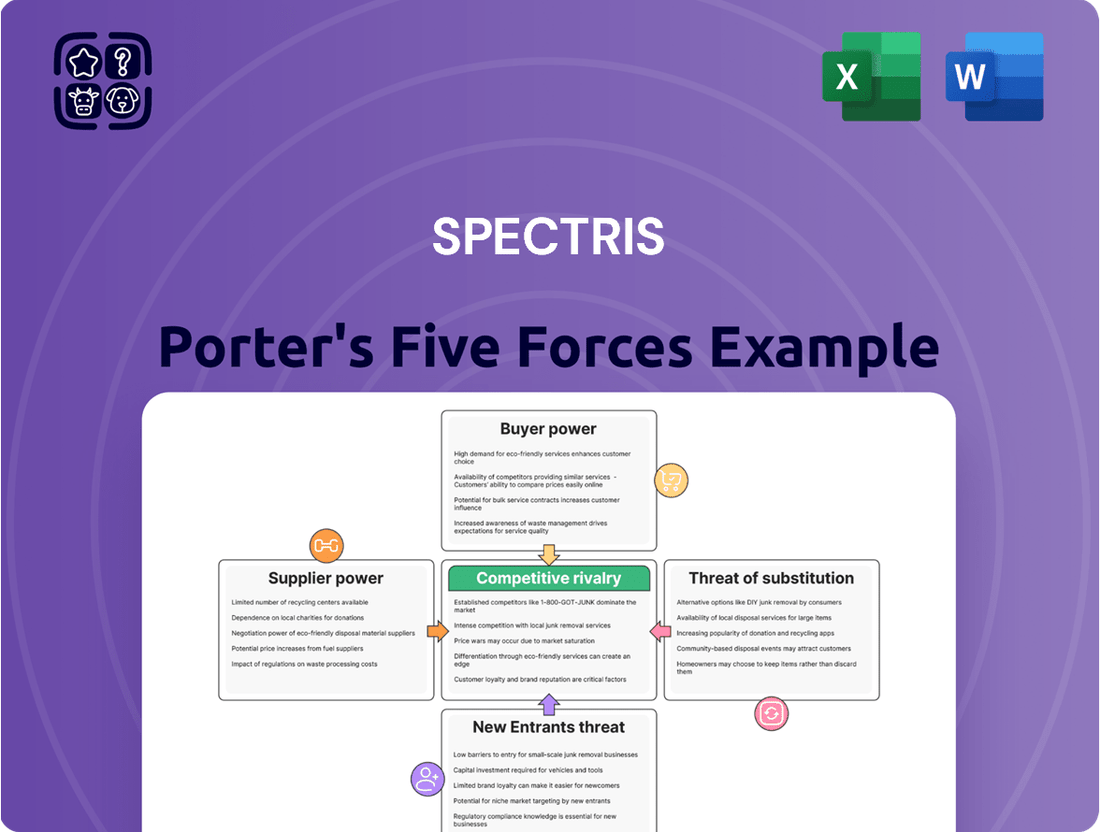
Spectris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Spectris Bundle
Spectris, a leader in precision instrumentation and test equipment, operates within a dynamic and competitive landscape. Understanding the forces shaping its market is crucial for strategic planning. The intensity of rivalry among existing players, the bargaining power of buyers, and the threat of new entrants all play significant roles in Spectris's industry.
Furthermore, the availability of substitute products and the bargaining power of suppliers present additional challenges and opportunities. A thorough Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive framework to assess these pressures and identify Spectris's competitive advantages and potential vulnerabilities.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Spectris’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Spectris' reliance on suppliers for highly specialized components and advanced materials, essential for its precision instruments, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. The proprietary nature of some of these inputs, often developed through extensive R&D, means few alternative suppliers exist. This scarcity can lead to increased costs for Spectris, as these niche suppliers command premium pricing due to their unique offerings.
Supplier concentration significantly influences bargaining power. If Spectris relies on a small number of suppliers for specialized components or proprietary technology, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for many advanced instrumentation companies, experienced continued consolidation, with a few major players controlling a significant portion of advanced chip production. This concentration allows these dominant suppliers to command higher prices and potentially dictate terms, impacting Spectris's input costs and product development timelines.
Spectris faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly when those suppliers provide highly integrated or proprietary components. For instance, switching suppliers for specialized sensors or control systems can incur substantial costs for Spectris. These costs aren't just about the price of new components; they include the expense and time involved in re-engineering existing products, re-calibrating new systems, and re-qualifying them to meet stringent industry standards. This makes it difficult for Spectris to readily switch, giving incumbent suppliers leverage.
The deep integration of certain supplier components into Spectris's product lines further strengthens supplier relationships and limits Spectris's flexibility. The complexity of integrating entirely new components or systems from different vendors requires extensive testing and validation. This process can delay product launches and increase development expenditures. Consequently, suppliers of these critical, hard-to-replace parts can command higher prices and more favorable terms, impacting Spectris's profitability.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers possessing advanced technological capabilities or substantial intellectual property might consider integrating forward into Spectris's business. This means they could start producing their own finished instruments or software, essentially becoming direct competitors.
While this is not a frequent occurrence for suppliers of highly specialized components, the threat can escalate if Spectris's market segment proves exceptionally profitable and relatively easy to enter. A supplier’s forward integration would directly impact Spectris by reducing its market share and potentially increasing competitive pressure.
- Technological Expertise: Suppliers with unique, hard-to-replicate technologies are better positioned to integrate forward.
- Market Attractiveness: High profit margins and growing demand in Spectris's market segments could incentivize suppliers to consider forward integration.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of numerous suppliers or a fragmented supplier base might reduce the likelihood of any single supplier attempting forward integration.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
The uniqueness of a supplier's offerings significantly impacts their bargaining power with Spectris. When a supplier possesses proprietary technology or intellectual property that is crucial for Spectris's product performance and differentiation, this supplier gains considerable leverage. For instance, if a supplier provides a patented component that is integral to Spectris's high-precision measurement instruments, making it difficult for Spectris to source comparable alternatives, that supplier's position is strengthened.
This exclusivity means Spectris has limited options for replacing such a supplier without compromising product quality or innovation. The reliance on such unique inputs directly translates to a higher bargaining power for the supplier, potentially influencing pricing and terms unfavorably for Spectris.
- Critical Patented Technology: Suppliers holding patents on essential components used by Spectris can command higher prices due to the lack of direct substitutes.
- Proprietary Manufacturing Processes: Unique or highly specialized manufacturing techniques employed by a supplier can make them indispensable, increasing their negotiating strength.
- Differentiation Through Inputs: If a supplier's unique materials or technologies enable Spectris to offer distinct product features, that supplier's bargaining power is elevated.
Spectris's suppliers hold considerable bargaining power, particularly those providing highly specialized, proprietary components or advanced materials critical for its precision instruments. The limited availability of alternative suppliers for these unique inputs, often a result of extensive research and development, allows these suppliers to command premium pricing. For example, in 2024, the market for advanced sensors and specialized calibration equipment remained concentrated, with a few key providers holding significant sway over pricing and supply availability for companies like Spectris.
The integration of these specialized components into Spectris’s product lines is often deep, making switching suppliers costly and time-consuming due to re-engineering, recalibration, and requalification requirements. This dependency grants suppliers leverage in negotiations, impacting Spectris's cost structure and product development timelines.
| Factor | Impact on Spectris | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Proprietary Components | High reliance, difficult to substitute | Strong |
| Supplier Concentration | Limited supplier options | High |
| Switching Costs | Significant re-engineering and validation needed | Elevated |
| Technological Uniqueness | Essential for product performance and differentiation | Very Strong |
What is included in the product
Spectris Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the markets in which Spectris operates.
It meticulously examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors to inform Spectris' strategic decisions.
Quickly assess and mitigate competitive threats with a visual overview of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Spectris's customer base, while diverse, can see significant bargaining power emerge from customer concentration and size within certain market niches. For instance, if a handful of major industrial players or government agencies represent a substantial percentage of Spectris's sales in a particular product line, these large buyers possess considerable leverage.
This leverage translates into their ability to negotiate for reduced pricing, more favorable payment schedules, or bespoke product modifications. In 2023, Spectris reported that its top ten customers represented approximately 20% of its total revenue, highlighting a degree of concentration that can indeed influence pricing power.
Such concentrated demand can exert downward pressure on Spectris's profit margins. It also limits the company's flexibility in setting terms and conditions, as appeasing these key accounts often becomes a strategic imperative to maintain sales volume.
Customer switching costs for Spectris vary significantly based on product integration. For highly specialized test equipment embedded in critical production lines, the cost of switching is substantial, encompassing re-training personnel, re-validating processes, and complex system integration. This high switching cost inherently strengthens Spectris's bargaining power against these customers.
Conversely, for more standardized instruments or software solutions, customers may face lower switching costs. If Spectris's pricing becomes uncompetitive or its service levels decline, these customers have a greater ability to migrate to rival offerings. This flexibility for certain customer segments presents a counterpoint to Spectris's overall bargaining power.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when numerous alternative providers offer similar high-tech instruments, test equipment, and software. This abundance of choice, whether from direct rivals or through substitute technologies that fulfill precision measurement and control needs, allows buyers to exert pressure on Spectris regarding pricing and product specifications. For instance, in the semiconductor testing market, a sector Spectris serves, the availability of multiple equipment suppliers can lead to intense price competition, as customers can readily switch if terms aren't favorable.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Spectris's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity, largely influenced by how crucial its instruments are to their daily operations and their existing financial limitations. In sectors where competition is fierce, businesses often actively look for the most economical instruments, making them highly responsive to price changes. For example, in a market segment where Spectris's competitors offer similar performance at a lower cost, customers are more likely to switch based on price alone.
However, for applications where accuracy and dependability are absolutely critical, such as in advanced medical diagnostics or aerospace manufacturing, customers tend to be less concerned with the initial price. In these scenarios, the cost of instrument failure or inaccuracy far outweighs the purchase price, leading customers to prioritize superior performance and reliability from Spectris.
- High Price Sensitivity: Occurs in competitive markets where alternative solutions are readily available and cost is a primary decision factor.
- Low Price Sensitivity: Found in mission-critical applications where precision, reliability, and uptime are paramount, justifying a higher investment.
- Impact of Switching Costs: For customers with high switching costs associated with recalibration or integrating new systems, price sensitivity might be lower as they are less inclined to change suppliers frequently.
- Budgetary Constraints: The overall budget allocated for instrumentation within a customer's organization can significantly influence their price sensitivity, regardless of the instrument's criticality.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
For Spectris, the bargaining power of customers is influenced by the potential for backward integration, especially with large industrial clients possessing strong R&D. While the development of highly specialized, high-tech measurement equipment in-house is rare, customers might consider creating their own solutions for more routine testing needs. This theoretical capability can, in turn, provide these powerful customers with leverage during negotiations.
This threat is more pronounced when customers face high switching costs or when the measurement solutions Spectris offers are becoming commoditized. For instance, a large automotive manufacturer with a dedicated testing division might explore developing in-house calibration systems for certain engine components if the cost and complexity are manageable, potentially impacting Spectris's sales in that segment.
Consider the automotive sector, a key market for Spectris. In 2024, the global automotive testing, inspection, and certification market was valued at an estimated $25 billion, with significant investment in R&D for advanced vehicle technologies. While Spectris’s core offerings in areas like engine testing and materials analysis are highly sophisticated, a large OEM could, in theory, develop internal capabilities for simpler emission testing or material property verification.
- Customer R&D Capabilities: Large clients with substantial R&D budgets are more likely to explore in-house solutions.
- Standardization of Needs: The threat is greater for more common or less technically demanding testing applications.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with changing suppliers can empower customers to seek alternatives, including in-house development.
- Market Dynamics: A highly competitive market for testing solutions can increase customer bargaining power.
Spectris customers can exert significant influence due to market concentration and their own scale. When a few major clients represent a large portion of sales for specific product lines, they gain leverage for better pricing and terms. For instance, Spectris’s 2023 financials indicated that its top ten customers accounted for approximately 20% of total revenue, a figure that underscores the potential for these buyers to impact profit margins and dictate terms.
The availability of numerous alternative suppliers offering similar high-tech instruments also empowers customers. If Spectris faces strong competition in areas like semiconductor testing, buyers can easily switch for more favorable pricing or specifications, directly challenging Spectris’s pricing flexibility.
Customer price sensitivity for Spectris varies; while critical applications demanding high accuracy reduce price sensitivity, competitive markets with readily available alternatives increase it, pushing customers to seek the most cost-effective options. This dynamic is evident in the automotive sector, valued at approximately $25 billion in 2024 for testing, inspection, and certification services, where price competition is a significant factor for many buyers.
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Spectris Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. This comprehensive Spectris Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the competitive landscape, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for Spectris to strategize effectively and maintain its market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Spectris operates within the precision measurement and control market, a sector characterized by a substantial number of global and specialized niche competitors. This diverse competitive environment means Spectris constantly contends with a wide array of players, from large, established technology conglomerates to agile, focused smaller enterprises, each vying for market dominance.
For instance, in the materials testing segment, Spectris's Instron brand competes with companies like MTS Systems and Shimadzu, while its Malvern Panalytical division faces rivals such as Thermo Fisher Scientific and Anton Paar in the particle characterization space. This broad competitive spectrum means Spectris must continuously innovate and clearly define its unique value proposition to stand out.
The sheer volume and varied strengths of these competitors intensify the rivalry, putting pressure on pricing, product development cycles, and customer acquisition strategies for Spectris. This dynamic landscape underscores the critical need for Spectris to maintain a strong focus on technological advancement and market differentiation to secure and grow its market share.
The precision measurement and control industry presents a mixed growth landscape. While digitalization and automation are fueling rapid expansion in specific segments, other areas exhibit maturity. This maturity can significantly heighten competitive rivalry as firms fight harder for established market share. For instance, Spectris highlights its exposure to sectors like semiconductor manufacturing equipment, which has seen robust demand, alongside more stable, mature markets.
Spectris thrives on product differentiation powered by advanced technology, aiming for superior accuracy and seamless software integration. This focus on application-specific solutions creates distinct value, steering clear of pure price wars. For instance, Spectris's investment in its Malvern Panalytical division, a leader in materials analysis, highlights its commitment to cutting-edge instrumentation.
Exit Barriers
High fixed costs in areas like research and development, specialized manufacturing facilities, and retaining highly skilled engineers create substantial exit barriers for companies operating in the precision measurement and control sector. These significant investments mean that exiting the market is often a very costly proposition, even when a company is facing financial difficulties.
Consequently, these high exit barriers compel competitors to stay in the market longer than they might otherwise, even during periods of low profitability. This persistence directly contributes to sustained and often intense competitive rivalry. For instance, the substantial capital expenditure required for advanced metrology equipment, which can run into millions of dollars, makes a quick divestment impractical for many players.
- High R&D Investment: Companies like Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence and Zeiss continuously invest billions annually in developing new sensing technologies and software, making it difficult to recoup these costs if they were to exit.
- Specialized Manufacturing: Maintaining cleanroom environments and precision calibration labs for sensor production requires ongoing, high fixed costs that are not easily transferable.
- Skilled Workforce: The need for highly trained metrologists and calibration technicians creates a human capital dependency that is hard to liquidate.
- Prolonged Competitive Pressure: The reluctance to incur losses from exiting means underperforming companies often remain, intensifying price competition and innovation pressure for all market participants.
Intensity of Competition on Price and Features
The competitive landscape for Spectris is marked by intense rivalry, often playing out through aggressive pricing strategies and a rapid pace of feature development. Direct competitors might engage in price wars, particularly for products that have become more standardized. This forces Spectris to continually assess its pricing while also investing in research and development to stay ahead through innovation.
For instance, in the industrial automation sector, where Spectris operates, price competition can be fierce. Companies like Keyence and Cognex, while often differentiating on advanced capabilities, also face pressure to offer competitive pricing, especially in segments with lower technological barriers. Spectris’s strategy to compete on value, supported by its advanced metrology and test solutions, aims to mitigate the impact of pure price competition.
- Price Wars: Competitors may engage in aggressive price cuts to gain market share, impacting profit margins across the industry.
- Feature Innovation: A rapid introduction of new features by rivals necessitates continuous investment in R&D for Spectris to maintain its competitive edge.
- Value vs. Price: Spectris's focus on providing superior value through advanced technology and solutions is key to differentiating itself from price-focused competitors.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the demand for precision measurement and testing equipment remains strong, but economic uncertainties can amplify price sensitivities among buyers, intensifying competitive pressures.
Spectris faces intense rivalry from numerous global and specialized competitors in the precision measurement and control market. This competition manifests as pressure on pricing and rapid product development cycles, requiring Spectris to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings, as seen with its Instron and Malvern Panalytical brands competing against established players like MTS Systems and Thermo Fisher Scientific respectively.
The industry's high fixed costs in R&D, specialized manufacturing, and talent retention create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain active even during periods of low profitability, thereby sustaining competitive pressure. For example, the multi-million dollar investment required for advanced metrology equipment makes divestment impractical for many. This persistence intensifies rivalry, particularly when companies focus on price rather than value.
In 2024, the precision measurement and testing equipment market continues to see robust demand, especially in areas like semiconductor manufacturing, but economic uncertainties can amplify price sensitivities, intensifying competition. Spectris's strategy of competing on value through advanced technology and application-specific solutions, rather than solely on price, is crucial for navigating this dynamic landscape and mitigating the impact of price wars.
| Competitor Example | Spectris Division | Market Segment | Competitive Pressure Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| MTS Systems | Instron | Materials Testing | Price & Innovation |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | Malvern Panalytical | Particle Characterization | Technology & Feature Development |
| Keyence | Industrial Automation | Automation & Sensing | Price Sensitivity & Advanced Capabilities |
| Zeiss | Metrology & Inspection | Precision Measurement | High R&D Investment & Specialization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Spectris's offerings comes from alternative technologies that can achieve similar measurement or control results. For instance, the rise of non-contact sensing methods or AI-powered data analysis could offer comparable insights without relying on Spectris's specialized instruments. Spectris needs to stay vigilant about these technological shifts to ensure its solutions remain competitive.
Emerging simpler, lower-cost measurement solutions also pose a significant threat. Consider the growing availability of smart sensors and cloud-based analytics platforms that can perform certain tasks at a fraction of the cost of traditional, high-precision equipment. Spectris's ability to innovate and demonstrate superior value will be crucial in mitigating this threat.
For large industrial clients, developing in-house measurement or testing capabilities can act as a substitute for Spectris's offerings, especially for routine or highly specialized needs. If the cost and complexity of Spectris's solutions become prohibitive compared to the perceived benefits, a customer might opt to build their own internal systems. This trend is more pronounced in less critical or highly standardized applications where off-the-shelf components can be integrated.
Manual processes or less precise methods can indeed pose a threat to Spectris, especially in scenarios where extreme accuracy isn't the primary concern. For instance, in certain low-stakes manufacturing checks or basic quality control, a business might opt for simpler, cheaper manual gauging instead of Spectris's advanced metrology solutions. This is particularly true if budget limitations are a significant factor. For example, a small workshop might not invest in a multi-million dollar coordinate measuring machine if its tolerances are relatively forgiving and manual calipers suffice for its needs.
Software-only Solutions
The rise of sophisticated software-only solutions presents a significant threat to Spectris's traditional hardware-centric business. As data analytics and simulation technologies mature, virtual prototyping, digital twins, and advanced modeling can increasingly replicate or even surpass the outcomes of physical testing and measurement in specific applications. This trend could diminish the demand for some of Spectris's physical instruments.
For instance, the global market for simulation and modeling software was projected to reach approximately $11.2 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to be around 12% through 2028, indicating a strong and growing preference for digital solutions. This suggests that industries may opt for purely software-based approaches to reduce reliance on physical equipment, impacting Spectris's market share in areas where these software alternatives offer comparable or superior value.
- Software substitutes can reduce the need for physical testing equipment.
- Virtual prototyping and digital twins are key examples of these substitutes.
- The simulation and modeling software market is growing rapidly, indicating increasing adoption.
- Spectris's integrated software offerings help, but standalone software solutions remain a competitive threat.
Cross-Industry Technology Transfers
Innovations emerging from entirely different sectors pose a significant threat of substitution for Spectris. For example, advancements in sensor technology initially created for consumer wearables or advanced medical diagnostics could be adapted for industrial precision measurement. These cross-industry transfers mean Spectris must actively monitor developments far beyond its traditional markets.
The rapid pace of technological change means that a solution currently unique to Spectris's offerings could be replicated or surpassed by repurposed technology from sectors like automotive electronics or telecommunications. For instance, breakthroughs in miniaturization and power efficiency in mobile devices could enable new, lower-cost measurement tools that compete directly with Spectris's higher-end products. In 2023, the global market for industrial sensors was valued at approximately $26.6 billion, a figure expected to grow, indicating the potential for new entrants leveraging diverse technological foundations.
- Cross-Industry Innovation: Sensor breakthroughs in consumer electronics, like improved MEMS accelerometers, could be adapted for industrial vibration analysis.
- Medical Device Adaptations: Non-invasive diagnostic sensors might find applications in Spectris's materials testing segments.
- Automotive Technology Spillovers: Advanced automotive lidar and radar systems could offer alternative positioning and measurement solutions.
- Agility is Key: Spectris must maintain vigilance across technology landscapes to preemptively address these evolving substitute threats.
The threat of substitutes for Spectris's precision measurement and control equipment is primarily driven by advancements in digital technologies and the increasing accessibility of lower-cost alternatives. Industries are exploring software-centric solutions and repurposed technologies from other sectors, which can perform similar functions, potentially at a reduced cost or with greater flexibility.
For example, the global market for simulation and modeling software reached an estimated $11.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This rapid expansion highlights a shift towards virtual prototyping and digital twins, which can substitute for some physical testing and measurement needs. Furthermore, innovations in sensors from consumer electronics, such as advanced MEMS technology valued in the billions globally, could be adapted for industrial use, offering alternative measurement capabilities.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on Spectris | Market Trend Data (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software-Based Solutions | Virtual prototyping, Digital twins, Advanced analytics | Reduces reliance on physical testing equipment | Simulation & Modeling Software Market: $11.2B (2023), ~12% CAGR (to 2028) |
| Repurposed Technologies | Consumer-grade sensors, Automotive electronics | Offers lower-cost or more accessible measurement alternatives | Industrial Sensors Market: $26.6B (2023) |
| In-house Capabilities | Developing custom testing rigs | Potential for customers to bypass Spectris for specific needs | N/A (Client-specific) |
| Manual Processes | Basic manual gauging | Relevant for non-critical applications where high precision is not paramount | N/A (Highly fragmented) |
Entrants Threaten
The precision measurement and control industry, particularly for sophisticated, high-tech instruments, necessitates considerable financial outlay. This includes significant investment in research and development to stay at the forefront of innovation, the construction and equipping of specialized manufacturing facilities, and the acquisition of complex, often proprietary, machinery. These substantial upfront costs present a formidable hurdle for any new company seeking to enter the market, effectively limiting the number of potential competitors.
For instance, the development of advanced semiconductor testing equipment can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. Spectris, with its existing robust infrastructure and continuous, substantial investments in research and development, further solidifies this barrier. In 2023, Spectris reported R&D expenses of approximately £165 million, demonstrating their commitment to innovation and reinforcing their position against potential new entrants who would need to match such expenditure.
Spectris and its competitors possess a significant barrier to entry through their extensive intellectual property. This includes numerous patents, proprietary algorithms, and specialized manufacturing techniques that are fundamental to their precision measurement instruments.
The sheer cost and time required to replicate this advanced technology from the ground up make it incredibly difficult for new companies to enter the market. For example, the development of a new high-precision sensor could easily cost tens of millions of dollars and take several years of research and development, a hurdle most startups cannot overcome.
This deep well of intellectual property acts as a robust protective moat, safeguarding Spectris's market share and profitability. Newcomers would struggle to compete on technological sophistication and performance without significant investment and time, effectively deterring many potential entrants.
Spectris, like other established players in its markets, leverages significant economies of scale. This means they can produce goods and services at a lower cost per unit due to high-volume operations in manufacturing, purchasing, and research and development. For instance, in 2024, Spectris's substantial global presence allowed for more efficient sourcing of raw materials, translating into a competitive edge.
Furthermore, Spectris benefits from a well-established experience curve. Years of operation have honed their product development processes and deepened their understanding of customer needs and market dynamics. This accumulated expertise is difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
New companies entering Spectris's sectors would face considerable challenges in matching these cost advantages and operational efficiencies. Achieving comparable per-unit costs and market knowledge would necessitate massive upfront investment and a considerable period to develop, making it a significant hurdle for potential competitors in 2024.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Spectris's established global sales networks and service infrastructure represent a significant barrier for new entrants. Building such a comprehensive presence across diverse industrial sectors demands substantial investment and time, making it challenging for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in 2024, Spectris continued to invest heavily in expanding its service capabilities, aiming to deepen customer relationships through enhanced on-site support and technical expertise. This focus on a robust service ecosystem, coupled with long-standing customer loyalty cultivated over years of reliable performance, creates a formidable hurdle for any potential competitor seeking to gain market share.
Gaining access to Spectris's established distribution channels and customer base is another major challenge. New entrants would struggle to build the necessary trust and secure shelf space or equivalent access within these vital networks. Customer loyalty, often cemented by the proven reliability and performance of Spectris's precision instrumentation, acts as a powerful deterrent to market entry. In 2023, Spectris reported that over 70% of its revenue came from repeat customers, underscoring the strength of these ingrained relationships.
- Significant Investment Required: Establishing global sales and service networks comparable to Spectris's requires multi-year, multi-million-dollar commitments.
- Customer Trust and Loyalty: New entrants face the arduous task of building credibility and displacing established, trusted suppliers in critical industrial applications.
- Distribution Channel Access: Securing partnerships with distributors already aligned with Spectris's product lines or convincing them to carry new, unproven offerings is difficult.
- Long Sales Cycles: In many of Spectris's target markets, sales cycles are lengthy, requiring sustained effort and significant upfront expenditure before any revenue is generated.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certification
New entrants face significant challenges due to the complex regulatory environments in Spectris's core markets. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical demand rigorous certification for instruments and equipment, making market entry a substantial undertaking.
For instance, the medical device industry, a key sector for Spectris, is heavily regulated by bodies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe. Obtaining approvals for new diagnostic or testing equipment can take years and involve extensive clinical trials, a considerable investment for any new player. In 2024, the average time for FDA approval of a new medical device ranged from several months to over a year, depending on the device's complexity and risk class.
Similarly, the aerospace sector mandates adherence to strict airworthiness standards, requiring new entrants to demonstrate exceptional safety and reliability. These stringent requirements translate into high upfront costs for research, development, testing, and compliance, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
The automotive industry also presents a high barrier with evolving standards for emissions, safety, and connectivity. Companies looking to supply advanced testing and measurement solutions must navigate these evolving regulations, which can be costly and time-consuming to meet. In 2024, the automotive industry continued its push towards electrification and autonomous driving, introducing new certification requirements for components and systems.
- Stringent industry standards: Aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors demand high levels of precision and reliability.
- Lengthy certification processes: Obtaining necessary approvals can be a multi-year, resource-intensive endeavor.
- High compliance costs: New entrants must invest heavily in meeting regulatory requirements, impacting profitability.
- Evolving regulatory landscapes: Keeping pace with changes in standards, particularly in areas like data security and sustainability, adds to the challenge.
The threat of new entrants for Spectris is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D, specialized manufacturing, and proprietary technology, alongside established brand loyalty and complex regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2023, Spectris's R&D investment reached approximately £165 million, a figure difficult for newcomers to match. Navigating stringent industry standards in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, which can involve multi-year certification processes as seen with FDA approvals averaging several months to over a year in 2024, further deters potential competitors.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (Spectris/Industry) |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, and technology. | Significant financial hurdle. | Spectris R&D 2023: £165 million. |
| Intellectual Property | Patents, proprietary algorithms, and manufacturing techniques. | Difficult to replicate; requires time and investment. | Development of new high-precision sensor can cost tens of millions. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs from high-volume operations and accumulated expertise. | New entrants struggle to match cost advantages and market knowledge. | Spectris's global presence in 2024 enabled efficient sourcing. |
| Distribution & Customer Loyalty | Established sales networks, service infrastructure, and repeat customers. | Challenging to build trust and secure market access. | Spectris reported >70% revenue from repeat customers in 2023. |
| Regulatory Environment | Strict industry standards and lengthy certification processes. | High compliance costs and time-to-market delays. | FDA medical device approvals can take months to over a year (2024 average). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Spectris Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Spectris' annual reports, investor presentations, and relevant industry publications. This allows for a thorough understanding of their market position and competitive landscape.
