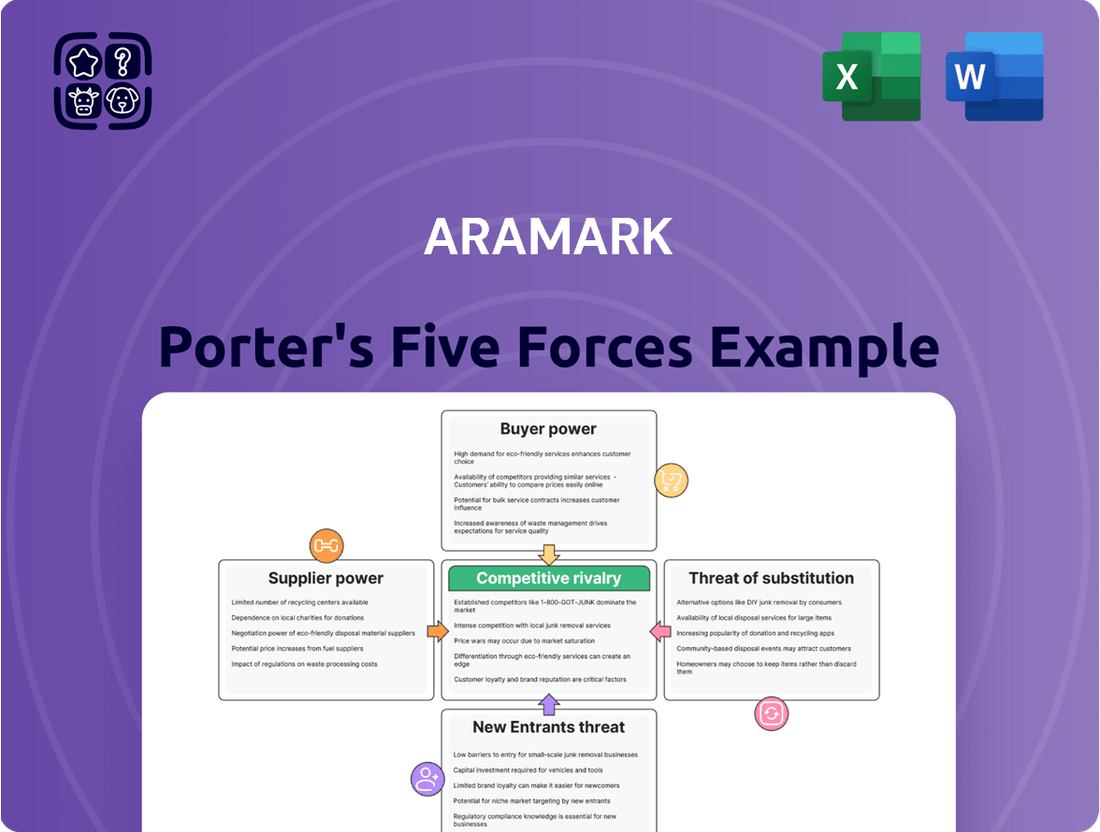
Aramark Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aramark Bundle
Aramark navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp Aramark's market position and future potential.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Aramark’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Aramark's reliance on a broad spectrum of suppliers, from food and beverages to specialized equipment and uniforms, positions it within a complex supply chain. The company's operational scale means it engages with numerous vendors, each with varying degrees of influence.
The food service and equipment supply sectors, critical for Aramark's operations, are notably concentrated. Major global players like Sysco Corporation, US Foods, and Performance Food Group dominate these markets. For instance, Sysco reported revenues of $73.1 billion in fiscal year 2023, highlighting its significant market presence and scale.
This market concentration grants these large suppliers considerable bargaining power. Their ability to influence pricing, terms, and availability of essential goods can directly impact Aramark's cost structure and operational efficiency. The sheer volume these suppliers handle allows them to negotiate favorable terms, potentially limiting Aramark's leverage.
Aramark's commitment to supplier diversity is a key strategy for managing supplier power. By aiming to increase spending with small, local, and diverse businesses to 25% by 2025, Aramark reduces its reliance on any single dominant supplier. This diversification not only strengthens its negotiating position but also fosters broader economic participation.
Supplier switching costs for Aramark can be considered moderate. While not always explicitly detailed in financial reports, changing major food or equipment providers typically involves significant logistical hurdles, the need to renegotiate contracts, and the potential for service disruptions. These factors create a degree of stickiness for existing supplier relationships.
Forward Integration Threat from Suppliers
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration into managed services is generally low for Aramark. Their primary suppliers, dealing in food, facilities products, or uniforms, typically focus on their core competency of supply, not the complex service delivery that defines Aramark's business. Such a strategic shift would represent a substantial departure from their existing models and place them in direct competition with their current customer base, a move most suppliers would find unviable.
For instance, a major food distributor's business model is centered on logistics and product provision, not managing cafeterias or event catering. The capital investment and operational expertise required for Aramark's service-oriented business are vastly different from a supplier's current operations. This specialization creates a natural barrier to forward integration.
Consider the scale: Aramark operates in diverse sectors, including education, healthcare, and sports & entertainment, each with unique service requirements. Suppliers would need to develop broad capabilities across these varied service landscapes, which is a significant undertaking compared to their established supply chain roles. In 2023, Aramark reported revenue of $13.8 billion, highlighting the substantial scale of services they provide, which would be difficult for most individual suppliers to replicate independently.
- Low Likelihood of Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers of food, facilities products, and uniforms are unlikely to enter Aramark's managed services sector due to the significant business model shift and direct competition implications.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Suppliers' primary strength lies in supply chain management and product provision, not the intricate service delivery that Aramark specializes in.
- Barriers to Entry for Suppliers: The capital, operational expertise, and diverse service capabilities required to compete with Aramark represent substantial hurdles for most suppliers.
Input Differentiated by Suppliers
Aramark's bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by product differentiation. While many standard food and operational supplies are sourced from numerous vendors, limiting individual supplier leverage, certain specialized items can shift the balance. For instance, if a supplier provides unique, high-quality ingredients or proprietary uniform materials that are critical to Aramark's service offering, that supplier gains increased bargaining power.
The availability of substitutes and the concentration of suppliers play a key role. For commodity items like basic food staples or cleaning supplies, Aramark benefits from a broad supplier base, typically with over 100,000 active suppliers in a given year, which keeps individual supplier power in check. However, for specialized equipment or custom-designed uniforms, the supplier pool is smaller, potentially increasing their influence.
In 2024, Aramark's supply chain likely saw continued focus on cost optimization and supplier relationship management. While specific data on supplier price increases for differentiated goods isn't publicly detailed, the general inflationary environment would have put pressure on procurement. Aramark's scale, however, allows for significant purchasing volume, which can be leveraged to negotiate favorable terms even with specialized suppliers.
- Differentiated Offerings: Suppliers providing unique ingredients or proprietary materials can command greater leverage.
- Commodity Sourcing: The wide availability of standard supplies from multiple vendors limits individual supplier power.
- Supplier Concentration: A smaller pool of suppliers for specialized items can increase their bargaining strength.
- Purchasing Volume: Aramark's substantial scale often allows it to negotiate favorable terms across its supplier base.
The bargaining power of Aramark's suppliers is a significant factor, particularly for those providing essential goods and services. The concentration within key supply sectors, such as food and equipment, means that a few large players can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms. This concentration is evident with major food distributors like Sysco, which reported revenues of $73.1 billion in fiscal year 2023, showcasing their market dominance.
While Aramark's vast operational scale, with revenues of $13.8 billion in 2023, allows it to leverage its purchasing volume, the specialized nature of some supplies can shift power towards suppliers. For instance, suppliers of unique ingredients or proprietary materials gain increased leverage. Conversely, for commodity items, Aramark benefits from a broad supplier base, often engaging with over 100,000 active suppliers annually, which helps to mitigate individual supplier power.
Despite inflationary pressures in 2024, Aramark's purchasing volume remains a key negotiation tool. The moderate switching costs associated with changing major suppliers, involving logistical challenges and potential service disruptions, also contribute to the existing supplier relationships' stickiness. The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Aramark's service business remains low due to the substantial differences in business models and required expertise.
What is included in the product
Aramark's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of competition, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within its diverse service sectors.
Easily visualize Aramark's competitive landscape with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that highlights key pressures and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Aramark's extensive reach across education, healthcare, and business sectors means it serves a wide array of clients. This broad customer base typically limits the bargaining power of any individual client, as no single contract represents an overwhelming portion of Aramark's revenue.
While this diversity generally weakens customer power, certain large, institutional clients, particularly those in government or major university systems, can wield significant influence. For instance, securing contracts with large school districts or major healthcare networks involves substantial revenue, potentially giving these clients more leverage in negotiations.
Aramark's reliance on profit and loss contracts, typically spanning 3-5 years, grants customers significant bargaining power. During the negotiation and renewal phases of these agreements, clients can leverage their business to secure more favorable terms. This contractual structure, while offering some revenue predictability, inherently positions customers as a key force in shaping Aramark's pricing and service delivery.
Aramark focuses on keeping clients happy to ensure they renew their contracts. In 2023, they reported a strong 78% retention rate across their institutional business, showing clients are generally satisfied with the services provided.
This high retention is crucial, but it also gives customers leverage. When contracts are up for renewal, clients know Aramark wants to keep them, allowing them to negotiate for better terms or pricing, thus increasing their bargaining power.
Customer's Ability to In-House Services
A significant threat to Aramark stems from clients' capacity to manage services internally. A notable portion of organizations still opt for in-house operations for food, facilities, or uniform management. This capability grants customers substantial bargaining power.
Clients can leverage their ability to self-provide as a negotiating tactic, threatening to bring services in-house if outsourcing terms are not deemed favorable. This directly impacts Aramark's pricing and contract conditions.
- Client Retention Risk: The potential for clients to internalize services poses a direct risk to Aramark's revenue streams.
- Negotiating Leverage: Clients with the capacity for in-house operations gain significant leverage in contract negotiations.
- Market Dynamics: The prevalence of in-house service models in certain sectors can influence Aramark's competitive positioning.
- Cost Sensitivity: Clients assessing the cost-effectiveness of outsourcing versus internal provision directly impacts Aramark's pricing strategies.
Price Sensitivity and Cost-Value Proposition
Clients, particularly in education and healthcare, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. They are actively seeking cost-effective solutions that still deliver high-quality service. This means Aramark must clearly articulate its value proposition and demonstrate operational efficiency to secure and retain business, as the cost-value relationship is a primary factor in their procurement decisions.
For instance, in the 2023 fiscal year, Aramark reported revenue of $21.2 billion, reflecting the scale of its operations and the importance of competitive pricing across its diverse client base. The ability to offer compelling value for money is a critical differentiator in a market where clients have numerous alternatives and are constantly evaluating their spending.
- Price Sensitivity: Many clients, especially in public sectors like education and healthcare, operate with tight budgets and scrutinize costs heavily.
- Cost-Value Proposition: Aramark must prove that its services provide superior value relative to their price point to win and retain contracts.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Clients often compare Aramark's pricing and service offerings against competitors, making transparency and demonstrable efficiency crucial.
Aramark's diverse client base generally dilutes individual customer power, but large institutional clients can exert significant influence due to contract size.
Clients' ability to manage services internally or switch providers grants them substantial bargaining leverage, especially during contract renewals, impacting Aramark's pricing and terms.
Price sensitivity among clients, particularly in sectors like education and healthcare, necessitates Aramark demonstrating strong value for money to secure and retain business.
| Factor | Impact on Aramark | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Client Concentration | Low overall, but high for key accounts | Aramark's broad client base limits individual client leverage. However, large contracts with entities like major universities or healthcare systems can represent significant revenue, increasing their negotiation power. |
| Switching Costs & Internalization Capability | Moderate to High | Clients capable of bringing services in-house (e.g., food service management, facilities) can threaten to do so, giving them leverage. Aramark's 78% institutional retention rate in 2023 indicates client satisfaction, but the option to self-manage remains a powerful negotiation tool. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Many clients, especially in public sectors, are cost-conscious. Aramark's $21.2 billion in fiscal year 2023 revenue underscores the need for competitive pricing and a clear cost-value proposition. |
Full Version Awaits
Aramark Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Aramark Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You're viewing the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights without any surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Aramark navigates a landscape teeming with rivals, from small local caterers to large multinational corporations, across its food, facilities, and uniform divisions. This intense rivalry is a defining characteristic of its operating environment.
The sheer scale of the global food service market, valued at an estimated $4.3 trillion in 2023, underscores the vast number of participants Aramark must contend with. This fragmented nature means no single entity dominates, intensifying the competitive pressures.
Aramark faces formidable competition from major global players like Compass Group and Sodexo. These companies offer a broad spectrum of services, mirroring Aramark's own diversified portfolio, and possess extensive international reach. For example, Compass Group's reported revenues often significantly surpass Aramark's, underscoring the intensity of competition for contracts and market share across various sectors.
Competitors in the food service and facilities management sectors frequently offer similar services, creating intense competition for clients. This overlap means companies like Aramark often find themselves in bidding wars for contracts across diverse industries, from education to healthcare.
For instance, in 2024, Aramark continued to face robust competition from players like Compass Group and Sodexo, both of whom possess extensive portfolios and global reach. These rivals often present comparable service packages, making the bidding process highly price-sensitive and service-quality driven.
Aramark's success in securing new business and retaining existing clients is directly impacted by this competitive landscape. The constant need to differentiate and offer compelling value propositions is crucial for maintaining and growing market share against these well-established competitors.
Differentiation Strategies
Aramark actively differentiates itself by investing in technology, offering integrated facility management, and tailoring services to specific industries. This approach helps them stand out in a competitive landscape.
Innovation is key for Aramark to maintain its edge. For instance, their focus on AI for service optimization and commitment to sustainability are critical differentiators.
- Technology Integration: Aramark leverages technology for enhanced service delivery and operational efficiency.
- Customized Solutions: They provide tailored offerings for diverse sectors like healthcare, education, and sports & entertainment.
- Sustainability Focus: Investments in eco-friendly practices and reporting are becoming a significant competitive advantage.
Market Share and Growth Focus
Aramark maintains a strong market position, particularly evident in its 55.20% share of the Services Sector as of Q1 2025 among publicly traded entities. However, the company is under pressure to accelerate its revenue growth beyond that of its rivals.
In fiscal year 2024, Aramark achieved an 8% overall revenue increase and a 10% rise in organic revenue, signaling a commitment to expansion. For fiscal year 2025, the company is prioritizing strategic growth initiatives and optimizing its capital deployment to outpace competitors.
- Market Share: Aramark held 55.20% of the Services Sector revenue among publicly traded companies in Q1 2025.
- Revenue Growth (FY2024): Reported an 8% increase in total revenue and 10% in organic revenue.
- Future Focus (FY2025): Emphasis on strategic growth and capital optimization to enhance competitive standing.
Aramark faces intense rivalry from both large global competitors and smaller, specialized firms across its diverse service offerings. This competitive pressure is amplified by the fragmented nature of the food service and facilities management markets, where differentiation is key to winning and retaining clients.
Major players like Compass Group and Sodexo often mirror Aramark's service breadth and global reach, leading to fierce competition for contracts. This dynamic necessitates continuous innovation and a strong value proposition to maintain market share.
In fiscal year 2024, Aramark reported an 8% total revenue increase and a 10% organic revenue growth, demonstrating efforts to compete effectively. However, the company aims to accelerate this growth to outpace rivals in 2025.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx. USD Billions) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Aramark | ~$23.7 (FY2024 est.) | Food Service, Facilities, Uniforms |
| Compass Group | ~$31.5 | Food Service, Support Services |
| Sodexo | ~$25.5 | Food Service, Facilities Management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for Aramark's outsourced services is a client's decision to manage food, facilities, and uniform needs internally. Many organizations, particularly those with specific requirements or a desire for greater control, opt for in-house operations, presenting a direct alternative to outsourcing.
A considerable portion of companies still maintain in-house departments for services like catering or facility management. For instance, while the exact percentage varies by industry, a significant number of businesses, especially smaller ones or those in niche sectors, find it more cost-effective or strategically advantageous to keep these functions in-house, limiting Aramark's market reach.
Clients might bypass a broad provider like Aramark for niche specialists. For instance, a university might contract a premium, local catering firm for its dining halls, or a large corporation could choose a boutique firm for specialized event catering, bypassing Aramark's integrated offerings.
This trend is fueled by a desire for tailored solutions and potentially better quality or cost-effectiveness in specific service areas. In 2024, the market for specialized contract services continues to grow, with many smaller, agile companies carving out significant market share by focusing on particular client needs.
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes for Aramark. For instance, AI-powered personalization in foodservice and advanced data integration in facilities management allow clients to handle operations more efficiently, potentially reducing their reliance on full-service providers. In 2024, the global market for AI in foodservice was projected to reach billions, highlighting the growing capability of these technologies to offer alternative solutions.
Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Uniform Management
The threat of do-it-yourself (DIY) uniform management for companies is a significant factor influencing the uniform services industry. Instead of contracting with a specialized provider like Aramark, businesses can opt to source uniforms directly from manufacturers. This internal approach allows them to handle all aspects of uniform distribution, cleaning, and upkeep themselves.
This DIY model can be particularly appealing for larger organizations with established internal logistics and maintenance capabilities. For instance, a major retail chain might find it more cost-effective to manage its uniform inventory and cleaning processes in-house, especially if they already operate extensive laundry facilities for other operational needs. The overall market for uniform and textile rental services in the US was valued at approximately $10.3 billion in 2023, indicating a substantial sector where such internal management decisions can have a notable impact.
- Direct Sourcing: Companies can bypass uniform service providers by purchasing uniforms directly from manufacturers, potentially securing better bulk pricing.
- Internal Management: Handling distribution, laundry, and maintenance internally gives businesses greater control over quality and scheduling.
- Cost Savings Potential: For organizations with existing infrastructure, managing uniforms in-house may offer cost efficiencies compared to outsourcing.
- Industry Impact: The significant size of the uniform rental market suggests that even a small shift towards DIY management by major players could influence industry dynamics.
Alternative Food and Beverage Options
The threat of substitutes for Aramark's food and beverage services is significant, especially in sectors like business and industry. Clients can easily shift to alternative dining models, such as utilizing food courts with diverse independent vendors, which offer variety and potentially lower price points.
Increased reliance on vending machines for convenient snacks and meals presents another substitute, particularly for quick service needs. Furthermore, in corporate environments, a growing trend sees employees opting to bring their own meals from home, reducing demand for catered or on-site food services.
For instance, in 2024, the at-home meal kit market continued to grow, with many consumers citing cost savings and perceived health benefits as primary drivers. This directly impacts the demand for external food services, including those provided by companies like Aramark.
- Food Courts: Offer a diverse range of independent vendors, providing choice and potentially competitive pricing.
- Vending Machines: Provide a convenient and accessible substitute for quick snacks and beverages.
- Packed Lunches: Employees bringing meals from home represent a direct reduction in demand for on-site food services.
Clients can manage food, facilities, and uniforms internally, bypassing outsourced providers like Aramark. This DIY approach is appealing for organizations with existing infrastructure or specific needs, potentially leading to cost savings and greater control. In 2024, the growing market for specialized contract services highlights how smaller, agile firms can capture market share by focusing on niche client demands, further fragmenting the landscape and increasing substitution threats.
| Substitute Type | Examples | Impact on Aramark |
| In-house Management | Companies managing their own catering, laundry, or facility maintenance. | Direct loss of potential contracts, reduced market penetration. |
| Niche Specialists | Boutique catering firms or specialized event planners. | Loss of integrated service contracts, competition on specific service offerings. |
| Technological Solutions | AI in foodservice, advanced data integration in facilities management. | Clients may reduce reliance on full-service providers by adopting more efficient internal tech. |
| Direct Sourcing (Uniforms) | Purchasing uniforms directly from manufacturers. | Circumvents uniform rental and maintenance services, impacting a significant revenue stream. |
| Alternative Dining Models | Food courts, increased use of vending machines, employees bringing meals from home. | Reduced demand for on-site food and beverage services, particularly in corporate settings. |
Entrants Threaten
The managed food, facilities, and uniform services sector demands significant upfront capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in establishing robust supply chains, acquiring specialized equipment, and building a skilled workforce to compete with established players like Aramark. For instance, in 2024, the cost of setting up a comprehensive catering operation, including kitchens, transportation fleets, and initial inventory, can easily run into millions of dollars, deterring many potential entrants.
Aramark and its competitors benefit from deeply entrenched client relationships, often solidified through multi-year service agreements. These long-standing partnerships represent a significant barrier for new companies attempting to enter the market. For instance, many large university systems or government entities have contracts with Aramark that extend for several years, making it difficult for a newcomer to displace the incumbent.
Existing large players like Aramark benefit from significant economies of scale in procurement, logistics, and operational efficiency. This allows them to negotiate better prices for supplies and spread fixed costs over a larger volume, leading to lower per-unit costs. For example, in 2023, Aramark reported revenues of $4.26 billion for its Food, Facilities, and Services segment, indicating a substantial operational footprint.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost advantages without substantial upfront investment and achieving a comparable scale of operations quickly. The high capital requirements to build out infrastructure and secure large contracts create a considerable barrier. Without achieving similar volume, new companies would likely face higher per-unit costs, making it difficult to compete on price with established giants like Aramark.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
The food, healthcare, and facilities management industries, where Aramark operates, are heavily regulated. New companies entering these sectors must contend with a complex web of health, safety, and operational compliance requirements. For example, in 2024, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continued to enforce stringent food safety regulations, requiring significant investment in process controls and documentation for any new food service provider. Similarly, healthcare facilities face rigorous standards from bodies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), demanding adherence to patient care protocols and infection control measures. Obtaining necessary certifications, such as HACCP for food safety or various accreditations for healthcare services, represents a substantial hurdle and cost for potential new entrants.
These regulatory and certification demands act as a significant barrier to entry for new competitors. Navigating these requirements demands specialized knowledge, dedicated resources, and a considerable time investment, often making it difficult for smaller or less established entities to compete with incumbents like Aramark, which already possess established compliance frameworks and expertise. In 2024, the cost of initial regulatory compliance for a new food service operation could easily range from tens of thousands to over a hundred thousand dollars, depending on the scale and specific services offered.
- Health and Safety Regulations: Strict adherence to food safety standards, workplace safety protocols, and environmental regulations is mandatory across Aramark's operating sectors.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Obtaining certifications like HACCP, ISO standards, or healthcare accreditations requires significant investment and operational alignment.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial upfront and ongoing costs associated with meeting and maintaining regulatory compliance, including training, auditing, and process implementation.
- Time to Market: The lengthy process of securing necessary permits and certifications can delay a new entrant's ability to operate and generate revenue.
Brand Reputation and Trust
Building a strong brand reputation and trust in critical services like food safety and facilities management is a significant barrier for new entrants. This trust is earned over time through consistent, high-quality performance, a factor that newcomers simply haven't had the opportunity to establish. For instance, in the competitive contract food services sector, where Aramark operates, client retention rates are often tied to perceived reliability and safety protocols, which are hard-won credentials.
New entrants would find it challenging to immediately gain the credibility necessary to attract and retain clients away from established providers like Aramark. Consider that in 2024, the food service management industry, a key segment for Aramark, saw continued emphasis on health and safety certifications, with companies investing heavily in training and compliance. A new company would need to demonstrate equivalent or superior standards from day one, a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
- Brand Loyalty: Established players benefit from existing client relationships built on years of dependable service.
- Reputational Capital: A strong track record in areas like food safety directly translates into client confidence.
- Time to Credibility: New entrants require substantial time and investment to build a comparable level of trust.
- Client Inertia: Businesses are often hesitant to switch providers for essential services unless there's a compelling reason, reducing the threat from new, unproven entities.
The threat of new entrants for Aramark is moderate to low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for operations and supply chains, estimated in the millions for comprehensive services in 2024, deter many. Furthermore, established client relationships and multi-year contracts create significant switching costs and inertia for potential customers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Aramark Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Aramark's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld. We also incorporate insights from competitor financial statements and relevant trade publications to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
