced by the limited availability of high-skilled maritime labor. Finding experienced captains, engineers, and specialized crew members is difficult due to the unique skill sets and stringent international regulations governing the industry. This scarcity can give these professionals, often represented by unions or operating in a globally competitive market, considerable leverage.
Attica Group, like other shipping companies, must actively compete to attract and retain this essential workforce. This competition can translate into upward pressure on wages and benefits, impacting operational costs. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of certified maritime officers was a persistent issue, with some reports indicating a deficit of over 100,000 officers needed to meet demand.
- Limited Pool of Skilled Professionals: The specialized nature of maritime roles creates a constrained supply of qualified personnel.
- Union Influence and Global Demand: Collective bargaining power and international demand for talent can drive up labor costs.
- Competition for Talent: Attica Group faces direct competition from other shipping lines and related industries for these critical employees.
- Impact on Operating Costs: The need to secure and retain skilled labor can lead to increased wage and benefit expenses for the company.
Proprietary Technology and Software Vendors
Suppliers of specialized maritime navigation systems, ticketing platforms, and fleet management software often possess proprietary technology, giving them significant bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the maritime technology market saw continued consolidation, with a few key players dominating advanced navigation and data analytics solutions. The complexity and expense associated with migrating from these established, integrated systems can be substantial, creating a strong dependency for companies like Attica Group.
This reliance translates into leverage for these vendors, influencing licensing fees, ongoing maintenance contracts, and the necessity of timely software upgrades. The cost of switching can easily run into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars, depending on the scale of operations and the integration of the existing software suite. This makes it difficult for Attica Group to negotiate aggressively on pricing or terms without risking operational disruption.
- Proprietary Rights: Vendors hold exclusive rights to critical maritime software and hardware.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating to alternative systems is complex and expensive for Attica Group.
- Vendor Dependency: Attica Group relies on these specialized suppliers for essential operational technologies.
- Pricing Leverage: Suppliers can dictate terms for licensing, maintenance, and upgrades due to this dependency.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Attica Group is substantial, particularly concerning specialized maritime components and technology. Companies providing advanced navigation systems, fleet management software, and even critical engine parts often hold proprietary rights and enjoy a limited competitive landscape. For instance, in 2024, the maritime technology sector continued to see consolidation, with a few dominant players offering integrated solutions. This concentration means Attica Group faces high switching costs, often running into hundreds of thousands of dollars, to change providers, thus granting these suppliers significant leverage over pricing and contract terms.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Attica Group | Example Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Fuel | Limited number of major suppliers, global crude oil price volatility | Directly impacts operational expenses and profitability | VLSFO prices saw significant fluctuations in 2023; continued volatility expected in 2024 |
| Shipyards & Engineering Firms | Scarcity of specialized facilities for large ferry construction/maintenance | High switching costs, potential for extended downtime | Major refits can cost millions; limited capacity can lead to longer waiting times |
| Port Authorities | Monopolistic or heavily regulated nature, control over essential services | Influence on fees, regulations, and operational access | Increased operational costs in major European ports in 2024; Greek ports saw rising berthing fees in 2023 |
| Skilled Maritime Labor | Shortage of experienced professionals, union influence, global demand | Upward pressure on wages and benefits | Global shortage of certified maritime officers estimated at over 100,000 in 2024 |
| Specialized Technology Providers | Proprietary software/hardware, high migration costs | Dependency on vendors for essential operational systems | Consolidation in maritime tech market in 2024; switching costs can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars |
What is included in the product
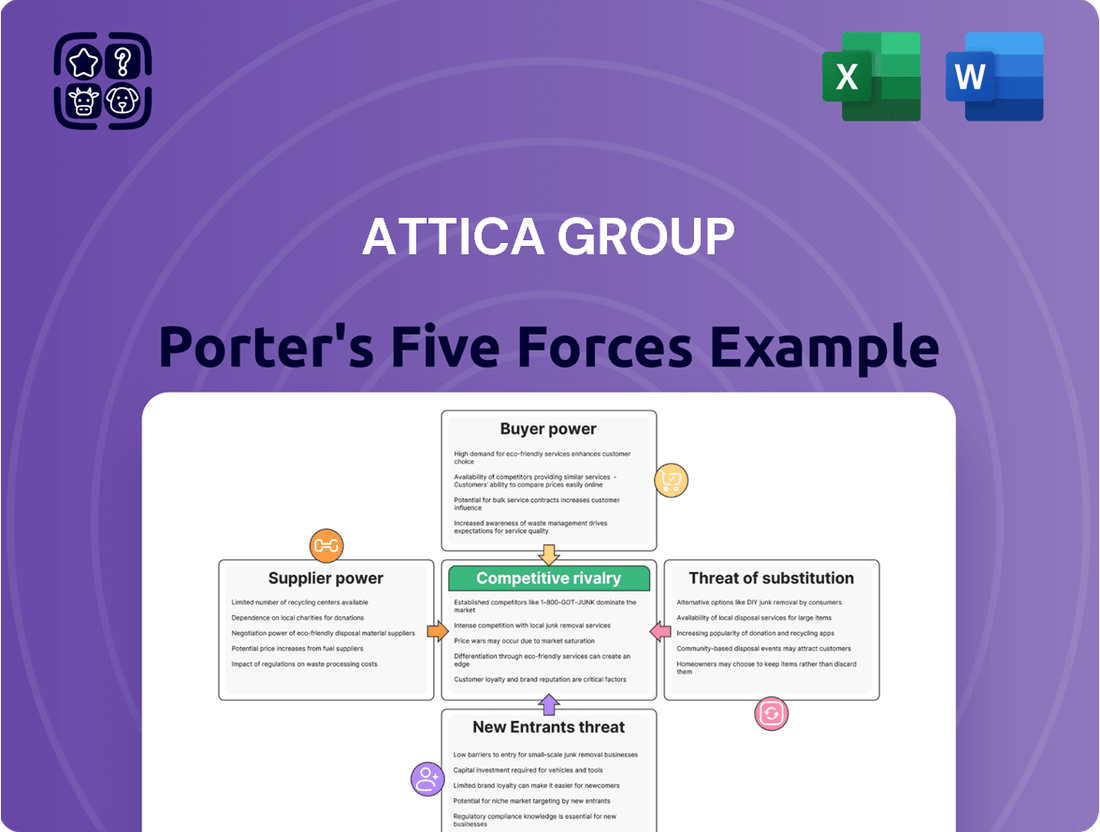
Tailored exclusively for Attica Group, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Customers Bargaining Power
Leisure travelers, especially outside of peak holiday periods, are very focused on price. They actively look for deals and the best value for their money, making them a significant force for Attica Group.
The ability for customers to easily compare prices online across various ferry companies and even other travel options like flights or buses significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This transparency means Attica Group needs competitive pricing to win over these travelers.
For instance, during the 2023 summer season, many ferry routes saw increased competition, leading to promotional offers. Attica Group's strategy in 2024 will likely involve carefully calibrating prices to attract this price-conscious segment without eroding profitability, potentially through loyalty programs or off-peak discounts.
The bargaining power of customers for Attica Group is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative ferry operators. While Attica Group, with brands like Superfast Ferries and Blue Star Ferries, is a major player, competition exists on many of its key routes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Adriatic. For instance, in 2024, several other operators continued to serve popular Greek island routes and Adriatic crossings, offering passengers a choice.
This competitive environment means customers can readily compare offerings and switch between companies based on factors like ticket prices, departure times, and onboard amenities. In 2024, reports indicated that price sensitivity remained a key driver for many travelers, particularly during off-peak seasons, further amplifying customer leverage. The ease of switching and the availability of comparable services directly empower customers to negotiate better terms, whether through lower fares or improved service levels.
Online travel agencies (OTAs) and ferry ticket aggregators significantly boost customer bargaining power by consolidating numerous ferry operators into easily comparable platforms. This transparency forces companies like Attica Group to compete more intensely on price and service. For instance, in 2024, the global online travel market continued its robust growth, with a significant portion of bookings for ferry services likely influenced by these aggregators, giving customers more options and leverage.
Commercial Freight Customers' Demand for Reliability and Cost-Efficiency
Commercial freight customers, such as trucking firms and logistics companies, place a high value on dependable service, on-time deliveries, and cost-effective pricing for their shipments. These clients often enter into extended agreements, focusing on the overall economic efficiency of the transportation solutions provided.
The bargaining power of these customers is significant, as they can leverage the substantial volume and consistent nature of their business to negotiate more favorable contract terms. For instance, a major logistics provider might secure preferential rates by committing to a large, predictable volume of freight, directly impacting Attica Group's pricing strategies and profitability on those routes.
- Customer Concentration: The presence of a few large freight customers can disproportionately influence pricing and service level agreements.
- Switching Costs: While switching carriers can involve some effort, the potential for cost savings often incentivizes customers to explore alternatives if service or price expectations are not met.
- Information Availability: Freight customers have access to market pricing and competitor service offerings, enabling them to make informed negotiation decisions.
- Price Sensitivity: For many commercial freight operations, transportation costs are a major expense, making them highly sensitive to price fluctuations and competitive offers.
Seasonal Demand Fluctuations and Loyalty Programs
Customer bargaining power for Attica Group is notably influenced by seasonal demand, intensifying during off-peak times when ferry capacity is underutilized. To mitigate this, Attica Group actively implements loyalty programs and offers early booking incentives. These initiatives are designed to foster repeat patronage and diminish price sensitivity among its most frequent customers, thereby enhancing customer loyalty.
These strategies are crucial for managing the inherent volatility in customer demand. For instance, in 2023, Attica Group reported a significant increase in passenger numbers during peak summer months, but off-peak periods often present a challenge for maintaining consistent revenue. Loyalty programs, such as the Attica Premium Club, aim to smooth out these fluctuations by rewarding consistent engagement. This approach helps to build a more predictable revenue stream by encouraging customers to book even outside of the busiest travel seasons.
- Customer bargaining power rises during off-peak travel seasons when ferry capacity is not fully utilized.
- Attica Group utilizes loyalty programs and early booking discounts to build customer stickiness and reduce price sensitivity.
- These strategies aim to encourage repeat business and create a more stable demand pattern throughout the year.
Customers wield considerable bargaining power, especially leisure travelers highly attuned to price and seeking the best value, particularly outside peak periods. The ease of comparing ferry prices online with competitors and alternative transport options like flights significantly amplifies this power, compelling Attica Group to maintain competitive pricing. For example, in 2023, increased competition on many routes led to widespread promotional offers, a trend likely to continue influencing Attica Group's pricing strategies in 2024.
Commercial freight customers, including trucking and logistics firms, also exert strong influence due to the volume and consistency of their business. These clients can negotiate favorable contract terms, such as preferential rates for guaranteed freight volumes, directly impacting Attica Group's revenue and pricing on key routes. Information availability regarding market prices and competitor services further empowers these customers to negotiate effectively.
Attica Group mitigates customer bargaining power through loyalty programs and early booking incentives, aiming to foster repeat business and reduce price sensitivity, especially during off-peak seasons. These strategies are vital for stabilizing revenue, as demonstrated by the focus on building consistent engagement to counter the inherent demand volatility observed in 2023.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Attica Group's Response (Examples) |
|---|---|---|
| Leisure Travelers | Price sensitivity, ease of online comparison, availability of alternatives | Competitive pricing, off-peak discounts, loyalty programs |
| Commercial Freight Customers | Volume commitments, service reliability, cost-effectiveness | Volume-based rate negotiation, service level agreements |
| All Customers | Seasonal demand fluctuations | Early booking incentives, loyalty programs to encourage off-peak travel |
Same Document Delivered
Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Attica Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the ferry industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Greek and Eastern Mediterranean ferry market is a crowded space with several strong domestic and regional competitors. Companies like Anek Lines, Minoan Lines, and Seajets have built significant brand loyalty and operate extensive route networks, directly challenging Attica Group for both passenger and freight business.
The ferry industry demands substantial investment in ships, maintenance, and port facilities, creating high fixed costs for operators like Attica Group. This capital intensity drives a constant need to maximize capacity utilization.
In 2023, Attica Group operated a fleet of 42 vessels, highlighting the significant fixed asset base. The pressure to fill these vessels, especially during off-peak seasons, can lead to intense price competition as companies try to cover their substantial overheads.
Competitors within the ferry industry, including those vying with Attica Group, frequently target the same popular and profitable routes, resulting in direct service overlaps. This intense competition for market share often triggers a cycle of schedule adjustments, service improvements, and aggressive promotional campaigns designed to capture customer loyalty. For instance, in 2024, key routes saw increased frequency from multiple operators, intensifying the battle for passengers.
Brand Differentiation and Service Quality Competition
Competitive rivalry in the ferry industry is intense, with companies like Attica Group actively differentiating themselves beyond just transportation. This differentiation occurs through a strong emphasis on brand reputation, the modernity of their vessel fleet, the quality of onboard amenities, and the overall customer service experience provided. Attica Group, for instance, strategically utilizes its distinct brands – Superfast Ferries, Blue Star Ferries, and Hellenic Seaways – to appeal to various customer segments, from those seeking speed and modern comfort to those prioritizing a more traditional or value-oriented travel experience.
The ferry sector sees significant competition where brand image and service quality are key battlegrounds. Competitors vie for customer loyalty by investing in:
- Brand Reputation: Established brands like Attica Group's Hellenic Seaways and Blue Star Ferries benefit from years of operation and customer trust.
- Vessel Modernity: Newer, more fuel-efficient, and amenity-rich vessels attract passengers. For example, Attica Group has consistently invested in fleet upgrades, with recent deliveries and refurbishments aiming to enhance passenger experience and operational efficiency.
- Onboard Amenities: Offering competitive dining options, Wi-Fi, entertainment, and comfortable seating areas plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining passengers.
- Customer Service: Friendly and efficient staff can significantly impact a passenger's perception and likelihood of repeat business.
Attica Group's strategy of leveraging its diverse brand portfolio allows it to cater to different market needs and price sensitivities, thereby intensifying the competitive pressure on rivals who may have a more homogenous offering. Continuous investment in both fleet modernization and service enhancement is therefore not just beneficial but essential for Attica Group and its competitors to maintain and grow their market share in this dynamic environment.
Impact of Regulatory Environment and Subsidized Routes
Government regulations, such as licensing and the awarding of subsidized routes to guarantee island connectivity, significantly influence the competitive arena. These regulations can alter market structure and the economic feasibility of specific ventures, thereby complicating competitive interactions.
Attica Group navigates these regulatory landscapes, which can create barriers to entry for new players and solidify the positions of established operators on certain routes. For instance, the Greek Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Insular Policy oversees ferry route allocations, often prioritizing social service over pure profit maximization for subsidized routes.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Government policies and licensing requirements dictate market access and operational parameters for ferry companies.
- Subsidized Routes: The allocation of subsidized routes to ensure essential services to remote islands can impact profitability and competitive advantages, as these routes may not be inherently profitable but are crucial for social connectivity.
- Market Structure Influence: These regulatory interventions can shape the overall market structure, potentially limiting the number of competitors on specific routes or creating protected market segments.
The competitive rivalry within the Greek and Eastern Mediterranean ferry market is fierce, with established players like Attica Group facing significant challenges from rivals such as Anek Lines, Minoan Lines, and Seajets. These competitors actively vie for passenger and freight business by operating extensive route networks and cultivating strong brand loyalty.
The sector's high capital intensity, with companies like Attica Group operating large fleets—42 vessels in 2023—necessitates high capacity utilization, often leading to aggressive pricing strategies and service overlaps on popular routes. In 2024, increased service frequency on key routes by multiple operators further intensified this competition.
Differentiation is crucial, with companies like Attica Group emphasizing brand reputation, fleet modernity, onboard amenities, and customer service to capture market share. Attica Group's multi-brand strategy (Superfast Ferries, Blue Star Ferries, Hellenic Seaways) allows it to target diverse customer segments, amplifying competitive pressure on rivals with more uniform offerings.
Government regulations, including route licensing and subsidies for essential island connectivity, significantly shape the competitive landscape. These regulations can create barriers to entry and influence market structure, as seen with the Greek Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Insular Policy's role in route allocation, often balancing social service needs with commercial viability.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For longer-distance passenger travel, especially routes connecting mainland Greece to major islands or international destinations, air travel presents a strong substitute for ferry services like those offered by Attica Group. Airlines typically provide significantly faster transit times, a critical consideration for passengers prioritizing speed over other factors, even if airfare is higher or luggage capacity is more restricted.
Attica Group faces direct competition from airlines on numerous routes where both modes of transport are viable options. For instance, in 2024, the Athens to Crete route, a significant corridor for Attica Group, saw substantial passenger volume handled by airlines, offering travel times of under an hour compared to several hours by ferry. This speed advantage allows airlines to capture a segment of the market that values time efficiency above all else.
The threat of substitutes for Attica Group's ferry services, particularly for short-distance connections, is relatively low in the Greek archipelago. While bridges and road networks can serve as direct substitutes for ferry travel, their presence is limited across the islands. For instance, the Cyclades islands, a core operational area for Attica Group, are not connected by bridges to the mainland or to each other, making sea travel essential.
Where such infrastructure exists, like the Rio-Antirrio bridge connecting the Peloponnese to mainland Greece, it can divert some short-haul traffic. However, Attica Group's strategic focus remains on routes where sea transport is the predominant or sole viable option, minimizing direct competition from land-based alternatives.
Customers might choose smaller, local ferry operators for unique island-hopping adventures or opt for private boat charters for personalized travel experiences. While these don't directly compete with Attica Group's extensive, scheduled routes, they appeal to specific market niches and can siphon off some passenger volume.
Emergence of High-Speed Rail for Mainland Travel
While Attica Group's core business is sea transport, advancements in mainland Greece's infrastructure present a subtle threat of substitutes. Improved high-speed rail and road networks could potentially siphon off passenger and freight traffic that would traditionally connect to ferry services for island journeys. This impacts the first and last mile of travel, indirectly influencing overall ferry demand.
For instance, investments in the national railway network, such as upgrades to the Athens-Thessaloniki line, can make overland travel more competitive for certain routes. By 2024, significant progress was reported on the electrification and modernization of key rail corridors, aiming to reduce travel times and increase capacity. This enhanced connectivity on the mainland might offer an alternative for travelers who previously relied on ferries for longer segments of their journey or for freight that could be routed more efficiently overland.
- Mainland Infrastructure Development: Upgrades to Greek rail and road networks offer alternative transport options.
- Indirect Impact on Ferry Demand: Improved mainland connectivity can affect the first/last mile for ferry passengers and freight.
- Competitive Overland Travel: Enhanced rail services on routes like Athens-Thessaloniki can reduce reliance on sea transport for certain journeys.
- 2024 Infrastructure Focus: Continued investment in rail modernization aims to boost efficiency and speed for overland travel.
Digital Communication Technologies Reducing Need for Physical Travel
The rise of digital communication technologies presents a subtle but growing threat to ferry services like those operated by Attica Group. As video conferencing and remote collaboration tools become more sophisticated and widely adopted, the necessity for some business-related travel diminishes. This trend, which gained significant momentum in the early 2020s, can lead to a gradual reduction in demand for inter-regional travel, including ferry routes that cater to business purposes.
While Attica Group serves both essential and leisure travel segments, the erosion of business travel demand due to digital alternatives is a factor to consider. For instance, global business travel spending, which had seen a rebound in 2023, is projected to continue its recovery but the long-term impact of hybrid work models on business trip frequency remains a point of analysis for the sector. In 2024, many companies are still evaluating their travel policies, and the ease of virtual meetings could influence a portion of potential travelers who might otherwise opt for ferry services.
- Digital Communication Impact: Increased adoption of video conferencing reduces the need for some business travel.
- Subtle Demand Erosion: This trend can subtly decrease overall demand for inter-regional travel, affecting ferry services.
- Attica Group's Segments: Attica Group serves both essential and leisure travel, making it susceptible to shifts in business travel patterns.
- 2024 Context: Companies continue to refine hybrid work policies, influencing travel decisions in the current year.
For longer-distance passenger travel, especially routes connecting mainland Greece to major islands or international destinations, air travel presents a strong substitute for ferry services like those offered by Attica Group. Airlines typically provide significantly faster transit times, a critical consideration for passengers prioritizing speed over other factors, even if airfare is higher or luggage capacity is more restricted.
Attica Group faces direct competition from airlines on numerous routes where both modes of transport are viable options. For instance, in 2024, the Athens to Crete route, a significant corridor for Attica Group, saw substantial passenger volume handled by airlines, offering travel times of under an hour compared to several hours by ferry. This speed advantage allows airlines to capture a segment of the market that values time efficiency above all else.
The threat of substitutes for Attica Group's ferry services, particularly for short-distance connections, is relatively low in the Greek archipelago. While bridges and road networks can serve as direct substitutes for ferry travel, their presence is limited across the islands. For instance, the Cyclades islands, a core operational area for Attica Group, are not connected by bridges to the mainland or to each other, making sea travel essential.
Where such infrastructure exists, like the Rio-Antirrio bridge connecting the Peloponnese to mainland Greece, it can divert some short-haul traffic. However, Attica Group's strategic focus remains on routes where sea transport is the predominant or sole viable option, minimizing direct competition from land-based alternatives.
Customers might choose smaller, local ferry operators for unique island-hopping adventures or opt for private boat charters for personalized travel experiences. While these don't directly compete with Attica Group's extensive, scheduled routes, they appeal to specific market niches and can siphon off some passenger volume.
While Attica Group's core business is sea transport, advancements in mainland Greece's infrastructure present a subtle threat of substitutes. Improved high-speed rail and road networks could potentially siphon off passenger and freight traffic that would traditionally connect to ferry services for island journeys. This impacts the first and last mile of travel, indirectly influencing overall ferry demand.
For instance, investments in the national railway network, such as upgrades to the Athens-Thessaloniki line, can make overland travel more competitive for certain routes. By 2024, significant progress was reported on the electrification and modernization of key rail corridors, aiming to reduce travel times and increase capacity. This enhanced connectivity on the mainland might offer an alternative for travelers who previously relied on ferries for longer segments of their journey or for freight that could be routed more efficiently overland.
- Mainland Infrastructure Development: Upgrades to Greek rail and road networks offer alternative transport options.
- Indirect Impact on Ferry Demand: Improved mainland connectivity can affect the first/last mile for ferry passengers and freight.
- Competitive Overland Travel: Enhanced rail services on routes like Athens-Thessaloniki can reduce reliance on sea transport for certain journeys.
- 2024 Infrastructure Focus: Continued investment in rail modernization aims to boost efficiency and speed for overland travel.
The rise of digital communication technologies presents a subtle but growing threat to ferry services like those operated by Attica Group. As video conferencing and remote collaboration tools become more sophisticated and widely adopted, the necessity for some business-related travel diminishes. This trend, which gained significant momentum in the early 2020s, can lead to a gradual reduction in demand for inter-regional travel, including ferry routes that cater to business purposes.
While Attica Group serves both essential and leisure travel segments, the erosion of business travel demand due to digital alternatives is a factor to consider. For instance, global business travel spending, which had seen a rebound in 2023, is projected to continue its recovery but the long-term impact of hybrid work models on business trip frequency remains a point of analysis for the sector. In 2024, many companies are still evaluating their travel policies, and the ease of virtual meetings could influence a portion of potential travelers who might otherwise opt for ferry services.
- Digital Communication Impact: Increased adoption of video conferencing reduces the need for some business travel.
- Subtle Demand Erosion: This trend can subtly decrease overall demand for inter-regional travel, affecting ferry services.
- Attica Group's Segments: Attica Group serves both essential and leisure travel, making it susceptible to shifts in business travel patterns.
- 2024 Context: Companies continue to refine hybrid work policies, influencing travel decisions in the current year.
The threat of substitutes for Attica Group is moderate, primarily driven by air travel for longer routes and, to a lesser extent, by improved mainland infrastructure and digital communication for specific segments. While island geography limits land-based substitutes, the speed and convenience of air travel remain a significant competitive factor. Additionally, shifts in business travel patterns due to remote work technologies can indirectly impact demand for ferry services.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Attica Group | Example Route (2024) | Attica Group's Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Travel | Faster transit times, higher cost, limited luggage | High for long-distance passenger routes | Athens to Crete | Focus on customer experience, onboard amenities, and competitive pricing on specific routes. |
| Mainland Infrastructure (Rail/Road) | Improved connectivity, potential for faster overland travel | Moderate, impacts first/last mile and freight | Athens to Thessaloniki (rail upgrades) | Optimize port connections and offer integrated ticketing solutions. |
| Digital Communication | Virtual meetings, reduced need for business travel | Low to Moderate, impacts business travel segment | General business travel | Focus on leisure and essential travel segments, explore business travel packages. |
| Private Charters/Local Ferries | Niche market, personalized experiences | Low, appeals to specific market segments | Island hopping in Cyclades | Maintain service quality and network coverage for core passenger needs. |
Entrants Threaten
The passenger shipping industry demands substantial upfront capital for acquiring or leasing state-of-the-art vessels, which are highly specialized assets. This significant financial commitment, coupled with the long operational life of these ships, acts as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. Attica Group, for instance, leverages its advantage with an established and modern fleet, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on scale and efficiency.
The maritime industry is heavily regulated, presenting a significant barrier to new entrants. Companies must navigate a complex web of national and international rules covering everything from vessel safety and emissions to crew welfare and operational permits. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continuously updates environmental regulations, such as those aimed at reducing sulfur oxide emissions, which require substantial investment in new technologies or fuel types.
Obtaining the necessary licenses and certifications for specific routes and vessel types is a lengthy and expensive undertaking. This process often involves rigorous inspections and compliance checks, which can deter smaller, less capitalized potential competitors. Attica Group, with decades of experience, has established robust systems for managing these regulatory demands, giving it an advantage over newcomers.
Attica Group benefits from established brand loyalty under names like Superfast Ferries and Blue Star Ferries, cultivated over many years. This loyalty makes it difficult for new players to attract customers away from familiar and trusted services. For instance, in 2023, Attica Group reported carrying over 7 million passengers, a testament to its strong customer base.
The company's extensive network of routes is a significant barrier to entry. Customers often choose operators offering comprehensive coverage and frequent departures, a level of service that new entrants would find challenging and costly to build quickly. This network effect creates a stickiness for existing customers, further deterring new competition.
Limited Access to Port Infrastructure and Slots
The threat of new entrants in the ferry industry, particularly concerning port infrastructure and sailing slots, is significantly mitigated by established players like Attica Group. Prime port berths and favorable sailing slots are often scarce and managed by port authorities. Existing operators, such as Attica Group, typically benefit from preferential access or long-term agreements, making it challenging for newcomers to secure the necessary operational bases and competitive schedules.
For instance, Attica Group's strategic port relationships, cultivated over years of operation, provide a distinct advantage. In 2024, securing prime berthing at major Greek ports, like Piraeus, often involves lengthy negotiation processes and existing contractual obligations. New entrants would face substantial hurdles in obtaining comparable access, thereby limiting their ability to launch and scale operations effectively against established carriers.
- Limited Availability of Prime Port Berths: Key port facilities are often at full capacity or allocated to incumbent operators.
- Preferential Access for Established Companies: Long-term contracts and relationships give existing firms an edge in securing operational slots.
- High Capital Investment for New Infrastructure: Building or leasing new port facilities is prohibitively expensive for most new entrants.
- Attica Group's Established Port Networks: Attica Group benefits from existing, strong relationships with port authorities, facilitating smoother operations and schedule adherence.
Economies of Scale in Operations and Procurement
Existing large-scale operators, such as Attica Group, leverage significant economies of scale in critical areas like fuel procurement, vessel maintenance, and crew training. These cost advantages create a formidable barrier for smaller, new entrants aiming to compete on price or operational efficiency.
Attica Group's substantial fleet enables optimized operational costs, for instance, by spreading fixed costs over a larger number of routes and passengers. In 2024, the ferry industry continues to see consolidation, with larger players like Attica Group benefiting from bulk purchasing power, which can reduce per-unit operating expenses considerably compared to smaller competitors.
- Fuel Procurement: Bulk purchasing of fuel by large operators leads to lower per-unit costs, a key advantage in the fuel-intensive ferry business.
- Fleet Utilization: Larger fleets allow for more efficient deployment and higher utilization rates, spreading maintenance and crewing costs more thinly.
- Marketing and Branding: Established brands with larger customer bases can achieve lower customer acquisition costs through economies of scale in marketing efforts.
The threat of new entrants into the passenger ferry sector is generally low, primarily due to the immense capital required for fleet acquisition and port infrastructure. Attica Group's established presence and modern fleet, built over years, present a significant hurdle for newcomers. For example, the cost of a new large ferry can easily exceed €100 million, a figure that deters many potential competitors.
Regulatory complexities and the need for specialized licenses further erect barriers. Navigating international maritime laws and obtaining operational permits is a resource-intensive process. Attica Group's long-standing compliance with standards set by bodies like the IMO, which in 2024 continues to push for stricter environmental regulations, provides a stable operational framework that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
Customer loyalty and established route networks also play a crucial role. Attica Group, operating under well-known brands like Blue Star Ferries, benefits from repeat business, making it difficult for new companies to gain market share. In 2023, Attica Group carried over 7 million passengers, demonstrating the strength of its existing customer base and the challenge new entrants face in attracting this demographic.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Attica Group's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of vessel acquisition and port infrastructure. | Prohibitive for most new players. | Established fleet and operational scale. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, safety, and environmental compliance. | Time-consuming and expensive to navigate. | Proven track record and robust compliance systems. |
| Customer Loyalty & Brand Recognition | Established brands attract and retain customers. | Difficult to attract customers from trusted operators. | Strong brand equity (e.g., Blue Star Ferries). |
| Route Network & Port Access | Securing prime berths and schedules is challenging. | Limited operational flexibility and competitive disadvantage. | Extensive route coverage and established port relationships. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Attica Group is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Maritime Strategies International, and regulatory filings from relevant maritime authorities.
