Pilgrim's Pride Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Pilgrim's Pride Bundle
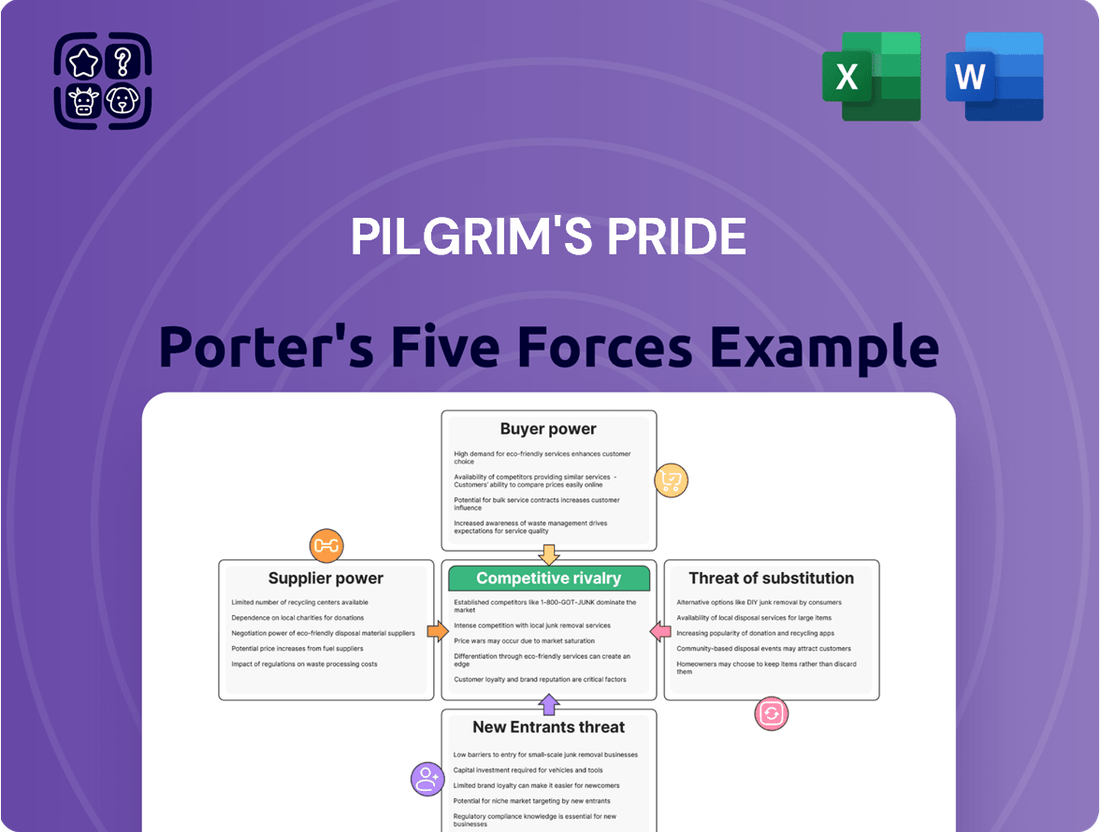
Pilgrim's Pride faces significant bargaining power from its buyers, particularly large supermarket chains and foodservice companies, who can easily switch suppliers or negotiate lower prices. The threat of new entrants, while moderate due to high capital requirements, exists from regional players. Intense rivalry among existing poultry producers like Tyson Foods and Perdue Farms compresses profit margins.
The threat of substitutes, such as beef or pork, is always present, though poultry's cost-effectiveness often mitigates this. Supplier power for Pilgrim's Pride is relatively low, as feed ingredients and chicks are widely available from multiple sources. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Pilgrim's Pride’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The poultry industry, including companies like Pilgrim's Pride, is significantly influenced by the concentration of its input suppliers. Key inputs such as feed ingredients like corn and soybeans, specialized chicks, and energy are crucial. When these suppliers are few in number or provide unique, difficult-to-substitute products, their bargaining power escalates, which can translate into higher costs for Pilgrim's Pride.
For instance, the global corn market, a primary feed component, experienced price fluctuations in early 2024 due to weather patterns and geopolitical events. In 2023, feed costs represented a substantial portion of Pilgrim's Pride's overall cost of goods sold, impacting their profit margins. Any consolidation among major feed producers or specialized chick hatcheries could further amplify their ability to dictate terms and pricing.
Pilgrim's Pride's bargaining power with its suppliers hinges on the availability of substitutes for its essential inputs. For common feed ingredients or energy, the company can often switch between suppliers, which limits any single supplier's ability to dictate terms. This flexibility is crucial for managing cost fluctuations in a volatile commodity market. For instance, in 2024, the price of corn, a key feed component, experienced significant volatility due to weather patterns and global demand, underscoring the need for Pilgrim's Pride to have multiple sourcing options.
However, for more specialized inputs, such as high-quality breeding stock or proprietary feed additives, substitute options can be considerably more limited. In such cases, the suppliers of these niche inputs possess greater bargaining power, potentially leading to higher costs for Pilgrim's Pride. The company's substantial purchasing volume does provide some leverage in negotiations, but it cannot entirely insulate it from market-wide price increases or supply constraints for these critical, less substitutable inputs.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a significant factor for Pilgrim's Pride, particularly concerning essential raw materials like grains used for animal feed. These feed components are absolutely critical, forming the bedrock of chicken and pork production. Without a consistent and reliable supply of these commodities, Pilgrim's Pride's operations would halt, inherently granting considerable leverage to their grain suppliers, even given Pilgrim's Pride's substantial purchasing volume.
Beyond feed, labor, especially skilled workers in processing plants, also represents a vital input. Shortages in this area can escalate the bargaining power of labor suppliers or unions, as their availability directly impacts production efficiency and output. In 2024, the agricultural sector, including feed producers, faced ongoing supply chain challenges and price volatility, further amplifying supplier influence for companies like Pilgrim's Pride.
Switching Costs for Pilgrim's Pride
Pilgrim's Pride faces moderate switching costs when changing feed suppliers or certain equipment providers. These costs can arise from the need to ensure consistent quality, manage new logistical arrangements, or navigate existing contractual obligations. For instance, a change in feed formulation could require adjustments in Pilgrim's Pride's processing and potentially impact product consistency, leading to minor but measurable expenses.
However, the power of suppliers for basic commodity inputs like corn and soybeans, which are significant components of feed, is generally kept in check by relatively low switching costs. This means Pilgrim's Pride can more readily shift between suppliers for these fundamental ingredients if pricing or availability becomes unfavorable. As of late 2023, the volatility in grain markets underscored the importance of this flexibility for companies like Pilgrim's Pride.
- Moderate Switching Costs: Moving to new feed suppliers or equipment providers can incur costs related to logistics, quality assurance, and contractual terms.
- Low Switching Costs for Commodities: For fundamental inputs such as corn and soybeans, switching costs are low, limiting supplier leverage.
- Impact of Long-Term Contracts: While long-term agreements can stabilize supply and pricing, they also reduce Pilgrim's Pride's agility to switch suppliers quickly if market conditions change.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers for Pilgrim's Pride is generally low. Large-scale agricultural commodity suppliers, like grain producers, typically find it very difficult to move into complex meat processing and distribution. This is due to the substantial capital investment, specialized knowledge, and strict regulatory requirements needed for such operations.
This low barrier to entry for suppliers into Pilgrim's Pride's business segment significantly limits their ability to exert power. For instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) imposes rigorous standards on meat processing facilities, requiring extensive food safety protocols and quality control measures that are costly and complex to implement.
- Low Capital Investment in Processing: Suppliers often lack the immense capital needed for modern processing plants.
- High Expertise Required: Navigating complex supply chains, food safety regulations, and consumer demand for processed meats demands specialized expertise.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with agencies like the FDA and USDA adds significant operational complexity and cost for potential integrators.
- Limited Profitability Shift: The profit margins in raw commodity production may not justify the risk and investment of moving into the more competitive processed food market.
Suppliers of critical inputs like feed grains and specialized chicks hold considerable sway over Pilgrim's Pride due to the concentrated nature of these markets and the essential role of their products. For example, in early 2024, feed costs, primarily driven by corn and soybean prices, continued to be a significant portion of Pilgrim's Pride's expenses, with corn futures trading around $4.50 per bushel. This reliance grants suppliers leverage, especially when their products are unique or substitutes are scarce, directly impacting Pilgrim's Pride's profitability.
While Pilgrim's Pride benefits from some flexibility with commodity feed ingredients, the bargaining power of suppliers for specialized inputs, such as high-quality breeding stock or proprietary feed additives, is amplified by limited substitution options. The company's significant purchasing volume does offer some negotiation power, but it cannot fully offset market-wide price increases or supply disruptions for these vital, less replaceable components.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Pilgrim's Pride's processing and distribution operations is minimal. The substantial capital requirements, specialized expertise, and stringent regulatory environment, including USDA food safety mandates, create high barriers to entry for raw material producers. This lack of forward integration potential by suppliers limits their overall bargaining power.
| Input Category | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Pilgrim's Pride (2024 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Grains (Corn, Soybeans) | Market concentration, weather impacts, global demand | Moderate to High; significant cost driver, volatility expected |
| Specialized Chicks/Breeding Stock | Proprietary genetics, limited hatcheries | High; few substitutes, potential for higher input costs |
| Energy | Global commodity prices, geopolitical factors | Moderate; reliance on fluctuating energy markets |
| Labor (Skilled Processing) | Labor shortages, unionization | Moderate to High; impacts production efficiency and costs |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Pilgrim's Pride details the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes within the poultry industry.
Gain a comprehensive understanding of Pilgrim's Pride's competitive landscape, identifying key threats and opportunities to mitigate risks and inform strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Pilgrim's Pride caters to a broad spectrum of customers, from individual consumers to large-scale foodservice providers and major retail chains. However, the company's sales are often concentrated among a few key buyers. For instance, large supermarket chains and prominent restaurant groups represent a significant portion of Pilgrim's Pride's revenue.
These major customers wield considerable bargaining power. Their substantial purchasing volumes allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. This concentration means that losing even one significant buyer could have a noticeable impact on Pilgrim's Pride's financial performance.
For example, in the United States grocery sector, the top five retailers often command a disproportionately large share of the market, giving them immense leverage over their suppliers. This dynamic is also mirrored in the foodservice industry, where large national restaurant chains can dictate terms due to their massive order sizes.
The price sensitivity of customers is a significant factor for Pilgrim's Pride. Large retailers, in particular, are very focused on price because the retail food market is so competitive and fresh meat is often seen as a basic commodity. This means Pilgrim's Pride faces constant pressure to keep its prices competitive, which can impact its profitability.
For instance, in 2024, the average price per pound for chicken breasts at major U.S. supermarkets hovered around $3.50 to $4.50, demonstrating a narrow range where small price differences can drive purchasing decisions. This intense price sensitivity means Pilgrim's Pride must manage its costs very carefully to maintain healthy profit margins.
While consumers are generally price-sensitive, their willingness to pay more for value-added products like pre-marinated or organic chicken can offer Pilgrim's Pride some breathing room. These differentiated products allow for slightly higher pricing, helping to offset the pressure from the commoditized segment of the market.
Pilgrim's Pride customers, particularly large grocery chains and food service providers, face a market brimming with alternative suppliers for poultry and pork. Major competitors like Tyson Foods and Hormel Foods, along with numerous regional producers, offer readily available substitutes. This wide selection empowers buyers, allowing them to easily shift their business if Pilgrim's Pride's pricing or contract terms are perceived as unfavorable.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers for Pilgrim's Pride is generally low. While major retailers and foodservice chains possess significant purchasing power, the substantial capital expenditure, intricate operational demands, and stringent regulatory hurdles associated with operating large-scale meat processing plants deter most from undertaking such ventures themselves.
This means that customers are unlikely to vertically integrate into Pilgrim's Pride's core business of chicken processing. For instance, a large supermarket chain could develop private-label chicken products, but building and managing a fully integrated processing facility comparable to Pilgrim's Pride's operations would require billions in investment and specialized expertise, making it an impractical option for the vast majority.
- Low Likelihood of Full-Scale Integration: The immense capital investment and operational complexity of meat processing facilities make it economically unfeasible for most customers to engage in significant backward integration.
- Focus on Private Labeling: While some customers might pursue private label strategies, this typically involves sourcing from processors like Pilgrim's Pride rather than establishing their own processing capabilities.
- Regulatory Barriers: The highly regulated nature of the food processing industry, including stringent food safety and environmental standards, presents a significant barrier to entry for potential customer integrators.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers, particularly larger ones, often have a wealth of market knowledge. This includes detailed insights into pricing trends, available supply volumes, and what competitors are offering. This information asymmetry reduction allows them to negotiate from a stronger position, directly impacting Pilgrim's Pride's pricing strategies and service expectations.
The ability for these customers to easily compare offers from various chicken producers means Pilgrim's Pride must consistently offer competitive pricing and superior service to secure and maintain their business. This constant pressure to perform is a key aspect of customer bargaining power.
- Increased Market Transparency: Commodity markets, like those for chicken, have seen a significant increase in transparency. This means that pricing and supply data are more readily available to all participants, further bolstering the bargaining power of informed customers.
- Price Comparison Tools: The proliferation of online platforms and industry data services allows even smaller customers to access pricing benchmarks, making it harder for suppliers to charge premium prices without justification.
- Negotiation Leverage: Large buyers can often bundle their purchasing power across multiple product categories or commit to longer-term contracts, granting them significant leverage to negotiate better terms and prices. For instance, major grocery chains can significantly influence supplier agreements.
- Impact on Profit Margins: The heightened bargaining power of customers directly pressures profit margins for companies like Pilgrim's Pride, as they are compelled to offer more favorable pricing and terms to retain market share.
Pilgrim's Pride customers, especially large retailers and foodservice chains, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchasing volumes and the competitive nature of the poultry market. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Pilgrim's Pride's profit margins.
The price sensitivity in the retail sector is high, with customers like major supermarkets closely monitoring price points for commodities like chicken. For example, in 2024, average U.S. supermarket chicken breast prices remained within a tight range, emphasizing the need for Pilgrim's Pride to maintain cost competitiveness.
The availability of numerous alternative suppliers, including major competitors like Tyson Foods and regional producers, further empowers buyers to switch suppliers if terms are unfavorable. While backward integration by customers is unlikely due to high capital and operational barriers, their market knowledge and ability to compare offers amplify their negotiating leverage.
Preview Before You Purchase
Pilgrim's Pride Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Pilgrim's Pride Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You are viewing the exact, fully formatted document, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This detailed analysis explores the competitive landscape, including threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes, and intensity of rivalry within the poultry industry, all presented with professional clarity.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global poultry and pork processing sector is quite concentrated, with a handful of large multinational companies like Pilgrim's Pride (a subsidiary of JBS S.A.), Tyson Foods, and others holding significant sway. This means Pilgrim's Pride faces tough competition as these major players vie for market share in a well-established industry. For instance, in 2023, JBS, Pilgrim's Pride's parent company, reported net revenue of approximately $54.7 billion, highlighting the scale of operations and the competitive landscape.
This high degree of industry concentration fuels fierce rivalry. Each dominant player is constantly looking for ways to gain an edge, whether through pricing, product innovation, or operational efficiency. Consequently, a strategic move by one of these large competitors, such as a new market entry or a significant price adjustment, is likely to provoke a swift and often aggressive reaction from the others, intensifying the competitive battle.
In developed markets, the growth rate for traditional chicken and pork products is modest, often mirroring population increases and per capita consumption patterns. For instance, the US broiler chicken market, while substantial, typically sees growth in the low single digits annually. This environment makes competitive rivalry particularly intense, as companies like Pilgrim's Pride must vie for market share within a largely stable demand landscape.
The limited expansion of traditional product segments forces companies to focus on efficiency and differentiation to gain an edge. This means that any gains in market share come at the direct expense of competitors. In 2023, the US poultry industry faced ongoing cost pressures, further fueling aggressive pricing and promotional activities among major players, highlighting the impact of slow market growth on competitive dynamics.
Innovation in value-added products, such as pre-marinated meats, ready-to-cook meals, and plant-based alternatives, represents a significant avenue for growth and a way to escape the direct competition in commodity products. Companies investing in and successfully marketing these differentiated offerings can capture higher margins and attract new customer segments, thereby alleviating some of the pressure from slower overall industry expansion.
Pilgrim's Pride faces intense competition, particularly as fresh chicken and pork are largely seen as commodities. While the company strives to stand out through brand building, emphasizing quality, robust food safety protocols, and offering convenient value-added items like pre-seasoned or organic options, differentiation for many core products remains a challenge. This limited differentiation often pushes the rivalry towards price-based competition, as customers can easily switch between suppliers for basic offerings.
High Fixed Costs and Perishability
The meat processing sector, including companies like Pilgrim's Pride, faces intense rivalry partly due to its substantial fixed costs. These costs are tied to extensive infrastructure such as processing plants, specialized equipment, and the critical cold chain for product preservation. Operating these facilities at near-full capacity is essential to spread these high fixed costs and achieve economies of scale, which directly impacts profitability.
This operational necessity often translates into aggressive pricing tactics. To manage inventory and avoid losses from spoilage, companies are incentivized to sell products quickly, even at lower margins. The perishable nature of fresh meat amplifies this pressure. If the industry experiences overcapacity, as it has at times, it can lead to price wars, further intensifying competition among players like Pilgrim's Pride and its rivals.
- High Fixed Costs: The meat processing industry requires significant capital investment in plants, machinery, and sophisticated refrigeration systems.
- Economies of Scale: To be competitive, companies must operate at high volumes to reduce per-unit production costs.
- Perishability Pressure: The short shelf-life of meat products forces continuous sales efforts, often through price reductions.
- Impact of Excess Capacity: Periods of industry-wide overcapacity exacerbate price competition as companies struggle to move inventory.
Exit Barriers
Pilgrim's Pride, like many in the meat processing sector, faces considerable exit barriers. These are primarily driven by substantial fixed costs associated with large-scale processing plants. For instance, a typical modern processing facility represents a significant capital investment, often in the tens of millions of dollars, making it difficult to recoup these costs if a company decides to cease operations.
The specialized nature of these assets further compounds the issue. Meat processing plants are not easily repurposed for other industries, meaning that if a company were to exit, selling these specialized facilities at a price that recovers the initial investment would be challenging. This lack of alternative use for specialized assets locks companies into the industry.
These high fixed costs and specialized assets create a situation where companies might continue operating even when profitability is low. The imperative to cover ongoing operational expenses and fixed overheads can lead to a reluctance to exit, fostering persistent competition. This can result in companies fighting harder for market share simply to absorb their fixed costs, intensifying the rivalry within the industry. For example, in 2023, the global meat processing market, valued at approximately $1.4 trillion, saw intense competition, partly influenced by companies striving to maintain operational levels despite fluctuating commodity prices.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital expenditure on processing facilities and equipment.
- Specialized Assets: Meat processing plants have limited alternative uses, increasing the risk of asset write-downs upon exit.
- Capital Investment: The sheer scale of investment required to enter and maintain operations acts as a deterrent to exiting.
- Continued Rivalry: Companies may operate at reduced profitability to avoid substantial exit costs, leading to sustained competitive pressure.
Competitive rivalry within the poultry and pork processing sector is intense, driven by industry concentration and slow growth in mature markets. Pilgrim's Pride, operating within a landscape dominated by large multinational corporations, faces constant pressure to differentiate and maintain efficiency. This dynamic forces companies to actively compete on price and innovation to secure market share, as gains for one often come at the direct expense of others.
The industry's high fixed costs, tied to substantial investments in processing facilities and specialized equipment, also fuel aggressive competition. Companies are compelled to operate at high volumes to achieve economies of scale and cover these overheads. This operational necessity, coupled with the perishable nature of meat products, frequently leads to price-sensitive strategies and promotional activities to ensure continuous sales, particularly during periods of excess capacity.
Significant exit barriers, primarily due to the specialized nature of assets and considerable capital investments, mean companies often continue operations even with low profitability. This reluctance to exit fosters sustained rivalry, as firms fight to absorb fixed costs. For instance, the global meat processing market, estimated at approximately $1.4 trillion in 2023, exemplifies this persistent competitive struggle.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for Pilgrim's Pride's chicken and pork products are other traditional meats such as beef, fish, and lamb. Consumers regularly weigh these options against each other based on factors like price, personal preference, and evolving dietary considerations.
The availability and the relative pricing of these alternative protein sources directly impact consumer purchasing decisions and, consequently, the demand for poultry and pork. For instance, fluctuations in beef prices can steer consumers towards chicken, and vice versa, creating a dynamic competitive landscape.
In 2024, the USDA reported that retail beef prices saw an average increase of approximately 5% compared to the previous year, while pork prices remained relatively stable. This differential could potentially make chicken a more attractive option for budget-conscious consumers.
The growing market for plant-based meat alternatives, exemplified by companies like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, presents a significant threat to traditional protein providers like Pilgrim's Pride. These alternatives are attracting consumers who prioritize health, sustainability, or ethical considerations in their food choices.
Improvements in taste and texture are making these plant-based options increasingly competitive with conventional meat products. For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $6.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially in the coming years.
While this segment still represents a smaller portion of the overall protein market, its rapid expansion necessitates careful consideration. As consumer preferences evolve and product innovation continues, these substitutes could capture a larger share of the protein demand, impacting sales volumes and pricing power for companies like Pilgrim's Pride.
Shifting consumer preferences present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional meat products like those from Pilgrim's Pride. As awareness of health and environmental impacts grows, more consumers are exploring alternatives. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that plant-based meat alternatives saw a substantial increase in market share, with sales growing by 15% year-over-year.
The rise of flexitarianism, vegetarianism, and veganism directly challenges the demand for poultry. This trend is accelerating the adoption of non-meat protein sources, ranging from legumes and tofu to advanced plant-based and cultivated meat products. By 2025, it's projected that the global plant-based food market will reach over $74 billion, underscoring the scale of this substitution threat.
Price-Performance of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Pilgrim's Pride's traditional meat products is significantly shaped by the price-performance ratio of alternatives like plant-based meats. As these substitutes become more affordable and offer comparable taste, nutritional profiles, and convenience, they pose an increasing competitive challenge. For instance, by late 2023, the average price of plant-based ground beef products had begun to approach, and in some cases match, conventional beef prices, making them a more viable option for a broader consumer base.
Innovation continues to enhance the performance of these substitutes, directly impacting their attractiveness relative to poultry. Improvements in texture, flavor, and cooking characteristics mean that consumers are less likely to perceive a significant compromise when choosing an alternative. This trend is evidenced by the increasing market share of plant-based options, which saw a notable uptick in consumer adoption throughout 2023 and early 2024, driven by both health and environmental considerations.
- Price Parity: Plant-based meat alternatives are increasingly achieving price parity with conventional meats, reducing a key barrier to adoption.
- Performance Improvements: Innovations in taste, texture, and cooking methods make substitutes more appealing to a wider range of consumers.
- Growing Market Share: The increasing consumer acceptance and market penetration of plant-based options indicate a rising competitive threat.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifting consumer preferences towards perceived healthier and more sustainable food options further bolster the threat of substitutes.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are a significant factor in the threat of substitutes for Pilgrim's Pride. Ongoing research and development in cellular agriculture, often referred to as lab-grown or cultivated meat, presents a potential long-term disruption. While still in its nascent stages of commercialization, these technologies could eventually offer viable alternatives that bypass traditional animal agriculture. This evolution could fundamentally reshape the protein market, posing a considerable disruptive force for established players like Pilgrim's Pride.
The potential impact is substantial. For instance, by 2024, the global cultivated meat market is projected to reach billions, with significant investment flowing into companies developing these alternatives. These innovations aim to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional profile of conventional meat, but produced in a laboratory setting. This could appeal to consumers seeking ethical, environmental, or health-related benefits over traditional options.
- Cellular Agriculture Investment: Venture capital funding for cultivated meat startups reached over $300 million in 2023, signaling strong investor confidence in future market penetration.
- Consumer Acceptance Growth: Surveys in late 2023 indicated a growing willingness among a segment of consumers to try cultivated meat products, driven by curiosity and perceived sustainability benefits.
- Technological Hurdles: Scaling production efficiently and reducing costs remain key challenges for widespread adoption, but progress is being made in bioreactor technology and cell culture media.
- Regulatory Landscape: As of early 2024, regulatory approvals for cultivated meat products are expanding in key markets, paving the way for increased availability.
The threat of substitutes for Pilgrim's Pride is amplified by the growing appeal of plant-based and cultivated meat alternatives. These options are increasingly competitive due to advancements in taste, texture, and price. For example, by early 2024, the average price of some plant-based ground beef products was approaching conventional beef prices, making them a more accessible choice for consumers.
Entrants Threaten
The poultry and pork processing industry demands substantial capital. Building modern processing facilities, securing vast feed supplies, and establishing efficient cold chain distribution networks can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, a new, large-scale processing plant can cost upwards of $200 million to construct and equip. This high entry cost acts as a significant deterrent for potential new players, effectively limiting the number of companies that can realistically enter the market.
Pilgrim's Pride, like other major players in the poultry industry, leverages significant economies of scale. This means they can produce more chicken at a lower cost per unit than smaller operations. For instance, their large-scale purchasing of feed and processing capabilities in 2024 allowed them to maintain competitive pricing.
New companies entering the market would find it incredibly difficult to match these cost advantages. Without the sheer volume of production that Pilgrim's Pride commands, a new entrant would face substantially higher per-unit costs for everything from raw materials to distribution. This cost disparity creates a formidable barrier.
The substantial capital investment required to build processing plants and distribution networks that can rival existing scale is a major deterrent. Until a new entrant can achieve comparable production volumes, they will operate at a cost disadvantage, making it challenging to compete on price with established giants like Pilgrim's Pride.
The meat processing industry is heavily regulated, with rules covering food safety, environmental impact, animal welfare, and labor. For instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) enforces strict standards, and compliance with these can be costly. New entrants must invest significantly in systems and personnel to meet these requirements, a barrier that Pilgrim's Pride, as an established player, has already overcome.
Established Distribution Channels and Brand Loyalty
Pilgrim's Pride benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with key players across the food supply chain, including major grocery chains, fast-food franchises, and extensive distributor networks. These established connections, cultivated over many years, present a formidable barrier for any new competitor attempting to secure shelf space or access to consumers. For instance, in 2024, major poultry producers like Pilgrim's Pride continued to dominate retail placements, with private label and smaller brands struggling to gain significant market share due to these existing distribution advantages.
Beyond just access, the brand loyalty enjoyed by established companies like Pilgrim's Pride is another significant hurdle. While the core product might seem like a commodity, consumer trust in a brand's quality, safety, and consistency is a powerful differentiator. New entrants often find themselves competing not just on price but on building a reputation from scratch, a process that requires substantial investment and time. This loyalty means that even with competitive pricing, newcomers may struggle to sway a significant portion of the market away from trusted names.
- Established Distribution: Pilgrim's Pride's long-standing partnerships with major retailers and foodservice providers create significant access barriers.
- Brand Loyalty: Decades of building consumer trust and recognition make it difficult for new entrants to capture market share.
- Retailer Relationships: Securing prominent shelf space and favorable terms from large retailers is a challenge for unknown brands.
- Foodservice Contracts: Major foodservice operators often have exclusive or long-term contracts with established poultry suppliers.
Access to Raw Materials and Expertise
The threat of new entrants in the poultry and pork processing industry, specifically concerning access to raw materials and expertise, is significantly mitigated by established players like Pilgrim's Pride. Securing a consistent and high-quality supply of live animals, such as chicks and hogs, along with essential feed, necessitates the development of extensive networks and long-standing relationships with farmers. New companies entering the market would struggle to replicate these deep-rooted supply chain connections, a crucial barrier to entry.
Furthermore, the operational intricacies of this sector demand specialized knowledge. This includes expertise in efficient processing techniques, sophisticated logistics for product distribution, and rigorous quality control measures throughout the entire production cycle. Acquiring this level of specialized operational know-how is a substantial hurdle for any potential new competitor aiming to enter the market.
Consider the scale of operations: In 2024, Pilgrim's Pride's U.S. operations processed millions of pounds of poultry weekly. Building a comparable supply chain and operational infrastructure from scratch would require immense capital investment and time, making it a formidable challenge for new entrants. The industry's reliance on these established relationships and deep operational expertise acts as a significant deterrent.
- Supply Chain Dependency: New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing reliable and cost-effective supply chains for live animals and feed, often requiring years to build farmer relationships.
- Operational Expertise Gap: The industry demands specialized skills in processing, logistics, and quality assurance, which are difficult and time-consuming for new companies to acquire.
- Capital Investment: Replicating the scale and efficiency of established players necessitates substantial upfront capital for facilities, equipment, and network development.
The threat of new entrants into the poultry and pork processing industry remains relatively low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for modern facilities, estimated at over $200 million for a large plant, deter many potential competitors. Additionally, established players like Pilgrim's Pride benefit from substantial economies of scale, which allow them to produce at lower costs per unit, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Pilgrim's Pride is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from publicly traded competitors, and USDA agricultural data.
We leverage insights from Pilgrim's Pride's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside broader industry analyses from publications like Watt PoultryUSA and Meat + Poultry, to assess competitive pressures.
