Scholastic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Scholastic Bundle
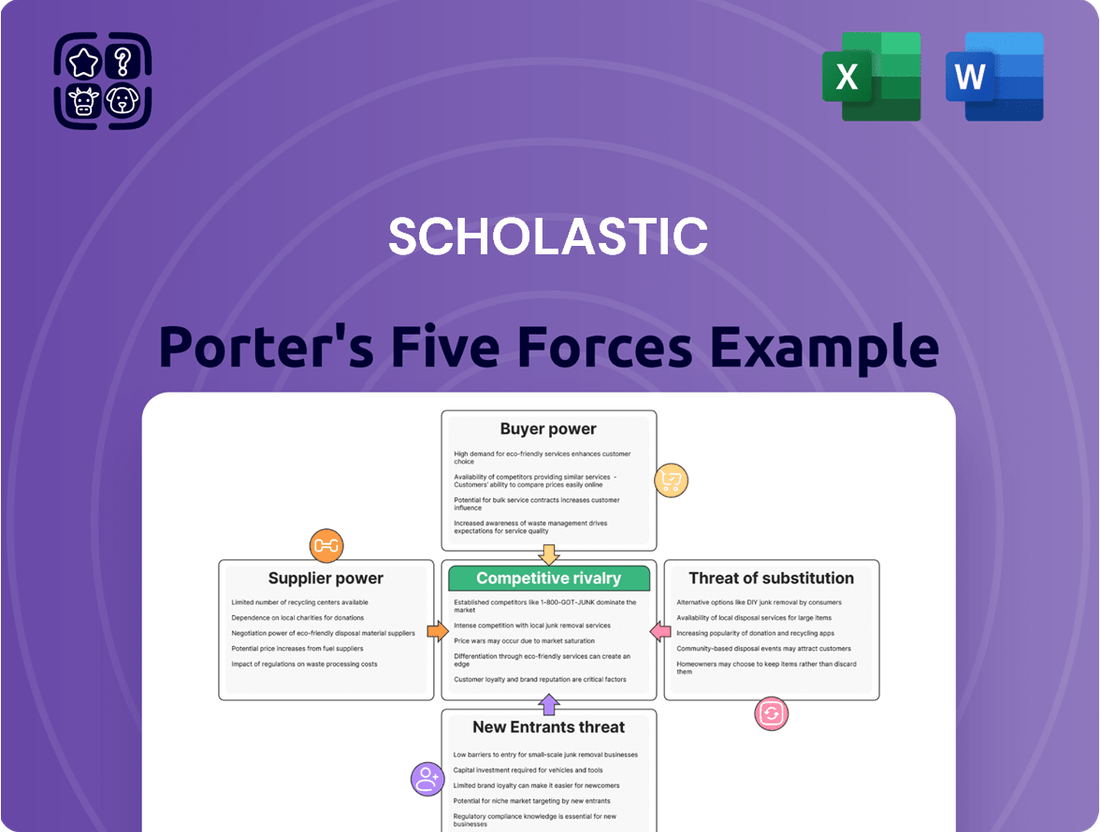
Porter's Five Forces offers a powerful lens to dissect Scholastic's competitive landscape, revealing the underlying pressures that shape its profitability. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitutes is crucial for strategic planning.
This snapshot highlights the critical factors influencing Scholastic's market position, but the true depth of insight lies within a comprehensive analysis. Discover how each force specifically impacts Scholastic's operations and long-term viability.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Scholastic’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Scholastic's Children's Book Publishing segment, a major revenue driver, is heavily dependent on a limited pool of highly successful authors and their associated intellectual property. The scarcity of creators who can produce best-selling titles gives these individuals substantial bargaining power.
This leverage translates into stronger negotiation positions for authors regarding royalty rates and contractual terms. For instance, a phenomenon like the Harry Potter series, initially published by Scholastic in the US, demonstrated how a single author's immense popularity could significantly influence publisher economics.
The ability of these key authors to secure lucrative deals elsewhere, or to retain greater control over their IP, can directly increase Scholastic's content acquisition costs. This concentration of talent means that a few authors can wield considerable influence over a significant portion of Scholastic's sales and profitability.
Scholastic's reliance on printing and paper manufacturers is a key factor in supplier power. While the industry often has many options, specific requirements for high-quality or specialized printing, coupled with potential supply chain disruptions, can significantly amplify the leverage of these suppliers. For instance, in early 2024, the global paper market experienced volatility, with some specialty paper prices seeing increases of up to 5% due to increased demand and production costs, impacting industries like publishing.
Given Scholastic's extensive operations, particularly its large-scale distribution through book fairs and clubs, any substantial price hikes or delivery delays from printers and paper manufacturers could directly squeeze profit margins and hinder the efficient delivery of products to its customer base. The publishing sector has grappled with challenges such as shorter print runs becoming more common, and ongoing global supply chain complexities that can create bottlenecks and increase costs for essential materials like paper.
Scholastic's increasing reliance on educational technology providers for its Education Solutions segment amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. As Scholastic integrates digital platforms, software, and AI into its offerings, it becomes more dependent on specialized EdTech firms.
Providers possessing unique or proprietary technologies can leverage this position to negotiate higher prices or impose more stringent contract terms. This is especially true as schools increasingly demand personalized and data-driven learning experiences, making these specialized solutions highly sought after.
The broader education technology market is experiencing substantial growth, with projections indicating the AI-in-education sector alone could reach $20 billion by 2027. This expanding market size strengthens the negotiating leverage of EdTech suppliers, as demand outpaces supply for cutting-edge solutions.
Specialized Talent for Media and Entertainment
Scholastic's strategic focus on children's media, exemplified by its acquisition of 9 Story Media Group in 2019 for an undisclosed sum, highlights its reliance on specialized talent. This includes highly skilled animators, producers, and content creators crucial for developing and expanding Scholastic's intellectual property (IP) across various platforms, particularly on YouTube. The demand for such specialized skills in the competitive media landscape can significantly influence Scholastic's production costs.
The bargaining power of these specialized talent pools is a significant factor for Scholastic. If the availability of experienced animators and media producers remains constrained, or if they are in high demand from competing entertainment companies, their ability to negotiate higher salaries and better terms will increase. This directly impacts the profitability of Scholastic's entertainment ventures, which are geared towards monetizing its rich IP library.
- Talent Scarcity: The animation and media production sector often faces shortages of highly skilled professionals, increasing their leverage.
- IP Monetization Dependence: Scholastic's expansion onto platforms like YouTube relies heavily on the quality and appeal of content created by this specialized talent.
- Production Cost Impact: Higher talent costs can directly reduce the profit margins for Scholastic's entertainment division.
- Acquisition Strategy: Investments like the 9 Story Media Group acquisition aim to secure or expand access to this talent pool.
Potential for Forward Integration by Content Creators
While traditional publishers like Scholastic have historically held significant supplier power, the evolving digital landscape presents a theoretical avenue for content creators to exert more influence. The growth of self-publishing platforms allows authors to bypass traditional gatekeepers, potentially giving successful independent creators more leverage in negotiations. This trend is evident in the burgeoning self-publishing market, which saw significant growth in recent years, with millions of new titles being published annually.
This nascent potential for forward integration by content creators, though not yet a dominant force for major entities like Scholastic, could shift the balance. If individual authors or smaller content studios can establish robust direct-to-consumer channels and demonstrate consistent sales independently, they gain bargaining chips. For instance, Amazon's Kindle Direct Publishing empowers authors to reach global audiences, a trend that continued to expand throughout 2024.
- Emerging Direct-to-Consumer Models: Platforms like Substack and Patreon allow writers to build direct relationships with readers, reducing reliance on traditional publishers.
- Growth in Self-Publishing: The number of self-published books continues to rise, offering authors alternative distribution channels. In 2023 alone, Amazon reported over 4 million titles available through Kindle Direct Publishing.
- Potential for Creator Leverage: Successful independent creators can negotiate better terms with publishers or distributors due to their proven ability to reach and engage an audience.
The bargaining power of Scholastic's suppliers is a significant factor, particularly concerning content creators and specialized talent. High-demand authors and skilled media professionals can command higher royalty rates and salaries, directly impacting Scholastic's costs. For instance, the animation and media production sector often experiences talent shortages, increasing the leverage of skilled animators and producers, which can raise production expenses for Scholastic's entertainment ventures.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Scholastic's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of each force, allowing for immediate strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Scholastic's primary customers, schools and parents, exhibit significant price sensitivity, particularly when purchasing educational materials and books in bulk. For instance, K-12 schools often face tight budgets, with their spending directly influenced by public funding allocations. This financial pressure means that even modest price increases for Scholastic products can lead to reduced order volumes or a shift to less expensive alternatives.
In 2024, many school districts across the United States continued to grapple with budget shortfalls, impacting their purchasing power for supplementary educational resources. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics indicated that per-pupil spending varied significantly by state, with some experiencing stagnant or declining budgets. This financial environment makes Scholastic's pricing strategy a critical factor in maintaining its market share within the education sector.
The children's book and educational materials market is robustly competitive, featuring a multitude of publishers and EdTech firms providing similar offerings. This abundance of choice, encompassing major publishing houses, independent imprints, and online learning platforms, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power.
Scholastic contends with substantial competitive pressures within the educational publishing sector. For instance, the global educational technology market was valued at approximately $96.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a dynamic landscape where alternatives are readily available to consumers.
The consolidation of school districts into larger entities or purchasing consortia significantly bolsters the bargaining power of Scholastic's customers. These aggregated buying groups, representing a substantial portion of the educational content market, can leverage their collective demand to secure better pricing and more tailored offerings.
For instance, in 2024, a major consortium of over 500 school districts across several states collectively negotiated volume discounts that could reduce per-unit costs by as much as 15% for educational materials. This unified approach allows them to exert considerable influence over Scholastic's pricing, directly impacting the profitability of its Education Solutions division.
Access to Information and Reviews
Customers today, including educators and parents, wield significant bargaining power thanks to unprecedented access to information. Online reviews, detailed product comparisons, and vibrant educational forums empower them to thoroughly research and evaluate offerings before making a purchase. This transparency directly influences Scholastic, necessitating competitive pricing and a consistent focus on product quality to meet informed consumer expectations. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 70% of parents consult online reviews before buying educational materials for their children.
The proliferation of online content and digital platforms has further amplified customer choice and readily available information. This digital landscape allows consumers to easily compare Scholastic's products against a vast array of alternatives, from independent publishers to global ed-tech providers. This increased competition and accessibility to information places considerable pressure on Scholastic to innovate and maintain a strong value proposition. In 2024, the global ed-tech market was valued at approximately $120 billion, a testament to the diverse range of options available to educational consumers.
- Increased Transparency: Customers can easily access and compare product features, pricing, and user feedback across multiple platforms.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Access to reviews and comparative data allows customers to make more knowledgeable choices, putting pressure on Scholastic to deliver superior value.
- Competitive Landscape: The digital age has broadened the competitive set, offering consumers numerous alternatives to traditional Scholastic products.
- Price Sensitivity: With easy price comparison, customers are more likely to seek out the best deals, impacting Scholastic's pricing strategies.
Shift Towards Open Educational Resources (OER) and Free Content
The rising tide of Open Educational Resources (OER) and readily available free online educational materials significantly pressures Scholastic's traditional paid offerings. This shift diminishes the perceived value of purchased textbooks and supplementary content, particularly for institutions and families operating under tight budgets. For instance, in 2024, the global OER market was valued at approximately $18 billion, showcasing a substantial alternative to traditional educational materials.
Consequently, Scholastic must continually innovate to justify its pricing and maintain customer loyalty. Differentiation becomes paramount, focusing on unique content, engaging interactive platforms, or robust support services that free alternatives cannot easily replicate. The competitive landscape now includes not only other publishers but also a vast array of teacher-generated content and OER repositories.
- Increased OER Adoption: Many school districts are actively integrating OER to reduce costs, with some reporting savings of up to 30% on instructional materials.
- Growth of Digital Content Platforms: Free and low-cost digital learning platforms continue to expand their user base, offering extensive libraries of educational resources.
- Teacher-Created Content: Online communities and platforms facilitate the sharing of teacher-created lesson plans and materials, providing free alternatives for educators.
- Focus on Value-Added Services: Scholastic's strategy likely involves enhancing its digital platforms with personalized learning paths, assessment tools, and professional development for educators.
Scholastic's customers, primarily educational institutions and parents, possess considerable bargaining power due to market saturation and the availability of alternatives. This allows them to demand lower prices and better terms, directly impacting Scholastic's profitability.
The ease with which customers can compare prices and access reviews online empowers them to seek the best value. In 2024, over 70% of parents surveyed consulted online reviews before purchasing educational materials. This transparency forces Scholastic to remain competitive on pricing and product quality.
The growth of Open Educational Resources (OER) and free digital content presents a significant challenge. In 2024, the OER market was valued at approximately $18 billion, offering budget-conscious schools and families cost-effective alternatives to Scholastic's paid products.
| Customer Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Scholastic | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Reduced order volumes or shift to cheaper alternatives if prices rise. | School districts facing budget shortfalls, impacting purchasing power. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Bolsters customer ability to negotiate better terms. | Global EdTech market valued at $120 billion in 2024, indicating diverse options. |
| Consolidated Buying Power | Leverages collective demand for discounts and tailored offerings. | Major consortia negotiated up to 15% volume discounts in 2024. |
| Information Access & Transparency | Demands competitive pricing and high product quality. | Over 70% of parents use online reviews before purchasing educational materials. |
| Open Educational Resources (OER) | Diminishes perceived value of paid content. | OER market reached $18 billion in 2024, providing free alternatives. |
What You See Is What You Get
Scholastic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Scholastic Porter's Five Forces Analysis, meaning the document you see is precisely what you will receive immediately after completing your purchase. You can be confident that no placeholders or sample content are present; this is the fully formatted, ready-to-use analysis. This ensures you get the exact, professionally written report you need for your strategic planning without any surprises. It's your deliverable, instantly accessible and ready for your immediate application.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Scholastic navigates intensely competitive landscapes across children's publishing, educational resources, and media. Major publishing houses such as Penguin Random House and HarperCollins represent significant traditional rivals, while the burgeoning educational technology sector sees formidable competition from companies like McGraw Hill and Pearson. The K-12 education market, a core area for Scholastic, is particularly crowded, with numerous entities vying for market share. For instance, the global education technology market was valued at approximately $127.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $350 billion by 2030, indicating substantial growth but also intense competition.
The publishing industry, including companies like Scholastic, is burdened by substantial fixed costs. These expenses span content acquisition, meticulous editing, physical printing, and complex distribution networks. This financial reality necessitates high sales volumes to achieve profitability, fueling fierce competition among publishers for market dominance and the acquisition of popular authors and their works.
This environment drives intense rivalry as publishers vie for best-selling titles and the authors who create them. In 2023, the global book publishing market was valued at approximately $120 billion, underscoring the significant revenue potential and the high stakes involved in capturing market share. Securing exclusive rights and long-term author contracts becomes a critical strategic imperative.
Scholastic enjoys robust brand recognition, especially within the educational sector, thanks to its long-standing presence through school book fairs and book clubs. These channels have historically been a significant revenue driver, with book clubs and book fairs contributing substantially to their earnings in 2023.
However, the competitive landscape is dynamic; rivals are actively working to cultivate their own brand loyalty. They achieve this by offering fresh content, employing targeted marketing strategies, and enhancing digital engagement to capture market share and challenge Scholastic's established customer base.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Race
Competitive rivalry in the education and publishing sector is fierce, largely fueled by the imperative to differentiate products. This differentiation extends beyond traditional print to encompass engaging narratives, interactive digital experiences, and robust educational solutions tailored for diverse learning needs. For Scholastic, staying competitive means a constant race to innovate.
The landscape is rapidly evolving with technologies like AI-driven personalized learning and augmented reality, alongside growing consumer interest in eco-friendly themes. Scholastic must actively integrate these trends to maintain its edge. For instance, the children's interactive book market is seeing significant growth, with AI integration paving the way for truly personalized storytelling experiences.
Key areas of differentiation and innovation include:
- Development of AI-powered personalized reading platforms that adapt to individual student progress and preferences.
- Integration of augmented reality (AR) features in physical books to create immersive and interactive learning environments.
- Expansion of digital content libraries offering a wider range of educational games, e-books, and multimedia resources.
- Focus on sustainability and eco-friendly materials in book production to align with growing environmental consciousness among consumers and educators.
Market Fragmentation and Niche Players
The publishing and education sectors are marked by significant fragmentation, with numerous smaller, specialized publishers and EdTech startups actively competing. These niche players often focus on specific content areas or innovative learning approaches, presenting a dynamic challenge to established companies like Scholastic.
This competitive landscape means that larger entities must remain agile, adapting their strategies or pursuing acquisitions to incorporate new technologies and content. For instance, in 2024, the children's book market continued to see innovation from independent publishers, who often cater to underserved genres or pedagogical styles.
- Market Fragmentation: The presence of many small, specialized publishers and EdTech firms creates a fragmented competitive environment.
- Niche Focus: These smaller players often carve out market share by concentrating on specific content areas or unique learning methodologies.
- Adaptation Pressure: Larger companies like Scholastic face pressure to evolve their strategies or acquire innovative startups to stay competitive.
- Innovation from Independents: Independent publishing houses are actively innovating, particularly in children's literature, offering diverse and specialized content.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic for Scholastic, stemming from both traditional publishing houses and the rapidly expanding educational technology sector. This intense competition, evident in the global education technology market projected to reach $350 billion by 2030, forces companies to constantly innovate in content and delivery methods.
Scholastic faces pressure from numerous smaller, specialized publishers and EdTech startups that focus on niche markets and innovative learning approaches. These agile competitors challenge established players, highlighting the need for adaptation and strategic acquisitions to integrate new technologies and content, as seen in the dynamic children's book market in 2024.
The imperative to differentiate products drives fierce competition, pushing companies beyond traditional print to create engaging digital experiences and tailored educational solutions. Scholastic must actively integrate emerging trends like AI-driven personalization and augmented reality to maintain its competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
High fixed costs in publishing, covering everything from content acquisition to distribution, necessitate high sales volumes. This financial reality intensifies the competition for best-selling titles and authors, with the global book publishing market valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023, underscoring the significant stakes.
| Rivalry Factor | Description | Impact on Scholastic |
|---|---|---|
| Number and Balance of Competitors | Numerous traditional publishers (Penguin Random House) and EdTech firms (McGraw Hill) compete. The market is fragmented with many smaller players. | Requires continuous product innovation and strategic partnerships to maintain market share. |
| Industry Growth Rate | The education technology market is growing rapidly, projected to reach $350 billion by 2030. The book market is substantial but more mature. | Opportunities exist in EdTech, but growth in traditional publishing faces intense competition for market share. |
| Switching Costs for Buyers | Relatively low for consumers, but can be higher for educational institutions adopting comprehensive digital platforms. | Scholastic must offer compelling value and ease of integration to retain institutional clients and attract new ones. |
| Product Differentiation | Crucial for survival. Innovations include AI personalization, AR features, and expanded digital libraries. | Scholastic must invest heavily in R&D and content development to stand out from competitors offering similar or novel solutions. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For children's books, public libraries present a significant threat by offering free access to reading materials, directly competing with Scholastic's sales. This free alternative reduces the perceived value of purchasing new books, especially for parents and educators. In 2024, library circulation numbers continue to be robust, with many systems reporting millions of items borrowed annually, underscoring their reach.
Second-hand markets, both online platforms like eBay and local thrift stores, provide low-cost options for children's books. These markets allow consumers to acquire books at a fraction of the new price, diminishing the incentive for new purchases from Scholastic. The used book market is a substantial industry, with many small businesses and individuals participating, contributing to a significant volume of transactions.
These substitutes effectively fulfill the fundamental need for reading material and educational content for children, bypassing Scholastic's revenue streams. While they don't generate direct sales for Scholastic, they capture a portion of the demand that might otherwise be met by new product purchases.
Furthermore, a resurgence in independent bookshops, often focusing on community engagement and curated selections, offers an alternative purchasing experience. While not a direct substitute in terms of price, these shops can attract customers seeking a more personalized and experiential approach to book buying, potentially diverting some sales from larger publishers.
The rise of free and low-cost digital content, from e-books and audiobooks to educational videos on platforms like YouTube, presents a substantial threat of substitutes for Scholastic. Online learning platforms such as Coursera and Khan Academy also offer convenient and often personalized learning experiences that can directly compete with traditional educational materials.
This digital shift means Scholastic faces potential revenue displacement as consumers increasingly turn to these online alternatives. The convenience and accessibility of digital formats, coupled with the availability of free resources, directly challenge Scholastic's established business model.
The online educational content market is a key indicator, with projections suggesting it will reach $350 billion by 2025. This significant market growth highlights the increasing consumer preference for digital learning solutions, a trend Scholastic must actively address to mitigate the threat of substitutes.
Teachers frequently develop and distribute their own instructional content, and the widespread availability of Open Educational Resources (OER) offers free alternatives to purchased curriculum and supplementary materials. This significantly lessens dependence on commercial publishers for educational resources. For instance, OER Commons reported over 3,000,000 registered users by 2024, highlighting the scale of this trend.
The existence of readily available, high-quality OER, coupled with teacher-created materials, acts as a strong substitute. This dynamic exerts downward pressure on prices for traditional educational publishers. The K-12 supplemental materials market, valued at approximately $10 billion in 2024, directly feels this competitive pressure from free and low-cost alternatives.
Entertainment Alternatives to Reading
The threat of substitutes for traditional reading among children is significant, as their attention is now divided among numerous entertainment options. Streaming services like Netflix and Disney+, video games, and social media platforms all vie for young audiences' time and engagement. In 2024, the debate around integrating audiobooks and film adaptations in educational settings highlighted how these alternatives are increasingly seen as direct competitors, and sometimes even replacements, for the act of reading itself.
These digital and interactive alternatives offer immediate gratification and diverse sensory experiences that can be more appealing than solitary reading for some children. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that the average screen time for children aged 8-12 exceeded 5 hours per day, with a significant portion dedicated to entertainment apps and video streaming, directly competing with time that could be spent reading.
- Streaming Services: Platforms offer a vast library of content, from animated shows to movies based on popular books.
- Video Games: Interactive and immersive gaming experiences capture significant leisure time.
- Social Media & Apps: Short-form content and interactive apps provide quick entertainment bursts.
- Audiobooks & Digital Reading: While still reading-adjacent, they represent a shift from traditional print and compete for the same attention span.
Homeschooling Resources and Parent-Led Curricula
The rise of homeschooling and parent-led curricula presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional educational material providers like Scholastic. Parents increasingly seek flexible, customizable, and often more affordable alternatives to conventional schooling. These independent resources, ranging from online platforms to bespoke lesson plans, cater directly to this demand.
The homeschooling market has seen substantial growth, reflecting this shift. Data indicates that approximately 37% of education startups in recent years have focused specifically on K-12 online education or homeschooling solutions. This expansion means a wider array of readily available substitutes for Scholastic's offerings, putting pressure on market share.
These alternatives often leverage digital communities and open-source educational content, further reducing the cost and increasing accessibility for homeschooling families. For instance, platforms offering free or low-cost lesson plans and interactive learning modules directly compete with packaged curricula and supplementary materials.
The threat is amplified by the inherent flexibility and cost-effectiveness that many of these substitute resources provide. Parents can curate learning experiences tailored to their child's specific needs and budget, bypassing the standardized approach often associated with larger publishers.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Diversified Content: A vast ecosystem of independent creators and platforms offering specialized curricula and learning materials.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many homeschooling resources are significantly cheaper or even free compared to traditional educational products.
- Community Support: Online forums and groups provide shared resources, advice, and curricula, fostering a collaborative substitute market.
- Market Growth: The increasing number of education startups targeting the homeschooling sector underscores the demand for these alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Scholastic is multifaceted, encompassing free public libraries, a thriving second-hand book market, and increasingly, digital alternatives. These substitutes fulfill the fundamental need for reading and educational content, directly impacting Scholastic's sales and revenue streams.
The burgeoning digital content sphere, including streaming services, video games, and social media, also diverts children's attention from traditional reading, presenting a significant challenge. Furthermore, the rise of homeschooling and parent-led curricula offers a customizable and often more affordable alternative to Scholastic's educational materials.
| Substitute Category | Description | Impact on Scholastic | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Libraries | Free access to reading materials | Reduces demand for new book purchases | Robust circulation numbers, millions of items borrowed annually |
| Second-Hand Markets | Low-cost pre-owned books | Diminishes incentive for new purchases | Substantial industry with significant transaction volume |
| Digital Content & Entertainment | Streaming, video games, social media | Competes for children's attention and leisure time | Average screen time for 8-12 year olds exceeds 5 hours daily |
| Open Educational Resources (OER) & Teacher-Created Content | Free and low-cost educational materials | Reduces dependence on commercial publishers | OER Commons reported over 3 million registered users by 2024 |
| Homeschooling & Parent-Led Curricula | Flexible, customizable, and affordable alternatives | Captures demand for educational solutions | ~37% of recent education startups focus on K-12 online/homeschooling |
Entrants Threaten
Scholastic's formidable brand recognition and deeply entrenched distribution networks present a substantial hurdle for potential newcomers. The company's ability to connect directly with students and educators through its iconic book fairs and book clubs is a powerful deterrent. These channels, cultivated over decades, offer unparalleled reach and trust within the educational ecosystem.
Consider that Scholastic's book clubs are present in over 70% of K-12 schools, a testament to their established presence. Furthermore, their annual book fairs touch roughly 120,000 schools, demonstrating the sheer scale of their proprietary distribution. Replicating this level of access and brand loyalty would demand immense capital and a prolonged period of market penetration for any new entrant.
While digital platforms have democratized some aspects of publishing, Scholastic's established, large-scale operations still present a significant financial hurdle for new entrants. Building a comprehensive publishing and distribution network demands considerable investment in securing rights, printing physical books, managing complex logistics, and executing broad marketing campaigns. This substantial capital requirement, estimated to be in the tens of millions for a company of Scholastic's size, naturally acts as a powerful deterrent to potential competitors seeking to enter the traditional book market.
The threat of new entrants in children's publishing, particularly concerning content acquisition and intellectual property, is significantly mitigated by existing barriers. Scholastic's established position is bolstered by its deep and extensive network of relationships with creators. They maintain partnerships with over 5,000 authors and illustrators, a testament to their long-standing presence and the trust they've built within the creative community.
For newcomers, securing the rights to popular authors and beloved intellectual property presents a substantial hurdle. This is not just about financial offers; it's about building rapport and demonstrating a commitment to a creator's vision, something established firms like Scholastic have cultivated over decades. New entrants struggle to attract top-tier talent and assemble a compelling and diverse content portfolio necessary to compete effectively.
Regulatory Requirements and Educational Standards
The educational solutions market, particularly for K-12, is heavily influenced by significant regulatory hurdles and evolving educational standards. New companies entering this space must dedicate substantial resources to ensure their offerings align with diverse and often rigorous curriculum requirements mandated by school districts and state governments. For instance, in 2024, many states continued to update their science and math standards, requiring educational providers to adapt their content accordingly.
These compliance demands act as a considerable barrier to entry. Companies need to understand and implement specific pedagogical approaches, assessment methodologies, and data privacy regulations, such as those related to the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the United States. Failure to meet these standards can prevent market access or lead to disqualification in procurement processes.
Government investment is a key factor driving growth and shaping these requirements. In 2023, the U.S. Department of Education allocated billions towards educational technology and curriculum development, often with specific stipulations for evidence-based practices and equitable access. This focus means new entrants must demonstrate not only pedagogical soundness but also alignment with broader governmental educational goals.
The financial commitment required to meet these educational standards and regulatory frameworks is substantial:
- Curriculum Alignment: Costs associated with researching, developing, and validating educational content to meet state-specific standards can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per subject area.
- Compliance and Legal: Ensuring adherence to data privacy laws (e.g., FERPA, GDPR) and accessibility standards (e.g., WCAG) necessitates legal review and technical adjustments, adding significant overhead.
- Procurement Processes: Navigating complex and often lengthy government procurement cycles, which may involve pilot programs and extensive documentation, requires dedicated sales and compliance teams.
- Investment in R&D: Continuous investment in research and development is needed to keep pace with evolving educational research and technological advancements, further increasing the capital needed to compete.
Rapid Technological Advancements and AI Integration
The accelerating pace of technological change, especially in areas like AI and immersive learning, significantly increases the threat of new entrants. New players must possess substantial technological expertise and capital to even begin competing effectively. This high barrier means startups need to offer advanced digital tools and highly personalized learning experiences right from the start to make an impact.
AI is fundamentally reshaping the educational landscape by enabling truly tailored learning journeys for each student. For instance, by 2024, the global AI in education market was projected to reach approximately $20 billion, highlighting the significant investment and innovation required to enter this space. Companies entering now must leverage these sophisticated AI capabilities to offer differentiated value.
- AI-driven personalization: New entrants must offer adaptive learning platforms that adjust content and pace based on individual student performance.
- Immersive technologies: Integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for more engaging and effective learning experiences is becoming a necessity.
- Data analytics for insights: Robust data collection and analysis capabilities are crucial for understanding student progress and refining educational strategies.
- Significant R&D investment: Continuous investment in research and development is needed to keep pace with rapid technological evolution.
The threat of new entrants for Scholastic is significantly low due to substantial barriers to entry. These include the company's deeply ingrained brand recognition, extensive distribution networks like book fairs reaching over 120,000 schools, and strong relationships with over 5,000 authors and illustrators.
The financial investment required to replicate Scholastic's scale, from securing intellectual property to managing logistics and marketing, is immense, likely in the tens of millions. Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements in the K-12 educational solutions market, demanding alignment with evolving state standards and privacy laws, add considerable complexity and cost for newcomers.
The rapid technological advancements, particularly in AI-driven personalization and immersive learning, also raise the bar, requiring significant capital and expertise. For instance, the global AI in education market was projected to reach around $20 billion by 2024, indicating the high cost of entry for innovative digital solutions.
| Barrier | Description | Estimated Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Brand Recognition & Distribution | Decades of presence in over 70% of K-12 schools via book clubs and fairs. | Very High |
| Capital Requirements | Establishing publishing, distribution, and marketing networks. | High (tens of millions) |
| Creator Relationships | Partnerships with over 5,000 authors and illustrators. | High |
| Regulatory & Compliance | Meeting state educational standards and data privacy laws (e.g., FERPA). | High |
| Technological Expertise | AI and immersive learning capabilities needed for modern educational solutions. | High (significant R&D investment) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Scholastic Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from academic journals, educational market research reports, and government education statistics to understand the competitive landscape. We also incorporate insights from industry associations, company financial statements, and news archives to capture key industry dynamics.
