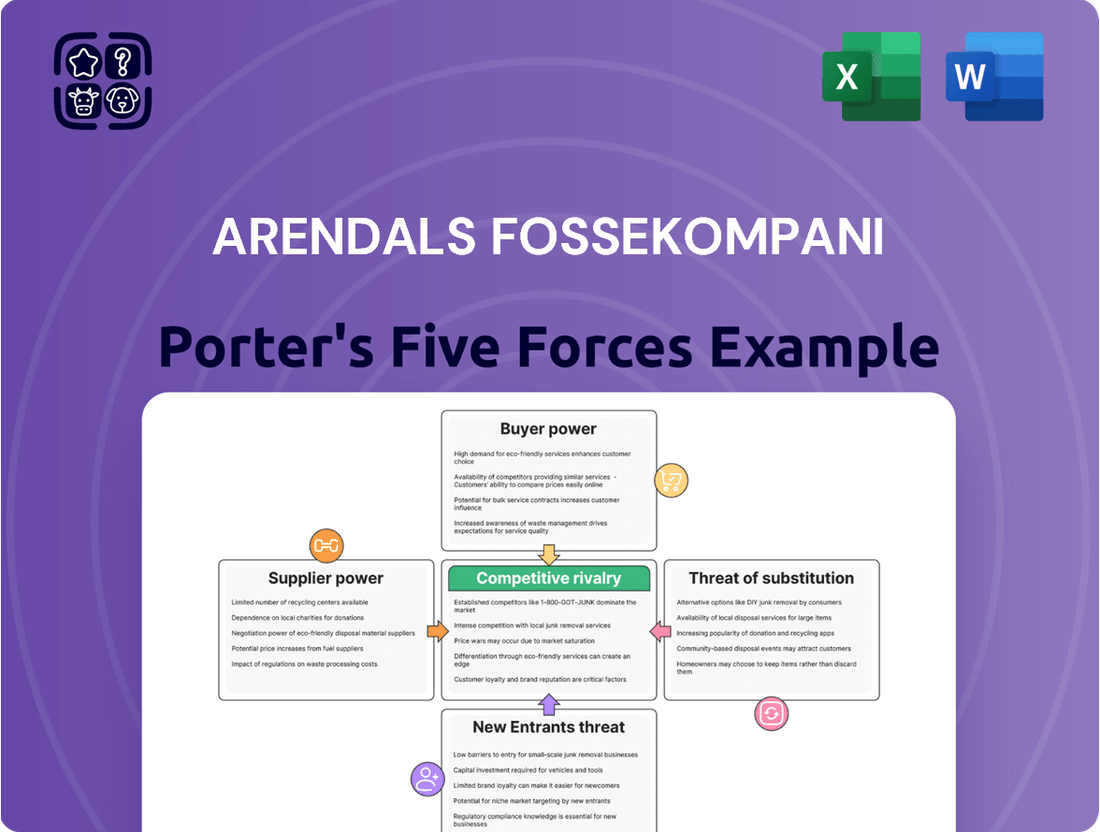
Arendals Fossekompani Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arendals Fossekompani Bundle
Arendals Fossekompani navigates a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the significant threat of substitutes, particularly from renewable energy sources. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Arendals Fossekompani’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Arendals Fossekompani's significant investments in renewable energy, particularly in battery technology and energy storage, place it in a position where suppliers of critical raw materials like lithium and cobalt, as well as specialized equipment such as advanced turbines and solar panels, can wield considerable influence. The concentration of these specialized suppliers globally means Arendals Fossekompani may face limited alternatives for certain components.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is further shaped by market dynamics. For example, the global lithium-ion battery market, a key area for Arendals Fossekompani's expansion, is projected for substantial growth. However, ongoing efforts to localize battery production and secure supply chains within regions like the US and Europe are designed to mitigate dependence on a few dominant suppliers. This strategic shift could gradually alter the supplier power balance in the coming years, potentially reducing the leverage of highly concentrated global sources by 2024 and beyond.
Arendals Fossekompani's reliance on suppliers for maintenance and specialized equipment for its hydropower assets, such as turbine upgrades or hydrological monitoring systems, presents a moderate level of supplier power. While the hydropower sector has a mature technology base, meaning many suppliers exist, the need for highly specialized components or services for critical infrastructure can still grant significant leverage to certain suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Arendals Fossekompani, particularly in areas like battery technology and other sustainable innovations, is significantly shaped by the speed of technological advancements and the accessibility of substitute materials or production methods. For instance, breakthroughs in solid-state battery development could alter the demand for specific raw materials, thereby influencing the leverage held by existing suppliers.
Supplier Power 4
Arendals Fossekompani's approach, emphasizing long-term ownership and active engagement within its portfolio, indicates a strategic effort to cultivate robust, potentially integrated, supplier relationships. This active management could diminish supplier leverage over time as the company gains enhanced visibility and greater control across its supply chains.
The company's financial reports for 2023 highlight a continued focus on operational efficiency and strategic investments in its core energy and industrial technology segments. While specific supplier concentration data isn't publicly detailed, the proactive management style suggests a deliberate strategy to mitigate risks associated with supplier dependency.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Arendals Fossekompani's active ownership model fosters deeper supplier integration, potentially reducing reliance on individual suppliers and increasing bargaining power.
- Strategic Sourcing: The company's focus on long-term value creation likely involves strategic sourcing initiatives to secure favorable terms and ensure supply chain stability.
- Portfolio Synergy: By actively managing its portfolio companies, Arendals Fossekompani can identify opportunities for consolidated purchasing or shared supplier agreements, thereby enhancing its collective bargaining power.
Supplier Power 5
Geopolitical shifts and evolving trade policies can significantly impact the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly for critical raw materials essential to green technologies. For instance, the 2024 global trade landscape, marked by ongoing trade disputes and nationalistic industrial policies, has already demonstrated how these factors can concentrate supply chains and elevate supplier leverage. Disruptions, such as those experienced in 2023 due to regional conflicts impacting rare earth mineral extraction, or the imposition of tariffs on key components, directly increase the cost and limit the availability of vital inputs for companies like Arendals Fossekompani. This heightened dependency amplifies the suppliers' ability to dictate terms.
The concentration of suppliers for specialized components or raw materials also plays a crucial role. If only a few entities control the production of essential inputs, their bargaining power naturally increases. For example, in the battery technology sector, which is crucial for energy storage solutions, a limited number of countries dominate the supply of lithium and cobalt. As of early 2024, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Australia remain the largest producers of cobalt and lithium respectively, creating a potential bottleneck for global manufacturers and granting significant leverage to suppliers within these regions.
- Geopolitical Instability: Events like the ongoing conflict in Eastern Europe continue to disrupt global energy markets and critical mineral supply chains, directly affecting input costs for renewable energy infrastructure.
- Trade Tariffs and Protectionism: The implementation of tariffs on key materials, such as those seen in trade disputes between major economic blocs in 2023-2024, can artificially inflate prices and reduce supplier options.
- Concentration of Key Resources: A significant portion of global rare earth elements, vital for wind turbines and electric vehicles, are sourced from a limited number of countries, giving those suppliers substantial pricing power.
- Technological Dependencies: The specialized nature of components required for advanced green technologies means that companies often rely on a few key innovators or manufacturers, enhancing supplier bargaining strength.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Arendals Fossekompani is influenced by the concentration of critical raw material sources and specialized technology providers. For instance, the dominance of a few nations in cobalt and lithium production, like the Democratic Republic of Congo and Australia respectively, grants significant leverage to suppliers in these regions as of early 2024. This concentration, coupled with geopolitical factors and trade policies, can amplify supplier influence.
Arendals Fossekompani's strategic investments in renewable energy, particularly battery technology, expose it to suppliers of essential components and raw materials. The company's efforts to diversify supply chains and explore localized production aim to mitigate this supplier power, but the rapid pace of technological advancement in areas like solid-state batteries could shift the landscape, impacting the leverage of existing material suppliers.
The company's proactive supplier relationship management and portfolio synergy strategies are designed to enhance its collective bargaining power. By fostering deeper integration and potentially consolidating purchasing, Arendals Fossekompani seeks to secure more favorable terms and ensure supply chain stability, thereby counteracting the inherent power of concentrated suppliers.
| Key Input Material | Dominant Suppliers (Regions/Countries) | Estimated Global Market Share (approx. 2024) | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Australia, Chile, China | Australia: ~28% Chile: ~22% |
High; limited number of major producers, increasing demand for EVs. |
| Cobalt | Democratic Republic of Congo, Australia, Cuba | DRC: ~70% | Very High; extreme concentration in one country, ethical sourcing concerns. |
| Rare Earth Elements | China | ~60-70% | Very High; China's near-monopoly impacts wind turbine and EV magnet production. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability of Arendals Fossekompani by examining industry rivals, buyer and supplier power, new entrants, and substitute products.
Arendals Fossekompani's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, visual representation of competitive pressures, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic planning.
This analysis acts as a pain point reliever by offering actionable insights into industry attractiveness and potential threats, enabling more informed and confident decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Arendals Fossekompani's buyer power is influenced by the nature of its investments. For its renewable energy segment, large industrial clients and grid operators possess significant leverage. These entities often purchase substantial volumes of energy, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms and long-term power purchase agreements. In 2024, the global renewable energy market saw continued growth, with large-scale off-take agreements being crucial for project financing and profitability.
In the battery technology sector, Arendals Fossekompani's clients, such as electric vehicle manufacturers and energy storage system integrators, can wield significant bargaining power. The burgeoning electric vehicle market, projected to reach over 30 million units sold globally in 2024, means large buyers can negotiate favorable terms due to their substantial order volumes.
The bargaining power of customers for Arendals Fossekompani's sustainable technologies hinges on market adoption and the availability of alternatives. For instance, if a new renewable energy solution offers significant cost savings or efficiency gains compared to existing options, customer leverage would likely be diminished.
In 2024, the demand for green hydrogen, a key area for sustainable technology development, continued to grow. However, the relatively high production costs and limited infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations in many regions still give customers some bargaining power, as they weigh the benefits against the current practicalities and overall expense.
Conversely, for established sustainable technologies like solar power, where the market is more mature and competitive, customers generally possess greater bargaining power. This is evident in the declining prices of solar panels, driven by increased manufacturing capacity and technological advancements, allowing buyers to negotiate more favorable terms.
Buyer Power 4
Arendals Fossekompani's strategic emphasis on the green transition means its customers are increasingly motivated by sustainability and regulatory mandates. This can lead to a customer segment willing to pay more for certified green products, lessening their price sensitivity and, consequently, their bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for renewable energy solutions saw significant growth, with many industrial clients actively seeking suppliers aligned with their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets. This trend suggests that customers prioritizing sustainability may exhibit lower bargaining power due to a reduced focus on cost alone.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Customers focused on achieving sustainability goals may be less sensitive to price variations for green energy solutions.
- Premium for Certified Solutions: A segment of Arendals Fossekompani's customer base may be willing to pay a premium for products and services that meet rigorous green certifications.
- Supplier Lock-in: The specialized nature of green transition solutions can sometimes lead to a degree of supplier lock-in, further diminishing customer bargaining power.
- Regulatory Driven Demand: Evolving environmental regulations can compel customers to adopt specific solutions, limiting their ability to negotiate terms based solely on price.
Buyer Power 5
Arendals Fossekompani's long-term ownership strategy fosters stable, strategic relationships with its portfolio companies and their customers. This approach cultivates collaborative environments where bargaining power is less about adversarial negotiation and more about mutual growth and shared value creation, rather than solely focusing on immediate price reductions.
This focus on partnership can mitigate excessive customer bargaining power by aligning incentives. For instance, if Arendals Fossekompani's portfolio companies are essential service providers, customers may have less leverage if switching costs are high and the service is critical to their operations. In 2024, the energy sector, where many of Arendals Fossekompani's investments lie, saw continued demand for reliable power, potentially limiting customer ability to dictate terms aggressively.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Long-term partnerships can lead to customers valuing reliability and service over marginal price differences.
- Collaborative Innovation: Shared goals can result in joint efforts to improve products or services, benefiting both parties.
- Customer Loyalty: A focus on relationship building enhances customer retention, diminishing their power to demand concessions.
- Strategic Alignment: When customer needs are deeply understood and integrated into business strategy, their bargaining position is often softened.
Arendals Fossekompani's customer bargaining power varies significantly across its diverse portfolio. For large industrial clients in the renewable energy sector, high volume purchases enable substantial negotiation leverage, a trend amplified in 2024's growing renewable market. Similarly, major electric vehicle manufacturers, key customers in battery technology, can command favorable terms due to significant order volumes, especially with the EV market's rapid expansion in 2024.
However, Arendals Fossekompani can mitigate customer power through strategic alignment and fostering long-term partnerships. When customers prioritize sustainability and regulatory compliance, their price sensitivity decreases, and they may even pay a premium for certified green solutions. This focus on collaborative growth and essential services can reduce the inclination for aggressive price negotiations.
| Customer Segment | Key Influencing Factors | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Industrial Clients (Renewable Energy) | Volume of purchase, long-term contracts | High | Continued growth in renewable energy market, crucial off-take agreements |
| EV Manufacturers (Battery Technology) | Order volume, market demand | High | Rapid expansion of EV market, projected over 30 million units sold globally in 2024 |
| Clients prioritizing Sustainability | ESG targets, regulatory mandates | Lower (due to reduced price sensitivity) | Increased demand for ESG-aligned suppliers |
| Clients of Established Technologies (e.g., Solar) | Market maturity, availability of alternatives | Moderate to High | Declining solar panel prices due to increased capacity |
What You See Is What You Get
Arendals Fossekompani Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Arendals Fossekompani delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This detailed report provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning and future outlook of Arendals Fossekompani.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Arendals Fossekompani faces intense competition within the burgeoning green transition sectors. The market for renewable energy, battery technology, and sustainable solutions is a magnet for capital, drawing in a diverse array of competitors from private equity, established energy giants, and specialized asset managers. This influx of players intensifies the rivalry for promising projects and technological advancements. For instance, the global renewable energy market alone was valued at approximately $1,053.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $2,171.4 billion by 2030, according to some market analyses, highlighting the significant growth and the crowded nature of the space.
Competitive rivalry within the renewable energy investment sector is notably fierce. This is driven by escalating demand for clean energy solutions and significant capital inflows from both public and private sources. Investors are actively competing to acquire promising companies and projects, creating a dynamic and often challenging market landscape.
The battery technology sector, particularly for electric vehicle (EV) batteries and broader energy storage solutions, is characterized by intense competition. Established automotive manufacturers and battery giants are locked in a battle with numerous agile startups, all striving to capture significant market share.
This rivalry is further amplified by a relentless drive for cost reduction and groundbreaking technological innovation. The pursuit of next-generation technologies, such as solid-state batteries, which promise enhanced safety and energy density, is a key factor intensifying the competitive landscape.
For instance, in 2024, global investments in battery manufacturing capacity are projected to exceed $100 billion, reflecting the high stakes and aggressive expansion efforts by major players like CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic, alongside emerging companies.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Arendals Fossekompani's strategy of active, long-term ownership and a focus on business-to-business companies within the energy and technology sectors sets it apart from more passive investment approaches. This deliberate positioning creates a unique competitive landscape.
However, the company faces significant rivalry from other industrial investors and venture capital firms that share a similar long-term outlook and a specialization in these specific sectors. These players often possess substantial capital and deep industry expertise, directly challenging Arendals Fossekompani's market position.
- Direct Competitors: Industrial conglomerates and specialized venture capital funds targeting energy and technology B2B markets.
- Strategic Overlap: Competitors also employ long-term investment horizons and active ownership models.
- Market Dynamics: The intensity of rivalry is influenced by the availability of attractive investment opportunities and the capital deployed by competing entities.
Competitive Rivalry 5
While Norway, with its abundant hydropower, offers a solid foundation for the green transition, competitive rivalry is intensifying. Other nations are demonstrating greater ambition and faster progress in developing green value chains, impacting investment flows and the overall competitive positioning for companies like Arendals Fossekompani.
This regional competition means that while Norway has natural advantages, the pace of innovation and investment elsewhere can create a dynamic where opportunities might shift. For instance, countries actively courting green hydrogen production are attracting significant global capital, potentially diverting some of the focus and funding that might otherwise come to Norwegian initiatives.
- Norway's Hydropower Advantage: Strong base for green energy initiatives.
- Global Green Transition Pace: Other countries are progressing faster in green value chains.
- Investment Diversion: Ambitious nations are attracting significant global capital for green projects.
- Competitive Landscape Impact: This rivalry affects investment opportunities and market positioning.
Arendals Fossekompani operates in sectors experiencing intense competition, particularly in renewable energy and battery technology, where global investment is substantial. For example, global renewable energy market was valued at approximately $1,053.8 billion in 2023. The company's focus on B2B energy and technology sectors pits it against other long-term industrial investors and venture capital firms with similar strategies and deep sector knowledge.
| Sector | 2023 Market Value (USD Billion) | Projected 2024 Investment (USD Billion) | Key Competitor Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | 1,053.8 | N/A (Growth continues) | PE, Energy Giants, Asset Managers |
| Battery Manufacturing | N/A (Rapidly growing) | >100 | Automotive OEMs, Battery Giants, Startups |
SSubstitutes Threaten
In the renewable energy sector, traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas continue to represent a significant threat of substitution for Arendals Fossekompani. Despite the global momentum towards decarbonization and the falling costs of renewable energy sources, fossil fuels can still offer a temporary cost advantage, particularly during periods of volatile energy prices. For instance, in early 2024, some regions experienced a temporary resurgence in coal-fired power generation due to specific market conditions, highlighting the persistent, albeit diminishing, allure of these substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Arendals Fossekompani, particularly in its energy storage and renewable energy segments, is a significant consideration. While lithium-ion batteries are currently prevalent, emerging battery technologies like solid-state batteries, which promise greater safety and energy density, could disrupt the market. Furthermore, advancements in alternative energy storage methods, such as pumped hydro storage and hydrogen fuel cells, offer different pathways for grid stability and energy management, potentially reducing reliance on traditional battery solutions.
For Arendals Fossekompani's hydropower assets, while a stable technology, substitutes like geothermal or nuclear power present a threat, particularly where hydropower potential is constrained. In 2024, global renewable energy investment saw significant growth, with solar and wind leading, but baseload alternatives remain crucial for grid stability.
4
In the sustainable technologies arena, the threat of substitutes is significant, stemming from alternative methods to address environmental concerns. For example, carbon capture and storage (CCS) can be viewed as a substitute for direct emission reductions in certain industrial applications, potentially impacting the demand for renewable energy solutions. Similarly, advancements in energy efficiency can decrease the overall need for new energy generation technologies, including those offered by companies like Arendals Fossekompani. In 2024, the global market for carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies was projected to reach approximately $10 billion, indicating a growing alternative approach to emissions management.
These substitutes can erode the market share of traditional sustainable energy providers by offering different pathways to achieve environmental goals. For instance, a factory might invest in advanced insulation and process optimization to reduce its energy consumption by 20% rather than solely relying on sourcing cleaner electricity. This shift in focus towards efficiency can directly reduce the addressable market for energy suppliers. In 2023, the International Energy Agency reported that energy efficiency measures saved the equivalent of the European Union's total energy consumption, highlighting the substantial impact of efficiency as a substitute.
- Carbon Capture Technologies: Offer an alternative to direct emission reduction, potentially diverting investment from renewable energy projects.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Reduce the overall demand for energy, thereby lessening the need for new energy generation capacity.
- Technological Advancements: New innovations in waste-to-energy or advanced battery storage could also present substitute solutions for grid stability and power provision.
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Government incentives favoring specific alternative technologies over others can also create substitute pressures.
5
The threat of substitutes for Arendals Fossekompani is significant, particularly due to the accelerating pace of innovation in green technologies. As new solutions emerge, they could challenge the competitive position of AFK's existing portfolio companies. For instance, advancements in battery storage technology or alternative renewable energy sources like advanced geothermal or tidal power could offer comparable or superior energy generation and distribution capabilities, potentially at a lower cost or with greater efficiency.
Arendals Fossekompani must therefore remain agile, continuously evaluating and investing in emerging technologies to stay ahead of potential disruptions. This proactive approach is crucial to mitigate the risk of their current assets becoming obsolete. By staying abreast of developments, AFK can strategically adapt its portfolio, ensuring long-term competitiveness in the evolving energy landscape. The company's commitment to research and development is a key factor in navigating this dynamic environment.
- Technological Obsolescence: Rapid advancements in renewable energy and storage solutions pose a direct threat to the long-term viability of existing energy infrastructure.
- Cost Competitiveness: Emerging green technologies may offer lower operational costs or higher energy yields, making them more attractive substitutes.
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Government incentives or mandates favoring newer technologies could accelerate the adoption of substitutes.
- Investment in R&D: Arendals Fossekompani's ongoing investment in research and development is critical to identify and integrate next-generation solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Arendals Fossekompani is multifaceted, encompassing traditional energy sources, alternative green technologies, and efficiency improvements. While hydropower is a stable technology, substitutes like advanced geothermal or even nuclear power can emerge, especially where hydropower potential is limited. In 2024, global renewable energy investments continued to surge, with solar and wind dominating, but the need for reliable baseload power means these alternatives remain relevant.
Emerging battery technologies beyond lithium-ion, such as solid-state batteries, present a significant substitute threat in energy storage, promising enhanced safety and density. Furthermore, alternative energy storage methods like pumped hydro and hydrogen fuel cells offer different approaches to grid stability. In the sustainable technology sphere, carbon capture and storage (CCS) acts as a substitute for direct emission reductions, potentially diverting investment from renewable projects. Energy efficiency measures also reduce overall energy demand, impacting the market for new generation capacity. For instance, the International Energy Agency reported in 2023 that energy efficiency saved the equivalent of the EU's total energy consumption, underscoring its impact.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Arendals Fossekompani | 2024 Market Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Energy Sources | Coal, Oil, Natural Gas | Temporary cost advantage during price volatility; persistent, though diminishing, market presence. | Some regions saw temporary resurgence in coal in early 2024 due to market conditions. |
| Alternative Green Technologies | Solid-state batteries, Hydrogen fuel cells, Advanced geothermal, Tidal power | Potential for superior performance, lower cost, or greater efficiency, challenging existing assets. | Global renewable energy investment in 2024 saw solar and wind leading, but baseload alternatives remain critical. |
| Energy Efficiency | Improved insulation, Process optimization | Reduces overall energy demand, shrinking the addressable market for energy suppliers. | IEA reported 2023 efficiency savings equivalent to EU's total energy consumption. |
| Emissions Management | Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) | Offers alternative to direct emission reduction, potentially diverting investment from renewables. | CCUS market projected around $10 billion in 2024, indicating growing adoption. |
Entrants Threaten
The renewable energy and green technology sectors are experiencing massive growth, attracting significant investment. Global energy transition investments reached an impressive $2.1 trillion in 2024 alone. This surge in capital makes these markets incredibly appealing to new players, effectively lowering the financial hurdles to entry.
The threat of new entrants for Arendals Fossekompani, particularly in emerging green technology sectors like battery storage, is moderate but growing. While Arendals Fossekompani has deep roots in hydropower, the broader sustainable technology market is seeing innovation that lowers entry barriers. For instance, the cost of lithium-ion battery packs has seen a dramatic decline, falling by over 90% in the last decade, making it more feasible for new companies to establish a presence.
The threat of new entrants for Arendals Fossekompani is moderate, largely influenced by the capital-intensive nature of the hydropower sector. However, supportive government policies and incentives for renewable energy, such as those promoting green hydrogen production, can lower entry barriers. For instance, Norway's commitment to decarbonization and its robust regulatory framework for hydropower development create a relatively stable environment, but significant upfront investment in infrastructure remains a substantial hurdle for newcomers.
4
The threat of new entrants for Arendals Fossekompani, particularly in the renewable energy and climate technology sectors, is moderate. While significant capital investment is typically required for large-scale infrastructure projects like hydropower, the growing availability of venture capital and private equity specifically targeting climate tech is lowering financial barriers. Investors are actively seeking opportunities in these high-growth areas, making it easier for new, innovative companies to emerge.
This trend is supported by the increasing global investment in clean energy. For instance, in 2024, global investment in the energy transition reached an estimated $2 trillion, a substantial increase from previous years, indicating a strong appetite for new players in the sustainable energy market. This influx of capital can fund disruptive technologies and business models, potentially challenging established companies.
- Growing Venture Capital in Climate Tech: Funds dedicated to climate solutions saw significant growth in 2024, with billions deployed globally.
- Lowered Capital Requirements for Niche Technologies: Innovations in areas like distributed solar or advanced battery storage may require less upfront capital than traditional large-scale projects.
- Policy Support for Renewables: Government incentives and subsidies in many regions encourage new entrants by reducing operational costs and risks.
- Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in areas such as green hydrogen production or carbon capture can create new market opportunities for agile newcomers.
5
The threat of new entrants for Arendals Fossekompani is generally moderate. The company's established infrastructure in renewable energy, particularly hydropower, represents a significant capital investment barrier. For instance, developing new large-scale hydropower projects requires billions in upfront capital and years of planning and construction, deterring many potential new players.
However, the energy sector is dynamic, and disruptive technologies could lower entry barriers. While traditional energy infrastructure is a hurdle, new entrants focusing on decentralized renewable solutions or advanced energy storage technologies might find pathways to compete. For example, the rapid growth in battery storage solutions could allow new, agile companies to integrate with existing grids without the massive upfront costs of traditional power generation.
Arendals Fossekompani's active ownership model, fostering specialized knowledge and long-term relationships, also serves as a deterrent. This deep industry expertise and established network are not easily replicated by newcomers. Yet, in emerging technological niches within the broader energy landscape, innovative business models could potentially circumvent these traditional advantages.
Consider the evolving landscape of green hydrogen production, an area where Arendals Fossekompani is actively investing. While established players have an advantage, new entrants with novel electrolysis technologies or unique supply chain integrations could emerge, posing a threat. The company's 2024 strategy includes significant investments in expanding its renewable energy portfolio, aiming to solidify its competitive position against potential disruptors.
The threat of new entrants for Arendals Fossekompani is moderate, largely due to the substantial capital requirements for traditional renewable energy infrastructure like hydropower. Developing a new large-scale hydropower plant can easily cost billions of dollars and take many years to complete, creating a significant barrier for most new companies.
However, the growing investment in emerging green technologies is making entry more feasible for agile newcomers. Global investment in the energy transition reached approximately $2 trillion in 2024, with a notable surge in venture capital for climate tech, which saw billions deployed globally in the same year. This influx of capital can fund innovative business models and technologies, potentially lowering entry barriers in niche markets.
While Arendals Fossekompani benefits from deep industry expertise and established relationships, advancements in areas like battery storage and green hydrogen production offer new avenues for potential competitors. For example, the cost of lithium-ion battery packs has fallen by over 90% in the last decade, making these solutions more accessible for new market participants.
Government policies and incentives supporting renewable energy also play a role in shaping this threat. These initiatives can reduce operational costs and risks for new entrants, encouraging innovation and competition within the sector.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to Arendals Fossekompani |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity (Hydropower) | High Barrier | Established infrastructure requires massive upfront investment. |
| Venture Capital in Climate Tech | Lowered Barrier | Billions deployed globally in 2024, funding innovative startups. |
| Technological Advancements (e.g., Batteries) | Lowered Barrier | Cost of lithium-ion battery packs down over 90% in 10 years. |
| Policy Support for Renewables | Lowered Barrier | Incentives reduce costs and risks for new players. |
| Industry Expertise & Relationships | High Barrier | Deep knowledge and networks are difficult for newcomers to replicate. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Arendals Fossekompani is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and data from reputable financial information providers. These sources offer comprehensive insights into the company's operational landscape and competitive environment.
