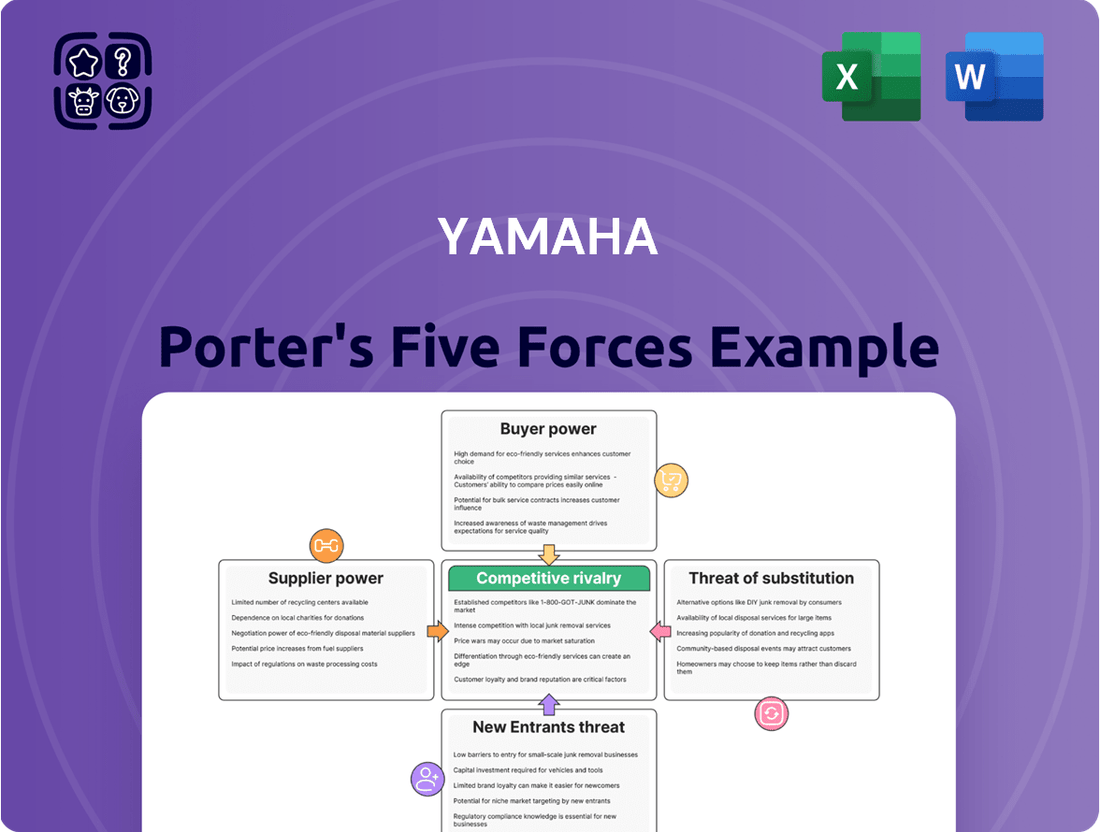
Yamaha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Yamaha Bundle
Yamaha's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder in the musical instrument and powersports industries. The power of suppliers and the availability of substitutes also play a significant role in Yamaha's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Yamaha’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Yamaha procures a wide array of components, from electronic parts and specialized metals to wood and plastics, with the specific needs varying across its product lines like musical instruments and motorcycles. For highly specialized components, where alternative suppliers are scarce or the technology is proprietary, these suppliers can command greater influence.
However, for more common materials, Yamaha's substantial purchasing volume often translates into significant bargaining power, allowing it to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, Yamaha's robust sales figures, exceeding 1.7 trillion JPY for its musical instruments segment alone, underscore its capacity to leverage scale in its supplier negotiations for many raw materials.
Yamaha's bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. For many common components, like standard fasteners or basic electronic parts, the cost and effort to switch suppliers are minimal, giving Yamaha leverage. However, the situation changes dramatically for specialized parts.
When Yamaha requires custom-designed engines, unique acoustic components, or proprietary digital signal processors, the complexity of switching becomes a major factor. These components often require extensive research and development, specialized manufacturing processes, and rigorous testing and integration into Yamaha's product lines. The financial outlay for redesign, retooling production lines, and re-qualifying new suppliers can be substantial, potentially running into millions of dollars depending on the component's integration level.
For instance, developing a new high-fidelity audio chip for their premium sound systems could involve years of collaboration and significant investment from both Yamaha and the chip manufacturer. If a supplier holds a patent on a critical technology or has deeply integrated their components into Yamaha's existing platforms, finding and onboarding an alternative supplier with comparable expertise and quality can be a lengthy and costly endeavor. This dependency, especially for highly engineered and proprietary parts, directly translates to increased bargaining power for those specific suppliers.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of Yamaha's suppliers. If Yamaha relies heavily on a specific raw material or component with few alternatives, the suppliers of that input gain considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry, which shares many component suppliers with motorcycle manufacturers like Yamaha, experienced supply chain disruptions for certain semiconductors. This scarcity for some electronic components meant suppliers of those critical parts could command higher prices, directly impacting manufacturers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly impacts Yamaha's bargaining power. If a supplier possesses the resources and strategic motivation to enter Yamaha's market as a direct competitor, their leverage grows considerably.
While less frequent for standard component manufacturers, this risk is more pronounced for suppliers of unique or patented technologies. Such providers could potentially bypass Yamaha and offer their innovations directly to consumers or other manufacturers, thereby diminishing Yamaha's control over its supply chain and product development.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: Suppliers capable of forward integration can dictate terms more forcefully, knowing they can compete directly.
- Niche Technology Risk: For specialized technologies, suppliers may see direct market entry as a more profitable strategy than simply supplying Yamaha.
- Market Disruption Potential: A supplier integrating forward could disrupt Yamaha's established market position and customer relationships.
- Strategic Importance of Key Suppliers: Yamaha's reliance on any single supplier for critical, hard-to-replicate components amplifies this threat.
Impact of Input Costs on Yamaha's Profitability
Fluctuations in the cost of essential inputs like metals, plastics, and rare earth elements for electronics directly impact Yamaha's manufacturing expenses. These volatile raw material prices can squeeze profit margins if not effectively managed.
For instance, Yamaha Motor reported in 2024 that rising costs for labor, materials, and other operational expenses had an adverse effect on its operating income. This demonstrates the significant leverage suppliers hold over Yamaha's cost structure and profitability.
- Significant Cost Pressures: Soaring prices for key raw materials and labor in 2024 directly impacted Yamaha's cost of goods sold.
- Profit Margin Erosion: Increased input costs without corresponding price increases can lead to a reduction in Yamaha's operating profit margins.
- Supplier Dependence: Yamaha's reliance on specific suppliers for critical components gives these suppliers considerable bargaining power.
- Impact on Pricing Strategy: The need to absorb or pass on higher supplier costs influences Yamaha's product pricing and competitive positioning.
For many standard components, Yamaha's substantial purchasing power, evidenced by its 2024 musical instrument segment sales exceeding 1.7 trillion JPY, allows it to negotiate favorable terms. However, for highly specialized or proprietary parts, where switching costs are high, suppliers gain significant leverage. The availability of substitute inputs and the threat of forward integration by suppliers further shape this dynamic, with niche technology providers posing a particular risk.
Yamaha's profitability is directly affected by input cost fluctuations; for example, Yamaha Motor noted in 2024 that rising labor and material costs impacted its operating income, underscoring supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact on Yamaha | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Specialization | High for specialized parts, low for common parts | Critical semiconductors faced scarcity, increasing supplier power |
| Switching Costs | High for custom-designed components, low for standard parts | Significant investment required for integrating new specialized suppliers |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for unique materials, high for commodities | Supply chain disruptions highlighted dependence on specific inputs |
| Forward Integration Threat | Higher for technology-focused suppliers | Potential for suppliers to enter Yamaha's market directly |
| Raw Material Price Volatility | Directly impacts manufacturing expenses and profit margins | Rising costs cited as a factor affecting operating income |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Yamaha, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its diverse markets.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Yamaha's customer base is broad, including serious musicians, motorsport fans, and everyday users. For sophisticated instruments and high-performance vehicles, customers often prioritize quality and brand reputation over minor price differences. This suggests a lower bargaining power for these segments.
However, in markets like consumer audio equipment or entry-level motorcycles, customers are more attuned to price. Yamaha utilizes a mix of pricing, including value-based and competitive approaches, to cater to these varying sensitivities.
In 2024, Yamaha's musical instruments division saw continued demand from professionals, indicating a resilience to price fluctuations. Conversely, the powersports segment, particularly for recreational vehicles, experienced some price sensitivity, with a notable 3% increase in sales volume for its more affordable models in the latter half of the year.
Customers today wield significant bargaining power, largely due to the explosion of readily available information. E-commerce platforms and online review sites empower buyers with detailed insights into product features, quality benchmarks, and competitive pricing across the entire market. This transparency is a game-changer, allowing consumers to effortlessly compare alternatives and identify the best value propositions.
For instance, in the competitive consumer electronics market, a consumer can easily access side-by-side comparisons of specifications and user reviews for products like Yamaha's digital pianos or audio equipment. In 2023, the global e-commerce market size reached an estimated $6.3 trillion, highlighting the sheer volume of transactions influenced by online information accessibility. This vast digital marketplace means that brands like Yamaha must consistently offer compelling value to retain customer loyalty.
For many of Yamaha's products, particularly consumer electronics and musical instruments, the cost for a customer to switch to a competitor is generally low. For instance, a consumer buying a new digital piano can easily explore brands like Roland or Kawai for their next purchase, with minimal financial or operational disruption.
However, this can change for specialized or integrated systems. Consider a professional musician who has invested heavily in a Yamaha digital audio workstation and associated software; switching to a different ecosystem might incur significant costs in retraining, data migration, and ensuring compatibility with existing hardware.
While precise figures are proprietary, the broader consumer electronics market often sees replacement cycles where customers can readily compare and switch brands. In 2023, the global musical instruments market was valued at approximately $17 billion, indicating a competitive landscape where brand loyalty can be influenced by factors beyond initial purchase price.
Volume of Purchases by Individual Customers
In the business-to-consumer (B2C) markets where Yamaha operates, such as musical instruments and motorcycles, individual customer purchases are generally quite small when compared to the company's overall sales volume. This means that any single customer, or even a small group of them, has very little leverage to negotiate prices or demand specific terms. For instance, a single purchase of a piano or a scooter doesn't represent a significant portion of Yamaha's global revenue, diminishing the individual buyer's bargaining power.
However, the situation can shift dramatically in Yamaha's business-to-business (B2B) sectors. Consider scenarios involving large-scale audio system installations for concert halls or the supply of industrial machinery to manufacturing plants. In these instances, a handful of major clients might account for a substantial percentage of sales within that specific segment. Such significant clients can indeed wield considerable bargaining power, potentially influencing pricing, service agreements, and even product specifications due to the sheer volume of their business.
- B2C Impact: Individual customer purchases in segments like musical instruments and motorcycles are typically minor relative to Yamaha's total revenue, significantly limiting their individual bargaining power.
- B2B Influence: In business-to-business segments, such as large audio installations or industrial equipment, a few major clients can represent a substantial portion of sales, granting them greater leverage.
- Segment Dependence: The bargaining power of customers is highly dependent on the specific market segment and the relative size of their purchases within Yamaha's diverse product portfolio.
- Volume Threshold: For customers to exert significant bargaining power, their purchase volume must reach a threshold where it represents a meaningful percentage of Yamaha's sales in a given product category or overall.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Consumer Demand
Economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping consumer demand, directly impacting Yamaha's sales. When the economy is strong, consumers typically have more disposable income, leading to increased spending on non-essential items like musical instruments, motorcycles, and recreational vehicles. Conversely, economic downturns can significantly dampen purchasing power.
For instance, in the United States during 2024, higher interest rates and persistent inflation have put a strain on household budgets. This economic pressure has directly affected Yamaha's marine products division. As consumers face reduced discretionary spending, purchases of larger ticket items like boats and marine engines have seen a noticeable slowdown, demonstrating the direct link between economic health and demand for Yamaha's diverse product lines.
- Economic Sensitivity: Yamaha's product portfolio, encompassing discretionary goods, makes it particularly vulnerable to shifts in economic cycles.
- Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates: Rising inflation and higher interest rates in key markets like the US in 2024 have demonstrably reduced consumer purchasing power for items such as Yamaha's marine products.
- Demand Fluctuations: Economic downturns lead to a decrease in disposable income, directly translating to lower demand for Yamaha's recreational and hobby-related products.
Yamaha's customer bargaining power varies significantly across its diverse product lines. In many consumer-facing segments, such as musical instruments and entry-level motorcycles, individual buyers have limited leverage due to the low volume of their purchases relative to Yamaha's overall sales. However, this power increases substantially in B2B contexts where large clients can influence terms due to their significant order volumes.
The ease with which customers can switch to competitors, often referred to as switching costs, is generally low for many of Yamaha's products. This accessibility to alternative brands, amplified by readily available online information and reviews, empowers consumers. For example, a 2023 valuation of the global musical instruments market at approximately $17 billion underscores a competitive environment where customer choice is paramount.
Economic conditions directly impact customer purchasing power. In 2024, factors like inflation and rising interest rates, as seen in the US impacting demand for marine products, have constrained discretionary spending. This economic sensitivity means that customers, when facing tighter budgets, become more price-conscious, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage in certain markets.
| Customer Segment | Switching Costs | Bargaining Power Factor | 2024 Market Insight |
| Individual Consumers (Musical Instruments, Motorcycles) | Low | Low (due to low individual purchase volume) | Continued demand for professionals; some price sensitivity in entry-level models. |
| Professional Musicians (Specialized Equipment) | High (for integrated systems) | Moderate (due to investment in ecosystems) | Resilience in professional instrument sales. |
| Large Corporate Clients (B2B Audio, Industrial) | Variable | High (due to significant purchase volume) | Potential to influence pricing and terms for substantial orders. |
| General Consumers (Electronics) | Low | Moderate (due to information accessibility) | E-commerce growth ($6.3T in 2023) empowers comparison shopping. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Yamaha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Yamaha Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape for Yamaha. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted document immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use, ensuring no surprises and full utility.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Yamaha faces intense competition across its various business lines. In the musical instrument sector, it vies with established names like Roland, Kawai, and Fender, each holding significant market share. For instance, the global musical instruments market was valued at over $17 billion in 2023, indicating a crowded and dynamic landscape.
The motorcycle segment is particularly fierce, with Yamaha competing head-to-head against giants such as Honda, Suzuki, Kawasaki, and KTM. In 2023, the global motorcycle market generated revenues exceeding $75 billion, showcasing the sheer volume of players vying for consumer attention and sales.
Furthermore, Yamaha's audio equipment division contends with formidable competitors including Bose, Samsung's HARMAN division, and numerous other specialized audio manufacturers. This broad spectrum of competition, from global conglomerates to niche specialists, underscores the constant pressure Yamaha experiences to innovate and maintain its market position.
The industry growth rate presents a mixed picture for Yamaha. While the musical instruments segment is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4% to 5.7% between 2024 and 2029, offering a stable revenue stream, the audio equipment market is set for more substantial expansion, with projections indicating a CAGR of 7.06% from 2025 to 2030. This robust growth in audio presents a significant opportunity.
However, Yamaha's crucial motorcycle and powersports divisions face more complex dynamics. Developed markets, in particular, have shown mixed conditions, with some segments experiencing slower growth or even declines. This contrasts with the more optimistic outlook in its electronics and musical instrument businesses.
Yamaha excels at product differentiation, leveraging its reputation for superior quality, continuous innovation, and a rich brand heritage spanning over a century. This approach cultivates significant brand loyalty, especially in its premium offerings like high-end musical instruments and performance motorcycles, where customers often prioritize performance and reputation over price.
This strong brand loyalty acts as a buffer against intense price competition, particularly in niche markets. For instance, Yamaha's acoustic guitars consistently rank high in customer satisfaction surveys, reflecting a deep-seated trust in the brand's craftsmanship and sound quality.
However, maintaining this differentiation proves more challenging in mass-market segments. While Yamaha offers a broad product portfolio, including entry-level instruments and scooters, the competitive landscape here often intensifies, with rivals frequently competing on price, making it harder for Yamaha to command premium pricing.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Industries where Yamaha operates, such as musical instruments and motorcycles, are characterized by substantial fixed costs. These costs are tied to research and development, extensive manufacturing facilities, and broad distribution channels. For example, the automotive sector, which includes motorcycles, often sees fixed costs representing a significant portion of total capital expenditure.
These high fixed costs can fuel aggressive price competition, particularly when demand softens. Companies feel compelled to maintain production levels to spread these overheads, leading to price wars as they try to capture market share.
Furthermore, significant exit barriers intensify this rivalry. These barriers can include specialized machinery, dedicated labor forces, and long-term supplier contracts that make it costly and difficult for companies to leave the market. This inflexibility forces players to compete fiercely within the existing structure.
- High Capital Investment: Industries like motorcycle manufacturing require substantial upfront investment in factories and technology, often in the billions for global operations.
- Economies of Scale Pressure: To recoup large fixed costs, companies must achieve high production volumes, driving a constant need to sell more units, which can lead to price cuts.
- Specialized Assets: The tooling and equipment used in manufacturing motorcycles or musical instruments are often highly specialized, limiting their resale value and increasing exit costs.
- Brand Loyalty and R&D: Continuous investment in R&D and brand building adds to fixed costs, creating a barrier for new entrants and intensifying competition among established players.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Yamaha's proactive approach to strategic partnerships and acquisitions is a key factor in navigating competitive rivalry. For instance, their collaboration with Shippeo aims to streamline supply chain operations, a critical area for efficiency in manufacturing. Furthermore, the acquisition of Torqeedo GmbH strengthens Yamaha's position in the burgeoning electric marine propulsion market, a significant growth area.
This strategic maneuvering is mirrored across the industry. Competitors are also consolidating their positions through similar actions. Bose's acquisition of McIntosh Group and Samsung's purchase of Roon exemplify this trend, highlighting a broader industry movement towards acquiring technology and market access. This ongoing consolidation suggests a heightened level of competition where strategic alliances and M&A activity are becoming standard tools for gaining an edge.
- Yamaha's partnership with Shippeo targets supply chain optimization.
- Acquisition of Torqeedo GmbH bolsters Yamaha's electric marine propulsion capabilities.
- Industry consolidation is evident with Bose acquiring McIntosh Group.
- Samsung's acquisition of Roon indicates strategic positioning in audio technology.
Yamaha operates in highly competitive markets, including musical instruments, motorcycles, and audio equipment, facing established giants like Honda, Roland, and Bose. The global motorcycle market alone exceeded $75 billion in 2023, highlighting the intense rivalry. This crowded landscape forces Yamaha to constantly innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain market share and customer loyalty across its diverse product lines.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Yamaha is significant, as customers seeking entertainment or transportation can find alternatives that meet their needs in different ways. For musical instruments, these substitutes range from digital music production software, which allows for virtual instrument creation, to other leisure activities that compete for disposable income and attention. In 2024, the global digital audio workstation market was valued at over $1.5 billion, demonstrating a robust alternative for music creation.
In the powersports segment, Yamaha faces substitutes like public transportation, conventional automobiles, and other recreational pursuits. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles and ride-sharing services directly impacts the demand for personal recreational vehicles. For instance, ride-sharing services in major urban centers continue to grow, offering a cost-effective and convenient alternative to personal powersports ownership for many consumers.
The threat of substitutes for Yamaha's products significantly hinges on their relative price and performance. When alternative products offer similar or even better functionality at a lower cost, the pressure on Yamaha intensifies. This is particularly evident in the musical instrument segment, where digital pianos and electronic drum kits provide more budget-friendly entry points compared to traditional acoustic instruments, attracting a wider range of consumers, especially beginners.
In the motorcycle division, a similar trend is observed. The growing popularity of smaller, more economical motorcycles as substitutes for larger, premium models directly impacts Yamaha's market share and pricing power. For instance, in 2024, the global market for entry-level motorcycles saw robust growth, driven by affordability and fuel efficiency, presenting a clear challenge to manufacturers of higher-displacement bikes.
Customer willingness to switch to substitutes is a significant factor for Yamaha. This propensity is influenced by the ease of switching, the cost involved, and the overall value customers perceive from alternative options. For instance, a musician might consider a digital audio workstation (DAW) software, which can cost as little as $100 for basic versions in 2024, as a substitute for traditional instruments, especially if they prioritize convenience and affordability.
The increasing prevalence of e-commerce platforms and mobile technology further facilitates this substitution. Consumers can readily compare prices and features of various musical instruments and entertainment alternatives online, making it simpler to explore options beyond Yamaha's traditional offerings. Reports from 2024 indicate that online retail sales for musical instruments have seen a steady increase, suggesting a growing comfort level with digital purchasing and a broader exposure to substitutes.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological progress often lowers the cost and improves the performance of substitute products, making them more attractive. For instance, in the music industry, advancements in digital synthesizers and MIDI controllers have significantly boosted their appeal and accessibility, offering alternatives to traditional acoustic instruments.
Consider the automotive sector: the increasing sophistication and range of electric vehicles (EVs) present a growing substitute threat to internal combustion engine (ICE) motorcycles. As EV technology matures, their performance, charging infrastructure, and overall cost-effectiveness are steadily improving, potentially drawing consumers away from traditional motorcycle purchases.
- Technological innovation in areas like battery technology and motor efficiency directly impacts the viability of electric bikes as substitutes for gasoline-powered motorcycles.
- Market penetration of EVs globally reached approximately 16% of all new car sales in 2023, a significant increase from previous years, indicating a broader trend of technological substitution across transportation sectors.
- Improvements in digital audio workstations (DAWs) and virtual instruments have democratized music creation, offering powerful alternatives to expensive hardware and studio time, thereby impacting the market for traditional musical equipment.
Shifting Consumer Lifestyles and Preferences
Changes in consumer lifestyles, particularly the waning demand for outdoor recreation gear that surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, can elevate the threat of substitutes for companies like Yamaha. As consumer spending patterns evolve, resources previously allocated to recreational activities might be redirected towards entirely different categories, making existing products less attractive. For instance, a post-pandemic return to office work might reduce the need for camping equipment, pushing consumers toward home entertainment or other services.
Conversely, trends like increasing urbanization and the pervasive influence of social media can simultaneously foster demand for certain Yamaha product lines, such as musical instruments. The desire for personal expression and creative outlets, often amplified through online platforms and community engagement, can drive individuals to take up music. This creates a dynamic where while some product categories face intensified substitution threats due to lifestyle shifts, others might see increased demand, illustrating the nuanced impact of changing consumer behavior.
For example, the global musical instruments market was valued at approximately $15.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a resilience to broader lifestyle shifts in certain segments. However, the rise of digital music creation tools and accessible online tutorials offers readily available substitutes for traditional instrument learning and practice, posing a threat to established markets.
- Shifting Lifestyles: A decline in pandemic-fueled outdoor recreation spending can lead consumers to substitute these activities with other forms of leisure.
- Urbanization & Social Media: These factors can boost demand for personal musical instruments as outlets for creativity and online expression.
- Market Dynamics: The musical instruments market, valued around $15.5 billion in 2023, shows segment-specific vulnerabilities to substitutes like digital music production tools.
The threat of substitutes for Yamaha is substantial, stemming from various alternatives across its diverse product portfolio. For musical instruments, digital music production software and other leisure activities represent key substitutes, with the global digital audio workstation market exceeding $1.5 billion in 2024. In the powersports segment, substitutes include public transport, conventional cars, and alternative recreational pursuits, with ride-sharing services in urban areas offering a growing alternative to personal vehicle ownership.
The attractiveness of substitutes is heavily influenced by their price and performance relative to Yamaha's offerings. Budget-friendly digital pianos and electronic drum kits, for example, provide accessible entry points for aspiring musicians, challenging traditional acoustic instruments. Similarly, the increasing demand for smaller, more economical motorcycles in 2024 directly competes with Yamaha's higher-displacement models, impacting market share and pricing strategies.
Customer willingness to switch is a critical factor, driven by the ease and cost of adoption, alongside the perceived value of alternatives. Digital audio workstations, with basic versions available for around $100 in 2024, present a compelling substitute for musicians prioritizing convenience and affordability. E-commerce platforms further ease this transition by enabling easy price and feature comparisons across a wide array of musical instruments and entertainment options.
Technological advancements continuously enhance the performance and reduce the cost of substitutes, intensifying competitive pressure. Improvements in electric vehicle technology, including battery efficiency and charging infrastructure, are making EVs increasingly viable substitutes for gasoline-powered motorcycles. Concurrently, advancements in digital synthesizers and MIDI controllers broaden the appeal and accessibility of electronic music creation tools as alternatives to traditional instruments.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Factors Influencing Substitution | Yamaha's Affected Segments | Relevant 2024 Data Point |
| Digital Music Creation | DAWs, Virtual Instruments, Music Production Software | Cost, Accessibility, Ease of Use, Creative Potential | Musical Instruments (Keyboards, Guitars, Drums) | Global DAW market > $1.5 billion |
| Alternative Transportation | Ride-sharing, Public Transport, Electric Scooters | Cost, Convenience, Environmental Concerns, Urban Mobility | Motorcycles, Scooters | Growth in ride-sharing services in major cities |
| Other Leisure Activities | Gaming, Streaming Services, Social Media, Other Sports | Disposable Income, Entertainment Value, Time Commitment | All Yamaha Segments (Indirectly) | Consumer spending shifts away from recreational goods |
| Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Electric Motorcycles, Electric Cars | Performance, Range, Charging Infrastructure, Purchase Price | Motorcycles | Increasing EV market penetration |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the musical instrument manufacturing sector, where Yamaha is a major player, demands considerable upfront capital. Consider the investment needed for research and development to create innovative new products, the construction and equipping of advanced manufacturing plants, and the establishment of robust global distribution and sales networks. These high initial costs create a significant hurdle for any new company aspiring to compete with established giants like Yamaha.
Similarly, the powersports industry, another key segment for Yamaha, presents substantial capital requirements. Building a new powersports brand involves massive investment in engineering, design, testing, and production facilities for vehicles like motorcycles, ATVs, and snowmobiles. Furthermore, establishing a reliable supply chain and a widespread dealer network across diverse geographical markets adds another layer of significant financial commitment, effectively deterring many potential entrants.
For context, in 2023, Yamaha Motor reported capital expenditures of approximately ¥277.7 billion (around $1.9 billion USD based on average exchange rates), highlighting the scale of investment required to maintain and expand operations in competitive markets. This figure underscores the financial muscle needed to even consider entering such industries, making it a formidable barrier for new players.
Established players like Yamaha leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing, sourcing components, and marketing efforts. This translates to lower per-unit production costs, a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, Yamaha's vast global production network in 2024 allows for bulk purchasing discounts on raw materials and components, further driving down their cost base.
New entrants would find it exceptionally challenging to match Yamaha's cost efficiencies without achieving substantial production volumes from the outset. This lack of scale makes competing on price a difficult proposition. Without the ability to spread fixed costs over a large output, their initial pricing would likely be uncompetitive, hindering market penetration.
Yamaha benefits from a robust global brand reputation, meticulously cultivated over many decades, especially within the musical instruments and motorcycle sectors. This deep-rooted brand loyalty means potential new entrants face a substantial barrier, as they would need to pour significant resources into branding and marketing to even begin to challenge Yamaha's established consumer connection.
Access to Distribution Channels
The threat of new entrants into the musical instrument market, particularly for a company like Yamaha, is significantly impacted by access to distribution channels. Yamaha has cultivated an extensive and well-established global network. This includes dedicated specialty stores, a robust online presence, and a vast array of authorized dealerships worldwide.
New companies attempting to enter this market will find it exceptionally difficult to replicate such widespread reach. They must either invest heavily in building their own distribution infrastructure from scratch, a process that is both capital-intensive and time-consuming, or they need to secure shelf space and partnerships within existing retail networks. This latter option often involves facing fierce competition for limited space and potentially unfavorable terms from established distributors who are already aligned with major players like Yamaha.
Consider the sheer scale: By the end of 2024, Yamaha Corporation reported a consolidated net sales figure of ¥1.75 trillion, a substantial portion of which is driven by its musical instrument division and its ability to get products into the hands of consumers globally. New entrants simply do not possess this existing infrastructure, making it a significant barrier. For example, a new entrant might struggle to secure placement in major music retail chains that already dedicate significant floor space and marketing efforts to Yamaha products.
- Extensive Global Reach: Yamaha's established network of specialty stores, online channels, and dealerships offers unparalleled market access.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants face substantial financial and temporal investments to build comparable distribution capabilities.
- Competition for Retail Space: Securing placement in established retail channels is challenging due to existing relationships with major brands like Yamaha.
- Brand Loyalty and Recognition: Existing brands benefit from consumer trust, further complicating market entry for new players.
Regulatory Hurdles and Proprietary Technology
The powersports industry, where Yamaha operates, presents significant regulatory hurdles for new entrants. Compliance with stringent safety standards, emissions regulations, and environmental protection laws requires substantial investment and expertise. For instance, in the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets strict emissions standards for off-road vehicles, which can be costly for new manufacturers to meet.
Yamaha's strong position is further bolstered by its proprietary technologies and extensive patent portfolio. These innovations in engine design, materials science, and manufacturing processes create a high barrier to entry. Replicating Yamaha's advanced technological capabilities and efficient production lines would demand considerable time and capital, making it challenging for newcomers to compete on a level playing field.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants in powersports face significant upfront costs for meeting safety and environmental regulations, which can run into millions of dollars.
- Patented Technologies: Yamaha holds numerous patents, particularly in areas like fuel injection systems and lightweight alloy construction, which are difficult and expensive to circumvent.
- Research and Development Investment: The substantial ongoing investment Yamaha makes in R&D to maintain its technological edge deters potential competitors who lack similar financial resources.
- Manufacturing Expertise: Yamaha's decades of experience and specialized manufacturing processes, refined for efficiency and quality, are not easily replicated by new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Yamaha is generally low to moderate, largely due to the substantial capital requirements, established brand loyalty, and complex distribution networks inherent in its core industries. High upfront costs for research, development, manufacturing, and global sales infrastructure present significant barriers.
In 2023, Yamaha Motor's capital expenditures were approximately ¥277.7 billion (roughly $1.9 billion USD), showcasing the immense investment needed. This financial muscle, combined with economies of scale in manufacturing and sourcing, allows Yamaha to maintain cost efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to match.
Yamaha's strong brand reputation, built over decades, further deters new entrants. For instance, in the musical instrument sector, a new company must invest heavily in marketing to even begin challenging Yamaha's established consumer connection, a task made even harder by the difficulty in securing widespread distribution channels.
The powersports industry adds regulatory compliance and proprietary technology as further deterrents. Meeting stringent safety and emissions standards, coupled with circumventing Yamaha's patented innovations, requires substantial financial and technical resources, making market entry a formidable challenge.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for Yamaha |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment in R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Yamaha Motor's 2023 CapEx of ¥277.7 billion. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Established trust and recognition among consumers. | Decades of cultivated loyalty in musical instruments and motorcycles. |
| Distribution Channels | Extensive global networks of stores, dealerships, and online presence. | Yamaha's widespread network for musical instruments and powersports. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Unique innovations and protected intellectual property. | Patents in engine design and lightweight materials for powersports. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent safety, emissions, and environmental laws. | EPA emissions standards for off-road vehicles in powersports. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Yamaha leverages data from company annual reports, investor relations websites, and industry-specific trade publications to understand competitive dynamics. We also incorporate market research reports and economic indicators to assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
