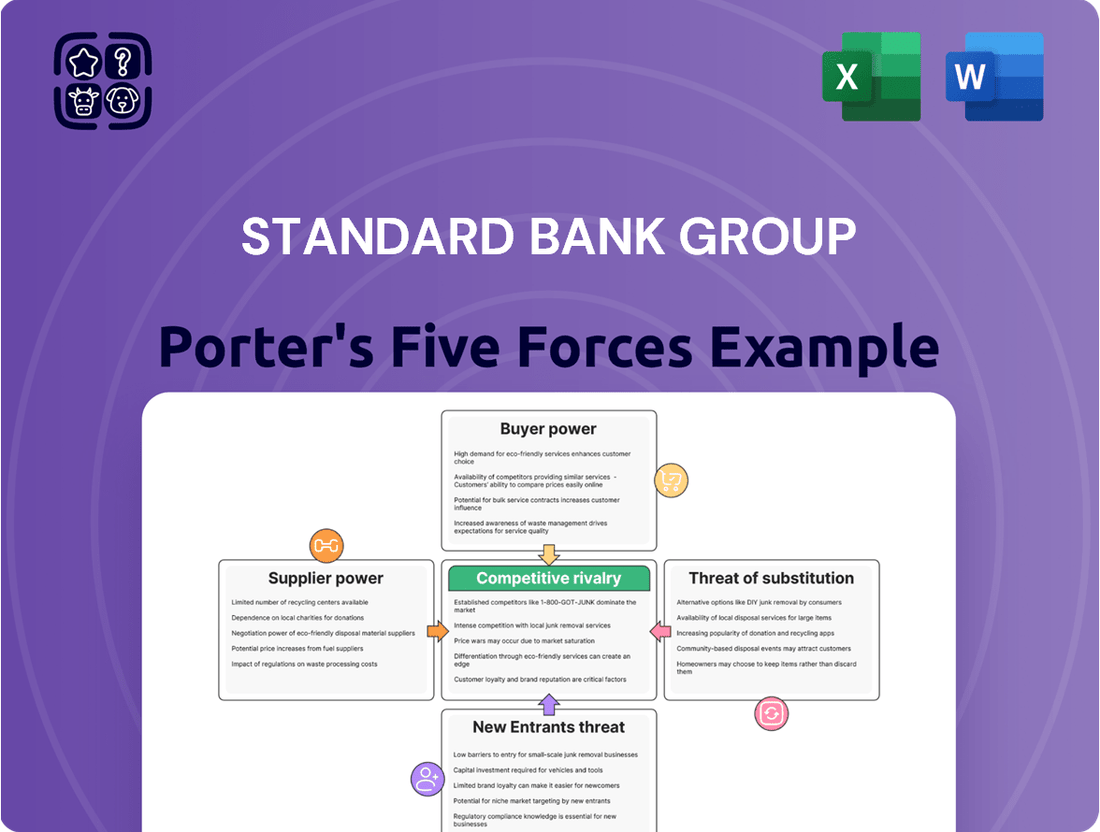
Standard Bank Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Standard Bank Group Bundle
Standard Bank Group operates in a dynamic financial landscape, facing significant pressures from competitors and evolving customer expectations. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The threat of new entrants in banking is moderate, as regulatory hurdles and capital requirements create barriers, yet fintech innovations can disrupt traditional models. Buyer power is substantial, with customers seeking better rates and digital experiences, pushing banks to innovate and offer competitive pricing.
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly technology providers and data services, presents a growing challenge, as banks increasingly rely on external expertise. The threat of substitutes is also a key consideration, with alternative financial services and payment platforms constantly emerging.
Intense rivalry among existing players, including traditional banks and emerging fintech firms, shapes Standard Bank Group's strategic decisions and pricing strategies. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Standard Bank Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Standard Bank's reliance on technology and infrastructure providers for critical software, hardware, and cloud services means these suppliers can wield considerable influence. This is particularly true when specialized or proprietary technologies are involved, as the cost and complexity of switching to a new vendor can be quite high, often creating significant switching costs for the bank.
The bargaining power of these technology suppliers is therefore assessed as moderate to high. Standard Bank's substantial investment in IT, amounting to R22.4 billion in 2024, underscores its dependence on these external partners to maintain and advance its digital operations and crucial payment systems, giving suppliers leverage.
The banking industry, including Standard Bank Group, heavily relies on specialized human capital. Professionals with expertise in areas like cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and complex financial modeling are in high demand. This scarcity directly translates to increased bargaining power for these skilled individuals, allowing them to command higher salaries and more attractive benefit packages.
In 2024, the competition for top tech talent within financial services intensified, with reports indicating salary increases of up to 15% for certain specialized roles. Standard Bank, with its extensive operations across Africa, faces the ongoing challenge of attracting and retaining this critical talent pool. This necessitates significant investment in competitive compensation, continuous professional development programs, and a compelling employer brand to maintain its workforce advantage.
Banks, including Standard Bank Group, depend on interbank lending, capital markets, and significant deposits from institutional investors for their funding needs. The leverage these suppliers hold is directly tied to how easily the bank can access funds elsewhere, influenced by overall market liquidity and prevailing interest rates. For instance, in a tight liquidity environment, suppliers can demand higher rates, increasing a bank's cost of capital. Standard Bank's strong credit ratings and diverse funding strategies, such as its access to international capital markets, help to lessen the bargaining power of these crucial funding sources.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
Standard Bank Group, operating in a highly regulated financial sector, faces significant bargaining power from its regulatory and compliance service providers. These firms, offering essential legal, audit, and advisory services, are critical for navigating complex global and local regulations. For instance, the implementation of standards like ISO 20022 requires specialized expertise, increasing the leverage of these providers. The potential financial and reputational damage from non-compliance means Standard Bank must often accept terms dictated by these specialized service providers.
The specialized knowledge required for regulatory adherence means fewer providers can adequately serve a global institution like Standard Bank. This limited supply of qualified experts directly translates into higher costs and less room for negotiation for the bank. As of 2024, the financial services industry continues to see increased regulatory scrutiny, further solidifying the position of these compliance service providers.
- High demand for specialized expertise: Financial institutions require deep knowledge of evolving regulations, such as those related to data privacy and anti-money laundering.
- Cost of non-compliance: The penalties for failing to meet regulatory standards are substantial, incentivizing banks to use top-tier compliance services.
- Limited provider pool: The niche nature of regulatory and compliance services means a smaller number of firms possess the necessary qualifications and experience.
- Impact of new standards: The ongoing adoption of global standards like ISO 20022 creates immediate needs for new compliance solutions, often from existing, powerful providers.
Physical Infrastructure and Utilities
While Standard Bank Group is actively pursuing digital channels, its need for physical infrastructure, including branches, ATMs, and data centers, means suppliers of real estate, utilities, and security services still hold some sway. The cost and reliability of these essential services, especially power and connectivity, can vary significantly across the diverse African markets Standard Bank operates in, impacting operational expenses. For instance, the cost of electricity in South Africa, a key market, saw an average increase of 12.7% for the 2023-2024 period, directly affecting utility bills for the bank's physical footprint.
Standard Bank is strategically managing its physical presence to mitigate supplier power. Initiatives include reducing the square meterage of its remaining branches and optimizing its ATM network. By consolidating operations and leveraging technology, the bank aims to decrease its overall demand for these physical resources, thereby lessening the bargaining power of suppliers in these categories. This focus on efficiency is crucial as the bank navigates rising operational costs and seeks to enhance its digital-first strategy.
- Real Estate: Ongoing consolidation of physical branches reduces the bank's reliance on large office spaces.
- Utilities: Fluctuations in energy prices, like the significant electricity tariff hikes in South Africa, directly influence operating costs.
- Connectivity: Reliable and affordable internet infrastructure is critical for data centers and ATMs, with supplier availability varying by region.
- Security Services: Maintaining physical security for branches and ATMs remains a necessary expense, with supplier pricing a factor.
Suppliers of specialized technology and critical infrastructure can exert significant bargaining power over Standard Bank, especially when proprietary solutions are involved. The substantial R22.4 billion invested in IT in 2024 highlights the bank's dependence, making switching costs for advanced software and cloud services a key factor in supplier leverage.
The demand for highly skilled professionals in areas like cybersecurity and AI grants these individuals considerable bargaining power, leading to increased salary and benefit expectations. In 2024, competition for these roles in financial services saw salary hikes up to 15% for certain specialists, impacting Standard Bank's talent acquisition costs.
Funding sources, including interbank lending and institutional deposits, hold leverage influenced by market liquidity and interest rates. Standard Bank's strong credit ratings and diverse funding strategies help mitigate this power. Furthermore, regulatory and compliance service providers, essential for navigating complex global rules, possess high bargaining power due to specialized knowledge and the severe penalties for non-compliance, a situation exacerbated by increased scrutiny in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Leverage Factor | Impact on Standard Bank | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Specialized/Proprietary Tech, High Switching Costs | Increased costs for essential IT services | R22.4 billion IT investment |
| Skilled Human Capital | Scarcity of Expertise (Cybersecurity, AI) | Higher salary and benefit demands | Up to 15% salary increases for specialists |
| Funding Sources | Market Liquidity, Interest Rates | Potential for higher cost of capital | Dependent on market conditions |
| Regulatory & Compliance Services | Niche Expertise, High Cost of Non-Compliance | Less negotiation power, higher service fees | Increased regulatory scrutiny |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Standard Bank Group, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate threats from competitors, new entrants, and substitute products, enabling Standard Bank to proactively adjust strategies and maintain market leadership.
Customers Bargaining Power
Standard Bank's diverse customer base, ranging from individual retail clients to large corporations and governments, creates varied levels of customer bargaining power. Retail customers, while having limited individual sway due to standardized offerings, can exert collective influence through digital channels and the ease of switching providers.
Corporate and institutional clients, on the other hand, wield greater bargaining power owing to their substantial transaction volumes and specialized financial requirements. For instance, in 2024, Standard Bank's retail segment continued to grow, with a significant portion of its customer base being individuals, highlighting the importance of managing this broader group's collective sentiment and ease of switching.
For basic banking services, customers today face remarkably low switching costs, largely due to the rise of digital platforms and regulatory efforts aimed at making it easier to move accounts. This ease of transition significantly boosts their bargaining power, pushing banks like Standard Bank to be more competitive with pricing and to continually enhance their digital offerings to keep customers engaged. In 2023, Standard Bank reported a notable shift, with digital transactions accounting for over 80% of customer interactions, underscoring the diminished reliance on physical branches and the increased customer ability to switch based on digital experience and cost.
The digital age has dramatically boosted information transparency for customers. Think about it: comparison websites for banking products, loans, and investments are everywhere. This means consumers can easily see which bank offers the best rates or the lowest fees. For example, in 2024, platforms like MoneySuperMarket in the UK or Bankrate in the US provided millions of customers with side-by-side comparisons of financial services.
This ease of comparison directly empowers customers. They are no longer in the dark about what other providers offer. They can now actively seek out better deals and demand more value from their existing financial institutions. This puts pressure on banks to remain competitive not just on product features, but also on pricing and service quality.
Standard Bank is aware of this trend. Their strategic focus on digitalization, as highlighted in their 2023 and 2024 reports, aims to improve the client experience and build stronger relationships. By making information more accessible and services more user-friendly through digital channels, they are responding to this increased customer power.
Digital Adoption and Self-Service Capabilities
The increasing embrace of digital banking by customers significantly bolsters their bargaining power. As more individuals utilize mobile apps and online platforms for their banking needs, they gain greater control and convenience, lessening their dependence on physical branches or direct interaction with bank staff. This shift empowers them to seek out the most seamless and cost-effective digital experiences available.
Standard Bank Group's own performance metrics highlight this trend. As of the first half of 2024, the bank reported a substantial increase in its digital active client base, with over 10 million digitally engaged customers. Furthermore, the consistent high ratings of its mobile banking application reflect customer satisfaction and a clear preference for self-service capabilities, reinforcing their ability to demand superior digital offerings.
- Digital Engagement: Standard Bank's digitally active client base surpassed 10 million in H1 2024, indicating a strong customer preference for digital channels.
- App Performance: High user ratings for Standard Bank's mobile app signify customer satisfaction with self-service features, enhancing their bargaining power for continued digital convenience.
- Reduced Reliance: The growing adoption of digital self-service reduces customer dependence on traditional, potentially more costly, banking interactions.
- Demand for Seamlessness: Customer preference for intuitive digital platforms drives expectations for continuous improvement and integration across banking services.
Demand for Tailored and Value-Added Services
Customers, especially in wealth management and corporate banking, are increasingly seeking personalized solutions and services that go beyond basic offerings. This trend empowers them to negotiate better terms.
Standard Bank has recognized this shift, dedicating resources to areas like sustainable finance and specialized wealth management. For instance, in 2024, Standard Bank launched new ESG-focused investment products, directly addressing the growing customer appetite for socially responsible options, which can be leveraged in discussions about service packages and fees.
- Personalized Financial Advice: Customers expect advice tailored to their unique financial situations and goals, not generic recommendations.
- Value-Added Services: This includes access to market insights, exclusive research, digital tools, and dedicated relationship managers.
- Sustainable and Ethical Investments: A significant segment of customers, particularly younger demographics and institutional investors, prioritize investments aligned with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles.
- Negotiating Power: The ability to articulate specific needs for these tailored services gives customers leverage in negotiating pricing and service level agreements.
The bargaining power of customers for Standard Bank is significantly amplified by the ease of switching and the availability of information, particularly in the digital realm. Customers can readily compare offerings, pushing banks to compete on price and digital experience. This dynamic is evident in the growing preference for digital self-service, as shown by Standard Bank's over 10 million digitally engaged customers in H1 2024, and high ratings for its mobile app, which reinforce their ability to demand superior digital services and reduced transaction costs.
| Factor | Impact on Standard Bank Customers | Evidence (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Switching | Low switching costs empower customers to seek better deals. | Digital platforms and regulatory efforts facilitate account portability. |
| Information Transparency | Customers can easily compare financial products and pricing. | Rise of comparison websites for banking services globally. |
| Digital Preference | Customers favor seamless, cost-effective digital experiences. | Over 80% of Standard Bank customer interactions were digital in 2023; 10M+ digitally active clients by H1 2024. |
| Demand for Personalization | Customers negotiate for tailored services like ESG investments. | Standard Bank launched new ESG-focused products in 2024 to meet this demand. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Standard Bank Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis of Standard Bank Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the banking giant. You're looking at the actual document, meaning that once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally written and formatted analysis, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Standard Bank faces formidable competition from established banks in Africa, especially in its home market of South Africa. Key rivals like FirstRand, Absa, Nedbank, and Capitec possess significant market presence and are actively enhancing their digital offerings, intensifying the battle for customers.
These incumbent institutions are not standing still; they are making substantial investments in technology and innovation to retain and attract clients. This digital push means Standard Bank must continuously adapt and improve its own digital services to remain competitive and capture market share.
For instance, Capitec Bank, known for its customer-centric approach and low fees, has rapidly gained market share, particularly among younger demographics, by leveraging digital channels effectively. This aggressive growth by competitors puts pressure on Standard Bank to innovate its product suite and customer experience.
The competitive landscape for Standard Bank is intensifying, largely fueled by rapid digital transformation. Banks are no longer just competing on traditional services but on the sophistication and user-friendliness of their digital channels, particularly mobile applications and online banking platforms.
Standard Bank has been a proactive participant in this digital race. In 2023, the bank reported a substantial 20% year-on-year growth in its active mobile app users, reaching over 10 million. This surge highlights the critical importance of digital engagement in retaining and attracting customers.
Furthermore, digital transaction volumes on Standard Bank’s platforms saw a remarkable 25% increase in the same period. This upward trend underscores the shift in customer behavior towards digital channels and the direct correlation between digital investment and market competitiveness.
Standard Bank's ambition for pan-African expansion fuels intense competition. As many African banks, including Standard Bank itself, chase growth across the continent, they increasingly clash in the same emerging markets. This broad regional push means banks are not just competing locally but across multiple borders, often encountering vastly different regulatory landscapes and economic volatilities.
For instance, Standard Bank's presence in key markets like Nigeria and South Africa means it directly contends with other major players like Access Bank and FirstRand, both of whom are also actively expanding their footprints. This cross-border rivalry intensifies as each institution aims to capture a larger slice of the growing African banking pie, leading to price wars and aggressive customer acquisition strategies.
Product and Service Diversification
Standard Bank faces intense rivalry not just from traditional banks but also from entities offering a broad spectrum of financial services. This includes wealth management, insurance, and investment banking, creating a complex competitive landscape. The group's strategic emphasis on these diversified offerings highlights its commitment to staying ahead in this multifaceted market.
Standard Bank's robust performance in its insurance and asset management divisions underscores the effectiveness of its diversification strategy. For instance, in 2023, the Group's headline earnings from Personal & Corporate Banking, which often includes wealth and investment services, remained a significant contributor. Their deliberate focus on sustainable finance further illustrates how they leverage diversification to gain a competitive edge, attracting clients and capital through forward-looking offerings.
- Diversification into Wealth Management: Standard Bank offers a range of wealth management solutions, catering to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients, broadening its revenue streams beyond core banking.
- Insurance as a Growth Driver: The Group's insurance business has shown consistent growth, contributing positively to overall financial results and providing a stable income source that complements transactional banking.
- Investment Banking Capabilities: Standard Bank's investment banking arm engages in corporate finance, mergers and acquisitions, and capital markets, placing it in direct competition with global and regional investment houses.
- Sustainable Finance Initiatives: By actively pursuing sustainable finance, Standard Bank differentiates itself, aligning with growing investor and customer demand for environmentally and socially responsible financial products.
Focus on Customer Experience and Brand Strength
Competitive rivalry within the banking sector is intensifying, with institutions increasingly differentiating themselves through superior customer experience, exceptional service quality, and robust brand strength, rather than solely on price. Standard Bank Group, for instance, has been recognized for its customer experience in consumer banking, a crucial factor in attracting and retaining clients in a crowded market.
This focus on non-price competitive factors is supported by industry trends. For example, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of banking customers consider customer service a primary driver for choosing or leaving a bank. Standard Bank's own improved brand ranking across Africa further underscores how a strong brand narrative and consistent positive customer interactions can mitigate direct price competition.
- Customer Experience Focus: Banks are investing heavily in digital platforms and personalized services to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Brand as a Differentiator: A strong, trusted brand reputation builds loyalty and can command premium pricing.
- Service Quality Impact: High-quality service leads to better customer retention and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Standard Bank's Performance: Recent accolades for customer experience and an upward trend in brand rankings demonstrate the effectiveness of this strategy.
Standard Bank operates in a highly competitive environment, particularly within South Africa and across its pan-African footprint. Rivals like FirstRand, Absa, and Nedbank are aggressively investing in digital transformation, mirroring Standard Bank's own efforts to enhance mobile and online banking services. For example, in 2023, Standard Bank saw its active mobile app users grow by 20% to over 10 million, indicating the critical importance of digital engagement against competitors also vying for customer attention. This intense rivalry extends to emerging markets where multiple banks, including Standard Bank, are vying for market share, often leading to aggressive customer acquisition strategies and a focus on differentiated offerings beyond just price.
| Competitor | Key Markets | Digital Focus | 2023 Performance Highlight (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FirstRand | South Africa, Rest of Africa | Digital platforms, personalized banking | Strong growth in digital transaction volumes |
| Absa | South Africa, Rest of Africa | Mobile banking, fintech partnerships | Increased investment in AI-driven customer service |
| Nedbank | South Africa, Rest of Africa | Digital onboarding, data analytics | Expansion of digital lending solutions |
| Capitec Bank | South Africa | Low-fee digital services, customer-centric app | Continued rapid customer acquisition, especially among younger demographics |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Mobile money and digital payment platforms present a substantial threat to Standard Bank Group. These services, widely adopted across Africa due to high mobile penetration, offer convenient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional banking for everyday transactions and remittances. For instance, by the end of 2023, mobile money accounts in Africa reached over 1.5 billion, facilitating billions of dollars in transactions annually, bypassing traditional banking channels.
The ability of these platforms to operate with leaner overheads and often lower transaction fees directly challenges the revenue streams of incumbent banks like Standard Bank. This shift means customers may opt for these digital solutions for their payment needs, reducing reliance on conventional banking products and services, thereby impacting customer acquisition and retention for Standard Bank.
Fintech lending and crowdfunding platforms pose a significant threat by offering alternative financing channels, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individuals seeking faster, more accessible credit than traditional banks. These platforms bypass lengthy approval processes, making them attractive substitutes for conventional bank loans.
Standard Bank recognizes this disruption and is actively engaging with the fintech sector through innovation challenges, aiming to foster collaboration and integrate new technologies. In 2024, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, highlighting the scale of competition and the need for incumbents like Standard Bank to adapt.
Non-bank financial service providers pose a significant threat. Retailers are increasingly embedding financial solutions, like buy-now-pay-later schemes, directly into their sales processes, offering alternatives to traditional credit. In 2023, the global buy-now-pay-later market was valued at over $130 billion and is projected to grow substantially.
Insurance companies are also expanding into investment products, directly competing with banks for customer savings and wealth management. Similarly, specialized asset managers can offer competitive investment vehicles that bypass traditional banking channels. For instance, many fintech platforms now provide investment services with lower fees than those typically found at large banks.
Standard Bank is actively mitigating this threat through strategic partnerships and a diversified product suite that includes insurance and asset management arms. This integrated approach allows them to offer a broader range of financial services, potentially retaining customers who might otherwise seek substitutes elsewhere.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Solutions
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology present a growing threat of substitution for traditional banking services, especially in areas like cross-border payments and digital asset management. While not yet a mainstream replacement for everyday banking, their potential to disrupt established financial flows is significant.
Standard Bank's leadership, including its CEO, has publicly acknowledged and even endorsed the development of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). This indicates a proactive stance and an understanding of how these new technologies could reshape the financial landscape. For instance, by mid-2024, several countries were actively piloting CBDCs, exploring their potential to improve payment efficiency and financial inclusion, directly challenging traditional remittance and payment systems where banks currently hold a dominant position.
- Disruptive Potential: Blockchain-based solutions offer faster, cheaper, and more transparent alternatives for remittances and value transfer, potentially bypassing conventional banking channels.
- Growing Adoption: While still in early stages for many daily transactions, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization, which fluctuates but has seen significant growth in recent years, indicates increasing investor and user interest in these alternative assets and technologies.
- CBDC Developments: Central bank digital currencies, supported by insights from leaders like Standard Bank's CEO, represent a state-sanctioned digital currency that could further compete with or complement traditional banking services.
Informal Financial Systems
Informal financial systems, like stokvels and community lending, remain strong substitutes for formal banking across many African markets. These systems cater to a significant portion of the population, offering accessible financial services outside traditional channels. For instance, in South Africa alone, stokvels manage billions of dollars annually, demonstrating their substantial economic impact and reach.
Standard Bank is actively working to counter this threat by enhancing financial inclusion and digital offerings. Their strategy aims to attract these unbanked and underbanked segments into formal banking services. By providing user-friendly digital platforms and tailored products, Standard Bank seeks to offer a more convenient and comprehensive alternative to informal arrangements.
- Stokvels in South Africa: Estimated to manage over R44 billion (approximately $2.4 billion USD as of mid-2024) annually, highlighting their significant role in savings and investment.
- Digital Adoption: Standard Bank reported a substantial increase in digital transactions, with mobile banking and online platforms becoming increasingly popular, indicating a shift in customer behavior.
- Financial Inclusion Goals: The bank has set ambitious targets to onboard millions of new customers through its digital channels, directly addressing the market served by informal systems.
The threat of substitutes for Standard Bank Group is multifaceted, encompassing digital payment platforms, fintech lending, non-bank financial providers, cryptocurrencies, and informal financial systems. These substitutes offer convenience, lower costs, and faster access to financial services, directly challenging traditional banking models.
Mobile money platforms, with over 1.5 billion accounts in Africa by late 2023, facilitate billions in transactions, bypassing banks. Fintech lending and crowdfunding offer quicker credit access, while retailers embed buy-now-pay-later options. The global fintech market exceeding $1.1 trillion in 2024 underscores this competitive landscape.
Cryptocurrencies and CBDCs, with several countries piloting CBDCs by mid-2024, represent emerging threats in payments and asset management. Informal systems like South Africa's stokvels, managing over R44 billion annually, also provide significant competition by offering accessible financial solutions outside formal channels.
| Substitute Category | Key Offering | Impact on Standard Bank | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | Mobile money, digital wallets | Reduced transaction fees and customer reliance on traditional banking | 1.5 billion+ mobile money accounts in Africa (end 2023) |
| Fintech Lending | P2P lending, crowdfunding | Alternative financing channels, faster credit access | Global fintech market valued at over $1.1 trillion (2024) |
| Non-Bank Financial Services | BNPL, embedded finance, specialized investments | Competition for customer savings and credit | BNPL market valued over $130 billion (2023) |
| Digital Assets & CBDCs | Cryptocurrencies, central bank digital currencies | Potential disruption of cross-border payments and digital assets | Multiple CBDC pilots underway globally (mid-2024) |
| Informal Financial Systems | Stokvels, community lending | Catering to unbanked/underbanked segments | Stokvels manage over R44 billion annually in South Africa |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Standard Bank Group, faces substantial regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2024, Basel III Endgame regulations continue to shape capital adequacy ratios, demanding significant reserves. These stringent capital requirements, coupled with complex licensing procedures for new full-service banks, effectively deter many potential entrants. This creates a protected environment for established players.
Digital-only banks and challenger banks present a significant threat to traditional players like Standard Bank Group. These nimble, tech-focused institutions, such as Revolut and Monzo, operate with substantially lower overheads by eliminating the need for extensive physical branch networks. This cost advantage allows them to offer highly competitive pricing and specialized digital services.
While regulatory hurdles remain, the agility and customer-centric approach of these new entrants are proving effective in attracting a growing segment of digitally native consumers. For instance, by mid-2024, challenger banks globally had amassed hundreds of millions of customers, demonstrating their rapid market penetration and ability to disrupt established banking models. Their focus on user experience and innovative features, often at lower fees, directly challenges traditional banks to adapt their own digital offerings.
Fintech startups are increasingly targeting specific, underserved niches within financial services, presenting a significant threat to incumbent institutions like Standard Bank. These agile companies, often unburdened by legacy systems, can rapidly develop specialized solutions for areas like cross-border payments, peer-to-peer lending, or digital wealth management. For instance, the global fintech market size was estimated to be over $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, with a substantial portion driven by these specialized players. Their ability to offer lower fees and a more streamlined user experience in these focused segments can attract customers away from traditional banks.
Technological Disruption and Innovation
Technological advancements, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data analytics, are significantly lowering the barriers to entry for new financial service providers. These innovations allow challengers to create cutting-edge solutions with considerably less initial capital outlay than traditional banking models required. For instance, fintech startups can now offer sophisticated digital banking, lending, and payment services, directly competing with established institutions.
Standard Bank is actively responding to this threat by integrating data and AI into its operations to maintain its competitive edge. In 2023, the bank reported a significant increase in digital transaction volumes, underscoring its commitment to technological adoption. This strategic focus on leveraging advanced analytics helps Standard Bank to personalize customer offerings and improve operational efficiency, thereby mitigating some of the disruptive impact of new entrants.
- AI Adoption: Standard Bank is investing in AI to enhance customer service through chatbots and to improve fraud detection.
- Cloud Computing: The bank is migrating more services to the cloud to enable scalability and faster deployment of new digital products.
- Data Analytics: Enhanced data analytics capabilities are being used to gain deeper customer insights and tailor product development.
- Fintech Collaboration: Standard Bank actively explores partnerships with fintech firms to leverage their innovative technologies and reach new customer segments.
Access to Customer Data and Ecosystem Building
New entrants, especially major technology firms, pose a significant threat by potentially using their vast existing customer bases and rich data troves to offer financial services. This allows them to rapidly build integrated ecosystems that can be highly attractive to consumers. For instance, by 2024, many large tech companies have deepened their financial service offerings, leveraging user data for personalized product development and streamlined integration within their existing platforms.
Standard Bank's strategy to counter this threat centers on enhancing client experience and fostering sustainable growth. By building robust customer relationships and cultivating loyalty, the bank aims to create sticky ecosystems of its own. This proactive approach is crucial as the financial landscape becomes increasingly competitive, with non-traditional players entering the market.
- Leveraging Existing Data: Tech giants can deploy extensive customer data to personalize financial product offerings, a key advantage.
- Ecosystem Integration: New entrants can seamlessly integrate financial services into their broader digital offerings, increasing convenience for users.
- Standard Bank's Defense: Focus on client experience and loyalty programs aims to retain customers and build a competitive ecosystem.
- 2024 Market Trends: Continued expansion of embedded finance by non-financial companies highlights the growing threat of ecosystem disruption.
The threat of new entrants for Standard Bank Group is multifaceted, encompassing agile fintechs, digital-only banks, and even major tech companies. While regulatory barriers and capital requirements remain significant, technological advancements are lowering entry costs for specialized financial services. These new players often leverage lower overheads and a focus on user experience to attract customers, particularly digitally native segments.
The rapid growth of challenger banks, evidenced by hundreds of millions of global customers by mid-2024, highlights their disruptive potential. Fintech startups, targeting niches like cross-border payments, further intensify competition. Standard Bank is actively investing in AI, cloud computing, and data analytics, as seen in its increased digital transaction volumes in 2023, to counter these threats and enhance customer offerings.
Major tech firms entering financial services pose a substantial risk due to their vast customer bases and data capabilities, allowing for integrated ecosystems. Standard Bank's strategy to combat this involves strengthening client relationships and building its own competitive ecosystem through enhanced client experience and loyalty programs.
| Threat Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Standard Bank | Mitigation Strategies | 2024 Data/Trends |
| Fintech Startups | Niche focus, lower fees, agile tech | Customer attrition in specific segments | Partnerships, specialized digital offerings | Global fintech market over $2.4 trillion (2023) |
| Digital-Only/Challenger Banks | Low overheads, superior UX, competitive pricing | Rapid customer acquisition, pressure on traditional models | Digital transformation, AI-driven services | Hundreds of millions of global customers by mid-2024 |
| Tech Giants | Large user base, data advantage, ecosystem integration | Potential for embedded finance disruption | Enhance client experience, build proprietary ecosystems | Deepening financial service offerings by tech firms |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Standard Bank Group is built upon a robust foundation of data, including their annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We supplement this with insights from reputable industry research firms, financial news outlets, and economic data providers to capture the broader market landscape and competitive dynamics.
