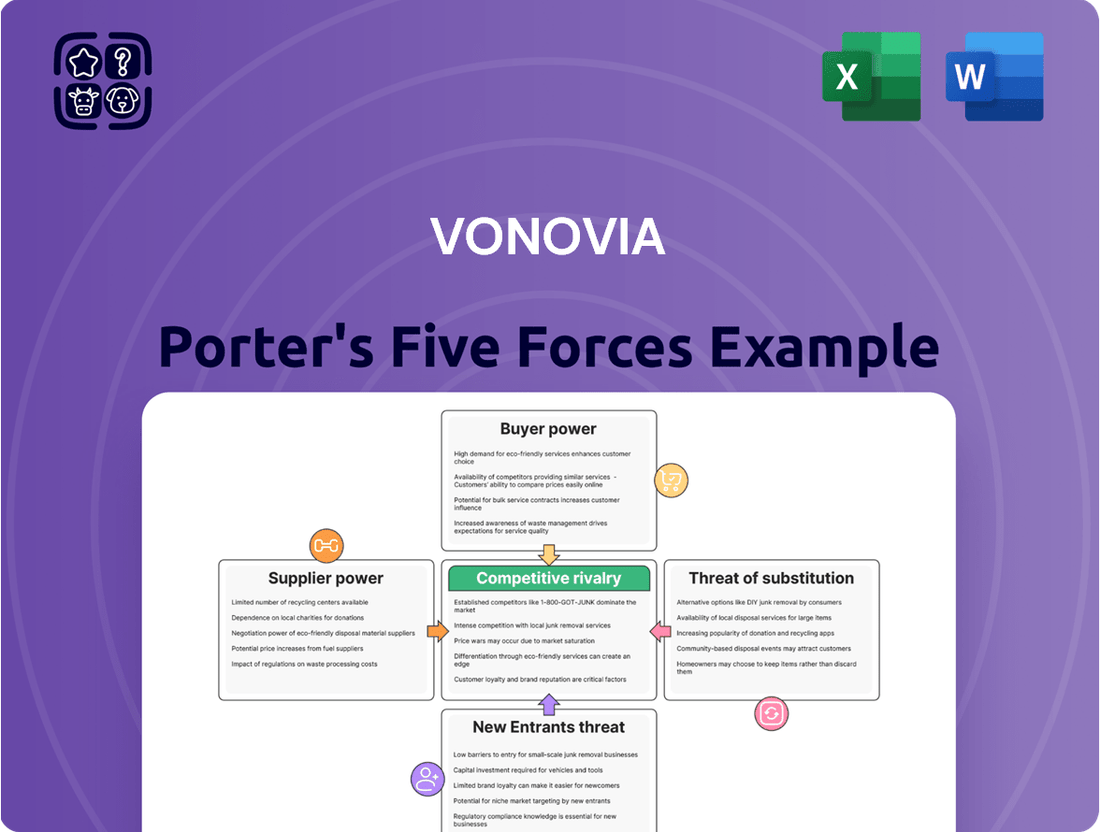
Vonovia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Vonovia Bundle
Vonovia, a giant in the European housing market, faces a complex web of competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing players, the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers, and the ever-present threat of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success. This brief overview hints at the pressures Vonovia navigates, but the full picture is far more detailed.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis dives deep into each of these elements, revealing the specific dynamics impacting Vonovia's profitability and market share. It unpacks the leverage held by tenants, the influence of construction material providers, and the potential disruption from alternative housing solutions.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Vonovia’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Vonovia is influenced by market concentration. If a few large construction firms or specialized maintenance providers dominate, they can exert greater influence on pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the German construction sector faced skilled labor shortages, potentially increasing the leverage of major contracting companies.
However, Vonovia's substantial operational scale, managing over 560,000 residential units as of year-end 2023, provides a significant counter-advantage. This scale allows Vonovia to negotiate bulk purchasing agreements and long-term contracts, often securing more favorable pricing and conditions than smaller competitors might achieve.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Vonovia is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Vonovia faces high costs in moving from one supplier to another, particularly for integrated systems or specialized property management software, the existing supplier gains leverage. Consider that in 2023, Vonovia's operating expenses were €3.7 billion, and a substantial portion of this could be tied to supplier contracts where switching is complex.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Vonovia is influenced by the uniqueness and differentiation of the materials and services they provide. When suppliers offer highly specialized or essential components with limited substitutes, their leverage grows. This is particularly relevant for Vonovia in areas like advanced sustainable building materials or cutting-edge smart home technologies, where few alternatives exist.
In 2024, the demand for green building certifications and smart home integration is expected to continue its upward trend, increasing the importance of suppliers who can meet these specific needs. For instance, a supplier of certified low-carbon concrete or a provider of sophisticated energy management systems for residential buildings would hold significant power due to the specialized nature of their offerings and the growing market demand for such innovations within the real estate sector.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers for Vonovia hinges on how crucial their inputs are to Vonovia's operational costs and the quality of its properties. Suppliers providing essential construction materials or vital facility management services, which directly influence property value and maintenance expenses, wield significant influence. For instance, in 2024, the construction sector experienced continued volatility in material prices, such as concrete and steel, impacting developers and property managers like Vonovia. This volatility can strengthen suppliers' positions if demand for these materials outstrips supply.
Key factors influencing supplier power include:
- Concentration of Suppliers: If a few suppliers dominate the market for specific essential components or services, their collective bargaining power increases.
- Uniqueness of Input: Suppliers offering specialized products or services that are difficult for Vonovia to substitute possess greater leverage.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing suppliers for critical inputs, whether financial, operational, or technical, empower existing suppliers.
- Threat of Forward Integration: If suppliers can credibly threaten to enter Vonovia's business themselves, they gain leverage.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for Vonovia is influenced by the threat of forward integration. If suppliers, particularly large construction conglomerates, were to enter property development or management, they could significantly increase their leverage over Vonovia. This potential move would compel Vonovia to cultivate strong supplier relationships to mitigate such a risk.
For instance, in 2024, the construction industry, a key supplier sector for property management and development, faced ongoing labor shortages and rising material costs, estimated at 5-10% increases for certain key inputs like concrete and steel. This environment already gives some larger construction firms considerable sway.
- Supplier Forward Integration: The possibility of suppliers entering Vonovia's core business of property development or management.
- Construction Conglomerates: Large, diversified construction firms are the most likely to pose a threat of forward integration.
- Industry Pressures (2024): Labor shortages and material cost increases (5-10%) in construction enhance supplier bargaining power.
- Relationship Management: Vonovia must maintain strong supplier relationships to counter potential integration threats.
Vonovia's supplier bargaining power is shaped by supplier concentration and input uniqueness. In 2024, skilled labor shortages in German construction bolstered larger contractors' leverage, a trend impacting Vonovia's procurement. The company's vast scale, managing over 560,000 units by year-end 2023, allows it to negotiate favorable bulk terms, acting as a counterbalance to supplier influence.
Switching costs also play a role; for instance, Vonovia's 2023 operating expenses of €3.7 billion included contracts where changing providers for critical systems could be complex and costly, strengthening existing supplier positions. Suppliers of specialized items like sustainable building materials or smart home technology, in demand in 2024, also command greater power due to limited alternatives.
| Factor | Vonovia Impact | 2024 Context |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Labor shortages favor larger construction firms |
| Input Uniqueness | Specialized inputs grant leverage | Demand for green tech increases supplier power |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower existing suppliers | Complex systems increase switching difficulty |
| Vonovia's Scale | Large scale provides negotiation advantage | Over 560,000 units (end 2023) aids bulk purchasing |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Vonovia's operating environment, assessing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Pinpoint the exact sources of competitive pressure—from buyer power to new entrants—and proactively address them.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Vonovia's customers, primarily tenants, is significantly shaped by the availability of alternative housing. In areas where there are many vacant properties or where demand for housing is softening, tenants gain leverage to negotiate favorable lease terms or switch to landlords offering better deals. For instance, in late 2023, Germany experienced a slight increase in the vacancy rate in some urban centers, offering tenants more choices and thus increasing their power.
Conversely, when housing markets are tight, with low vacancy rates and high demand, the bargaining power of tenants naturally decreases. In such scenarios, landlords like Vonovia face less pressure to offer concessions, as they can readily find new tenants. Vonovia's strong presence in many German cities means that in markets where they are a dominant provider, tenant options are inherently limited, further concentrating power with the landlord.
The bargaining power of customers for Vonovia, primarily its tenants, is influenced by the cost and hassle associated with switching. For instance, in 2024, the average cost of moving within Germany, considering factors like movers, packing, and potential temporary housing, can easily run into hundreds or even thousands of euros. This financial barrier, alongside the logistical complexities of finding new accommodation and managing the relocation process, significantly dampens a tenant's inclination to switch providers.
This "stickiness" means that even if comparable rental options are available, the effort and expense involved often deter tenants from exercising their power to switch. Vonovia benefits from this inertia, as it reduces the churn rate and provides a more stable rental income stream.
Buyer power significantly influences Vonovia's operations, particularly concerning tenant price sensitivity. When economic conditions tighten, like the rising inflation observed through much of 2023 and into early 2024, tenants have less disposable income. This makes them more inclined to resist rent increases or even seek lower prices, thereby strengthening their bargaining position against landlords like Vonovia.
Vonovia's strategic focus on providing affordable housing is a direct response to this buyer power. By offering competitive or lower-than-market rents, they aim to reduce tenant sensitivity to price changes. For example, in 2023, while general inflation rates were high, Vonovia's rental income growth was carefully managed to balance market demands with tenant affordability, aiming for a stable occupancy rate rather than aggressive price hikes.
Buyer Power 4
The bargaining power of customers for Vonovia is significantly influenced by Germany's robust regulatory environment. Rent control measures and tenant protection laws are key factors. These regulations limit landlords' ability to arbitrarily increase rents or terminate leases, thereby bolstering the position of tenants.
These legal frameworks directly impact Vonovia's pricing flexibility and operational freedom. For instance, in 2023, Germany's federal government extended a rent brake (Mietpreisbremse) in many areas, capping rent increases to 15% above local comparable rents when re-letting apartments. This directly curtails Vonovia's potential revenue growth from rent adjustments.
Furthermore, tenant protection laws make it more difficult and costly for landlords to evict tenants, even in cases of non-payment or lease violations, requiring adherence to strict legal procedures. This increases the overall leverage tenants possess in their dealings with Vonovia.
- Regulatory Impact: Rent control and tenant protection laws in Germany significantly enhance customer bargaining power.
- Pricing Constraints: Measures like the Mietpreisbremse limit Vonovia's ability to adjust rental prices freely.
- Operational Limitations: Stricter eviction rules reduce landlord flexibility and increase tenant leverage.
- Compliance Necessity: Vonovia must navigate and comply with these regulations, impacting its strategic decisions.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers for Vonovia is significantly influenced by tenant organization and advocacy. Collective action through tenant unions or similar groups can amplify individual tenant concerns, leading to greater leverage in negotiations. These organized bodies can push for improved living conditions and influence housing policy, directly impacting Vonovia's operational environment.
While individual tenants might possess limited power against a large entity like Vonovia, their collective strength can be substantial. For example, in Germany, tenant associations actively engage with housing companies, advocating for rent stability and better maintenance standards. In 2024, discussions around rent control and tenant rights remained prominent in the German housing market, highlighting the ongoing influence of organized tenant groups.
- Tenant Unions: These groups provide a unified voice for tenants, enabling them to negotiate collectively with landlords.
- Advocacy Groups: Organizations focused on housing rights can lobby for legislative changes that benefit tenants.
- Collective Bargaining: Organized tenants can demand better lease terms, improved property maintenance, and fairer rent adjustments.
- Public Opinion: Tenant advocacy can shape public perception, potentially pressuring companies like Vonovia to adopt more tenant-friendly practices.
The bargaining power of Vonovia's customers, primarily tenants, is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative housing and the costs associated with moving. In 2024, the average cost of moving within Germany can range from several hundred to over a thousand euros, acting as a significant deterrent for tenants considering a switch, which benefits Vonovia by reducing churn.
Tenant price sensitivity is heightened during periods of economic strain, such as the inflation experienced in late 2023 and early 2024, compelling tenants to resist rent increases and seek more affordable options. Vonovia's strategy of offering competitive rents aims to mitigate this by maintaining stable occupancy rates rather than pursuing aggressive price hikes.
Germany's regulatory landscape, including rent control measures like the Mietpreisbremse, which capped rent increases to 15% above local comparable rents when re-letting apartments in 2023, directly constrains Vonovia's pricing flexibility and enhances tenant leverage. Tenant protection laws also make evictions more complex, further empowering tenants.
Tenant organizations and advocacy groups play a crucial role in amplifying individual tenant concerns, leading to collective bargaining power. In 2024, ongoing discussions about rent control and tenant rights in Germany underscore the sustained influence of these organized groups on housing market dynamics.
| Factor | Impact on Vonovia | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Housing Availability | Increases tenant power in softer markets. | Slight increase in urban vacancy rates in late 2023. |
| Switching Costs (Moving Expenses) | Reduces tenant inclination to switch. | Average moving costs can exceed €1,000. |
| Tenant Price Sensitivity (Inflation) | Drives demand for lower rents. | Inflationary pressures in late 2023/early 2024 impacted disposable income. |
| Regulatory Environment (Rent Control) | Limits rent adjustment potential. | Mietpreisbremse capped rent increases to 15% above local rates in many areas in 2023. |
| Tenant Organization | Enhances collective bargaining leverage. | Tenant rights discussions remained prominent in the German housing market in 2024. |
Full Version Awaits
Vonovia Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Vonovia Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the real estate sector. This detailed analysis will equip you with critical insights into Vonovia's strategic positioning and potential challenges. The document is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The German residential real estate market, while dominated by Vonovia, features significant competition. Deutsche Wohnen and LEG Immobilien are substantial listed rivals, directly vying for market share and attractive portfolios. This intense rivalry is further amplified by a multitude of smaller, regional landlords and housing cooperatives, particularly in specific local markets.
The competitive rivalry within the residential real estate sector, a key factor for companies like Vonovia, is significantly shaped by market growth rates. In 2024, the German residential real estate market experienced a slowdown, with transaction volumes decreasing. This environment tends to intensify competition as companies vie more aggressively for a shrinking pool of available properties and tenants, potentially leading to price pressures.
When market growth is sluggish, as it has been in parts of Europe recently, existing players are more inclined to compete fiercely for market share. This can manifest as more aggressive bidding on properties, enhanced customer service offerings, or innovative product development to attract and retain tenants. For instance, in 2023, some German cities saw slight declines in rental prices, indicating increased competition among landlords.
Conversely, a booming market allows companies to expand their portfolios and increase revenues without needing to directly challenge competitors for their existing assets. However, even in growth periods, differentiation through service quality, sustainability initiatives, or specialized housing segments remains crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Vonovia, for example, has been investing in energy efficiency upgrades, a differentiator that can attract environmentally conscious tenants.
The fragmentation of the residential real estate market also plays a role. While large players like Vonovia exist, the presence of numerous smaller, regional property management firms and private investors means that rivalry can be widespread. This diverse competitive landscape necessitates continuous adaptation and strategic maneuvering to maintain market leadership.
The competitive rivalry in the residential rental market, particularly for standard properties, is intense due to a lack of significant product differentiation. This commoditization means companies like Vonovia often find themselves competing primarily on price, location, and the quality of tenant services, rather than unique property features. This pressure can indeed lead to downward pressure on rental yields as companies vie for tenants.
In 2024, the German rental market continued to see high demand, but this also fueled competition. For instance, while Vonovia invested heavily in modernization, the fundamental offering of a rental apartment remains similar across many providers. This intense rivalry means that any increase in rental prices must be carefully balanced against the risk of tenant churn to competitors who might offer slightly lower rents or more convenient service packages.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The real estate sector, particularly for large entities like Vonovia, experiences significant competitive rivalry. High exit barriers are a major contributing factor. These barriers include the inherent illiquidity of substantial property portfolios and the massive capital investments required to acquire and maintain them. This means that companies find it difficult and costly to leave the market, even during challenging economic periods. Consequently, firms are compelled to engage in aggressive competition to secure tenants and generate revenue, rather than simply selling off assets to exit.
This market dynamic effectively traps competitors, intensifying the struggle for market share and profitability. For instance, in 2024, the German rental market, a key operational area for Vonovia, continued to see high occupancy rates, but also sustained competition for desirable properties and tenants, particularly in major urban centers. Companies must constantly innovate and offer competitive rental terms and property management services to retain and attract residents.
- Illiquidity of Assets: Large real estate portfolios are not easily or quickly sold, locking companies into the market.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront and ongoing capital is needed, making market exit financially prohibitive.
- Forced Competition: Companies must compete vigorously to maintain occupancy and revenue, even in unfavorable market conditions.
- Tenant Retention Focus: The inability to exit quickly shifts strategic focus towards retaining existing tenants and attracting new ones through competitive offerings.
Competitive Rivalry 5
The competitive rivalry within the German real estate market, particularly for a company like Vonovia, is shaped by strategic alliances and consolidation. Past mergers, such as the significant consolidation observed in the German housing market, have reduced the number of independent players, leading to the emergence of larger, more powerful competitors. This consolidation can intensify the competition for acquiring new properties or portfolios, thereby altering existing market power dynamics.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a dynamic interplay of mergers and acquisitions (M&A). For instance, in 2023, significant M&A activity continued to reshape the sector, with companies seeking scale and efficiency. This trend suggests that rivalry isn't just about organic growth but also about strategic maneuvering through deal-making, which can create formidable rivals with expanded market share and resources.
- Mergers and acquisitions are key drivers of competitive intensity, as seen with ongoing consolidation in the European real estate sector.
- Past consolidation in Germany has created larger entities, increasing the scale of competition for prime assets.
- Strategic alliances can emerge as competitors seek to pool resources or expertise, further complicating the rivalry.
- The ongoing pursuit of scale through M&A by competitors directly impacts Vonovia's strategic options and market positioning.
The competitive rivalry for Vonovia is intense, fueled by the illiquidity of real estate assets and high capital investment, which forces companies to compete rather than exit. This dynamic is evident in 2024 German market trends, where despite high occupancy, firms like Vonovia face constant pressure to attract and retain tenants through competitive offerings.
The German residential market, though led by Vonovia, sees significant competition from major listed rivals like Deutsche Wohnen and LEG Immobilien, alongside numerous smaller regional players. This fragmented yet substantial competition intensifies the struggle for market share, especially in a slowing market environment where transaction volumes decreased in 2024, potentially leading to price pressures.
Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is a key strategy, as seen with ongoing M&A activity in 2023 reshaping the sector. This pursuit of scale creates formidable competitors and directly influences Vonovia's market positioning and strategic choices.
| Competitor | Approximate Number of Units (as of late 2023/early 2024) | Key Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Vonovia | ~700,000 | Germany, Sweden, Austria |
| Deutsche Wohnen | ~155,000 | Germany (primarily Berlin) |
| LEG Immobilien | ~160,000 | Germany (primarily North Rhine-Westphalia) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Homeownership is the most significant substitute for Vonovia's rental services. The appeal of buying a home versus renting is heavily influenced by economic conditions. For instance, in Germany, where Vonovia is a major player, average mortgage interest rates remained relatively low for much of 2023, around 3.5%, making ownership a more attractive proposition for some. However, by early 2024, these rates saw an uptick, potentially dampening the immediate appeal of buying.
Alternative housing models present a notable threat to traditional rental apartment providers like Vonovia. Co-living spaces, for instance, are gaining traction, especially among younger demographics seeking community and flexibility. In 2024, the co-living market continued its expansion, with notable growth in major European cities where Vonovia has a strong presence. These alternatives, while not always a direct long-term replacement, can siphon off demand from specific segments, particularly those prioritizing social interaction or short-to-medium-term flexibility over a traditional lease.
The perceived value and convenience of renting versus owning or other housing options significantly shape the threat of substitution for Vonovia. If renting offers clear advantages, such as greater flexibility to relocate for jobs or a lack of maintenance burdens, this can reduce the appeal of ownership and therefore the threat to Vonovia's core business. For instance, in 2024, rising interest rates in many European markets made outright homeownership less accessible for some, potentially increasing the attractiveness of renting as a more manageable financial commitment.
Conversely, if the desire for stability, long-term asset building, and customization drives consumer choice, then owning a home or exploring alternative housing models that offer these benefits would pose a greater threat. The societal emphasis on property as a primary investment vehicle can bolster this threat. In 2023, despite economic headwinds, the long-term investment case for real estate remained a strong motivator for many potential buyers, presenting a direct alternative to Vonovia's rental offerings.
Threat of Substitution 4
The threat of substitutes for Vonovia, primarily concerning alternative housing solutions like cooperatives or build-to-rent developments, is significantly influenced by prevailing economic conditions and evolving consumer preferences. During periods of economic uncertainty, such as potential recessions, the appeal of renting as a more flexible and less capital-intensive option often increases. This can bolster the demand for rental properties, potentially benefiting companies like Vonovia, but it also highlights the attractiveness of substitute housing models that may offer similar flexibility.
Conversely, a robust economy can shift preferences towards homeownership, thereby reducing the direct substitution threat from renting. However, this economic strength can also fuel investment in other forms of housing ownership or development, such as shared equity schemes or custom-built homes, which act as substitutes. For instance, rising interest rates, a common feature in strengthening economies, can make mortgages less affordable, pushing more individuals towards rental markets and thus increasing the perceived threat from alternative rental providers.
In 2024, the German housing market, Vonovia's core territory, has experienced fluctuating economic signals. While inflation concerns have eased somewhat from previous years, interest rates remain elevated, impacting affordability for potential homebuyers. This environment makes renting a more viable option for many, but also puts pressure on rental prices. The threat of substitutes is therefore shaped by the delicate balance between affordability, lifestyle choices, and investment opportunities in the housing sector.
Key factors influencing the threat of substitutes for Vonovia in 2024 include:
- Economic Sensitivity: Shifts in disposable income and consumer confidence directly impact the willingness and ability to invest in homeownership versus renting.
- Alternative Housing Models: The growth of co-living spaces, micro-apartments, and build-to-rent projects offers direct competition to traditional rental offerings.
- Interest Rate Environment: Higher mortgage rates can increase demand for rentals, but also make investment in buy-to-let properties by individuals a more attractive substitute for institutional landlords.
- Regulatory Landscape: Government policies promoting affordable housing or specific ownership models can alter the competitive landscape and the attractiveness of substitutes.
Threat of Substitution 5
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the threat of substitutes for rental companies like Vonovia. For instance, incentives encouraging homeownership can directly compete with the rental market. In 2024, many European governments continued to offer various programs, such as subsidized mortgages or tax deductions for property owners, which can make purchasing a home more appealing than renting.
Conversely, tighter lending regulations, which were observed in some markets throughout 2024, can make it harder for individuals to secure mortgages. This can, in turn, bolster demand for rental properties, thereby mitigating the threat of substitutes. The effectiveness of these policies varies by region, impacting Vonovia’s market dynamics differently across its operational areas.
The availability and attractiveness of alternative housing solutions, such as co-living spaces or build-to-rent developments, also represent a growing substitution threat. These models often cater to specific demographics, offering flexibility and community, which can appeal to renters seeking alternatives to traditional long-term leases. By 2024, the co-living sector had seen notable investment, indicating its increasing relevance.
- Government incentives for homeownership can increase the threat of substitutes for rental providers like Vonovia.
- Stricter mortgage lending criteria can reduce the appeal of homeownership, thereby lessening the substitution threat.
- Alternative housing models, such as co-living, are emerging as significant substitutes in the rental market.
- Policy shifts in 2024 regarding housing affordability directly influence the competitive landscape for rental companies.
The threat of substitutes for Vonovia is primarily driven by the appeal of homeownership and the rise of alternative housing models. Economic factors, particularly interest rates and affordability, significantly influence consumer choices between renting and buying. In 2024, higher mortgage rates in Germany, for instance, made renting more attractive for some, yet also spurred investment in buy-to-let properties as a substitute.
| Substitute Type | Key Influencing Factors (2024) | Impact on Vonovia |
|---|---|---|
| Homeownership | Mortgage interest rates, housing prices, disposable income | Higher rates can increase demand for rentals, but robust property markets offer a strong alternative |
| Co-living/Alternative Models | Demand for flexibility, community, affordability | Siphons off specific demographic segments, particularly younger renters |
| Government Policies | Homeownership incentives, lending regulations | Can either bolster or mitigate the threat of substitutes depending on policy direction |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for a company like Vonovia is generally considered low, primarily due to the substantial capital requirements involved in the residential real estate sector. Acquiring and managing a portfolio of the scale Vonovia operates demands significant financial investment, creating a high barrier for new companies aiming to enter the market and compete effectively on size and scope. For instance, Vonovia's portfolio in 2024 comprised approximately 530,000 units, representing billions in asset value, which would be incredibly challenging for a new entrant to replicate quickly.
The threat of new entrants for Vonovia, a major player in the German real estate market, is relatively low. This is primarily due to the significant economies of scale that incumbents like Vonovia already enjoy. Managing a vast portfolio of properties, as Vonovia does, allows for substantial cost advantages in areas like property maintenance, procurement of services, and administrative overhead. For instance, Vonovia's purchasing power for maintenance and renovation services can secure better pricing than a smaller, newer company could achieve.
New entrants would face considerable hurdles in replicating Vonovia's operational efficiencies. Building out the necessary infrastructure and achieving the volume to match Vonovia's cost per unit would require immense capital investment and time. Without this scale, new companies would struggle to compete on price or service quality, especially in a market where established players benefit from optimized processes developed over years of operation.
The threat of new entrants in the German residential real estate market, particularly for a company like Vonovia, is somewhat mitigated by significant barriers to entry. Access to suitable land and existing property portfolios is a considerable hurdle. Established players, including Vonovia, benefit from extensive networks and years of experience in identifying and acquiring prime locations, which are increasingly scarce in desirable urban areas.
Newcomers struggle to secure comparable assets and scale quickly to compete effectively. For instance, in 2023, the total transaction volume in German commercial real estate, a significant portion of which involves residential properties, saw a notable decrease, making it harder for new entities to enter the market through acquisitions.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants for Vonovia is generally considered moderate, largely due to significant barriers to entry in the German real estate market. These hurdles include stringent regulatory frameworks and intricate planning processes that demand specialized expertise and substantial capital investment. For instance, navigating Germany's complex zoning laws, obtaining building permits, and adhering to environmental regulations can be a time-consuming and costly endeavor for any new player looking to establish a significant presence.
These regulatory complexities translate into higher upfront costs and increased risk for potential new competitors. Acquiring land, securing financing, and managing the development process under strict German building codes and environmental standards require considerable resources and a deep understanding of the local landscape. This is particularly true in established markets where Vonovia operates, often involving the acquisition and modernization of existing, older properties which come with their own set of compliance challenges.
The capital-intensive nature of real estate development and management further acts as a deterrent. Building or acquiring a substantial portfolio of properties, as Vonovia possesses, requires immense financial backing. New entrants would need to secure significant funding to compete effectively, making it difficult for smaller or less capitalized firms to gain a foothold. For example, the sheer scale of Vonovia's portfolio, encompassing hundreds of thousands of residential units, represents a massive barrier to entry for any newcomer aiming for comparable market share.
- Regulatory Complexity: German zoning laws, building permits, and environmental regulations create substantial entry barriers.
- Capital Intensity: The high cost of acquiring and developing real estate requires significant financial resources.
- Specialized Knowledge: Navigating German property markets necessitates in-depth understanding of local laws and practices.
- Economies of Scale: Established players like Vonovia benefit from scale advantages in procurement and management, making it harder for new entrants.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants for a company like Vonovia is generally considered moderate to low. Incumbents, such as Vonovia, benefit significantly from established advantages that are difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly. These include deep-rooted tenant relationships, strong brand recognition built over years, and extensive operational expertise in managing and developing large property portfolios.
Newcomers often struggle to gain the immediate trust and operational efficiency that established players possess. They lack the ingrained market understanding and the economies of scale that Vonovia leverages. For instance, Vonovia's significant footprint in the German market, managing hundreds of thousands of units, provides substantial purchasing power and operational efficiencies that are hard to match from day one.
Barriers to entry in the residential real estate sector, particularly for large-scale operators, are substantial.
- Capital Intensity: Acquiring and developing substantial property portfolios requires enormous capital investment, a significant hurdle for new players.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex zoning laws, building permits, and tenant protection regulations demands specialized knowledge and resources.
- Reputation and Trust: Building a reliable reputation for property management and tenant services takes time and consistent performance, areas where established firms like Vonovia excel.
- Economies of Scale: Existing large operators benefit from cost efficiencies in maintenance, financing, and administration due to their sheer size, making it difficult for smaller new entrants to compete on price.
The threat of new entrants for Vonovia remains moderate, primarily due to the significant capital requirements and established economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents. New players face substantial hurdles in acquiring portfolios of comparable size and operational efficiency, making it difficult to compete on price or service from the outset. For example, Vonovia's 2024 portfolio of approximately 530,000 units represents a massive capital investment that is hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, regulatory complexities within the German real estate market, including stringent zoning laws and planning processes, add considerable cost and time for new entrants. Acquiring suitable land and navigating these legal frameworks requires specialized expertise that established companies like Vonovia have already developed. This creates a prolonged and expensive path to market entry.
The existing market structure, characterized by large, established players, also presents a significant barrier. Vonovia's strong brand recognition, established tenant relationships, and optimized operational processes, built over years, are difficult for newcomers to match. These factors contribute to a competitive landscape where achieving immediate scale and trust is a considerable challenge.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Acquiring and managing large property portfolios requires billions in investment. | High barrier; difficult for new firms to match scale. |
| Economies of Scale | Incumbents benefit from cost advantages in procurement, maintenance, and administration. | Lowers cost per unit for established players, making competition difficult. |
| Regulatory Environment | Complex zoning, permits, and environmental laws in Germany. | Increases costs, time, and complexity for new market entrants. |
| Brand & Reputation | Established trust and tenant relationships built over time. | Newcomers struggle to gain immediate credibility and market acceptance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Vonovia Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including Vonovia's annual reports and investor presentations, as well as industry-specific market research from reputable firms like Scope Ratings and Fitch.
