3SBio Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
3SBio Bundle
3SBio faces moderate bargaining power from its suppliers, as specialized raw materials are crucial for its biopharmaceutical products. The threat of substitutes is relatively low due to the unique nature of its advanced therapies. However, intense competition from established and emerging players significantly impacts its market position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore 3SBio’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The biopharmaceutical sector's dependence on highly specialized raw materials, including unique cell lines and critical reagents, often means a concentrated supplier base. This limited availability significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers, as finding and qualifying alternatives is a complex, expensive, and lengthy process that can easily disrupt production schedules and compromise product integrity.
The intricate manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals, such as recombinant proteins and antibodies, demands highly specialized processes and sophisticated equipment. This complexity significantly bolsters the bargaining power of suppliers in this sector.
Suppliers offering advanced manufacturing technologies and contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) wield considerable influence. Their power stems from the substantial capital investment and deep technical expertise necessary for biopharmaceutical production, making it difficult for companies like 3SBio to easily switch providers.
For instance, the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market was valued at approximately $20.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating the significant financial commitment and specialized nature of these services. This reliance on a limited pool of expert suppliers grants them leverage in negotiations.
The biopharma sector's supply chains are facing significant strain due to geopolitical risks, a trend emphasized in 2025 outlooks. These vulnerabilities can directly translate into increased bargaining power for suppliers, especially those offering critical components or specialized manufacturing capabilities.
Legislation like the BIOSECURE Act, targeting relationships with Chinese contract manufacturers, exemplifies how geopolitical shifts can alter supplier dynamics. This could empower non-Chinese suppliers or necessitate costly diversification, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
Suppliers possessing unique intellectual property or proprietary technologies, such as novel drug delivery systems or advanced purification techniques, wield significant bargaining power. This allows them to dictate terms and command premium pricing for their specialized inputs, which are critical for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. For instance, companies that have developed exclusive methods for cell culture expansion or protein refolding can leverage this advantage. In 2024, the biopharmaceutical sector continued to see increased reliance on specialized technology providers, with some component suppliers reporting double-digit percentage increases in pricing for patented materials.
This intellectual property advantage translates into higher costs for companies like 3SBio if they are dependent on these specialized suppliers. The inability to easily substitute these proprietary technologies means that suppliers can effectively set higher prices, impacting the overall cost of goods sold. For example, a supplier holding a patent for a specific bioreactor membrane technology essential for producing a high-purity therapeutic protein could charge significantly more than a generic alternative, if one even exists.
- Proprietary Technologies: Suppliers with unique, patented technologies for biopharmaceutical production processes.
- Intellectual Property: Exclusive rights to novel drug delivery systems or specialized manufacturing methods.
- Pricing Power: The ability of these suppliers to command higher prices due to the lack of viable substitutes.
- Dependency: Companies relying on these specialized inputs face increased costs and limited negotiation leverage.
Limited Sourcing Options
While 3SBio actively seeks a diverse supplier base, the specialized nature of biopharmaceutical manufacturing often restricts the availability of qualified and compliant suppliers for critical raw materials and components. This limited pool of options for essential inputs directly strengthens the bargaining power of these suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the global biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing market experienced significant growth, driving demand for specialized inputs and potentially concentrating supply chains for certain advanced materials.
- Limited Qualified Suppliers: The stringent regulatory requirements and technical expertise needed for biopharmaceutical inputs mean fewer companies can meet these standards, creating a concentrated supplier market.
- High Switching Costs: Changing suppliers for critical biopharmaceutical components can involve extensive validation processes, regulatory approvals, and potential production disruptions, making switching costly for 3SBio.
- Supplier Concentration: In specific niches, a small number of suppliers may dominate the market, giving them considerable leverage in price negotiations and contract terms.
- Impact on Input Costs: This supplier concentration can lead to higher input costs for 3SBio, directly affecting its cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for 3SBio is significantly influenced by the specialized nature of biopharmaceutical inputs and the limited number of qualified providers. This concentration, coupled with high switching costs and proprietary technologies held by suppliers, allows them to exert considerable leverage. For example, in 2024, the increasing demand for advanced cell culture media and purification resins, often patented, led to price increases of up to 15% from key suppliers, directly impacting 3SBio's production costs.
| Factor | Impact on 3SBio | Supplier Leverage Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited qualified suppliers for critical raw materials and components. | A few key suppliers dominate specialized reagents, enabling price control. |
| Proprietary Technology | Reliance on patented manufacturing processes or unique cell lines. | Suppliers of novel purification membranes can command premium pricing. |
| Switching Costs | High costs associated with validating new suppliers and regulatory approvals. | Changing a critical reagent supplier can cost millions and delay production by months. |
| Geopolitical Risks | Supply chain vulnerabilities can empower suppliers of essential components. | Increased demand for domestically sourced bioprocessing materials in 2024 boosted supplier pricing power. |
What is included in the product
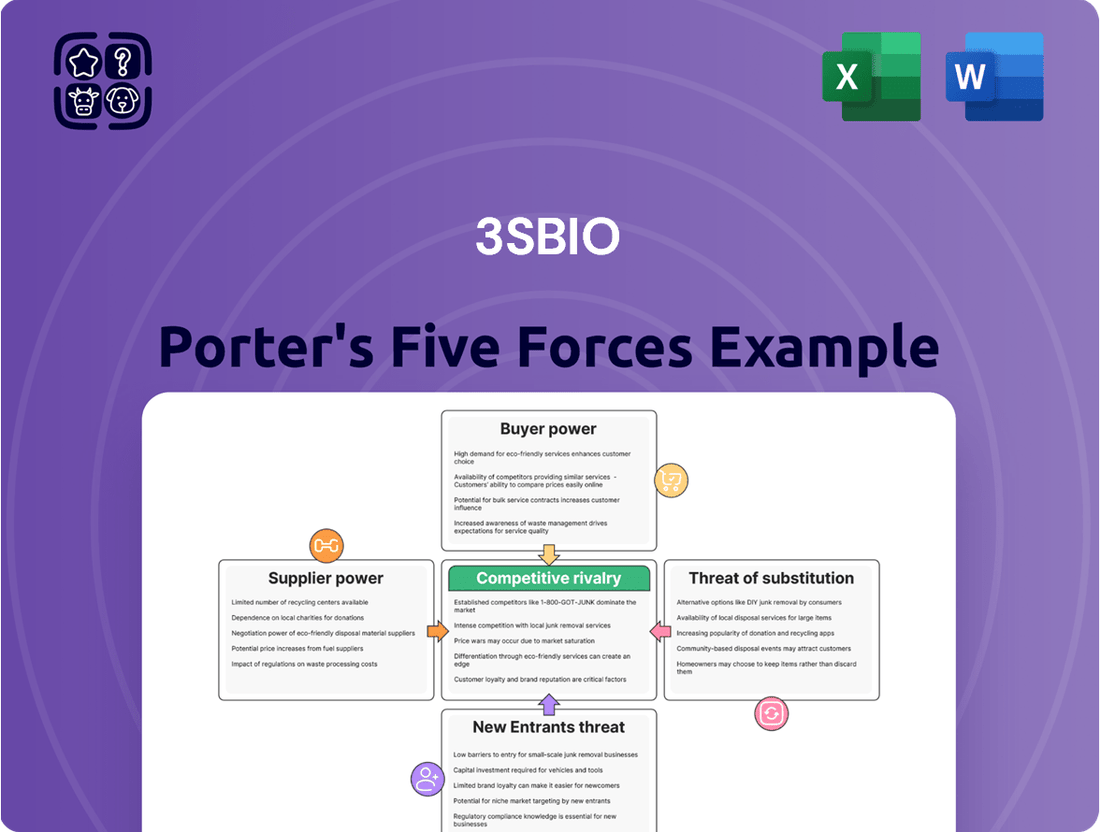
3SBio's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intensity of rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model that adapts to your specific industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
The significant expense associated with developing and producing biologic drugs naturally empowers customers, such as national healthcare systems and government agencies, to push for more cost-effective alternatives. This pressure directly fuels the market for biosimilars, granting these purchasers considerable negotiation power, particularly in regions that maintain centralized drug reimbursement lists.
The increasing availability of biosimilars significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. The global biosimilars market is on a strong growth trajectory, with projections indicating it could reach US$93.1 billion by 2030.
As patents on original biologic drugs expire, biosimilar alternatives enter the market, offering comparable effectiveness and safety profiles at reduced prices. This creates a competitive environment where customers, particularly healthcare providers and payers, can negotiate for lower costs or readily switch to more affordable options, thereby pressuring original manufacturers.
In China, where 3SBio is a significant player, the government and national insurance programs act as powerful customers for pharmaceuticals. Their decisions on inclusion in reimbursement lists, such as the 2024 National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) which impacts products like 3SBio's TPIAO, directly affect sales volumes and pricing power.
These large-scale purchasers leverage their market presence through mechanisms like volume-based centralized procurement, often referred to as bulk purchasing. This practice allows them to negotiate substantial price reductions, thereby amplifying their bargaining power and influencing the profitability of pharmaceutical companies like 3SBio.
Patient-Centric Healthcare Models
The increasing focus on patient-centric healthcare models, which prioritize personalized and proactive services, can subtly shift power towards patients. This trend empowers individuals to influence treatment choices and demand greater value.
Patients, often organized through advocacy groups or by directly impacting physician prescribing habits, are increasingly vocal about their needs. This can translate into demand for specific therapies and a push for improved access and affordability in the healthcare market.
- Growing Patient Influence: In 2024, patient advocacy groups continued to gain traction, influencing regulatory bodies and pharmaceutical companies to consider patient outcomes and preferences more heavily in drug development and pricing.
- Demand for Personalized Medicine: The market for personalized medicine, driven by patient demand for tailored treatments, is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by the end of the decade, indicating a significant shift in consumer power.
- Transparency and Access: Patients are increasingly demanding greater transparency in healthcare costs and access to treatments, putting pressure on providers and manufacturers to justify their pricing and improve service delivery.
Access to Information and Alternatives
Increased transparency in drug pricing and efficacy data, a trend significantly amplified in recent years, empowers customers like healthcare providers and patients. This enhanced visibility allows them to scrutinize costs versus benefits, directly impacting their purchasing decisions.
The growing availability of alternative treatments, including biosimilars and generics, further strengthens customer bargaining power. For instance, by mid-2024, the FDA had approved over 40 biosimilars, offering significant cost savings and choice to patients and payers.
- Informed Decisions: Customers can now compare drug prices and clinical trial results more readily, leading to more strategic purchasing.
- Negotiation Leverage: Access to comparative data and alternative options provides leverage for negotiating prices with pharmaceutical companies.
- Market Shift: The rise of biosimilars, with an estimated market value projected to reach $100 billion by 2029, directly challenges originator drug pricing power.
- Patient Advocacy: Empowered patients are increasingly demanding greater transparency and value, influencing market dynamics.
Customers, particularly large healthcare systems and government payers, wield significant bargaining power due to the high cost of biologic drugs. The increasing availability of biosimilars, with over 40 approved by the FDA by mid-2024, directly fuels this power by offering cost-effective alternatives and enabling negotiation for lower prices. This dynamic is further amplified by centralized procurement practices and growing patient advocacy for transparency and value, putting pressure on originator drug manufacturers.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Biosimilar Availability | Increases bargaining power by providing cheaper alternatives. | Over 40 biosimilars approved by FDA by mid-2024. |
| Centralized Procurement | Enhances power through volume discounts and negotiation. | Government tenders and bulk purchasing are common in many markets. |
| Patient Advocacy & Transparency Demands | Empowers patients to influence pricing and access. | Growing influence on regulatory bodies and pricing discussions. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
3SBio Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This preview accurately reflects the comprehensive 3SBio Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive, detailing the competitive landscape, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
3SBio faces fierce competition in its core therapeutic areas, including oncology, nephrology, and immunology. These sectors are crowded with both established global pharmaceutical giants and emerging domestic players, all aggressively pursuing market share through substantial investments in research and development and extensive marketing campaigns.
The pharmaceutical industry, including players like 3SBio, experiences intense rivalry driven by a relentless pursuit of innovative drugs and the expansion of product pipelines. This focus on R&D creates a dynamic environment where companies constantly strive to be the first to market with groundbreaking treatments.
3SBio itself demonstrates this competitive drive with a substantial pipeline featuring 30 product candidates, a significant portion of which are innovative drugs. The fact that 10 of these are in Phase III clinical trials highlights the high stakes and the active R&D race underway.
While the biopharmaceutical market is generally competitive, 3SBio has carved out significant leadership in particular therapeutic areas. For instance, in 2024, 3SBio held an impressive 66.6% market share in Mainland China for TPIAO, a key treatment for thrombocytopenia. Similarly, its rhEPO products commanded a substantial 42.0% market share in 2024 for anemia treatment.
Strategic Partnerships and M&A Activity
The biopharmaceutical landscape is characterized by intense rivalry, often fueled by strategic partnerships and mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Companies are actively pursuing these avenues to broaden their product pipelines and secure a stronger competitive footing. This trend is clearly visible in 3SBio's recent licensing deal with Pfizer for SSGJ-707, a move that underscores the industry's dynamic and competitive nature.
This strategic alliance allows 3SBio to access innovative technology and potentially expand its market reach, directly impacting its competitive standing. Such collaborations are becoming a critical component of growth strategies in the biopharma sector, as companies navigate the complexities of drug development and market access.
- 3SBio's licensing agreement with Pfizer for SSGJ-707 highlights the increasing reliance on strategic partnerships to bolster competitive advantage.
- The biopharma industry's M&A activity reached a global total of $130 billion in 2023, indicating a strong trend towards consolidation and portfolio expansion.
- These partnerships and M&A deals are crucial for companies like 3SBio to access new technologies, expand their therapeutic areas, and compete effectively against larger, established players.
Pricing Pressure and Reimbursement Policies
Competitive rivalry in the biopharmaceutical sector, including companies like 3SBio, is significantly intensified by pricing pressure, especially within markets that operate under national reimbursement schemes. This dynamic forces companies to carefully consider their pricing strategies to ensure market access and achieve necessary sales volumes.
The ability to secure favorable inclusion on reimbursement lists is paramount for biopharmaceutical firms. Without it, market penetration and commercial success become exceedingly difficult, directly impacting revenue streams and competitive positioning.
For instance, in 2024, many global healthcare systems continued to scrutinize drug prices, leading to increased negotiation demands from payers. Companies that can demonstrate clear value and cost-effectiveness are better positioned to navigate these pressures. In 2023, the average price increase for new drugs in the US, before rebates, was reported to be around 4.5%, a figure that many payers are actively working to curb.
- Pricing pressure is a major driver of competition in markets with national reimbursement systems.
- Favorable reimbursement listing is critical for market access and sales volume for biopharmaceutical companies.
- Companies must balance innovation costs with the need for affordable pricing to succeed.
3SBio faces intense competition from both global pharmaceutical giants and domestic players in its key therapeutic areas like oncology and immunology. This rivalry is fueled by aggressive R&D spending and marketing efforts, as companies race to develop and launch innovative treatments.
The company's significant pipeline, with 10 drugs in Phase III trials as of mid-2025, demonstrates its active participation in this competitive R&D landscape. However, this also means substantial investment is required to stay ahead.
In 2024, 3SBio maintained strong market positions, holding a 66.6% share in China for TPIAO and 42.0% for its rhEPO products, showcasing its ability to compete effectively within specific niches despite the broader industry competition.
Strategic partnerships, like the 2024 licensing deal with Pfizer for SSGJ-707, are crucial for 3SBio to access new technologies and enhance its competitive standing, reflecting a broader industry trend where collaborations are key to navigating market complexities.
| Therapeutic Area | 3SBio Market Share (2024) | Key Competitors | Industry Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia (TPIAO) | 66.6% (Mainland China) | Global Pharma, Domestic Biotechs | Focus on innovative biologics |
| Anemia (rhEPO) | 42.0% | Amgen, Johnson & Johnson, Domestic Players | Biosimilar development and market penetration |
| Oncology | Fragmented | Roche, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Merck, Numerous Chinese Companies | Immuno-oncology, targeted therapies |
| Immunology | Fragmented | AbbVie, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chinese Biotechs | Biologics, personalized medicine |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct threat to 3SBio comes from biosimilars. These are versions of existing biologic drugs that are very similar and often come with a lower price tag. As original biologic drugs become more expensive and their patents expire, the market for biosimilars grows, presenting a significant substitution risk for 3SBio's established, older-generation products.
For certain medical needs, traditional small molecule drugs can act as viable substitutes for biopharmaceuticals. This is particularly true when these smaller molecules demonstrate comparable effectiveness, present fewer adverse reactions, or come with a more accessible price point.
While 3SBio does have small molecule drugs within its product offerings, the company's primary competitive advantage and strategic focus are firmly rooted in its biopharmaceutical capabilities. This means that while substitutes exist, 3SBio's core business is not directly threatened by them in its main areas of operation.
Alternative therapies and non-pharmacological interventions pose a significant threat, especially in therapeutic areas where drug efficacy is not overwhelmingly superior. For example, in dermatology, the demand for topical treatments might be substituted by cosmetic procedures or advanced skincare routines. Similarly, for weight management, lifestyle changes and bariatric surgery can serve as direct alternatives to pharmaceutical solutions.
The market for non-drug interventions is substantial and growing. In 2024, the global wellness market, which encompasses many non-pharmacological approaches, was valued at over $5.6 trillion. This indicates a strong consumer preference for holistic and alternative health solutions, directly impacting the market share potential for pharmaceutical companies like 3SBio.
Emerging Advanced Therapies
The emergence of advanced therapies, such as cell and gene therapies, poses a long-term substitution threat to traditional treatments. While these innovative approaches are still navigating development hurdles and accessibility issues, their potential to offer fundamentally different and potentially more effective treatment paradigms is significant.
As these technologies mature, they are expected to become more cost-effective and widely available. For instance, the global cell and gene therapy market was valued at approximately $8.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating increasing investment and progress in this area. This trajectory suggests that by 2030, these therapies could capture a meaningful share of existing treatment markets, offering alternative solutions that could displace current offerings.
- Maturing Technologies: Cell and gene therapies are moving from experimental stages to clinical application, with an increasing number of approvals in recent years.
- Potential for Superior Outcomes: These therapies aim to address diseases at their genetic root, potentially offering one-time curative treatments compared to ongoing management of chronic conditions.
- Market Growth Indicators: The significant projected growth in the cell and gene therapy market underscores the increasing viability and potential impact of these advanced treatments as substitutes.
Innovation from Competitors
The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by relentless innovation, and this poses a significant threat of substitution for companies like 3SBio. Competitors are constantly developing new drugs with novel mechanisms of action or improved efficacy. For instance, a breakthrough biologic from a rival could render an existing therapy obsolete, even if it isn't a direct biosimilar. This rapid pace of discovery means that a company's current market-leading product can quickly be displaced by a superior alternative.
The threat is amplified by the fact that new treatments can emerge from various therapeutic areas, not just direct competitors. A novel approach to treating a disease, even if developed by a company outside 3SBio's immediate competitive set, could still offer a substitute for existing therapies. For example, if 3SBio's flagship product is a monoclonal antibody for a specific autoimmune condition, the introduction of a gene therapy or a small molecule drug with a similar or better outcome profile would represent a potent substitute. The overall R&D spending in the biopharmaceutical sector reached approximately $250 billion globally in 2023, underscoring the intensity of this innovative drive.
- Rapid Development Cycles: Biopharma R&D can yield new treatments quickly, potentially shortening the lifecycle of existing products.
- Therapeutic Area Overlap: Innovations in adjacent or even unrelated therapeutic areas can still present substitution risks.
- Mechanism of Action Advancement: New biological pathways or drug delivery systems can offer significant advantages over current treatments.
- Increased R&D Investment: The substantial global investment in biopharmaceutical research fuels the constant introduction of new and potentially substitute products.
The threat of substitutes for 3SBio is multifaceted, ranging from biosimilars and small molecule drugs to non-pharmacological interventions and advanced therapies like cell and gene treatments. The biopharmaceutical industry's rapid innovation also introduces new drugs with novel mechanisms that can displace existing therapies. The global wellness market, valued at over $5.6 trillion in 2024, highlights a growing consumer interest in alternatives to traditional pharmaceuticals.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2023/2024 Data Point | Implication for 3SBio |
| Biosimilars | Lower-cost versions of existing biologics | Patent expirations increase biosimilar market share | Direct competition for older-generation products |
| Small Molecule Drugs | Traditional chemical compounds | Can offer comparable efficacy/fewer side effects | Potential alternative for certain indications |
| Non-Pharmacological Interventions | Lifestyle changes, procedures, wellness services | Global wellness market > $5.6 trillion (2024) | Reduces demand for pharmaceutical solutions |
| Cell & Gene Therapies | Advanced genetic/cellular treatments | Market valued at ~$8.7 billion (2023) | Long-term threat of curative alternatives |
| Industry Innovation | New drugs with superior mechanisms/efficacy | Biopharma R&D spending ~ $250 billion (2023) | Risk of existing products becoming obsolete |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical industry presents a formidable barrier to entry due to exceptionally high research and development costs. Bringing a new drug to market can cost upwards of $2.8 billion and take as long as 15 years. These substantial financial requirements effectively deter many potential new players from entering the innovative biopharmaceutical space.
The threat of new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like 3SBio, is significantly mitigated by stringent regulatory approval processes. These hurdles are not minor; they are substantial barriers requiring extensive resources and specialized knowledge.
New players must navigate complex, lengthy, and costly procedures, including rigorous clinical trials and obtaining approvals from authorities such as China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). For instance, the average time to bring a new drug to market can exceed ten years, with development costs often running into hundreds of millions, even billions, of dollars.
Established biopharmaceutical companies like 3SBio possess robust patent portfolios, a critical component of their intellectual property. These patents, covering novel drug compounds and manufacturing processes, represent a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. For instance, the average patent term for a new drug can be around 20 years from filing, though effective market exclusivity is often shorter due to development and regulatory timelines.
Complex Manufacturing and Distribution Networks
The biopharmaceutical industry presents significant barriers to entry due to the intricate nature of manufacturing and distribution. Producing biopharmaceuticals demands highly specialized facilities, adherence to rigorous quality control standards, and considerable capital outlays. For instance, companies like 3SBio have invested heavily in advanced manufacturing capabilities to ensure product safety and efficacy.
Establishing a robust nationwide sales and distribution network is another formidable challenge for potential new entrants. 3SBio's extensive reach, serving over 11,000 hospitals across China as of its latest reports, exemplifies the scale of infrastructure required. Building such a network necessitates significant time, resources, and strategic partnerships, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
- High Capital Investment: Biopharmaceutical manufacturing requires substantial upfront investment in specialized facilities and equipment.
- Stringent Quality Control: Adherence to strict regulatory standards for product quality and safety is non-negotiable.
- Complex Distribution Networks: Creating an efficient supply chain to reach a wide customer base, such as hospitals, is a major hurdle.
- Established Market Presence: Companies with existing distribution channels and hospital relationships, like 3SBio, have a competitive advantage.
Brand Recognition and Market Access
Established companies like 3SBio enjoy significant advantages due to their strong brand recognition and long-standing relationships within the healthcare ecosystem. This makes it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in building the necessary trust and securing market access, especially when competing against incumbents with proven track records and established distribution networks. For instance, 3SBio's leadership in key therapeutic areas, built over years of successful product development and commercialization, presents a formidable barrier.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Companies like 3SBio have cultivated strong brand loyalty among healthcare professionals and patients, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction.
- Distribution Network Access: Existing players possess well-developed distribution channels and relationships with hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, which are crucial for market penetration.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated, and new entrants must navigate complex approval processes, which can be time-consuming and costly, further deterring new competition.
The threat of new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector, particularly for a company like 3SBio, is considerably low due to substantial barriers. These include immense capital requirements for research, development, and manufacturing, often reaching billions of dollars per drug. Furthermore, navigating complex and lengthy regulatory approval processes, such as those mandated by the NMPA and FDA, demands specialized expertise and significant investment, acting as a strong deterrent for potential newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Metric (2024 Data Approximation) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (R&D) | Cost to bring a new drug to market | Very High | $2.8 billion+ per drug |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Time and cost of clinical trials & approvals | Very High | 10+ years and hundreds of millions in costs |
| Intellectual Property | Patent protection for novel compounds | High | ~20 year patent term (effective exclusivity shorter) |
| Manufacturing & Quality Control | Specialized facilities and strict standards | High | Significant capital outlay for GMP facilities |
| Distribution & Market Access | Building nationwide networks and hospital relationships | High | 3SBio serves 11,000+ hospitals in China |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our 3SBio Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and regulatory filings from key players in the biopharmaceutical sector.
