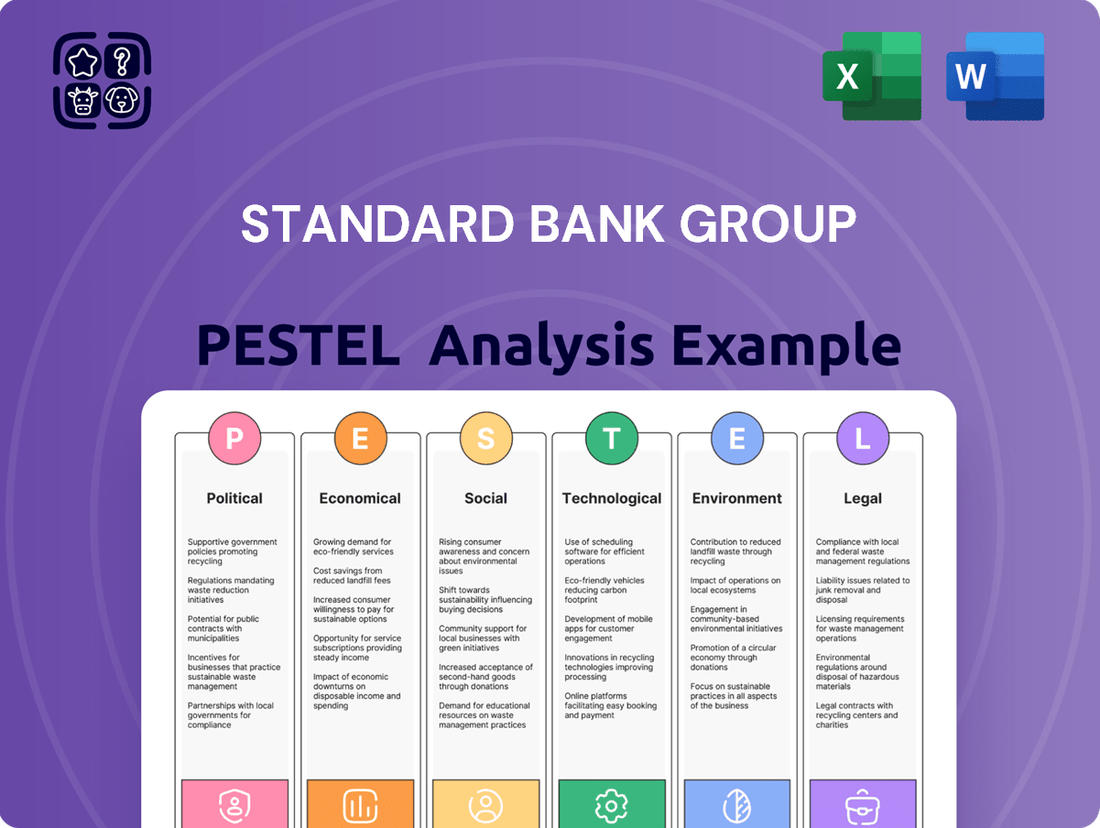
Standard Bank Group PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Standard Bank Group Bundle
Gain an edge with our in-depth PESTLE Analysis—crafted specifically for Standard Bank Group. Discover how evolving political landscapes, economic fluctuations, and technological advancements are shaping the company’s future. Understand the social and environmental pressures, alongside critical legal and regulatory shifts, that impact its operations. Use these comprehensive insights to strengthen your own market strategy and identify potential growth opportunities. Download the full version now and get actionable intelligence at your fingertips.
Political factors
Standard Bank's extensive operations across 14 African countries mean that government stability and policy consistency are paramount. For instance, in Nigeria, a key market, ongoing discussions around economic reforms and foreign exchange policies in 2024-2025 directly impact the banking sector's profitability and operational ease.
Political stability fosters investor confidence, a crucial element for Standard Bank's growth ambitions. Countries like South Africa, which experienced a period of heightened political uncertainty leading up to the 2024 general elections, saw a corresponding dip in investor sentiment. Predictable policy environments, however, encourage capital inflows, benefiting the entire financial ecosystem.
Conversely, sudden policy reversals or geopolitical tensions can create significant headwinds. The bank must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes; for example, changes in banking capital requirements or monetary policy in countries like Angola or Mozambique can swiftly alter the operating environment and affect Standard Bank's financial performance.
The regulatory framework, including central bank policies and tax laws, directly shapes Standard Bank's ability to conduct business, manage risk, and generate returns. In 2024, for example, several African nations were reviewing their financial sector regulations to align with international standards, presenting both opportunities for modernization and potential compliance challenges for the bank.
The banking sector across Africa, including Standard Bank's operating regions, is shaped by a dynamic regulatory environment. Efforts to harmonize with global standards such as Basel III and Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations are ongoing, influencing capital adequacy and risk management frameworks. For instance, as of early 2024, many African nations are still implementing or refining Basel III standards, requiring banks to hold higher levels of capital against their risk-weighted assets.
Standard Bank must meticulously adhere to a patchwork of national banking laws, varying capital requirements, and robust anti-money laundering (AML) regulations across its diverse markets. Non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties and the potential loss of operating licenses, directly impacting business continuity and strategic planning. For example, a major regulatory fine in South Africa or Nigeria could necessitate immediate capital injections or operational adjustments.
Navigating these complex and often stringent rules is paramount for maintaining trust and operational integrity. The bank's strategic decisions, from product development to market expansion, are inherently influenced by the need for regulatory compliance. This includes ongoing investment in compliance technology and personnel to effectively manage risks and reporting obligations, ensuring that Standard Bank remains a stable and trusted financial institution.
Standard Bank's cross-border operations are significantly shaped by evolving trade policies. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which officially began trading in January 2021, aims to create a single market for goods and services across Africa, potentially boosting intra-African trade by 81% by 2035 according to UNCTAD projections. This presents a substantial opportunity for Standard Bank to expand its trade finance and banking services to facilitate these increased financial flows.
Regional economic blocs, such as the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the East African Community (EAC), also influence Standard Bank’s activities by fostering deeper economic ties and harmonizing regulations. As these blocs promote greater integration, the bank can leverage these frameworks to offer more seamless financial solutions across member states, thereby enhancing its market reach and service offerings.
However, global policy shifts, like potential changes in trade stances from major economies such as the United States, can introduce economic headwinds. For instance, a slowdown in global trade or the imposition of new tariffs could dampen export volumes and investment flows, impacting Standard Bank's revenue streams derived from international trade finance and corporate banking activities.
Political Risk and Geopolitical Tensions
Standard Bank's expansive operations across numerous African nations mean it's inherently exposed to a spectrum of political risks. These include heightened geopolitical tensions, the potential for civil unrest, and the ever-present risk of expropriation of assets by governments. Such instability can significantly deter foreign investment, disrupt market dynamics, and lead to volatility in local currency exchange rates, directly impacting the bank's financial performance and the quality of its loan portfolio. For instance, the political climate in regions like the Sahel has seen increased instability, potentially affecting economic growth and investor confidence.
The bank's strategy must therefore incorporate robust risk management frameworks to continuously monitor and mitigate these political challenges. This involves understanding country-specific political landscapes, engaging with local stakeholders, and diversifying its exposure to buffer against localized disruptions. In 2024, Standard Bank’s commitment to navigating these complexities is underscored by its ongoing focus on strong governance and compliance across all its markets, aiming to maintain stability amidst diverse political environments.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Increased regional conflicts or border disputes can disrupt trade and economic activity in affected countries.
- Civil Unrest: Protests or social instability can lead to operational disruptions and damage to infrastructure.
- Expropriation Risk: Government policies that could lead to the seizure of assets pose a direct threat to foreign investments.
- Policy Changes: Sudden shifts in government regulations or taxation policies can negatively impact banking operations and profitability.
Government Support and Development Agendas
Government support and development agendas are pivotal for Standard Bank's growth across Africa. Initiatives promoting financial inclusion, for instance, open up new customer segments and transaction opportunities. In 2024, many African nations are intensifying efforts to broaden access to financial services, with governments actively encouraging digital banking solutions and mobile money adoption.
Infrastructure development projects, often spearheaded by governments, create substantial demand for project finance and related banking services. Standard Bank's involvement in funding these vital sectors, such as energy and transportation, directly contributes to economic expansion and provides the bank with profitable lending avenues.
Support for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) through government-backed loan guarantees or funding programs is another key area. By partnering with development financial institutions, Standard Bank can leverage these programs to de-risk lending to SMEs, thereby boosting employment and economic diversification. For example, in 2023, Standard Bank was a key participant in a syndicated loan facility supporting SMEs in South Africa, totaling R500 million.
- Financial Inclusion Drives: Governments are prioritizing digital finance expansion, aiming to bring millions of unbanked individuals into the formal financial system.
- Infrastructure Investment: Significant government spending on roads, energy, and telecommunications creates a strong demand for corporate banking and project finance.
- SME Ecosystem Support: Public-private partnerships and credit guarantee schemes are being enhanced to bolster SME access to capital, a core focus for Standard Bank.
- Alignment with National Goals: Standard Bank's strategic partnerships with bodies like the African Development Bank ensure its lending aligns with and benefits from national development plans.
Political stability is a cornerstone for Standard Bank's operations, with policy continuity in its 14 African markets being crucial. The 2024 Nigerian elections, for instance, highlighted the impact of political transitions on economic policy, affecting banking sector operations.
Regulatory frameworks, including central bank mandates and tax laws, directly influence Standard Bank's business. In 2024, several African nations were updating financial regulations, creating both compliance challenges and modernization opportunities.
Trade policies, such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), offer significant growth potential for Standard Bank's trade finance services. However, global trade policy shifts can introduce economic volatility, impacting international banking revenues.
Government support, particularly in financial inclusion and infrastructure development, creates opportunities for Standard Bank. For example, government-backed SME initiatives, like a R500 million facility in South Africa in 2023, directly benefit the bank's lending activities.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of how global and regional macro-environmental factors influence Standard Bank Group, covering political stability, economic trends, social demographics, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks.
A concise, actionable summary of Standard Bank Group's PESTLE analysis that directly highlights key opportunities and threats, simplifying strategic decision-making.
Provides a clear, structured overview of Standard Bank Group's external environment, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of potential challenges and leverage of emerging trends.
Economic factors
Standard Bank Group's fortunes are significantly influenced by the economic growth and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) trajectories within the African nations it serves. While the continent's financial services sector is generally robust, challenges such as increasing living expenses and slowing GDP growth in certain areas pose constraints on this expansion.
Looking ahead, Standard Bank projects a moderation of economic headwinds across sub-Saharan Africa. They anticipate an uptick in real GDP growth for the region, coupled with a more controlled inflation environment in 2025.
For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected sub-Saharan Africa's GDP growth to be around 3.8% in 2024, a slight improvement from previous years, with expectations for continued, albeit varied, growth into 2025, which directly impacts Standard Bank's operating landscape.
Fluctuations in interest rates and inflation are critical to Standard Bank's financial health. Higher rates can boost net interest income but also slow down lending as borrowing becomes more expensive for customers. For instance, South Africa's repo rate stood at 8.25% as of early 2024, a level that impacts both the bank's funding costs and its clients' ability to borrow.
Inflation directly influences consumer spending power and the bank's cost of doing business. While elevated inflation can necessitate higher interest rates, the South African Reserve Bank's proactive stance aims to manage these pressures. Anticipating potential interest rate cuts in late 2024 or 2025 could offer a significant boost to consumers and revive economic activity, benefiting Standard Bank's loan growth.
Currency fluctuations and volatile exchange rates across Africa present a substantial hurdle for Standard Bank Group. For instance, the South African Rand (ZAR) experienced significant depreciation against major currencies in early 2024, impacting the reported earnings of South African companies with international operations. This volatility directly affects Standard Bank's consolidated financial statements, as earnings generated in foreign currencies are translated back into ZAR, potentially distorting growth figures.
Managing foreign exchange risk is therefore critical for Standard Bank. The bank operates in numerous African markets, each with its own currency dynamics. A weakening of currencies in key markets like Nigeria or Angola, relative to the ZAR, can diminish the value of assets and income streams held in those countries when viewed from a South African perspective. For example, if the Nigerian Naira depreciates sharply against the ZAR, it directly reduces the ZAR equivalent of profits earned by Standard Bank's Nigerian subsidiary.
The impact of average currency movements on ZAR growth necessitates a robust hedging strategy. While Standard Bank aims for diversification across the continent, significant currency devaluations in one or more of its major operating regions can create headwinds for overall ZAR-denominated growth. This requires careful monitoring and proactive management of its exposure to minimize adverse impacts on its balance sheet and profitability.
Consumer Spending and Credit Demand
Consumer spending and the demand for credit are pivotal for Standard Bank, impacting both its retail and business operations. In 2024, South Africa's consumer confidence remained somewhat subdued, with the FNB/BER Consumer Confidence Index hovering around -10 in Q1 2024, indicating a cautious outlook among consumers. However, projections for 2025 suggest a potential uplift.
Anticipated interest rate cuts in 2025, following monetary policy tightening in previous periods, are expected to provide a much-needed boost to household finances. Lower borrowing costs can stimulate demand for credit, particularly for large purchases like vehicles and housing, thereby benefiting Standard Bank's lending portfolios.
This improved economic environment, characterized by potentially higher disposable incomes and increased willingness to borrow, should translate into greater client activity. Standard Bank could see an uptick in transactional volumes and a healthier trend in credit performance as consumers and businesses become more confident in their ability to manage debt.
- South Africa's consumer confidence in Q1 2024 was around -10, signaling consumer caution.
- Projections for 2025 indicate potential interest rate reductions, which could lower borrowing costs.
- Lower interest rates are anticipated to stimulate demand for consumer credit, especially for durable goods.
- Increased client activity and improved credit trends are expected to benefit Standard Bank's banking segments in 2025.
Investment Climate and Capital Inflows
The investment climate in Africa significantly shapes Standard Bank’s corporate and investment banking operations. Despite a generally positive outlook for African fintech, recent trends indicate a slowdown in equity funding, with global financial conditions tightening. This environment can directly influence the volume of capital flowing into the continent, impacting Standard Bank's ability to facilitate large-scale transactions.
For instance, while the African fintech sector saw substantial growth, venture capital funding across emerging markets experienced a notable cooling in late 2023 and early 2024 compared to the highs of 2021. Standard Bank is strategically positioned to navigate these shifts by leveraging its broad, diversified portfolio and forging key partnerships to continue attracting and channeling investment capital into the region.
Key factors influencing capital inflows for Standard Bank include:
- Investor confidence in African markets: While generally strong, it's susceptible to global economic headwinds.
- Equity funding trends: A decline in equity funding globally can reduce the pool of capital available for African ventures.
- Global financial conditions: Rising interest rates and a stronger US dollar can make emerging market investments less attractive.
- Standard Bank's strategic approach: The bank's focus on diversification and partnerships aims to mitigate these risks and attract consistent capital.
Standard Bank's performance is closely tied to economic growth across sub-Saharan Africa, with projections for 2025 indicating a modest recovery. The IMF anticipated sub-Saharan Africa's GDP to grow around 3.8% in 2024, with continued, albeit varied, expansion into 2025, directly influencing the bank's operating environment and potential for loan growth.
Interest rate policies remain a critical factor, with South Africa's repo rate at 8.25% in early 2024 affecting borrowing costs. Anticipated interest rate cuts later in 2024 or 2025 could stimulate consumer spending and business investment, benefiting Standard Bank's lending activities.
Currency volatility, particularly the South African Rand, poses a significant challenge. Depreciation against other currencies impacts the translated value of earnings from foreign operations, underscoring the need for robust foreign exchange risk management strategies.
| Economic Indicator | 2024 Projection/Value | 2025 Outlook | Impact on Standard Bank |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa GDP Growth | ~3.8% (IMF, 2024) | Continued, varied growth | Positive for loan demand and transactional volumes |
| South Africa Repo Rate | 8.25% (Early 2024) | Potential cuts | Lower borrowing costs, potential for increased credit demand |
| South Africa Consumer Confidence | ~-10 (Q1 2024) | Potential uplift | Increased spending and credit uptake |
| Global Equity Funding | Cooling trend | Continued caution | May impact large-scale corporate transactions |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Standard Bank Group PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use, offering a comprehensive PESTLE analysis of the Standard Bank Group. This detailed report meticulously breaks down the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the bank's operations and strategic decisions. By examining these critical external influences, the analysis provides invaluable insights into the opportunities and threats Standard Bank Group faces within its diverse operating environments. What you see is what you’ll be working with, ensuring transparency and immediate utility for your strategic planning needs.
Sociological factors
Africa's population is projected to reach 2.5 billion by 2050, with a significant portion being young. This burgeoning youth demographic, coupled with a rapid urbanization trend across the continent, creates a substantial and growing customer base for Standard Bank. For instance, by 2030, it's estimated that 56% of Africa's population will live in urban areas, a marked increase from today.
These demographic transformations directly fuel the demand for a wide array of financial services. As more people move to cities and enter the workforce, there's a greater need for personal banking, accessible credit, and increasingly, sophisticated digital payment solutions and mobile money services, which are already seeing significant adoption across Africa. Standard Bank's strategy hinges on serving these evolving needs.
Standard Bank is actively working to broaden financial inclusion to capture this expanding market. By 2024, over 60% of the African population remains unbanked or underbanked, highlighting the immense opportunity. The bank's focus on digital platforms and partnerships aims to bring more individuals and small businesses into the formal financial system, thereby unlocking new revenue streams.
A significant portion of Africa's population, estimated at around 40% in some regions as of 2024, remains unbanked or underserved by formal financial institutions. This presents a substantial opportunity for Standard Bank to drive financial inclusion. The bank's strategy involves developing accessible digital banking solutions and educational programs to bring more individuals and small businesses into the formal financial ecosystem.
Standard Bank is actively investing in initiatives to boost financial literacy across its markets, recognizing its importance for economic empowerment. For instance, in 2024, their financial education programs reached over 500,000 individuals, aiming to equip them with the knowledge to manage their finances effectively and utilize banking services more confidently.
Mobile money platforms are proving to be a critical enabler for financial inclusion in Africa, with adoption rates soaring. In 2024, over 60% of transactions in several key African markets where Standard Bank operates were conducted via mobile platforms, underscoring their potential to onboard previously unbanked segments of the population.
African consumers are rapidly embracing digital platforms for their banking needs, with mobile phone penetration acting as a significant catalyst. This trend is fueled by the sheer convenience offered by digital payments and online banking services, making them increasingly popular across the continent.
Standard Bank is actively responding to this evolving landscape by bolstering its digital capabilities. The bank is investing heavily in innovative technologies to streamline its services and create a more engaging client experience, recognizing that digital adoption is fundamentally reshaping how banking is done.
This strategic pivot has a direct influence on how Standard Bank develops its products and delivers its services. For example, the increasing use of mobile money platforms, which saw significant growth in Africa during 2023, necessitates new digital-first product designs and agile service delivery models.
Socio-Economic Development and Job Creation
Standard Bank plays a significant role in fostering socio-economic development by actively supporting job creation across the African continent. Its lending and investment strategies are particularly focused on empowering Small, Medium, and Micro Enterprises (SMMEs), which are vital engines for economic expansion and employment generation.
Through targeted initiatives, such as the issuance of social bonds and the implementation of risk participation agreements, Standard Bank enhances its capacity to lend to SMMEs. This support is crucial for these businesses to grow, innovate, and consequently, hire more people. For instance, in 2023, Standard Bank Group reported that its financing for SMMEs contributed to the creation and retention of an estimated 1.3 million jobs across its operating markets.
- Supporting SMMEs: Standard Bank's financial products and advisory services are designed to meet the specific needs of SMMEs, enabling them to overcome common growth barriers.
- Job Creation Impact: The Group's commitment to SMME financing directly translates into tangible job creation, with a significant portion of its lending portfolio directed towards these growth-oriented businesses.
- Economic Growth Contribution: By bolstering SMMEs, Standard Bank contributes to broader economic development, fostering entrepreneurship and increasing overall productivity within African economies.
- Sustainable Finance: Initiatives like social bonds demonstrate a commitment to sustainable development, linking financial performance with positive social outcomes, including employment opportunities.
Societal Expectations and Corporate Responsibility
Societal expectations are increasingly pressuring financial institutions like Standard Bank to actively engage in corporate responsibility, moving beyond traditional banking roles. This translates to a demand for fair customer treatment, robust employee engagement, and a proactive stance on critical issues such as climate change and the eradication of financial crime.
Standard Bank's stated purpose, deeply embedded in driving Africa's growth, aligns with these evolving societal demands by focusing on fostering sustainable and inclusive economic development across the continent. This commitment is crucial for maintaining social license to operate and building long-term stakeholder trust.
Key areas reflecting these societal expectations for Standard Bank include:
- Customer Fairness: Ensuring transparent pricing, accessible financial products, and effective complaint resolution mechanisms.
- Employee Welfare: Promoting diversity and inclusion, offering competitive compensation and benefits, and investing in employee development.
- Environmental Stewardship: Integrating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles into lending practices and operations, and supporting green finance initiatives. For instance, in 2023, Standard Bank continued to expand its sustainable finance offerings, aiming to mobilize capital for climate-resilient projects across Africa.
- Social Impact: Contributing to community development through financial literacy programs and initiatives that support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Standard Bank's strategic response to Africa's evolving demographic landscape is centered on leveraging the continent's youthful population and rapid urbanization. By 2030, a projected 56% of Africans will reside in urban areas, creating a significant demand for financial services that Standard Bank is poised to meet.
The bank is actively expanding financial inclusion, recognizing that over 60% of the African population remained unbanked or underbanked in 2024. This focus on digital platforms and partnerships is key to bringing more individuals and SMEs into the formal financial system, unlocking substantial market potential.
Standard Bank's commitment to socio-economic development is evident in its support for SMMEs, which are crucial for job creation. In 2023, its financing for these enterprises helped create or retain an estimated 1.3 million jobs across its operating markets.
| Societal Factor | Standard Bank's Response/Impact | Key Data/Examples |
| Demographic Shift (Youth & Urbanization) | Expanding customer base, demand for digital financial services. | Africa's population to reach 2.5 billion by 2050; 56% urban by 2030. |
| Financial Inclusion | Onboarding unbanked/underbanked, digital solutions. | Over 60% unbanked/underbanked in 2024; 60%+ mobile transactions in key markets (2024). |
| Job Creation & SMME Support | Targeted financing and advisory for SMMEs. | 1.3 million jobs created/retained via SMME financing (2023). |
| Corporate Social Responsibility | Focus on customer fairness, employee welfare, environmental stewardship, social impact. | Expanded sustainable finance offerings (2023); 500,000+ reached by financial education programs (2024). |
Technological factors
Digital banking and mobile money have fundamentally reshaped financial services across Africa, offering unprecedented access to financial tools. Standard Bank is strategically prioritizing its digital transformation, with a goal to boost the number of digitally active retail clients. This focus on mobile technology is key to delivering convenient and accessible banking solutions, particularly for populations historically excluded from traditional financial systems.
The African fintech scene is buzzing with activity, seeing constant new developments in alternative lending, Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services, and fully digital banks. For Standard Bank, this means facing off against nimble fintech startups that can adapt quickly.
Standard Bank is actively forming partnerships to bring digital financial services into its fold and improve what it offers to customers. These collaborations are key to staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology is further transforming how financial services are delivered and consumed across Africa, creating new opportunities and challenges.
As digital banking services expand across Africa, the imperative for robust cybersecurity and stringent data privacy measures for Standard Bank is undeniable. The increasing reliance on digital platforms means that safeguarding client information against evolving cyber threats is a top priority. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a significant rise in sophisticated cyberattacks targeting financial institutions continent-wide, underscoring the critical need for advanced protective systems.
Standard Bank must therefore maintain continuous investment in its technological infrastructure to bolster resilience and compliance with data protection laws, which are becoming more prevalent across its operating markets. Failure to adapt could lead to data breaches, reputational damage, and substantial financial penalties. The bank's commitment to enhancing its cybersecurity posture directly impacts its ability to foster and retain customer trust in an increasingly digital financial landscape.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Blockchain Integration
The financial services landscape is rapidly evolving with the convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology. These powerful tools are not just buzzwords but are actively reshaping how institutions operate and deliver value. For instance, AI is being deployed to automate complex financial operations, from fraud detection to personalized customer service, significantly boosting efficiency. Meanwhile, blockchain offers a decentralized and transparent ledger system that can revolutionize domestic payments, streamline cross-border transactions, and enhance security in supply chain finance.
Standard Bank is strategically positioning itself to harness these technological advancements. The group is actively exploring the integration of AI and blockchain to enhance operational efficiency, bolster security measures, and develop innovative financial products and services. This forward-thinking approach aims to provide customers with a more seamless and secure banking experience. For example, by mid-2024, many leading banks were reporting substantial improvements in transaction processing times and a reduction in operational costs through AI-driven automation. The adoption of blockchain for cross-border payments is also gaining traction, with pilot programs showing potential for near-instantaneous settlement times, a significant leap from traditional methods.
- AI-driven analytics are enhancing fraud detection rates, with some institutions reporting a 30% decrease in fraudulent transactions by early 2025.
- Blockchain pilots for cross-border payments are demonstrating potential to reduce transaction fees by up to 50% and settlement times from days to minutes.
- Supply chain finance leveraging blockchain is improving transparency and reducing risk, with early adopters seeing a 15% reduction in dispute resolution times.
- Standard Bank’s investment in digital transformation, including AI and blockchain, signals a commitment to future-proofing its operations and offerings.
Infrastructure Development and Connectivity
The availability and quality of digital infrastructure across Africa are crucial for Standard Bank's technological progress. Improved internet connectivity directly supports the bank's digital transformation, facilitating wider adoption of its services. For instance, in 2024, several African nations significantly boosted their fiber optic network expansion, aiming to bring high-speed internet to previously underserved areas.
Expanding fiber connectivity and enhancing digital service accessibility are vital for Standard Bank's digital initiatives. This infrastructure development is key to ensuring that the bank's digital solutions reach a broader customer base across the continent. By 2025, projections indicate continued investment in digital infrastructure, with a focus on increasing broadband penetration rates in key markets.
- Increased Fiber Deployment: Governments and private sector players are investing heavily in fiber optic networks, aiming to connect more urban and rural areas.
- Mobile Broadband Growth: Mobile internet access continues to expand, providing a foundational layer for digital banking services, especially in regions with limited fixed-line infrastructure.
- Digital Service Adoption: As infrastructure improves, the uptake of mobile banking, digital payments, and other online financial services is expected to accelerate, benefiting banks like Standard Bank.
- Data Center Development: Investments in local data centers are also growing, enhancing the reliability and speed of digital services for businesses and consumers.
Technological advancements, particularly in digital banking and mobile money, are reshaping financial services across Africa. Standard Bank is prioritizing digital transformation to increase digitally active retail clients, leveraging mobile technology for accessible banking solutions. The burgeoning African fintech sector, with its innovations in alternative lending and digital banks, presents both competition and partnership opportunities for the bank.
The integration of AI and blockchain technology is further transforming financial services, enhancing efficiency, security, and enabling new products. Standard Bank is actively exploring these technologies to improve operations and customer experience, with AI-driven analytics showing promise in fraud detection. Blockchain pilots for cross-border payments are demonstrating significant reductions in fees and settlement times, with early 2025 data suggesting up to a 50% fee reduction and near-instantaneous settlement.
The expansion of digital infrastructure, including fiber optic networks and mobile broadband, is critical for Standard Bank's digital initiatives. Improved connectivity directly supports wider adoption of its services, with significant investments in network expansion continuing through 2025. This infrastructure development is key to reaching a broader customer base, with projections indicating accelerated uptake of mobile banking and digital payments as accessibility grows.
| Technology Area | Impact on Standard Bank | Key Data/Trends (2024-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Banking & Mobile Money | Increased customer access and engagement | Goal to boost digitally active retail clients; significant growth in mobile money adoption continent-wide. |
| Fintech Innovation | Competition and partnership opportunities | Rise of nimble fintech startups; Standard Bank actively forming partnerships for digital service integration. |
| AI & Blockchain | Enhanced efficiency, security, and new products | AI improving fraud detection (up to 30% decrease reported by early 2025); Blockchain pilots reducing cross-border payment fees (potential 50%) and settlement times. |
| Digital Infrastructure | Enabling wider service reach and adoption | Continued investment in fiber optic networks and mobile broadband expansion; projections for increased broadband penetration rates. |
Legal factors
Standard Bank navigates a complex web of banking regulations, primarily overseen by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) and the Prudential Authority (PA). These bodies enforce stringent rules on capital adequacy, liquidity management, and overall risk exposure. For instance, the phased implementation of Basel III standards, which continues through 2025, mandates higher capital buffers to absorb potential losses. Failure to adhere to these prudential standards can result in significant penalties and damage to the bank's reputation.
Following South Africa's grey-listing by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) in February 2024, Standard Bank, like other financial institutions, faces heightened scrutiny and more stringent requirements for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) compliance.
This grey-listing necessitates a robust response from Standard Bank, demanding the implementation of comprehensive risk management processes, enhanced due diligence, and the diligent reporting of suspicious transactions to regulatory authorities.
Failure to adequately address these deficiencies not only risks further international sanctions and reputational damage but also impacts the integrity of the financial system, potentially increasing the cost of doing business and restricting access to international capital markets.
Standard Bank's commitment to strengthening its AML/CTF frameworks is crucial for navigating this challenging regulatory environment and maintaining its position as a trusted financial partner.
The increasing reliance on digital platforms in banking means Standard Bank must strictly follow data protection and privacy laws. This includes South Africa's Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) and comparable legislation in other African nations where it operates. For instance, in 2023, the number of data breaches reported in South Africa continued to be a significant concern, underscoring the importance of compliance.
Standard Bank needs strong data governance structures to protect customer details and meet changing legal mandates. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines and reputational damage, impacting customer trust. As of early 2024, regulatory bodies are increasingly enforcing these privacy standards with greater scrutiny.
Consumer Protection and Fair Practices
Consumer protection laws are paramount for Standard Bank Group, influencing how it interacts with its customer base. These regulations mandate fair practices, transparency in product offerings, and robust complaint resolution mechanisms. For instance, in South Africa, the Financial Advisory and Intermediary Services Act (FAIS) requires financial services providers to act honestly, fairly, and with integrity in rendering financial services.
Adherence to these legal frameworks is crucial for maintaining customer trust and avoiding significant penalties. In 2024, financial institutions globally faced increased scrutiny regarding data privacy and fair lending practices, leading to potential fines for non-compliance. Standard Bank's commitment to these principles helps mitigate legal risks and protects its reputation in the competitive banking sector.
Key areas of legal focus include:
- Fair Treatment of Customers: Ensuring all products and services are explained clearly and that customers receive appropriate advice.
- Data Privacy and Security: Complying with regulations like POPIA in South Africa and GDPR-like principles in other operating regions to safeguard customer data.
- Complaint Handling: Establishing efficient and accessible channels for customers to lodge and resolve grievances.
- Disclosure Requirements: Providing customers with all necessary information about fees, terms, and conditions of financial products.
Corporate Governance and Reporting Standards
Standard Bank Group places significant emphasis on robust corporate governance, adhering to frameworks like the King IV Report in South Africa. This commitment ensures a structured approach to ethical leadership and accountability. For the financial year ended December 31, 2023, Standard Bank reported a headline earnings per share of 1770.6 cents, underscoring its operational performance within its governance structure.
The bank's comprehensive reporting practices, encompassing detailed annual financial statements and integrated sustainability disclosures, are crucial for stakeholder trust. These reports provide a transparent view of the group's financial health and its environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. For instance, their 2023 Integrated Report highlights progress on their ESG strategy, including key performance indicators related to climate risk and social impact.
This adherence to high reporting standards is not merely a compliance exercise but a strategic imperative. It facilitates informed decision-making for investors and other stakeholders, ensuring long-term value creation. The group’s market capitalization as of mid-2024 reflects investor confidence, partly driven by its transparent and accountable governance and reporting.
- King IV Principles: Guiding Standard Bank's ethical and effective leadership.
- Transparency: Demonstrated through annual financial statements and sustainability disclosures.
- Stakeholder Accountability: Ensured by clear and comprehensive reporting.
- 2023 Financials: Headline earnings per share of 1770.6 cents highlight operational success.
Standard Bank operates under a robust legal framework, heavily influenced by South African and international banking regulations. The ongoing implementation of Basel III standards, set to continue through 2025, requires the bank to maintain higher capital reserves to manage potential financial shocks. Additionally, South Africa's grey-listing by the FATF in February 2024 has intensified scrutiny on Standard Bank's Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) measures, necessitating stricter compliance and reporting protocols.
Environmental factors
Climate change presents significant challenges and prospects for Standard Bank. Physical risks like extreme weather events and transition risks from evolving regulations could impact its operations and loan portfolios. For instance, increased drought in Southern Africa could affect agricultural loans, a key sector for the bank.
Conversely, the transition to a lower-carbon economy offers substantial opportunities in green finance. Standard Bank is actively pursuing these by financing renewable energy projects across Africa, aiming to address the continent's energy deficit sustainably. In 2023, the bank committed to mobilizing $100 billion in sustainable finance by 2025, with a significant portion directed towards climate solutions.
The bank is proactively embedding climate-related risks into its core enterprise risk management framework. This involves assessing the potential financial impacts of climate change scenarios on its assets and liabilities, ensuring that lending and investment decisions align with a sustainable future. This integration is crucial for long-term resilience and capitalizing on the growing green economy.
Standard Bank is actively driving sustainable finance, aiming to channel over R450 billion towards green and social projects by 2028. This ambitious target underscores their commitment to environmental responsibility and supporting a low-carbon future.
A significant portion of these funds will be directed towards renewable energy initiatives and infrastructure development crucial for the transition to a greener economy. This focus highlights the bank's strategic alignment with global sustainability trends.
By prioritizing financing for activities that facilitate a low-carbon economy, Standard Bank is positioning itself as a key player in addressing climate change challenges within the African continent. Their efforts directly contribute to sustainable development goals.
Standard Bank is significantly stepping up its ESG reporting, moving towards global benchmarks like the IFRS Sustainability Disclosures. This commitment means more detailed information on how the bank's operations affect society, the economy, and the environment.
The bank's latest sustainability reports, a key part of its disclosure strategy, highlight material ESG risks and opportunities. For instance, in their 2023 report, they detailed a 15% reduction in financed emissions intensity compared to their 2019 baseline, demonstrating concrete progress in environmental stewardship.
These enhanced disclosures are crucial for investors and stakeholders seeking transparency. In 2024, Standard Bank aims to further integrate climate-related financial disclosures, aligning with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) recommendations, with a specific focus on Scope 3 emissions reporting.
The evolving regulatory landscape, particularly in South Africa and other key markets, is driving this push for more robust ESG data. This proactive approach positions Standard Bank to meet increasing stakeholder expectations and navigate the growing importance of sustainability in financial performance.
Energy Transition and Fossil Fuel Financing
Standard Bank Group is navigating the complex landscape of the energy transition, aiming to balance Africa's growing energy demands with critical climate objectives. The bank has publicly committed to facilitating a just transition, a move that acknowledges the continent's unique development needs and its reliance on traditional energy sources for now.
While actively investing in renewable energy infrastructure across Africa, Standard Bank is also strategically financing new oil and gas projects. This approach is underpinned by stringent environmental and social risk management protocols. The bank's stated intention is to progressively reduce its exposure to upstream oil and gas activities, targeting a significant decrease by the year 2030.
- Commitment to Just Transition: Standard Bank prioritizes enabling Africa's energy transition while ensuring affordability and reliability.
- Renewable Energy Investment: The bank is a key financier of renewable energy projects across the continent.
- Oil & Gas Financing Strategy: Continued financing of new oil and gas projects is subject to robust environmental and social risk controls.
- Exposure Reduction Target: Standard Bank aims to limit its exposure to upstream oil and gas by 2030.
Nature-Related Risks and Biodiversity
Standard Bank is actively enhancing its grasp of nature-related financial risks, opportunities, and its own dependencies and impacts on ecosystems. This includes a focus on biodiversity, a critical component of environmental sustainability.
The bank's commitment is further evidenced by its participation in pilot projects specifically designed to deepen the understanding of these risks for financial institutions in South Africa. This proactive approach signals a significant evolution in how Standard Bank integrates biodiversity and ecosystem health into its core business and lending practices.
In 2024, the UN Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) reported that financial institutions managing assets worth $130 trillion were beginning to integrate nature-related risks into their strategies, highlighting a global trend Standard Bank is aligning with.
- Nature-Related Risk Assessment: Standard Bank is developing methodologies to identify and quantify risks stemming from biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation across its portfolio.
- Pilot Project Participation: Involvement in initiatives to understand nature-related risks for South African banks demonstrates a commitment to practical application and knowledge sharing.
- Biodiversity Integration: The bank is increasingly considering the impact of its financing activities on biodiversity and natural capital.
- Ecosystem Dependencies: Standard Bank recognizes its operational and financial reliance on healthy ecosystems and is working to manage these dependencies.
Standard Bank is actively navigating the environmental landscape by focusing on climate action and sustainable finance. The bank aims to mobilize R450 billion towards green and social projects by 2028, with a significant portion dedicated to renewable energy and infrastructure to support a low-carbon economy.
Climate change presents both risks and opportunities. Physical risks like extreme weather could impact loan portfolios, while the transition to a greener economy offers avenues for growth in green finance. Standard Bank reported a 15% reduction in financed emissions intensity by 2023 compared to a 2019 baseline.
The bank is also enhancing its understanding of nature-related financial risks and biodiversity impacts, participating in pilot projects to integrate these considerations into its business practices. This aligns with global trends, as institutions managing $130 trillion in assets were integrating nature-related risks by 2024.
Standard Bank is committed to a just energy transition in Africa, balancing energy demand with climate goals. While investing in renewables, they continue to finance new oil and gas projects under strict environmental controls, aiming to reduce upstream oil and gas exposure by 2030.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
The Standard Bank Group PESTLE analysis is informed by a comprehensive review of public and proprietary data, encompassing official government publications, reputable financial institutions, and leading market research firms. This ensures a robust understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental landscapes affecting the bank.
