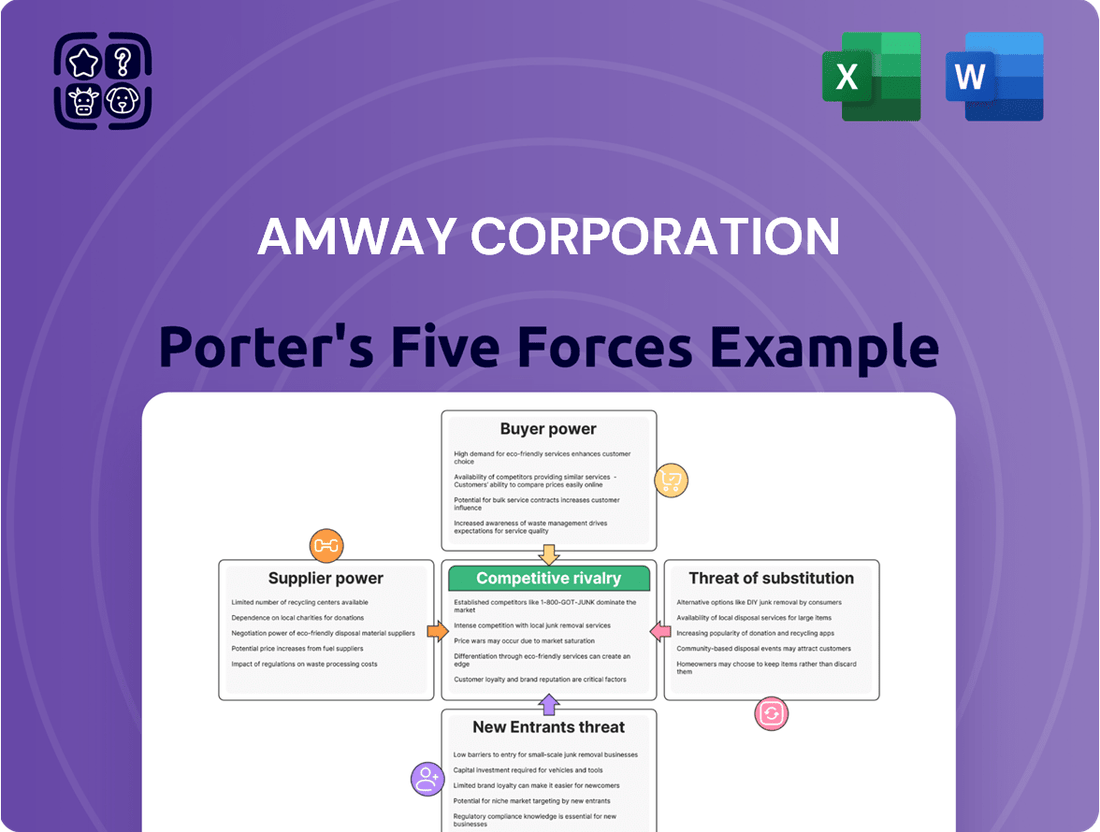
Amway Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Amway Corporation Bundle
Amway Corporation navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder. The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Amway Corporation’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Amway's significant vertical integration, particularly with its Nutrilite brand in nutrition, means it manufactures many of its own products. This internal production capability directly reduces its dependence on external suppliers, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
For the components and raw materials Amway does source externally, the concentration of those suppliers plays a crucial role. If a particular input has a limited number of providers, those suppliers gain leverage. Conversely, a broad supplier base for essential inputs empowers Amway.
For Amway's proprietary product lines, like Nutrilite's specialized ingredients sourced from its own farms, the switching costs for Amway would be substantial. This gives Amway's internal farming and R&D operations significant bargaining power as suppliers. For instance, developing and securing the unique botanical extracts used in Nutrilite products involves considerable investment in agricultural practices and scientific research, making it difficult and costly to find comparable alternatives.
Conversely, for more generic components or raw materials that Amway might procure externally, the switching costs would likely be low. This would empower Amway, as it could readily shift to different suppliers if terms became unfavorable. Amway's substantial investments in its own manufacturing facilities and ongoing research and development efforts further solidify its control over its internal supply capabilities, reducing reliance on external suppliers for critical elements.
Amway's focus on science-backed, innovative products, especially in nutrition and beauty, means some inputs could be highly specialized or patented. This uniqueness can give those suppliers more leverage. For instance, if a key ingredient in a popular Nutrilite supplement is sourced from a single, highly regulated farm with unique growing conditions, that supplier holds considerable power.
However, Amway actively works to control its supply chain. The company's significant investment in its own research and development, alongside proprietary farms for its Nutrilite brand, creates internal, unique inputs. This vertical integration reduces reliance on external suppliers for critical components, thereby lessening the bargaining power of those outside suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Amway's suppliers is minimal. Given Amway's direct selling model and its robust, globally recognized brand, it's highly improbable that its raw material providers would venture into direct sales themselves. These suppliers typically focus on manufacturing and distribution of components, not on building and managing vast independent business owner (IBO) networks.
Amway's established brand equity and its extensive network of over 4.5 million IBOs worldwide present a formidable barrier to entry. For a supplier to successfully integrate forward, they would need to replicate this complex sales infrastructure, which is a significant undertaking and unlikely to be a viable strategy for companies primarily focused on raw material production.
In 2024, Amway reported global sales of approximately $8.4 billion, underscoring the scale and efficiency of its direct selling model. This substantial market presence makes it exceedingly difficult for any supplier to disrupt Amway's operations through forward integration.
- Supplier Focus: Raw material suppliers concentrate on manufacturing, not direct consumer engagement.
- Brand Barrier: Amway's strong brand and 4.5 million+ IBOs create a significant hurdle for integration.
- Model Disparity: The core business models of suppliers and Amway are fundamentally different.
- Market Scale: Amway's 2024 global sales of $8.4 billion demonstrate the difficulty of challenging its distribution network.
Importance of Amway to Supplier's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers for Amway is influenced by how crucial Amway is to their business. If Amway accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier's leverage diminishes. For instance, if Amway is a significant customer, a supplier might be hesitant to demand higher prices or less favorable terms, fearing the loss of that substantial revenue stream.
Conversely, if Amway represents only a small fraction of a supplier's clientele, the supplier possesses greater bargaining power. In such scenarios, the supplier can more readily dictate terms, knowing that Amway's business is not essential to their overall financial health. This dynamic can lead to suppliers demanding better pricing or specific contractual advantages.
Amway's extensive global reach and its significant investments in manufacturing facilities indicate that it is likely a major client for many of its raw material and component suppliers. For example, Amway's 2023 annual report highlighted continued investment in its supply chain infrastructure, suggesting a substantial volume of purchases from its vendor base. This scale of operation often translates into suppliers relying heavily on Amway's consistent demand, thereby reducing the suppliers' individual bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: If a supplier's revenue is heavily reliant on Amway, their bargaining power is weakened.
- Amway's Scale: Amway's global operations, involving numerous product lines and markets, make it a large-volume purchaser.
- Investment in Manufacturing: Amway's capital expenditures in production facilities imply significant and ongoing demand for inputs.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: Consequently, many suppliers may have limited ability to negotiate unfavorable terms with Amway due to their dependence on Amway's orders.
Amway's considerable vertical integration, especially with its Nutrilite brand, means it produces many items internally, reducing reliance on outside suppliers and thus their bargaining power. For externally sourced components, the concentration of suppliers is key; fewer suppliers mean more leverage for them, while a diverse supplier base favors Amway. Amway's substantial investments in its own manufacturing and R&D further strengthen its control over critical inputs, diminishing external supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of Amway's suppliers is generally considered moderate to low. This is primarily due to Amway's significant scale as a purchaser and its strategic vertical integration, particularly within its Nutrilite nutrition line. For instance, Amway's 2024 global sales of approximately $8.4 billion indicate it represents a substantial portion of revenue for many of its suppliers, making those suppliers hesitant to impose unfavorable terms for fear of losing Amway's business.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Amway's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Integration (Nutrilite) | Reduces reliance on external suppliers | Strong internal sourcing capabilities |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power | Generally diversified supplier base for common inputs |
| Switching Costs (Proprietary Inputs) | High switching costs empower specialized suppliers | Mitigated by R&D and internal production |
| Switching Costs (Generic Inputs) | Low switching costs empower Amway | Amway can easily change suppliers |
| Supplier Dependence on Amway | High dependence weakens supplier power | Amway is a major client for many suppliers |
| Amway's Market Scale (2024 Sales: $8.4B) | Large scale reduces supplier leverage | Significant volume purchaser |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Amway Corporation, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its direct selling industry.
Effortlessly identify Amway's competitive landscape with a visual breakdown of each force—ideal for pinpointing strategic vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Amway's customer base is incredibly broad, encompassing millions of independent business owners (IBOs) and the end consumers they serve. This vast network means that no single IBO or consumer accounts for a substantial chunk of Amway's overall sales, resulting in very low individual buyer concentration.
While individual buyers hold little sway, the collective power of the IBO network is a factor to consider. IBOs can shift their focus to competing direct selling opportunities or seek alternative product suppliers, which could influence Amway's market position.
Switching costs for Amway's Independent Business Owners (IBOs) are generally low. IBOs can readily move to competing direct selling companies or even traditional retail channels, particularly for products that are not highly specialized. This ease of transition means Amway must continuously work to retain its IBO base.
For end consumers, the situation is similar. The market offers a wide array of comparable products from numerous retailers, making it simple for customers to switch their purchasing habits without incurring significant costs or effort. This low switching cost environment necessitates Amway's focus on building strong customer relationships.
Amway actively tries to mitigate these low switching costs by fostering a sense of community and offering unique product solutions. These strategies aim to build loyalty among both IBOs and consumers, making them less inclined to seek alternatives. For instance, Amway's extensive training and support systems for IBOs can represent an investment that might deter immediate switching.
The extensive availability of health, beauty, and home care products from various channels, including traditional retail, online marketplaces, and competing direct selling firms, presents Amway customers with a plethora of alternatives. This broad selection of substitute goods directly amplifies customer bargaining power, as they can readily switch to a competitor if Amway's offerings or pricing are not perceived as favorable. For instance, the global e-commerce market for beauty and personal care alone was projected to reach over $716 billion in 2023, highlighting the intense competition and readily available alternatives for consumers.
Buyer Information
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for Amway. With the internet, both Independent Business Owners (IBOs) and end consumers can easily access detailed information about product ingredients, pricing strategies, and a wide array of competing brands. This increased transparency directly challenges Amway's ability to dictate prices, as buyers are now better equipped to compare offerings and seek more favorable terms or alternatives.
This shift in information access means customers are more empowered than ever.
- Informed Comparisons: Buyers can readily compare Amway's product quality, ingredient sourcing, and pricing against numerous competitors, including direct-to-consumer brands and those available through traditional retail channels.
- Price Sensitivity: The ease of price comparison puts pressure on Amway's margins, as customers can identify and opt for lower-priced alternatives if perceived value is similar or superior.
- Brand Loyalty Erosion: Increased product knowledge and access to alternatives can weaken brand loyalty, making it harder for Amway to retain customers solely on reputation or established relationships.
Price Sensitivity
Amway's customers, particularly those purchasing through direct selling, can exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is amplified when Amway products are perceived as premium-priced compared to alternatives available through traditional retail channels. For instance, in 2024, economic pressures in several key markets may have led consumers to scrutinize discretionary spending more closely, increasing their focus on price points for health and beauty products, a core Amway category.
This price sensitivity directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. They can more readily switch to competitors offering similar quality at lower prices, or simply reduce their consumption of Amway products. This forces Amway to continuously justify its pricing, often by emphasizing product quality, unique formulations, or the value of the direct selling experience itself.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: Customers are more likely to compare Amway's prices with those of competitors in the direct selling and retail markets.
- Value Proposition: Amway must effectively communicate the superior value of its products to counter price-based decision-making.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of lower-priced alternatives in the broader consumer goods market exerts pressure on Amway's pricing strategies.
The bargaining power of Amway's customers is moderate to high, primarily due to the wide availability of substitute products and low switching costs for both end consumers and Independent Business Owners (IBOs). The digital age has further amplified this power by providing easy access to price and product comparisons, forcing Amway to remain competitive on value and quality.
Customers can easily switch to numerous competitors offering similar health, beauty, and home care products, especially with the global e-commerce market for beauty and personal care projected to exceed $716 billion in 2023. This ease of comparison and availability of alternatives means Amway must continuously justify its pricing and product benefits to retain its customer base.
Economic conditions in 2024 may also increase customer price sensitivity, pushing them to scrutinize discretionary spending and seek out more budget-friendly options. This necessitates Amway's focus on communicating its unique value proposition beyond mere price points.
| Factor | Impact on Amway | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer power | Global e-commerce beauty market > $716 billion (2023) |
| Switching Costs (IBOs/Consumers) | Low, increases customer power | Easy to shift to competing direct selling or retail channels |
| Information Access | Empowers customers | Easy online comparison of ingredients, pricing, and brands |
| Price Sensitivity | High, increases customer power | Economic pressures in 2024 may drive focus on price for core categories |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Amway Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Amway Corporation, offering a deep dive into the competitive landscape that shapes its business strategy. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the direct selling industry, all crucial for understanding Amway's market position and future prospects.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Amway faces intense competition in the global direct selling arena, contending with established giants such as Natura & Co., Herbalife, and Nu Skin. These companies, along with a multitude of smaller, emerging direct selling firms, vie for market share and distributor networks. For instance, Natura & Co. reported consolidated net revenue of approximately $10.2 billion in 2023, showcasing the scale of Amway's rivals.
Beyond direct selling, Amway also competes with traditional retail channels and burgeoning e-commerce platforms. Consumers have a vast array of purchasing options, from brick-and-mortar stores to online marketplaces, all offering similar product categories. This broad competitive landscape means Amway must constantly innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain its position.
While Amway experienced a 3% global sales decline in 2024 due to currency fluctuations, with its nutrition segment showing 2% growth, the overall direct selling industry is anticipated to expand. This market growth can soften competitive intensity by increasing the available customer base.
However, competition remains fierce, particularly for market share within specific product lines and geographic areas. Amway's performance, therefore, is still heavily influenced by the actions and success of its rivals in capturing consumer attention and loyalty.
Amway carves out its market position by emphasizing science-backed innovation, especially evident in its prominent Nutrilite and Artistry product lines. This commitment to research and development allows them to offer unique health and wellness solutions, such as those targeting gut health, which appeal to a health-conscious consumer base.
While Amway’s dedication to quality and scientific backing is a key differentiator, the competitive landscape is crowded. Many rivals offer comparable product categories, meaning Amway must consistently invest in new product development and marketing to sustain its distinctiveness and prevent its offerings from becoming commoditized.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for Amway's Independent Business Owners (IBOs) and their end consumers are generally low. This means that either party can easily move to a competitor without significant financial or operational hurdles. This low barrier to switching directly fuels intense competition within the direct selling industry.
The low switching costs compel Amway and its rivals to continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain existing customers and attract new ones. Companies must constantly work to build brand loyalty and differentiate their products and compensation plans.
- Low switching costs for IBOs mean they can easily join other direct selling companies.
- Consumers can readily switch to alternative brands or retailers if Amway products are not perceived as superior or competitively priced.
- This ease of transition intensifies competitive rivalry, forcing companies to focus heavily on customer satisfaction and product innovation.
- In 2024, the direct selling industry continues to see new entrants, further fragmenting the market and highlighting the importance of managing customer retention amidst low switching costs.
Exit Barriers
The direct selling industry, including Amway, faces substantial exit barriers. These include highly specialized supply chains, massive investments in building and maintaining extensive distributor networks, and the significant value placed on brand recognition. These factors can trap even unprofitable companies in the market, thereby increasing competitive intensity.
Amway's global infrastructure, a result of decades of operation, and its deeply entrenched Independent Business Owner (IBO) network represent considerable sunk costs. These substantial investments make it economically challenging for Amway, or its competitors, to simply cease operations or divest significant portions of their business without incurring substantial losses.
Consider these aspects:
- High Capital Investment: Building out global logistics and supporting millions of distributors requires immense capital, creating a high hurdle for new entrants and a significant cost for exiting players.
- Specialized Assets: The infrastructure is often tailored for direct selling, meaning assets like warehouses or IT systems for distributor management may have limited alternative uses, increasing exit costs.
- Brand Equity and IBO Loyalty: Amway's brand recognition and the loyalty of its IBOs are valuable intangible assets. Divesting or closing operations would mean forfeiting this established value, making a clean exit difficult.
Amway operates in a highly competitive direct selling environment, facing rivals like Natura & Co. and Herbalife, with Natura & Co. reporting around $10.2 billion in net revenue for 2023. This intense rivalry is further amplified by low switching costs for both distributors and consumers, making customer retention a constant challenge. The industry's overall growth, projected to continue, may slightly temper this intensity by expanding the customer pool.
Despite Amway's focus on innovation, such as its Nutrilite line, many competitors offer similar product categories, necessitating continuous investment in new products and marketing to maintain differentiation. The ease with which distributors and customers can switch to competitors means companies must prioritize value and loyalty programs. The direct selling market saw continued fragmentation with new entrants in 2024, underscoring the importance of managing customer retention amid these low switching costs.
The competitive rivalry is shaped by significant exit barriers, including specialized supply chains and extensive distributor networks, which can keep even struggling companies in the market, thus maintaining high competitive pressure. Amway’s substantial investments in its global infrastructure and IBO network create considerable sunk costs, making a complete exit economically unviable and contributing to sustained market competition.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Product Areas | Competitive Strategy Highlight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natura & Co. | $10.2 billion | Beauty, Personal Care, Home Care | Strong brand portfolio, sustainability focus |
| Herbalife | $3.1 billion | Nutrition, Weight Management | Distributor empowerment, global reach |
| Nu Skin Enterprises | $2.2 billion | Personal Care, Nutrition | Technology integration, anti-aging focus |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers have a wealth of readily available alternatives for Amway's core product categories. Traditional retailers like Walmart and CVS, alongside e-commerce giants such as Amazon, offer a vast selection of health, beauty, and home care items. For instance, in 2024, the global beauty market alone was valued at over $500 billion, with a significant portion of this driven by mass-market products readily accessible through these channels.
Many of these substitutes present a compelling price-performance trade-off. Consumers can often find comparable quality products at considerably lower price points than Amway's offerings. This accessibility and affordability of alternatives directly challenge Amway's premium pricing strategy, forcing consumers to weigh the value proposition more critically.
The general public's growing acceptance of diverse income streams, such as other direct selling ventures, affiliate marketing, and various side hustles, increases the likelihood that Independent Business Owners (IBOs) may switch to alternative opportunities. This trend is amplified by the fact that in 2024, the gig economy continued its expansion, with platforms facilitating flexible work arrangements becoming more prevalent, making it easier for individuals to explore multiple income avenues simultaneously.
For consumers, the decision to substitute Amway products is often driven by practical considerations like convenience and price. In 2024, consumers demonstrated a heightened sensitivity to value, with many actively seeking out comparable products from retailers offering greater convenience or lower price points, especially as inflation impacted household budgets.
The threat of substitutes for Amway's diverse product lines, spanning nutrition, beauty, personal care, and home care, is substantial. Consumers can easily find comparable products from a wide array of sources, including private label brands offered by major retailers, other direct selling companies, and traditional brick-and-mortar or online consumer goods brands. This broad availability means Amway faces constant pressure to differentiate its offerings and maintain competitive pricing.
Perceived Switching Costs for Customers
The perceived effort and cost for customers to switch from Amway products to substitutes are generally low. Consumers can easily purchase similar items from alternative sources without significant disruption or financial penalty.
For instance, in the health and wellness sector, where Amway has a strong presence with brands like Nutrilite, the availability of comparable vitamins and supplements from retailers like GNC or online giants such as Amazon means consumers face minimal barriers to switching. In 2023, the global dietary supplements market was valued at approximately $175.8 billion, indicating a highly competitive landscape with numerous readily available alternatives.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily find comparable products from numerous competitors.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers often prioritize price, making it easier to switch if alternatives are cheaper.
- Brand Loyalty vs. Convenience: While some customers may have loyalty, the convenience of readily available alternatives often outweighs this.
- Product Availability: Amway products are often available through direct selling, but similar products are widely accessible through traditional retail and e-commerce channels.
Marketing and Innovation by Substitute Providers
The threat of substitutes is heightened by the relentless marketing and innovation efforts of competing providers. Traditional retailers and burgeoning e-commerce platforms, alongside other direct selling organizations, are consistently pouring resources into advertising, developing novel products, and implementing aggressive pricing tactics. This dynamic landscape means Amway faces continuous pressure to maintain its market standing.
For instance, in 2024, the global direct selling market was valued at approximately $190 billion, showcasing the significant presence of numerous players vying for consumer attention. Companies within this space are increasingly leveraging digital marketing, influencer collaborations, and subscription models to attract and retain customers, directly impacting Amway's customer acquisition and loyalty strategies.
- Marketing Spend: Competitors are allocating substantial budgets to digital advertising and social media campaigns, reaching a broad consumer base.
- Product Development: Continuous introduction of new or improved products by rivals forces Amway to accelerate its own innovation cycles.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitive pricing, including discounts and bundled offers, can sway price-sensitive consumers away from Amway's offerings.
- Distribution Channels: The proliferation of online marketplaces and omnichannel retail strategies provides consumers with more convenient access to alternative products.
The threat of substitutes for Amway products is significant due to the wide availability of comparable items across various retail channels. Consumers can easily access alternatives from mass-market retailers, specialty stores, and online platforms. For example, in 2024, the global health and wellness market, a key sector for Amway, was projected to exceed $1.8 trillion, with a substantial portion of this market share held by easily accessible consumer brands.
Many substitutes offer a favorable price-performance ratio, making them attractive to budget-conscious consumers. The ease with which consumers can switch to these alternatives, often with minimal cost or effort, further amplifies this threat. This competitive pressure necessitates that Amway consistently demonstrates the unique value proposition of its products.
| Category | Amway's Position | Key Substitutes | Market Size (Approx. 2024) | Switching Cost |
| Nutrition | Nutrilite vitamins and supplements | GNC, Nature's Bounty, Amazon private label | Global dietary supplements market: ~$190 billion | Low |
| Beauty | Artistry skincare and cosmetics | L'Oréal, Estée Lauder, Sephora private label, mass-market brands (e.g., Maybelline) | Global beauty market: ~$500+ billion | Low |
| Home Care | Amway Home cleaning products | Procter & Gamble (Tide, Dawn), SC Johnson (Windex, Pledge), retailer brands | Global household cleaning market: ~$250+ billion | Low |
Entrants Threaten
Starting a direct selling business can seem accessible, but building a global multi-level marketing giant like Amway demands substantial capital. This includes significant investment in product research and development, manufacturing facilities, a complex distribution network, and robust support systems for its Independent Business Owners (IBOs).
Amway's commitment to infrastructure is evident, with over $120 million invested in facility expansions and upgrades. This level of investment acts as a considerable barrier to entry for potential new competitors aiming to establish a similar scale of global operation.
Amway leverages substantial economies of scale across its operations, from manufacturing and R&D to its extensive global distribution network. This scale allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, significantly reducing per-unit production expenses. For instance, in 2023, Amway reported net sales of $8.4 billion, reflecting the sheer volume of products and services they manage.
New companies entering the direct selling market face a formidable barrier here. They would need to invest heavily to match Amway's production volume and reach, a challenge that is difficult to overcome without substantial initial capital. This cost disadvantage makes it hard for newcomers to compete on price or match Amway's investment in product development and marketing, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
Amway's decades-long presence has cultivated deep brand loyalty among its Independent Business Owners (IBOs) and a significant consumer base. This established recognition, built over time as a direct selling pioneer, makes it incredibly difficult for new entrants to gain comparable trust and visibility in the market.
Access to Distribution Channels
Amway's direct selling model is heavily reliant on its expansive network of Independent Business Owners (IBOs) for product distribution. This established infrastructure presents a significant barrier for potential new entrants.
Establishing a comparable distribution network requires immense investment in recruitment, training, and logistical support, a hurdle that new competitors often find difficult to overcome. For instance, Amway reported over 3 million IBOs globally as of 2024, a scale that is exceptionally challenging to replicate.
- Vast IBO Network: Amway's strength lies in its millions of IBOs worldwide, providing unparalleled reach.
- Recruitment and Training Costs: New entrants face substantial expenses to build and maintain a similar sales force.
- Brand Loyalty and Trust: Amway's long-standing presence fosters customer and distributor loyalty, making it hard for newcomers to gain traction.
- Logistical Infrastructure: The company's developed supply chain and support systems for IBOs are difficult and costly for new players to match.
Regulatory Environment and Legal Challenges
The multi-level marketing (MLM) industry, under which Amway operates, is subject to intense regulatory oversight. Historically, many MLM companies have faced legal challenges and investigations concerning their compensation structures and product claims, creating a high barrier for new entrants. For instance, in 2023, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) continued its focus on deceptive practices within the direct selling industry, issuing warnings and pursuing enforcement actions against companies that do not comply with consumer protection laws.
Navigating this complex and often evolving regulatory landscape presents a significant hurdle for potential new competitors. New entrants must invest heavily in legal counsel and compliance infrastructure to ensure adherence to rules that vary by jurisdiction. Failure to do so can result in substantial fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage, effectively deterring many from entering the market.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: The direct selling and MLM sectors are under continuous examination by consumer protection agencies globally.
- Legal Precedents: Past legal actions against MLM companies set precedents that new entrants must carefully consider to avoid similar pitfalls.
- Compliance Costs: Establishing robust compliance frameworks to meet diverse regulatory requirements represents a significant upfront investment for new businesses.
- Evolving Legislation: Keeping pace with changes in consumer protection and business opportunity laws requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
The threat of new entrants for Amway is generally considered low due to several significant barriers. These include the immense capital required for global operations, the need for extensive product development and manufacturing capabilities, and the established brand loyalty cultivated over decades. Amway's sheer scale, evidenced by its $8.4 billion in net sales in 2023, creates substantial economies of scale that new competitors struggle to match.
Amway's vast network of over 3 million Independent Business Owners (IBOs) globally as of 2024 is a critical deterrent. Replicating this extensive distribution and support system demands enormous investment in recruitment, training, and logistics, making it exceedingly difficult for new players to gain comparable market reach and operational efficiency.
The direct selling industry faces considerable regulatory scrutiny. New entrants must navigate complex legal frameworks and compliance requirements, which involve significant investment in legal counsel and robust internal controls. The Federal Trade Commission's continued focus on deceptive practices in 2023 highlights the risks and costs associated with non-compliance, further discouraging new market entrants.
| Barrier to Entry | Amway's Position | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Substantial investment in R&D, manufacturing, and global distribution. | High cost to establish comparable infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale | $8.4 billion net sales (2023) creates cost advantages. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs. |
| IBO Network Size | Over 3 million IBOs globally (2024). | Difficult and costly to build a competing sales force. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Decades of presence and established reputation. | Challenging for newcomers to gain consumer and distributor trust. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex global regulations. | Significant investment in legal and compliance infrastructure required. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Amway Corporation is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including Amway's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Euromonitor and Statista, and publicly available financial filings. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and reports from business intelligence platforms to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
