AIXTRON Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AIXTRON Bundle
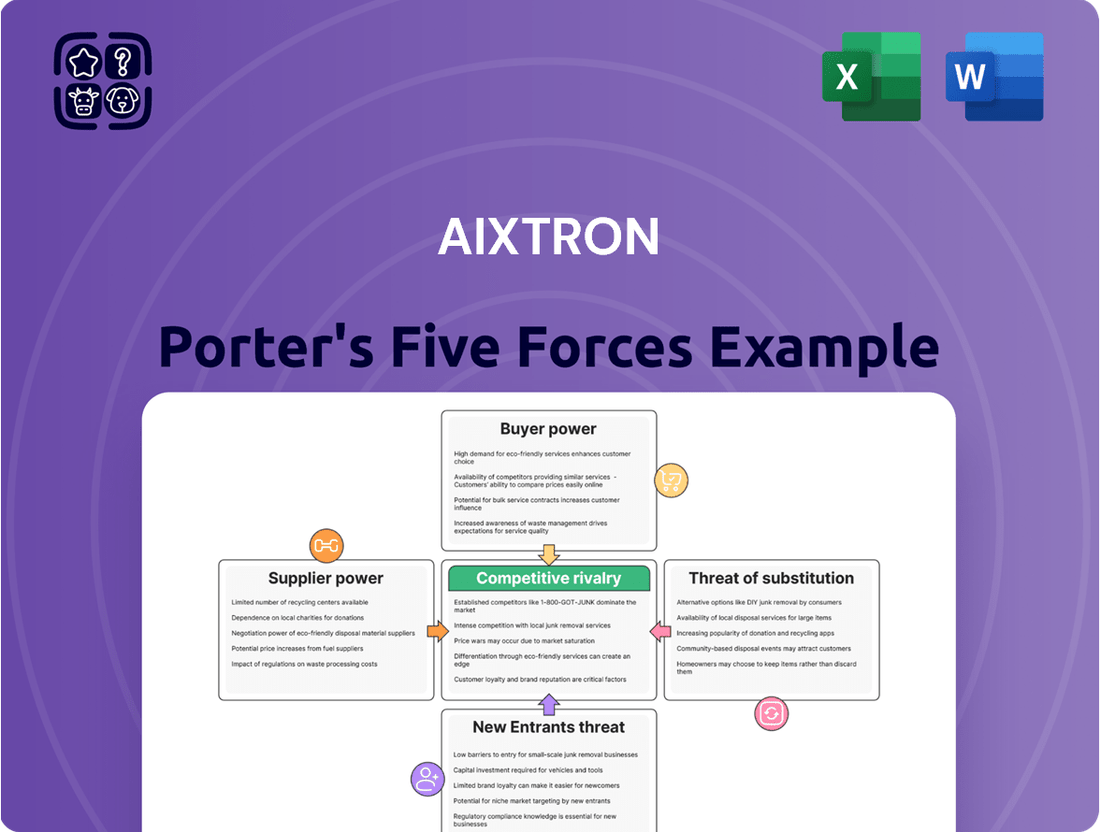
AIXTRON operates within a dynamic semiconductor equipment market, where understanding the intensity of competitive rivalry and the threat of new entrants is crucial. The bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers, alongside the ever-present threat of substitutes, significantly shapes AIXTRON's strategic landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AIXTRON’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
AIXTRON's reliance on highly specialized components for its deposition equipment grants significant leverage to its suppliers. The unique nature of these inputs, like advanced precursor chemicals or precision-engineered mechanical parts, means AIXTRON has limited options for finding alternative sources. This dependency can translate into higher costs and potential supply chain vulnerabilities if a critical supplier experiences operational difficulties.
Suppliers holding patents or proprietary technology for essential components can significantly influence AIXTRON. These unique offerings, critical for AIXTRON's advanced equipment, leave the company with few viable alternatives, enabling suppliers to command higher prices or dictate contract terms, especially for specialized materials or integrated sub-systems.
The bargaining power of suppliers for AIXTRON is significantly influenced by the substantial switching costs involved. These costs encompass not only the financial outlay for re-qualifying new suppliers and adapting existing designs but also the potential for disruptive production delays. For instance, integrating new components into complex semiconductor manufacturing equipment can take months, impacting AIXTRON's ability to respond to market shifts.
These high switching costs effectively reduce AIXTRON's flexibility and bolster the leverage of its current suppliers. The intricate nature of semiconductor equipment manufacturing means that a change in a critical component supplier requires extensive testing and validation, making it a time-consuming and expensive undertaking for AIXTRON.
Supplier Industry Consolidation
Supplier industry consolidation, where a few large players emerge, significantly amplifies their ability to dictate terms. This concentration means AIXTRON might face a reduced number of critical input providers, potentially leading to less competitive pricing and more stringent supply agreements. For instance, in the semiconductor equipment sector, where AIXTRON operates, a trend towards fewer, specialized suppliers for key components like advanced deposition sources can give those suppliers considerable leverage.
- Consolidation: Fewer, larger suppliers gain more market influence.
- Impact on AIXTRON: Reduced sourcing options and increased negotiation pressure.
- Industry Example: Specialized component suppliers in semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
Forward Integration Threat from Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into AIXTRON's deposition equipment manufacturing, while rare, represents a significant theoretical bargaining chip. This potential, even if unlikely, highlights the critical need for AIXTRON to cultivate robust supplier relationships and strategic alliances to mitigate such risks.
If a key supplier were to pursue forward integration, it would place them in direct competition with AIXTRON's primary business operations. This could dramatically shift the power dynamic, potentially impacting AIXTRON's market share and profitability.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into AIXTRON's core deposition equipment market.
- Strategic Importance: Underscores the need for strong supplier partnerships.
- Competitive Impact: Direct competition could significantly disrupt AIXTRON's business model.
AIXTRON's suppliers of highly specialized components, such as advanced precursor chemicals or precision-engineered parts, hold substantial bargaining power due to the unique nature of these inputs. This limited availability of alternatives means AIXTRON faces potential cost increases and supply chain disruptions if a key supplier encounters issues. For instance, the semiconductor industry, where AIXTRON operates, relies on a concentrated number of suppliers for critical, proprietary components.
The high switching costs for AIXTRON, involving extensive re-qualification and design adaptation, further solidify supplier leverage. These costs can extend production timelines, hindering AIXTRON's market responsiveness. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment sector continued to see consolidation, with a few key players dominating the supply of specialized materials, granting them significant pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on AIXTRON | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Component Specialization | Limited sourcing options, increased costs | High demand for advanced deposition precursors |
| Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, supplier dependency | Months-long validation for new components |
| Supplier Consolidation | Fewer suppliers, greater negotiation pressure | Key suppliers in the deposition equipment market are highly concentrated |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects AIXTRON's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the semiconductor equipment market.
AIXTRON's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a dynamic dashboard that visualizes competitive intensity, allowing for immediate identification of areas requiring strategic attention.
Customers Bargaining Power
AIXTRON's customer base is dominated by a few large, global semiconductor manufacturers. These giants, like TSMC or Intel, often account for a substantial portion of AIXTRON's revenue, giving them considerable sway. For instance, in 2023, AIXTRON's top customers represented a significant chunk of their sales, highlighting the concentration.
The sheer volume of equipment these major players purchase allows them to negotiate aggressively for better pricing, payment terms, and even customized product specifications. This concentrated demand means customers can easily switch suppliers if their demands aren't met, putting pressure on AIXTRON to remain competitive and responsive.
The semiconductor industry's cyclical nature significantly influences customer bargaining power. During downturns, when demand weakens, customers often scale back capital expenditures, which amplifies their leverage. This can lead to project delays or demands for more favorable pricing, directly affecting AIXTRON's order book and overall revenue. For instance, AIXTRON saw a dip in its order intake during 2024, largely attributed to a slowdown in the power electronics sector.
Customers' capacity to delay or postpone equipment orders significantly impacts suppliers like AIXTRON. This flexibility is particularly pronounced during economic downturns or when existing market capacities are already high. For instance, in 2024, a slowdown in certain sectors meant customers could push back purchases, creating pressure on AIXTRON to adjust pricing or delivery schedules to secure sales.
This postponement capability directly translates into reduced demand for AIXTRON's advanced deposition equipment. When customers can wait, they often do, especially if they anticipate better pricing or more favorable contract terms in the future. This dynamic was evident in the power electronics and LED markets throughout 2024 and is projected to remain a key factor influencing AIXTRON's sales pipeline into 2025.
Demand for Advanced and Cost-Effective Solutions
Customers in the semiconductor and materials processing industries are consistently seeking deposition solutions that offer enhanced performance and greater cost-efficiency. This drives a need for continuous innovation from suppliers like AIXTRON to remain competitive. For instance, the drive for smaller, faster, and more power-efficient chips fuels demand for advanced deposition techniques.
This persistent customer pressure for better technology at a lower price point can constrain AIXTRON's ability to dictate pricing and requires significant ongoing investment in research and development. AIXTRON's G10 system family, for example, is designed to address these evolving customer requirements for both performance and economic viability.
- Customer Demand for Innovation: Buyers require deposition equipment that enables higher chip densities and improved material properties.
- Cost-Efficiency Imperative: Reducing manufacturing costs per unit is a critical driver for customer purchasing decisions.
- Impact on Pricing Power: Strong customer demand for advanced, cost-effective solutions limits AIXTRON's pricing flexibility.
- R&D Investment Necessity: AIXTRON must continuously innovate, as demonstrated by its G10 system family, to meet these market pressures.
Customer's Internal Production Capabilities
Some large semiconductor manufacturers possess or are developing internal capabilities for specific equipment or component production. This reduces their dependence on external suppliers like AIXTRON for all their needs.
While AIXTRON's technology is highly specialized, the potential for customers to insource certain processes can limit AIXTRON's pricing power. For instance, if a major chipmaker could develop even a portion of the deposition equipment internally, it would lessen their need to purchase the entirety from AIXTRON, thereby influencing negotiations.
This dynamic compels AIXTRON to consistently innovate and maintain its technological edge. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment market saw continued investment in advanced manufacturing, with companies like TSMC and Intel reportedly exploring in-house solutions for specific process steps to gain greater control and potentially reduce costs.
The bargaining power of customers is influenced by their internal production capabilities:
- Customer's Internal Production Capabilities: Large customers may develop in-house capabilities for certain equipment or components, reducing reliance on AIXTRON.
- Reduced Dependence: This insourcing potential acts as a check on AIXTRON's pricing power, as customers have alternatives.
- Technological Imperative: AIXTRON must continuously lead in technology to offset this customer bargaining power.
- Market Trends: In 2024, significant capital expenditure by leading semiconductor firms in advanced manufacturing technologies suggests a growing interest in internal process control and potential insourcing.
AIXTRON's bargaining power with customers is significantly shaped by the concentration of its buyer base, with a few major semiconductor manufacturers accounting for a substantial portion of its revenue. This concentration, evident in 2023 sales figures where top customers represented a considerable percentage of revenue, grants these large entities considerable leverage in negotiations for pricing and product specifications.
The semiconductor industry's cyclical nature amplifies customer bargaining power, especially during downturns. In 2024, a slowdown in certain sectors led to customers delaying purchases, forcing AIXTRON to consider pricing adjustments and delivery schedule modifications to secure sales, impacting its order book.
Customers' continuous demand for enhanced performance and cost-efficiency in deposition solutions necessitates ongoing innovation from AIXTRON, as seen with its G10 system family. This pressure limits AIXTRON's pricing flexibility and requires substantial R&D investment to maintain its technological edge against potential customer insourcing of certain processes, a trend observed among leading semiconductor firms in 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on AIXTRON | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Dominance of a few large semiconductor manufacturers | High customer leverage on pricing and terms | Top customers represented a significant portion of 2023 revenue. |
| Industry Cyclicality | Fluctuations in semiconductor demand | Amplifies customer power during downturns | 2024 saw order delays due to sector slowdowns. |
| Demand for Innovation & Cost-Efficiency | Customer need for better performance at lower cost | Limits pricing power, necessitates R&D investment | AIXTRON's G10 system family addresses these needs. |
| Customer Insourcing Potential | Customers developing internal capabilities | Reduces dependence, provides negotiation leverage | Leading firms explored internal process control in 2024. |
Same Document Delivered
AIXTRON Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete AIXTRON Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape impacting the company. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
AIXTRON competes in the specialized global market for deposition equipment, facing fierce rivalry from a concentrated group of major players. This niche environment, while expanding, sees competitors intensely pursuing a limited pool of significant customers, often resulting in aggressive pricing strategies and accelerated innovation cycles to secure market share.
Competitive rivalry in the semiconductor equipment sector, particularly for AIXTRON, is intense and fundamentally driven by the relentless pursuit of technological advancement. Companies are in a constant race to develop and deploy next-generation systems that enable smaller, faster, and more efficient microchips. This innovation cycle means that leadership in this space is fleeting without continuous investment in research and development.
AIXTRON's competitive standing is significantly influenced by its ability to maintain technological leadership, exemplified by its G10 system family and its pioneering work in 300mm Gallium Nitride (GaN) wafer technology. These advancements are critical for meeting the evolving demands of the semiconductor industry, especially for high-growth areas like advanced displays and power electronics. For instance, GaN technology is crucial for applications requiring high efficiency and high-frequency operation, such as 5G infrastructure and electric vehicles.
Sustaining this technological edge necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in R&D. In 2023, AIXTRON reported R&D expenses of €173.3 million, which represents a notable portion of its overall revenue and underscores the commitment required to stay ahead in this highly competitive environment. This financial commitment is essential for developing new deposition technologies and improving existing platforms to meet future market needs.
The semiconductor equipment sector is characterized by substantial fixed costs, meaning that achieving high capacity utilization is absolutely vital for companies to turn a profit. When demand dips, manufacturers might resort to aggressive pricing strategies to keep their production lines running, which in turn fuels intense competition among industry players.
This pressure to fill capacity can significantly squeeze gross margins. For instance, AIXTRON's reported gross margin for the first quarter of 2024 was 45.2%, a figure that reflects the ongoing challenges of balancing high fixed costs with fluctuating market demand and competitive pricing pressures.
Market Share Dynamics in Key Segments
Competitive rivalry is intense, especially in fast-growing areas such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) power electronics. AIXTRON has secured a leading position in SiC deposition technology.
However, other companies are also pouring resources into these markets, creating a dynamic environment where market share is constantly being contested. This necessitates a sustained strategic approach for AIXTRON.
- AIXTRON's SiC market leadership is challenged by significant competitor investments.
- The power electronics sector, particularly SiC and GaN, is a hotbed of intense competition.
- Continuous innovation and strategic adaptation are crucial for maintaining AIXTRON's market standing.
Geopolitical Factors and Regional Competition
Geopolitical tensions significantly shape the semiconductor landscape, driving national strategies to bolster domestic manufacturing. For instance, the US CHIPS and Science Act, with its over $52 billion in funding, and similar initiatives in Europe and Asia, aim to reduce reliance on specific regions. This can lead to increased competition from companies heavily supported by government subsidies and preferential policies, altering the competitive dynamics beyond purely technological advancements.
These regional investment initiatives directly impact competitive rivalry by fostering the growth of local players. Countries are actively encouraging semiconductor production within their borders, which can shift customer demand away from established global suppliers towards these newly empowered domestic competitors. This creates a complex competitive environment where government backing plays a crucial role alongside innovation and market share.
- Government Subsidies: Countries like South Korea, Taiwan, and the United States are channeling billions into semiconductor manufacturing to secure supply chains and foster domestic industry growth.
- Regionalization Trends: The push for localized production, exemplified by significant investments from TSMC in Arizona and Intel's expansion in Europe, alters global manufacturing footprints.
- Trade Policies: Export controls and tariffs, such as those implemented by the US targeting advanced chip technology to China, directly influence market access and competitive positioning.
- National Security Concerns: Geopolitical factors elevate semiconductor manufacturing to a matter of national security, intensifying government involvement and potentially creating protectionist measures that favor domestic firms.
The competitive landscape for AIXTRON is marked by intense rivalry, primarily from a few dominant global players in the deposition equipment market. This concentrated competition means that innovation and customer relationships are paramount, as companies vie for a limited customer base.
AIXTRON's strength lies in its technological leadership, particularly in areas like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) deposition, which are critical for emerging high-growth sectors. For instance, in 2023, AIXTRON reported R&D expenses of €173.3 million, highlighting a significant commitment to staying ahead technologically.
The industry faces pressure from high fixed costs, often leading to aggressive pricing during demand downturns to maintain capacity utilization. AIXTRON's first-quarter 2024 gross margin of 45.2% reflects these ongoing competitive pressures and the need to balance operational efficiency with market dynamics.
Geopolitical factors and government initiatives, such as the US CHIPS Act, are also reshaping competition by promoting regional manufacturing and potentially favoring domestic players through subsidies, adding another layer of complexity to the market.
| Metric | 2023 Value (€ million) | Q1 2024 Value (€ million) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| R&D Expenses | 173.3 | N/A (Q1 2024 data not directly comparable for R&D) | Indicates commitment to technological advancement amid rivalry. |
| Gross Margin | N/A (Annual 2023 not provided in this context) | 45.2% | Reflects pricing pressures and cost management in a competitive market. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While AIXTRON is a leader in Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), other deposition techniques like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are gaining traction. These alternatives can achieve high-quality thin films, potentially for some of the same semiconductor and optoelectronics applications AIXTRON serves. For instance, ALD offers superior conformality and precise thickness control, which can be critical for advanced chip manufacturing.
The threat from substitutes intensifies if these alternative technologies become more cost-effective or offer performance advantages for specific market segments. For example, advancements in PVD for certain display technologies could reduce reliance on MOCVD. AIXTRON's ongoing commitment to R&D, including enhancing the efficiency and output of its MOCVD systems, is crucial to maintaining its competitive edge against these evolving substitute threats.
The threat of substitutes for AIXTRON is evolving with the rise of new semiconductor materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN). These materials are increasingly replacing traditional silicon in power electronics, offering enhanced performance characteristics. AIXTRON's focus on equipment for these advanced materials positions it well, but future material innovations could still present a substitution risk.
The compound semiconductor market, fueled by SiC and GaN adoption, is experiencing robust growth. For instance, the SiC market alone was valued at approximately $2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $12 billion by 2030, indicating a significant shift away from purely silicon-based solutions. While AIXTRON is a key enabler of this transition, unforeseen breakthroughs in entirely novel materials could necessitate further adaptation.
The integration of functions at the chip level presents a significant threat of substitutes for deposition equipment manufacturers like AIXTRON. As chip designs become more sophisticated, with multiple functionalities consolidated onto single chips, the demand for certain specialized deposition processes used for discrete components may decline.
For instance, advancements in heterogeneous integration and advanced packaging techniques mean that components previously requiring separate fabrication steps, each potentially involving deposition, can now be combined. This consolidation reduces the overall number of manufacturing stages and, consequently, the need for some types of deposition equipment.
This trend necessitates that AIXTRON and similar companies focus on developing deposition systems capable of handling these more complex, integrated structures. The market is shifting towards versatile tools that can deposit multiple materials or perform complex patterning in fewer steps, rather than a series of single-purpose machines.
Software-Defined or Virtualized Solutions
The threat of substitutes for AIXTRON's core deposition equipment is generally low, as these are highly specialized and capital-intensive machines. However, in certain niche areas, advancements in software-defined or virtualized solutions could indirectly impact demand.
While not a direct replacement for the physical deposition hardware, these software-centric approaches might influence the types of materials and the precision required for components that AIXTRON's equipment produces. This represents a long-term, indirect potential threat that AIXTRON will need to monitor.
- Software-defined networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) are examples of virtualization trends that reduce reliance on dedicated hardware in IT infrastructure, but their direct impact on semiconductor manufacturing equipment is limited.
- The core functionality of deposition equipment involves precise physical processes, making direct software substitution for the hardware itself highly improbable in the foreseeable future.
- AIXTRON's focus on advanced deposition technologies for critical semiconductor components means that the physical capabilities of their equipment remain paramount, limiting the substitutability by purely software-based solutions.
Shift in End-User Application Architectures
Significant shifts in end-user application architectures, such as a move away from certain optoelectronic components or a drastic change in data communication methods, could reduce demand for specific types of components AIXTRON's equipment produces. For instance, the increasing prevalence of cloud-based computing and edge AI could alter the demand for on-premise hardware, potentially impacting the market for deposition equipment used in traditional data center components. AIXTRON must closely monitor these evolving trends to ensure its technology remains relevant to future market needs and to adapt its product offerings accordingly.
The semiconductor industry, a key market for AIXTRON, is in constant flux. For example, the drive towards more energy-efficient computing could see a shift in the types of materials and manufacturing processes required, potentially making existing equipment less desirable if it cannot accommodate these new demands. AIXTRON's ability to innovate and pivot its technology in response to these architectural changes is crucial for mitigating the threat of substitutes.
- Evolving Data Architectures: The rise of distributed computing and edge processing may lessen reliance on centralized hardware, impacting demand for components used in traditional server infrastructure.
- Material Innovation: Advancements in new semiconductor materials or entirely different computing paradigms could render current deposition technologies obsolete for specific applications.
- Connectivity Shifts: Changes in how data is transmitted, such as the adoption of new optical communication standards or wireless technologies, could reduce the need for specific optoelectronic components that AIXTRON's equipment helps produce.
- AI Integration: The increasing integration of AI at the edge could lead to specialized hardware designs that bypass traditional chip architectures, altering component requirements.
While AIXTRON's core MOCVD technology is specialized, alternative deposition methods like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) pose a threat if they become more cost-effective or offer performance advantages for specific applications. For instance, ALD's superior conformality is critical for advanced chip nodes, potentially reducing reliance on MOCVD for certain processes.
The growing adoption of new semiconductor materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN) in power electronics, a market valued at over $2.1 billion in 2023 for SiC alone, presents a substitution risk if entirely novel materials emerge that bypass current deposition needs.
Consolidation of functions through heterogeneous integration and advanced packaging can reduce the demand for deposition equipment used in discrete components. This trend, exemplified by the increasing complexity of chip designs, necessitates AIXTRON's focus on versatile deposition systems capable of handling integrated structures.
Direct substitution of AIXTRON's physical deposition hardware by purely software-based solutions is unlikely in the near future, as the core functionality relies on precise physical processes. However, evolving data architectures and shifts in end-user applications, such as the rise of edge AI, could indirectly influence demand for specific components AIXTRON's equipment produces.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the semiconductor deposition equipment market demands substantial capital for research, development, and advanced manufacturing. Building and maintaining sophisticated cleanroom facilities alone can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers. For instance, AIXTRON's commitment to innovation, as seen in their substantial R&D spending, underscores the high investment needed to compete effectively.
Developing and refining advanced deposition technologies, crucial for AIXTRON's business, requires immense scientific and engineering expertise. This includes long development cycles and significant ongoing research and development (R&D) spending, creating a high barrier for newcomers.
New entrants would face a formidable challenge in acquiring or developing the specialized knowledge and intellectual property necessary to compete. AIXTRON's 40-year history of innovation has solidified its position, making it difficult for new players to replicate its technological depth and market presence.
Established players like AIXTRON benefit from deeply entrenched customer relationships and a high degree of trust with leading semiconductor manufacturers. This is paramount in an industry where equipment is expensive and downtime is costly. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this level of confidence and market penetration, as customer qualification alone can take considerable time and effort.
Intellectual Property and Patent Portfolios
AIXTRON, a leader in deposition equipment, possesses a formidable intellectual property moat. Their extensive patent portfolios, covering core deposition technologies, act as significant barriers to entry. For instance, as of their 2023 annual report, AIXTRON highlighted its ongoing commitment to R&D with a substantial portion of revenue dedicated to innovation, directly contributing to the strength and breadth of these patents.
Newcomers face the daunting task of navigating this intricate patent landscape. Developing deposition technologies that are both competitive and non-infringing on AIXTRON's existing intellectual property presents a substantial hurdle. This legal and technical challenge effectively protects AIXTRON's established technological lead and market position.
- Extensive Patent Portfolios: AIXTRON holds a significant number of patents related to its core deposition technologies, safeguarding its innovations.
- High Barrier to Entry: The complexity and breadth of AIXTRON's intellectual property make it difficult and costly for new companies to enter the market without infringing.
- Protection of Technological Lead: These patents are crucial in maintaining AIXTRON's competitive advantage and technological superiority in the deposition equipment sector.
- R&D Investment: AIXTRON's continued investment in research and development, as evidenced by its 2023 financial disclosures, fuels the expansion and strengthening of its patent portfolio.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Effects
Established players like AIXTRON benefit significantly from economies of scale in production and purchasing, alongside experience curve effects that drive down costs with increased output. For instance, AIXTRON's extensive history and global reach, evidenced by over 3,500 systems sold worldwide, translate into optimized manufacturing processes and stronger supplier relationships. This accumulated experience allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs than a new entrant would initially face.
Newcomers to the deposition equipment market would therefore start at a considerable cost disadvantage. They lack the established infrastructure, bulk purchasing power, and refined operational efficiencies that AIXTRON has cultivated over years of operation. This makes it challenging for new entrants to compete effectively on price or match the operational efficiency of incumbents.
- Economies of Scale: AIXTRON's large-scale production lowers per-unit costs.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated knowledge leads to cost reductions over time.
- Market Entry Barrier: New entrants face higher initial costs compared to established firms.
- AIXTRON's Track Record: Over 3,500 systems sold globally demonstrates significant experience and scale.
The threat of new entrants into AIXTRON's deposition equipment market is moderate to low. Significant capital investment is required for R&D and advanced manufacturing facilities, with cleanroom construction alone costing hundreds of millions. AIXTRON's substantial R&D spending, a core part of its strategy, highlights this high entry barrier.
Furthermore, the industry demands specialized expertise and extensive intellectual property, which AIXTRON has cultivated over its 40-year history. Replicating this technological depth and navigating AIXTRON's robust patent portfolio, strengthened by continuous R&D investment as noted in their 2023 reports, presents a considerable challenge for newcomers.
Established customer relationships built on trust are also a key barrier. Semiconductor manufacturers require proven reliability, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market penetration. AIXTRON's global presence, evidenced by over 3,500 systems sold, underscores its established market position and experience curve advantages, which translate into cost efficiencies unavailable to new players.
| Factor | AIXTRON's Position | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (R&D, manufacturing facilities) | Significant barrier due to substantial initial investment |
| Technological Expertise & IP | Extensive, protected by patents | Difficult and costly to replicate or design around |
| Customer Relationships | Deeply entrenched, high trust | Challenging for new players to gain initial customer adoption |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Strong, with over 3,500 systems sold globally | New entrants face higher initial cost disadvantages |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our AIXTRON Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from AIXTRON's official investor relations materials, annual reports, and SEC filings. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry analysis firms and market research reports that cover the semiconductor equipment sector.
