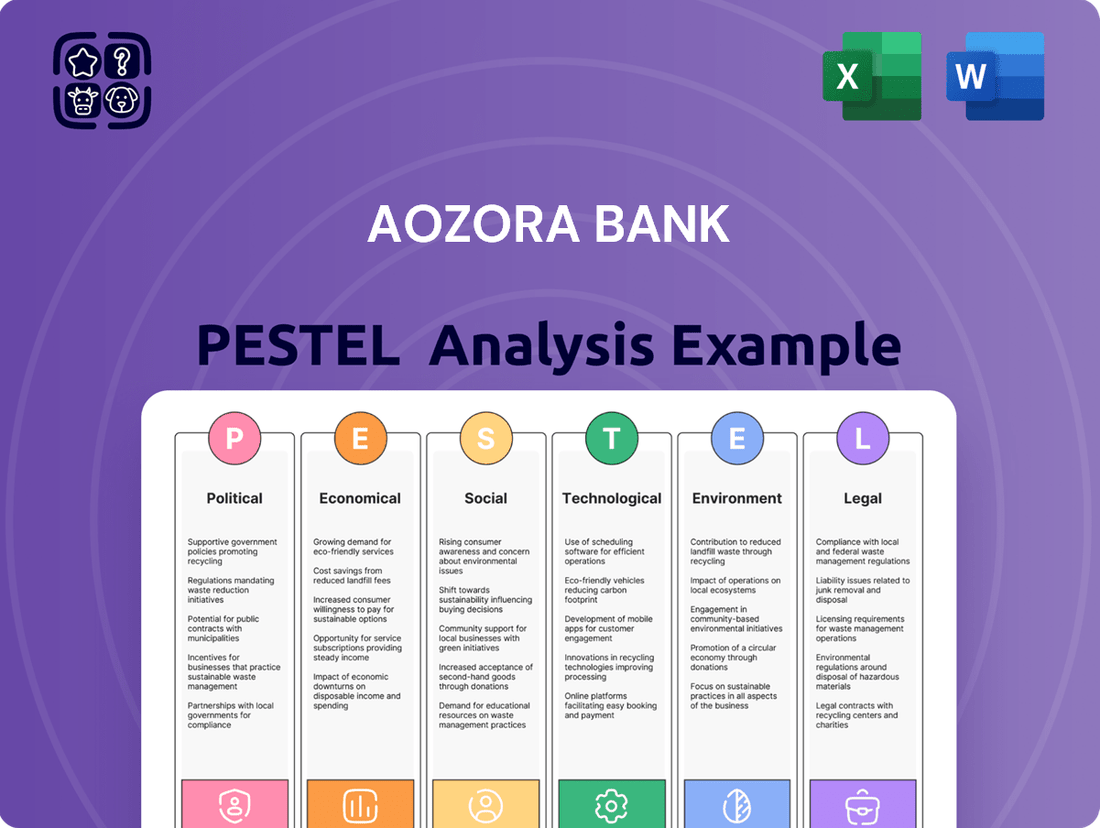
Aozora Bank PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Aozora Bank Bundle
Uncover the critical Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors shaping Aozora Bank's trajectory. Our comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence to navigate these external forces effectively. Download the full version now to gain a strategic advantage and make informed decisions for Aozora Bank's future.
Political factors
Aozora Bank navigates Japan's stringent financial landscape, overseen by the Financial Services Agency (FSA) and the Bank of Japan (BOJ). Recent legislative updates to the Banking Act and related financial statutes are designed to bolster market stability, safeguard consumers, and encourage enduring economic expansion.
The FSA's strategic agenda for 2024-2025 highlights critical areas such as enhancing corporate governance, driving digital innovation, and advancing sustainable finance initiatives. These directives directly influence Aozora Bank's operational framework and strategic planning, particularly concerning its commitment to responsible financial practices and technological integration.
The Bank of Japan's move away from negative interest rates in March 2024, followed by a hike to 0.5% by January 2025, is a pivotal political factor impacting Aozora Bank. This policy shift is designed to foster a more normalized economic climate in Japan.
This normalization is expected to benefit banks like Aozora by potentially widening their net interest margins, as the cost of borrowing and lending adjusts to a positive rate environment. This could lead to improved profitability for the bank.
Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA) launched the 'Action Programme for Corporate Governance Reform 2024: Principles into Practice' in June 2024. This initiative strongly pushes for the real-world application of corporate governance enhancements by listed firms.
These reforms are designed to boost transparency, strengthen accountability, and foster sustainability within Japanese corporations. Consequently, Aozora Bank, as a listed entity, faces direct implications for its operational procedures and financial reporting quality, aligning with these national governance objectives.
International Trade Relations and Geopolitical Risks
Global economic trends and geopolitical risks, such as U.S. tariff threats and broader international uncertainties, can impact Japan's export-reliant economy and subsequently the banking sector. For instance, the World Bank projected global growth to slow to 2.4% in 2024, down from 2.6% in 2023, citing persistent inflation and high interest rates. This slowdown can reduce demand for Japanese exports, affecting corporate clients and Aozora Bank's loan portfolio.
Aozora Bank's engagement in international business means it is exposed to cross-border transaction and investment risks influenced by these factors. Geopolitical tensions, like those in Eastern Europe, can disrupt supply chains and impact global financial markets, leading to increased volatility. For example, the ongoing trade friction between major economies can lead to currency fluctuations, affecting the value of international assets and liabilities held by the bank.
- Trade Tensions: Ongoing U.S.-China trade disputes and potential new tariffs could dampen global trade volumes, impacting Japanese exporters who are key clients for banks like Aozora.
- Geopolitical Instability: Regional conflicts or political instability in key trading partner nations can disrupt business operations and investment flows, creating uncertainty for international banking activities.
- Currency Volatility: Fluctuations in exchange rates, driven by geopolitical events or differing monetary policies, directly affect the profitability of cross-border transactions and the value of foreign investments.
Sustainable Finance Initiatives and Government Support
The Japanese government is making a strong push for sustainable finance. In 2024, they issued Japan Climate Transition Bonds specifically to fund decarbonization projects. This policy environment creates a significant avenue for financial institutions like Aozora Bank.
Aozora Bank can leverage this government support to expand its green finance offerings. By assisting clients in their transition towards a net-zero economy, the bank aligns itself with national environmental objectives and taps into a growing market demand for sustainable investments.
- Government Focus: Japan's commitment to sustainable finance is a key political driver.
- Bond Issuance: The 2024 issuance of Japan Climate Transition Bonds signals active government engagement in funding green initiatives.
- Opportunity for Aozora: This creates a favorable landscape for Aozora Bank to develop and offer green financial products and services.
The Bank of Japan's shift from negative interest rates in March 2024 to 0.5% by January 2025 is a significant political development. This policy change aims to normalize Japan's economic environment, potentially boosting Aozora Bank's net interest margins by adjusting borrowing and lending costs.
Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA) emphasizes corporate governance reform, with its June 2024 'Action Programme' pushing for practical application by listed firms. This directly impacts Aozora Bank's transparency and accountability, aligning with national governance goals.
Government support for sustainable finance, exemplified by the 2024 issuance of Japan Climate Transition Bonds, presents a clear opportunity for Aozora Bank. This policy encourages the bank to expand its green finance offerings, supporting clients' transitions to a net-zero economy.
Global political factors, such as U.S. tariff threats and geopolitical instability, create economic uncertainty. The World Bank's projected slowdown in global growth to 2.4% for 2024, down from 2.6% in 2023, highlights risks to Japan's export-reliant economy and Aozora Bank's client base.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis examines the external macro-environmental factors impacting Aozora Bank, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It provides a comprehensive overview of how these forces create both challenges and strategic advantages for the bank.
A PESTLE analysis of Aozora Bank provides a clear, summarized version of external factors for easy referencing during strategic planning, alleviating the pain of sifting through raw data.
Economic factors
The Bank of Japan's move away from negative interest rates in March 2024, followed by anticipated further hikes in 2024 and 2025, is a significant tailwind for Japanese banks like Aozora Bank. This policy shift directly supports an expansion of net interest margins (NIMs), as lending rates can now rise more freely, improving profitability.
For Aozora Bank, this normalization of interest rates means a better environment for earning on its loan portfolio. While specific NIM figures for Aozora Bank in late 2024 or early 2025 will depend on its asset-liability management, the broader industry trend indicates a positive impact on profitability from higher lending yields.
Japan's inflation rate, while showing some moderation, continues to hover above the Bank of Japan's (BOJ) 2% target, primarily fueled by persistent increases in food and energy prices. For instance, in April 2024, the core inflation rate excluding fresh food was reported at 2.2% year-on-year, a slight dip from previous months but still elevated.
The BOJ's strategy involves a measured approach to interest rate adjustments. This caution is designed to foster a more robust economic recovery, ensuring that growth is sustainable. Such a policy environment directly impacts Aozora Bank by influencing the demand for loans and the overall profitability of its lending operations.
Japanese corporations are showing a strong appetite for borrowing, fueled by active mergers and acquisitions and ongoing capital expenditure projects. This robust demand for loans presents a significant positive for the banking industry, directly benefiting institutions like Aozora Bank by boosting lending volumes and enhancing profitability.
Capital Adequacy and Risk Management
Japanese financial institutions, including Aozora Bank, are generally well-capitalized and maintain ample liquidity. This strong foundation helps them navigate economic uncertainties. For instance, as of the end of fiscal year 2023, the average Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio for major Japanese banks exceeded 12%, well above the Basel III minimum requirements.
Aozora Bank specifically manages its capital based on 'risk capital' principles to ensure sufficient buffers against potential losses. This approach involves sophisticated modeling to quantify and hold capital against various risk types, including credit, market, and operational risks. Regulatory requirements for capital adequacy ratios, monitored by the Financial Services Agency (FSA), remain a key focus for the bank's strategic planning and risk management framework.
Key aspects of Aozora Bank's capital adequacy and risk management include:
- Robust Capital Buffers: Maintaining capital levels significantly above regulatory minimums to absorb unexpected losses.
- Risk-Based Capital Management: Utilizing 'risk capital' to align capital allocation with the bank's risk profile.
- Regulatory Compliance: Continuously adhering to and monitoring capital adequacy ratio requirements set by the FSA.
- Liquidity Management: Ensuring sufficient liquid assets to meet short-term obligations and withstand market stress.
Global Financial Market Fluctuations
Aozora Bank's engagement in investment banking and international operations inherently ties its performance to the volatility of global financial markets. Recent trends, such as the increasing interconnectedness between Japanese financial institutions and international non-bank financial entities, amplify this susceptibility. For instance, the MSCI World Index experienced significant swings throughout 2024, reflecting broader geopolitical and economic uncertainties that directly impact Aozora's trading and investment portfolios.
The ripple effects of global economic events can quickly transmit through the financial system. Consider the impact of interest rate hikes by major central banks like the US Federal Reserve; these decisions can influence capital flows into and out of Japan, affecting Aozora's asset valuations and funding costs. As of late 2024, global inflation concerns and ongoing supply chain adjustments continue to create an unpredictable environment for financial institutions worldwide.
- Global Market Volatility: Major indices like the S&P 500 and Nikkei 225 have shown heightened volatility in 2024 due to inflation and geopolitical tensions.
- Interconnectedness: Increased partnerships between Japanese banks and foreign NBFIs mean that shocks in international markets can have a more immediate impact on the Japanese financial sector.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Fluctuations in global interest rates directly affect the cost of capital and the valuation of Aozora Bank's international investments.
- Economic Uncertainty: Ongoing global economic adjustments, including inflation and supply chain issues, create a challenging operating landscape for banks with international exposure.
The Bank of Japan's pivot away from negative interest rates in March 2024, with expectations for further adjustments in 2024-2025, provides a significant boost to Japanese banks like Aozora. This policy shift is poised to widen net interest margins by allowing lending rates to rise, thereby enhancing profitability. The ongoing moderate inflation, around 2.2% as of April 2024, also supports this trend by maintaining a favorable environment for increased lending yields.
Japanese corporate borrowing remains robust, driven by M&A activity and capital expenditures, directly benefiting Aozora Bank through increased lending volumes. Furthermore, the banking sector, including Aozora, is well-capitalized, with average CET1 ratios exceeding 12% by fiscal year-end 2023, ensuring resilience against economic shocks.
Aozora Bank's international operations expose it to global market volatility, as seen in the swings of indices like the MSCI World in 2024. Global economic adjustments, including inflation and supply chain issues, create an unpredictable landscape, impacting asset valuations and funding costs for banks with international exposure.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Aozora Bank | Supporting Data/Trend (2024-2025) |
| Monetary Policy (BOJ Rate Hikes) | Increased Net Interest Margins (NIMs) | BOJ moved away from negative rates in March 2024; further hikes anticipated. |
| Inflation | Supports higher lending yields | Core inflation (ex-food) at 2.2% year-on-year in April 2024. |
| Corporate Borrowing Demand | Higher lending volumes, improved profitability | Strong appetite for loans due to M&A and capital expenditures. |
| Capital Adequacy | Financial resilience | Average CET1 ratio for major Japanese banks exceeded 12% (FY2023). |
| Global Market Volatility | Impact on international investments and funding costs | MSCI World Index experienced significant swings in 2024. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Aozora Bank PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Aozora Bank meticulously examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape influencing the bank's future.
Sociological factors
Japan's rapidly aging population, with approximately 29.1% of its population aged 65 and over as of 2023, presents a significant demographic shift impacting Aozora Bank. This trend directly influences consumer banking needs, shifting demand towards wealth management, retirement planning, and inheritance services.
The increasing proportion of older citizens necessitates that Aozora Bank adapt its product offerings and service delivery models. For instance, a growing elderly customer base might require more personalized financial advice and simpler transaction processes, potentially impacting the bank's digital strategy and branch network utilization.
Japanese consumers increasingly prioritize convenience, leading to a surge in demand for digital and mobile banking solutions. Aozora Bank is responding by enhancing its digital offerings, including advanced mobile platforms and AI-powered chatbots, to better serve these evolving customer needs.
This digital shift is evident in the growing adoption rates; for instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 80% of Japanese banking transactions will occur through digital channels, a significant increase from previous years.
As Japan's economy navigates shifts, a critical need for improved financial literacy is emerging across the population. This presents a significant opening for institutions like Aozora Bank to expand their offerings in financial consulting and wealth management solutions, catering to both everyday retail clients and affluent individuals seeking to grow their assets.
Data from the 2023 Basic Survey on Household Finances indicated that only 44% of Japanese households felt confident in their financial planning abilities. This gap highlights the demand for accessible, expert guidance, a space where Aozora can leverage its expertise to build deeper customer relationships and drive product adoption.
Workforce Dynamics and Talent Acquisition
The banking sector is navigating significant workforce shifts, with a growing emphasis on attracting and retaining talent, particularly in burgeoning fields like fintech and sustainable finance. Aozora Bank is actively addressing this by prioritizing investments in human capital, aiming to cultivate a skilled and adaptable workforce.
Aozora Bank’s human resources strategy is designed to foster a supportive and inclusive workplace, which is crucial for retaining employees. This approach includes actively seeking out diverse talent pools to bring a wider range of perspectives and skills into the organization.
- Talent Attraction Focus: Aozora Bank aims to attract individuals with expertise in areas such as digital banking solutions and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives.
- Retention Strategies: The bank is implementing programs to improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover, recognizing the high cost associated with recruitment and training in a competitive market.
- Skills Gap Mitigation: By investing in training and development, Aozora Bank seeks to bridge any emerging skills gaps within its workforce, ensuring it remains competitive.
Public Trust and Corporate Social Responsibility
Maintaining public trust is paramount for any financial institution, and Aozora Bank is no exception. In 2024, Japanese banks faced increased scrutiny regarding their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, with consumer confidence directly linked to perceived corporate responsibility. Aozora Bank's proactive engagement in sustainability, such as its investments in green finance and community development projects, directly addresses these concerns, aiming to bolster its reputation and foster deeper stakeholder connections.
Aozora Bank's commitment extends to providing value-added financial services that contribute to societal development. This approach is vital for building enduring relationships with customers, investors, and the wider community. For instance, in early 2025, the bank announced a new initiative focused on supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in adopting sustainable business models, a move expected to resonate positively with a public increasingly prioritizing ethical business practices.
- Reputation Management: Public trust directly impacts customer loyalty and investor confidence.
- ESG Integration: Aozora Bank's focus on sustainability aligns with growing investor demand for responsible investments.
- Societal Contribution: Value-added services that benefit society can create a positive brand image.
- Stakeholder Relations: Transparent and responsible operations strengthen bonds with all stakeholders.
Japan's demographic landscape is a key sociological driver for Aozora Bank, with an aging population and a growing demand for digital convenience shaping its strategy. The bank is also focusing on enhancing financial literacy among its customers and adapting its workforce to meet evolving industry needs.
Public perception and trust are critical, pushing Aozora Bank to prioritize strong ESG practices and community engagement to build lasting stakeholder relationships.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on Aozora Bank | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Aging Population | Increased demand for wealth management, retirement, and inheritance services. | Approx. 29.1% of Japan's population is 65+ (2023). |
| Digital Adoption | Shift towards digital and mobile banking solutions. | Projected 80%+ of banking transactions via digital channels by end of 2024. |
| Financial Literacy | Opportunity for expanded financial consulting and wealth management. | Only 44% of Japanese households confident in financial planning (2023). |
| Workforce Trends | Need to attract talent in fintech and ESG, focus on retention. | Ongoing investment in human capital and diverse talent acquisition. |
| Public Trust & ESG | Emphasis on corporate responsibility and sustainability. | Increased scrutiny on ESG practices; Aozora investing in green finance. |
Technological factors
Aozora Bank is making substantial investments in digital transformation, with a focus on enhancing its mobile banking capabilities and deploying AI-powered chatbots to streamline operations and elevate customer interactions. This strategic push aims to meet evolving customer expectations for seamless digital financial services.
The Japanese banking sector as a whole is experiencing a surge in AI adoption, with institutions channeling significant capital into AI-driven solutions to optimize back-office functions and personalize customer service. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that over 70% of major Japanese banks will have implemented AI for fraud detection, a testament to the technology's growing importance.
As digital banking services at Aozora Bank continue to grow, the importance of strong cybersecurity and data protection cannot be overstated. The bank must invest in and continuously update its IT infrastructure and security protocols to safeguard sensitive customer data from evolving threats, ensuring operational resilience and maintaining client confidence.
In 2024, financial institutions globally faced increasing cyberattacks, with data breaches costing an average of $4.45 million according to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report. Aozora Bank's commitment to enhancing its information security strategy is crucial to prevent such financial and reputational damage, especially as digital transactions become more prevalent.
Aozora Bank is leveraging blockchain technology for its transaction processes, aiming to enhance security and achieve cost reductions. This adoption aligns with a broader trend in the financial sector to streamline operations through DLT.
Japan's evolving regulatory landscape for digital assets, including stablecoins, is a crucial technological factor. As of early 2025, discussions are ongoing regarding the integration of these digital assets into traditional financial systems, which is expected to accelerate DLT adoption in banking services.
API Integration and Open Banking
Japan’s push for API integration and open banking is a significant technological shift. Banks, including Aozora Bank, are now mandated to create and share policies for working with electronic payment providers. This regulatory environment is designed to foster innovation, enabling the creation of novel digital financial services and embedded finance solutions.
This move towards open banking is already showing traction. For instance, by the end of 2023, many Japanese financial institutions had begun to actively develop their API strategies. This enables Aozora Bank to potentially partner with fintech companies, offering customers more integrated and convenient financial experiences.
- Regulatory Mandate: Japanese banks must publish policies for collaboration with electronic payment service providers.
- Innovation Driver: API integration facilitates the development of new digital financial services.
- Embedded Finance: Creates opportunities for financial services to be integrated into non-financial platforms.
- Market Trend: Growing adoption of API strategies by Japanese financial institutions as of late 2023.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
Aozora Bank is leveraging artificial intelligence, particularly AI-driven chatbots, to dramatically cut down customer service response times. This integration signifies a broader trend where AI and automation are fundamentally altering the Japanese banking landscape, boosting efficiency and refining customer engagement.
The impact of these technologies is substantial. For instance, AI-powered tools can process loan applications and analyze market data with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This not only streamlines internal operations but also enables Aozora Bank to offer more personalized and responsive services to its clients.
Key technological advancements reshaping the Japanese banking sector include:
- AI-powered customer service: Chatbots are handling a growing volume of customer inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
- Automation of back-office processes: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is being deployed to automate repetitive tasks, reducing errors and operational costs.
- Data analytics and machine learning: These technologies are enhancing risk management, fraud detection, and the development of tailored financial products.
- Digital transformation initiatives: Banks are investing in cloud computing and advanced cybersecurity to support these new technological capabilities.
Aozora Bank's technological strategy centers on digital transformation, integrating AI chatbots for enhanced customer service and investing in blockchain for secure transactions. Japan's banking sector is rapidly adopting AI, with over 70% of major banks expected to use it for fraud detection by the end of 2024, highlighting the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. The bank's focus on API integration and open banking, driven by regulatory mandates, aims to foster innovation and create new digital financial services, mirroring a trend where many Japanese institutions were developing API strategies by late 2023.
| Technology Area | Aozora Bank Focus | Industry Trend (Japan) | Impact/Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation | Mobile banking enhancement, AI chatbots | Widespread AI adoption for efficiency and personalization | Improved customer experience, streamlined operations |
| Cybersecurity | IT infrastructure and security protocol updates | Increasing investment to combat rising cyber threats | Data protection, operational resilience, client confidence |
| Blockchain | Transaction process enhancement | Growing adoption for operational streamlining | Enhanced security, cost reduction |
| Open Banking/APIs | Compliance with regulatory mandates, potential fintech partnerships | Mandatory API policy creation, growing API strategy development | Innovation in digital services, embedded finance opportunities |
Legal factors
Aozora Bank's operations are fundamentally shaped by the Japanese Banking Act, which dictates everything from its licensing and organizational structure to its permitted business activities and crucial customer protection measures.
Significant legislative shifts are anticipated, with planned amendments in 2024 and 2025 focusing on deregulation. These changes are designed to empower banks like Aozora to more effectively navigate the persistent challenge of low interest rates and to foster innovation in response to rapid FinTech advancements.
Aozora Bank must navigate stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) regulations enforced by Japan's Financial Services Agency (FSA). These rules mandate a risk-based approach to customer due diligence and the reporting of suspicious transactions, with the FSA setting firm compliance deadlines for all financial institutions.
Failure to meet these AML/CFT requirements can result in significant penalties, impacting Aozora Bank's operational capacity and reputation. For instance, in 2023, global financial institutions faced billions in AML fines, highlighting the critical need for robust compliance frameworks.
Aozora Bank, like all financial institutions, must strictly adhere to Japan's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). This includes implementing enhanced data security protocols tailored for banks, ensuring the responsible handling of sensitive customer financial details. Recent amendments, effective from April 1, 2022, have further tightened requirements for data breach notifications and cross-border data transfers, impacting how Aozora manages its customer information.
Securities-Related Business Regulations
In Japan, local banks like Aozora Bank typically need a special license from the Financial Services Agency (FSA) to offer services related to securities. This regulatory requirement stems from the Banking Act, which enforces a clear division between banking operations and commercial activities.
Consequently, banks are generally mandated to conduct securities business through a separate subsidiary, adhering to the principle of separation. This structure ensures compliance and manages potential conflicts of interest within financial institutions.
- FSA Licensing: Aozora Bank requires specific FSA approval for securities-related activities.
- Banking Act Separation: The law mandates a separation between banking and commerce, impacting how securities services are offered.
- Subsidiary Requirement: Banks must operate securities businesses through dedicated subsidiary firms.
ESG Disclosure Requirements
While the Banking Act doesn't directly impose ESG mandates, Aozora Bank, as a listed entity, must adhere to Japan's Corporate Governance Code. This code encourages robust governance practices, which increasingly encompass environmental, social, and governance considerations.
A significant development occurred in 2023 with amendments to the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act. These changes now require listed companies, including financial institutions like Aozora Bank, to disclose specific sustainability-related information within their annual securities reports. This move signals a growing regulatory push for greater transparency in ESG matters.
- Corporate Governance Code Compliance: Listed banks must follow Japan's Corporate Governance Code, which indirectly promotes ESG integration.
- 2023 Financial Instruments and Exchange Act Amendments: Mandates disclosure of certain sustainability-related matters in annual securities reports for listed companies.
- Increased ESG Transparency: This legal shift compels companies to be more open about their sustainability performance and strategies.
Aozora Bank operates under the comprehensive Japanese Banking Act, which governs its licensing, business scope, and customer protection. Anticipated deregulation in 2024 and 2025 aims to bolster banks' resilience against low interest rates and spur FinTech innovation.
Strict adherence to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CFT) regulations is paramount, enforced by the Financial Services Agency (FSA). Non-compliance carries severe penalties; for instance, global financial institutions faced billions in AML fines in 2023, underscoring the critical need for robust frameworks.
The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) mandates enhanced data security, with recent amendments (effective April 2022) tightening breach notification and cross-border data transfer rules for institutions like Aozora.
Aozora Bank must also comply with the Corporate Governance Code, which encourages ESG integration, and the 2023 amendments to the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, requiring listed companies to disclose sustainability-related information, thereby increasing ESG transparency.
Environmental factors
Aozora Bank, like many financial institutions, must navigate the multifaceted risks presented by climate change. These include physical risks, such as the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters impacting collateral and business operations, and transition risks, stemming from policy shifts, evolving market preferences, and technological advancements aimed at decarbonization.
Regulators are increasingly focused on these climate-related financial risks. For instance, the Bank of Japan and the Financial Services Agency (FSA) are actively engaged in climate scenario analyses to help banks understand and quantify the potential impacts on their loan and investment portfolios.
These analyses are crucial for Aozora Bank to build resilience. By stress-testing portfolios against various climate scenarios, the bank can identify vulnerabilities and develop strategies to mitigate potential losses, ensuring long-term stability and a sustainable business model in a changing world.
Japan's commitment to sustainability is accelerating, with the government actively promoting green finance. In 2023, the issuance of climate transition bonds reached ¥5.3 trillion, a significant increase from previous years, signaling strong investor appetite for environmentally conscious projects. This trend offers Aozora Bank a substantial opportunity to expand its green lending portfolio, supporting Japanese businesses in their transition towards net-zero emissions.
Aozora Bank can leverage this momentum by offering specialized financial products and advisory services to clients seeking to decarbonize their operations. For instance, by facilitating access to capital for renewable energy projects or energy efficiency upgrades, the bank can play a crucial role in Japan's broader environmental goals. This focus aligns with the increasing demand from institutional investors for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliant investments, a market segment that saw global inflows of over $2 trillion in 2024.
Aozora Bank is actively weaving environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into its core business strategy, recognizing sustainability as a critical driver for long-term success. This commitment is evident in their proactive support for environmentally conscious startups via venture debt, aiming to foster innovation in green technologies and sustainable practices.
The bank's strategic focus extends to facilitating industrial transition, a move that directly addresses the urgent need for decarbonization and resource efficiency across various sectors. By channeling capital towards these vital areas, Aozora Bank aligns its operations with global efforts to achieve sustainable growth and mitigate climate change impacts.
For instance, in 2024, Aozora Bank continued its focus on supporting businesses contributing to a low-carbon economy, with a significant portion of its venture debt portfolio directed towards companies in renewable energy and circular economy sectors. This strategic allocation reflects a growing trend among financial institutions to prioritize investments that yield both financial returns and positive environmental outcomes.
Carbon Neutrality Targets and Financed Emissions
Japan's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 necessitates substantial investment, with financial institutions like Aozora Bank playing a crucial role. This involves not only direct investments but also supporting clients in their decarbonization efforts.
The spotlight is increasingly on 'financed emissions,' which are the greenhouse gas emissions generated by a bank's loan and investment portfolios. By 2024, major Japanese banks are expected to enhance disclosure of these financed emissions, aligning with global trends and investor expectations.
- 2050: Japan's target year for carbon neutrality.
- Increasing Scrutiny: Financial institutions face growing pressure to report and manage financed emissions.
- Client Support: Banks are expected to guide and finance clients' transition to lower-carbon operations.
- Disclosure Requirements: Expect stricter reporting mandates for financed emissions by 2024.
Regulatory and Disclosure Frameworks for Climate Risk
Japanese financial regulators, notably the Financial Services Agency (FSA) and the Bank of Japan (BOJ), are actively shaping robust frameworks to guide financial institutions in identifying and managing climate-related financial risks. This proactive stance aims to integrate climate considerations into the core of financial sector operations.
A key component of these evolving frameworks involves enhancing corporate disclosure of sustainability information. By March 2025, Japanese companies are expected to align their sustainability reporting with international standards, such as those set by the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB). This standardization is crucial for comparability and transparency.
- FSA and BOJ Initiatives: Developing guidelines for climate risk assessment and management in financial institutions.
- Enhanced Disclosure: Mandating more comprehensive reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
- ISSB Alignment: Targeting March 2025 for Japanese corporate disclosures to meet international sustainability reporting benchmarks.
- Risk Mitigation: Encouraging financial institutions to integrate climate risk into their strategies and governance structures.
Environmental factors significantly shape Aozora Bank's operational landscape, particularly concerning climate change and sustainability initiatives. Japan's commitment to carbon neutrality by 2050 drives regulatory and market pressures for banks to manage financed emissions and support client decarbonization. The increasing issuance of green finance instruments, like the ¥5.3 trillion in climate transition bonds in 2023, highlights a growing opportunity for Aozora Bank to expand its green lending portfolio.
Regulators like the FSA and Bank of Japan are mandating enhanced corporate disclosure of sustainability information, with a target for Japanese companies to align with ISSB standards by March 2025. This push for transparency affects how Aozora Bank assesses and integrates climate-related financial risks into its strategies, influencing investment decisions and product development.
Aozora Bank's strategic focus on supporting environmentally conscious startups and facilitating industrial transition, as seen in its venture debt allocations in 2024, positions it to capitalize on the growing demand for ESG-compliant investments. This proactive approach aligns with global investor trends, which saw over $2 trillion in global ESG inflows in 2024, underscoring the financial viability of sustainable banking practices.
| Factor | Description | Data Point/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Risk | Physical and transition risks impacting operations and portfolios. | Increasing frequency of natural disasters. |
| Green Finance | Government and market push for environmentally friendly investments. | ¥5.3 trillion in climate transition bonds issued in 2023. |
| Regulatory Focus | FSA and BOJ initiatives on climate risk management and disclosure. | Target for ISSB alignment in corporate disclosures by March 2025. |
| ESG Investment | Growing investor demand for sustainable and responsible investments. | Over $2 trillion in global ESG inflows in 2024. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Aozora Bank PESTLE analysis is meticulously constructed using data from official Japanese government publications, reports from international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank, and reputable industry-specific market research. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the bank.
