ATI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ATI Bundle
ATI's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful industry forces, from the bargaining power of its customers to the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ATI’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ATI's reliance on specialized raw materials such as titanium sponge and nickel significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. These materials are critical for aerospace and defense, where performance demands are exceptionally high.
The unique, often non-negotiable properties of these metals mean that few, if any, alternative materials can adequately substitute. This lack of alternatives leaves ATI with limited options, making them more susceptible to price increases from suppliers who hold strong market positions.
For instance, the global titanium sponge market, a key input for ATI, saw prices fluctuate significantly in 2024 due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand from the aerospace sector. This volatility underscores the power of suppliers when substitutes are scarce.
The market for high-performance metals and alloys, crucial for ATI's operations, is characterized by a concentrated supplier base. This means there are typically only a handful of highly specialized companies capable of producing these materials.
This limited number of suppliers grants them significant leverage. They can often dictate pricing and terms to buyers like ATI, as ATI has fewer alternative sources for its essential raw materials. For instance, the titanium industry, a key area for ATI, is dominated by a few major global players, directly influencing the cost of titanium alloys.
High switching costs significantly bolster the bargaining power of ATI's suppliers. For instance, if ATI needs to change its supplier for specialized aerospace alloys, the process can involve extensive re-qualification of the new material, which can take months and cost millions. This is compounded by the need to potentially alter manufacturing processes and risk production delays, making it economically prohibitive to switch. In 2023, ATI reported significant investments in advanced manufacturing capabilities, highlighting the specialized nature of its inputs.
Proprietary Technologies and Expertise
Some suppliers may hold a significant edge due to proprietary technologies or specialized expertise in crafting critical advanced alloys or components essential for ATI's high-performance products. This unique knowledge base translates directly into enhanced bargaining power for these suppliers.
ATI's reliance on these select suppliers for cutting-edge materials, which are often not readily available elsewhere, further amplifies the suppliers' leverage. For instance, in the aerospace sector, where material innovation is paramount, suppliers with patented manufacturing processes for specialized titanium alloys could command premium pricing and dictate terms.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with unique, patented manufacturing processes for advanced materials.
- Specialized Expertise: Deep knowledge in producing niche, high-specification alloys or components.
- Critical Input: Materials that are indispensable for ATI's product performance and innovation.
- Limited Alternatives: Few, if any, comparable suppliers exist in the market.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration, meaning they might start manufacturing components that ATI currently produces or even begin selling directly to ATI's customers, represents a potential shift in bargaining power. This scenario, while less frequent, could occur if a key supplier possessed the necessary capital and specialized knowledge to bypass ATI's role in the value chain.
Should a significant supplier decide to vertically integrate forward, they could potentially capture a larger portion of the profit margin and diminish ATI's market share. For instance, if a supplier of advanced aerospace materials began producing finished, complex sub-assemblies, it would directly compete with ATI's own manufacturing capabilities.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers may move into ATI's manufacturing processes or directly serve ATI's customers.
- Impact on ATI: Reduced market share and increased supplier leverage if they produce complex components.
- Mitigating Factors: High capital investment and specialized expertise are significant barriers for suppliers.
The bargaining power of ATI's suppliers is substantial, driven by the critical nature of specialized materials like titanium sponge and nickel, which have few viable substitutes. This reliance is amplified by a concentrated supplier base where a few dominant players dictate terms, as seen with global titanium producers influencing alloy costs.
High switching costs, involving extensive re-qualification and potential production disruptions, further solidify supplier leverage. For example, the significant investments ATI made in advanced manufacturing in 2023 highlight the specialized nature of its inputs, making supplier changes costly and time-consuming.
Proprietary technologies and specialized expertise held by suppliers of advanced alloys also grant them considerable power, enabling premium pricing. The threat of forward integration by suppliers, though less common, could further challenge ATI's market position by directly competing in manufacturing or customer supply.
| Factor | Impact on ATI | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base | Limited sourcing options, increased price leverage for suppliers | Dominance of a few global players in titanium production |
| High Switching Costs | Economic disincentive to change suppliers, locking ATI in | Months-long re-qualification processes, millions in costs |
| Criticality of Inputs | Essential materials for high-performance products, non-negotiable quality | Titanium sponge price volatility due to supply chain issues |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers with unique processes command premium pricing | Patented manufacturing for specialized titanium alloys |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to ATI's specific industry context.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive threats with a dynamic, visual representation of each force.
Gain a clear, actionable understanding of industry profitability drivers and potential vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
ATI's high-performance titanium and nickel-based alloys are crucial for demanding sectors like aerospace, defense, and medical. These materials are not easily substituted due to their specialized nature and the critical performance and safety standards they must meet. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace industry continued to rely heavily on advanced materials for new aircraft development and upgrades, where ATI's products are indispensable.
The stringent requirements for these applications mean customers have limited alternative suppliers, thereby diminishing their bargaining power. This differentiation is a key factor in ATI's ability to maintain pricing and secure long-term contracts. The specialized manufacturing processes and certifications required for these alloys create significant barriers to entry for potential competitors.
ATI frequently enters into long-term agreements and strategic partnerships with its significant customers, especially within the aerospace and defense industries. These arrangements ensure predictable demand, thereby diminishing customer influence on pricing because they are contractually obligated to purchase from ATI over extended durations.
These commitments offer substantial benefits for ATI. For instance, in 2023, ATI announced securing $4 billion in new sales commitments extending through 2040. This substantial backlog is largely driven by demand for ATI's advanced nickel alloys, crucial components for the jet engine market, solidifying ATI's customer relationships and reducing the bargaining power of these customers.
The materials ATI supplies are absolutely essential for customers' high-value products, including jet engines, airframes, and critical medical devices. This means that even if ATI’s materials represent a notable cost, their performance and unwavering reliability are far more important to customers than a slight price difference.
Because ATI's materials are so vital to the function and success of their customers' end products, customers are less likely to switch suppliers based on price alone. For example, in the aerospace industry, the failure of a single component can have catastrophic consequences, making the proven quality of ATI's materials a non-negotiable factor.
Fragmented Customer Base (in some segments)
While ATI's significant business is with major aerospace and defense contractors, it also caters to sectors like electronics and specialty energy. In these latter segments, the customer base can be more dispersed, meaning individual buyers typically hold less sway when negotiating prices or specific contract conditions.
This fragmentation in certain markets limits the collective bargaining power of customers. For example, in 2024, ATI's diverse end-market exposure, including a significant portion in specialty materials beyond aerospace, helped mitigate the impact of any single customer group's demands.
- Fragmented customers in specialty sectors reduce individual customer leverage.
- ATI's broad market reach dilutes the power of any single customer segment.
- Diversification across electronics and specialty energy provides a buffer against concentrated customer demands.
Customer Switching Costs
For ATI's customers, the cost of switching to a different material supplier can be substantial. This is primarily due to the stringent qualification processes, regulatory approvals, and performance validation that are mandatory in industries like aerospace and medical devices. These hurdles create significant barriers, effectively limiting the bargaining power customers might otherwise wield.
The rigorous testing and certification required for materials used in critical applications like aerospace and medical fields act as a strong deterrent to switching. This is particularly true for customers utilizing established platforms and designs where re-validation of new materials would be both time-consuming and expensive. For instance, in the aerospace sector, a single material change on a legacy aircraft program could necessitate extensive recertification, potentially costing millions and delaying production.
- High Qualification Costs: Customers face significant expenses in qualifying new material suppliers, often involving extensive testing and validation.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Industries like aerospace and medical require lengthy and complex regulatory approval processes for material changes, adding to switching costs.
- Performance Validation: Ensuring that alternative materials meet the exact performance specifications of existing ones is a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
- Established Platforms: For existing aircraft or medical device designs, the inertia of established materials and the cost of re-certification heavily favor the incumbent supplier.
The bargaining power of ATI's customers is generally low due to the specialized nature of its high-performance alloys and the critical applications they serve. In 2024, the aerospace sector, a key market for ATI, continued to demand materials with exceptional reliability, limiting customer flexibility in supplier choice.
Switching costs for ATI's customers are substantial, involving rigorous qualification and regulatory approval processes, especially in aerospace and medical industries. For example, recertifying a material for an existing aircraft program can cost millions and cause significant production delays, reinforcing customer reliance on established suppliers like ATI.
While ATI serves diverse markets, including electronics and specialty energy, the concentrated nature of its aerospace and defense business means these major clients have significant purchasing volume. However, the indispensable nature of ATI's materials in these high-value end products, such as jet engines, mitigates the customers' ability to leverage their buying power for price concessions.
What You See Is What You Get
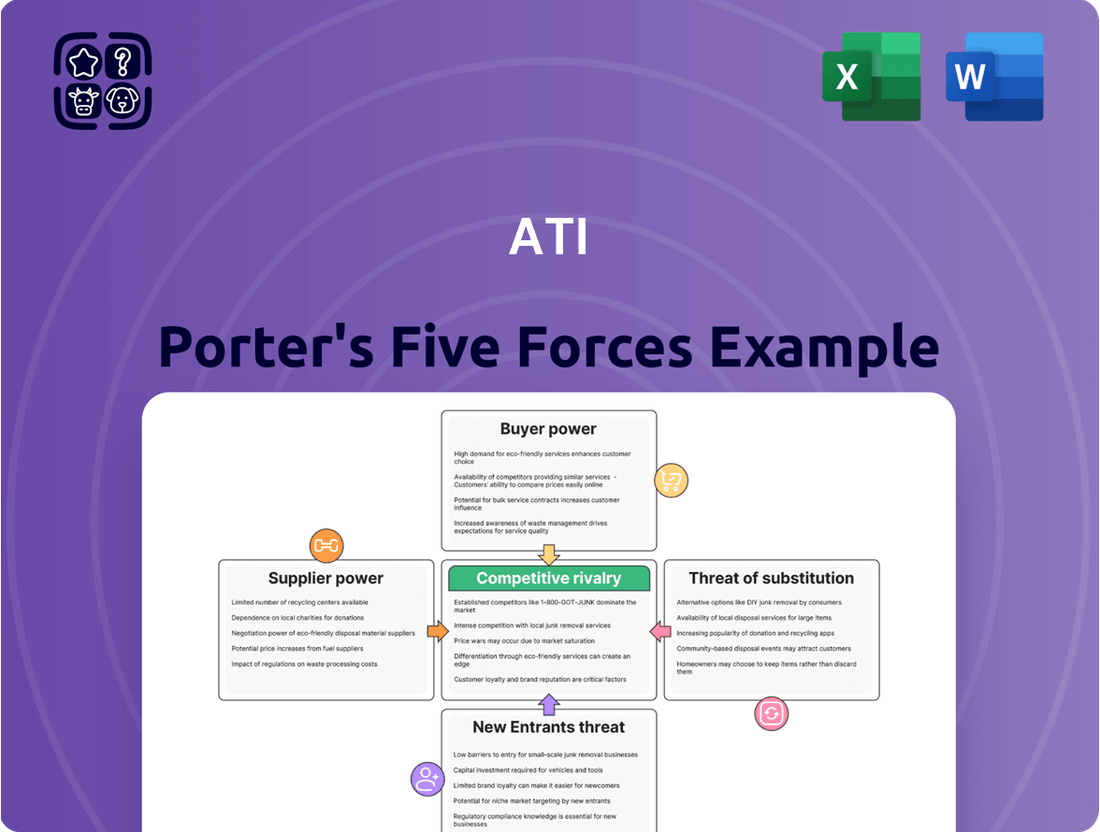
ATI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ATI Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see is the exact, professionally formatted analysis that will be available for immediate download upon purchase, ensuring you get precisely what you need for your strategic planning. No placeholders or sample content, just the full, ready-to-use strategic framework.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The specialty metals and high-performance alloys sector is quite consolidated, with a few dominant companies like ATI, VSMPO-AVISMA, TIMET, and Carpenter Technology. This means competition is fierce as these major players vie for market share and crucial long-term supply agreements.
This high industry concentration naturally drives intense rivalry, often centered on innovation and the superior performance of their advanced material solutions. For instance, ATI's focus on aerospace and defense markets, where performance is paramount, highlights this competitive dynamic.
Competitive rivalry at ATI is intense, largely fueled by a relentless pursuit of technological innovation. Companies vie to develop and produce materials with demonstrably superior properties, moving beyond simple price competition. This focus on differentiation through advanced materials science and manufacturing processes is key to ATI's strategy.
ATI's commitment to materials science and its sophisticated manufacturing capabilities enable the creation of unique alloys. These specialized materials offer distinct advantages, such as enhanced strength, corrosion resistance, or thermal stability, which command premium pricing and reduce direct head-to-head price wars. For instance, ATI's development of advanced nickel-based superalloys for aerospace applications highlights this value-driven approach.
In 2023, ATI reported significant investments in research and development, underscoring the critical nature of innovation in maintaining its competitive standing. This ongoing commitment to R&D is not just about creating new products but also about refining existing ones and optimizing production, ensuring ATI remains at the forefront of materials technology and can effectively counter competitive pressures.
The aerospace and defense sector, a key area for ATI, is characterized by exceptionally long sales cycles, often spanning several years from initial contract negotiation to final delivery. This extended timeline, coupled with the immense capital required for advanced manufacturing, sophisticated R&D, and stringent regulatory compliance, creates formidable barriers to entry. For instance, developing a new commercial aircraft can cost tens of billions of dollars, a sum prohibitive for most new market entrants.
These high upfront costs and lengthy revenue generation periods significantly stabilize the competitive landscape. Established players, like ATI, benefit from their existing infrastructure and market relationships, making it difficult for smaller or newer companies to compete effectively on scale or cost. In 2024, the global aerospace market was valued at approximately $900 billion, with a significant portion tied to long-term defense contracts and large commercial aircraft orders, underscoring the capital-intensive nature of the industry.
Global Market Reach
ATI operates within a global aerospace and defense market, meaning it contends with international competitors. This worldwide reach means rivals can originate from any region, creating intense pressure on pricing, product quality, and the ability to deliver on time. For example, in 2024, the aerospace sector continued to see significant global competition, with major players like Boeing and Airbus, alongside emerging manufacturers in Asia, vying for market share.
The interconnectedness of the global aerospace and defense supply chain further amplifies this rivalry. Companies must constantly innovate and optimize their operations to remain competitive against a diverse set of players, each with unique strengths and cost structures. Geopolitical shifts and evolving trade policies also play a crucial role, potentially altering market access and competitive advantages for ATI and its rivals.
- Global Competition: ATI faces direct competition from established international aerospace and defense manufacturers.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: The global nature of the supply chain allows rivals from various regions to challenge ATI on price, quality, and delivery.
- Geopolitical Influence: International trade policies and geopolitical events can significantly impact the competitive landscape for ATI.
Strategic Partnerships and Long-Term Contracts
A significant factor in competitive rivalry involves establishing strategic partnerships and securing long-term supply contracts with key customers. ATI actively seeks these arrangements to guarantee consistent demand and mitigate intense competition. For instance, in 2024, ATI's commitment to multi-year agreements with major aerospace and defense manufacturers solidified its market standing, providing a predictable revenue stream and a competitive edge.
These long-term commitments act as a substantial barrier to entry for new competitors. By locking in significant portions of customer demand, ATI makes it more challenging for rivals to gain market share. The company's ability to offer reliable, long-term supply solutions is a critical differentiator.
- Securing long-term contracts: ATI's focus on multi-year agreements with major clients in 2024 provides revenue stability.
- Reduced competitive pressure: These partnerships limit the ability of competitors to attract ATI's key customers.
- Market share protection: Long-term commitments help safeguard ATI's existing market share.
- Customer loyalty: Strategic partnerships foster stronger relationships and customer loyalty.
Competitive rivalry in the specialty metals sector is intense, driven by a few dominant players like ATI, VSMPO-AVISMA, TIMET, and Carpenter Technology. This concentration means companies fiercely compete on innovation and material performance, especially in demanding markets like aerospace. ATI's strategy emphasizes developing advanced alloys with superior properties, which reduces direct price competition and creates value.
In 2024, ATI's significant R&D investments highlight the crucial role of innovation in staying ahead. The aerospace and defense markets, where ATI is a major player, are capital-intensive with long sales cycles, creating high barriers to entry. For example, the global aerospace market was valued around $900 billion in 2024, underscoring the scale of investment required.
ATI faces global competition, with rivals from various regions challenging its market position on price, quality, and delivery. Strategic partnerships and long-term supply contracts, like those ATI secured in 2024 with major aerospace manufacturers, are key to mitigating this rivalry by ensuring stable demand and customer loyalty.
| Key Competitors | Market Focus | Competitive Strategy Example |
| VSMPO-AVISMA | Aerospace, Industrial | Large-scale production of titanium products |
| TIMET | Aerospace, Medical, Industrial | Specialization in titanium and titanium alloys |
| Carpenter Technology | Aerospace, Defense, Medical | High-performance specialty alloys, powder metallurgy |
| ATI (Allegheny Technologies Incorporated) | Aerospace, Defense, Energy, Medical | Advanced materials, innovation, long-term customer partnerships |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary threat of substitutes for traditional high-performance metals in aerospace stems from advanced composites like carbon fiber reinforced polymers and lightweight alloys such as aluminum-lithium. These materials boast superior strength-to-weight ratios, directly impacting fuel efficiency and performance. For instance, by 2024, the global advanced composites market is projected to reach over $20 billion, demonstrating significant growth and adoption.
While composite materials and other advanced materials present alternatives, their performance often falters in demanding conditions where ATI's specialty metals shine. For example, in the extreme heat and pressure found within jet engines, titanium and nickel-based alloys demonstrate superior resistance and structural integrity, making them difficult to replace in critical applications.
The threat of substitutes for advanced materials, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, is significantly dampened by high qualification and certification barriers. These processes are not merely checks; they involve rigorous testing, validation, and often years of proving material performance and safety in demanding environments. For instance, a new alloy intended for an aircraft component must undergo extensive fatigue testing, corrosion resistance studies, and flight-testing simulations, a process that can cost millions and take over five years to complete.
These substantial regulatory hurdles and the imperative for proven reliability create a high switching cost for customers. Businesses in these critical industries are hesitant to adopt unproven alternatives due to the immense risk to product safety, performance, and potential liability. In 2024, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) continues to enforce stringent material approval processes, making it exceptionally challenging for new entrants to gain traction without demonstrating an equivalent or superior safety and performance record.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs
Customers often weigh a delicate balance between cost and performance when choosing materials. While a substitute might appear cheaper upfront, its overall value proposition, considering factors like durability and upkeep, can be significantly lower compared to ATI's advanced offerings.
For instance, in the aerospace sector, a lower-cost alternative might not withstand the extreme temperatures and stresses that ATI's specialized alloys are engineered for, leading to higher lifecycle costs and potential safety concerns. This performance gap is a critical factor in customer retention.
In 2024, the global aerospace market, a key sector for ATI, was valued at approximately $900 billion, with material innovation being a significant driver of competitiveness. This highlights the substantial financial implications of material selection.
- Cost vs. Performance: Customers scrutinize initial price against long-term operational benefits.
- Lifecycle Value: Maintenance, durability, and suitability for demanding environments are key differentiators.
- Market Context (2024): The aerospace industry, valued around $900 billion, demonstrates the financial impact of material choices.
- ATI's Advantage: Specialized materials often outperform cheaper substitutes in critical applications, justifying their premium.
Continuous Material Innovation by ATI
ATI's commitment to continuous material innovation significantly mitigates the threat of substitutes. The company's substantial investment in research and development, evidenced by their ongoing focus on new specialty alloy formulations, directly addresses this. For instance, ATI's 2023 R&D expenditure was approximately $150 million, a key driver in developing advanced materials that outperform existing alternatives in critical sectors like aerospace and defense.
By consistently improving the performance characteristics of its alloys, such as enhanced strength-to-weight ratios or improved corrosion resistance, ATI makes it more challenging for substitute materials to offer a comparable value proposition. This proactive approach ensures that ATI's proprietary materials remain the superior choice for high-demand applications where performance is paramount, thereby solidifying their market position against potential threats.
- Ongoing R&D Investment: ATI dedicates significant resources to developing next-generation specialty alloys.
- Performance Enhancement: Focus on improving material properties to outpace substitutes.
- Competitive Edge: Innovation maintains ATI's leadership in demanding applications.
- Market Preference: Superior performance ensures ATI's materials are the preferred choice.
The threat of substitutes for ATI's specialty metals is generally low due to high switching costs and performance requirements. While advanced composites and lightweight alloys exist, they often cannot match the extreme temperature and pressure resistance of ATI's titanium and nickel-based alloys in critical applications like jet engines. The extensive certification and qualification processes for new materials in sectors like aerospace, which can take years and cost millions, further deter customers from adopting unproven alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the FAA's strict material approval processes continue to be a significant barrier for new entrants.
| Material Type | Key Differentiator | Substitute Threat Level | Switching Cost Factor | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATI Specialty Metals (e.g., Titanium, Nickel Alloys) | Extreme temperature & pressure resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio | Low | High (Certification, Reliability) | Aerospace, Defense, Medical |
| Advanced Composites (e.g., Carbon Fiber) | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | Moderate (in non-extreme applications) | Moderate (Performance limitations in heat) | Aerospace (structures), Automotive |
| Lightweight Alloys (e.g., Aluminum-Lithium) | Lightweight | Moderate (Performance limitations in heat/pressure) | Moderate (Performance limitations in heat) | Aerospace (structures) |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty metals industry demands substantial capital for advanced manufacturing facilities, specialized equipment, and ongoing research and development. For instance, establishing a new, state-of-the-art specialty metals plant can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, making it a daunting entry point.
Newcomers face significant challenges in achieving the economies of scale that drive cost competitiveness. ATI, with its established, large-scale operations, benefits from lower per-unit production costs, a hurdle that new entrants must overcome to compete effectively on price.
The development of high-performance metals, such as titanium and nickel-based alloys, requires significant investment in research and development, coupled with deep materials science expertise. For instance, ATI's own advanced manufacturing capabilities for aerospace components represent years of accumulated knowledge and capital expenditure. This intricate process, involving proprietary technologies and specialized know-how, acts as a substantial deterrent for potential newcomers, demanding immense resources and time to replicate.
The aerospace, defense, and medical sectors, critical markets for ATI, are heavily regulated. Obtaining certifications like FAA approval for aerospace components or FDA clearance for medical-grade alloys is a complex, time-consuming, and expensive undertaking. For instance, the development and certification of a new aerospace material can take over a decade and cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
These rigorous standards create a significant barrier to entry. New companies must invest heavily in research, development, testing, and compliance, making it difficult to compete with established players like ATI who have already navigated these hurdles and built a reputation for quality and reliability.
Established Customer Relationships and Long-Term Contracts
ATI benefits from deep-rooted customer relationships, especially within the defense and aerospace industries. These long-standing ties, often solidified by multi-year supply agreements, create significant barriers to entry for new competitors. For instance, in 2024, ATI's continued success in securing long-term contracts with major aerospace manufacturers underscores the stickiness of its customer base.
These established connections and the contractual obligations they represent make it exceedingly challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold. New entrants would need to overcome not only technological hurdles but also the inertia and trust built over years of partnership. ATI's consistent renewal of major contracts in 2024, some extending well into the next decade, highlights the formidable nature of these customer relationships as a deterrent.
- Long-Term Contracts: ATI's multi-year agreements with key aerospace and defense clients lock in demand and create switching costs for customers.
- Customer Loyalty: Established relationships foster loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to poach existing business.
- Switching Costs: The integration of ATI's materials into complex manufacturing processes for aerospace and defense applications creates high switching costs for customers.
- Market Penetration Difficulty: New entrants face a steep uphill battle to displace incumbent suppliers like ATI due to these entrenched relationships and contracts.
Access to Raw Materials and Supply Chains
New companies entering the aerospace and defense materials market face significant challenges in securing consistent access to high-quality raw materials like titanium sponge and specialized alloying elements. These materials are critical for producing advanced alloys, and their availability can be volatile.
Established companies, such as ATI, have cultivated long-standing relationships with key suppliers, creating robust and reliable supply chains. This deep integration and preferential access to raw materials present a substantial barrier to entry for newcomers who may struggle to secure the necessary volumes or quality at competitive prices.
- Supply Chain Integration: ATI's established supply chain provides a significant advantage, ensuring material availability and quality control.
- Supplier Relationships: Long-term partnerships with raw material providers offer preferential terms and consistent supply, a difficult advantage for new entrants to replicate.
- Material Scarcity: The specialized nature of certain raw materials, like high-purity titanium sponge, means supply can be limited, favoring existing, high-volume purchasers.
The threat of new entrants in the specialty metals industry, particularly for companies like ATI, is significantly mitigated by several high barriers. These include the immense capital required for advanced manufacturing and R&D, the need to achieve economies of scale for cost competitiveness, and the deep technical expertise and proprietary technologies involved in producing high-performance materials. For instance, the cost of building a new specialty metals facility can easily exceed hundreds of millions of dollars.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements, especially in aerospace and defense, necessitate lengthy and costly certification processes, which new players must navigate. ATI's established customer relationships, often secured by long-term contracts, also create substantial switching costs and customer loyalty, making market penetration extremely difficult for newcomers. In 2024, ATI's continued success in securing long-term aerospace contracts highlights this entrenched market position.
Access to critical raw materials through integrated supply chains and strong supplier relationships further solidifies ATI's competitive advantage, limiting the ability of new entrants to secure necessary inputs reliably and affordably.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for ATI |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of advanced manufacturing facilities and R&D. | Establishing a new specialty metals plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Economies of Scale | Need to match established players' lower per-unit production costs. | ATI's large-scale operations provide a cost advantage over smaller, new entrants. |
| Technical Expertise & IP | Proprietary technologies and deep materials science knowledge. | ATI's advanced manufacturing for aerospace components involves years of accumulated knowledge. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and expensive certifications for critical sectors. | FAA approval for aerospace components can take over a decade and cost hundreds of millions. |
| Customer Relationships & Contracts | Entrenched ties and multi-year agreements create switching costs. | ATI's continued long-term contracts with major aerospace manufacturers in 2024. |
| Supply Chain Integration | Preferential access to raw materials and robust supplier networks. | ATI's established relationships ensure reliable access to titanium sponge and alloying elements. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and public financial disclosures. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive pressures.
