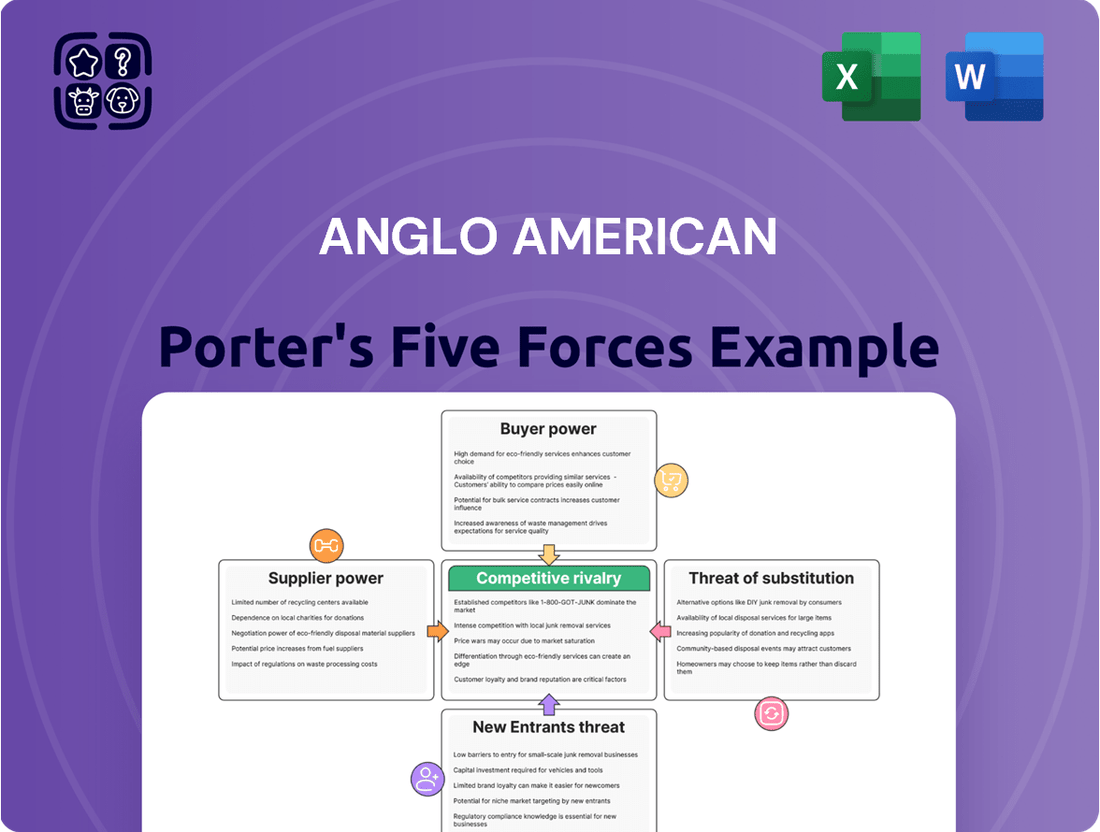
Anglo American Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Anglo American Bundle
Anglo American operates within a complex mining landscape shaped by powerful forces. Understanding buyer power, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for navigating this industry. This brief overview only hints at the intricate dynamics at play.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Anglo American’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining equipment sector is highly concentrated, with a few global giants like Caterpillar and Komatsu controlling a significant portion of the market for heavy machinery. This dominance grants them considerable bargaining power, especially when dealing with large mining operations such as those of Anglo American. For instance, in 2023, Caterpillar reported revenues of over $67 billion, underscoring its market presence.
The specialized nature of mining equipment, often requiring bespoke solutions for specific geological conditions, means that switching suppliers can be incredibly costly and disruptive. This high switching cost, coupled with the integrated nature of many advanced mining systems, further solidifies the suppliers' leverage over mining companies. The investment in proprietary technology and training for these systems can run into millions of dollars, making a change of vendor a substantial undertaking.
Critical technology providers hold significant bargaining power over mining giants like Anglo American. As the mining sector increasingly adopts advanced automation, AI, and digital solutions to boost efficiency and safety, these specialized suppliers become indispensable. Anglo American's substantial investments in these technologies, aiming for productivity gains and cost reductions, underscore the critical role these providers play in maintaining a competitive advantage.
The intricate and proprietary nature of these cutting-edge technologies severely restricts Anglo American's options for alternative suppliers. For instance, in 2024, Anglo American continued its focus on digital transformation initiatives, including the deployment of autonomous haulage systems and advanced data analytics platforms, which are often sourced from a limited number of highly specialized firms.
The global mining sector, including giants like Anglo American, grapples with a persistent shortage of skilled labor, especially in critical technical and operational areas. This scarcity directly bolsters the bargaining power of these skilled workers, enabling them to command higher wages and better benefits, which can impact a company's operational costs and profitability.
For instance, reports from 2024 indicate that the demand for experienced geologists and mining engineers significantly outstrips supply, leading to increased recruitment costs and longer hiring timelines for mining firms. This situation necessitates substantial investment in robust training programs and the creation of highly competitive compensation structures to attract and retain essential talent.
Energy and Logistics Dependence
Anglo American's mining operations are inherently energy-hungry, making energy suppliers a significant factor in their bargaining power. In 2023, the company's energy costs represented a substantial portion of its operating expenses, with fluctuations in global energy prices directly impacting profitability. Regions with less stable power grids amplify the leverage of energy providers, as reliable supply is critical for continuous production.
Logistics and transportation are equally vital, especially for bulk commodities like iron ore and coal. Suppliers of specialized rail, shipping, and port services hold considerable sway, particularly when Anglo American relies on specific infrastructure for its output. For instance, disruptions in rail networks, as seen in some South African coal corridors, can lead to significant delays and increased costs, demonstrating the suppliers' impact.
- Energy Intensity: Mining operations consume vast amounts of electricity and fuel, making energy suppliers a key cost driver.
- Logistics Dependence: Efficient transportation of raw materials and finished products relies heavily on specialized logistics providers.
- Infrastructure Constraints: Limited access to specific rail lines or port facilities can increase the bargaining power of logistics suppliers.
- Cost Pass-Through: Suppliers can pass on increased energy or operational costs, directly affecting Anglo American's bottom line.
Limited Raw Material Inputs for Suppliers
Even though Anglo American is a major player in raw materials, its own suppliers for specialized equipment and advanced technologies can experience limitations. These suppliers rely on their own raw material inputs, such as specific metals and components needed for manufacturing sophisticated mining machinery. For instance, disruptions in the supply chain for rare earth elements, crucial for certain electronic components in mining equipment, could directly affect the availability and cost of these essential tools for Anglo American.
This dependency creates a significant bargaining power for these specialized suppliers. If they face raw material constraints, it can lead to increased prices or extended lead times for the machinery Anglo American needs. In 2023, the global mining equipment market experienced price increases averaging 5-10% due to ongoing supply chain challenges and demand for critical minerals used in manufacturing, illustrating this very point.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Anglo American's reliance on specialized equipment manufacturers means it's susceptible to disruptions in their upstream supply chains.
- Component Scarcity: Shortages of specific metals or advanced components required for mining machinery can directly impact equipment availability and cost.
- Cascading Cost Increases: Price hikes or delays from equipment suppliers, driven by their own raw material constraints, translate into higher operational costs and potential project delays for Anglo American.
- Supplier Leverage: Manufacturers of complex mining technology, facing their own input limitations, can exert greater pricing and delivery power over their customers like Anglo American.
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment and critical technologies wield considerable bargaining power over Anglo American due to the high cost and complexity of switching. This is exacerbated by the limited number of providers capable of delivering advanced, often bespoke, solutions. For instance, in 2024, Anglo American's continued investment in autonomous systems highlights its dependence on a select group of technology firms.
The concentration within the mining equipment sector, with giants like Caterpillar and Komatsu dominating, means these suppliers can dictate terms. Their significant market share, demonstrated by Caterpillar's over $67 billion revenue in 2023, translates into leverage. Furthermore, the specialized nature of mining machinery and the high switching costs associated with integrated systems further strengthen supplier positions.
The scarcity of skilled labor in mining, particularly for specialized technical roles, also empowers suppliers of human capital and training services. In 2024, the demand for experienced geologists and engineers continues to outstrip supply, driving up recruitment costs and necessitating competitive compensation packages, which can be influenced by the providers of these essential skills.
Energy and logistics providers also hold significant sway, especially given the energy-intensive nature of mining and the reliance on specialized transportation. In 2023, energy costs were a substantial portion of Anglo American's operating expenses, and disruptions in logistics, like those seen in certain rail corridors, demonstrate the critical dependence on these suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Anglo American | 2023/2024 Data Point |
| Mining Equipment Manufacturers | Market concentration, specialized technology, high switching costs | Potential for higher equipment prices, extended lead times | Caterpillar revenue > $67 billion (2023) |
| Technology Providers (Automation, AI) | Indispensability of advanced solutions, proprietary nature of tech | Reliance on limited vendors for efficiency gains | Continued focus on digital transformation initiatives (2024) |
| Skilled Labor Providers/Agencies | Labor shortages in critical roles | Increased recruitment costs, higher wage demands | High demand for geologists/engineers (2024) |
| Energy Suppliers | Energy intensity of operations | Exposure to energy price volatility | Energy costs a substantial operating expense (2023) |
| Logistics & Transportation | Dependence on specialized infrastructure | Vulnerability to service disruptions and cost increases | Impact of rail network disruptions noted |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive forces impacting Anglo American, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive threats, allowing for proactive strategy development and pain point mitigation.
Customers Bargaining Power
Anglo American's core products, including copper, iron ore, and platinum group metals (PGMs), are essentially commodities. This lack of differentiation means customers are very sensitive to price changes. For instance, in 2023, the average realized price for copper for Anglo American was $8,440 per tonne, and any significant upward movement could drive buyers to seek cheaper alternatives from competitors.
Because these materials are so similar across suppliers, buyers have the flexibility to switch to whoever offers the best price at any given moment. This significantly limits Anglo American's ability to dictate terms or maintain high profit margins when market conditions shift. The company's revenue is therefore directly tied to the often volatile global commodity markets.
Anglo American's industrial customers, such as major steelmakers and automotive manufacturers, often buy in massive quantities. This scale gives them considerable power to negotiate better pricing. For instance, a single large steel producer might account for a significant portion of Anglo American's iron ore sales, enabling them to demand concessions.
Shifts in downstream industries significantly bolster customer bargaining power. For instance, the automotive sector's pivot to electric vehicles is reducing demand for platinum group metals (PGMs) in traditional catalytic converters, a key market for Anglo American. Similarly, China's drive for green steel impacts its appetite for iron ore, directly affecting Anglo American's sales.
Growing Influence of Lab-Grown Diamonds
Anglo American, through its De Beers division, is experiencing a notable shift in customer bargaining power, largely driven by the burgeoning lab-grown diamond market. These synthetic alternatives, indistinguishable from natural diamonds in core properties, offer a more accessible price point. By mid-2024, lab-grown diamond prices were often 50-70% lower than comparable natural diamonds, significantly empowering consumer choice and demanding a strategic response from traditional producers.
The appeal of lab-grown diamonds extends beyond cost, resonating with a growing consumer base prioritizing ethical sourcing and environmental sustainability. This consumer sentiment directly challenges the established narrative of natural diamonds. For instance, reports in early 2024 indicated that over 70% of younger consumers (under 30) considered lab-grown diamonds as a viable and attractive option for engagement rings, a demographic increasingly influencing market trends.
- Cost Advantage: Lab-grown diamonds are significantly cheaper, with prices for a 1-carat, D-color, VVS1 clarity stone averaging around $1,500-$2,500 in mid-2024, compared to $6,000-$8,000 for a natural equivalent.
- Ethical and Sustainability Appeal: Consumers are increasingly drawn to the perceived lower environmental impact and ethical sourcing of lab-grown diamonds, a factor highlighted in numerous consumer surveys throughout 2023 and 2024.
- Market Share Growth: The market share of lab-grown diamonds in the overall diamond jewelry market has been steadily increasing, projected to reach 10-15% by the end of 2024, up from single digits in previous years.
- Industry Re-evaluation: This trend is forcing companies like De Beers to adapt their marketing and product strategies, including the introduction of their own lab-grown diamond offerings, to retain market relevance and cater to evolving consumer preferences.
Customer Focus on Sustainability and ESG
Customers are increasingly scrutinizing suppliers for robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance and sustainable mining operations. This heightened awareness translates into greater customer power, enabling them to dictate higher ethical and environmental standards for Anglo American.
For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of global consumers indicated a willingness to pay a premium for products from companies with strong ESG commitments, with some reports suggesting this figure could reach over 60% in developed markets. This trend directly impacts Anglo American, as failing to align with these evolving customer expectations can jeopardize market access and strain valuable customer relationships.
- Growing ESG Demand: Consumers and business partners are actively seeking out suppliers with demonstrable ESG credentials.
- Leverage for Customers: This demand gives customers the ability to negotiate for more sustainable and ethically sourced materials.
- Market Access Impact: Anglo American's ability to meet these ESG standards directly influences its standing with key buyers and its overall market position.
The bargaining power of customers for Anglo American is significant due to the commodity nature of its core products, leading to price sensitivity and easy switching between suppliers. Large industrial buyers, like steelmakers, wield considerable influence due to their purchasing volume, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms. Furthermore, evolving consumer preferences, particularly the rise of lab-grown diamonds and a strong demand for ESG compliance, empower customers to dictate higher standards and impact market access.
| Factor | Impact on Anglo American | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Commodity Nature & Price Sensitivity | Customers easily switch for lower prices. | Copper prices fluctuated, with average realized prices for Anglo American in 2023 at $8,440/tonne. |
| Large Volume Buyers | Major industrial clients negotiate significant discounts. | Specific customer concentration data is proprietary, but major steel and auto manufacturers represent key segments. |
| Lab-Grown Diamond Competition | Undercuts natural diamond value proposition. | Lab-grown diamond prices in mid-2024 were 50-70% lower than natural diamonds. |
| ESG Demands | Customers demand higher ethical and environmental standards. | Over 60% of consumers in developed markets willing to pay a premium for ESG-compliant products (early 2024 reports). |
Full Version Awaits
Anglo American Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Anglo American Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, professionally written document, complete with detailed insights into the competitive landscape of the Anglo American sector. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, ready-to-use file, allowing you to leverage its strategic information without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Anglo American faces fierce rivalry from global giants like BHP, Rio Tinto, and Glencore, all boasting diversified portfolios and substantial financial clout. This intense competition is evident in their ongoing efforts to capture market share and secure access to new mining concessions.
These diversified players often engage in strategic bidding for exploration rights and develop similar operational strategies, intensifying the battle for resources. For instance, in 2024, major mining companies continued to invest billions in exploration and development projects worldwide, directly impacting Anglo American's ability to expand.
The inherent volatility of commodity prices significantly fuels competitive rivalry. When prices fall, companies aggressively compete for market share and try to preserve profitability, often leading to price wars.
For instance, 2024 proved particularly challenging for miners of commodities other than gold. Many experienced declining revenues and EBITDA, forcing them to focus intensely on operational efficiency and cost management to stay afloat.
This pressure can compel companies to adopt aggressive pricing strategies, especially in oversupplied markets, to move their production and maintain cash flow, further intensifying the competitive landscape.
The mining sector, including companies like Anglo American, is inherently marked by substantial fixed costs. Think of the massive investment in exploration, mine development, and processing equipment; these are not expenses you can easily recoup. For instance, establishing a new mine can easily run into billions of dollars. This capital intensity creates a significant hurdle for companies looking to scale back or exit the market, as their assets are highly specialized and difficult to repurpose or sell quickly.
Because of these high fixed costs, mining companies are often compelled to continue operating, even when commodity prices are low. The logic is that it's better to generate some revenue to cover ongoing operational and fixed costs than to cease production entirely and incur a complete loss on those investments. This behavior can lead to an oversupply of commodities, intensifying competition among players like Anglo American as they strive to maintain market share and cover their substantial financial commitments.
Anglo American's portfolio of long-life mining assets, while a strategic advantage for sustained production, also embodies these significant sunk costs. For example, their operations in South Africa and South America involve extensive infrastructure and long-term resource commitments. In 2023, Anglo American reported capital expenditure of approximately $3.8 billion, underscoring the continuous investment required to maintain and develop these high-cost assets.
Race for Future-Enabling Minerals
The mining sector is experiencing an intense competition to secure critical minerals like copper, vital for the global energy transition. Anglo American is strategically positioning itself by focusing on these future-enabling products, directly confronting competitors who are also heavily investing in similar resource portfolios.
This heightened rivalry spans across the entire value chain, from the initial stages of exploration and project development to securing crucial off-take agreements with end-users. Companies are vying for access to deposits and for the capital required to bring new supply online.
- Copper Demand Surge: Global copper demand is projected to nearly double by 2035, reaching 50 million tonnes, driven by electrification and renewable energy infrastructure.
- Investment Race: Major mining companies, including BHP, Rio Tinto, and Glencore, are allocating billions of dollars to copper and nickel exploration and development projects.
- Project Pipeline Competition: Anglo American faces direct competition for advanced copper projects, such as those in Chile and Peru, where exploration rights and permits are highly contested.
- Off-take Agreement Bidding: Securing long-term supply contracts with electric vehicle manufacturers and renewable energy developers is becoming a competitive battleground, with premium pricing emerging for guaranteed supply.
Operational Excellence and Cost Leadership
Anglo American's drive for operational excellence and cost leadership is a key battleground in the mining industry. By simplifying its portfolio and aggressively optimizing costs, the company aims to unlock substantial cost savings and boost its EBITDA margins. In 2023, Anglo American reported a significant reduction in its cost base, contributing to a stronger financial performance despite market headwinds.
Companies that master efficient extraction and lower production costs inherently gain a substantial edge. This allows them to remain profitable even when commodity prices fluctuate. For instance, Anglo American's focus on improving productivity at mines like Quellaveco has been a cornerstone of its strategy to outpace competitors on cost efficiency.
- Portfolio Simplification: Anglo American has been actively divesting non-core assets to concentrate on higher-performing operations.
- Cost Optimization Initiatives: The company targets significant cost benefits across its value chain, from exploration to processing.
- EBITDA Margin Improvement: These efforts are directly linked to enhancing profitability, with recent reports showing positive trends in EBITDA margins for key commodities.
- Efficiency Gains: Operational improvements are crucial for maintaining competitiveness, especially in a capital-intensive sector like mining.
The competitive rivalry within the mining sector, impacting Anglo American, is intense due to the presence of global behemoths like BHP, Rio Tinto, and Glencore. These diversified players, with substantial financial backing, actively compete for market share and prime mining concessions.
This rivalry is amplified by the high fixed costs inherent in mining, compelling companies to maintain production even during price downturns. For example, in 2023, Anglo American's capital expenditure was around $3.8 billion, highlighting the ongoing investment needed to sustain operations and stay competitive.
The race for critical minerals, such as copper, essential for the green energy transition, further intensifies this competition. Major players are pouring billions into copper and nickel projects, creating a direct contest for exploration rights and advanced development opportunities.
| Competitor | Key Commodities | 2023 Revenue (approx.) | 2023 EBITDA Margin (approx.) |
| BHP | Iron Ore, Copper, Coal, Nickel | $60 billion | 45% |
| Rio Tinto | Iron Ore, Aluminium, Copper, Diamonds | $47 billion | 38% |
| Glencore | Coal, Copper, Oil, Zinc | $215 billion | 8% |
| Anglo American | Platinum Group Metals, Diamonds, Coal, Copper, Iron Ore | $28 billion | 25% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for Anglo American, especially through its De Beers brand, is the burgeoning lab-grown diamond market. These synthetic gems are increasingly indistinguishable from mined diamonds in all key aspects but offer a more attractive price point. For instance, by mid-2024, retail prices for comparable lab-grown diamonds were often 50-70% lower than their natural counterparts, a gap that continues to pressure the traditional diamond sector.
The automotive industry's shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) poses a significant substitution threat to platinum group metals (PGMs), primarily impacting their use in catalytic converters. As battery electric vehicles gain market share, the demand for PGMs in this crucial application is expected to decline over the long term.
While hybrid vehicles still utilize PGMs, the accelerating adoption of pure EVs directly reduces the need for these metals. For Anglo American, whose PGM portfolio is substantial, this transition represents a clear strategic challenge and a potential long-term erosion of demand in a historically core market.
The rise of green steel technologies, like electric arc furnaces (EAFs) using scrap and hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI), presents a significant substitution threat to traditional iron ore demand. These methods lessen the need for high-carbon iron ore, potentially steering consumption towards higher-grade, purer ores or entirely different materials.
This shift directly impacts Anglo American's substantial iron ore business, as the market moves away from the conventional blast furnace route. In 2024, the global steel industry continued its focus on decarbonization, with green steel production methods gaining traction, although the full transition remains a long-term endeavor.
Recycling and Circular Economy
The growing focus on recycling and circular economy principles presents a significant threat of substitutes for Anglo American. As advanced recycling technologies for metals like copper and platinum group metals (PGMs) mature, they offer an alternative to newly mined resources.
Improved recycling infrastructure makes secondary metals a more viable and efficient substitute for primary mining output. This shift emphasizes resource efficiency over traditional extraction methods.
- Metal Recycling Growth: The global metal recycling market is projected to reach USD 100 billion by 2028, indicating substantial growth in secondary supply.
- Copper Recycling Efficiency: Modern recycling processes can recover over 95% of copper from electronic waste, directly competing with primary copper production.
- PGM Recovery Advancements: Innovations in PGM recycling from catalytic converters and spent industrial catalysts are enhancing the availability of these precious metals from secondary sources.
Technological Advancements Reducing Material Intensity
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes, particularly as they reduce the material intensity of products. Innovations in areas like additive manufacturing (3D printing) allow for lighter, more efficient designs that require less raw material. For example, by 2024, the global 3D printing market was projected to reach over $50 billion, showcasing a growing trend towards material optimization.
These advancements can directly impact demand for traditional commodities. Consider the automotive sector; lighter composite materials and more efficient battery technologies for electric vehicles could reduce the reliance on metals like steel and aluminum per vehicle. This shift is already visible, with the average weight of electric vehicles often being managed through advanced material science.
The long-term implication is a gradual erosion of demand for certain mined resources as substitute materials and processes become more prevalent and cost-effective. This trend poses a strategic challenge for companies like Anglo American, requiring continuous adaptation and investment in research and development to stay ahead of evolving material needs.
- Material Substitution: Development of advanced composites, polymers, and ceramics can replace traditional metals in various applications.
- Design Optimization: Technologies like AI-driven design and simulation enable the creation of products requiring less material input.
- Digitalization: Increased reliance on digital services and virtual experiences can reduce the need for physical goods and their associated material consumption.
- Circular Economy: Enhanced recycling and reuse technologies can decrease the demand for virgin materials.
The threat of substitutes for Anglo American is multifaceted, impacting its core commodities. The lab-grown diamond market, a direct substitute for natural diamonds, continues to gain traction, with prices significantly lower than mined equivalents by mid-2024. This trend, coupled with the automotive industry's shift to electric vehicles, reduces demand for platinum group metals used in catalytic converters.
Furthermore, the rise of green steel manufacturing, utilizing scrap and hydrogen, lessens the reliance on traditional iron ore. Recycling advancements also present a substitute, offering secondary metals as an alternative to newly mined resources. Technological innovations, such as 3D printing, are enabling material optimization, potentially decreasing the overall material intensity of manufactured goods.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Anglo American | Key Trend/Data Point (as of 2024/near future) |
|---|---|---|
| Lab-Grown Diamonds | Direct competition with De Beers | Lab-grown diamond prices often 50-70% lower than natural diamonds (mid-2024). |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Reduced demand for Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) in catalytic converters | Accelerating EV adoption directly impacts PGM usage. |
| Green Steel Technologies | Lower demand for traditional iron ore | Focus on decarbonization in steelmaking favors alternative methods. |
| Metal Recycling & Circular Economy | Alternative to primary mining output | Global metal recycling market projected to reach USD 100 billion by 2028. |
| Advanced Manufacturing (e.g., 3D Printing) | Reduced material intensity in products | Global 3D printing market projected to exceed $50 billion (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer scale of capital needed for mining operations presents a massive hurdle for new companies wanting to enter the sector. Think about the upfront costs for exploration, building mines, and all the necessary infrastructure – it’s astronomical. For instance, developing a new large-scale mine can easily run into billions of dollars, a sum that deters many potential competitors.
This high capital requirement means that only well-established companies or those with substantial backing from investors can even consider entering the market. The cost of acquiring advanced mining technology and equipment, essential for efficient and safe operations, further inflates these entry barriers. For example, a single large dragline excavator can cost tens of millions of dollars.
The mining industry is heavily regulated, with new projects facing arduous environmental impact assessments and the need to secure social licenses to operate. These intricate legal and community engagement requirements demand considerable expertise, time, and capital, acting as a significant barrier for potential new players. For instance, obtaining the necessary permits for a major new mine can easily add several years to the development schedule, increasing upfront costs and risk.
The availability of economically viable and high-quality mineral deposits is a significant barrier for new entrants in the mining sector. These prime resources are often already secured by established major players, limiting opportunities for newcomers. For instance, in 2023, the global exploration budget for metals and mining reached approximately $11.4 billion, highlighting the substantial upfront investment required with no certainty of discovering commercially viable reserves.
Need for Specialized Expertise and Technology
The mining industry, particularly for companies like Anglo American, requires substantial investment in specialized expertise and advanced technology, acting as a significant barrier to entry. Modern mining operations rely heavily on sophisticated geological surveying, complex engineering solutions, and efficient operational management. For instance, the development of autonomous mining fleets, a key area of technological advancement, involves considerable R&D expenditure and specialized engineering talent.
Access to and proficiency with cutting-edge technologies such as AI-driven predictive maintenance, advanced data analytics for resource discovery, and remote operational control systems are crucial for competitive mining. Companies looking to enter this space would need to either build these capabilities from scratch or acquire them, which is a costly and time-consuming process. This technological and knowledge threshold effectively deters less-equipped new entrants.
- Specialized Expertise: Requires deep knowledge in geology, mining engineering, and environmental management.
- Technological Investment: High costs associated with automation, AI, and data analytics for efficient operations.
- Capital Intensity: Significant upfront capital is needed for exploration, equipment, and infrastructure.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex environmental and safety regulations demands specialized legal and compliance teams.
Established Supply Chains and Customer Relationships
Established mining giants like Anglo American benefit from deeply entrenched global supply chains and logistics. These networks are not easily replicated by newcomers. For instance, in 2024, Anglo American's extensive infrastructure, including ports and rail, facilitated the efficient movement of millions of tonnes of commodities, a significant barrier to entry.
Furthermore, long-standing relationships with major industrial customers are critical. New entrants face the daunting task of building trust and securing contracts with these key buyers, who often prioritize reliability and proven performance. In 2024, Anglo American continued to leverage these relationships, securing significant off-take agreements for its diverse product portfolio.
- Established Global Supply Chains: New entrants struggle to match the scale and efficiency of existing networks.
- Customer Loyalty and Trust: Building relationships with major buyers takes considerable time and investment.
- Logistical Infrastructure: Significant capital is required to develop comparable transportation and storage capabilities.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents can leverage their size to achieve lower production and distribution costs.
The threat of new entrants for Anglo American is generally low due to the immense capital requirements, with new mine development costing billions of dollars. Established players also benefit from secured prime mineral deposits and extensive, hard-to-replicate logistical infrastructure. For example, in 2024, Anglo American's integrated operations relied on significant investments in ports and rail, a major deterrent for newcomers.
Navigating stringent regulatory environments, including complex environmental assessments and social license requirements, adds considerable time and cost, further limiting new entrants. The need for specialized expertise in geology, engineering, and environmental management, coupled with substantial investment in advanced technologies like AI and automation, also creates high barriers.
Securing long-standing customer relationships and building trust in a market that values proven performance is another significant hurdle. Newcomers struggle to match the economies of scale and established supply chains that provide cost advantages to incumbents like Anglo American.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Example for Anglo American (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Massive upfront investment for exploration, mine construction, and infrastructure. | Development of a new large-scale mine can exceed billions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex environmental, safety, and social license requirements. | Permitting for a major new mine can add years and significant costs. |
| Access to Resources | Prime mineral deposits are often already controlled by major players. | Global exploration budgets reached $11.4 billion in 2023, indicating high competition for viable sites. |
| Technological Sophistication | Need for advanced technology like AI, automation, and data analytics. | Investment in autonomous mining fleets requires significant R&D and specialized talent. |
| Supply Chain & Logistics | Established global networks and infrastructure are difficult to replicate. | Anglo American's extensive port and rail infrastructure facilitated millions of tonnes of commodity movement. |
| Customer Relationships | Building trust and securing contracts with major buyers takes time. | Anglo American leveraged existing relationships for significant off-take agreements. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Anglo American Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available data. This includes extensive review of Anglo American's annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific research from mining consultancies and market intelligence firms.
