AQ Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AQ Group Bundle
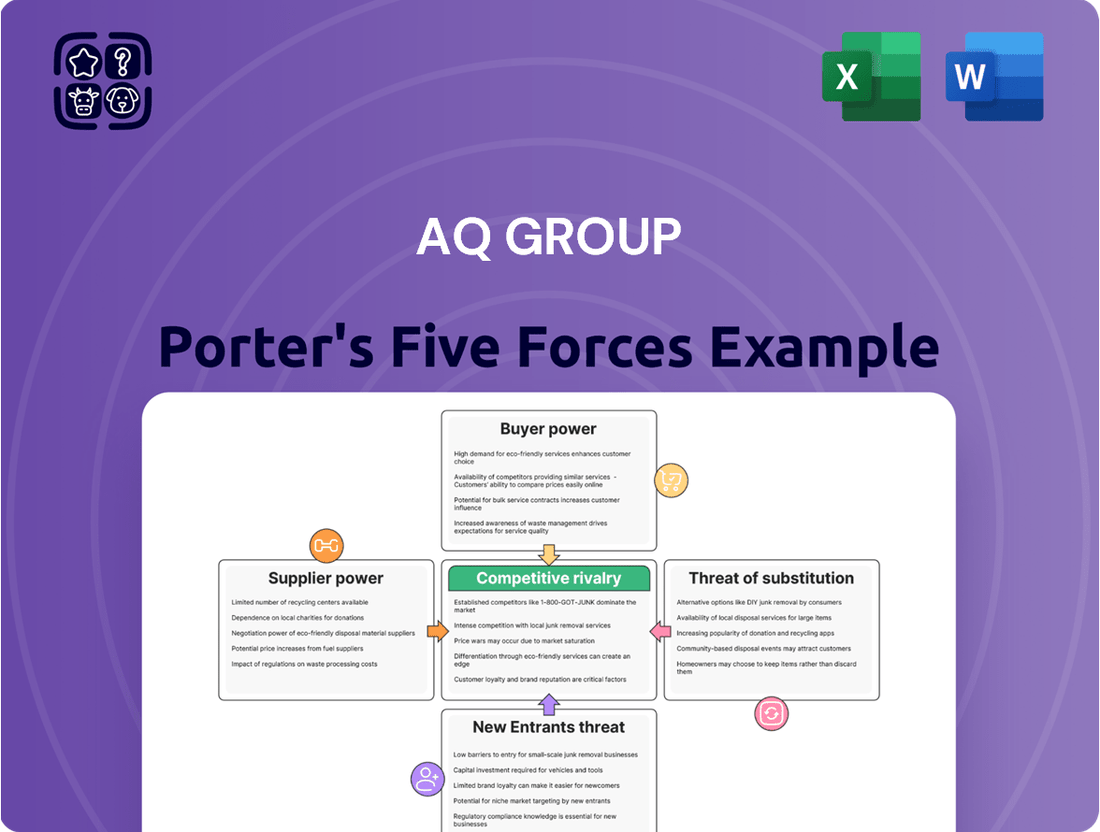
AQ Group's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the intense rivalry among existing players to the constant threat of new entrants disrupting the market. Understanding the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this dynamic environment. Furthermore, the availability and attractiveness of substitute products can significantly impact AQ Group's market share and profitability.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore AQ Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
AQ Group's reliance on specialized materials for its electrical cabinets, wiring harnesses, and inductive components significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power. These industrial applications demand unique, high-performance inputs, making it difficult for AQ Group to easily switch suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the global market for advanced copper alloys, a key material in high-performance wiring, saw price increases of up to 8% due to supply chain constraints and increased demand from the electric vehicle sector, directly impacting AQ Group's input costs.
The cost of key raw materials like copper, aluminum, and various metals, which are essential for inductive components and wiring harnesses, can fluctuate significantly. For instance, copper prices saw substantial swings in 2024, influenced by global demand and geopolitical factors, impacting manufacturers reliant on this commodity. This volatility directly affects AQ Group's production costs and profit margins.
When raw material prices surge, suppliers of these commodities gain considerable bargaining power. They can leverage these price increases to demand higher prices from buyers like AQ Group. In early 2024, reports indicated that lead times for certain specialized electronic components were extending, further strengthening the hand of suppliers in negotiation.
For specialized components essential in high-demand sectors like electric vehicles and advanced industrial machinery, the number of suppliers capable of meeting AQ Group's rigorous quality and performance specifications can be quite restricted. This limited availability of qualified suppliers, especially for critical parts, gives them considerable leverage. For instance, in the rapidly expanding EV battery component market, only a handful of companies globally possess the advanced manufacturing capabilities and certifications required, allowing them to command premium pricing.
Supplier switching costs for AQ Group
For AQ Group, switching suppliers for highly integrated or custom-designed components can be a significant undertaking. These transitions often necessitate substantial costs, encompassing re-engineering of products, rigorous re-testing of components, and obtaining necessary re-certifications, all of which can impact production timelines and budgets.
These elevated switching costs inherently limit AQ Group's operational flexibility and, consequently, amplify the bargaining power of their existing, incumbent suppliers. Suppliers who provide specialized or deeply embedded solutions can leverage this dependency to their advantage.
- High Switching Costs: Re-engineering, re-testing, and re-certification processes for custom components represent a considerable financial and time investment for AQ Group.
- Supplier Leverage: The difficulty in changing suppliers for critical, integrated parts strengthens the position of those suppliers in negotiations.
- Reduced Flexibility: AQ Group faces diminished agility in sourcing and supplier relationships due to the entrenched nature of these specialized components.
- Potential for Increased Prices: Suppliers with high switching cost barriers may be able to command higher prices or less favorable terms.
Strategic importance of supplier innovation
Suppliers who can provide innovative technologies or materials that significantly boost AQ Group's product performance or operational efficiency wield considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true when these innovations are difficult for AQ Group to replicate internally or source from alternative suppliers.
AQ Group's strategic acquisitions in inductive components, such as mdexx and Michael Riedel, highlight a deliberate effort to bolster its internal capabilities. This move can be interpreted as a strategy to reduce its dependence on external suppliers for critical technologies, thereby mitigating supplier power in those specific areas.
- Supplier Innovation as a Power Lever: Suppliers offering unique, cutting-edge technological solutions or advanced materials that directly improve AQ Group's product features or manufacturing processes gain leverage.
- Strategic Acquisitions to Mitigate Power: AQ Group's acquisitions of mdexx and Michael Riedel demonstrate a proactive approach to integrating key technologies, aiming to internalize expertise and lessen reliance on external providers.
- Impact on Cost and Performance: The ability of suppliers to innovate can directly influence AQ Group's product cost, quality, and market competitiveness, amplifying the supplier's bargaining position.
AQ Group faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the specialized nature of its inputs and the limited number of qualified providers, especially for advanced materials and components crucial for sectors like electric vehicles. High switching costs for custom-designed parts further entrench suppliers, allowing them to influence pricing and terms. For example, in 2024, extended lead times for specialized electronic components amplified supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on AQ Group | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Materials | Increases supplier power due to difficulty in finding alternatives. | Copper alloy prices rose up to 8% due to supply constraints. |
| Limited Supplier Pool | Restricts AQ Group's options, giving dominant suppliers leverage. | Few companies globally meet EV battery component manufacturing standards. |
| High Switching Costs | Discourages AQ Group from changing suppliers, strengthening incumbents. | Re-engineering and re-certification for custom parts are costly and time-consuming. |
| Supplier Innovation | Suppliers offering critical technological advancements gain leverage. | AQ Group's acquisitions of mdexx and Michael Riedel show efforts to reduce this dependency. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape for AQ Group, dissecting the intensity of rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
AQ Group's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the concentration and size of its industrial clientele. These customers, often major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and system integrators within sectors like electric power and electric vehicles, represent substantial purchasing volumes.
The sheer market influence of these large industrial buyers allows them to exert considerable pressure on pricing and contract terms. For instance, a single major automotive OEM could represent a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, giving them leverage in negotiations.
This concentration means AQ Group must carefully manage relationships with its key accounts, as losing even one could have a material impact on its financial performance. In 2024, the ongoing global push towards electrification in the automotive sector, a key market for AQ Group, further concentrates purchasing power among a few dominant players.
AQ Group's components are absolutely essential for the smooth operation and dependability of their customers' final products, especially in crucial sectors. This interdependence means customers have significant leverage. They demand top-notch quality, punctual deliveries, and competitive pricing because their own product's success hinges on AQ's performance. For instance, in 2023, AQ Group reported that a substantial portion of their revenue, over 70%, came from their top ten customers, highlighting the critical nature of these relationships and the bargaining power these large clients possess.
AQ Group's emphasis on long-term strategic partnerships, while fostering stability, inherently increases customer bargaining power. These enduring relationships create a mutual dependency where customers, already integrated into AQ's operations, can leverage their ongoing business to negotiate more favorable pricing and tailored solutions.
For instance, if a key customer represents a significant portion of AQ Group's revenue, say 15% as reported in their 2024 annual statement, they gain considerable leverage. This large customer base can then pressure AQ for better terms, potentially impacting AQ's profit margins, especially if switching costs for the customer are perceived as low.
Potential for customer in-house production
Large industrial clients of AQ Group possess the inherent capability to bring certain production processes in-house, particularly when dealing with high-volume orders or when the underlying technology matures and becomes more accessible. This looming possibility of backward integration serves as a significant bargaining chip for these customers during price and contract negotiations.
For instance, if a major automotive manufacturer that sources components from AQ Group decides that the volume of a particular part justifies the investment, they could establish their own production line. This threat directly impacts AQ Group's pricing power and market position.
- In-house production reduces reliance on suppliers like AQ Group.
- High volumes can make vertical integration economically viable for customers.
- Technological commoditization lowers the barrier to entry for in-house production.
- This potential directly influences AQ Group's negotiation leverage.
Customer switching costs for AQ Group's customized solutions
AQ Group's focus on highly customized solutions for its clients significantly elevates customer switching costs. When a customer integrates AQ Group's specialized components into their own product lines or manufacturing processes, the effort and expense required to switch to a different supplier can be substantial.
These costs typically encompass redesigning the customer's product to accommodate a new supplier's components, re-testing and re-qualifying the modified product to meet industry standards, and potentially retraining staff on new integration procedures. For instance, in the automotive sector, re-qualification alone can take many months and represent a significant investment.
These integration challenges effectively lock customers into existing relationships with AQ Group, thereby diminishing their bargaining power. This is particularly true for clients who rely on AQ Group's expertise for niche applications or complex assemblies where finding an equally capable alternative is difficult.
While specific figures for AQ Group's customer switching costs aren't publicly detailed, industry benchmarks suggest that the total cost of switching suppliers for highly engineered components can range from 10% to 25% of the annual contract value, impacting the overall profitability and operational continuity for the customer.
- High Integration Costs: Customers investing in AQ Group's customized solutions face significant expenses in redesigning and re-qualifying their own products if they switch suppliers.
- Technical Expertise Lock-in: AQ Group's specialized knowledge in developing unique components creates a reliance that makes finding comparable alternatives challenging for customers.
- Reduced Customer Bargaining Power: The substantial investment and disruption associated with switching suppliers limits customers' ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms once a relationship is established.
- Industry Examples: In sectors like aerospace or advanced manufacturing, where precision and compliance are paramount, switching costs for customized parts can represent a considerable portion of a project's budget.
The bargaining power of AQ Group's customers is a significant force, primarily driven by the concentration and purchasing volume of its industrial clientele, which often includes major original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in sectors like electric vehicles. These large buyers can exert considerable pressure on pricing and terms due to their substantial market influence, a trend amplified in 2024 by the global shift towards electrification. For instance, in 2023, over 70% of AQ Group's revenue stemmed from its top ten customers, underscoring their immense leverage and the critical nature of these relationships.
Furthermore, customers' ability to integrate AQ Group's components into their own complex systems creates high switching costs, effectively limiting their bargaining power. These costs involve redesign, re-testing, and re-qualification, which can represent 10-25% of a contract's annual value. This integration challenge, particularly for specialized components, fosters dependency and strengthens AQ Group's position by making it difficult for customers to find comparable alternatives.
| Factor | Impact on AQ Group | Customer Leverage | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High revenue dependency on few key clients | Significant due to large order volumes | Electrification trend concentrates demand among fewer EV OEMs |
| Switching Costs | High integration and re-qualification expenses | Low, due to substantial investment in customization | Specialized components require lengthy validation processes |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential loss of business if customers produce in-house | Moderate to High, especially for commoditized parts | Technological maturity can lower entry barriers for large customers |
Full Version Awaits
AQ Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete AQ Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces impacting the industry. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, which details the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This professionally written analysis is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
AQ Group navigates a fiercely competitive global landscape, contending with a multitude of manufacturers specializing in electrical cabinets, wiring harnesses, and inductive components. This broad product offering means AQ Group encounters rivals across diverse industrial sectors, from automotive to industrial automation. The sheer volume of players underscores the intense rivalry.
The company’s global market presence directly amplifies this competitive pressure. AQ Group’s operations span multiple continents, meaning it faces different sets of competitors in each region, each with their own local strengths and market dynamics. For instance, in 2024, the European electrical cabinet market saw significant competition from established players like Schneider Electric and Siemens, alongside a growing number of smaller, specialized firms.
Rivalry is further intensified by the varying specializations of competitors. Some may excel in high-volume, standardized wiring harnesses, while others focus on niche, high-precision inductive components. This diversity in competitive focus means AQ Group must constantly adapt its strategies to counter threats from both broad-spectrum competitors and those with deep expertise in specific product categories.
While certain established industrial sectors may exhibit slower growth, AQ Group operates in dynamic areas like electric vehicles and broader electrification initiatives, which are currently experiencing significant expansion. For instance, the global electric vehicle market was projected to reach over $800 billion by 2024, a substantial increase from previous years.
This robust industry growth is a double-edged sword for competitive rivalry. On one hand, it offers abundant market opportunities, potentially diluting the intensity of direct competition as companies focus on capturing new demand. However, this very growth attracts numerous players, leading to fierce competition for market share within these burgeoning segments.
The electrification trend, in particular, is a major driver. Investments in charging infrastructure and battery technology are soaring, with the global EV battery market alone expected to surpass $200 billion by 2024. This creates a highly competitive landscape where innovation and efficiency are paramount.
Consequently, while the expanding market can temper rivalry by providing ample room for growth, the presence of many ambitious companies vying for dominance means that competition remains intense, especially for securing contracts and technological leadership in these high-growth sectors.
AQ Group actively combats competitive rivalry by emphasizing superior quality and precise delivery in its solutions. This focus on excellence, coupled with a commitment to building enduring partnerships, distinguishes AQ Group from competitors who might primarily compete on price alone.
The intensity of rivalry is directly influenced by how effectively other companies can replicate AQ Group's value proposition. When competitors can match or exceed AQ Group's service and reliability, the competitive landscape becomes more challenging, pushing the focus beyond cost to a broader spectrum of value.
In 2024, the market saw continued investment in quality control and customer relationship management by key players in AQ Group's sectors, reflecting the importance of these differentiators. For instance, companies in the industrial automation space, a key area for AQ Group, reported an average of 15% of their R&D budgets allocated to enhancing product reliability and after-sales service.
Acquisition strategy and market consolidation
AQ Group's acquisition strategy significantly influences competitive rivalry by actively seeking to bolster its technological edge, manufacturing scale, and geographical presence. This proactive approach, exemplified by recent acquisitions of mdexx and Michael Riedel in 2025, signals a clear intent to consolidate market share and enhance its competitive standing.
This consolidation dynamic intensifies rivalry as AQ Group aims to integrate complementary businesses, potentially leading to greater market power and a more concentrated industry structure. Such moves can pressure competitors to respond with their own strategic maneuvers, such as mergers, divestitures, or increased innovation investment, to maintain their market positions.
- AQ Group's 2025 acquisitions of mdexx and Michael Riedel demonstrate a clear intent to consolidate market segments.
- This strategy aims to enhance technological capabilities, production capacity, and market reach.
- The pursuit of consolidation intensifies competitive rivalry by potentially altering market structure.
Price sensitivity versus value proposition
In certain market segments, particularly for standard components, the competition among players like AQ Group can become quite fierce, driven primarily by price. This commoditization means that if a product can be easily replicated, customers will naturally gravitate towards the lowest cost option. For instance, a report from 2024 indicated that in the general electronics component market, price wars are a common feature, impacting profit margins significantly.
However, AQ Group's strategy cleverly navigates this by focusing on its value proposition in more specialized areas. For demanding industrial applications, such as those in aerospace or advanced manufacturing, customers are less concerned with the absolute lowest price and more focused on the performance, durability, and reliability of the components. This allows AQ Group to differentiate itself and command premium pricing based on the superior quality and tailored solutions it offers, rather than engaging in a race to the bottom on price.
- Price-Driven Segments: In markets where components are easily substitutable, like basic electronic parts, price becomes the primary competitive factor.
- Value-Driven Segments: For high-stakes industrial applications, customers prioritize performance, reliability, and customization, enabling AQ Group to compete on value.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: This duality in customer priorities shapes the nature of rivalry, shifting from pure price competition to a blend of price and value depending on the specific market segment AQ Group serves.
- 2024 Market Insight: Data from 2024 suggests that companies focusing on specialized, high-performance components are better positioned to maintain profitability despite broader market pressures on pricing.
AQ Group faces intense rivalry from numerous global and regional manufacturers across its product lines, including electrical cabinets and wiring harnesses. The company's broad product portfolio means it encounters competition across diverse industrial sectors, from automotive to automation, with the sheer volume of players highlighting the fierce nature of this rivalry.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by varying competitor specializations, ranging from high-volume producers to niche, high-precision component specialists, demanding constant strategic adaptation from AQ Group. For instance, in 2024, the European electrical cabinet market showed significant competition from giants like Schneider Electric and Siemens, alongside many agile smaller firms.
While market growth, particularly in electrification and electric vehicles, offers opportunities, it also attracts more competitors, intensifying the fight for market share. The global EV market's projected growth to over $800 billion by 2024 illustrates this dynamic, with companies like AQ Group vying for dominance in these expanding segments.
AQ Group counters this rivalry by focusing on superior quality and reliable delivery, distinguishing itself from competitors who may primarily compete on price. This emphasis on value is crucial, especially as market data from 2024 indicates that companies specializing in high-performance components are better positioned to maintain profitability amidst pricing pressures.
| Competitive Factor | AQ Group's Approach | Market Context (2024 Data) | Impact on Rivalry |
| Breadth of Competitors | Faces rivals across diverse sectors and regions | Numerous players in automotive, automation, and energy sectors | High intensity due to broad market coverage |
| Competitor Specialization | Navigates both broad-spectrum and niche specialists | Some focus on high-volume wiring harnesses, others on precision inductive components | Requires adaptable strategies to counter varied threats |
| Market Growth vs. Competition | Leverages growth in electrification while managing increased competition | EV market projected over $800 billion by 2024; EV battery market over $200 billion by 2024 | Growth attracts more players, intensifying competition for market share |
| Differentiation Strategy | Emphasizes quality, reliability, and partnerships over price | Companies in industrial automation allocate ~15% of R&D to reliability and service | Differentiates from price-focused competitors, commanding premium value |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The ongoing evolution of wireless and integrated technologies poses a potential threat to AQ Group. Innovations like wireless power transmission and advanced integrated circuit boards could diminish the need for conventional wiring harnesses and individual inductive components in certain markets. This shift, if these technologies achieve widespread adoption and competitive pricing, could offer viable alternatives, impacting AQ Group's traditional product lines.
Customers are increasingly looking at modular and standardized component solutions. This trend makes it easier for them to source parts from various suppliers. For AQ Group, this means their highly customized and integrated solutions might face more competition from readily available, off-the-shelf alternatives. For instance, the growing adoption of universal connector standards in electronics could reduce reliance on proprietary AQ Group designs.
New breakthroughs in power electronics and energy storage are presenting significant threats of substitution for traditional inductive components and electrical cabinets. For instance, advancements in solid-state transformers and advanced battery management systems could offer more integrated and efficient power management solutions, reducing the need for AQ Group's current product offerings. The global market for energy storage systems is projected to grow significantly, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% through 2030, underscoring the potential for these substitutes to gain substantial market share.
Customer's shift to in-house manufacturing capabilities
Large industrial customers, despite the significant investment required, may opt to bring the manufacturing of electrical cabinets or wiring harnesses in-house. This strategic move, often driven by the pursuit of cost efficiencies or a desire for greater control over their supply chain, directly substitutes for the outsourcing services AQ Group provides. For example, a major automotive manufacturer might invest in its own assembly lines for critical electrical components, reducing its reliance on external suppliers like AQ Group. This trend reflects a broader industry movement towards vertical integration, especially among high-volume producers.
This customer shift represents a potent substitute threat for AQ Group. While the initial capital outlay for in-house production is substantial, the long-term potential for cost savings and enhanced operational control can outweigh these upfront expenses for certain customer segments. This can directly impact AQ Group’s revenue streams as these customers reduce their outsourcing volumes.
The threat of customers developing their own manufacturing capabilities is particularly relevant in sectors with high standardization and predictable demand. For instance, in 2024, several large-scale construction projects have explored bringing electrical panel assembly in-house to manage timelines and costs more directly, bypassing traditional contract manufacturers.
- Customer Internalization: Large industrial clients may choose to manufacture electrical cabinets or wiring harnesses internally to gain strategic advantages or achieve cost reductions.
- Substitution Effect: This vertical integration by customers acts as a direct substitute for AQ Group's outsourcing services, potentially decreasing demand for their offerings.
- Cost vs. Control: While costly, the pursuit of long-term cost savings and supply chain control can incentivize customers to invest in their own production capabilities.
- Sector Vulnerability: Industries with high standardization and predictable demand are more susceptible to this substitution threat.
Software-defined hardware trends
The rise of software-defined hardware presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like AQ Group. As more functionality shifts to software, the need for specialized, complex physical hardware components can diminish. This trend could mean that solutions requiring extensive, purpose-built hardware might be replaced by more adaptable, software-driven systems. For instance, in the automotive sector, over-the-air updates are increasingly enabling new features and performance enhancements, potentially reducing the reliance on entirely new hardware iterations for certain upgrades.
This shift impacts traditional hardware manufacturers by potentially lowering the perceived value of their physical products. If a core function can be achieved through software, the demand for the associated hardware may decrease, or the pricing power of the hardware itself could be eroded. This indirect substitution means that AQ Group must consider how evolving software capabilities can fulfill customer needs that were previously met solely through hardware. For example, some industrial automation tasks that once required bespoke control units are now being handled by more generic hardware running sophisticated control software.
- Software-defined infrastructure can reduce the need for specialized hardware, impacting traditional component sales.
- Over-the-air updates in automotive are a prime example of software substituting for hardware upgrades.
- The value proposition for physical components may decrease as software takes on more functionality.
- Companies need to adapt to a landscape where software innovation can directly compete with hardware-centric solutions.
The threat of substitutes for AQ Group stems from evolving technologies and customer strategies that offer alternative ways to meet similar needs. Innovations in wireless power, modular electronics, and software-defined systems can diminish demand for AQ Group's traditional wiring harnesses and inductive components. Furthermore, customers internalizing production capabilities poses a direct substitution risk.
For instance, the global market for wireless power transmission is expected to reach nearly $26 billion by 2027, indicating a significant potential for substitutes to traditional wired power solutions. Additionally, in 2024, several major electronics manufacturers have publicly stated their intention to increase in-house component production to gain greater control over their supply chains and reduce costs, directly impacting outsourcing providers.
| Substitute Area | Example | Market Trend/Data | Impact on AQ Group |
| Wireless Power | Wireless charging for industrial equipment | Global market projected to reach $26B by 2027 | Reduces need for wired connections. |
| Modular Electronics | Standardized connector systems | Increasing adoption in consumer electronics | Displaces proprietary designs. |
| Software-Defined Systems | Over-the-air updates for vehicle functions | Growing trend in automotive sector | Lowers reliance on new hardware. |
| Customer Internalization | In-house assembly of electrical cabinets | Several major manufacturers increasing in-house production in 2024 | Directly replaces outsourcing services. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing manufacturing operations for high-quality, specialized industrial components like electrical cabinets, wiring harnesses, and inductive components demands substantial capital expenditure. For instance, setting up a state-of-the-art facility for producing complex electrical cabinets can easily run into tens of millions of dollars for machinery, automation, and specialized tooling alone. This significant upfront investment acts as a considerable barrier, deterring many potential new entrants from entering AQ Group's market space.
Developing and producing high-performance components for sectors like electric vehicles and advanced industrial applications demands significant technical expertise and ongoing investment in research and development. For instance, the automotive industry's shift to EVs requires specialized knowledge in battery technology, power electronics, and lightweight materials, areas where established players have years of accumulated intellectual capital.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in rapidly acquiring the necessary engineering talent and building robust R&D capabilities. The cost and time involved in cultivating this deep technical understanding can be prohibitive, acting as a strong deterrent to market entry.
AQ Group's success hinges on its deep-seated customer trust and long-term partnerships, particularly with its demanding industrial clientele. Newcomers struggle to replicate this, as these clients prioritize proven performance and unwavering reliability, making it incredibly difficult for new entrants to gain a foothold. For instance, in 2023, industrial sectors often reported customer retention rates exceeding 90% for established suppliers, a testament to the loyalty built over years of consistent service and quality.
Stringent regulatory hurdles and certifications
Stringent regulatory hurdles and certifications represent a significant threat of new entrants for AQ Group. For instance, components used in electric power, electric vehicles, and various industrial applications must meet demanding safety standards like ISO 9001, UL certifications, and specific regional compliance mandates. Successfully navigating this labyrinth of requirements incurs substantial costs and time, acting as a powerful deterrent for newcomers. In 2024, the cost of obtaining and maintaining these certifications can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the complexity and scope of the product and its target markets.
These rigorous compliance processes create a substantial barrier to entry, effectively limiting the number of new players that can realistically compete. New entrants often lack the established infrastructure and expertise to efficiently manage these ongoing regulatory demands. This can translate into longer product development cycles and higher initial investment compared to established companies like AQ Group, which have already invested in meeting these standards.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with standards such as IEC, UL, and CE marking is mandatory for electrical components.
- Quality Certifications: Obtaining ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and IATF 16949 (Automotive Quality Management) is often a prerequisite.
- Environmental Regulations: Adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) is crucial.
- Industry-Specific Approvals: Certain sectors, like aerospace or medical, require even more specialized and costly certifications.
Economies of scale and cost competitiveness
Established global manufacturers like AQ Group leverage significant economies of scale in procurement, production, and distribution. This cost advantage makes it difficult for new entrants to compete on price without substantial upfront investment and market share.
For instance, in 2024, major players in the automotive supply chain, a sector AQ Group operates within, often have manufacturing costs per unit that are 10-20% lower than smaller, emerging companies due to their high production volumes.
- Economies of Scale: Established firms benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing by incumbents leads to better raw material pricing.
- Distribution Efficiency: Extensive logistics networks reduce shipping costs for larger companies.
- Price Competition Barrier: New entrants struggle to match the cost-competitiveness of established giants.
The threat of new entrants for AQ Group is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for specialized manufacturing, coupled with the need for deep technical expertise and R&D investment, deter many potential competitors. Established customer loyalty and stringent regulatory compliance further solidify AQ Group's market position.
Economies of scale enjoyed by AQ Group also present a considerable challenge for new players attempting to compete on price. For example, in 2024, industry reports indicated that established automotive component suppliers achieved production cost savings of 10-20% compared to smaller entrants, driven by higher volumes.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for specialized machinery and facilities. | Significant financial hurdle. | Tens of millions of dollars for advanced manufacturing setup. |
| Technical Expertise & R&D | Need for specialized knowledge and continuous innovation. | Prohibitive development costs and time. | EV sector demands expertise in battery tech and power electronics. |
| Customer Loyalty | Strong, long-term relationships with demanding industrial clients. | Difficulty in gaining market access and trust. | Industrial sectors reported >90% customer retention for established suppliers in 2023. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex safety and quality certifications. | Substantial costs and time delays. | Certification costs can range from $10,000s to $100,000s annually. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from high-volume production and procurement. | Inability to match price competitiveness. | 10-20% lower per-unit production costs for large players. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial statements, analyst reports, industry trade journals, and proprietary market research. This comprehensive approach ensures a deep understanding of competitive pressures and strategic opportunities within the AQ Group's operating environment.
