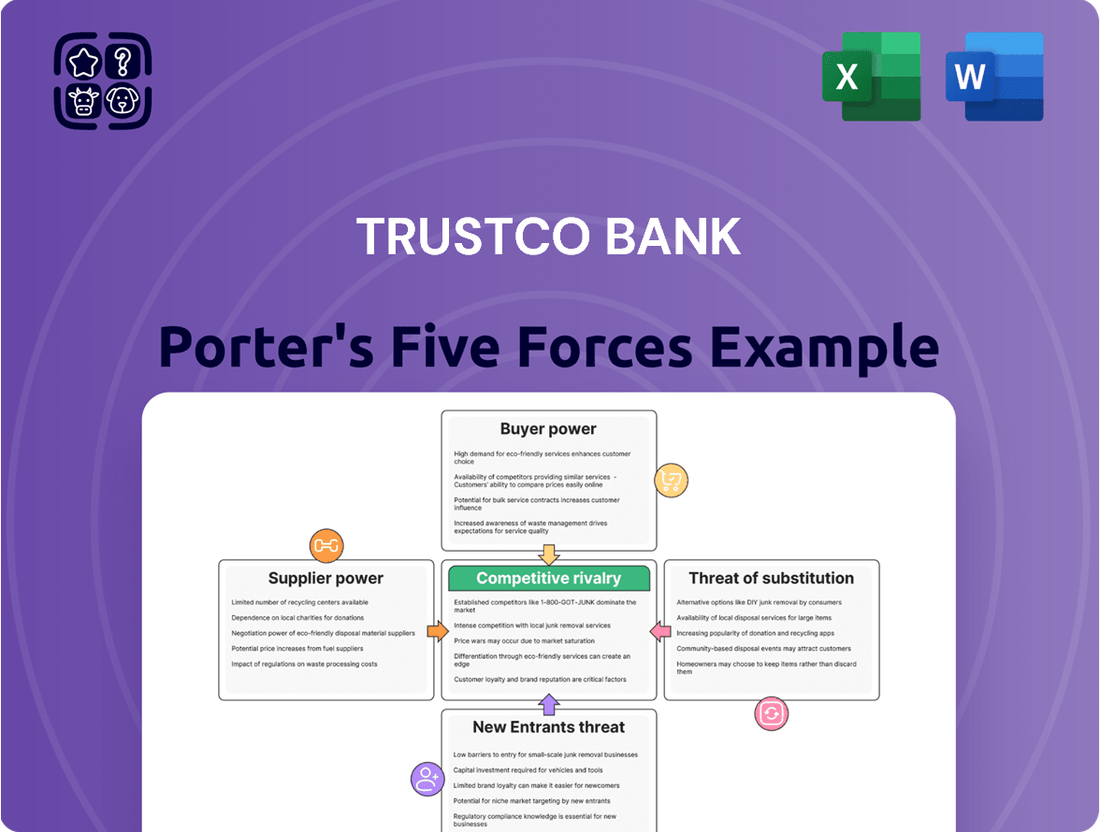
TrustCo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
TrustCo Bank Bundle
TrustCo Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing distinct competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning. For instance, the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers significantly shape TrustCo Bank's market position.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a comprehensive deep dive into these critical elements. It dissects TrustCo Bank's competitive environment, revealing the underlying strengths and weaknesses of each force.
Gain actionable insights into TrustCo Bank's industry dynamics, from supplier leverage to the viability of substitute products. This detailed report empowers you to make informed strategic decisions.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of TrustCo Bank’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
TrustCo Bank's primary suppliers are technology vendors crucial for its core banking systems, cybersecurity, and digital operations. The bargaining power of these tech suppliers can range from moderate to high.
This power is particularly pronounced when dealing with specialized software or complex, integrated platforms. Banks often face significant switching costs, involving extensive data migration and potential operational disruptions, which can make moving to a new vendor a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a bank to switch its core banking system was estimated to be in the tens of millions of dollars, a clear indicator of the leverage held by incumbent technology providers. This substantial investment incentivizes banks to maintain relationships with existing, reliable vendors, thereby strengthening supplier bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for TrustCo Bank is significantly shaped by providers of financial data and analytics. The uniqueness and depth of their data offerings, coupled with the banking industry's growing dependence on data for risk assessment and customer understanding, amplify their influence. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that financial institutions spent an average of 15% of their IT budget on data analytics solutions, highlighting the critical nature of these inputs.
Human capital, especially skilled professionals in finance, technology, and compliance, acts as a key supplier group for TrustCo Bank. The intense competition for these specialists within the financial services industry allows them to exert considerable bargaining power. This can directly influence TrustCo's operational costs through higher salaries and benefits, as well as impact the bank's ability to attract and retain top talent.
Supplier Power 4
Regulatory bodies and compliance service providers wield considerable influence over TrustCo Bank, acting as powerful de facto suppliers. Their mandates and the constant evolution of financial regulations necessitate significant investment in technology, personnel, and external expertise to ensure adherence. For instance, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and its associated Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements demand robust systems and ongoing vigilance, adding substantial operational costs.
The cost of non-compliance with these regulations can be severe, ranging from hefty fines to reputational damage, which effectively elevates the bargaining power of these entities. TrustCo’s reliance on specialized consultants to navigate the intricate landscape of financial laws, such as those pertaining to data privacy (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) or capital adequacy ratios set by bodies like the Federal Reserve, further underscores this power. In 2024, the global financial services sector saw increased regulatory scrutiny, with fines for non-compliance reaching billions, a clear indicator of this supplier power.
- Regulatory Mandates: Compliance with evolving financial laws (e.g., AML, KYC, data privacy) dictates operational procedures and technology investments for TrustCo.
- Cost of Non-Compliance: Fines and reputational damage for failing to meet regulatory standards, estimated in the billions globally for financial institutions in 2024, empower regulatory bodies.
- Specialized Expertise: TrustCo's need for external consultants to interpret and implement complex regulations, such as those from the SEC or OCC, highlights supplier influence.
- Technology Integration: The requirement to adopt and maintain specific technological solutions for reporting and risk management further strengthens the position of technology providers aligned with regulatory frameworks.
Supplier Power 5
Real estate lessors for TrustCo Bank's physical branches act as suppliers. Their bargaining power is influenced by the desirability and availability of locations within TrustCo's key operating states: New York, Florida, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Vermont.
In markets with limited prime commercial real estate, such as parts of Manhattan or Boston, lessors can leverage their position to negotiate higher rental rates. This directly impacts TrustCo's operational expenses, as lease agreements represent a significant cost. For instance, commercial rents in prime Manhattan locations can exceed $100 per square foot annually as of early 2024, a stark contrast to less competitive markets.
- Supplier Type: Real estate lessors for physical branch locations.
- Impact on TrustCo: Higher rental costs due to lessor power in desirable markets.
- Key Markets: New York, Florida, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Vermont.
- 2024 Data Point: Prime Manhattan commercial rents exceeding $100/sq ft annually, illustrating potential cost pressure.
The bargaining power of suppliers for TrustCo Bank is a significant factor, particularly concerning technology vendors and financial data providers. High switching costs for core banking systems, estimated in the tens of millions of dollars for a bank in 2024, grant considerable leverage to incumbent software providers.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on specialized data analytics, with financial institutions allocating an average of 15% of their IT budget to these solutions in 2024, empowers data suppliers. This dependence, driven by the need for risk assessment and customer insights, strengthens their position.
Skilled human capital, especially in finance, technology, and compliance, also acts as a powerful supplier group, driving up operational costs through competitive salary demands. Regulatory bodies, through their mandates and the severe penalties for non-compliance, effectively position themselves as influential suppliers, necessitating significant investment in compliance technologies and expertise.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on TrustCo | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Vendors | Specialized software, high switching costs | Increased costs for core systems, potential operational disruption | Switching core banking system costs tens of millions |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Uniqueness of data, industry dependence | Higher spending on analytics solutions | Average 15% of IT budget allocated to data analytics |
| Human Capital (Skilled Professionals) | Intense competition for talent | Higher salary and benefit costs, talent acquisition challenges | N/A (General industry trend) |
| Regulatory Bodies & Compliance Services | Mandates, cost of non-compliance | Investment in technology, personnel, and consultants | Global financial services fines for non-compliance in billions |
| Real Estate Lessors | Location desirability, market availability | Higher rental expenses in prime locations | Prime Manhattan rents > $100/sq ft annually |
What is included in the product
This analysis tailors Porter's Five Forces to TrustCo Bank, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its strategic positioning.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing TrustCo Bank's Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
TrustCo Bank caters to a broad customer base, encompassing individuals, businesses, and institutional clients. For individual retail customers, the bargaining power is typically quite low. This is mainly because many banking products are standardized, and there are many other banks and financial institutions offering similar services.
However, the increasing prevalence of digital banking channels has amplified price transparency for these customers. For instance, in 2024, online comparison tools make it easier for consumers to see interest rates and fees across various institutions, giving them more leverage to seek better terms, though the sheer volume of customers often dilutes individual impact.
Customers wield moderate bargaining power concerning deposit accounts. This power is amplified in competitive banking environments where consumers can readily switch institutions to secure higher interest rates or more advantageous account terms. TrustCo Bank's emphasis on deposit retention and competitive product offerings underscores this dynamic, reflecting the need to appease customer demands to maintain a stable funding base.
Borrowers, especially those needing substantial commercial loans, wield considerable sway. Their ability to secure financing from various institutions allows them to negotiate better interest rates and more favorable terms, directly impacting a bank's profitability on these transactions.
In 2024, the average interest rate for commercial real estate loans in the US hovered around 7.5% to 8.5%, but large, creditworthy borrowers could often secure rates below this range through aggressive negotiation.
This buyer power is amplified when clients can easily switch providers or when alternative financing options, such as private debt or capital markets, become more attractive due to economic conditions or regulatory changes.
For TrustCo Bank, understanding and managing the bargaining power of its key commercial clients is crucial for maintaining competitive loan pricing and fostering long-term relationships.
Buyer Power 4
Institutional clients who rely on TrustCo Bank for trust and investment management services often wield significant bargaining power. These sophisticated customers frequently demand highly customized solutions tailored to their specific investment objectives and risk appetites. Furthermore, they typically engage in rigorous price comparisons, pushing for competitive fee structures and potentially negotiating lower rates based on the volume of assets under management. For instance, in 2024, large institutional asset managers often seek fee reductions exceeding 5 basis points on portfolios surpassing $1 billion, directly impacting TrustCo's revenue margins.
The bargaining power of customers within TrustCo Bank's retail segment is generally lower, primarily due to the fragmented nature of individual depositors and borrowers. However, for clients with substantial deposit balances or significant loan portfolios, TrustCo may offer more personalized terms and potentially slightly more favorable interest rates to retain their business. This is a common practice across the banking industry, where customer loyalty is often cultivated through preferential treatment for high-value clients.
- Customization Demands: Institutional clients require bespoke trust and investment strategies, increasing their leverage.
- Fee Sensitivity: Large clients often negotiate for reduced fees, impacting TrustCo's profitability.
- Volume-Based Negotiation: Higher asset values translate into greater bargaining power for institutional customers.
- Retail Client Fragmentation: Individual customers generally have less individual power, though high-balance clients can negotiate.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers for TrustCo Bank is amplified by the evolving digital landscape. The proliferation of digital banking and fintech solutions means customers have unprecedented convenience and access to comparative information, making it simpler to evaluate TrustCo's offerings against competitors. This ease of comparison directly translates to greater leverage for customers.
This shift is evident in the growing adoption of digital financial services. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 80% of retail banking transactions in many developed markets were conducted digitally, a figure expected to climb further. This digital fluency empowers customers to readily switch providers if they perceive better value or service elsewhere, increasing pressure on TrustCo to remain competitive on pricing and service quality.
Key factors influencing customer bargaining power include:
- Increased Information Availability: Customers can easily access and compare interest rates, fees, and service features across numerous financial institutions, including online-only banks and fintech apps.
- Lower Switching Costs: Digital platforms have reduced the effort and time required to open new accounts or transfer funds, diminishing customer inertia and making switching providers more feasible.
- Availability of Substitutes: The market offers a wide array of banking and financial services, from traditional banks to neobanks and specialized fintech apps, providing customers with numerous alternatives.
TrustCo Bank faces varying levels of customer bargaining power. While individual retail customers have limited individual leverage due to standardized products and a vast customer base, institutional clients and those with substantial balances wield significant influence. This power is amplified by digital channels offering easy comparison and lower switching costs, forcing TrustCo to remain competitive in pricing and service to retain these valuable relationships.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Level | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Individual Customers | Low to Moderate | Standardized products, numerous alternatives, but growing digital price transparency. |
| High-Balance Retail Customers | Moderate | Ability to negotiate preferential terms due to significant deposit or loan volume. |
| Commercial Borrowers (Large) | High | Access to multiple financing sources, ability to negotiate rates below market averages (e.g., below 7.5% for CRE in 2024). |
| Institutional Clients (Trust & Investment) | High | Demand for customization, fee sensitivity (seeking >5 bps reduction in 2024), and significant asset volume. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
TrustCo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for TrustCo Bank details the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products within the banking sector. Each force is thoroughly examined to provide actionable insights into TrustCo Bank's competitive landscape and strategic positioning. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted analysis immediately upon purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking sector where TrustCo operates, specifically in New York, Florida, Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Vermont, is incredibly crowded. Think of it as a busy marketplace with many players all trying to attract the same customers. This includes local regional banks, massive national institutions, and member-focused credit unions, all competing fiercely for deposits and loans.
This intense rivalry directly impacts profitability, as the need to attract and retain customers often leads to lower interest rates on loans and higher rates on deposits, squeezing profit margins for everyone involved. For instance, as of late 2024, the average interest rate on a new 30-year fixed-rate mortgage hovered around 6.5% to 7.5% across these states, a testament to the competitive pressure.
Competitive rivalry within the banking sector, especially for traditional services like checking accounts and personal loans, is intense. Many banks offer very similar products, making it hard to stand out through unique features. This often forces institutions to compete more on factors like interest rates, fees, and the overall customer experience. In 2024, the average interest rate on a new auto loan hovered around 7%, highlighting the price sensitivity consumers have for these core banking products.
Competitive rivalry within the loan market, encompassing residential, commercial, and consumer segments, is exceptionally intense. Traditional banks face significant pressure from a growing array of non-bank lenders, including fintech companies and specialized credit funds. This heightened competition directly impacts loan yields, as institutions are often forced to offer more favorable terms and lower interest rates to attract and retain customers. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage hovered around 7%, a figure that can fluctuate based on competitive pressures and market conditions.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Merger and acquisition (M&A) activity in the regional banking sector continues to shape competitive dynamics. This consolidation trend intensifies rivalry by creating larger institutions with expanded market share and enhanced economies of scale. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. banking sector saw a significant number of M&A deals, with several regional banks combining to bolster their competitive standing against larger national players.
These mergers often lead to increased pressure on smaller or less efficient regional banks, forcing them to innovate or face acquisition themselves. The drive for greater operational efficiency and broader product offerings means that banks actively seeking M&A opportunities are often well-positioned to compete aggressively on price and service. This dynamic directly impacts TrustCo Bank by potentially increasing the number of formidable competitors within its operating regions.
- Increased Market Power: Emerging larger banks from mergers possess greater financial resources and a wider customer base, enabling them to offer more competitive rates and a broader suite of services.
- Economies of Scale: Consolidated entities can achieve lower operating costs per unit, allowing them to absorb market shocks more effectively and potentially offer more attractive pricing.
- Intensified Competition: The trend forces remaining regional banks, including TrustCo, to sharpen their strategies to retain market share and attract new customers amidst heightened competition.
- Strategic Responses: TrustCo Bank may need to consider its own strategic responses, such as targeted acquisitions or enhanced digital offerings, to maintain its competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry in the banking sector is intensifying, driven by significant digital transformation efforts. Banks are pouring resources into areas like mobile banking, artificial intelligence, and enhanced online services as primary battlegrounds to capture and keep customers. This creates a highly dynamic and competitive environment where innovation and customer experience are paramount.
In 2024, the competition is particularly fierce as established banks strive to keep pace with nimble fintech challengers and evolving customer expectations. For TrustCo Bank, this means a constant need to adapt and invest in technology to remain relevant and competitive.
- Digital Investment: Banks are allocating substantial capital to digital upgrades. For instance, many are focusing on improving their mobile app functionalities, with some aiming for feature parity with leading fintech apps by late 2024.
- AI Integration: The adoption of AI for customer service, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice is becoming standard. Early adopters of AI-powered chatbots reported faster query resolution times.
- Customer Acquisition: Banks are increasingly using digital channels and promotional offers to attract new customers, leading to higher customer acquisition costs.
- Service Offerings: The battle extends to the breadth and quality of digital services, including seamless account opening, intuitive payment systems, and personalized investment tools.
The banking sector is characterized by intense competition, with TrustCo Bank facing rivals ranging from large national institutions to local credit unions across its operating states. This rivalry extends across various financial products, from mortgages to auto loans, forcing banks to compete on price, service, and digital offerings to attract and retain customers. For example, in 2024, the average interest rate for a new 30-year fixed-rate mortgage was around 7%, a clear indicator of competitive pressures.
Mergers and acquisitions are further consolidating the market, creating larger, more efficient competitors that can offer better pricing and broader services. This trend necessitates that banks like TrustCo continuously innovate and adapt their strategies to maintain market share and profitability. The digital landscape is a key battleground, with significant investment in mobile banking and AI aimed at enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
| Competitive Factor | Description | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Number of Competitors | Numerous regional, national banks, and credit unions in NY, FL, MA, NJ, VT. | High, with many institutions offering similar core products. |
| Price Competition | Competition on interest rates for loans and deposits. | Average 30-year fixed mortgage rate ~7%; average auto loan rate ~7%. |
| Product Differentiation | Limited differentiation in traditional banking products. | Focus shifts to customer experience and digital services. |
| M&A Impact | Consolidation creates larger, more competitive entities. | Increased M&A activity in regional banking in 2023. |
| Digital Competition | Investment in mobile banking, AI, and online services. | Banks enhancing mobile app features and AI integration. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies pose a substantial threat of substitution for traditional banks like TrustCo Bank. They offer specialized services like peer-to-peer lending, digital payment solutions, and user-friendly investment apps that often circumvent conventional banking infrastructure. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at over $2 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong shift towards these alternative channels.
The threat of substitutes for TrustCo Bank is significant, particularly from non-bank lenders and online lending platforms. These entities offer alternative avenues for consumers and businesses seeking various types of loans, directly challenging TrustCo's traditional lending operations. For instance, in 2024, the online lending market continued its robust growth, with platforms facilitating billions in personal and small business loans, often with faster approval times and potentially lower overhead costs than traditional banks.
These digital disruptors bypass the need for physical branches, a substantial cost center for established institutions like TrustCo. This allows them to operate more leanly and potentially offer more competitive rates. The convenience and accessibility of online applications further enhance their appeal to a broad customer base, particularly younger demographics who are comfortable with digital financial services.
Investment firms and robo-advisors present a significant threat of substitutes for TrustCo's core trust and investment management services. These alternatives often compete on price, with many robo-advisors charging annual management fees as low as 0.25%, compared to traditional wealth management fees which can range from 1% to 2%. This cost advantage, coupled with the convenience of automated portfolio management and digital access, appeals strongly to a growing segment of tech-savvy investors seeking lower-cost, hands-off solutions.
4
Emerging technologies present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. While blockchain and cryptocurrencies are still developing for widespread use, they offer alternative methods for payments and transactions that bypass conventional financial institutions. For instance, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024, indicating growing interest and potential displacement of traditional payment rails.
These digital assets, along with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, could reduce reliance on banks for services like remittances, lending, and even account holding. By offering potentially lower fees and faster transaction times, these substitutes appeal to a growing segment of users, especially younger demographics. The continued innovation in this space means banks must adapt to remain competitive.
Consider these points regarding substitutes:
- Digital Payment Platforms: Services like PayPal and Venmo have already captured a significant share of the peer-to-peer payment market, reducing the need for traditional bank transfers for everyday transactions. In 2023, PayPal reported processing over $1.5 trillion in total payment volume.
- Cryptocurrencies: As adoption grows, cryptocurrencies offer an alternative for cross-border payments and even as a store of value, potentially impacting foreign exchange services and savings accounts offered by traditional banks. The daily trading volume in cryptocurrencies often exceeds hundreds of billions of dollars.
- Fintech Innovations: Startups are continuously developing new financial products and services that directly compete with bank offerings, from digital lending to robo-advisory services, often with a more user-friendly and cost-effective approach. The fintech sector attracted over $150 billion in venture capital funding globally in 2023.
- Peer-to-Peer Lending: Platforms that connect borrowers directly with lenders can bypass traditional bank loan processes, offering an alternative for individuals and small businesses seeking capital.
5
The threat of substitutes for TrustCo Bank is significant, particularly due to the rise of embedded finance. These integrated financial services, appearing within non-financial platforms, offer customers convenient alternatives that bypass traditional banking channels. For example, buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) options at online retailers directly compete with credit card services offered by banks like TrustCo. In 2023, the global BNPL market was valued at over $100 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in consumer payment preferences.
These substitutes reduce the switching costs for customers who might previously have been locked into traditional banking relationships. Think about it: instead of opening a new credit card or taking out a personal loan from a bank, consumers can often access financing directly at the point of sale through embedded solutions. This trend is amplified by the increasing digitalization of financial services, making it easier for fintech companies and even non-financial businesses to offer competing products.
- Embedded Payment Solutions: Platforms offering seamless in-app purchases or point-of-sale financing directly challenge traditional credit and debit card services.
- Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL): Services like Klarna and Afterpay provide installment payment options that substitute for credit cards, with BNPL transaction volumes in the US alone projected to reach hundreds of billions by 2025.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending: Online platforms connect borrowers and lenders directly, offering an alternative to personal loans from banks.
- Digital Wallets: Services such as PayPal and Venmo provide payment and transfer functionalities that can reduce the need for traditional bank account transactions for everyday spending.
The threat of substitutes for TrustCo Bank is considerable, largely driven by the increasing accessibility and appeal of alternative financial solutions. These substitutes often offer greater convenience, lower costs, or specialized features that traditional banks may not provide as efficiently. For instance, digital payment platforms and cryptocurrencies are steadily eroding the reliance on traditional banking for everyday transactions and remittances.
In 2024, the growth of fintech continued to present a significant challenge, with companies offering streamlined digital lending and investment services. These platforms are attracting customers, particularly younger demographics, with user-friendly interfaces and competitive pricing structures. The ease of opening accounts and accessing services online bypasses the need for physical branches, a key cost advantage for these digital disruptors.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | 2024 Market Insight | Impact on TrustCo Bank |
| Digital Payment Platforms | Peer-to-peer transfers, online checkout | Global digital payments market projected to exceed $3 trillion. | Reduces transaction volume through traditional channels. |
| Online Lending Platforms | Personal loans, small business loans | Billions facilitated in online lending, often with faster approvals. | Direct competition for loan origination. |
| Robo-Advisors | Automated investment management | Annual fees often below 0.50%, attracting fee-sensitive investors. | Challenges TrustCo's wealth management services. |
| Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL) | Point-of-sale installment financing | US BNPL transaction volume expected to reach hundreds of billions. | Substitutes for credit card services. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank, and traditional banks in general, remains quite low. This is primarily due to the significant regulatory landscape that new players must navigate. For instance, establishing a new bank requires meeting substantial capital requirements, obtaining various federal and state licenses, and adhering to complex compliance protocols, all of which represent substantial barriers to entry. In 2024, the average cost to start a new bank can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, making it a challenging proposition for many aspiring institutions.
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank is generally moderate. Establishing a full-service bank requires substantial capital, often in the billions, for regulatory compliance, technology infrastructure, and physical branches. For instance, in 2024, acquiring a national bank charter can involve extensive legal and capital requirements, making it a significant hurdle.
Furthermore, building brand recognition and customer trust takes considerable time and investment, especially in a mature market. Challenger banks and fintech firms can enter with lower overheads, focusing on digital-first strategies, but they often struggle to gain the broad customer base and deposit stability that traditional banks like TrustCo possess.
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank is moderate. Establishing a strong brand and earning customer trust in the banking sector is a significant hurdle. New banks must invest heavily in marketing and customer service to match the established relationships TrustCo has cultivated over years, particularly within local communities. For example, in 2024, the average time for a new fintech to gain a substantial customer base was reported to be several years, requiring substantial capital outlay.
4
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank, while generally moderate due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles in traditional banking, is significantly amplified by the rise of fintech companies and digital-only banks. These 'neobanks' possess the agility to penetrate specific market segments with streamlined, low-overhead digital services, effectively bypassing some of the established barriers to entry that traditional institutions face. For instance, by focusing solely on digital platforms, neobanks avoid the substantial costs associated with maintaining physical branch networks, a key differentiator impacting their competitive pricing and customer acquisition strategies.
These agile competitors can rapidly innovate and adapt to evolving customer preferences, often leveraging advanced data analytics and AI to personalize offerings. This digital-first approach allows them to capture market share by providing superior user experiences and competitive rates. In 2024, the digital banking sector continued its robust growth, with reports indicating that neobanks are increasingly attracting younger demographics and those seeking convenient, mobile-centric financial solutions. This trend suggests a persistent and growing challenge to incumbent banks like TrustCo.
- Fintech's Lower Overhead: Digital-only banks often operate with significantly lower overhead costs compared to traditional banks, enabling them to offer more competitive pricing.
- Niche Market Focus: Neobanks excel at targeting specific customer segments or financial needs, such as international money transfers or specialized lending, with highly tailored digital solutions.
- Rapid Innovation Cycles: Their lean structures allow for faster development and deployment of new features and services, outpacing the slower innovation cycles of more established institutions.
- Regulatory Arbitrage: While subject to regulations, some fintech models may initially operate under lighter regulatory frameworks or find ways to navigate existing rules more efficiently, creating a temporary advantage.
5
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank is moderate, largely due to the significant capital requirements and regulatory hurdles inherent in the banking sector. However, technological advancements are reshaping this landscape.
New, agile entrants leveraging AI and automation can significantly lower operational costs. For instance, by 2024, fintech companies have demonstrated the ability to onboard customers digitally in minutes, a stark contrast to traditional banking processes. This allows them to offer competitive services without the burden of legacy systems that established players like TrustCo Bank must manage.
Here’s a breakdown of factors influencing new entrants:
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a full-service bank necessitates substantial capital for infrastructure, compliance, and initial operations, acting as a considerable barrier.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex banking regulations, including Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws, requires specialized expertise and investment.
- Technological Disruption: Fintech startups can bypass traditional infrastructure, offering specialized digital services (e.g., payments, lending) with lower overhead, thereby posing a competitive threat.
- Brand Loyalty and Trust: Established banks like TrustCo benefit from existing customer relationships and a reputation for security, which new entrants must work hard to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for TrustCo Bank remains moderate. While the significant capital and regulatory requirements for traditional banking create high barriers, fintech and digital-only banks can enter with lower overhead and specialized offerings. For example, by 2024, the cost to establish a new chartered bank can easily exceed tens of millions of dollars, a sum many fintechs avoid by focusing on technology rather than physical infrastructure.
These digital competitors often bypass the need for extensive branch networks, reducing their operational costs and allowing for more competitive pricing. In 2024, neobanks continued to attract younger demographics with their mobile-first, user-friendly interfaces, posing a challenge to incumbents. Building brand trust also remains a hurdle for new entrants, a factor that benefits established institutions like TrustCo.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Substantial funds needed for licensing, technology, and operations. | High | Average cost to start a new bank in the tens of millions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to complex banking laws (e.g., KYC, AML). | High | Extensive legal and capital requirements for national bank charters. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation and customer loyalty. | Moderate to High | New fintechs take several years to build significant customer bases. |
| Technological Agility | Ability of fintechs to innovate and offer digital-first services. | Moderate | Neobanks bypass physical infrastructure costs, enabling lower overhead. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our TrustCo Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from TrustCo Bank's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate industry-wide data from financial news outlets, banking regulators, and market research reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
