Surgical Science Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Surgical Science Bundle
Surgical Science operates in a dynamic medical device market, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers is crucial for strategic planning.
The power of substitutes, though potentially lower in this specialized field, still warrants careful consideration of alternative treatment methods and technologies that could impact demand.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Surgical Science’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Surgical Science's reliance on specialized hardware, such as haptic feedback devices and advanced VR headsets, means suppliers of these critical components can wield considerable bargaining power. This is especially true if these components are proprietary or if there are few viable alternatives available in the market.
The cost of integrating these specialized parts can also be substantial, creating high switching costs for Surgical Science. For instance, if a key supplier were to increase prices for a unique haptic feedback system that forms the core of Surgical Science's simulator technology, the company would face significant disruption and expense in sourcing a replacement.
In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier of advanced processors for VR headsets, experienced supply chain constraints that led to price increases. This situation highlights the potential leverage suppliers of essential, hard-to-replicate technology can have over companies like Surgical Science.
Suppliers of proprietary software and development tools can significantly influence Surgical Science's operations. If key platforms, advanced graphics engines, or specialized programming interfaces are critical for the unique capabilities of their surgical simulators, these suppliers hold considerable leverage. This power is especially pronounced when these tools are de facto industry standards, with limited viable substitutes available, or when the cost and complexity of migrating to alternative solutions are prohibitively high.
The creation of lifelike medical simulations hinges on the input of surgeons, doctors, and anatomy specialists to guarantee precision and clinical applicability. These providers of specialized medical knowledge or consultancy services can wield considerable influence, particularly when they offer distinctive perspectives or access to a limited group of in-demand experts.
In 2024, the demand for highly specialized medical content for training platforms, especially in fields like minimally invasive surgery, has seen a notable increase. Companies relying on these niche experts often face pricing pressures as these individuals command premium rates for their unique expertise, reflecting their significant bargaining power.
Cloud Infrastructure and Data Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in cloud infrastructure and data services is significant for companies like Surgical Science, which increasingly rely on these platforms. Major cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer the scalable and secure infrastructure necessary for global deployment of simulation solutions, data storage, and analytics. This dependence grants them considerable leverage in setting costs and service agreements.
However, the intense competition among these leading cloud providers does temper their individual power. For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, with these three providers holding substantial market share, fostering a competitive environment that can benefit users through pricing and innovation. Surgical Science's ability to leverage this competition can help manage supplier power.
- High concentration of major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Global cloud market projected to exceed $700 billion by end of 2025
- Switching costs for cloud infrastructure can be substantial, increasing supplier lock-in
- Need for specialized data security and compliance standards favors established providers
Component Manufacturing and Assembly Partners
Surgical Science's reliance on component manufacturers and assembly partners for producing its simulator units means these suppliers hold a degree of bargaining power. This power is influenced by factors such as their production capacity, the quality control they implement, and their overall cost-effectiveness. For example, if a supplier can demonstrate a strong track record in meeting the stringent quality standards required for medical devices, their leverage in negotiations naturally increases.
The availability of alternative manufacturing partners also plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Surgical Science has limited options for specialized manufacturing processes or if few partners can meet the required medical device certifications, then existing suppliers can command more favorable terms. This is particularly true for suppliers offering niche components or unique assembly capabilities that are difficult to replicate elsewhere in the market.
In 2024, the global contract manufacturing market for medical devices was valued at approximately USD 38.5 billion, indicating a competitive landscape. However, for highly specialized components or assembly requiring specific certifications, the number of capable suppliers can be significantly smaller, thus concentrating power.
- Supplier Specialization: Suppliers with unique capabilities or expertise in medical device manufacturing can exert greater influence.
- Quality Control Standards: Adherence to rigorous quality assurance processes, essential for medical equipment, enhances a supplier's bargaining position.
- Alternative Supplier Availability: A limited pool of qualified alternative manufacturers increases the power of existing suppliers.
- Production Capacity: A supplier's ability to meet demand efficiently and at scale can be a significant bargaining chip.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration for Surgical Science, particularly concerning specialized hardware and proprietary software components. When suppliers offer unique, hard-to-replicate technology or critical development tools, their leverage increases due to high switching costs and limited alternatives.
The need for specialized medical expertise also grants certain suppliers significant influence. As demand for niche medical content, especially in areas like minimally invasive surgery, rises, experts in these fields can command premium rates, reflecting their strong bargaining position.
Cloud infrastructure providers also hold considerable power due to Surgical Science's reliance on their scalable and secure platforms for global deployment and data analytics. While competition among major providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud can temper individual power, the substantial switching costs and specialized security needs can still lead to supplier leverage.
Component manufacturers and assembly partners can also exert bargaining power, especially if they possess specialized capabilities, meet stringent medical device certifications, or if alternative suppliers are scarce. The global contract manufacturing market for medical devices, valued at approximately USD 38.5 billion in 2024, shows competition, but specialization concentrates power.
| Supplier Type | Factors Influencing Power | Example for Surgical Science |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Hardware (e.g., VR headsets, haptics) | Proprietary technology, few alternatives, high integration costs | Supplier of advanced haptic feedback devices critical for simulator realism |
| Proprietary Software & Tools | Industry-standard platforms, limited substitutes, high migration costs | Provider of specialized graphics engines for lifelike simulations |
| Medical Expertise & Content | Unique knowledge, in-demand specialists, niche training areas | Consultants providing precise anatomical data for surgical simulations |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Scalability, security, data storage needs, high switching costs | Major cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) |
| Component Manufacturers & Assembly | Specialized capabilities, medical certifications, production capacity, limited alternatives | Manufacturers of critical internal components requiring medical device compliance |
What is included in the product
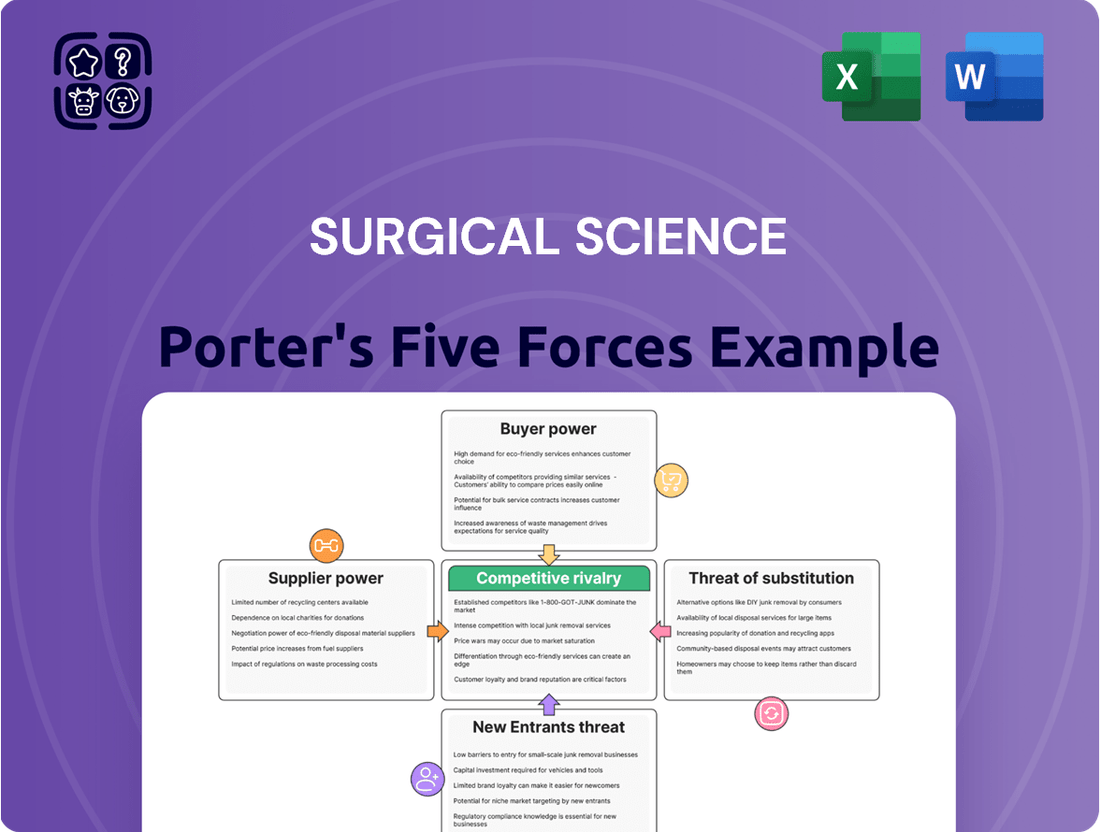
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the surgical simulation market, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and existing rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics, streamlining strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Surgical Science's main clients are sizable organizations such as hospitals, medical schools, and training facilities. These entities frequently purchase multiple units, allowing them to consolidate their buying power. For instance, a large hospital network might procure a substantial number of surgical simulators, giving them significant leverage.
This consolidated purchasing power enables these institutions to negotiate favorable pricing and customized terms with Surgical Science. Their ability to secure bulk discounts or specific product modifications directly impacts Surgical Science's pricing strategy and profit margins, highlighting the customers' bargaining strength.
Customers for surgical training solutions have a range of alternative methods available. These include established approaches like cadaver labs, hands-on proctored surgeries, and even animal models. Beyond these traditional routes, there are also various non-VR simulation tools that offer different learning experiences.
The presence of these substitutes, even if they don't directly replicate Surgical Science's specific VR technology, grants customers significant bargaining power. This leverage allows them to push for competitive pricing and demand a high return on investment from the solutions Surgical Science provides.
While customers, typically medical institutions and training centers, do have alternative simulation providers, the practicalities of adopting a new platform are substantial. These include the costs associated with training personnel on the new system, the effort required to integrate the simulation software with existing educational curricula, and the potential need for new or upgraded hardware to run the advanced features. For example, a major university hospital investing in a new surgical simulation suite in 2024 might face training expenses upwards of $50,000 for its faculty alone, alongside integration costs for their established medical school programs.
Consequently, once a surgical simulation system is in place and operational, these institutions are naturally disinclined to switch providers frequently. This stickiness can lessen the customers' immediate bargaining power when it comes to ongoing service agreements or incremental upgrades. However, the initial procurement phase still represents a significant opportunity for customers to exert considerable negotiation leverage, often securing favorable terms on the substantial upfront investment required for these sophisticated systems.
Price Sensitivity and Budget Constraints
Healthcare and educational institutions, key customers for Surgical Science, often face significant budget limitations. This price sensitivity means they scrutinize every purchase, pushing for competitive pricing and clear value propositions. For instance, a significant portion of hospital budgets is allocated to capital equipment, making them acutely aware of acquisition costs and ongoing operational expenses. This environment directly enhances the bargaining power of these customers.
Surgical Science must therefore not only offer competitive pricing but also clearly articulate the return on investment (ROI) for its simulation solutions. Customers will demand evidence that the technology leads to improved training efficiency, reduced errors, or better patient outcomes, all of which translate into cost savings or revenue generation. In 2024, many healthcare systems reported tighter margins, amplifying this demand for demonstrable ROI.
- Price Sensitivity: Healthcare and educational clients are highly sensitive to pricing due to budget constraints.
- ROI Demonstration: Surgical Science must prove a clear return on investment for its simulation products.
- Competitive Pressure: Customer budget limitations increase pressure for lower prices and value-added services.
- Budget Allocation: Capital equipment purchases are a major consideration in institutional budgets, influencing negotiation leverage.
Demand for Customization and Integration
Customers, particularly large medical institutions and training centers, often demand simulators be tailored to very specific surgical procedures or integrated into their current learning management systems and clinical workflows. This need for customization and seamless integration directly enhances their bargaining power.
Surgical Science’s ability to provide these bespoke solutions means customers can exert influence by dictating the precise features and functionalities required, often tying their willingness to pay to the successful integration of these elements. For instance, a major university hospital might require a simulator to perfectly replicate a new minimally invasive technique, demanding specific haptic feedback and visual fidelity, which can be a significant lever in negotiations.
- Customization Needs: Institutions frequently require simulators to be adapted for niche surgical specialties or specific training protocols, increasing customer leverage.
- Integration Requirements: The necessity for simulators to connect with existing IT infrastructure, such as learning management systems (LMS), gives customers power to dictate compatibility standards.
- Value of Tailored Solutions: Customers are often willing to pay a premium for customized products that align perfectly with their unique operational and educational objectives, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Procedural Specificity: The demand for simulators that precisely mirror complex surgical procedures grants customers significant influence over product development and feature sets.
The bargaining power of customers for Surgical Science is significant, primarily driven by the substantial size of their clients and the availability of substitutes. Major institutions like large hospital networks and universities possess considerable leverage due to their bulk purchasing capabilities, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing and customized terms. For example, a major university hospital investing in a new surgical simulation suite in 2024 might face training expenses upwards of $50,000 for its faculty alone, alongside integration costs for their established medical school programs, highlighting their ability to exert pressure on pricing.
Furthermore, the existence of alternative training methods, ranging from traditional cadaver labs to other simulation technologies, provides customers with options. This competitive landscape compels Surgical Science to offer compelling value and demonstrate a clear return on investment, especially considering that many healthcare systems reported tighter margins in 2024, amplifying the demand for demonstrable ROI.
| Customer Attribute | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidated Purchasing Power | High | Large hospital networks can negotiate bulk discounts. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate to High | Alternative simulation tools and traditional training methods exist. |
| Price Sensitivity & Budget Constraints | High | Healthcare budgets were tight in 2024, increasing scrutiny on capital equipment. |
| Need for Customization & Integration | High | Demand for specific procedural replication and LMS integration strengthens customer leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Low to Moderate (post-installation) | Initial investment and training create stickiness, reducing immediate bargaining power for upgrades. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Surgical Science Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Surgical Science Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive, fully formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs. It meticulously details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the surgical science industry. Rest assured, this is the exact, professionally written analysis you'll download immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into market dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The medical simulation market, especially in virtual reality, is seeing a significant increase in the number and variety of companies competing. This growth fuels intense rivalry as businesses battle for dominance and lucrative contracts with healthcare institutions.
We're seeing a mix of large, established players offering diverse simulation solutions alongside smaller, specialized startups focusing on particular surgical disciplines. For instance, companies like CAE Healthcare and Laerdal Medical provide broad portfolios, while newer entrants might focus exclusively on laparoscopic or orthopedic training.
This dynamic landscape means companies must constantly innovate and differentiate to capture market share. The increasing number of competitors, each bringing unique technologies and approaches, escalates the pressure to secure deals and maintain a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving sector.
Competitive rivalry in surgical simulation is fierce, driven by how well companies can make their products stand out. This differentiation often comes from how realistic the simulations are, the quality of the haptic feedback, the range of procedures offered, and how effective they are for training. Companies like Surgical Science are constantly pushing the boundaries to offer more advanced and lifelike experiences.
The pace of innovation is incredibly rapid. Competitors are pouring significant resources into research and development, meaning that a technological advantage can disappear quickly. For instance, advancements in AI-driven feedback and more sophisticated anatomical modeling are becoming standard expectations, requiring continuous investment to maintain a competitive edge.
Surgical Science’s commitment to R&D is evident in its product pipeline, which aims to address the evolving needs of surgical training. In 2024, the market saw continued growth in demand for simulation solutions that offer objective performance metrics and personalized learning pathways, areas where differentiation is key.
Developing advanced medical simulators demands massive initial outlays for research, software engineering, and hardware creation. These substantial fixed costs, combined with specialized equipment and the critical need to uphold a reputation in a specialized field, erect significant barriers to exiting the market.
Consequently, established players are often compelled to persevere within the industry, fiercely competing for market share rather than withdrawing. For instance, Surgical Science Sweden AB reported a significant increase in research and development expenses, reaching approximately SEK 230 million in 2023, underscoring the capital-intensive nature of product innovation in this sector.
Market Growth Rate
The medical simulation market is experiencing robust growth, a factor that significantly shapes competitive rivalry. As of late 2024, projections indicate continued expansion, with market research firm Grand View Research estimating the global medical simulation market to reach USD 11.6 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% from 2023 to 2030. This healthy growth rate generally tempers the intensity of rivalry, as there is sufficient market opportunity for multiple players to thrive without engaging in overly aggressive tactics to gain share.
However, the pace of growth can still influence competitive dynamics within specific segments. Where certain sub-sectors of medical simulation might see more moderate expansion or face saturation, competition can indeed intensify. Companies in these areas may resort to more aggressive pricing or marketing strategies to capture a larger portion of the available demand, potentially leading to price wars. For instance, while the overall market is strong, the market for basic procedural trainers might see more intense competition than advanced AI-driven simulation platforms.
- Market Growth: The global medical simulation market is projected to grow substantially, indicating a generally healthy competitive environment.
- Pace of Expansion: While overall growth is strong, slower expansion in niche segments can lead to heightened competition.
- Competitive Tactics: In more contested segments, companies might employ aggressive pricing and marketing to gain market share.
- Segment Variation: Competition intensity can vary significantly between different types of medical simulation products.
Strategic Stakes and Reputation
For companies like Surgical Science, leadership in the medical simulation sector carries substantial strategic weight. This leadership directly impacts brand reputation, the ability to forge crucial industry partnerships, and the pursuit of future growth avenues. The pursuit of this recognized leadership position, alongside securing major institutional clients, fuels intense competitive actions within the market.
These competitive actions often manifest as aggressive bidding strategies and significant investments in marketing and promotional activities. For instance, in 2024, the medical simulation market continued its robust expansion, with key players actively vying for market share. Companies are investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings, understanding that technological superiority is a critical component of their strategic stakes.
- Brand Reputation: A strong reputation as a market leader in medical simulation enhances trust and credibility with healthcare institutions, directly influencing purchasing decisions.
- Industry Partnerships: Securing partnerships with leading hospitals and medical universities is vital for market penetration and for gathering valuable feedback to drive product innovation.
- Future Growth: Dominance in simulation technology positions companies to capitalize on the growing demand for advanced surgical training and the increasing adoption of digital health solutions.
- Competitive Actions: The strategic importance of this sector leads to intense rivalry, characterized by innovative product launches and aggressive market penetration strategies by key players.
Competitive rivalry in surgical simulation is intense, driven by the need for differentiation through realistic simulations and advanced features. Companies like Surgical Science invest heavily in R&D, with Surgical Science Sweden AB spending approximately SEK 230 million in 2023 on R&D, highlighting the capital-intensive nature of innovation in this sector. This ensures they stay ahead in a market where technological advantages can be fleeting, as seen with advancements in AI feedback and anatomical modeling becoming industry standards.
| Company | 2023 R&D Spend (SEK million) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Science | ~230 | AI feedback, anatomical modeling, objective metrics |
| CAE Healthcare | (Not Publicly Disclosed for R&D Segment) | Broad simulation portfolios, diverse medical disciplines |
| Laerdal Medical | (Not Publicly Disclosed for R&D Segment) | Patient simulation, resuscitation training, digital learning |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Despite ethical and logistical hurdles, traditional cadaver and animal labs persist as fundamental surgical training tools. These methods are often seen as offering unparalleled realism in tactile feedback, a crucial aspect for mastering complex procedures.
While virtual reality simulations are gaining traction for their repeatability and safety, the ingrained perception of realism in cadaveric training presents a substantial substitute threat. This is particularly true for advanced surgical skill development.
The global anatomical models market, which includes cadaveric specimens, was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating continued reliance on these traditional methods despite emerging technologies.
Mannequin-based physical simulators present a significant threat of substitution for virtual reality (VR) training solutions like those offered by Surgical Science. These non-VR simulators provide a direct, tactile learning experience for a wide range of medical procedures, from simple stitching to complex laparoscopic surgeries.
Their affordability is a key factor, as they typically have lower upfront costs and do not necessitate the purchase of expensive VR headsets or supporting technology. This makes them particularly attractive to educational institutions and healthcare facilities operating with tighter budgets or those with users who may be less comfortable with advanced virtual reality interfaces.
In 2023, the global medical simulation market, which includes physical simulators, was valued at approximately $3.5 billion, with physical mannequins forming a substantial portion of this. The continued demand for these more traditional training methods demonstrates their enduring relevance as a substitute, especially in regions or departments prioritizing cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation over cutting-edge technology.
Live patient experience and proctored surgeries represent the ultimate form of surgical training, where seasoned surgeons directly guide trainees. While simulators are valuable for initial skill development, they cannot fully replicate the dynamic and complex environment of a real operating room. This continued reliance on hands-on practice with live patients acts as a significant substitute for the prolonged or exclusive use of simulators, particularly once fundamental competencies are achieved.
Video-Based Learning and Online Modules
Video-based learning and online modules represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional surgical education methods. These digital resources, including educational videos, interactive online modules, and virtual grand rounds, offer accessible and often more cost-effective ways to acquire surgical knowledge and observe procedures.
While these platforms cannot replicate the tactile experience of hands-on simulator training, they effectively substitute for certain aspects of knowledge transfer and procedural comprehension. This is particularly true in scenarios where access to advanced simulators or in-person training is limited.
The growth of this segment is substantial. For instance, the global e-learning market was projected to reach over $400 billion by 2026, indicating a strong and growing preference for online educational formats across various disciplines, including the medical field.
- Accessibility: Online platforms offer 24/7 access to educational content, breaking down geographical and time barriers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to physical training facilities and equipment, digital learning often presents a lower cost of entry for both institutions and learners.
- Scalability: Online modules can reach a vast number of learners simultaneously, making them highly scalable for widespread training initiatives.
- Content Diversity: A wide array of surgical specialties and procedures are covered, offering comprehensive learning opportunities.
Emerging Low-Cost Simulation Alternatives
Innovations in low-cost simulation are emerging as a significant threat. For instance, advancements in 3D printing allow for the creation of affordable anatomical models and task-specific trainers. These alternatives, while perhaps lacking the full immersion of virtual reality (VR) systems, offer a compelling value proposition due to their lower price point and simpler implementation. This makes them accessible to a wider array of educational institutions and for specialized skill development.
The cost-effectiveness of these emerging substitutes can attract customers who might find high-end VR simulators prohibitively expensive. For example, a basic 3D printed surgical model might cost a fraction of a sophisticated VR training module, making it an attractive option for institutions with tighter budgets. This accessibility broadens the market for simulation training, potentially drawing customers away from more advanced but costly solutions.
- 3D Printing: Enables creation of anatomical models and task-specific trainers at a lower cost than high-fidelity VR.
- Affordability: Lower price points make simulation training accessible to a wider range of institutions.
- Ease of Deployment: Simpler alternatives can be implemented more readily, reducing setup barriers.
- Targeted Skill Development: Effective for training very specific, isolated skills where full VR immersion may not be essential.
The threat of substitutes for Surgical Science's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing traditional methods and emerging low-cost alternatives. Cadaver and animal labs, despite ethical considerations, provide unparalleled tactile realism, a critical factor for advanced surgical training, and the global anatomical models market, valued at roughly USD 1.5 billion in 2023, shows their continued demand.
Mannequin-based physical simulators also present a significant challenge due to their lower cost and direct tactile experience, appealing to budget-conscious institutions, as evidenced by the global medical simulation market reaching approximately $3.5 billion in 2023.
Furthermore, video-based learning and online modules offer accessible and cost-effective knowledge transfer, tapping into a global e-learning market projected to exceed $400 billion by 2026, while innovations in 3D printing democratize simulation with affordable, targeted skill trainers.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantages | Market Relevance (Illustrative Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Cadaver/Animal Labs | Unparalleled tactile realism | Anatomical Models Market: ~USD 1.5 billion (2023) |
| Physical Simulators (Mannequins) | Lower cost, direct tactile feedback | Medical Simulation Market: ~USD 3.5 billion (2023) |
| Video/Online Learning | Accessibility, cost-effectiveness, scalability | Global E-learning Market: Projected >USD 400 billion (by 2026) |
| 3D Printed Simulators | Affordability, targeted skill development | Emerging segment with growing adoption |
Entrants Threaten
Developing sophisticated surgical simulation technology, especially in areas like virtual reality and haptics, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in specialized software engineers, biomechanical experts, and medical content developers. For instance, creating realistic anatomical models and responsive haptic feedback systems requires millions in R&D funding.
This substantial R&D expenditure acts as a formidable barrier. Newcomers often struggle to match the existing players' technological sophistication and product quality without immense financial backing. The sheer cost of innovation in this field naturally limits the number of new, well-funded entities that can credibly enter the market, thus reducing the threat.
Success in surgical science, particularly in areas like robotic surgery or advanced simulation, hinges on a highly specialized skill set. This includes deep medical understanding, sophisticated software engineering, precision hardware design, and effective instructional design for training. New entrants face a significant hurdle in assembling teams with this multifaceted expertise.
Attracting and retaining individuals possessing this rare combination of talents is both difficult and expensive. For instance, a senior robotic surgeon with a background in AI development might command an annual salary exceeding $500,000 in 2024, reflecting the scarcity of such professionals. This high cost of talent acquisition and retention creates a substantial barrier for startups lacking established industry connections or substantial financial backing.
Regulatory hurdles present a significant threat to new entrants in the surgical simulation market. While not all simulators are classified as medical devices, advanced systems or those used for certification purposes often require stringent approvals, such as those from the FDA or CE Mark.
The process of obtaining these approvals is both complex and time-consuming, creating a substantial barrier for new companies looking to enter the market. For instance, the average time to obtain FDA clearance for a new medical device can range from several months to over a year, involving extensive documentation and rigorous testing. This lengthy pathway, coupled with the associated costs, deters many potential new competitors.
Brand Reputation and Established Customer Relationships
The medical industry places a premium on reliability and a proven history, particularly for technologies that influence surgical training and patient outcomes. Established companies like Surgical Science have cultivated deep trust and enduring relationships with leading hospitals and academic institutions over many years. This makes it difficult for newcomers to quickly establish the necessary credibility and secure access to influential decision-makers within these critical organizations.
New entrants must overcome significant hurdles in replicating the brand equity and customer loyalty that incumbents enjoy. For instance, in 2024, a successful product launch in the medical simulation market often requires extensive clinical validation and endorsements from key opinion leaders, a process that can take years and substantial investment. Surgical Science, having solidified its market position, benefits from a strong brand reputation that new competitors find challenging to erode.
The established customer relationships translate into significant switching costs for healthcare providers. Once integrated into a hospital’s curriculum or a university’s training program, simulation platforms become deeply embedded, making it both costly and disruptive to adopt a new system. This loyalty is a key barrier, as evidenced by the long sales cycles and rigorous vetting processes typical for new medical technology introductions.
- Brand Reputation: The medical field prioritizes proven track records, making it hard for new entrants to gain trust.
- Customer Relationships: Established players like Surgical Science have built long-term ties with hospitals and universities.
- Switching Costs: Healthcare providers face significant disruption and expense when changing simulation systems.
- Credibility Challenge: New companies must invest heavily in validation and endorsements to compete.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
The threat of new entrants in surgical simulation is significantly mitigated by the substantial proprietary technology and intellectual property held by established players. Companies like Intuitive Surgical, a leader in robotic surgery and simulation, invest heavily in R&D, leading to a robust patent portfolio covering unique control systems and haptic feedback technologies. This intellectual property acts as a formidable barrier, requiring potential newcomers to either license these existing technologies or undertake costly, time-consuming research to develop novel, non-infringing solutions. For instance, the development of realistic anatomical models and sophisticated procedural simulations requires specialized expertise and significant upfront investment in software development and data acquisition.
This intellectual property creates a strong barrier, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate existing solutions without infringing on patents or investing heavily in novel R&D.
- Patented Technologies: Existing firms hold patents on unique simulation algorithms and hardware designs, such as advanced haptic feedback systems.
- Proprietary Algorithms: Complex algorithms that govern realistic tissue behavior and instrument interaction are difficult and expensive to reverse-engineer or replicate.
- Extensive Model Libraries: Companies have built vast libraries of virtual anatomical models and surgical procedures, representing years of data collection and development.
- R&D Investment: The high cost of research and development necessary to create competitive simulation platforms discourages new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in surgical simulation is low due to high capital requirements, with R&D costs for advanced VR and haptic systems potentially running into millions. Assembling teams with the necessary medical, engineering, and software expertise is also a major hurdle. For example, in 2024, top-tier simulation engineers can command salaries well over $200,000 annually.
Regulatory approvals, like FDA clearance, are complex and time-consuming, often taking over a year and significant investment, which deters many potential competitors. Established brands also benefit from deep customer loyalty and high switching costs in healthcare institutions, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Surgical Science, for instance, has built a strong reputation over years, requiring new entrants to invest heavily in clinical validation and key opinion leader endorsements.
Furthermore, proprietary technology and extensive patent portfolios held by industry leaders like Intuitive Surgical create substantial barriers. Developing novel, non-infringing solutions or licensing existing intellectual property demands significant financial and technical resources. The sheer scale of R&D investment required to create competitive simulation platforms, including vast libraries of anatomical models, actively discourages new market entrants.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Surgical Science Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and company investor relations materials to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
