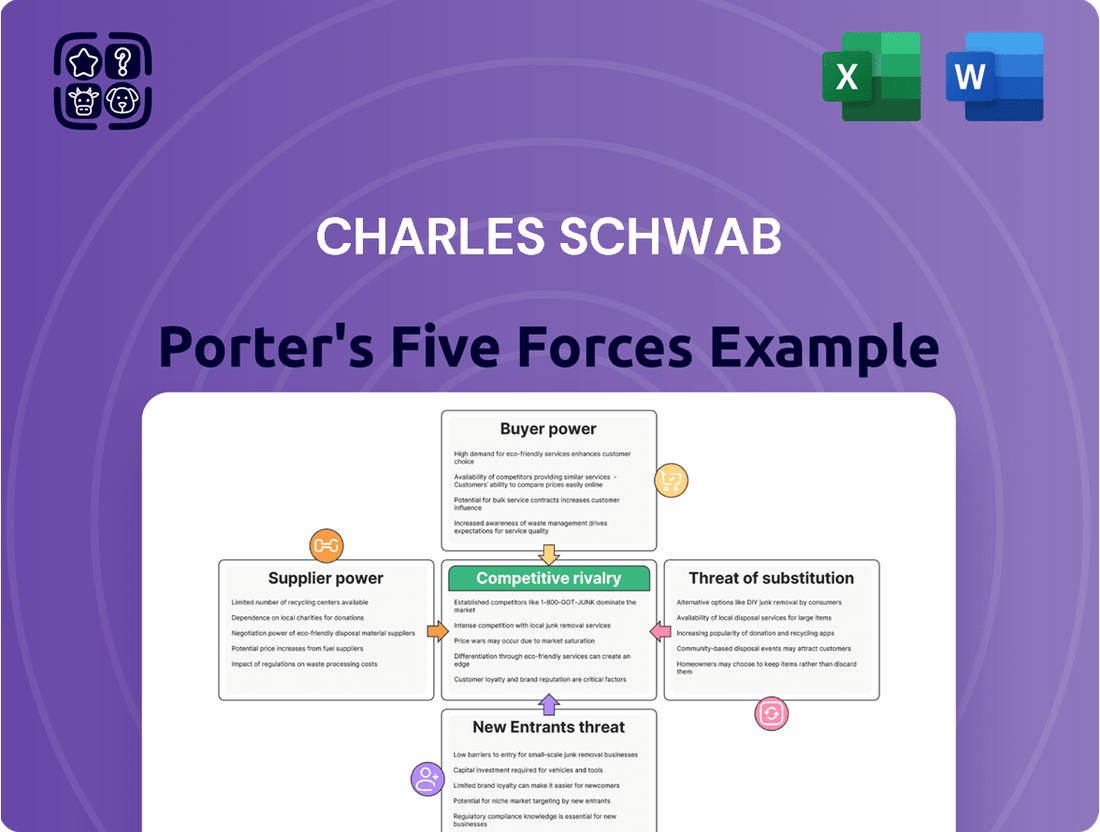
Charles Schwab Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Charles Schwab Bundle
Charles Schwab operates within a dynamic financial services landscape, shaped by powerful external forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for strategic planning. Furthermore, assessing the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute products or services provides a comprehensive view of Schwab's competitive environment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Charles Schwab’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Charles Schwab's dependence on a select group of specialized technology and data providers significantly boosts supplier bargaining power. These providers offer essential services like core banking systems, cloud infrastructure, and trading platform technologies, forming a concentrated market with few dominant players.
The market for core banking systems, for example, is heavily consolidated, with the top three providers controlling over 70% of the market share. Similarly, major cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud command substantial portions of the cloud infrastructure market. This concentration means these suppliers have considerable leverage in negotiating pricing and contract terms with Schwab.
Migrating from one core banking system or trading platform to another involves substantial financial and operational costs for a company like Charles Schwab. These high switching costs can range from $50-75 million for core banking system migrations and $30-45 million for trading platform replacements, with implementation times often spanning 18-24 months. This significant investment and time commitment reduces Schwab's flexibility. Consequently, the dependence on existing technology vendors is increased, thereby strengthening supplier power.
Charles Schwab's substantial IT infrastructure budget, estimated to be between $500 million and $600 million annually, underscores its reliance on key technology vendors. This significant investment is crucial for maintaining competitive services and robust cybersecurity measures.
The company's dependence on these suppliers for critical services like cloud computing and advanced cybersecurity solutions creates a notable dependency. These partnerships are often cemented through long-term agreements, typically spanning three to five years for cloud services.
The quality, reliability, and the pace of innovation from these technology vendors directly influence Schwab's capacity to deliver cutting-edge financial services and uphold stringent security standards.
Any disruptions or limitations from these essential tech partners can therefore significantly impact Schwab's operational efficiency and its ability to meet market demands, highlighting the suppliers' bargaining power.
Specialized Talent and Human Capital Suppliers
Specialized talent, particularly in financial advisory, technology, and cybersecurity, represents a unique supplier category for Charles Schwab. The intense competition for these skilled professionals, especially those proficient in emerging areas like AI and machine learning, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, in 2023, the demand for AI and machine learning engineers saw salary increases of up to 30% in the tech sector, a trend directly impacting recruitment costs for firms like Schwab.
This elevated demand means that these human capital suppliers can dictate terms, impacting Schwab's operational costs through higher compensation packages and recruitment fees. The need to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving fintech landscape, where technological innovation is paramount, further strengthens the position of these talent providers.
- High Demand for Fintech Expertise: The financial services industry, including Charles Schwab, faces a continuous need for professionals skilled in areas such as blockchain, AI, and data analytics.
- Talent Scarcity: The limited supply of individuals with deep expertise in these niche technological fields gives them considerable leverage.
- Impact on Recruitment Costs: In 2024, the average salary for a senior cybersecurity analyst in the financial sector could reach upwards of $150,000, reflecting the high cost of acquiring essential talent.
- Strategic Importance of Human Capital: Attracting and retaining top talent is critical for Schwab's ability to innovate and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Potential Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions on Hardware Components
Even though Charles Schwab is largely a service-based company, its operations are heavily reliant on a robust IT infrastructure. This infrastructure, in turn, depends on a consistent supply of hardware components.
Disruptions in the global supply chain, particularly the ongoing semiconductor shortages, directly affect the availability and cost of these crucial hardware elements. For instance, in 2023, lead times for certain server components extended significantly, sometimes by over six months, directly impacting IT procurement schedules.
This indirect power held by hardware suppliers can translate into higher operational costs for Schwab or delays in essential technology upgrades. Such impacts can hinder the company's ability to maintain peak operational efficiency and invest in innovative technological advancements, ultimately affecting service delivery and competitive positioning.
- Semiconductor Shortages Impact: Global semiconductor shortages, which saw prices for certain chips increase by 15-20% in late 2023, directly affect IT hardware costs.
- Extended Lead Times: Lead times for critical server and networking equipment, a key part of Schwab's infrastructure, stretched to over 6 months in 2023, creating procurement challenges.
- Increased IT Capital Expenditure: These supply chain issues can force IT departments to increase capital expenditure budgets to secure necessary hardware, impacting overall technology investment capacity.
- Operational Delays: Delays in hardware delivery can postpone crucial infrastructure upgrades or the deployment of new technologies, potentially impacting service performance.
Charles Schwab's reliance on specialized technology and data providers, coupled with the concentration within these markets, grants significant bargaining power to its suppliers. The consolidation in areas like core banking systems and cloud infrastructure means fewer, dominant players dictate terms, increasing Schwab's dependence.
High switching costs, estimated between $50-75 million for core banking systems and $30-45 million for trading platforms, further entrench this supplier leverage. These substantial financial and time commitments for migration, often 18-24 months, limit Schwab's flexibility and reinforce existing vendor relationships.
Furthermore, the intense competition for specialized talent, particularly in fintech and cybersecurity, empowers these human capital suppliers. For instance, AI/ML engineer salaries saw up to a 30% increase in 2023, driving up recruitment costs for firms like Schwab and allowing talent providers to influence compensation.
Global supply chain disruptions, notably semiconductor shortages, also indirectly bolster hardware suppliers' power. Extended lead times for server components in 2023, sometimes exceeding six months, can lead to increased IT procurement costs and delays in technology upgrades for Schwab.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Amplifying Power | Impact on Charles Schwab | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, Cloud) | Market concentration, high switching costs | Increased negotiation leverage for pricing and terms | Top 3 core banking providers hold >70% market share; Cloud infrastructure dominated by AWS, Azure, Google Cloud. |
| Specialized Talent (Fintech, Cybersecurity) | High demand, talent scarcity | Higher recruitment and compensation costs, potential talent retention challenges | AI/ML engineer salaries increased up to 30% in 2023; Senior cybersecurity analyst salaries can exceed $150,000 in 2024. |
| Hardware Component Suppliers | Global supply chain disruptions (e.g., semiconductors) | Potential for increased IT hardware costs and procurement delays | Semiconductor prices rose 15-20% in late 2023; Server component lead times extended over 6 months in 2023. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity of the financial services industry, examining threats from new entrants, substitutes, buyer and supplier power, and rivalry for Charles Schwab.
Instantly identify and strategize against competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Retail investors today experience remarkably low switching costs when considering a move between online brokerage platforms. This means that if Schwab, for example, doesn't meet an investor's needs, moving to a competitor is generally a straightforward process with few hurdles.
The widespread adoption of zero-commission trading, a trend that became even more pronounced in 2024, has drastically lowered the financial barrier to changing brokers. Investors are no longer deterred by hefty fees just to transfer their assets, making it simple to explore and adopt platforms offering superior features or customer service.
This ease of migration significantly bolsters the bargaining power of individual investors. They can readily shift their business to a competitor that offers more attractive pricing structures, better research tools, or a more user-friendly interface, forcing firms like Charles Schwab to remain highly competitive to retain their customer base.
Customers today are far more digitally adept, especially younger demographics like Millennials and Gen Z. They demand intuitive platforms and personalized guidance, readily switching providers if their expectations aren't met. This digital fluency directly translates to increased bargaining power.
With readily available online resources, consumers can effortlessly compare services, fees, and investment performance across the financial landscape. For instance, in 2024, online comparison tools make it simple for investors to scrutinize expense ratios and historical returns, empowering them to seek out the best value.
This easy access to information means customers are less reliant on any single financial institution for advice or execution. They can research investment strategies, market trends, and competitor offerings independently, shifting the balance of power in their favor.
The ability to quickly switch providers, often with minimal hassle due to streamlined online account transfers, further intensifies customer bargaining power. If a firm's digital offerings or fee structure become uncompetitive, customers have the leverage to take their business elsewhere.
Clients, especially those with significant assets, are increasingly seeking financial plans that are precisely tailored to their individual aspirations, ethical beliefs, and life events. This move away from one-size-fits-all approaches towards bespoke guidance, often powered by artificial intelligence and data analytics, necessitates ongoing investment by Charles Schwab in cutting-edge technologies to keep pace with these evolving client needs.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for personalized financial advice continued to surge, with a significant portion of surveyed high-net-worth individuals indicating a preference for advisors who could offer highly customized investment and wealth management strategies. This trend directly impacts the bargaining power of customers by increasing the switching costs associated with finding a provider that can meet these granular expectations.
Furthermore, the expectation for a holistic approach, encompassing not just investments but also tax planning, estate planning, and philanthropic goals, further empowers clients. They can leverage this demand to negotiate for more comprehensive service packages or seek out firms that excel in offering integrated wealth solutions, thereby strengthening their position.
Price Sensitivity and Fee Compression
The financial services industry, particularly brokerage, has seen dramatic fee compression. This is largely driven by the move to zero-commission trading, making customers very price-sensitive.
Firms like Charles Schwab must offer competitive pricing and clearly show their value proposition beyond just executing trades. This intense price competition directly impacts profitability and requires a constant focus on operational efficiency and delivering superior client experiences to retain market share.
- Zero-commission trading has become standard in the brokerage industry, forcing firms to seek alternative revenue streams.
- Customers now have a lower cost of switching between brokers, increasing their bargaining power.
- In 2023, Charles Schwab reported net interest revenue of $12.7 billion, highlighting a shift towards earning revenue from client assets rather than commissions.
- This price sensitivity pressures companies to innovate and offer value-added services to justify their fees or maintain margins.
Growth of Robo-Advisors and Hybrid Models
The increasing accessibility and affordability of automated financial advice, driven by the rapid growth of robo-advisors, significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers. This segment is projected to reach a substantial $69.32 billion by 2032, providing individuals with lower-cost alternatives to traditional financial advisory services. Customers can easily compare services and switch providers based on fees and performance.
Furthermore, the rise of hybrid models, blending digital platforms with human financial advisors, offers customers greater flexibility and personalized service. This dual approach caters to a wider range of client needs and preferences, allowing customers to choose the level of interaction they desire. This increased choice and the ability to tailor services directly impacts the bargaining power of customers, as they can demand more value and customization from financial institutions.
- Robo-advisor market growth: Projected to reach $69.32 billion by 2032.
- Customer benefits: Cost-effectiveness and accessibility of automated financial services.
- Hybrid models: Combine automated advice with human interaction, offering flexibility and choice.
- Impact on bargaining power: Customers can demand greater value and customization.
Customers in the brokerage industry, particularly retail investors, wield significant bargaining power due to low switching costs and increased price sensitivity. The widespread adoption of zero-commission trading, a trend solidified in 2024, has removed financial barriers to changing providers. This empowers investors to easily move their assets to platforms offering better value, forcing firms like Charles Schwab to remain highly competitive on fees and service quality to retain their client base.
Digital fluency and easy access to comparative data further amplify customer leverage. Investors, especially younger demographics, expect intuitive platforms and personalized guidance, readily switching if unmet. In 2024, readily available online tools allow effortless comparison of services, fees, and performance, reducing reliance on any single institution and shifting power towards the consumer.
The demand for highly tailored financial plans and holistic wealth management services also strengthens customer bargaining power. Clients seeking bespoke strategies, often incorporating AI and data analytics, can negotiate for more comprehensive packages or choose providers excelling in integrated solutions, increasing the switching costs for firms that cannot meet these granular expectations.
The rise of accessible robo-advisors, projected to reach $69.32 billion by 2032, offers cost-effective alternatives, further empowering customers to demand value and customization from financial institutions.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Trend/Data |
| Switching Costs | Low financial and procedural barriers to moving accounts between brokers. | High customer bargaining power. | Zero-commission trading standard, streamlined online transfers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly responsive to fees and pricing structures. | Increased pressure on firms for competitive pricing. | Net interest revenue for Charles Schwab was $12.7 billion in 2023, indicating a shift from commission-based to asset-based revenue. |
| Information Availability | Easy access to online tools for comparing services, fees, and performance. | Empowers customers to seek the best value and hold firms accountable. | Online comparison tools readily available for expense ratios and historical returns. |
| Digital Expectations | Demand for intuitive platforms and personalized, digitally-driven advice. | Customers readily switch if expectations are not met. | Millennial and Gen Z investors prioritize user experience and digital guidance. |
| Service Customization | Desire for tailored financial plans and integrated wealth management. | Customers can negotiate for comprehensive packages or switch to specialists. | High-net-worth individuals increasingly prefer highly customized strategies. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Charles Schwab Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Charles Schwab Porter's Five Forces analysis you see here details the competitive landscape, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, and the threat of substitute products or services. This in-depth report is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering actionable insights into Schwab's strategic positioning within the financial services industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Charles Schwab operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, challenged not only by legacy institutions like Fidelity and Vanguard, which boast significant brand recognition and vast customer bases, but also by nimble fintech innovators. These startups and robo-advisors are rapidly gaining market share by offering specialized, often lower-cost, digital-first investment solutions.
The industry's dynamism means companies are in a perpetual race to upgrade technology, expand digital capabilities, and differentiate through superior service and a comprehensive product range. For instance, Schwab itself has invested heavily in its digital platforms, a trend mirrored across the sector as firms strive to attract and retain clients in this evolving market.
The brokerage industry has seen a significant shift with the widespread adoption of zero-commission trading, intensifying price competition. This has pushed firms like Charles Schwab to differentiate beyond just transaction fees.
By eliminating commissions, brokerages have shifted the competitive focus to other value drivers. For Schwab, this means emphasizing superior client service, cutting-edge trading technology, and a comprehensive suite of investment products and advisory services to attract and retain customers.
This transition is evident in industry trends. For instance, in 2023, many retail investors continued to seek out platforms with low or no trading costs, a trend that began years prior and solidified with major players dropping commissions. This environment necessitates Schwab’s strategic focus on non-price related competitive advantages.
Competitive rivalry in the brokerage industry is intensely driven by technological innovation and the delivery of superior digital client experiences. Firms are channeling substantial resources into creating seamless online and mobile platforms that cover everything from account opening to sophisticated portfolio management tools.
Charles Schwab's own commitment to technology underscores this trend, with the company investing over $1.2 billion in 2023 alone. This significant outlay is essential for staying competitive as rivals increasingly deploy cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and advanced analytics. These advancements are crucial for attracting new clients and, importantly, for retaining existing ones by offering personalized and efficient digital interactions.
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The wealth management sector is actively consolidating, with firms merging and acquiring to expand their market presence, bolster resources, and broaden their service suites. This ongoing trend is creating larger, more powerful players that benefit from significant economies of scale and a more complete range of services, directly influencing Charles Schwab's competitive landscape.
For instance, in 2023 alone, the financial advisory and wealth management space saw numerous M&A deals, with significant transactions reshaping the industry's structure. These consolidations mean Schwab faces increasingly integrated competitors, often with broader client bases and more diverse product offerings, necessitating strategic responses to maintain market share and competitive advantage.
- Industry Consolidation: Wealth management firms are actively merging and acquiring to achieve greater scale and service diversification.
- Impact on Schwab: This trend results in larger, more resource-rich competitors, intensifying rivalry for Charles Schwab.
- Strategic Implications: Schwab must adapt its strategies to counter the enhanced competitive positioning of consolidated entities.
- Market Dynamics: Increased consolidation leads to fewer, but stronger, players, altering the competitive intensity.
Battle for Next-Generation Wealth Transfer
The wealth transfer expected to exceed $84 trillion by 2045 fuels intense rivalry among financial institutions vying for the attention of Gen X and Millennial inheritors. These younger investors prioritize digital platforms, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, and clear fee structures, forcing established players to innovate. This competitive pressure compels firms to enhance their digital capabilities and tailor product offerings to meet evolving client expectations.
Key competitive dynamics include:
- Digital-First Experience: Firms are investing heavily in user-friendly apps and online portals to cater to the tech-savviness of younger generations.
- Values-Based Investing: The demand for ESG and socially responsible investment options is a significant differentiator, pushing firms to expand their sustainable investment portfolios.
- Fee Transparency: Clients are increasingly scrutinizing fees, leading to a push for more straightforward pricing models and competitive expense ratios.
- Personalized Advice: While digital tools are crucial, the need for personalized financial guidance remains, prompting hybrid models combining technology with human advisors.
Charles Schwab faces intense competition from traditional rivals like Fidelity and Vanguard, as well as a growing wave of fintech startups and robo-advisors. The industry's zero-commission trading environment has intensified this rivalry, shifting the focus to client service, technology, and product breadth. Schwab's substantial $1.2 billion investment in technology during 2023 highlights the sector-wide drive to enhance digital platforms and personalized client experiences to attract and retain assets, especially with the looming $84 trillion wealth transfer.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Factors | 2023/2024 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Brokerages (e.g., Fidelity, Vanguard) | Brand recognition, vast customer base, comprehensive services | Maintaining market share through scale and established trust, but facing pressure to innovate digitally. |
| Fintech Startups/Robo-advisors | Digital-first approach, lower costs, specialized offerings | Rapidly gaining market share, forcing incumbents to accelerate digital transformation and service enhancements. |
| Consolidated Wealth Management Firms | Economies of scale, broader service suites, larger client bases | Increasingly powerful competitors, requiring strategic responses to maintain market position. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The proliferation of user-friendly self-directed online trading platforms and mobile apps presents a significant threat of substitutes for Charles Schwab. These platforms empower individual investors to bypass traditional brokerage services and manage their investments directly, often at a lower cost. For instance, by mid-2024, many popular fintech platforms reported millions of active users actively trading without dedicated financial advisors.
This trend allows investors to execute trades and manage portfolios independently, directly substituting Schwab's more comprehensive brokerage and advisory offerings. Investors prioritizing maximum control and minimal fees are increasingly drawn to these alternatives, directly impacting the demand for traditional, full-service brokerage models. The competitive landscape is further shaped by innovations that reduce transaction costs, making direct investing even more accessible.
Real estate and alternative investments like private equity and infrastructure present a significant threat of substitution for traditional securities offered by Charles Schwab. As investors increasingly look beyond stocks and bonds for wealth accumulation, these alternatives can divert substantial capital. For instance, the global private equity market was estimated to be over $12 trillion in early 2024, a figure that continues to grow.
This trend means that a portion of potential client assets, which could otherwise flow into Schwab's brokerage or asset management services, may be allocated to tangible assets or less liquid, potentially higher-return investments. The allure of diversification and uncorrelated returns in areas like real estate, which saw global transaction volumes remain robust in 2024 despite economic headwinds, directly competes for investor dollars.
Cryptocurrency platforms and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional financial institutions like Charles Schwab. These platforms offer alternative investment avenues, attracting investors drawn to the potential for high growth and the allure of decentralized financial systems. The global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024, showcasing the substantial capital flowing into this sector.
The increasing adoption of DeFi solutions, which enable peer-to-peer financial transactions without intermediaries, directly challenges the services typically provided by established brokerages. While crypto markets are known for their volatility, the persistent growth in user adoption and the development of more robust DeFi protocols mean these digital assets are becoming increasingly viable substitutes for traditional investment vehicles and financial services.
Traditional Banking Products and Savings
For risk-averse individuals or those prioritizing easy access to their money, traditional banking products like high-yield savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs) can act as substitutes for investment offerings from Charles Schwab. These options are particularly appealing when interest rates are elevated, potentially diverting funds that might otherwise be invested.
As of mid-2024, the Federal Reserve's benchmark interest rate remained at a multi-decade high, making traditional savings vehicles more competitive. For instance, average high-yield savings account rates in June 2024 hovered around 4.00%-4.50% APY, while CD rates for comparable terms often exceeded 5.00% APY. This contrasts with typical market returns, which can be more volatile.
- Increased Attractiveness of Savings Accounts: High interest rates make these low-risk options more appealing for capital preservation.
- Liquidity Preference: Customers valuing immediate access to funds may opt for savings accounts over investments with lock-in periods.
- Impact on Investment Flows: When savings rates are high, the opportunity cost of keeping money in non-interest-bearing accounts or lower-yielding investments increases, potentially shifting funds towards banking products.
- Customer Base Overlap: A significant portion of Charles Schwab's client base also utilizes traditional banking services, creating a direct substitution channel.
Do-It-Yourself Financial Planning Tools and Apps
The rise of do-it-yourself (DIY) financial planning tools and apps presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional advisory services. A vast array of these digital platforms, often free or available at a low cost, empower individuals to manage their finances, from budgeting and expense tracking to investment monitoring and basic financial advice. This accessibility bypasses the need for a full-service financial advisor or brokerage, particularly for individuals with straightforward financial situations or a strong inclination towards self-directed management.
These readily available digital solutions directly compete with the core offerings of established financial institutions. For instance, in 2024, the adoption of personal finance apps continued to surge, with millions of users leveraging these tools for daily financial management. Some platforms offer sophisticated features like automated savings, investment portfolio analysis, and even AI-driven financial insights, further diminishing the perceived necessity of human advisors for a growing segment of the population.
- Accessibility: DIY tools are easily accessible online and via mobile devices, often with user-friendly interfaces.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many platforms are free or charge nominal subscription fees, making them significantly cheaper than traditional advisory services.
- Empowerment: These tools provide individuals with greater control and understanding of their personal finances, fostering a sense of autonomy.
- Scalability: Digital solutions can serve a broad user base simultaneously, offering a scalable alternative to personalized human interaction.
The increasing availability of user-friendly, low-cost online trading platforms and fintech apps directly substitutes for Charles Schwab's brokerage services. These platforms empower individuals to manage investments independently, often at a fraction of the cost. By mid-2024, many such platforms reported millions of active users, highlighting a significant shift towards self-directed investing.
Alternative investments like real estate and private equity also pose a threat, diverting capital from traditional securities. The global private equity market, exceeding $12 trillion in early 2024, illustrates this trend. Similarly, cryptocurrency platforms and DeFi offer decentralized financial systems as substitutes for conventional brokerage services, with the global crypto market capitalization reaching approximately $2.5 trillion in early 2024.
Even traditional banking products like high-yield savings accounts and CDs can act as substitutes, especially when interest rates are high. As of mid-2024, elevated Federal Reserve rates made these low-risk options more attractive. For instance, average high-yield savings account rates were around 4.00%-4.50% APY, with CDs often exceeding 5.00% APY, competing directly for investor capital.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Impact on Schwab | 2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech Trading Platforms | Low fees, user-friendly interface, self-direction | Diverts retail investors seeking cost savings and control | Millions of active users on popular platforms by mid-2024 |
| Alternative Investments (Real Estate, Private Equity) | Diversification, potential for uncorrelated returns | Attracts capital away from traditional stocks and bonds | Global private equity market > $12 trillion (early 2024) |
| Cryptocurrency & DeFi | Decentralized finance, high growth potential | Challenges traditional financial intermediaries and investment vehicles | Global crypto market cap ~ $2.5 trillion (early 2024) |
| High-Yield Savings/CDs | Low risk, high liquidity, attractive interest rates | Captures capital that might otherwise be invested, especially in high-rate environments | Savings rates ~4.00%-4.50% APY, CDs >5.00% APY (mid-2024) |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the financial services sector, particularly to rival a firm like Charles Schwab, demands immense upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in sophisticated technology platforms, navigating complex regulatory landscapes, and establishing a trusted brand presence. For instance, in 2024, the cost of developing and maintaining cutting-edge trading and advisory software alone can run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
Established entities like Charles Schwab already leverage significant economies of scale. This advantage allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger operational base, resulting in lower per-unit costs for services and a wider array of offerings. Newcomers struggle to match this cost efficiency and service breadth from the outset, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
The financial services sector, including firms like Charles Schwab, faces significant threats from new entrants due to extensive regulatory hurdles and compliance costs. Entities such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) impose rigorous rules that demand substantial investment in legal expertise and technology to ensure adherence. For instance, in 2024, the cost of regulatory compliance for financial institutions continued to rise, with many reporting increased spending on compliance officers and reporting systems, making it difficult for smaller, less capitalized firms to enter and compete effectively.
Charles Schwab's formidable brand recognition and deeply ingrained customer trust present a significant barrier to new entrants. The company, entrusted with trillions in client assets, has cultivated a reputation for reliability and service over many years.
For any newcomer, replicating this level of confidence is an arduous task, especially in the financial services industry where client security and faith are foundational. Building this trust from the ground up requires substantial time, investment, and a proven track record, which new firms inherently lack.
Technological Disruption by Fintech Startups
Fintech startups, despite facing capital and regulatory hurdles, pose a significant threat of new entrants by leveraging cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain. These agile innovators can carve out specific niches within financial services by offering specialized solutions or enhanced user experiences.
For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, indicating substantial growth and the potential for new players to gain traction. These startups can disrupt established players by targeting underserved customer segments or by developing more efficient operational models.
- Technological Agility: Fintechs can rapidly deploy new technologies, outmaneuvering slower-moving incumbents.
- Niche Market Focus: Startups often succeed by concentrating on specific, often overlooked, customer needs or product categories.
- Customer Experience: Many fintechs prioritize user-friendly interfaces and seamless digital interactions, attracting customers away from traditional providers.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics allow fintechs to offer personalized services and more competitive pricing, further pressuring existing firms.
Difficulty in Acquiring a Large Customer Base
New entrants into the financial services industry, even with cutting-edge technology, struggle to quickly amass a substantial and varied clientele. Established players like Charles Schwab, boasting millions of active accounts and widespread distribution channels, create significant hurdles for newcomers aiming to achieve the scale necessary for profitability and long-term viability.
This difficulty in customer acquisition acts as a major barrier. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Charles Schwab reported having 34.0 million active brokerage accounts, a testament to its entrenched market position and customer loyalty. Building such a base from scratch requires immense capital investment in marketing, sales, and customer service, often proving prohibitive for emerging competitors.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): High marketing and advertising expenses to attract customers away from established brands significantly increase CAC for new entrants.
- Brand Loyalty: Existing customers of firms like Schwab often exhibit strong brand loyalty, built on trust and years of reliable service.
- Network Effects: Larger customer bases can create network effects, where the value of the service increases with more users, further disadvantaging smaller competitors.
- Distribution Channels: Schwab's established physical branches and extensive online presence offer a reach that new entrants find exceptionally difficult and costly to replicate.
The threat of new entrants for Charles Schwab is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements for technology and regulatory compliance, which were substantial in 2024. Additionally, established brand loyalty and economies of scale enjoyed by Schwab present significant barriers, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and service breadth.
While fintech startups leverage technology to target niches, their ability to quickly attract a substantial customer base comparable to Schwab's millions of accounts remains a challenge. The cost of customer acquisition and replicating established distribution channels are key deterrents.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact Example |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in technology and infrastructure. | Hundreds of millions for advanced trading platforms. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex compliance with bodies like SEC and FINRA. | Increased spending on compliance officers and reporting systems. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Cultivated reputation and deep customer faith. | Trillions in client assets managed, signifying strong trust. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational base. | Ability to offer a wider array of services cost-effectively. |
| Customer Acquisition | Difficulty in building a large, loyal customer base. | Schwab's 34.0 million active brokerage accounts as of Q1 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Charles Schwab is built upon a foundation of data from Schwab's own investor relations disclosures, including annual reports and SEC filings. We supplement this with insights from reputable financial news outlets, industry-specific publications, and independent market research reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
