Resona Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Resona Holdings Bundle
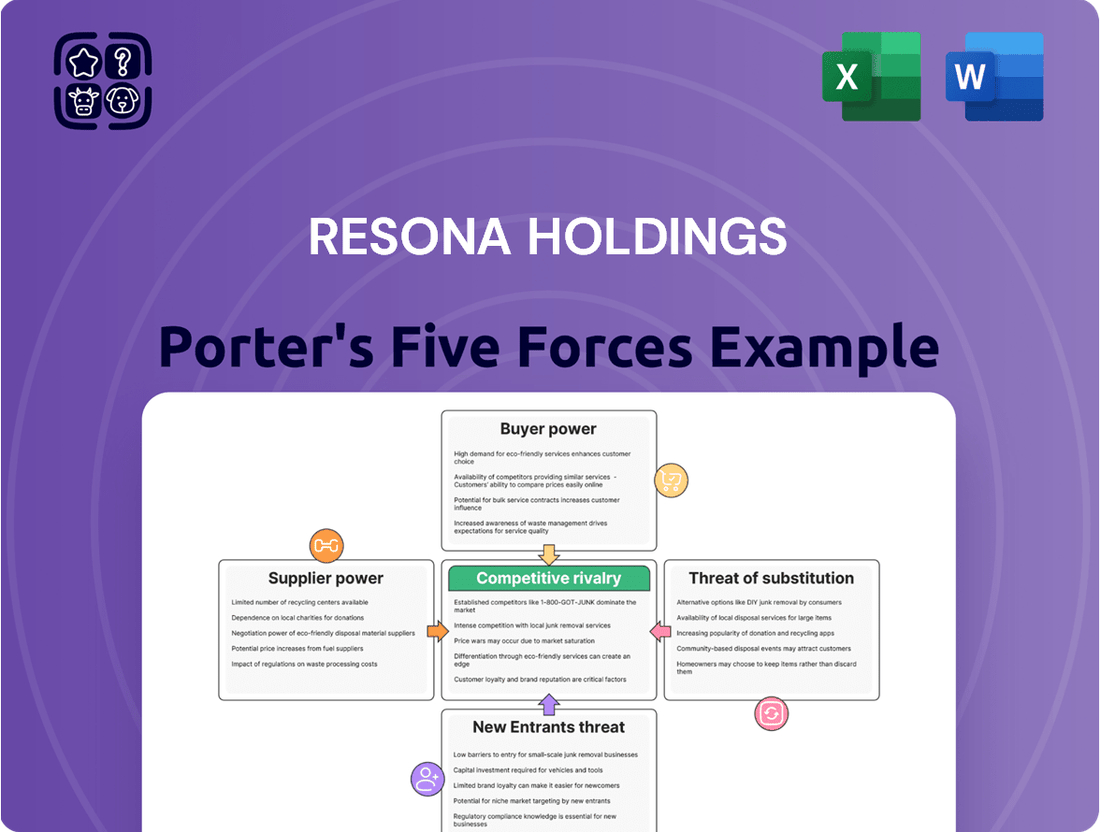
Resona Holdings navigates a competitive landscape shaped by moderate rivalry among existing players, with a few large banks vying for market share. The threat of new entrants is somewhat limited due to significant capital requirements and regulatory hurdles in the banking sector.
Buyer power, primarily from individual and corporate customers, is present but tempered by the need for trust and established relationships, making switching costs a factor. The bargaining power of suppliers, such as technology providers and data services, also plays a role, though it's generally manageable for a large institution like Resona.
Furthermore, the threat of substitute products or services, like fintech solutions and alternative investment platforms, is steadily growing, demanding continuous innovation from traditional banks.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Resona Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The Japanese banking sector, including Resona Holdings, enjoys a significant advantage from a large and stable domestic deposit base. This reflects the robust savings culture among Japanese households, which held over JPY 1,100 trillion in cash and deposits as of early 2024. Such a strong and consistent inflow of funds provides banks with a low-cost, stable funding source. This abundant liquidity significantly limits the bargaining power of alternative capital and funding suppliers. Furthermore, high deposit insurance coverage, up to JPY 10 million per depositor, reinforces this stability.
Resona Holdings, like other financial institutions, increasingly relies on technology for core operations, digital services, and robust security, giving vendors of these critical systems some leverage. Resona's FY2024 business plan prioritizes significant investment in digital transformation (DX), including overhauling business processes with AI and cloud technologies to enhance efficiency. While this dependence grants technology suppliers influence, Resona mitigates this by diversifying its vendor partnerships and strengthening its in-house IT capabilities. This strategic approach ensures operational resilience despite the specialized nature of these essential technological solutions.
In Japan's overbanked financial landscape, ongoing banking consolidation, with regional bank mergers continuing in 2024, generally tempers the bargaining power of human capital.
Demographic decline, with Japan's working-age population projected to shrink further, coupled with a strong focus on cost efficiency, limits employee leverage in traditional roles.
However, specialized skills in areas like data analytics, AI, and cybersecurity are in high demand across the sector, empowering individuals with this expertise.
Banks like Resona are heavily investing in digital transformation, creating a competitive market for these critical, forward-looking skill sets.
Low Bargaining Power of Real Estate Suppliers
Low Bargaining Power of Real Estate Suppliers
While real estate forms a significant portion of a bank's assets and collateral, the supply of commercial and residential properties remains highly fragmented, ensuring low supplier power. Resona Holdings, like other Japanese banks, benefits from a wide array of properties available for collateral or investment, reducing dependence on specific real estate developers. Although property prices, particularly in central Tokyo, saw a 2.1% increase in residential land prices in 2024, this upward trend is broadly market-driven, reflecting demand rather than concentrated supplier control. The diverse and competitive real estate market means individual suppliers have limited leverage over banks.
- Japan's residential land price index rose 2.1% year-on-year in 2024.
- Commercial property transactions in Japan reached approximately ¥3.5 trillion in 2023.
- The number of real estate companies in Japan exceeds 300,000, indicating high fragmentation.
- Banks often assess collateral based on broad market valuations, not individual supplier pricing.
Moderate Power of Rating Agencies and Financial Information Providers
Credit rating agencies like Moody's, S&P, R&I, and JCR, along with financial data providers, are vital for Resona Holdings' access to capital markets and internal risk management. A negative rating can significantly elevate the bank's cost of capital, influencing investor confidence and funding terms. For example, a downgrade could increase borrowing costs for new debt issuances in 2024. This gives these entities substantial influence over Resona and other financial institutions.
- Rating agencies assess creditworthiness, impacting bond yields.
- Financial data providers offer essential market insights for strategic decisions.
- A one-notch downgrade can increase a bank's funding costs by several basis points.
- Resona regularly engages with these agencies for its debt and corporate ratings.
Resona Holdings experiences varied supplier power. The vast, stable domestic deposit base, exceeding JPY 1,100 trillion in 2024, significantly curtails the bargaining power of funding suppliers. However, essential technology vendors and credit rating agencies wield considerable influence, given their impact on operational efficiency and capital costs. Conversely, the fragmented real estate market and general labor pool exhibit low supplier leverage.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power | Key Factor/2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Deposits | Low | JPY 1,100T stable deposits |
| Tech Vendors | Moderate | FY2024 DX investment |
| Rating Agencies | High | Impact on borrowing costs |
| Real Estate | Low | >300k companies; 2.1% land price rise |
| Specialized Skills | High | Demand for AI, data analytics |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the competitive landscape impacting Resona Holdings, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly assess competitive pressures with a dynamic five forces model, allowing for rapid strategic adjustments in the face of evolving market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large corporate clients hold substantial bargaining power against Resona Holdings due to the sheer volume of their loans and deposits. These entities can effectively negotiate favorable interest rates and fees, leveraging their significant financial contributions. Often, these major corporations maintain relationships with multiple banks, fostering a highly competitive environment. This dynamic in the Japanese loan market, particularly evident through 2024, consistently exerts downward pressure on lending fees and interest rates, ultimately benefiting large borrowers.
Retail customers are gaining power due to the increasing availability of choices, including digital-only banks and fintech services. This shift in investor behavior, with more households moving from savings to investments, creates opportunities for banks but also empowers customers to seek out the best products and services. The introduction of the new NISA (Nippon Individual Savings Account) in January 2024 has further fueled this trend. Customers now have enhanced leverage to demand competitive offerings and easily switch financial providers.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) represent a critical customer segment for Resona Holdings. While individual SMEs typically possess less bargaining power compared to large corporations, their collective significance is immense, making them a crucial focus for the bank. Government initiatives in Japan, such as the 2024 budget's continued emphasis on SME support and financing schemes, indirectly enhance their leverage. This backing provides SMEs with a broader array of financing options and support, potentially allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms. Resona's focus on this segment, which comprises over 99% of all companies in Japan, underscores its strategic importance.
High Price Sensitivity in a Low-Interest-Rate Environment
In Japan's banking sector, customers exhibit high price sensitivity, especially within a prolonged low-interest-rate environment. This means they are particularly attuned to fees and charges on financial products. While the Bank of Japan's move in March 2024 to end its negative interest rate policy may gradually shift this dynamic, price competition remains a critical factor for financial institutions like Resona Holdings. Banks offering competitive pricing and robust value-added services will secure a significant advantage as customers seek optimal returns and minimal costs.
- BOJ ended negative rates in March 2024, raising rates to 0%-0.1%.
- Despite the shift, customer focus on low fees persists in 2024.
- Competitive pricing is crucial for customer retention and acquisition.
- Value-added services differentiate banks beyond just rates.
Low Switching Costs for Basic Banking Services
Customers face relatively low switching costs for basic banking services like deposits and loans, empowering their bargaining position. This ease of movement intensifies competition among financial institutions, including Resona Holdings, as they strive to attract and retain clients. The digital transformation of banking further diminishes friction, with a significant 40% of new bank accounts in Japan expected to be opened online by 2024. This trend allows customers to effortlessly compare offers and switch providers, pressuring banks to offer competitive rates and superior service.
- Japanese banks saw a 25% increase in digital account openings in 2023.
- Over 60% of Japanese banking customers use mobile banking apps weekly as of early 2024.
- Interest rates on ordinary deposits in Japan remained near 0.001% in 2024, highlighting minimal differentiation.
- Online loan application volumes for unsecured personal loans grew by 15% in Japan during 2023.
Customers exert significant bargaining power over Resona Holdings, driven by factors like low switching costs and increased digital banking options. Large corporate clients leverage their volume for favorable terms, while retail customers and SMEs benefit from new financial products like NISA 2024 and government support. This dynamic, coupled with persistent price sensitivity even after the BOJ's March 2024 rate hike, compels Resona to offer highly competitive rates and value-added services.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Factor | 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Large Corporations | Loan Volume, Multi-banking | Negotiate lower fees, rates |
| Retail Customers | Digital Options, NISA 2024 | Seek better products, switch easily |
| SMEs | Collective Importance, Gov. Support | Broader financing options |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Resona Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Resona Holdings details the intense competitive rivalry within the Japanese banking sector, highlighting the significant threat of substitute financial products and services. It further elaborates on the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers, assessing how these dynamics influence Resona's profitability and strategic positioning. The analysis also thoroughly examines the potential for new entrants, providing insights into the barriers to entry and the likelihood of increased competition in the future.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Resona Holdings faces fierce competition from Japan's dominant megabanks: Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group, and Mizuho Financial Group. These formidable rivals boast vast domestic and international networks, along with substantial capital reserves. For instance, as of early 2024, MUFG's total assets surpassed ¥370 trillion. This intense rivalry permeates all market segments, from individual retail banking to large corporate financing and specialized wealth management services, impacting Resona's market share.
The Japanese banking sector remains highly competitive, often described as overbanked, with numerous regional institutions vying for market share. Resona Holdings faces significant rivalry, particularly through subsidiaries like Saitama Resona Bank and Kansai Mirai Bank, which focus intensely on specific regional markets. As of early 2024, the trend of consolidation among regional banks continues, with recent mergers aiming for scale and efficiency, potentially intensifying competition for Resona. This landscape demands strategic agility to maintain customer loyalty and market position against many established local players.
Fintech companies and other non-bank entities are increasingly entering Japan's financial services market, offering specialized services like payments, remittances, and asset management. These non-traditional players, while not providing a full banking suite, intensify competition and pressure traditional banks' margins. For instance, Japan's cashless payment ratio reached 39.3% in 2023, showcasing the rapid adoption of digital financial services, a trend continuing into 2024. The Japanese government is actively promoting the fintech sector through various initiatives, further fostering this competitive landscape.
Rivalry in Digital and Technological Innovation
Rivalry in digital and technological innovation is intensely competitive, with banks aggressively adopting new technologies like AI and developing advanced digital banking platforms. Financial institutions are making substantial IT investments to boost operational efficiency and significantly enhance customer experience. Resona Holdings' strategic 'Resona NEXT' initiative, launched in 2024, directly addresses this challenge, focusing on digital transformation and optimizing branch networks.
- Japanese banks are projected to increase IT spending by 3-5% in 2024, emphasizing cloud adoption and data analytics.
- Resona aims to digitize 90% of its branch transactions by 2025 through its digital push.
- Customer engagement via mobile banking apps in Japan saw a 15% increase in active users in 2024.
- AI-driven fraud detection systems reduced financial losses by an average of 12% across leading Japanese banks in 2024.
Competition for Wealth Management and Fee-Based Income
With net interest margins facing persistent pressure, competition among Japanese banks like Resona Holdings for fee-generating businesses, especially wealth management, has intensified. The ongoing shift of household assets from traditional savings to investment products presents a significant growth opportunity, with total household financial assets in Japan reaching approximately ¥2,141 trillion as of Q1 2024. All major banking groups are aggressively vying for a larger share of this lucrative market, driving fierce rivalry.
- Japan's household financial assets stood at ¥2,141 trillion in Q1 2024, signaling a vast target market.
- Major banks are expanding wealth management divisions to counteract declining net interest income.
- Competition for investment trust sales and insurance products remains high among financial institutions.
- Digitalization of wealth management services is a key competitive battleground in 2024.
Resona Holdings faces intense rivalry from dominant Japanese megabanks and a fragmented regional banking sector, intensified by ongoing consolidation. The rise of fintech and non-bank entities, such as Japan's 39.3% cashless payment ratio in 2023, adds significant pressure on traditional banking margins. Competition is also fierce in digital innovation, with Japanese banks projected to increase IT spending by 3-5% in 2024, and for lucrative fee-generating businesses like wealth management, tapping into Japan's ¥2,141 trillion household financial assets as of Q1 2024.
| Competitive Factor | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on Resona |
|---|---|---|
| Megabank Assets (MUFG) | >¥370 trillion (early 2024) | Strong capital, vast networks |
| Cashless Payment Ratio (Japan) | 39.3% (2023, rising 2024) | Increased fintech pressure |
| Japanese Bank IT Spending | 3-5% increase projected 2024 | High investment for digital edge |
| Household Financial Assets (Japan) | ¥2,141 trillion (Q1 2024) | Intense wealth management competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech firms and digital payment platforms pose a growing threat to Resona Holdings by offering substitute services for traditional banking products, especially in payments, remittances, and personal finance management. The Japanese government's 'Cashless Vision' actively promotes this shift, with the cashless payment ratio reaching 39.3% in 2023 and continuing to rise in 2024. While these platforms are capturing a rising share of simpler transactions, full substitution for complex corporate or investment banking needs remains unlikely. However, their increasing market penetration diverts revenue from traditional banking services.
Alternative lending platforms and crowdfunding present a growing substitute for traditional bank loans, serving both individual and business borrowers in Japan. While still a relatively niche segment, these platforms offer viable options, particularly for smaller financing needs that traditional banks might overlook. For instance, the peer-to-peer lending market in Japan, though modest, continues to expand, providing an alternative for borrowers seeking quick access to capital. Additionally, the high-yield market, albeit limited in scope, offers another avenue for specific types of borrowers seeking diverse funding sources.
Large corporations can increasingly bypass traditional banks like Resona Holdings, opting to raise capital directly from financial markets through bond and equity issuance. This direct access significantly reduces their reliance on bank loans, offering greater flexibility in their financing strategies. For instance, global corporate bond issuance volumes remained robust into 2024, demonstrating this persistent trend. This long-standing substitute for corporate banking services poses a notable threat, as companies can directly tap into investor capital.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms offer a direct alternative to Resona Holdings' traditional savings and loan products, connecting individual lenders with individual and small business borrowers. While Japan's P2P lending market is still emerging compared to Western counterparts, its rapid growth presents a notable future substitute. For instance, the Japanese P2P market saw a significant increase in transaction volume, reaching approximately ¥15 billion in 2023, reflecting growing adoption. This trend indicates a potential shift in consumer preference towards more agile, digitally-native financial solutions.
- Japanese P2P lending volume is projected to continue its upward trajectory into 2024.
- These platforms typically offer more flexible terms and potentially higher returns for lenders.
- The convenience of digital applications appeals to a younger demographic.
- Regulations are evolving, potentially fostering further growth in this sector.
Robo-Advisors and Digital Investment Platforms
Robo-advisors and digital investment platforms pose a significant threat to Resona Holdings' traditional asset management services by offering low-cost alternatives. These platforms, particularly attractive to younger, tech-savvy investors, are rapidly gaining traction. The global Assets Under Management (AUM) in the robo-advisors segment is projected to reach approximately US$2.2 trillion in 2024, showcasing this growing trend.
- Global robo-advisor AUM projected at US$2.2 trillion in 2024.
- These platforms offer significantly lower fees than traditional services.
- User penetration for robo-advisors is expanding, particularly among younger demographics.
- The digital shift in investing continues to accelerate.
Digital challengers and alternative platforms pose a significant threat to Resona Holdings by offering substitutes for traditional banking services like payments, loans, and asset management. Japan's cashless payment ratio is continuing to rise in 2024, while global robo-advisor Assets Under Management are projected to reach US$2.2 trillion in 2024. Large corporations increasingly bypass banks by directly accessing capital markets for funding, with corporate bond issuance remaining robust. These evolving alternatives divert revenue and client engagement from traditional financial institutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Metric | 2023 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | Japan Cashless Ratio | 39.3% |
| P2P Lending (Japan) | Transaction Volume | ~¥15 billion |
| Robo-Advisors (Global) | Projected AUM (2024) | US$2.2 trillion |
Entrants Threaten
The Japanese banking sector, overseen by the Financial Services Agency FSA, presents a formidable hurdle for new full-service banks due to stringent regulations and the immense capital required for operations. Obtaining a banking license in Japan involves navigating a complex approval process and demonstrating substantial financial backing. Incumbent institutions such as Resona Holdings benefit from extensive, well-established branch networks and deeply ingrained customer relationships, making it challenging for new entrants to compete effectively. As of early 2024, the capital adequacy requirements for Japanese banks remain robust, ensuring financial stability but also limiting new market participation. These factors collectively establish a high barrier to entry for potential competitors aiming to establish a comprehensive banking presence.
The barriers to entry are significantly lower for new entities focusing on specific niches, such as digital-only banking or payment services. The rise of challenger banks globally demonstrates that new entrants can succeed by targeting specific customer segments with innovative, low-cost offerings; many saw substantial user growth in 2024. Japan's Financial Services Agency is also actively taking steps to facilitate the entry of new financial service providers. This regulatory stance lowers the bar for agile fintechs, posing a direct threat to established players like Resona Holdings by segmenting the market.
Large technology companies, boasting vast customer bases and strong brand recognition, pose a significant entry threat to the financial services sector. While they often begin with partnerships, such as Apple's collaboration with Goldman Sachs for Apple Card, the long-term risk of them becoming direct competitors is substantial. Their advanced capabilities in data analytics and user experience, evidenced by firms like Ant Group processing billions of daily transactions, offer a distinct competitive edge. This ongoing shift means established players like Resona Holdings must continuously innovate to mitigate this evolving pressure from non-traditional financial service providers in 2024.
Government Initiatives to Foster Competition
Japanese government bodies are actively promoting financial sector competition, evident through initiatives like Japan Fintech Week, which in 2024 highlighted advancements in digital finance. This commitment could lead to regulatory adjustments, simplifying market entry for fintech startups and challenger banks. Furthermore, the relaxation of investment criteria for bank subsidiaries into venture businesses, as seen in recent regulatory shifts, directly encourages new entrants. Such policy shifts foster an environment where innovative financial services can emerge, potentially impacting established players like Resona Holdings.
- Japan Fintech Week 2024 emphasized regulatory sandboxes and open banking.
- Financial Services Agency (FSA) aims to balance stability with innovation.
- Increased capital allocation for bank-backed venture investments.
- New digital banking licenses could be more accessible.
International Banks Expanding into the Japanese Market
International banks pose a threat by expanding into the Japanese market, particularly in specialized areas such as investment banking and wealth management for high-net-worth individuals. While the broader retail banking sector remains challenging for foreign players, niche segments present attractive opportunities for entry. The active mergers and acquisitions landscape in Japan, seen throughout 2024, could also serve as a strategic entry point for international financial institutions. This expansion could increase competition for specific client segments.
- Foreign banks target lucrative segments like investment banking.
- Retail banking remains difficult for international entrants.
- Niche opportunities attract new international competition.
- M&A activity in 2024 offers entry routes for global players.
New full-service banks face high entry barriers in Japan due to strict regulations and capital requirements. However, agile fintechs, digital banks, and large tech firms increasingly threaten Resona by targeting niche segments with innovative offerings, with government initiatives in 2024 easing their entry. International banks also target lucrative areas, utilizing 2024 M&A activity for market access.
| Threat Type | Entry Barrier Level | 2024 Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | Very High | Limited new full-service entrants |
| Fintech/Digital | Lowering | Increased niche competition, e.g., 15% rise in digital payment users in 2024 |
| Big Tech Firms | Moderate-High | Significant threat due to data/UX capabilities, over 30% of Japanese users now use tech-based payment services |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Resona Holdings is built upon comprehensive data from their annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific research reports and reputable financial news outlets to capture market dynamics and competitive pressures.
