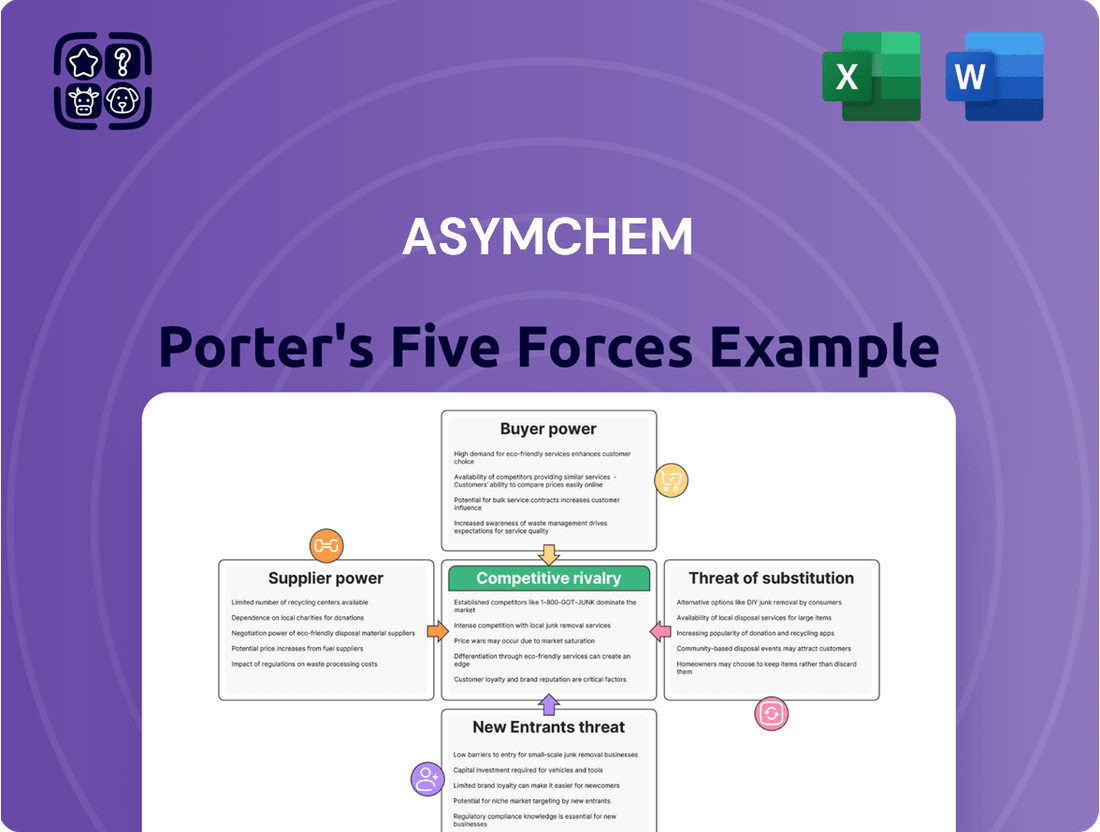
Asymchem Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asymchem Bundle
Asymchem operates in a dynamic pharmaceutical CDMO landscape, where supplier power is moderate due to specialized raw materials, and buyer power is significant as clients seek cost-effective solutions. The threat of new entrants is tempered by high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles, while the threat of substitutes is low given the specialized nature of API manufacturing.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Asymchem’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Asymchem, a leading Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO), depends heavily on suppliers for critical specialized raw materials, advanced intermediates, and sophisticated manufacturing equipment. The highly specific nature of these inputs, particularly for novel drug candidates and intricate molecular structures, often grants suppliers considerable bargaining power.
This supplier leverage is further magnified when there are few alternative sources for these essential components, or when the costs associated with switching suppliers are substantial. Such switching costs can arise from rigorous regulatory qualification processes and the need for extensive process validation, making it challenging for Asymchem to change its supply chain easily.
Suppliers of critical pharmaceutical components and services must meet rigorous quality standards and regulatory requirements, such as current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical excipients market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion, with a significant portion driven by demand for high-purity, compliant materials.
Suppliers demonstrating a consistent history of compliance and delivering superior quality materials are positioned to negotiate higher prices and secure more favorable terms. Asymchem, like other contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), cannot afford to compromise on the quality of its clients' products, making these compliant suppliers indispensable.
This dynamic is especially pronounced for specialized Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and excipients, where the number of qualified suppliers may be limited. In 2023, the global API market size reached an estimated $220 billion, underscoring the critical nature of reliable and compliant API sourcing.
Suppliers that bring cutting-edge technologies, unique chemical components, or advanced manufacturing machinery to the table can command greater influence. Asymchem, dedicated to providing innovative solutions, may find it beneficial to pay more for suppliers who can boost its capabilities, speed up development, or lower overall production expenses for its customers. This is particularly true for breakthroughs in areas such as continuous manufacturing processes or the use of biocatalysis.
Concentration of Suppliers
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Asymchem's bargaining power. If a few dominant suppliers control essential raw materials or specialized technologies, they gain leverage. This can translate into higher input costs and less favorable contract terms for Asymchem, particularly when sourcing niche or proprietary compounds critical for drug development.
For instance, in the Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector, reliance on a limited number of suppliers for advanced intermediates or specific chiral building blocks can create vulnerabilities. This is especially true if these suppliers possess patented processes or unique manufacturing capabilities that are difficult to replicate. Supply chain transparency and building resilience become paramount concerns for CDMOs like Asymchem to mitigate these risks.
- Supplier Concentration: A market with few suppliers for critical inputs grants those suppliers greater negotiation power.
- Impact on Asymchem: Asymchem may face increased costs and less favorable terms when sourcing specialized or patented materials.
- Industry Example: The CDMO sector often relies on specialized chemical suppliers, where a lack of alternatives can empower those suppliers.
Supplier's Forward Integration Threat
While raw material suppliers typically lack the inclination for forward integration into CDMO services, highly specialized technology providers might consider offering such services. This potential threat, though generally low, could enhance their negotiating leverage with Asymchem by positioning them as future direct competitors.
The significant capital investment and stringent regulatory requirements associated with establishing full-scale CDMO operations typically act as substantial barriers, effectively limiting the likelihood of widespread forward integration by suppliers.
- Limited Supplier Forward Integration: Specialized technology providers, not raw material suppliers, are the primary potential integrators.
- Potential Competitive Threat: Forward integration by suppliers could transform them into direct competitors for Asymchem.
- Barriers to Entry: High capital expenditure and regulatory hurdles significantly mitigate this threat for most suppliers.
Asymchem faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to the specialized nature of raw materials and equipment required in the pharmaceutical industry. Limited alternative sources and high switching costs, stemming from regulatory compliance and validation, further empower these suppliers.
Suppliers of critical components like APIs and excipients, which are essential for drug development and manufacturing, hold considerable sway. For instance, the global API market was valued at approximately $220 billion in 2023, highlighting the importance of these suppliers. Furthermore, the pharmaceutical excipients market, valued around $10.5 billion in 2024, demands high-purity materials, giving compliant suppliers leverage.
Suppliers possessing unique technologies or patented processes, particularly in areas like continuous manufacturing or biocatalysis, can command higher prices and favorable terms. This concentration of specialized suppliers can lead to increased input costs for Asymchem, making supply chain resilience and transparency crucial for mitigating risks.
| Factor | Impact on Asymchem | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased costs, less favorable terms | Reliance on niche suppliers for patented compounds |
| Switching Costs | Limited flexibility, supplier leverage | Rigorous regulatory qualification and validation processes |
| Supplier Specialization | Higher prices for advanced capabilities | Demand for high-purity APIs ($220B market in 2023) and excipients ($10.5B market in 2024) |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential competition from technology providers | High capital and regulatory barriers limit widespread integration |
What is included in the product
Asymchem's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity of the pharmaceutical CDMO market, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the impact of substitutes and rivalry.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, visual representation of Asymchem's market position.
Customers Bargaining Power
Asymchem's client base, spanning pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms from emerging biotechs to established giants, directly influences customer bargaining power. A concentration of revenue from a few major clients or high-value projects grants these customers significant leverage. They can then push for reduced pricing, expedited delivery schedules, or more advantageous contract terms.
The pharmaceutical sector, particularly large pharma companies, is projected to show the strongest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) among Asymchem's end-user segments in contract manufacturing. This trend suggests that as these larger clients grow, their influence over Asymchem’s operations and pricing could further increase, amplifying their bargaining power.
The Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) market is quite crowded, with many companies providing similar services. This means customers, especially those with large projects, have a good selection of providers to choose from. If Asymchem doesn't offer something unique or particularly valuable, clients can readily move to another CDMO, which naturally gives them more leverage.
In 2024, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $25.5 billion, and it's projected to grow significantly. This expansion means even more choices for pharmaceutical and biotech companies seeking development and manufacturing partners. With such a broad market, customers can easily compare pricing, capabilities, and timelines across multiple CDMOs, strengthening their position in negotiations.
Pharmaceutical companies are intensely focused on managing manufacturing expenses, particularly as governments and patient advocacy groups push for lower drug prices. This cost sensitivity directly impacts their selection of Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) like Asymchem, as they seek partners who can demonstrably lower the overall cost of drug production and enhance the value of their pharmaceutical assets.
This heightened awareness of cost provides significant leverage for these pharmaceutical clients. They are inclined to negotiate for lower prices, especially when dealing with established, commercially-produced drugs where the cost of goods sold is a critical factor in profitability. For instance, in 2024, the global pharmaceutical market experienced continued scrutiny on drug pricing, with payers and governments actively seeking cost reductions, putting pressure on all aspects of the supply chain, including CDMO services.
Customer's Backward Integration Threat
Large pharmaceutical clients, like Pfizer or Merck, have the substantial financial backing and technical know-how to build or enhance their own manufacturing facilities. This capability presents a credible threat of backward integration for Asymchem.
Should Asymchem’s pricing or terms become uncompetitive, these major players could opt to bring their production in-house, thereby increasing their leverage. For instance, in 2023, the global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $170 billion, indicating the scale of investment possible within the sector.
However, for many biopharmaceutical firms, outsourcing to specialized contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) like Asymchem remains a strategic necessity. This allows them to achieve cost savings, scale production efficiently, and tap into specialized expertise that would be prohibitively expensive to replicate internally.
- Customer Backward Integration Threat: Large pharmaceutical companies can leverage their financial resources to develop in-house manufacturing, directly impacting Asymchem's market position.
- Strategic Imperative of Outsourcing: Despite integration threats, many biopharma firms rely on CDMOs for cost efficiency, scalability, and specialized capabilities, a trend expected to continue.
- Market Context: The significant size of the contract manufacturing market underscores the potential for large clients to invest in their own capabilities if outsourcing terms are not favorable.
Regulatory and Quality Requirements
The pharmaceutical sector's highly regulated nature significantly empowers customers. They require Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) to demonstrate rigorous quality control and unwavering regulatory compliance. Asymchem's history of successful inspections by bodies like the FDA, NMPA, TGA, and MFDS is a key differentiator, but it also means clients will closely scrutinize these credentials, retaining considerable leverage in selecting a compliant partner.
This stringent regulatory landscape means clients have substantial bargaining power. They can dictate terms and demand high standards due to the critical nature of drug manufacturing and the associated risks of non-compliance. For instance, a single regulatory failure can lead to costly product recalls and severe reputational damage, making a CDMO's compliance record a paramount purchasing criterion.
- Strict Regulatory Environments: Pharmaceutical clients operate under intense scrutiny from global health authorities.
- Demand for Impeccable Quality: Customers prioritize CDMOs with robust quality management systems and a proven history of successful regulatory audits.
- Asymchem's Compliance Advantage: Asymchem's strong regulatory track record, including inspections by FDA, NMPA, TGA, and MFDS, provides a competitive edge.
- Customer Leverage: Clients use these stringent requirements to maintain significant bargaining power, ensuring they partner with compliant and reliable CDMOs.
Asymchem's customers, primarily large pharmaceutical and biotech firms, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the critical nature of their drug development pipelines. The crowded CDMO market in 2024, valued at approximately $25.5 billion, provides clients with numerous alternatives, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms.
The threat of backward integration by major pharmaceutical clients, who possess the capital to establish in-house manufacturing, further amplifies customer leverage. This is particularly true for established drugs where cost of goods sold is a key profitability driver. The global pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market's substantial size, around $170 billion in 2023, highlights the financial capacity of these large players.
Moreover, the highly regulated pharmaceutical industry empowers customers to demand stringent quality control and regulatory compliance from CDMOs. Asymchem’s strong compliance record with bodies like the FDA and NMPA is a crucial differentiator, but it also means clients can leverage these requirements to ensure they partner with the most reliable and compliant organizations.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context (2024 Focus) |
|---|---|---|
| Client Concentration | High for major clients | Large pharma growth driving increased influence. |
| Market Competition | High | Global CDMO market valued at ~$25.5 billion in 2024, offering ample choices. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Significant for large clients | $170 billion (2023) contract manufacturing market indicates capital availability. |
| Regulatory Demands | High | Strict compliance requirements (FDA, NMPA) give clients leverage in partner selection. |
What You See Is What You Get
Asymchem Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Asymchem Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to this professionally crafted report. You can trust that the insights and formatting presented in this preview are identical to the final deliverable, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) market is characterized by a significant number of competitors, ranging from large, well-established global entities to smaller, niche players. This fragmentation means Asymchem faces a broad competitive landscape.
Asymchem's global footprint, with operations in the UK, U.S., and China, places it in direct competition with companies that have similar international reach as well as those focused on specific regional markets. The sheer volume of competitors, both broad-service providers and those specializing in particular therapeutic areas or technologies, intensifies the rivalry for outsourcing contracts.
For instance, in 2023, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This expanding market attracts new entrants and encourages existing players to innovate and compete aggressively for market share, putting pressure on pricing and service offerings.
The global CDMO market is booming, expected to jump from $136.6 billion in 2024 to $191.6 billion by 2029, a healthy 7.0% compound annual growth rate. This robust expansion, while generally positive, can intensify competitive rivalry. As the industry grows, it naturally draws in new companies eager to capture market share and prompts existing players to invest in increased capacity. This dynamic ensures the competitive landscape remains active and challenging for all participants.
Asymchem distinguishes itself through cutting-edge technologies and a comprehensive service offering, spanning preclinical research to commercial manufacturing. This integrated approach, coupled with a focus on drug substance and drug product development, sets it apart. For instance, Asymchem announced a significant expansion of its cell therapy manufacturing capacity in 2024, aiming to meet growing demand for advanced therapies.
However, the competitive landscape remains intense. If rivals can readily replicate Asymchem's specialized capabilities or provide comparable end-to-end solutions, the pressure of competition will persist. The small molecule Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) sector, in particular, relies heavily on such differentiation to maintain its edge.
Switching Costs for Customers
For pharmaceutical companies, moving from one Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) to another is not a simple switch. It involves significant effort and expense related to technology transfer, updating regulatory submissions, and the potential for disruptions that could delay crucial drug development timelines. These hurdles do create a degree of loyalty for Asymchem's current customers.
However, the competitive landscape in the CDMO sector is fierce. This intense rivalry means that competitors are often willing to offer attractive incentives or even cover a portion of these switching costs to attract new clients away from established players like Asymchem. For instance, in 2023, the global CDMO market was valued at approximately $21.5 billion, and it’s projected to grow significantly, indicating a highly competitive environment where client acquisition is paramount.
- High Technology Transfer Costs: Moving complex manufacturing processes and intellectual property can cost millions and take many months.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Revalidating processes and updating regulatory filings with agencies like the FDA and EMA adds significant time and expense.
- Potential for Delays: Any hiccup in the transfer process can push back critical clinical trial phases or market launch dates, which is a major concern for pharma clients.
- Competitive Bidding: Rivals may undercut pricing or offer bundled services to offset a client's perceived switching costs, thereby pressuring established CDMOs.
Strategic Acquisitions and Consolidation
The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) sector is experiencing robust merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, a trend expected to persist. For instance, in 2023, the CDMO market saw a notable increase in deal value, with several large transactions aimed at expanding service offerings and geographical reach.
This consolidation strategy allows larger CDMOs to acquire niche expertise or fill critical service gaps, thereby enhancing their competitive position. As major players absorb smaller, specialized firms, they gain greater market share and can offer end-to-end solutions, intensifying pressure on independent CDMOs that lack such integrated capabilities.
This ongoing consolidation reshapes the competitive landscape by creating larger, more formidable entities. For example, companies like Lonza and Catalent have been active in strategic acquisitions, bolstering their portfolios in areas like biologics and advanced therapies, which in turn heightens rivalry for other market participants.
- Increased M&A activity in the CDMO sector is a key driver of competitive rivalry.
- Larger CDMOs acquire specialized firms to broaden their service portfolios and market reach.
- This consolidation leads to a more concentrated market, intensifying competition for remaining independent players.
- Strategic acquisitions enhance market share and create more comprehensive service offerings, pressuring competitors.
The competitive rivalry within the CDMO market is intense due to a large number of players, including global giants and niche specialists. Asymchem operates in a market projected to grow from $136.6 billion in 2024 to $191.6 billion by 2029, a 7.0% CAGR, which attracts new entrants and spurs aggressive competition. This expansion means companies must constantly innovate and offer competitive pricing and services to maintain market share.
While customer switching costs are high due to technology transfer and regulatory complexities, competitors may offer incentives to lure clients. Furthermore, significant merger and acquisition activity, such as strategic buys by companies like Lonza and Catalent, consolidates the market, creating larger, more capable competitors and intensifying pressure on independent CDMOs.
| Competitor Factor | Impact on Asymchem | Example/Data Point |
| Market Fragmentation | High rivalry from numerous players | Global CDMO market valued at ~$200 billion in 2023 |
| Customer Switching Costs | Provides some customer loyalty | Millions in costs and many months for technology transfer |
| M&A Activity | Increases competitive pressure | Lonza and Catalent actively acquiring firms in 2023-2024 |
| Market Growth | Attracts new competitors | Projected CDMO market growth: $136.6B (2024) to $191.6B (2029) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) services, like those Asymchem provides, is for pharmaceutical and biotech firms to handle drug development and manufacturing internally. Many large pharmaceutical corporations already possess their own manufacturing plants and research departments, offering a direct alternative to outsourcing.
However, the significant capital expenditure, the need for highly specialized technical knowledge, and the complex regulatory compliance landscape make in-house operations a substantial undertaking. For many companies, particularly smaller or emerging ones, leveraging a CDMO like Asymchem presents a more efficient and strategically sound path forward, mitigating these considerable barriers to entry and operation.
Companies can bypass full-service Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) by using specialized Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for early-stage development and then engaging separate Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) for production. This unbundling of services, while adding coordination complexity, could offer clients greater flexibility or cost efficiencies.
Asymchem, a prominent CDMO, provides integrated solutions, but clients might still opt for this fragmented approach if it proves more economical or adaptable to their specific project needs. The rise of integrated CRO-CDMOs itself highlights the evolving landscape and competitive pressures within the outsourcing market.
Advancements in drug discovery and manufacturing, like lab automation and AI, could theoretically lessen the demand for outsourced CDMO services. For instance, in 2023, the global laboratory automation market was valued at approximately USD 5.7 billion, indicating significant investment in in-house capabilities.
However, leading CDMOs such as Asymchem are not standing still; they are actively integrating these cutting-edge technologies into their own operations. Asymchem’s strategic focus on areas like continuous manufacturing and AI-powered development aims to solidify its position by offering enhanced efficiency and innovation, thereby mitigating the threat of substitutes.
Generic or Biosimilar Development
The expiration of patents for branded drugs opens the door for generic and biosimilar development. This creates new manufacturing opportunities for Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations (CDMOs) like Asymchem, but it also introduces significant competition for the original, higher-priced drugs. For instance, in 2024, the market for biosimilars continued its robust growth, with several key biologic drugs facing patent cliffs, potentially impacting the demand for specialized manufacturing services for originator products.
This competitive pressure from lower-cost alternatives can fundamentally alter market dynamics. Asymchem, having potentially supported the development and manufacturing of the original branded drug, may see a shift in demand. The focus could move from complex, proprietary manufacturing processes to more cost-efficient production methods for generics and biosimilars, requiring adaptation in service offerings and pricing strategies.
- Patent Expirations Drive Generic and Biosimilar Entry: As major drug patents expire, there's a surge in demand for manufacturing these less expensive alternatives.
- Increased Competition for Originator Products: The availability of generics and biosimilars directly challenges the market share and pricing power of branded drugs.
- Shift in CDMO Service Demand: Asymchem may need to pivot from high-margin originator services to cost-competitive generic and biosimilar manufacturing.
- Market Dynamics and Pricing Pressure: The influx of substitutes forces a re-evaluation of manufacturing costs and service pricing to remain competitive.
Shift to Different Therapeutic Modalities
The pharmaceutical industry's ongoing evolution towards novel therapeutic modalities like gene and cell therapies presents a potential substitution threat if Asymchem's service offerings don't keep pace. While Asymchem has strategically expanded its capabilities beyond traditional small molecules to include chemical macromolecules, peptides, and oligonucleotides, a swift industry-wide pivot to areas where its expertise is less developed could diminish demand for its current CDMO services.
For instance, the global gene therapy market was valued at approximately $8.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial shift in R&D focus. If Asymchem cannot rapidly scale its capacity and expertise in these burgeoning fields, companies developing these advanced therapies might opt for CDMOs with more established platforms, thereby substituting Asymchem's offerings.
- Therapeutic Modality Shift: The increasing investment and clinical success in gene and cell therapies represent a direct alternative to traditional small molecule drugs.
- Asymchem's Expansion: Asymchem is actively broadening its CDMO capabilities to encompass peptides, oligonucleotides, and chemical macromolecules, demonstrating an awareness of industry trends.
- Market Growth: The rapid expansion of markets like cell and gene therapy, with significant projected growth rates, highlights the potential for these modalities to capture market share from established drug types.
- Adaptation Imperative: Asymchem's ability to adapt its technological platforms and operational expertise to these new therapeutic areas will be crucial in mitigating the threat of substitution.
The threat of substitutes for Asymchem's CDMO services primarily stems from pharmaceutical companies bringing manufacturing in-house, the unbundling of CDMO services into separate CRO and CMO engagements, and the emergence of new therapeutic modalities like gene and cell therapies that may bypass traditional chemical synthesis.
While in-house manufacturing presents high capital and expertise barriers, advancements in automation, with the global lab automation market reaching approximately USD 5.7 billion in 2023, could make it more feasible. Asymchem mitigates this by integrating these technologies. Furthermore, the growing biosimilar market, with robust growth projected for 2024, necessitates cost-efficient manufacturing, a shift Asymchem must adapt to.
The significant growth in gene and cell therapies, with the market valued at around $8.5 billion in 2023, poses a challenge if Asymchem's capabilities do not evolve rapidly. Asymchem's strategic expansion into chemical macromolecules, peptides, and oligonucleotides is a proactive measure against this substitution threat.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Asymchem | Market Data Point (2023/2024) |
| In-house Manufacturing | High capital investment, specialized expertise required | Mitigated by Asymchem's technology integration | Lab Automation Market: ~$5.7 billion (2023) |
| Unbundled Services (CRO + CMO) | Potential cost savings, increased coordination complexity | Requires competitive pricing and integrated value proposition | N/A (Industry trend) |
| Generic/Biosimilar Competition | Lower cost, patent expirations | Need for cost-efficient manufacturing, potential shift in service focus | Biosimilar Market: Robust growth in 2024 |
| Novel Therapeutic Modalities | Gene/Cell Therapies, bypass traditional synthesis | Requires rapid expansion of new capabilities | Gene Therapy Market: ~$8.5 billion (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) like Asymchem, capable of handling everything from early-stage research to large-scale commercial production under stringent Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations, demands a colossal upfront investment. This includes building state-of-the-art facilities, acquiring advanced manufacturing equipment, and investing heavily in cutting-edge technology and skilled personnel. For instance, constructing a new cGMP-compliant manufacturing site can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable financial hurdle.
This significant capital requirement acts as a powerful deterrent, effectively shielding established players like Asymchem from a multitude of potential new competitors. The sheer scale of financial commitment needed to enter the market at a comparable level of capability and compliance means that only well-funded entities can realistically consider competing, thereby reducing the immediate threat of new entrants to Asymchem's operations.
The pharmaceutical sector presents a formidable barrier to entry due to extensive regulatory requirements. New companies must navigate complex compliance landscapes with agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and NMPA, demanding substantial investment in quality systems and certifications. Asymchem's proven track record, evidenced by over 65 successful regulatory inspections, highlights its established expertise and provides a significant competitive moat against potential new entrants seeking to establish similar credibility.
Asymchem's strength lies in its mastery of highly complex chemistry and advanced manufacturing processes like continuous flow and biocatalysis. This deep scientific and technical expertise, coupled with a portfolio of proprietary technologies and patents, presents a significant hurdle for any new company aiming to enter the contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) space.
Furthermore, the CDMO industry faces a persistent talent shortage for highly specialized professionals, making it exceptionally challenging for new entrants to assemble the skilled workforce necessary to operate at Asymchem's level. This scarcity of expertise further solidifies the barrier to entry.
Established Client Relationships and Reputation
Asymchem's established client relationships and strong reputation present a significant barrier to new entrants. With over 1,100 active clients and a 25-year track record of serving major pharmaceutical companies, Asymchem has cultivated deep trust and proven reliability within the industry. Newcomers would find it exceedingly difficult to replicate this level of established credibility and long-term partnerships.
The pharmaceutical sector demands rigorous quality assurance and a history of successful project execution, areas where Asymchem excels. Building the necessary trust and demonstrating consistent quality takes years, if not decades, making it challenging for any new competitor to gain immediate traction against a well-regarded incumbent like Asymchem.
- Established Client Base: Over 1,100 active clients, indicating significant market penetration and client loyalty.
- Long-Standing Reputation: A 25-year history of collaboration with top-tier pharmaceutical companies signifies proven expertise and reliability.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants face substantial hurdles in replicating Asymchem's established trust, quality, and long-term relationships.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Processes
Asymchem's robust portfolio of intellectual property, featuring over 300 patents related to advanced manufacturing technologies, significantly raises the barrier to entry. New companies would need to invest heavily in developing their own unique processes or incur substantial licensing fees for existing ones. This makes it challenging for potential competitors to match Asymchem's technological capabilities and cost-effectiveness.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the substantial R&D investment and time required to replicate Asymchem's proprietary processes. This intellectual capital acts as a powerful deterrent, as it would be difficult and costly for newcomers to offer comparable or innovative services without infringing on existing patents.
- Over 300 patents held by Asymchem in advanced manufacturing.
- High R&D investment required for new entrants to develop novel processes.
- Licensing costs for existing proprietary technologies are prohibitive.
- Limited ability for new entrants to offer competitive or differentiated services.
The threat of new entrants for Asymchem is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish compliant manufacturing facilities and advanced technological capabilities. Building a single cGMP-compliant site can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant barrier for most potential competitors. Furthermore, Asymchem's robust intellectual property, including over 300 patents, and its deep expertise in complex chemistry and advanced processes like continuous flow manufacturing, create substantial hurdles for newcomers seeking to replicate its offerings.
| Factor | Asymchem's Advantage | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Hundreds of millions for cGMP facilities | Prohibitive for most new companies |
| Technology & Expertise | Proprietary processes, continuous flow, biocatalysis | Requires significant R&D and time to replicate |
| Intellectual Property | Over 300 patents | High licensing costs or infringement risk |
| Regulatory Compliance | 65+ successful regulatory inspections | Demands substantial investment in quality systems |
| Client Relationships | 1,100+ active clients, 25-year history | Difficult to build trust and replicate established partnerships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Asymchem is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from reputable firms, and regulatory filings that detail operational and market dynamics.
