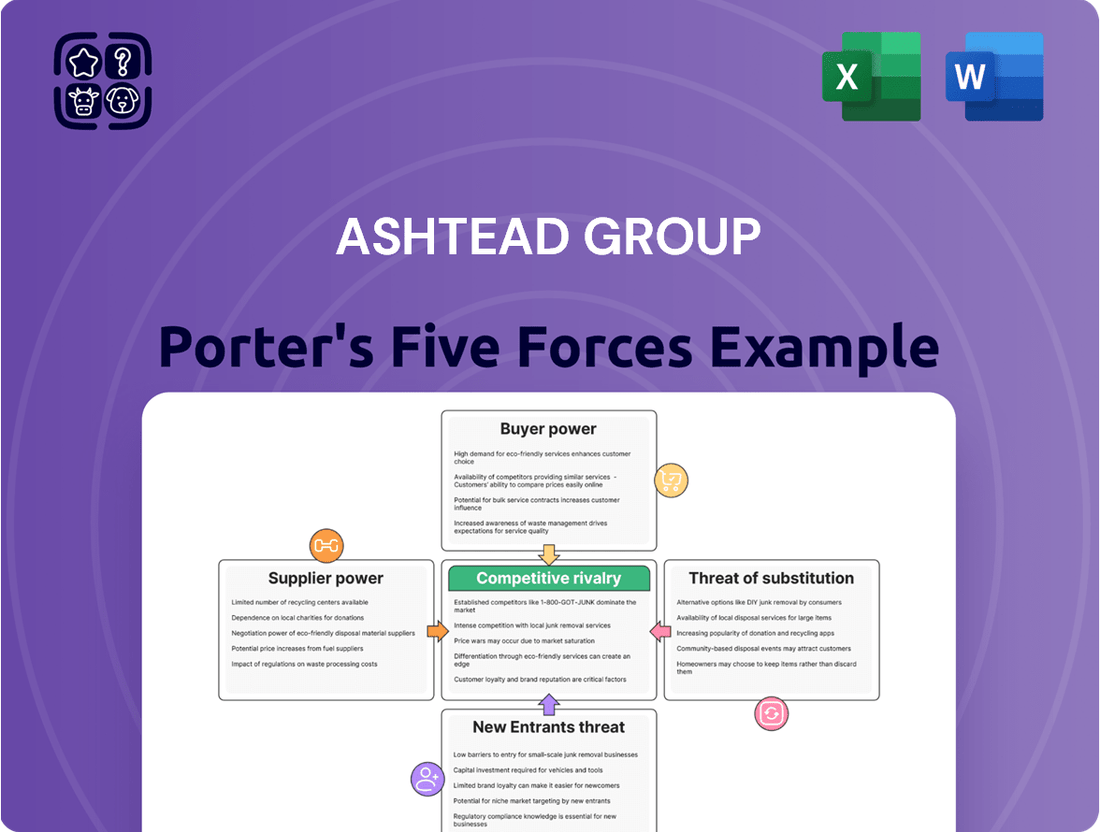
Ashtead Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ashtead Group Bundle
Ashtead Group navigates a competitive rental landscape where the threat of new entrants is moderate due to significant capital requirements for equipment fleets. The bargaining power of buyers, primarily construction and industrial firms, is also substantial, pushing for competitive pricing and service levels.
The intensity of rivalry among existing players, including Sunbelt Rentals and United Rentals, is high, leading to strategic pricing and service differentiation. Furthermore, the availability of substitute services, while limited in some specialized areas, does exist in broader equipment rental markets, adding another layer of pressure.
Supplier power for Ashtead is generally low, as they procure equipment from a diverse range of manufacturers, allowing for favorable terms. This balanced view of competitive forces is crucial for understanding Ashtead's market position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ashtead Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a key factor in the equipment rental industry. A limited number of major manufacturers produce the heavy machinery and specialized tools that companies like Ashtead Group rely on. For instance, in 2023, the global construction equipment market was dominated by a few large players, meaning if these key suppliers consolidate or act in unison, they can dictate terms.
This concentration can lead to significant supplier power, especially when demand for specific equipment is high. If these dominant suppliers raise prices or impose unfavorable contract terms, it directly impacts Ashtead's procurement costs and can affect the availability of essential fleet components, as seen with supply chain disruptions in 2022 affecting machinery delivery times.
Ashtead's strategy to mitigate this supplier power includes actively diversifying its supplier base where possible and exploring opportunities for in-house manufacturing or partnerships for critical components. This proactive approach helps reduce dependence on any single supplier and provides greater leverage in negotiations, ensuring better fleet replenishment and cost management.
Switching equipment suppliers presents significant hurdles for Ashtead. These include the expense of retooling maintenance procedures, the cost of training technicians on unfamiliar machinery, and the potential for integration problems with their current fleet management software. For instance, a major overhaul of a large rental fleet's diagnostic systems could easily run into millions of dollars in new software and specialized tools.
These substantial switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of Ashtead's existing suppliers. It becomes less financially appealing for Ashtead to transition to new vendors, even when more competitive pricing might be on offer. This inertia means suppliers can maintain their pricing power, as the disruption and investment required for Ashtead to change are considerable.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ashtead Group is significantly influenced by the uniqueness of the inputs they provide. For standard construction and industrial equipment, the market is often flooded with similar offerings. This abundance of choice means that individual suppliers have limited leverage because Ashtead can easily switch to a competitor if prices become unfavorable. For example, many manufacturers produce common excavators or scaffolding, making it difficult for any single supplier to command higher prices.
However, the dynamic shifts considerably when specialized or proprietary equipment is involved. Suppliers offering unique technology or highly specialized machinery can wield substantial bargaining power. Ashtead would face challenges in finding comparable alternatives for such niche products, giving these suppliers more room to negotiate terms and pricing. This is particularly relevant in areas like advanced surveying equipment or specialized rental technology where innovation is key and supply chains are less commoditized.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by equipment manufacturers presents a potential challenge for Ashtead Group. If manufacturers were to directly enter the equipment rental market, they could leverage their existing production capabilities and established brand recognition to compete. This scenario is more likely to be a concern for specialized or high-value equipment segments where manufacturers might see an opportunity to capture a larger portion of the value chain.
While broad-scale forward integration by manufacturers into general equipment rental is less common, it remains a factor to monitor. The financial health and strategic priorities of key suppliers are crucial. For instance, in 2024, major construction equipment manufacturers reported varying degrees of profitability, influencing their investment decisions. Companies like Caterpillar, a significant supplier in the broader industry, continued to invest in technology and digital solutions, which could hypothetically extend into rental services.
- Potential Impact: Direct competition from manufacturers could pressure Ashtead's rental rates and market share, particularly in niche equipment categories.
- Manufacturer Capabilities: Manufacturers possess inherent advantages in production scale, technical expertise, and existing customer relationships, which could be leveraged in a rental model.
- Industry Trends: The increasing focus on circular economy principles and service-based business models within manufacturing could incentivize some players to explore rental avenues.
- Mitigation: Ashtead's strategy of maintaining diverse supplier relationships and focusing on operational efficiency helps to mitigate the impact of any single supplier's potential forward integration.
Importance of Ashtead to Suppliers
As a major player in the equipment rental market, Ashtead Group, primarily through its Sunbelt Rentals division, represents a substantial buyer for numerous equipment manufacturers. Its significant purchasing volume grants Ashtead considerable negotiation power.
This leverage allows Ashtead to secure favorable pricing, volume discounts, and potentially even influence the design and features of the equipment it acquires. For instance, in 2023, Sunbelt Rentals' capital expenditure on rental fleet was approximately $4.3 billion, a substantial sum that gives it considerable sway with its suppliers.
The sheer scale of Ashtead's orders means suppliers are keen to maintain a strong relationship, as losing such a large customer could have a significant impact on their own production volumes and profitability. This dynamic naturally suppresses the bargaining power of suppliers.
- Significant Buyer: Ashtead's extensive fleet acquisition makes it a key customer for equipment manufacturers.
- Negotiating Leverage: Large purchase volumes enable Ashtead to negotiate favorable pricing and terms.
- Influence on Product Development: Ashtead can potentially influence product specifications based on its operational needs.
- Reduced Supplier Power: The dependency of some suppliers on Ashtead's business limits their ability to dictate terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ashtead Group is moderated by the concentration of manufacturers and the switching costs involved. While a few dominant players exist, Ashtead’s scale as a buyer, exemplified by its 2023 capital expenditure of $4.3 billion, provides significant leverage to negotiate favorable terms.
The uniqueness of equipment plays a crucial role; common items offer little supplier power due to abundant alternatives, whereas specialized machinery grants suppliers greater negotiation strength. Furthermore, the threat of manufacturers integrating forward into rental services is a consideration, though less common for broad equipment categories.
| Factor | Impact on Ashtead | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Potential for price increases and unfavorable terms. | Diversify supplier base, explore partnerships. |
| Switching Costs | High costs deter changing suppliers, strengthening existing supplier power. | Focus on long-term supplier relationships, efficient integration processes. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Specialized equipment increases supplier leverage. | Develop in-house expertise for critical components, seek alternative specialized suppliers. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Direct competition from manufacturers could impact rental rates. | Maintain strong operational efficiency, focus on superior customer service. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Ashtead Group, assessing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products within the equipment rental industry.
Quickly assess competitive intensity across all five forces—ideal for identifying and addressing Ashtead's key strategic vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ashtead Group's customer base is highly fragmented, encompassing everyone from individual DIYers to major industrial corporations and government agencies. This wide diversity means no single customer holds significant sway over Ashtead's pricing or terms.
For instance, Ashtead's rental fleet is utilized across numerous sectors, including construction, oil and gas, and events. This broad application prevents any one industry segment from dictating terms, thereby limiting individual customer bargaining power.
This customer fragmentation directly benefits Ashtead by creating a stable revenue stream and reducing the risk of losing a substantial portion of business due to the demands of a few large clients.
In 2024, Ashtead's continued expansion into new markets and service offerings further diversifies its customer portfolio, reinforcing this advantage and mitigating concentrated customer power.
For many of Ashtead Group's customers, particularly those needing standard equipment for shorter-term projects, switching rental providers is relatively straightforward with minimal associated costs. This ease of switching allows customers to readily compare prices and availability from different companies, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
However, for larger, more complex projects, such as major construction or industrial turnarounds, the situation changes. Customers often require integrated solutions, specialized equipment, and consistent service delivery, making the process of switching rental providers significantly more involved. The logistical challenges of coordinating new equipment, potential project delays, and the need for specialized training for new machinery can substantially increase switching costs for these customers, thus diminishing their bargaining power.
In 2024, the rental industry continues to see a mix of demand, with large infrastructure projects, particularly in the United States, driving the need for specialized and long-term rentals. For instance, Ashtead’s Sunbelt Rentals reported robust growth in its Specialty segment, which includes advanced technology and complex equipment, indicating that customers involved in these sectors face higher switching barriers.
Customers in construction and industry are indeed quite sensitive to price, particularly when renting standard tools or equipment that are considered commodities. This is because rental expenses are a direct line item in their project budgets, and higher costs can significantly affect profitability. For instance, if a contractor's bid is tight, the cost of renting essential equipment becomes a critical factor in their decision-making.
This price sensitivity can intensify during economic slowdowns. When the construction market is sluggish, as it has been in certain periods, companies like Ashtead Group face increased pressure. They often find themselves needing to compete more fiercely on price to secure rentals, which can naturally put a strain on their profit margins. In 2023, for example, while the broader economic landscape showed some recovery, specific construction sectors experienced fluctuating demand, leading some rental companies to offer more competitive pricing to maintain utilization rates.
Customer Information and Transparency
The growing accessibility of online comparison websites and pricing tools significantly enhances customer knowledge. This increased transparency allows customers to easily benchmark Ashtead's rental rates and service offerings against competitors, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
For instance, in the UK equipment rental market, where Ashtead (operating as A-Plant) is a major player, customers can readily find aggregated pricing information, making it harder for rental companies to maintain premium pricing without justification. This ease of comparison directly translates into heightened bargaining power.
- Increased Information Availability: Online platforms provide customers with a comprehensive view of market pricing and service levels.
- Comparative Pricing Tools: Websites enable direct comparison of rental costs and terms across multiple providers.
- Demand for Better Terms: Informed customers are more likely to negotiate for lower prices or improved service agreements.
- Price Sensitivity: Greater transparency can lead to increased price sensitivity among customers, forcing suppliers to compete more aggressively on cost.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly large construction or industrial firms, is a significant factor. These entities might consider acquiring their own equipment fleets instead of renting, especially for extended or recurring needs.
However, the substantial capital investment required for purchasing, coupled with ongoing expenses for maintenance, repairs, and depreciation, often renders renting a more financially sensible and flexible approach. This cost-benefit analysis typically favors rental, thereby mitigating the direct threat of customers integrating backward into equipment ownership. For example, in 2024, the average cost of a new medium-sized excavator can range from $100,000 to $200,000, representing a considerable upfront commitment.
- High Capital Outlay: Purchasing equipment requires significant upfront investment, diverting capital from core business activities.
- Maintenance & Operational Costs: Customers would bear the full burden of maintenance, repairs, insurance, and storage, adding to operational overheads.
- Depreciation & Obsolescence: Owned equipment depreciates over time and risks becoming obsolete with technological advancements, impacting resale value.
- Flexibility & Scalability: Rental services offer flexibility to scale equipment usage up or down based on project demands, avoiding underutilization of owned assets.
Ashtead Group benefits from a highly fragmented customer base, where individual clients, from small contractors to large corporations, have limited power to dictate terms. This broad customer spread across sectors like construction and events in 2024, including significant infrastructure projects in the US, means no single client can significantly influence Ashtead's pricing or operational demands.
While customers needing standard equipment for short-term projects can switch providers easily, those requiring specialized equipment for complex, long-term projects face higher switching costs. This is particularly evident in Ashtead's Sunbelt Rentals' Specialty segment, which saw strong growth in 2024, indicating customers in these areas have less bargaining power due to the complexity and integration required.
Price sensitivity remains a factor for standard equipment rentals, especially during economic fluctuations. However, the substantial capital outlay for purchasing equipment, estimated at $100,000 to $200,000 for a medium excavator in 2024, alongside maintenance and depreciation costs, generally makes renting a more financially attractive and flexible option for most customers, thus limiting their threat of backward integration.
| Factor | Impact on Ashtead's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers individual customer power | Broad customer base across diverse sectors |
| Switching Costs (Standard Equipment) | Increases customer power | Easy to switch for short-term, common rentals |
| Switching Costs (Specialized Equipment) | Decreases customer power | High for complex, long-term projects (e.g., Specialty segment growth) |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases customer power | Direct impact on project budgets, especially during economic slowdowns |
| Information Availability | Increases customer power | Online tools enable easy price and service comparison |
| Backward Integration Threat | Lowers customer power | High capital cost and operational burden of owning equipment |
Same Document Delivered
Ashtead Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ashtead Group details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the equipment rental industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making and maintaining a competitive edge.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The North American equipment rental market is quite concentrated, with a few dominant companies. Ashtead Group, through its Sunbelt Rentals division, and United Rentals are the clear leaders, holding substantial portions of the market. This oligopolistic setup means competition is fierce, often centering on price and service quality as these giants battle for supremacy.
While the broader equipment rental market anticipates expansion, a slowdown in specific areas, such as local commercial construction or residential renovations, could heighten competitive pressures. For Ashtead Group, this means that even with overall market growth, the intensity of rivalry can increase if demand falters in key segments.
When market growth decelerates, companies often shift their focus from capturing new demand to aggressively pursuing existing market share. This can lead to price wars or increased marketing efforts as firms vie for the same pool of customers. The industry has seen varied growth, with the US general tool rental market, a significant segment for Ashtead, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.5% through 2028, but localized economic factors can still create pockets of intensified competition.
Ashtead Group actively combats competitive rivalry by emphasizing product differentiation and specialization. They offer an extensive inventory of general tools alongside specialized equipment tailored for niche markets, such as the film and television industry and emergency response services. This broad yet focused approach helps to lessen direct price-based competition.
By strategically prioritizing specialty equipment, which typically yields higher profit margins, Ashtead can effectively navigate and mitigate the intense rivalry often found in more commoditized equipment rental segments. This focus allows them to capture value beyond basic rental rates.
Exit Barriers
The equipment rental industry, where Ashtead Group operates, is characterized by high capital intensity, meaning significant investment is required to acquire and maintain a fleet of specialized rental equipment. This substantial upfront cost, coupled with the need for ongoing maintenance and technological upgrades, creates substantial exit barriers. Companies find it difficult and costly to divest or dispose of these specialized assets, often leading them to continue operations even when profitability is low, rather than incur substantial losses on asset sales. This situation can contribute to sustained competitive pressure and potential market oversupply.
For instance, Ashtead Group's substantial investment in its rental fleet underscores this barrier. As of the first quarter of fiscal year 2025, the company reported capital expenditures of $1.6 billion, primarily for fleet additions and replacements. This continuous investment in a diverse range of equipment, from aerial work platforms to general construction tools, locks in capital and makes exiting the market a complex and financially burdensome undertaking.
The specialized nature of much of the equipment also limits resale options, further cementing these exit barriers. Unlike more standardized assets, highly specialized machinery may have a smaller pool of potential buyers, depressing resale values and making liquidation less attractive. Consequently, companies are often compelled to remain in the market, even in challenging economic conditions.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs for acquiring and maintaining specialized rental fleets.
- Specialized Assets: Limited resale markets for highly specialized equipment increase disposal costs.
- Operational Persistence: Companies may continue operating at low profitability to avoid asset write-downs.
- Market Oversupply Risk: Entrenched players, unable to exit easily, can contribute to prolonged periods of oversupply and price competition.
Strategic Acquisitions and Consolidation
Ashtead Group actively pursues a strategy of acquiring smaller, independent rental companies. This approach not only bolsters their market share but also strengthens their 'cluster' strategy, creating more efficient operational hubs. This consolidation trend, observed across the industry, means fewer, larger players are dominating the market.
The intensified competition for smaller regional firms is a direct consequence of this consolidation. Major players like Ashtead are not just growing organically; they are actively buying their way into new markets and expanding their geographic reach. This makes it harder for independent operators to compete on scale and resources.
This ongoing consolidation contributes to a more concentrated market structure within the equipment rental sector. For instance, in 2023, Ashtead reported a significant increase in revenue, driven in part by acquisitions. This growth indicates the effectiveness of their acquisition strategy in gaining a stronger competitive position.
- Market Share Expansion: Ashtead's acquisition strategy directly targets an increase in its overall market share.
- Operational Efficiency: Acquiring companies and integrating them into 'cluster' locations aims to improve logistics and reduce costs.
- Industry Consolidation: The trend of major players acquiring smaller firms is reshaping the competitive landscape.
- Increased Competition for Independents: Smaller regional rental companies face heightened pressure from larger, consolidated entities.
Competitive rivalry within the equipment rental sector is intense, largely driven by the market's concentrated nature and the significant capital investment required. Ashtead Group, through Sunbelt Rentals, and United Rentals are key players, often engaging in price and service competition. The industry's high capital intensity and specialized assets create substantial exit barriers, encouraging continued operation even at lower profitability, which can lead to market oversupply and sustained competitive pressure.
Ashtead's strategy of acquiring smaller competitors further intensifies this rivalry, expanding its market share and operational efficiency while consolidating the industry. This consolidation places considerable pressure on independent regional rental firms, as larger entities like Ashtead leverage scale and resources gained through acquisitions, as evidenced by Ashtead's reported revenue growth in 2023 partly due to acquisitions.
| Metric | Ashtead Group (Sunbelt Rentals) | United Rentals | Industry Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | High (Oligopolistic) | High (Oligopolistic) | Increasing due to consolidation |
| Key Competitive Factors | Price, Service, Fleet Specialization | Price, Service, Fleet Specialization | Price sensitivity, service quality |
| Impact of Capital Intensity | High exit barriers, potential oversupply | High exit barriers, potential oversupply | Deters new entrants, encourages persistence |
| Acquisition Activity | Active acquirer, driving consolidation | Active acquirer, driving consolidation | Major players expanding via M&A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customer ownership of equipment presents a significant substitute threat to Ashtead Group's rental model. Businesses may opt to purchase equipment, especially for high-utilization needs or extended project durations. For instance, a construction firm undertaking a multi-year infrastructure project might find buying specialized machinery more economical than renting over that entire period.
However, the rental model often prevails due to the substantial capital outlay required for ownership. High upfront purchase prices, coupled with ongoing expenses like maintenance, insurance, storage, and depreciation, can significantly burden a company's balance sheet. Ashtead Group's extensive fleet and flexible rental terms provide an attractive alternative, mitigating these ownership-related costs and capital commitments for its diverse customer base.
While manual labor or simpler methods can substitute for rented equipment on smaller or less demanding jobs, they often fall short in efficiency and safety. For instance, tasks like heavy lifting or extensive excavation are significantly faster and safer with specialized machinery. In 2024, the construction industry’s ongoing focus on project timelines and worker safety continues to reinforce the value proposition of equipment rental for these more complex operations.
Long-term equipment leasing presents a viable substitute for Ashtead's core rental business, particularly for clients with stable, extended operational requirements. These leasing arrangements often provide fixed monthly costs and can include comprehensive maintenance, offering a different financial and operational profile compared to short-term rentals.
Customers requiring equipment for multiple years might find leasing more predictable than managing fluctuating rental rates. For instance, a construction firm needing a fleet of excavators for a decade-long infrastructure project could opt for a lease over frequent short-term rentals. This predictable expenditure can be a significant draw.
While Ashtead's rental model excels in flexibility for project-based needs, leasing caters to a different segment of the market. The availability of competitive leasing options could divert customers who prioritize long-term asset utilization and cost certainty, impacting Ashtead's market share in those specific segments. In 2023, the global equipment leasing market was valued at over $300 billion, indicating a substantial market where substitutes are prevalent.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency
Rapid technological advancements pose a significant threat of substitution for Ashtead Group. New methods or highly efficient, smaller equipment could emerge, diminishing the demand for traditional, larger rental machinery. For instance, advancements in battery technology might lead to powerful, compact electric tools that replace the need for larger gasoline-powered equipment on certain job sites.
Ashtead actively combats this threat by consistently investing in its fleet to incorporate new technologies and maintain a diverse range of offerings. This includes a growing emphasis on compact, electric equipment, which directly addresses the shift towards more sustainable and efficient solutions. In 2024, Ashtead continued its strategic capital expenditure program, allocating significant resources to fleet modernization and expansion, ensuring its rental inventory remains competitive and aligned with evolving industry demands.
- Fleet Modernization: Ashtead's ongoing investment in its rental fleet ensures it remains current with technological advancements, including the integration of more fuel-efficient and technologically advanced machinery.
- Diversification of Offerings: The company's strategy includes expanding its range of compact and electric equipment, catering to a growing market segment seeking smaller, more sustainable rental solutions.
- Technological Integration: Ashtead explores and adopts new technologies that enhance equipment efficiency and reduce the need for traditional, larger rental units, thereby preempting substitute threats.
DIY Movement and Consumer-Grade Tools
The burgeoning DIY movement, especially among homeowners, fuels a demand for consumer-grade tools. This trend effectively substitutes the need for renting professional equipment for many smaller projects. For Ashtead Group, this primarily affects its general tool rental segments, rather than its core industrial equipment offerings.
While Ashtead's Sunbelt Rentals does serve the DIY market, the increasing availability and affordability of consumer tools present a substitution threat. For instance, the market for home improvement tools saw significant growth, with sales of power tools and hand tools remaining robust through 2024, indicating a strong consumer willingness to purchase rather than rent for personal use.
- DIY Growth: Homeowners increasingly undertake projects themselves, reducing reliance on rental equipment for minor tasks.
- Consumer Tool Availability: The market offers a wide array of affordable, high-quality consumer-grade tools.
- Segment Impact: This trend primarily impacts Ashtead's general tool rental business, not its heavy industrial equipment.
- 2024 Data: The home improvement sector, including tool sales, showed sustained strength in 2024, reinforcing this trend.
The threat of substitutes for Ashtead Group's rental services is multifaceted, encompassing ownership, leasing, technological advancements, and the DIY market. While ownership requires significant capital, leasing offers predictable costs for long-term needs, and the DIY trend impacts smaller-scale equipment rentals. Ashtead's strategy of fleet modernization and diversification aims to counter these substitute pressures by offering flexible, technologically advanced solutions.
| Substitute Category | Description | Impact on Ashtead | Mitigation Strategy | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment Ownership | Customers purchase equipment outright. | Reduces demand for rentals, especially for high-utilization needs. | Highlight cost savings of renting (no maintenance, storage, depreciation). | Continued focus on capital expenditure for businesses. |
| Equipment Leasing | Long-term rental agreements with fixed costs. | Diverts customers seeking cost certainty and predictable expenses. | Offer competitive leasing options or emphasize rental flexibility. | Global leasing market valued over $300 billion in 2023. |
| Technological Advancements | New, more efficient, or smaller equipment. | Can render older or larger rental equipment obsolete. | Invest in fleet modernization and new technologies (e.g., electric). | Ashtead's strategic capital expenditure for fleet upgrades. |
| DIY Market | Consumers purchase tools for personal projects. | Reduces demand for general tool rentals. | Focus on core industrial segments; acknowledge DIY market impact. | Robust sales in consumer power and hand tools in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the equipment rental sector, particularly to compete with established players like Ashtead Group, demands a massive upfront investment. Acquiring a broad range of high-value equipment, from construction machinery to specialized tools, quickly runs into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. For instance, a fleet comparable to Ashtead's would necessitate acquiring thousands of units across various categories, representing a significant financial hurdle.
Beyond just the machinery, new entrants must also fund the creation of a widespread physical infrastructure. This includes establishing numerous rental branches in strategic locations to serve diverse customer bases and building robust logistical capabilities for delivery and maintenance. This extensive network development adds another layer of substantial capital expenditure, making it difficult for smaller, less-capitalized firms to gain traction.
Economies of scale represent a significant barrier for potential new entrants into the equipment rental market. Established companies like Ashtead Group leverage their vast operational size to negotiate better prices on equipment purchases and maintenance, a cost advantage that new, smaller players simply cannot match. For instance, in 2024, Ashtead's substantial capital expenditure, reaching billions, allows for bulk buying and optimized logistics, creating a cost structure that is incredibly difficult to replicate.
The ability to achieve economies of scope further solidifies this advantage. Ashtead's diverse rental fleet, serving construction, industrial, and events sectors, allows for efficient allocation and utilization of resources across different customer segments. A new entrant would face immense challenges in building a comparable breadth of offerings and the associated operational efficiencies, making it tough to compete on both price and service availability.
Ashtead, primarily through its Sunbelt Rentals brand, benefits from robust brand recognition and deeply entrenched customer loyalty in its key markets. For instance, Sunbelt Rentals consistently ranks highly in customer satisfaction surveys, fostering repeat business and a strong preference over competitors. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating this established trust and loyalty, which requires substantial, long-term investment in marketing and service quality to attract and retain a diverse customer base.
Regulatory and Environmental Hurdles
The equipment rental sector faces significant regulatory and environmental challenges that deter new entrants. Compliance with stringent safety standards is paramount, requiring substantial upfront investment in training and equipment maintenance. For instance, in 2024, the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) Tier 4 Final emissions standards for non-road diesel engines necessitate the use of advanced, costly machinery, a barrier for smaller operators.
Navigating complex transportation laws, including weight restrictions and licensing for heavy equipment, adds another layer of operational difficulty. New entrants must also contend with evolving environmental regulations, such as those related to waste disposal and hazardous materials management, which demand specialized procedures and infrastructure.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with OSHA and other safety regulations requires investment in training and equipment.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to EPA's Tier 4 Final emissions standards impacts machinery costs.
- Transportation Laws: Navigating weight, size, and licensing requirements for heavy equipment is complex.
- Operational Burden: These combined hurdles increase the capital and operational costs for new entrants.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chain
New entrants face a significant hurdle in establishing efficient distribution channels and robust supply chains. Replicating Ashtead's established network for sourcing, maintaining, and deploying rental equipment across vast territories is a costly and time-consuming endeavor. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Ashtead reported capital expenditures of £2.3 billion, a substantial investment in fleet and infrastructure that new players would need to match or exceed.
Ashtead's deep-rooted supplier relationships and extensive branch network act as formidable barriers. These existing logistical capabilities provide a competitive edge in terms of speed, cost-effectiveness, and geographic coverage that newcomers would struggle to quickly build. The sheer scale of operations, supported by a fleet that consistently ranks among the largest in the industry, makes direct competition on this front exceedingly difficult.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Building a comparable network for equipment sourcing, maintenance, and distribution requires immense capital and operational expertise.
- Supplier Relationships: Ashtead's long-standing ties with manufacturers provide preferential access and pricing for new equipment.
- Branch Network Advantage: An extensive physical presence facilitates efficient delivery and customer service, a difficult moat to breach.
- Fleet Scale: The sheer size of Ashtead's rental fleet presents a significant capital barrier for aspiring competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Ashtead Group is relatively low due to the substantial capital required to build a comparable equipment fleet and operational infrastructure. Competitors face significant hurdles in replicating Ashtead's economies of scale, established brand loyalty, and complex supply chain capabilities. Furthermore, stringent safety and environmental regulations add further barriers, demanding significant investment and expertise.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ashtead Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Ashtead's annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific reports from leading market research firms like IBISWorld and Statista. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and competitor disclosures to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
