TriMark USA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
TriMark USA Bundle
TriMark USA operates in a landscape shaped by intense competitive rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of both their suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this market effectively. The availability of substitute products also presents a significant challenge to their established position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore TriMark USA’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
TriMark USA sources essential commercial kitchen equipment and design software from numerous suppliers. When a limited number of manufacturers control specialized or premium equipment, their leverage escalates. This concentration means TriMark's ability to secure specific, high-demand items without readily available substitutes directly enhances supplier bargaining power.
Switching suppliers presents significant hurdles for TriMark, necessitating thorough re-evaluation of product quality, the integration of new inventory management systems, and comprehensive staff retraining on potentially different equipment. These operational disruptions and associated expenses directly translate into high switching costs.
For TriMark, particularly within specialized product categories or where long-standing relationships with critical suppliers are in place, these high switching costs considerably bolster the bargaining power of those suppliers. This leverage is amplified when dealing with integrated design software or proprietary equipment components, where finding readily compatible alternatives can be exceptionally difficult and costly.
Suppliers providing unique, patented, or highly differentiated equipment and technologies possess considerable bargaining power. If specific equipment grants TriMark's clients a distinct competitive edge, TriMark's dependence on those particular suppliers intensifies. For instance, if a supplier offers energy-efficient kitchen appliances or advanced smart technology that clients demand, TriMark has less leverage. In 2024, the market for specialized commercial kitchen equipment saw continued innovation, with some suppliers securing patents for novel cooling or cooking technologies, thereby strengthening their negotiating position with distributors like TriMark.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by TriMark USA's suppliers significantly boosts their bargaining power. If a major foodservice equipment manufacturer, for instance, decides to bypass distributors like TriMark and sell directly to end-users or acquire smaller distribution networks, it directly challenges TriMark's business model. This could lead to reduced sales volume and pricing pressure for TriMark.
Consider a scenario where a large oven manufacturer, seeing robust demand, chooses to establish its own direct sales force and service centers. This move would effectively cut out the intermediary role TriMark plays, thereby diminishing TriMark's purchasing leverage and potentially forcing it to accept less favorable terms from other suppliers to remain competitive. In 2024, the foodservice equipment market experienced continued consolidation, with some manufacturers exploring direct-to-consumer models, particularly for online sales channels.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with strong brand recognition and existing customer relationships are better positioned for forward integration.
- Market Incentives: Rising margins in distribution or a desire to capture the full value chain can incentivize suppliers to integrate forward.
- Competitive Landscape: If competitors are already integrating forward, it increases the pressure on other suppliers to do the same to maintain market share.
- Impact on TriMark: Direct sales by suppliers can reduce TriMark's market access and necessitate aggressive pricing strategies.
Importance of TriMark as a Customer
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by how crucial a customer TriMark USA is to their business. When TriMark represents a significant portion of a supplier's annual sales, that supplier is more likely to be accommodating with pricing and terms to secure continued business. For instance, if a key supplier’s revenue is heavily reliant on TriMark, they would be hesitant to impose unfavorable conditions that could risk losing such a substantial account.
Conversely, if TriMark’s purchases are a small fraction of a supplier's overall revenue, the supplier’s incentive to negotiate favorably is reduced. In such scenarios, the supplier has less to lose by maintaining rigid pricing or terms, as their business is not disproportionately dependent on TriMark. This dynamic directly impacts TriMark's ability to leverage its purchasing volume for better deals.
- Customer Significance: TriMark's size and purchasing volume directly impact its leverage with suppliers. A larger share of a supplier's revenue grants TriMark greater negotiation power.
- Supplier Dependency: If a supplier relies heavily on TriMark for a substantial percentage of its income, they are more likely to offer favorable pricing and terms to maintain the relationship.
- Market Position: TriMark's position within its industry, coupled with its purchasing scale, can dictate the supplier's willingness to concede on price or service agreements.
Suppliers to TriMark USA wield significant bargaining power when they offer unique, patented, or highly differentiated products. In 2024, innovation in commercial kitchen technology, particularly in energy-efficient appliances and smart systems, gave some suppliers a stronger negotiating position. This leverage is amplified when TriMark's clients demand these specific, advanced features, making substitutes difficult to find and increasing TriMark's reliance on these key suppliers.
High switching costs for TriMark, including the expense of re-evaluating product quality, integrating new inventory systems, and retraining staff, further empower suppliers. These costs are particularly impactful for specialized equipment or proprietary components, where finding compatible alternatives is both challenging and costly, reinforcing supplier leverage.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, such as manufacturers selling directly to end-users, poses a direct challenge to TriMark's business model. This trend, observed in the foodservice equipment market throughout 2024 with increasing exploration of direct-to-consumer online channels, can reduce TriMark's market access and necessitate aggressive pricing strategies.
TriMark's importance as a customer also dictates supplier bargaining power; when TriMark represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier is more inclined to offer favorable terms. Conversely, if TriMark's purchases are a small fraction of a supplier's income, the supplier has less incentive to negotiate and may maintain rigid pricing, directly impacting TriMark's ability to secure better deals.
What is included in the product
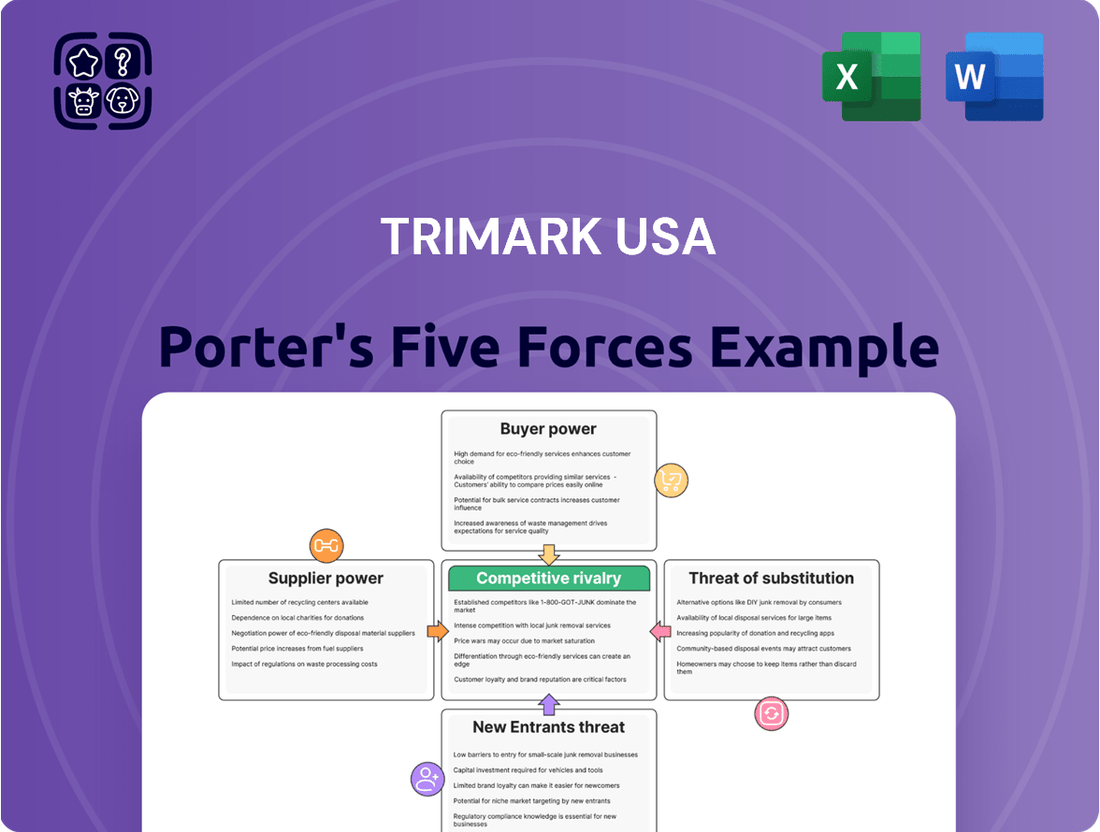
TriMark USA's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the industry's competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on TriMark USA's strategic positioning.
Eliminate the guesswork in strategic planning by instantly visualizing competitive threats and opportunities with an intuitive spider chart.
Streamline competitive analysis and decision-making with a pre-formatted, easy-to-understand summary of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
TriMark USA's customer base is quite varied, encompassing everything from small, independent eateries to large healthcare networks and university systems. This broad reach means they deal with a wide range of customer sizes and needs.
However, when major players like large, multi-unit restaurant groups or big corporate clients undertake significant projects, their sheer volume of business grants them considerable leverage. These substantial orders allow them to negotiate for more favorable pricing, tailored product offerings, and even extended payment schedules, directly impacting TriMark's margins.
For instance, a national fast-food chain ordering equipment for fifty new locations represents a massive commitment that gives them significant sway in negotiations. In 2024, the foodservice equipment market saw continued consolidation, with large chains increasingly using their scale to secure better deals from suppliers like TriMark.
Customers possess significant leverage due to the wide array of alternative providers available to them. Beyond TriMark USA, clients can readily source similar products and services from other national distributors, regional suppliers, and even directly from manufacturers. The proliferation of online marketplaces further amplifies this accessibility, presenting numerous competitive options.
This abundance of choice directly translates into increased bargaining power for customers. When it's easy for clients to find comparable offerings elsewhere, they are less reliant on any single supplier. For instance, in the broad commercial foodservice equipment market, a customer can easily compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, forcing TriMark to remain competitive.
To counter this, TriMark USA must actively cultivate a unique value proposition that extends beyond mere product availability. Differentiating through superior customer service, specialized industry expertise, and the provision of integrated, comprehensive solutions is crucial. This focus on added value helps to reduce the customer's perception of substitutability.
Customer switching costs can significantly impact the bargaining power of buyers in the foodservice equipment industry. For complex projects, such as outfitting a new restaurant or undertaking a major renovation, switching providers can be a cumbersome process. This might involve re-bidding entire projects, learning new design software or processes, and integrating equipment from different manufacturers, all of which can create substantial friction for the customer.
If TriMark USA, for instance, offers integrated design, procurement, and installation services, they can effectively raise these switching costs. When clients are deeply embedded in TriMark's ecosystem and workflow, the effort and potential disruption involved in moving to a competitor become a deterrent, thereby diminishing the customer's leverage.
However, the situation is different for simpler transactions. For routine supply orders of standard kitchenware or replacement parts, the costs associated with switching are generally minimal. Customers can easily compare prices and source items from various suppliers, giving them considerable bargaining power in these less integrated scenarios.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in sectors like hospitality and education, where TriMark USA operates, often exhibit high price sensitivity, particularly for commoditized equipment and supplies. This means they are very aware of prices and will readily switch suppliers for better deals. For example, in 2024, many businesses in the hospitality sector faced ongoing cost pressures, leading to a greater focus on procurement efficiency and price comparisons for essential goods.
Economic downturns or periods of tight operational budgets, which were a concern for many businesses in 2024, significantly amplify this customer price sensitivity. When companies are looking to cut costs, the price of goods becomes a primary deciding factor. This puts direct pressure on TriMark to offer competitive pricing to secure and retain business, potentially impacting its profitability and profit margins.
- Price Sensitivity in Hospitality: In 2024, the hospitality industry continued to navigate fluctuating consumer demand and rising operational costs, making price a critical factor in purchasing decisions for everything from kitchenware to furniture.
- Impact on Margins: The need for TriMark to maintain competitive pricing due to customer sensitivity can squeeze profit margins, especially if input costs remain high or increase.
- Demand for Value: Customers are not just looking for low prices but also for value, meaning they expect quality and reliability to be commensurate with the cost.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today possess an unprecedented amount of information. Online reviews, comparison websites, and readily available product specifications empower them to scrutinize offerings and pricing with ease. This transparency significantly shifts the balance of power, enabling them to negotiate more effectively with suppliers like TriMark USA.
- Informed Decisions: Access to data on competitors' pricing and product features allows customers to identify the best value, pressuring TriMark to remain competitive.
- Negotiation Leverage: Knowledge of market rates and alternative suppliers gives customers a stronger hand in price and terms discussions.
- Value Justification: TriMark must clearly articulate its unique selling propositions and the benefits of its services to justify its pricing structure.
- Brand Loyalty Impact: Without compelling value, customers can easily switch to alternatives, impacting TriMark's market share.
TriMark USA faces significant customer bargaining power due to the availability of numerous alternative suppliers and the ease with which customers can switch between them, especially for commoditized products. This is amplified by customer price sensitivity, particularly in sectors like hospitality which experienced ongoing cost pressures in 2024, driving a focus on procurement efficiency.
Large clients, such as national restaurant chains, leverage their order volume to negotiate favorable terms, impacting TriMark’s margins. For instance, a major chain outfitting numerous locations represents a substantial deal that grants considerable negotiation leverage.
The transparency afforded by online resources empowers customers with extensive product and pricing information, enabling them to negotiate more effectively and increasing pressure on TriMark to remain competitive on both price and value.
| Factor | Impact on TriMark USA | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | Reduces customer reliance on TriMark; increases negotiation power. | Continued market consolidation in foodservice equipment meant more large players could secure better deals from suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | Lower for routine orders, higher for integrated projects; can diminish leverage if costs are high. | Clients embedding in TriMark's workflow can face friction when considering competitors for complex projects. |
| Price Sensitivity | Forces competitive pricing, potentially squeezing profit margins. | Hospitality sector faced cost pressures, increasing focus on procurement efficiency and price comparisons. |
Same Document Delivered
TriMark USA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact TriMark USA Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive document delves into the competitive landscape of TriMark USA by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. You'll gain a deep understanding of the strategic factors influencing TriMark USA's profitability and market position. The detailed insights provided will empower you to make informed strategic decisions and anticipate future market shifts. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is what you get.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The foodservice equipment and supply sector is a crowded arena. TriMark USA navigates a landscape populated by large, national distributors, a multitude of regional distributors, and many smaller, specialized local suppliers. This sheer volume and variety of competitors mean TriMark is constantly facing pressure from all sides.
This intense fragmentation directly fuels competitive rivalry. Each of these players, regardless of size, is actively competing for market share, often through aggressive pricing and service offerings. For TriMark, this translates into facing competition across every single product category and every geographic region it serves.
For instance, in 2024, the foodservice equipment market continued to see significant activity from both established national players and emerging regional specialists. Reports indicate that while large distributors like TriMark hold substantial market share, the agility and localized service of smaller competitors often allow them to capture niche markets or specific customer segments, adding another layer to the competitive pressure.
The overall growth rate of the foodservice industry is a major driver of competitive rivalry for companies like TriMark USA. When the market is expanding, like it did in 2023 with a projected 4.5% increase in foodservice sales according to the National Restaurant Association, it provides more opportunities for all players to grow without directly poaching each other's customers. This generally leads to less aggressive competition.
However, if the industry growth slows down, competition tends to intensify. For instance, if the projected 2025 growth rate for the broader foodservice sector were to dip below 2%, we would likely see increased price sensitivity and promotional activities as companies fight harder for market share. This dynamic directly affects how fiercely TriMark USA's competitors vie for contracts and customer loyalty.
In a rapidly expanding market, the focus can shift from aggressive market share battles to strategic expansion and innovation. This was evident in early 2024 as many restaurant chains announced ambitious new store opening plans, fueled by strong consumer demand and a generally positive economic outlook for the sector. This environment can temper the intensity of rivalry.
TriMark USA strives to stand out by offering a full suite of services, encompassing design, sourcing, and installation, positioning itself as a one-stop shop for clients.
However, this differentiation is challenged if rivals can match these integrated offerings or excel in specific specialized areas. For instance, if a competitor can provide equally seamless project management or a highly sought-after niche product, TriMark's advantage diminishes, forcing competition to shift towards other factors like cost or delivery timelines.
The true differentiator lies in TriMark's capacity to deliver unique value that competitors find difficult to replicate, such as proprietary design software or exclusive supplier relationships that translate into cost savings or unique product availability for their customers.
In the foodservice equipment sector, where many products are standardized, the ability to bundle services effectively and provide exceptional project execution becomes paramount. For example, a competitor offering faster installation timelines or more flexible financing options could erode TriMark's perceived uniqueness, especially if TriMark's pricing isn't significantly lower.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers significantly impact competitive rivalry within the restaurant supply industry, potentially keeping underperforming competitors active and depressing prices. For a company like TriMark USA, this means facing rivals who might be operating at a loss simply because shutting down is too costly.
These barriers often stem from substantial investments in specialized fixed assets, like manufacturing facilities or large distribution networks, and unique inventory requirements. Long-term contracts with suppliers or customers also make exiting the market difficult and expensive. For instance, a competitor heavily invested in custom stainless steel fabrication equipment, a key asset in restaurant supply, would face considerable costs in selling or repurposing such specialized machinery.
- Significant Capital Investment: Many restaurant suppliers invest heavily in specialized equipment for manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics, making divestiture costly.
- Specialized Inventory: Holding a wide range of specific product lines, from custom kitchen equipment to niche tableware, can lead to unsellable inventory if operations cease.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with suppliers or large foodservice clients can create financial penalties or reputational damage for early termination, binding companies to the market.
- Brand Reputation and Goodwill: The effort invested in building a brand and customer relationships is lost upon exit, representing an intangible but significant barrier.
Switching Costs for Customers
When customer switching costs are low, the competition among companies like TriMark USA can become quite fierce. This is because it’s much easier for rivals to lure away clients if there’s no significant hurdle to changing providers. For basic equipment or routine supply needs, customers can simply shift to a competitor offering a better price or quicker delivery, as seen in the broad foodservice equipment market where many suppliers offer similar products.
However, TriMark USA actively works to increase these switching costs. By focusing on integrated project work, they aim to become deeply embedded within a client's operational workflow. This approach, often involving custom design, installation, and ongoing service for complex projects, makes it more difficult and costly for a client to transition to another supplier. For example, a restaurant chain undertaking a major kitchen renovation and relying on TriMark for the entire project, from design to equipment sourcing and installation, would face significant disruption and expense if they tried to switch mid-project.
- Low switching costs in standard product markets encourage price-based competition.
- TriMark USA differentiates by offering integrated solutions that increase client dependency.
- The complexity of custom projects creates higher barriers to switching providers.
- Client reliance on TriMark's project management and installation services raises switching costs.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for TriMark USA, stemming from a fragmented market with numerous national, regional, and local competitors. This intense competition often drives aggressive pricing and service strategies across all product categories and geographic areas. For instance, in 2024, the foodservice equipment sector saw continued vigorous competition from both large distributors and agile, specialized smaller firms vying for market share.
The growth rate of the foodservice industry directly influences the intensity of this rivalry; slower growth, potentially below 2% in 2025, typically leads to more aggressive competition as companies fight for existing customers. Conversely, expanding markets, like the strong consumer demand driving new restaurant openings in early 2024, can temper this rivalry by providing ample growth opportunities for all players.
TriMark USA attempts to differentiate through comprehensive service offerings, yet this advantage can be diminished if competitors match their integrated solutions or excel in niche areas. The ability to provide superior project execution, faster installation, or more flexible financing options can erode TriMark's perceived uniqueness, particularly if their pricing is not a clear advantage.
High exit barriers within the industry, such as significant investments in specialized fixed assets and long-term contracts, can keep less profitable competitors active, further intensifying rivalry. This means TriMark may face rivals operating at reduced margins simply due to the cost of exiting the market, a situation exacerbated by the specialized nature of restaurant supply equipment.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for foodservice operations extends beyond direct product alternatives to encompass entirely different business models that fulfill customer needs. For instance, the rise of meal kit delivery services, like HelloFresh which reported over $3 billion in revenue in 2023, offers a convenient at-home dining experience, bypassing the need for traditional restaurants. Similarly, ghost kitchens, operating solely for delivery and often utilizing shared facilities, reduce the capital expenditure on prime real estate and extensive front-of-house design, a core offering for companies like TriMark USA. These evolving consumer preferences and operational efficiencies present a significant challenge by diminishing the demand for traditional restaurant infrastructure and services.
The threat of substitutes for TriMark USA's equipment offerings is significant, particularly with the growing popularity of leasing over outright purchasing. Many customers, especially those dealing with high-value equipment or undertaking short-term projects, find leasing a more attractive financial proposition. This can divert potential buyers away from direct sales.
Dedicated equipment leasing companies provide a compelling alternative to purchasing, allowing clients to manage capital expenditure as operational expenditure. This financial flexibility is a key substitute for customers who may not want or be able to commit to a large upfront investment, impacting TriMark's direct sales volume.
For instance, in 2024, the global equipment leasing market was valued at over $300 billion, demonstrating the substantial scale of this substitute. Many businesses opt for leasing to access the latest technology without the burden of ownership, a trend that directly competes with TriMark's traditional equipment sales.
Large customers, particularly those with substantial purchasing power and sophisticated procurement departments, pose a significant threat by exploring direct sourcing from manufacturers. This bypasses distributors like TriMark, aiming for potential cost reductions. For instance, a large hotel chain with a dedicated purchasing team could negotiate bulk deals directly with kitchen equipment producers, cutting out the intermediary.
This direct sourcing acts as a substitute for TriMark's core distribution and procurement services. While it can yield savings for the end-user, it necessitates the customer possessing their own robust internal capabilities for project management, logistics, and installation, which not all clients may have readily available.
DIY Design and Procurement
The threat of substitutes for TriMark USA's services, particularly in DIY design and procurement, is present for certain client segments. Smaller businesses or those with existing in-house design capabilities may opt to manage their kitchen layouts and equipment sourcing themselves. This involves identifying and purchasing individual pieces of equipment from various suppliers, bypassing TriMark's integrated design and supply chain solutions.
This approach, while a substitute, demands considerable internal resources and expertise from the client. They would need to handle all aspects of design, vendor selection, negotiation, and logistics. For instance, a restaurant owner with a background in industrial design might feel comfortable managing this process independently, potentially saving on TriMark's service fees.
However, the complexity of commercial kitchen design, including specialized ventilation, plumbing, and code compliance, often makes a comprehensive, outsourced solution more efficient and cost-effective for many. TriMark's value proposition lies in its ability to streamline this process, leveraging its industry knowledge and supplier relationships to ensure optimal design and equipment selection. The burden of managing these intricate details independently can outweigh the perceived savings for many operators.
- DIY Design Risk: Clients with internal design expertise may bypass TriMark for independent procurement.
- Resource Intensive: Independent sourcing requires significant client investment in time and personnel.
- Complexity Barrier: Commercial kitchen design demands specialized knowledge often handled by experts like TriMark.
- Efficiency Trade-off: Clients weigh potential cost savings against the loss of TriMark's streamlined process and expertise.
Use of Multi-purpose or Residential-Grade Equipment
For extremely small or unconventional food service operations, the use of multi-purpose appliances or even residential-grade kitchen equipment presents a potential substitute threat. While these options lack the durability and capacity for high-volume commercial use, they can serve as a more economical choice for niche markets or very limited operations.
This alternative sourcing strategy can divert some demand away from specialized commercial equipment suppliers like TriMark USA. For instance, a small food truck or a pop-up vendor might opt for a high-quality residential oven rather than investing in a commercial-grade unit, especially if their sales volume is low and unpredictable.
The market for such alternatives is growing, particularly with advancements in home appliance technology making them more robust. While difficult to quantify precisely for TriMark's specific market segment, the broader trend shows increased interest in adaptable, multi-functional kitchen tools across various consumer and small business segments.
- Niche Market Appeal: Residential equipment is a low-cost substitute for very small or non-traditional food service setups.
- Cost Sensitivity: Operations with limited budgets may favor adapting home appliances over purchasing commercial-grade solutions.
- Volume Limitation: This substitute is generally unsuitable for businesses requiring high-volume output or continuous operation.
- Technological Advancement: Improved residential appliances offer greater versatility, potentially bridging the gap for smaller operators.
The threat of substitutes for TriMark USA is substantial, encompassing alternative business models, equipment sourcing methods, and even different types of equipment. These substitutes can reduce customer reliance on TriMark's core offerings, impacting sales and market share. For example, the expanding equipment leasing market, valued at over $300 billion globally in 2024, provides a direct alternative to purchasing, especially for businesses prioritizing operational expenditure and technological upgrades.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the foodservice equipment and design sector, where TriMark USA operates, demands substantial upfront capital. Newcomers need to finance extensive inventory, secure warehousing facilities, and establish appealing showrooms, which can easily run into millions of dollars. For instance, a mid-sized distributor might require $5-10 million just to stock a reasonable selection of equipment and maintain operational facilities.
Beyond physical assets, significant investment is needed for specialized design software, installation tools, and robust IT infrastructure. Furthermore, effective marketing campaigns and building strong credit relationships with manufacturers and suppliers are crucial, adding to the initial financial burden. These considerable capital requirements act as a formidable deterrent for potential new competitors looking to enter TriMark USA's market.
TriMark USA and its established competitors benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with key equipment manufacturers. These long-standing partnerships often translate into preferential pricing, exclusive distribution agreements, and guaranteed access to essential components, creating a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the foodservice equipment industry saw continued consolidation, with major suppliers prioritizing volume and reliability, favoring established clients like TriMark over unproven entrants.
TriMark USA, a significant player in its markets, likely enjoys substantial brand recognition and deep-seated customer loyalty. For any new competitor aiming to enter, overcoming this established trust requires a significant upfront investment in marketing and sales efforts, a process that typically takes considerable time and financial resources.
The reputation for reliability and exceptional service is paramount in this industry. In 2024, customer retention rates for leading providers often exceed 80%, underscoring the difficulty new entrants face in poaching established client bases. Building this level of confidence is a formidable barrier.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing large distributors, such as TriMark USA, leverage significant economies of scale across purchasing, logistics, and overall operations. This scale allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers and optimize their supply chains, translating into more competitive pricing and a higher level of service efficiency for their customers. For instance, in 2024, major players in the foodservice equipment distribution sector reported inventory turnover rates that outpaced smaller competitors, directly reflecting their operational advantages.
New entrants entering the market would initially face substantial hurdles in achieving similar economies of scale. Their smaller operational footprint would inevitably lead to higher per-unit costs for everything from procurement to warehousing and delivery. Lacking the years of accumulated experience and established infrastructure, these newcomers would find it challenging to match the cost-effectiveness and established operational efficiencies that incumbents like TriMark have cultivated.
- Economies of Scale: TriMark benefits from bulk purchasing power, reducing per-unit costs for goods and services.
- Logistical Efficiencies: Established distribution networks and optimized transportation routes lower delivery expenses.
- Experience Curve: Years of operation have refined processes, leading to greater productivity and lower waste.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Start-ups lack the volume and established processes, resulting in higher initial operating costs.
Regulatory Requirements and Certifications
The commercial foodservice sector, including companies like TriMark USA, faces significant hurdles due to stringent health, safety, and operational regulations. New companies entering this market must meticulously adhere to these rules, which govern everything from equipment standards to food handling practices.
Navigating this complex web of regulations and securing the required certifications and licenses is a substantial barrier. For instance, NSF International certification for food equipment, a common requirement, involves rigorous testing and adherence to public health standards. Obtaining these approvals often demands considerable investment in time and resources, making it difficult for smaller or less established players to compete effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face significant upfront costs for ensuring their products and operations meet all applicable health and safety standards, such as those mandated by the FDA and local health departments.
- Certification Processes: Obtaining necessary certifications, like UL listing for electrical safety or NSF certification for food contact surfaces, can be time-consuming and expensive, requiring specialized testing and documentation.
- Licensing and Permits: Securing various operational licenses and permits from federal, state, and local authorities adds another layer of complexity and cost to market entry.
- Industry Standards: Adherence to evolving industry best practices and standards, which can change based on new research or public health concerns, requires ongoing investment and adaptation.
The threat of new entrants in the foodservice equipment and design sector is moderate, largely due to the substantial capital investment required for inventory, warehousing, and showrooms, often running into millions. Established players like TriMark USA benefit from deep manufacturer relationships, preferential pricing, and exclusive agreements, creating significant barriers to entry. In 2024, the industry saw continued consolidation, favoring established clients and making it harder for newcomers to secure supply lines.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our TriMark USA Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including industry-specific market research reports, competitor financial statements, and trade association publications.
