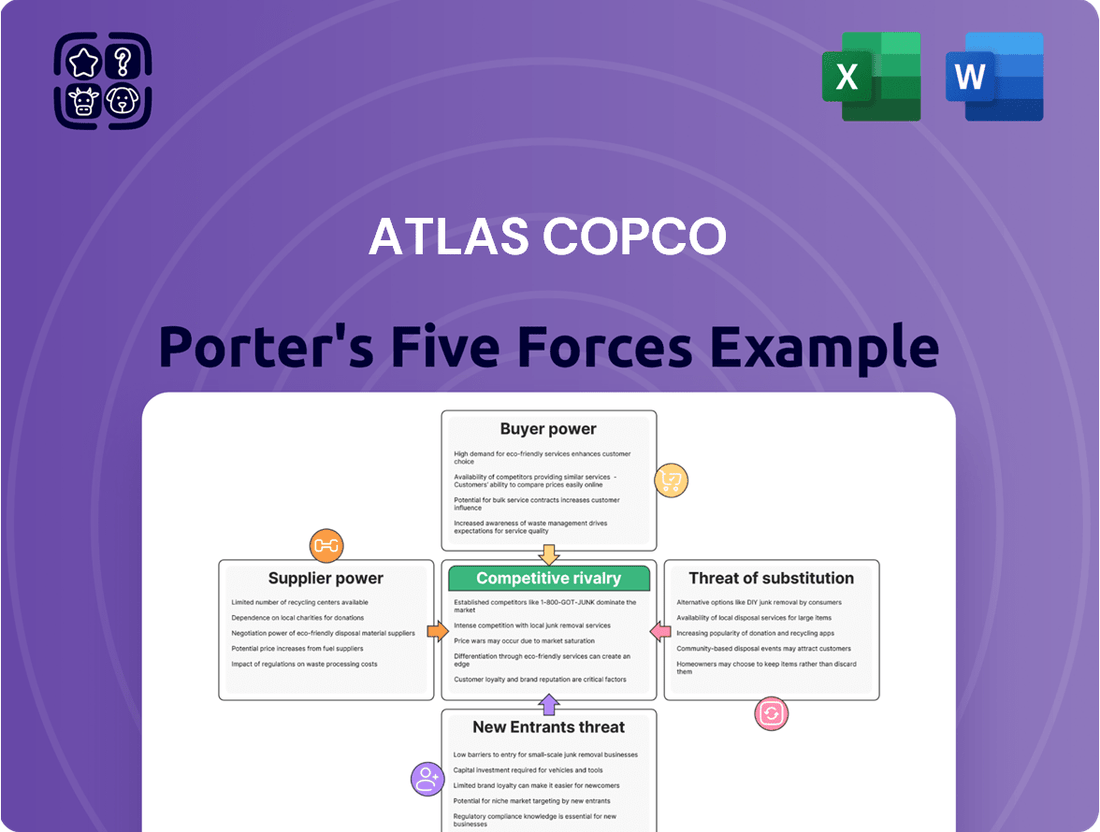
Atlas Copco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Atlas Copco Bundle
Atlas Copco operates in a competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for their strategic positioning. The availability of substitutes and the power of suppliers also significantly influence their market dynamics.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Atlas Copco’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
When the market for highly specialized components or raw materials that Atlas Copco needs is dominated by just a few suppliers, those suppliers gain significant bargaining power. This means they can often dictate terms, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or supply conditions for Atlas Copco.
This concentration limits Atlas Copco's ability to switch suppliers easily, forcing them to accept terms that might squeeze profit margins or impact production schedules. For instance, if a critical component for their industrial compressors is only produced by two or three global manufacturers, those manufacturers hold considerable sway.
Atlas Copco likely faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers for its specialized industrial equipment components. These costs can include the expense and time required for retooling production lines to accommodate new parts or the rigorous process of requalifying new suppliers for critical components that meet stringent quality and performance standards. For instance, if a key supplier for their compressors provides a highly integrated or proprietary component, the effort to find, test, and implement an alternative could be substantial, potentially running into millions of dollars in development and disruption costs.
Suppliers who offer proprietary technology or highly specialized machinery for Atlas Copco's advanced products, such as their energy-efficient compressors or semiconductor vacuum solutions, wield significant bargaining power. This uniqueness makes finding comparable alternatives difficult, giving these suppliers an advantage in price negotiations.
Threat of forward integration by suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Atlas Copco's business can significantly boost their bargaining power. If a supplier can start manufacturing similar products or components that compete directly with Atlas Copco, they gain leverage. This potential for forward integration forces Atlas Copco to cultivate strong supplier relationships and ensure competitive pricing to mitigate this risk.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers may possess the capability and incentive to move into manufacturing components or finished goods that directly compete with Atlas Copco's offerings.
- Increased Bargaining Power: This capability grants suppliers greater leverage in negotiations, potentially driving up costs for Atlas Copco.
- Strategic Response: To counter this, Atlas Copco must focus on maintaining strong supplier partnerships and competitive cost structures.
Raw material price volatility
Raw material price volatility is a significant factor affecting Atlas Copco. Fluctuations in the cost of essential inputs like steel and nonferrous metals, crucial for their industrial equipment, can directly impact profitability. For instance, global steel prices, a key component for many of Atlas Copco's products, experienced notable increases in late 2023 and early 2024 due to supply chain pressures and demand shifts.
While these price increases suggest some leverage for suppliers, Atlas Copco's robust and diversified product portfolio, spanning compressors, vacuum solutions, and power technique equipment, acts as a natural hedge. This diversification allows the company to absorb or pass on some of these cost increases across different market segments, thereby mitigating the overall risk associated with raw material price volatility.
- Steel Price Trends: Global benchmark prices for steel saw an upward trend in early 2024, with some sources indicating a rise of 5-10% compared to the previous year.
- Nonferrous Metal Costs: Prices for nonferrous metals like copper and aluminum, also vital for Atlas Copco's manufacturing, have shown similar volatility, influenced by global economic activity and geopolitical events.
- Diversification Benefit: Atlas Copco's broad product range allows for flexibility in pricing strategies and sourcing, reducing reliance on any single raw material or supplier.
Suppliers of specialized components or raw materials essential for Atlas Copco's advanced machinery, such as those for their industrial compressors or vacuum solutions, possess significant bargaining power. This is particularly true when the supplier base is concentrated, with only a few dominant manufacturers capable of producing these high-specification items.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified by the high switching costs Atlas Copco would incur. These costs involve not just financial outlays for retooling or requalifying new suppliers, but also the potential disruption to production schedules and the risk of compromising product quality. For instance, integrating a new supplier for a proprietary component could take months and cost millions.
Furthermore, suppliers who offer unique technologies or proprietary parts, making it difficult for Atlas Copco to find viable alternatives, can command higher prices. This situation is exacerbated if suppliers have the potential to integrate forward into Atlas Copco's business, directly competing with their product lines, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
| Factor | Impact on Atlas Copco | Example/Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased supplier leverage, potential for higher prices | Dominance of a few manufacturers for specialized compressor components. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and time for retooling/requalification | Millions of dollars in potential development and disruption costs for proprietary parts. |
| Supplier Uniqueness | Advantage in price negotiations due to proprietary technology | Suppliers of advanced vacuum pump technology for semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Leverage for suppliers to compete directly | Potential for component suppliers to offer finished solutions. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Atlas Copco, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industrial equipment market.
Effortlessly identify competitive threats and opportunities with a visual, interactive model of Atlas Copco's Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Atlas Copco's extensive reach across diverse sectors like manufacturing, construction, and infrastructure globally means its customer base is inherently fragmented. This wide distribution, serving numerous individual buyers rather than a few large ones, significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer or small group.
For customers considering a switch from Atlas Copco's comprehensive offerings, the hurdles can be significant. These switching costs encompass not only the financial outlay for new equipment but also the operational disruption of integrating a new system.
The effort involved in retraining staff on new machinery and ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure further amplifies these costs. For instance, a manufacturing plant reliant on Atlas Copco's integrated solutions might face weeks of downtime and substantial re-training expenses if they were to switch to a competitor, thereby limiting their bargaining power.
In 2024, the increasing complexity of industrial automation and interconnected systems means these switching costs are likely to remain a strong deterrent. Customers often find that the total cost of ownership, including the intangible costs of disruption and learning curves, makes staying with a familiar, integrated provider like Atlas Copco more economically sensible.
Atlas Copco's commitment to innovation and its development of sustainable productivity solutions, coupled with a diverse brand portfolio, allows it to offer highly differentiated products. This strategic focus on unique value propositions, rather than just price, builds strong brand loyalty among its customer base.
This product differentiation and the established reputation of Atlas Copco's brands significantly reduce customers' price sensitivity. Consequently, their inclination to switch to competitors based solely on cost is diminished, effectively lowering their overall bargaining power.
Customer price sensitivity and volume
Atlas Copco's customers, particularly large industrial clients making substantial capital expenditures on equipment such as compressors or mining machinery, can wield significant bargaining power. This power is amplified by their purchase volume, allowing them to negotiate more favorable pricing.
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor. Recent market trends, including a reported slowdown in industrial activity, suggest that customers may become more inclined to seek lower prices. This heightened sensitivity can translate into greater pressure on Atlas Copco to adjust its pricing strategies.
- Significant capital investments by customers in machinery like compressors and mining equipment increase their leverage.
- Weakening customer activity levels, observed in recent market reports, can heighten price sensitivity.
- Higher purchase volumes for large industrial clients translate to greater bargaining power.
Availability of alternative solutions
Customers often have a wide array of alternative solutions readily available from numerous competitors in the industrial equipment sector. This means that if Atlas Copco's pricing, product features, or service levels aren't perceived as superior or competitive, buyers can easily switch to another supplier. For instance, in the compressed air market, while Atlas Copco offers integrated solutions, customers can also source compressors, dryers, and filters from separate providers, potentially at a lower aggregate cost, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
The availability of these alternatives, even if they are less integrated or specialized, grants customers significant leverage. This is particularly true when Atlas Copco's pricing or service package isn't deemed sufficiently attractive. For example, in 2024, the industrial equipment market continued to see robust competition, with many manufacturers offering comparable products. This competitive landscape directly impacts Atlas Copco's ability to command premium pricing or enforce less favorable terms, as customers can readily compare offerings and costs across the market.
- Broad Market Competition: Numerous manufacturers offer comparable industrial equipment, providing customers with a wide selection of alternatives.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can leverage alternative offerings to negotiate better prices or terms with Atlas Copco.
- Integrated vs. Modular Solutions: While Atlas Copco might offer integrated systems, customers can opt for modular solutions from different vendors, potentially reducing overall costs.
- Market Dynamics in 2024: The industrial equipment sector in 2024 remained highly competitive, reinforcing customer bargaining power due to the readily available alternatives.
While large customers with significant purchase volumes can exert considerable bargaining power, Atlas Copco's fragmented customer base generally limits the leverage of individual buyers. The substantial switching costs associated with integrating new equipment, coupled with Atlas Copco's focus on product differentiation and brand loyalty, further diminish customers' ability to dictate terms. Market conditions in 2024, however, saw some customers exhibiting increased price sensitivity due to economic factors, prompting closer scrutiny of pricing strategies.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Atlas Copco's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low (Fragmented base) | Wide product portfolio reduces reliance on any single customer segment. |
| Switching Costs | High (Financial, operational, retraining) | Focus on integrated solutions and long-term customer relationships. |
| Product Differentiation | Low (Unique value propositions) | Investment in R&D for sustainable and advanced productivity solutions. |
| Price Sensitivity (2024 Trend) | Moderate (Increased due to economic climate) | Value-based pricing and service packages to justify costs. |
Full Version Awaits
Atlas Copco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Atlas Copco Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. You'll gain detailed insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, providing valuable strategic intelligence without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Atlas Copco operates in highly competitive markets, facing rivals like Ingersoll Rand, Gardner Denver, and Hitachi, particularly in the industrial air compressor segment. These established global players possess significant manufacturing capabilities and extensive distribution networks, directly challenging Atlas Copco's market share.
Industry growth rates significantly shape competitive rivalry. While the broader industrial equipment market shows positive momentum, specific sectors exhibit diverse expansion. For example, the industrial air compressor market is anticipated to expand, and the mining equipment sector is also experiencing robust growth, both of which can heighten competition for market share among players like Atlas Copco.
Atlas Copco differentiates itself through a strong focus on product innovation, particularly in areas like energy-efficient Variable Speed Drive (VSD) compressors and the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for smart monitoring and control. This strategy aims to create unique value propositions and move away from pure price competition.
While Atlas Copco invests heavily in research and development, its competitors are also actively developing similar advanced technologies. For instance, in 2023, the industrial compressed air market saw significant R&D spending across major players, with companies like Ingersoll Rand and Sullair also pushing advancements in energy efficiency and digital connectivity, intensifying the rivalry.
High fixed costs and exit barriers
The industrial equipment manufacturing sector, where Atlas Copco operates, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include significant investments in research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and extensive global distribution and service networks. For instance, establishing a new advanced manufacturing facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
These high upfront investments and the specialized nature of assets create formidable exit barriers. Companies find it difficult and costly to divest or repurpose specialized machinery and facilities, compelling them to remain operational and compete aggressively, even when market demand softens. This can lead to intense price competition as firms strive to cover their fixed costs.
- High R&D Spending: Companies in this sector often allocate 5-10% of their revenue to R&D to stay competitive, representing a significant fixed cost.
- Capital Intensive Manufacturing: Building and maintaining advanced manufacturing facilities requires billions in capital expenditure over time.
- Global Supply Chains: Establishing and managing worldwide distribution and service networks adds another layer of high fixed costs.
- Specialized Assets: Equipment and infrastructure are often highly specialized, limiting resale value and increasing exit costs.
Acquisition strategy and market consolidation
Atlas Copco's aggressive acquisition strategy, marked by 33 acquisitions in 2024 alone, significantly intensifies competitive rivalry. This proactive approach to market consolidation not only bolsters Atlas Copco's position but also signals a broader trend where larger players absorb smaller competitors, reshaping the industry landscape.
The pursuit of acquisitions fuels a dynamic where companies must constantly assess their competitive standing and strategic options. This consolidation can lead to fewer, larger competitors dominating market segments, thereby increasing the pressure on remaining independent firms.
- Market Consolidation Driver: Atlas Copco's 33 acquisitions in 2024 highlight its role in driving industry consolidation.
- Increased Competitive Pressure: This strategy intensifies rivalry by strengthening dominant players and potentially squeezing smaller competitors.
- Strategic Imperative: For other firms, this trend necessitates a proactive approach to market positioning and potential strategic alliances or divestitures.
The competitive rivalry within the industrial equipment sector, particularly for Atlas Copco, is intense due to the presence of well-established global players. Companies like Ingersoll Rand and Gardner Denver possess substantial manufacturing capacities and expansive distribution networks, directly challenging Atlas Copco's market share and forcing a constant drive for innovation and efficiency.
High fixed costs, driven by significant investments in R&D, advanced manufacturing facilities, and global supply chains, create substantial exit barriers. This compels firms to compete aggressively to cover their costs, often leading to price sensitivity and a focus on technological differentiation, as seen with Atlas Copco's emphasis on VSD compressors and IoT integration.
The market is also experiencing significant consolidation, exemplified by Atlas Copco's aggressive acquisition strategy, completing 33 acquisitions in 2024. This trend intensifies rivalry by strengthening dominant players and increasing pressure on smaller competitors to either scale up, form alliances, or risk being acquired.
Industry growth rates vary across segments, influencing competitive dynamics. While the overall industrial equipment market shows positive momentum, specific sectors like industrial air compressors and mining equipment are experiencing robust growth, attracting more competition as players vie for increased market share.
| Competitor | Key Product Segments | Approximate 2024 Revenue (USD Billions) | R&D Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingersoll Rand | Compressors, Power Tools, Fluid Management | ~10.0 | Energy efficiency, digital solutions, sustainability |
| Gardner Denver | Compressors, Pumps, Blowers | ~8.0 | Industrial IoT, performance optimization, emission reduction |
| Hitachi | Industrial Machinery, Construction Equipment | Varies by segment, significant in industrial equipment | Automation, energy management, advanced materials |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for industrial compressed air systems is growing. Direct electrical actuation or hydraulic systems can replace pneumatic tools in many scenarios, particularly when energy efficiency is a top priority. For instance, electric screwdrivers and drills offer comparable performance with lower energy consumption compared to their pneumatic counterparts.
Furthermore, advancements in battery technology are significantly reducing the need for traditional power sources in industrial tools. This shift means that portable, battery-powered tools are becoming increasingly viable alternatives, directly challenging the market for compressed air-dependent equipment and potentially impacting the demand for Atlas Copco's core offerings.
Industries are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency, prompting a search for alternative process designs that reduce reliance on compressed air or vacuum systems. For instance, advancements in additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, can streamline production processes, potentially lessening the need for traditional pneumatic tools in certain applications. This shift could represent a significant substitute threat for companies heavily invested in compressed air technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Atlas Copco's equipment and services is amplified by the growing trend of outsourcing. Instead of purchasing and maintaining their own industrial machinery, many companies are turning to equipment rental services or comprehensive outsourced solutions. This can be seen as a substitute for direct equipment sales and the ongoing maintenance contracts that Atlas Copco typically provides.
This shift doesn't necessarily replace the core product but rather alters the business model by offering a service-based alternative. For instance, the global equipment rental market was projected to reach over $115 billion in 2024, indicating a substantial shift towards rental rather than ownership.
Evolution of manufacturing and construction methods
The evolution of manufacturing and construction methods presents a significant threat of substitutes for Atlas Copco. For instance, the rise of modular construction, where building components are prefabricated off-site, can reduce the on-site need for certain heavy equipment and tools that Atlas Copco traditionally supplies. Similarly, advancements in additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, are beginning to create complex parts and even entire structures with less reliance on traditional machinery, potentially impacting demand for specialized industrial equipment.
This shift means that companies in these sectors might find alternative ways to achieve their production goals without needing the same types of tools or machinery Atlas Copco specializes in. For example, if a construction firm can assemble a building more efficiently using pre-fabricated modules, their need for on-site drilling or fastening equipment might decrease. In 2024, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately $150 billion, indicating a substantial and growing segment that could adopt alternative methods.
- Modular Construction Growth: The global modular construction market is projected to reach over $250 billion by 2028, signaling a significant shift in building practices.
- Additive Manufacturing Adoption: Additive manufacturing is increasingly used for producing specialized components in aerospace and automotive, areas where traditional manufacturing might have relied on Atlas Copco's equipment.
- Tooling Requirements: New methods may require different, potentially less specialized or entirely new categories of tools, bypassing existing Atlas Copco product lines.
- Reduced Reliance on Traditional Machinery: As these alternative methods mature, the overall demand for certain types of heavy industrial machinery could see a relative decline.
Shift towards sustainable and electric alternatives
The growing global emphasis on sustainability and decarbonization is a significant factor influencing the threat of substitutes for Atlas Copco. This trend is directly fueling demand for electric and hybrid equipment within the mining and construction sectors, areas where Atlas Copco is a major player.
While Atlas Copco is actively developing and offering its own range of electric and hybrid solutions, the rapid pace of technological advancement in these green alternatives presents a continuous challenge. New innovations could emerge, offering even more efficient or cost-effective substitutes that could disrupt Atlas Copco's existing product lines.
- Growing Market Share for Electric Mining Equipment: By 2024, the global electric mining equipment market was projected to reach over $10 billion, indicating a substantial shift away from traditional diesel-powered machinery.
- Technological Advancements in Battery Technology: Improvements in battery energy density and charging infrastructure are making electric alternatives more viable and competitive, potentially eroding the market for conventional equipment.
- Regulatory Pressures: Increasingly stringent environmental regulations in key markets are incentivizing the adoption of zero-emission equipment, further accelerating the threat of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for industrial compressed air systems is growing, with direct electrical actuation and hydraulic systems becoming viable alternatives, especially where energy efficiency is paramount. For example, electric tools often consume less energy than their pneumatic counterparts. Advancements in battery technology are also making portable, battery-powered tools a strong substitute for compressed air-dependent equipment, impacting demand for Atlas Copco's core products.
Industries are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency, leading to the exploration of alternative process designs that reduce reliance on compressed air. Innovations like additive manufacturing (3D printing) can streamline production, potentially lessening the need for traditional pneumatic tools in specific applications. This represents a significant substitute threat for companies heavily invested in compressed air technologies.
The trend toward outsourcing and equipment rental services presents another substitute threat. Instead of owning and maintaining machinery, many companies opt for rental or comprehensive outsourced solutions. This alters the business model by offering a service-based alternative to direct equipment sales and maintenance contracts. The global equipment rental market, projected to exceed $115 billion in 2024, highlights this substantial shift towards rental over ownership.
Entrants Threaten
The industrial equipment manufacturing sector, particularly for sophisticated machinery such as compressors, vacuum systems, and mining equipment, necessitates substantial capital outlays. These investments are crucial for research and development, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and building extensive global distribution and service networks.
For instance, setting up a new production line for advanced industrial compressors can easily run into tens of millions of dollars. This high barrier to entry significantly deters potential new competitors from challenging established players like Atlas Copco, who have already made these significant investments.
Established brand reputation and customer relationships pose a significant barrier for new entrants. Atlas Copco, with a history dating back to 1873, has cultivated a robust global brand synonymous with reliability and high performance. This long-standing presence has allowed them to forge deep, trust-based relationships with a diverse industrial customer base, supported by extensive and dependable service networks.
New companies entering the market would face considerable challenges in replicating this level of trust and customer loyalty. Building a comparable reputation and the intricate web of customer relationships that Atlas Copco enjoys would require substantial time, investment, and a proven track record of consistent quality and service delivery, making it difficult to compete effectively against such an entrenched player.
Atlas Copco's significant investment in research and development, evidenced by its substantial patent portfolio, acts as a formidable barrier to entry. For instance, their advancements in variable speed drive (VSD) compressors and specialized industrial tools require potential competitors to either develop comparable, costly technologies or face immediate competitive disadvantages.
Extensive distribution and service networks
Atlas Copco's extensive global sales and service network presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This vast infrastructure, crucial for providing comprehensive after-sales support and maintenance, requires substantial investment and time to replicate. For instance, in 2023, Atlas Copco maintained operations in over 180 countries, underscoring the sheer scale of their reach.
New competitors would face immense challenges in establishing a comparable network, hindering their ability to effectively reach and serve a broad customer base. The cost and complexity of building out a responsive service and distribution system globally are prohibitive for most emerging players. This existing network advantage allows Atlas Copco to offer superior customer experience and quicker response times, a critical differentiator in the industrial equipment market.
- Vast Global Reach: Atlas Copco operates in over 180 countries, demonstrating the scale of its distribution network.
- Comprehensive Support: The company provides extensive after-sales service and maintenance, a critical factor for industrial customers.
- High Entry Costs: Replicating such an extensive and responsive network requires significant capital and operational expertise, deterring new entrants.
- Customer Retention: The established network fosters customer loyalty through reliable support and accessibility.
Regulatory hurdles and certifications
The industrial equipment sector, where Atlas Copco operates, faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory requirements and the need for various certifications. These regulations often pertain to safety, environmental impact, and performance standards, varying considerably across different geographical markets.
New companies looking to enter this industry must invest substantial resources and time to understand and comply with these complex legal frameworks. For instance, obtaining certifications like CE marking in Europe or UL certification in North America for electrical equipment is a mandatory and often lengthy process.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: Adhering to safety and environmental standards can add 5-15% to initial product development costs for new entrants.
- Certification Timelines: Obtaining necessary certifications can take anywhere from 6 months to over 2 years, delaying market entry.
- Regional Variations: Navigating differing regulations in key markets like the EU, US, and China significantly increases complexity and expense.
- Impact on R&D: New entrants must factor in the cost of redesigning products to meet diverse international standards, potentially limiting innovation speed.
The threat of new entrants in the industrial equipment sector, where Atlas Copco operates, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital requirements for research, development, manufacturing, and establishing global distribution and service networks. For example, developing a new generation of energy-efficient industrial compressors can cost upwards of $50 million.
Furthermore, established brand reputation and deep customer relationships, built over decades, create significant hurdles for newcomers. Atlas Copco's brand, recognized for reliability, is supported by a vast service network operating in over 180 countries as of 2023, making it difficult for new players to match this level of customer trust and accessibility.
Stringent regulatory requirements and the need for various certifications, such as CE marking and UL certification, also act as formidable barriers. These compliance processes can add 5-15% to initial product development costs and delay market entry by up to two years, further deterring potential competitors.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example for Atlas Copco |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Deters new companies due to upfront costs. | Setting up a new advanced compressor plant can cost tens of millions of dollars. |
| Brand Reputation & Relationships | Long-standing trust and loyalty from customers. | New entrants struggle to build comparable credibility. | Atlas Copco's 150+ year history fosters deep customer relationships. |
| Regulatory & Certification Hurdles | Compliance with safety, environmental, and performance standards. | Increases costs and time-to-market for new players. | Obtaining CE marking in Europe can take 6-18 months. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale production. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs. | Atlas Copco's global production volumes lead to lower manufacturing costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Atlas Copco leverages data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit and Statista to assess competitive dynamics.
