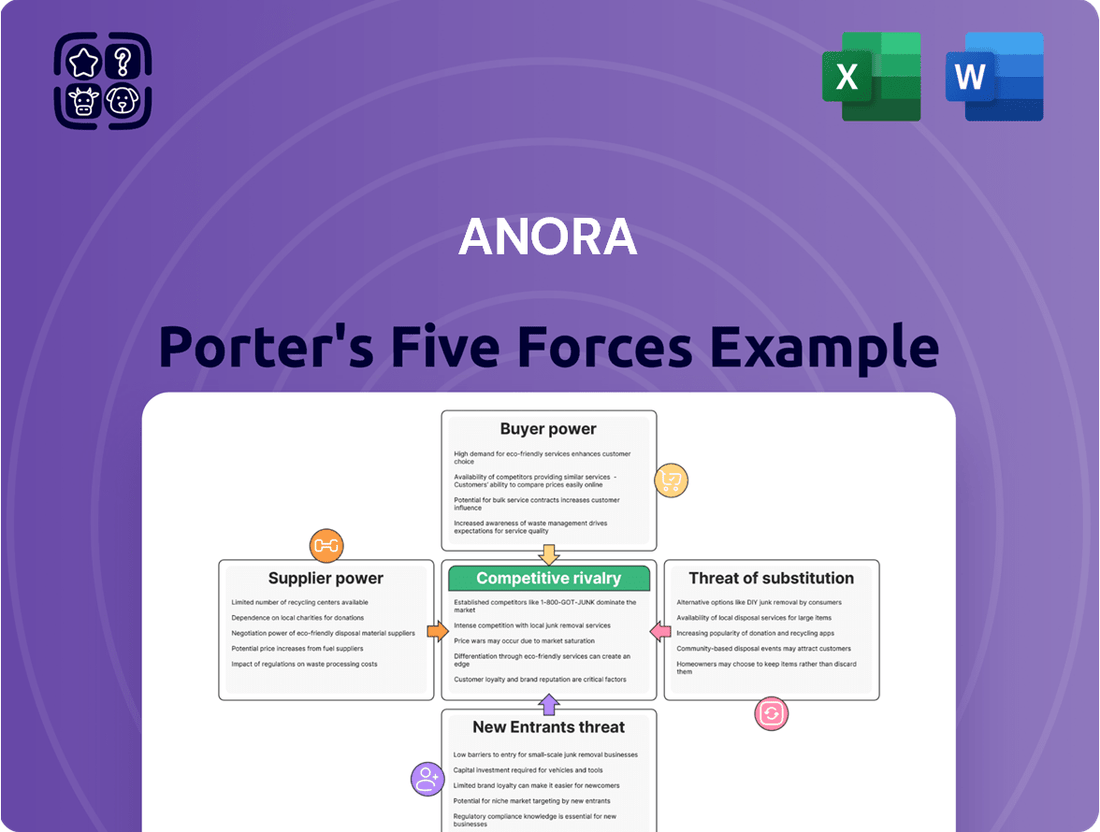
Anora Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Anora Bundle
Anora's competitive landscape is shaped by several critical forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the intensity of rivalry within its industry. Understanding these dynamics is key to navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Anora’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Anora Group's suppliers hinges on the availability and uniqueness of its core agricultural inputs, such as grapes, grains, and botanicals. If these are sourced from limited, specialized regions or possess unique qualities, suppliers can exert greater influence on pricing. For instance, a particular type of grape essential for a premium spirit, if only grown in a specific appellation, grants that supplier significant leverage.
In 2023, Anora Group reported that its cost of goods sold was €749.2 million, a significant portion of which would be tied to these raw material purchases. If a substantial percentage of these inputs come from a few dominant suppliers, or if the inputs themselves are highly differentiated and not easily substituted, Anora's ability to negotiate favorable terms diminishes. This concentration of supplier power can directly impact Anora's profitability by driving up input costs.
Suppliers of essential packaging like glass bottles, corks, and labels hold sway over Anora's costs. While common packaging materials offer many choices, unique or eco-conscious options can concentrate power with fewer suppliers, increasing their leverage.
Anora's dedication to sustainability, a key differentiator, could mean relying on specialized eco-friendly packaging providers. This reliance might bolster the negotiating position of these specific suppliers, potentially impacting Anora's input costs.
The concentration of suppliers is a key factor. If Anora relies on a few specialized suppliers for critical ingredients, like unique flavor profiles, these suppliers hold significant power. For instance, in 2024, the global market for certain natural flavor extracts saw consolidation, with the top three players controlling over 60% of the market share, increasing their leverage.
High switching costs for Anora can amplify supplier power. If changing a key ingredient requires extensive product reformulation, testing, and regulatory approval, suppliers can demand higher prices or less favorable terms. This is particularly true for proprietary or patented ingredients that are difficult to substitute.
Anora can mitigate supplier power through long-term contracts and strategic partnerships. Securing multi-year agreements can lock in pricing and supply, while collaborative relationships might foster shared innovation and reduce the incentive for suppliers to exploit their position. In 2024, many food and beverage companies explored such strategic sourcing to stabilize input costs amidst inflationary pressures.
Supplier Power 4
Labor, especially for specialized roles like distillation and brand development, can exert significant power. A scarcity of skilled professionals in the wine and spirits sector, a trend observed in recent years, can lead to increased wage demands and impact Anora's operational smoothness. This was particularly evident in 2024, with reports indicating a 5% rise in average wages for skilled trades within the beverage industry.
To mitigate this, Anora can focus on nurturing its internal workforce. Investing in training and development programs not only builds a loyal talent pool but also reduces reliance on external hiring. For instance, companies that prioritize employee development often see a 10-15% reduction in recruitment costs.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: A notable gap exists in specialized roles within the wine and spirits industry, impacting operational efficiency.
- Wage Inflation: Industry-wide wage increases, averaging around 5% in 2024 for skilled positions, directly affect labor costs.
- Talent Development: Internal training and retention strategies are crucial for managing labor supplier power and reducing recruitment expenses.
- Operational Impact: A lack of qualified personnel can disrupt production cycles and brand-building initiatives.
Supplier Power 5
Logistics and distribution service providers, particularly those with strong networks in the Nordic and Baltic regions, can exert considerable influence. The highly regulated alcohol distribution landscape in these areas makes it difficult to find suitable alternatives, potentially increasing Anora's transportation and warehousing expenses.
In 2023, Anora reported that its supply chain, including logistics, faced inflationary pressures. For instance, fuel costs, a significant component of logistics expenses, saw notable increases throughout the year, impacting operational expenditures.
- High dependence on specialized logistics: Anora relies on providers with specific licenses and infrastructure for alcohol transport and storage.
- Limited alternative providers: The regulated nature of the market restricts the number of compliant and efficient logistics partners available.
- Potential for increased costs: Challenges in securing alternative logistics can lead to higher transportation and warehousing fees for Anora.
- Impact of fuel prices: Fluctuations in fuel costs directly affect the profitability of logistics services, potentially being passed on to Anora.
Anora's suppliers, particularly those providing unique agricultural inputs like specific grape varietals or botanicals, hold significant power if these inputs are scarce or difficult to substitute. This leverage can drive up raw material costs, directly impacting Anora's cost of goods sold, which was €749.2 million in 2023.
The concentration of suppliers for critical ingredients, such as specialized flavor extracts where the top three players held over 60% market share in 2024, further amplifies their bargaining power. High switching costs for Anora, involving extensive reformulation and regulatory approvals for new ingredients, also strengthen supplier leverage.
Skilled labor, especially in specialized roles like distillation, presents another area of supplier power. A shortage of such talent in the wine and spirits sector, evidenced by a 5% average wage increase for skilled trades in 2024, can escalate labor costs for Anora.
Logistics providers with specialized networks in regulated markets like the Nordics also wield influence, as limited alternatives can lead to higher transportation and warehousing expenses for Anora, especially with fluctuating fuel costs impacting their operations.
| Factor | Impact on Anora | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Agricultural Inputs | Potential for increased raw material costs | Limited supply of unique grapes/botanicals grants supplier leverage |
| Ingredient Suppliers | Higher input costs due to supplier concentration | Top 3 flavor extract players control >60% market share |
| Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, increased supplier pricing power | Reformulation and regulatory approval are time-consuming and costly |
| Skilled Labor | Increased wage demands and recruitment challenges | 5% average wage increase for skilled beverage industry trades |
| Logistics Providers | Higher transportation and warehousing expenses | Fuel cost volatility and specialized Nordic distribution needs |
What is included in the product
Anora's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes.
Anora Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a structured framework to pinpoint and address competitive pressures, helping you proactively mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Anora Group faces considerable buyer power, especially in Nordic markets where state-owned alcohol monopolies like Alko in Finland and Systembolaget in Sweden dominate. These entities, acting as consolidated purchasers, wield significant influence over pricing and product selection due to their sheer volume of business, directly impacting Anora's revenue and profit margins.
Large retail chains and major HoReCa groups wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes. For instance, in 2024, major European supermarket chains like Carrefour and Tesco often negotiate bulk discounts, which can compress margins for beverage suppliers like Anora. Their ability to dictate shelf space and menu placement also gives them leverage, directly influencing Anora's market share and consumer visibility.
Anora's customers, encompassing both trade buyers like restaurants and retailers, and end-consumers, possess significant bargaining power due to the vast array of wine and spirits brands available. This abundance of choice means consumers can easily switch to competitors if Anora's offerings don't meet their expectations in terms of price, quality, or brand appeal. For instance, in 2024, the global spirits market saw numerous new entrants and product launches, intensifying competition and giving consumers more alternatives than ever before.
Buyer Power 4
Buyer power is a significant force for Anora, particularly in the wine and spirits sector where customers are often price-sensitive. This sensitivity is amplified in mature markets where consumers have ample information and readily compare prices across various brands and outlets. Economic downturns or reduced disposable income can further intensify this, pushing consumers towards more budget-friendly options.
Anora must carefully navigate this by balancing its premium brand image with competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, the global alcoholic beverage market saw continued pressure on pricing due to inflation and shifts in consumer spending habits. Companies like Anora need to ensure their value proposition remains strong, even when offering premium products.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers in mature markets like wine and spirits are well-informed and actively compare prices, impacting Anora's pricing strategies.
- Economic Impact: Fluctuations in disposable income and economic conditions directly influence customer willingness to pay for premium offerings.
- Balancing Act: Anora needs to maintain its premium positioning while implementing pricing that remains competitive in the current economic climate.
- Market Data: In 2024, inflation and changing consumer spending patterns continued to put pressure on pricing across the alcoholic beverage industry.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of Anora's customers is a significant factor, especially as purchasing groups and associations emerge. These consolidated entities can wield considerable influence by aggregating demand, allowing them to negotiate more favorable pricing and terms than individual buyers. For instance, a large retail chain or a consortium of smaller businesses could collectively demand discounts or specific service levels, directly impacting Anora’s profit margins.
Anora needs to proactively engage with these influential customer segments. Building strong, strategic relationships with key purchasing groups is crucial for securing long-term business and mitigating the downward pressure on prices. This might involve offering tiered pricing, loyalty programs, or customized solutions that provide added value beyond the basic product or service.
- Customer Aggregation: The ability of customers to band together, either formally through associations or informally through large purchasing blocs, amplifies their influence.
- Negotiating Leverage: Collective bargaining allows these groups to demand better pricing, improved payment terms, or enhanced product/service features from Anora.
- Strategic Engagement: Anora must identify and cultivate relationships with its most significant customer groups to ensure mutually beneficial agreements and maintain market stability.
- Impact on Margins: Unchecked buyer power can lead to price erosion, directly squeezing Anora's profitability and requiring careful margin management.
The bargaining power of Anora's customers is substantial, particularly in markets with consolidated buyers like Nordic alcohol monopolies. These entities, such as Systembolaget in Sweden, can dictate terms due to their significant purchasing volume, directly impacting Anora's pricing and product availability. For instance, in 2024, the continued consolidation of retail power across Europe means large chains can negotiate favorable pricing, potentially squeezing supplier margins.
Customers, both trade and end-consumers, have numerous alternatives in the global spirits market, which saw many new entrants in 2024. This abundance of choice empowers them to switch brands if Anora's offerings do not meet price or quality expectations. Economic pressures in 2024 also heightened price sensitivity, forcing companies like Anora to balance premium branding with competitive pricing strategies to maintain market share amidst inflation and shifting consumer spending.
| Customer Segment | Leverage Factors | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Nordic Alcohol Monopolies | Consolidated purchasing volume, state control | Dictated pricing and product selection for Anora |
| Large Retail Chains | High order volumes, shelf space control | Negotiated bulk discounts, impacting Anora's margins |
| End Consumers | Abundant brand choices, price comparison | Switching to lower-priced alternatives due to economic conditions |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Anora Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Anora Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive intensity and industry attractiveness. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing sections. You can confidently anticipate instant access to this ready-to-use analysis, empowering you with valuable strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry in the Nordic and Baltic wine and spirits market is fierce. Anora faces strong competition from global powerhouses like Diageo, Pernod Ricard, and Bacardi, alongside a significant number of local and regional producers. This dynamic creates a highly competitive landscape where players constantly vie for market share and consumer engagement.
In the mature Nordic markets, Anora's industry faces slow to moderate growth, which naturally heats up the competition. When the overall market isn't expanding rapidly, companies have to fight harder for every customer, leading to more aggressive strategies to gain market share. This often translates into intense price wars and significant spending on marketing to stand out.
For instance, in 2024, the alcoholic beverage market in the Nordic region, a key operating area for Anora, saw growth rates hovering around 1-2%. This relatively subdued expansion means that companies like Anora are constantly looking for ways to differentiate their offerings, whether through new product development, enhanced customer experiences, or strategic partnerships, to capture a larger portion of the existing demand.
Competitive rivalry in the wine and spirits sector is intense, largely driven by strong brand loyalty. Consumers often exhibit a preference for established brands, making it difficult for new entrants to capture market share. For instance, in 2024, major players like Diageo and Pernod Ricard continued to dominate global spirits sales, demonstrating the enduring power of well-established brand equity.
Competitors pour significant resources into marketing, advertising, and elaborate brand-building initiatives to cultivate and maintain this loyalty. This aggressive promotional activity creates a high barrier to entry, as emerging or less-recognized brands struggle to gain visibility and consumer trust. Anora must therefore consistently invest in strengthening its brand image and showcasing the appeal of its diverse product portfolio to remain competitive.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry in the beverage sector is intense, driven by companies differentiating their products through unique flavors, sustainable practices, premiumization, and innovative packaging. This strategy helps brands capture market share and command higher prices. Anora's broad product range and strong commitment to sustainability are central to its efforts to stand out.
In 2024, the global beverage market continued to see robust competition. For instance, companies focused on plant-based alternatives saw significant growth, with the plant-based milk market alone projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027. This highlights the consumer demand for differentiated and often healthier options, pushing competitors to innovate.
- Product Differentiation: Companies leverage unique flavors, sustainable sourcing, premium ingredients, and eye-catching packaging to carve out distinct market positions.
- Sustainability as a Differentiator: Anora's emphasis on eco-friendly production and packaging resonates with a growing consumer base, creating a competitive advantage.
- Market Dynamics: The beverage industry's high growth potential attracts numerous players, intensifying rivalry as firms vie for consumer attention and loyalty.
- Pricing Power: Successful differentiation allows companies to justify premium pricing, contributing to higher profit margins in a competitive landscape.
Competitive Rivalry 5
High exit barriers, such as significant fixed assets in production facilities and established distribution networks, discourage companies from leaving the market, even during periods of low profitability. This perpetuates intense competition among existing players, as they are committed to maintaining their market presence despite challenges.
Mergers and acquisitions are common strategies to consolidate power, as seen in the semiconductor industry where consolidation continues. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor market saw ongoing strategic moves, with companies like Intel focusing on foundry services to bolster their competitive position amidst intense rivalry.
- High fixed asset investment: Companies in capital-intensive industries often have substantial investments in plants and equipment, making it costly to divest.
- Established distribution channels: Long-term relationships with distributors and retailers create switching costs for both suppliers and customers.
- Brand loyalty and customer relationships: Building strong customer loyalty can make it difficult for new entrants or exiting firms to shift market share.
- Government regulations and subsidies: Certain industries may have regulatory hurdles or government support that influences a company's decision to exit or remain.
The competitive rivalry within the Nordic and Baltic wine and spirits market is intense, with Anora facing formidable opposition from global giants like Diageo and Pernod Ricard, as well as numerous local players. This high level of competition is exacerbated by the mature Nordic markets, where slow growth necessitates aggressive strategies for market share acquisition, often leading to price wars and substantial marketing expenditures. In 2024, the Nordic alcoholic beverage market experienced growth rates of approximately 1-2%, underscoring the need for differentiation through product innovation and enhanced customer experiences.
| Competitor | Market Presence | Key Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Diageo | Global powerhouse, strong presence in Nordic markets | Brand building, premiumization, extensive distribution |
| Pernod Ricard | Global leader, significant Nordic footprint | Product innovation, targeted marketing, strategic partnerships |
| Bacardi | Major player in spirits, growing Nordic engagement | Consumer engagement, digital marketing, new product launches |
| Local/Regional Producers | Niche markets, often strong in specific categories | Agility, unique product offerings, local consumer understanding |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Anora Group is significant, primarily stemming from the booming non-alcoholic beverage market. As health consciousness rises, consumers are increasingly turning to sophisticated alternatives like non-alcoholic spirits, wines, and beers, as well as innovative soft drinks that mimic the social and sensory experience of alcoholic beverages. This trend is particularly strong among younger demographics and those prioritizing wellness.
In 2024, the global non-alcoholic beverage market is projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, with the low and no-alcohol segment experiencing robust growth. For instance, sales of non-alcoholic spirits in key European markets saw double-digit increases in 2023, indicating a clear shift in consumer preference that directly impacts Anora's traditional product categories. This growing acceptance and availability of high-quality substitutes present a compelling alternative for consumers, potentially reducing demand for Anora's alcoholic offerings.
Other recreational substances, like cannabis in regions where it's legal and socially accepted, represent an emerging indirect threat to Anora Porter. As regulations continue to adapt and consumer tastes evolve, some individuals might opt for these alternatives for unwinding or socializing, potentially drawing demand away from traditional alcoholic drinks. This evolving landscape necessitates vigilant observation by Anora.
The threat of substitutes for Anora's alcoholic beverages is significant, as consumers have a wide array of alternative leisure and entertainment options vying for their disposable income. Instead of purchasing Anora's products, consumers might choose to spend their money on experiences like travel, dining out, or pursuing hobbies. For instance, in 2024, the global travel and tourism market was projected to reach over $9.6 trillion, indicating a substantial diversion of consumer spending away from other categories.
4
The growing popularity of home brewing and distilling, though still a niche market, presents a potential substitute for Anora's commercially produced alcoholic beverages. This trend, fueled by enthusiasts aiming for unique flavors or lower costs, could modestly impact demand, particularly among specific consumer groups. For instance, reports from 2024 indicate a continued interest in craft brewing kits, with online sales showing a steady uptick.
While the appeal of personalized or more affordable options is clear, significant regulatory barriers and the technical expertise required for consistent quality limit the widespread adoption of home production as a true substitute. This means that for the majority of consumers, commercially produced beverages remain the primary choice. The market for home distilling, in particular, faces strict legal limitations in many regions, further constraining its ability to substitute mainstream offerings.
The threat of substitutes can be summarized as follows:
- Home brewing and distilling offer alternative consumption options.
- This trend may slightly reduce demand for Anora's products in specific segments.
- Regulatory challenges and complexity limit the broad impact of home production.
- The overall threat from substitutes remains moderate due to these constraints.
5
While Anora Porter operates in the alcoholic beverage market, basic beverages like water, juice, and coffee represent a significant threat of substitutes. These non-alcoholic options fulfill the fundamental need for hydration and refreshment, especially for consumers prioritizing health, avoiding alcohol, or managing specific dietary needs. For instance, the global bottled water market alone was valued at approximately $350 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily, indicating a substantial consumer base for simple hydration solutions.
These substitutes can indirectly impact Anora's sales by reducing the occasions for alcoholic beverage consumption. When consumers seek refreshment or are in social settings where alcohol is not desired, they will opt for these readily available alternatives. This highlights the need for Anora to understand and cater to diverse consumer motivations beyond just social signaling or sensory experience.
The threat is amplified when considering the cost-effectiveness and accessibility of substitutes. In 2024, the average price of a premium bottled water or a specialty coffee can be significantly lower than a comparable alcoholic beverage, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious consumers. This cost differential is a key factor in consumer decision-making.
- Hydration Needs: Basic beverages like water and juice directly compete by fulfilling the primary need for hydration, a fundamental human requirement.
- Dietary and Health Considerations: Consumers with health goals, dietary restrictions (e.g., non-alcoholic, low-sugar), or those actively reducing alcohol intake will gravitate towards these substitutes.
- Occasion-Based Substitution: In many social or casual settings, non-alcoholic drinks are perfectly acceptable and often preferred, directly displacing potential alcohol sales.
- Cost and Accessibility: The lower price point and widespread availability of basic beverages make them an easily accessible and often more economical choice for consumers.
The threat of substitutes for Anora's portfolio is multifaceted, encompassing both direct replacements and alternative leisure activities. The burgeoning non-alcoholic beverage sector, projected to exceed $1.5 trillion globally in 2024, presents a significant challenge as consumers increasingly prioritize health and wellness. This shift is evident in the double-digit growth of non-alcoholic spirits sales in Europe during 2023, directly impacting Anora's traditional market share.
Beyond beverages, other recreational substances, where legal, and experiences like travel, which saw the global market projected over $9.6 trillion in 2024, divert consumer spending and attention. Even basic beverages like water, with a 2023 market valuation around $350 billion, fulfill fundamental hydration needs, often at a lower cost, making them accessible alternatives.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Projection/Value | Key Driver | Impact on Anora |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-alcoholic Beverages | >$1.5 trillion | Health consciousness, wellness trends | Direct displacement of alcoholic beverage consumption |
| Experiences (e.g., Travel) | >$9.6 trillion | Disposable income allocation, lifestyle choices | Diversion of consumer spending away from beverages |
| Basic Beverages (e.g., Water) | ~$350 billion (Bottled Water 2023) | Hydration, cost-effectiveness, accessibility | Fulfills basic needs, reduces occasions for alcohol |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new companies entering the Nordic and Baltic wine and spirits market, particularly those aiming to replicate Anora's broad product range, is considerably low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment needed to establish operations. For instance, setting up modern production facilities and securing reliable raw material sourcing can easily run into tens of millions of euros, creating a significant financial hurdle.
Beyond production, building robust distribution networks across multiple countries and developing a diverse portfolio comparable to Anora's requires extensive logistical infrastructure and marketing budgets. Anora itself has invested heavily in its supply chain and brand building over many years, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on scale and reach. This high barrier to entry effectively deters many potential new players from challenging established companies.
The threat of new entrants for Anora is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory barriers, especially within the Nordic region. Countries like Finland, Sweden, and Norway operate state-controlled alcohol monopolies, requiring extensive licensing and adherence to complex legal frameworks for market access. This can involve lengthy approval processes and considerable upfront investment in compliance, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a foothold.
Navigating these stringent sales and marketing regulations, alongside obtaining necessary permits, presents a time-consuming and costly challenge for potential competitors. Established companies such as Anora have already invested in and refined their compliance infrastructure, giving them a distinct advantage. For instance, Anora's deep understanding of these markets, developed over years of operation, allows them to navigate these hurdles more efficiently than a new entrant might.
The threat of new entrants for Anora Porter's business is relatively low. Existing players, including Anora, benefit from strong brand loyalty and well-established distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, major beverage companies often reported that over 70% of their sales came from repeat customers, highlighting the difficulty for newcomers to capture market share.
Consumers tend to favor trusted brands, and gaining access to retail shelf space or securing listings with state monopolies, common in certain industries, demands substantial investment in marketing and building relationships. New entrants face a significant hurdle in quickly establishing the credibility and product quality that consumers expect, a process that can take years and considerable capital.
4
The threat of new entrants for Anora is significantly tempered by the substantial economies of scale enjoyed by established players. Anora’s vast operational volume allows for considerably lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, raw material procurement, and logistics. This cost advantage makes it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to match Anora's pricing without incurring substantial initial financial losses, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
Consider these factors:
- Cost Advantage: Anora's large-scale operations in 2024, for instance, translate to buying power that smaller firms cannot replicate, directly impacting their cost of goods sold.
- Barriers to Entry: The capital required to achieve comparable production volumes and distribution networks presents a formidable financial hurdle for any new entrant aiming to compete effectively.
- Brand Loyalty and Reputation: Existing customer relationships and Anora's established brand reputation further solidify its market position, making it harder for new entrants to gain traction.
5
The threat of new entrants in the wine and spirits industry is moderate, largely due to significant barriers to entry. Access to specialized knowledge, experienced personnel, and established supplier relationships are crucial. For instance, developing the expertise required for quality distillation, blending, and effective marketing, alongside navigating complex regulatory landscapes, demands substantial time and investment. Newcomers often lack these deeply embedded advantages, making it challenging to compete from the outset.
The capital-intensive nature of production and distribution further deters new players. Setting up state-of-the-art distilleries or wineries, securing prime vineyard land, and establishing robust distribution networks require millions in upfront investment. For example, building a new craft distillery can easily cost upwards of $1 million to $5 million, depending on scale and equipment. This financial hurdle, coupled with the time needed to build brand recognition and consumer loyalty, significantly limits the influx of fresh competition.
- High Capital Requirements: Significant investment is needed for production facilities, raw materials, and distribution networks.
- Brand Loyalty and Reputation: Established brands benefit from decades of consumer trust and recognition, which is difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex licensing, taxation, and distribution laws across different regions presents a substantial challenge.
- Economies of Scale: Larger, established players often achieve lower production costs per unit, making it difficult for smaller new entrants to compete on price.
The threat of new entrants for Anora is low due to significant capital requirements, regulatory complexities, and established brand loyalty. For instance, the cost to build a modern winery or distillery can range from several million to tens of millions of euros, a substantial barrier. Furthermore, navigating the strict alcohol monopolies and licensing in Nordic countries, as Anora does, requires deep expertise and time, deterring many new players.
Established players like Anora benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit costs. In 2024, major beverage companies often reported that over 70% of their sales came from repeat customers, underscoring the difficulty for newcomers to gain market share against trusted brands with extensive distribution networks.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Anora's Position |
| Capital Investment | Very High (Production, Distribution) | Established infrastructure, significant scale |
| Regulatory Environment | Challenging (Licensing, State Monopolies) | Expertise in compliance, long-standing relationships |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Difficult to Build | Strong consumer trust, decades of brand building |
| Economies of Scale | Disadvantageous | Lower per-unit costs, competitive pricing power |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive suite of data sources, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and Forrester, and publicly available financial filings from regulatory bodies such as the SEC.
