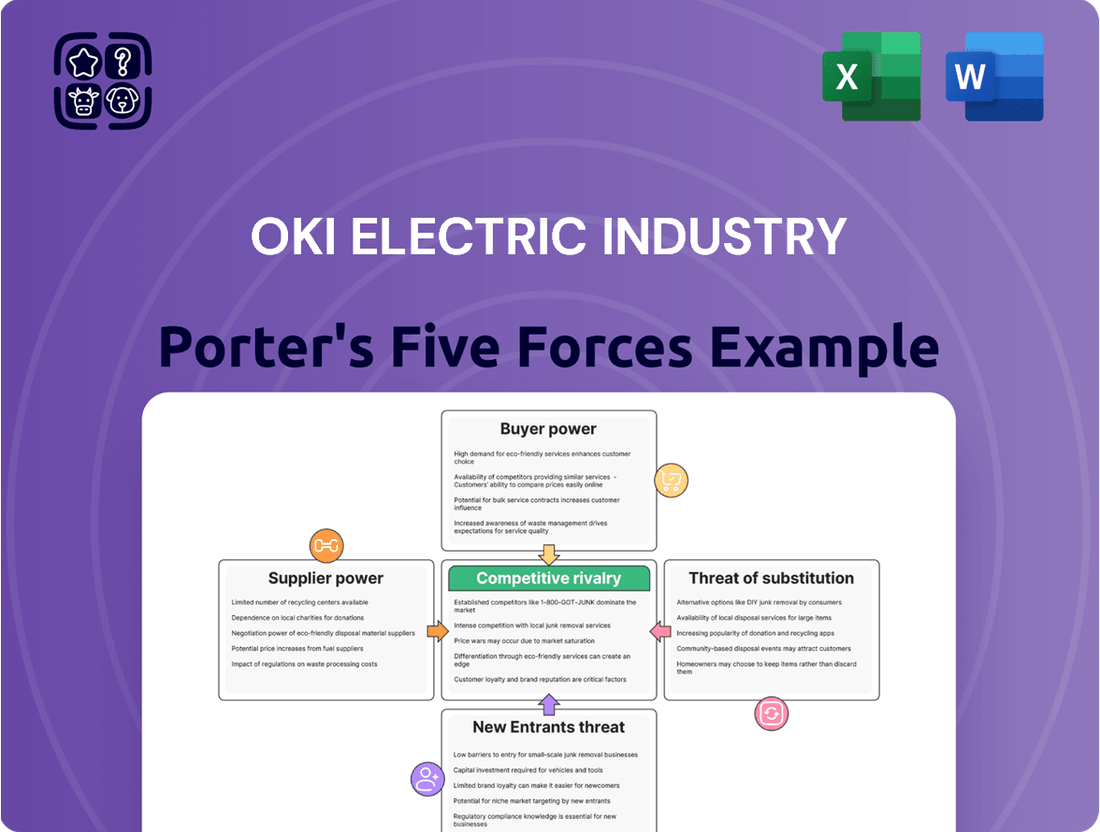
OKI Electric Industry Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
OKI Electric Industry Bundle
OKI Electric Industry navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants, particularly in the electronics sector. Buyer power can be significant, especially for large corporate clients, while supplier leverage varies depending on specialized components. The availability of substitutes also presents a persistent challenge, forcing OKI to innovate continually.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter this market. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore OKI Electric Industry’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
OKI Electric Industry's reliance on a concentrated base of key component suppliers, particularly for semiconductors and specialized network hardware, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. In 2024, the global semiconductor shortage, though easing, continued to highlight the leverage held by major chip manufacturers, impacting lead times and pricing for critical electronic components used in OKI's communication and IT infrastructure products. A limited number of suppliers for advanced optical components or specialized manufacturing equipment can dictate terms, potentially increasing OKI's cost of goods sold and influencing product launch schedules.
The uniqueness of supplier inputs significantly influences OKI Electric Industry's bargaining power with its suppliers. If suppliers provide highly specialized or proprietary components, such as patented semiconductor manufacturing equipment or custom-designed optical sensors, OKI faces substantial switching costs. This reliance on unique inputs, like advanced ASIC designs from a single provider, strengthens the supplier's leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor industry saw continued reliance on highly specialized fabrication equipment, with lead times for advanced lithography machines stretching into years, highlighting the power of such unique suppliers.
Switching suppliers for OKI Electric Industry involves significant financial and operational challenges, which directly impacts the bargaining power of its current suppliers. These switching costs can include the expense of retooling production lines to accommodate new components, the investment in retraining personnel to work with different equipment or materials, and the time and resources needed for re-certifying new parts to meet OKI's stringent quality standards.
For instance, if OKI relies on specialized semiconductor components, the cost of finding an alternative supplier, ensuring compatibility, and then re-validating the entire supply chain could run into millions of dollars. This high barrier means OKI is less inclined to switch, even if a competitor offers slightly lower prices, thereby strengthening the negotiating position of existing suppliers who are aware of these embedded costs.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by OKI Electric Industry's suppliers represents a significant factor in their bargaining power. If suppliers have the necessary resources, technological capabilities, and market understanding, they could potentially begin producing their own finished electronic products, directly competing with OKI.
This scenario would drastically increase supplier leverage, as they could transition from being mere component providers to direct rivals. For instance, a key semiconductor supplier with advanced manufacturing facilities might consider producing its own integrated circuits or even complete devices if the profit margins appear more attractive than supplying OKI. Such a move would disrupt OKI's supply chain and force competitive pricing adjustments.
Consider the automotive sector, where tier-one suppliers have increasingly moved into producing complete systems, sometimes bypassing traditional vehicle manufacturers. While specific data for OKI's suppliers in this regard isn't publicly detailed, the general trend in electronics manufacturing indicates that suppliers with strong R&D and production scale are more likely to explore such vertical integration strategies. For example, in 2024, some component manufacturers in Asia expanded their in-house design services, hinting at a readiness to offer more complete solutions.
- Supplier Capabilities: The degree to which OKI's suppliers possess design, manufacturing, and marketing expertise directly influences their ability to integrate forward.
- Market Conditions: Favorable market conditions, such as high demand for specific electronic products or perceived weaknesses in OKI's product offerings, could incentivize suppliers to integrate.
- Profitability Analysis: Suppliers will assess the potential profitability of producing finished goods versus supplying components, weighing investment costs against potential returns.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of other players in the market and the overall competitive intensity will shape a supplier's decision to enter as a direct competitor.
Supplier Importance to OKI's Product Quality
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor for OKI Electric Industry, particularly concerning the quality of its high-performance products like ATMs and telecommunications infrastructure. Suppliers of specialized components, such as advanced semiconductor chips or high-precision mechanical parts, hold significant leverage if their inputs are indispensable for OKI to achieve its desired product quality and reliability. If OKI relies heavily on a few suppliers for these critical materials, these suppliers can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms.
For OKI, maintaining a competitive edge often means incorporating cutting-edge technology and superior componentry. This reliance on specialized, high-quality inputs amplifies the bargaining power of the suppliers providing them. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor shortage highlighted how critical supplier relationships are; companies that could secure reliable, high-quality chip supplies maintained production and market share more effectively. This situation underscores the potential for suppliers of advanced electronics to command higher prices or dictate terms when their products are vital for OKI's innovation and performance standards.
- Component Dependency: OKI's dependence on a limited number of suppliers for critical, high-specification components for its ATMs and telecom equipment grants those suppliers considerable bargaining power.
- Quality Imperative: The need for superior quality inputs to maintain OKI's competitive edge in performance and reliability means suppliers of these essential items have significant leverage.
- Supplier Concentration: If few suppliers can meet OKI's stringent quality and technological requirements, their collective bargaining power increases, potentially impacting OKI's costs and supply chain stability.
- Market Dynamics: In sectors where technological advancements are rapid, suppliers of innovative components can leverage their unique offerings to negotiate favorable terms with manufacturers like OKI.
The bargaining power of suppliers for OKI Electric Industry is substantial, primarily due to the specialized nature of many components and a degree of supplier concentration. This leverage is amplified when suppliers provide critical inputs for OKI's high-performance products, such as advanced semiconductors for its telecommunications infrastructure and precision parts for ATMs. In 2024, the ongoing demand for advanced chips meant that key semiconductor manufacturers continued to hold considerable sway over pricing and delivery schedules.
The switching costs for OKI are also a significant factor; retooling, re-certification, and establishing new supplier relationships can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming. This makes OKI less agile in changing suppliers, thereby strengthening the position of existing ones. Furthermore, the potential for suppliers to engage in forward integration, moving from component provision to manufacturing finished goods, adds another layer of supplier leverage, as seen in the expanding capabilities of some electronics manufacturers in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on OKI | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Component Specialization | High dependence on unique inputs | Strong |
| Supplier Concentration | Limited alternatives for critical parts | Moderate to Strong |
| Switching Costs | Significant financial and operational hurdles | Strong |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition | Moderate |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously dissects the competitive forces impacting OKI Electric Industry, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Understand the competitive landscape instantly with a visual breakdown of OKI Electric Industry's Porter's Five Forces, offering immediate clarity on market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
OKI Electric Industry's customer bargaining power is significantly influenced by customer concentration and volume. The company's reliance on a few major clients, particularly within sectors like finance and retail where point-of-sale systems and banking terminals are critical, can give these large buyers considerable leverage. For instance, if a handful of financial institutions represent a substantial percentage of OKI's revenue from its banking solutions segment, they can effectively dictate terms, pushing for lower prices or more stringent service level agreements due to the sheer volume of their orders.
Customer switching costs for OKI Electric Industry's products and services are a key factor influencing customer bargaining power. If customers can easily shift to a competitor with minimal disruption, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases. For instance, a business relying on OKI's network equipment might find switching difficult if significant integration and retraining are required for a new vendor's solutions. This integration effort acts as a deterrent to switching, thus reducing the customer's bargaining leverage.
OKI Electric Industry's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. In areas where OKI's products are seen as more commoditized, such as certain electronic components, customers are likely to be highly attuned to price fluctuations. For instance, if a competitor offers a similar component at a lower price, buyers in these segments will readily switch, putting downward pressure on OKI's pricing power. This is particularly true for businesses operating on thin profit margins themselves, where cost optimization is paramount.
Conversely, for OKI's more specialized solutions, like advanced network equipment or customized industrial printers, customers may display lower price sensitivity. This is often because the perceived value of these offerings, including performance, reliability, and integration capabilities, outweighs minor price differences. For example, a critical infrastructure project relying on OKI's robust network solutions might prioritize functionality and support over a slightly cheaper alternative, understanding the potential long-term costs of failure. In fiscal year 2024, OKI reported a 10% increase in sales for its specialized solutions segment, indicating strong demand that can absorb higher price points.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly influences OKI Electric Industry's customer bargaining power. When customers have numerous alternative solutions to meet their needs, their ability to negotiate favorable terms with OKI intensifies. This means if OKI's products are priced too high or don't meet specific requirements, customers can readily switch to competitors or alternative technologies.
For instance, in the telecommunications equipment market where OKI operates, advancements in areas like VoIP solutions and cloud-based communication platforms can serve as substitutes for traditional PBX systems. This broadens customer choice. In 2023, the global Unified Communications and Collaboration (UCC) market, which encompasses many of these substitutes, was valued at approximately $104.7 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong competitive landscape.
- Increased Competition: A wide array of substitute products means OKI faces pressure from a broader set of competitors, not just direct rivals offering similar hardware.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are more likely to be price-sensitive when viable substitutes exist, forcing OKI to maintain competitive pricing to retain market share.
- Innovation Pressure: The presence of substitutes drives OKI to continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings to avoid being commoditized.
- Customer Loyalty: Without strong differentiation, customer loyalty can be weak, as switching costs to substitutes may be low.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge for OKI Electric Industry. This refers to the possibility that OKI's clients might decide to produce their own IT and telecommunications equipment internally, rather than continuing to buy from OKI. This would directly diminish OKI's sales and market share.
Large, resource-rich organizations, such as major financial institutions or extensive retail chains, are particularly well-positioned to explore this option. If these customers possess substantial financial reserves and the necessary technical acumen, they could invest in developing their own manufacturing capabilities. This potential move dramatically increases their bargaining power over suppliers like OKI.
For instance, a global banking conglomerate might analyze the cost savings and strategic control gained by bringing their internal communication systems development in-house. In 2024, major tech companies have been increasingly investing in custom silicon and in-house infrastructure solutions, signaling a broader trend that could impact suppliers across various industries.
- Customer Autonomy: Customers may seek to gain more control over their technology supply chain and reduce reliance on external vendors.
- Cost Reduction: In-house production can sometimes lead to lower costs for large-volume buyers, especially when considering the total cost of ownership.
- Strategic Control: Developing proprietary technology allows customers to tailor solutions precisely to their unique operational needs and competitive strategies.
- Industry Trends: A growing trend towards vertical integration across various sectors means customers are more likely to consider backward integration as a viable strategy.
OKI Electric Industry's customers wield significant bargaining power, particularly when they represent large volumes or operate in price-sensitive markets. For instance, major financial institutions purchasing banking terminals can leverage their order size to negotiate favorable pricing. Conversely, customers requiring OKI's specialized, high-performance network solutions may exhibit less price sensitivity due to the critical nature and integration complexity of these offerings. In fiscal year 2024, OKI reported a 10% increase in sales for its specialized solutions segment, reflecting strong demand that allows for higher pricing power in those areas.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power Influence | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Financial Institutions (Banking Terminals) | High | Significant leverage due to high volume | Negotiating bulk discounts on POS systems. |
| Retail Chains (POS Systems) | Moderate to High | Influence through order volume and potential for switching | Seeking competitive bids for network infrastructure. |
| Telecommunications Providers (Network Equipment) | Moderate | Balanced by switching costs and product differentiation | Evaluating long-term contracts for advanced communication solutions. |
| Industrial Manufacturers (Custom Printers) | Low to Moderate | Lower due to reliance on specialized features and reliability | Prioritizing performance and support over minor price variations. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
OKI Electric Industry Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis of OKI Electric Industry, providing a thorough examination of competitive forces. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase, offering actionable insights without any placeholders. Understand the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the potential of substitute products for OKI Electric Industry. This comprehensive report is ready for your immediate use, empowering your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
OKI Electric Industry operates in several competitive sectors, including printers, ATMs, and telecommunications infrastructure. The printer market, for instance, is characterized by a significant number of players, ranging from global giants like Canon and HP to specialized providers. This crowded landscape often results in intense price competition and aggressive product innovation as companies vie for market share.
In the ATM market, while the number of major manufacturers might be smaller, the competition remains fierce, with companies like Diebold Nixdorf and NCR dominating. These established players often possess strong brand recognition and extensive service networks, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction. OKI's position within these markets is shaped by how effectively it navigates this existing rivalry.
OKI Electric Industry operates across several sectors, including information and communication technology (ICT) and electronics manufacturing. The global ICT market, a key area for OKI, was projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.3% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. This moderate growth suggests that while there are opportunities, the landscape is not one of hyper-expansion where intense competition is solely driven by rapid market scaling.
OKI Electric Industry's competitive rivalry is shaped by how distinct its offerings are. In sectors where products are very similar, like basic electronics, price becomes the main battleground. However, when a company like OKI can make its products stand out through unique features, superior quality, or exceptional customer service, it gains pricing power and can avoid direct price wars.
For OKI, product differentiation is key. For example, in their printing solutions, they've focused on developing advanced security features and energy-efficient designs, setting them apart from more generic offerings. This strategy allows them to command a premium and build customer loyalty.
The degree of product differentiation directly impacts OKI's ability to manage competitive rivalry. In 2024, the electronics market continues to see intense competition, but companies with strong, recognizable differentiation, such as OKI's specialized printing technologies, are better positioned to maintain market share and profitability.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
Exit barriers for competitors in the telecommunications and electronics manufacturing sectors, where OKI Electric Industry operates, can be significant. These barriers include substantial investments in specialized manufacturing equipment and R&D, making it costly for companies to divest or repurpose these assets. For instance, the high cost of setting up and maintaining advanced semiconductor fabrication facilities or specialized network equipment production lines can deter smaller players from entering and larger ones from exiting. OKI Electric Industry's focus on areas like secure communication systems and embedded solutions often requires proprietary technology and deep integration with existing infrastructure, further raising exit costs.
Long-term contracts with clients, particularly in government or large enterprise sectors for critical infrastructure like secure payment terminals or network components, also act as a substantial exit barrier. Breaking these contracts often incurs penalties and reputational damage. The need to honor these commitments means companies may remain in the market even when facing profitability challenges. In 2023, the global market for secure payment terminals saw continued demand, with many vendors tied into multi-year service and supply agreements.
High fixed costs associated with maintaining production facilities, a skilled workforce, and ongoing regulatory compliance also contribute to elevated exit barriers. Companies might continue operating at a loss rather than incurring the immediate, significant costs of shutting down operations and managing workforce redundancies. This can lead to a situation where even underperforming companies remain active participants, intensifying competition and potentially suppressing overall industry profitability.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized machinery for producing telecommunications equipment or electronic components can cost millions, making it difficult to recoup investments upon exit.
- Long-Term Commitments: Contracts for critical infrastructure or services often span several years, obligating companies to remain operational.
- Specialized Workforce: The need for highly skilled engineers and technicians in areas like semiconductor manufacturing or advanced networking creates a barrier to easily dismantling operations.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty: Exiting a market can damage a company's brand and lead to lost future business opportunities, even in unrelated sectors.
Strategic Stakes of Competitors
Competitors in the electronics and information technology sectors, where OKI Electric Industry operates, often view success in these markets as critical to their long-term survival and expansion. For instance, major players like Fujitsu and NEC, both significant rivals in Japan and globally, derive substantial revenue and strategic positioning from their IT services and electronics divisions. These markets are not just revenue streams; they are foundational to their brand identity and technological innovation capabilities. In 2024, the ongoing digital transformation initiatives across industries globally underscore the strategic importance of these segments for all participants.
When a market represents a core area of focus for a competitor, expect intensified competition. This translates into aggressive investment in research and development to stay ahead of technological curves, robust marketing campaigns to capture market share, and strategic pricing to undercut rivals. For example, the semiconductor and telecommunications equipment sectors, where OKI has a presence, are characterized by high R&D spending. Companies like Intel and Qualcomm, facing OKI in certain product categories, invest billions annually in R&D; Intel, for example, planned capital expenditures of around $25 billion for 2024, much of which fuels innovation in competitive areas.
- Strategic Importance: Competitors view markets OKI participates in as crucial for their overall corporate strategy, influencing their investment decisions.
- Aggressive Competition: High strategic stakes lead to increased R&D investment, marketing efforts, and competitive pricing from rivals.
- Industry Dynamics: Sectors like IT services and electronics are vital for competitors’ brand identity and technological advancement.
- Investment Trends: For example, in 2024, the semiconductor industry saw significant R&D investment, with companies like Intel allocating substantial capital to innovation in areas that directly compete with OKI's offerings.
Competitive rivalry within OKI Electric Industry's operating sectors is intense. The electronics and ICT markets are populated by numerous global players, leading to price wars and rapid innovation cycles. For instance, the global printer market alone features giants like HP, Canon, and Epson, all vying for market share through aggressive pricing and feature development. This environment necessitates continuous differentiation and cost management for OKI.
Companies such as Diebold Nixdorf and NCR present significant competition in the ATM sector, leveraging established brands and service networks. OKI's success hinges on its ability to offer compelling value propositions that challenge these incumbents. In 2024, the drive for digitalization in financial services means that companies providing secure and efficient transaction hardware, like ATMs, face pressure to innovate rapidly to maintain relevance.
The strategic importance of the ICT and electronics sectors for OKI's competitors fuels this rivalry. Firms like Fujitsu and NEC view these segments as core to their identity and future growth, leading to substantial R&D investments. For example, the global semiconductor market, where OKI has some interests, saw companies investing billions in 2024 to maintain a competitive edge in advanced manufacturing and chip design.
| Sector | Key Competitors | Competitive Intensity Drivers | OKI's Strategic Focus | 2024 Market Insight |
| Printers | HP, Canon, Epson | Price competition, product innovation | Security features, energy efficiency | Continued demand for business printing solutions |
| ATMs | Diebold Nixdorf, NCR | Brand recognition, service networks | Reliability, integrated solutions | Digital transformation in banking |
| ICT Infrastructure | Cisco, Huawei, Ericsson | Technological advancement, deployment speed | Network security, specialized solutions | Growth in 5G deployment and IoT |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for OKI Electric Industry's products, particularly in areas like telecommunications equipment and printers, is a significant consideration. Customers can often find alternative solutions that offer similar functionality. For instance, in the printer market, a wide range of competitors offer devices with comparable print quality and features, often at aggressive price points. In 2024, the global printer market saw continued competition with brands like HP, Canon, and Epson vying for market share, frequently introducing lower-cost models or bundled service agreements that present viable alternatives to OKI's offerings.
OKI Electric Industry's customers may consider substitutes if switching offers clear advantages, such as lower costs or enhanced functionality. For instance, in the telecommunications sector where OKI operates, the availability of cloud-based communication platforms or alternative networking hardware from competitors can present significant substitution threats. A key factor is the perceived risk and effort involved in changing providers or technologies; if the transition is complex or requires substantial investment in new infrastructure or training, customers are less likely to switch. However, if a substitute offers a demonstrably superior value proposition with minimal disruption, customer propensity to substitute increases. For example, the rapid evolution of digital transformation initiatives across industries means businesses are constantly evaluating new solutions, potentially increasing the appeal of agile, cost-effective alternatives to existing OKI products.
The threat of substitutes for OKI Electric Industry's products is somewhat mitigated by the switching costs customers face. For instance, migrating complex network infrastructure or enterprise resource planning systems to a competitor's offering can involve substantial financial outlays for new hardware, software licenses, and implementation services. In 2024, the average cost for large enterprises to switch their core IT systems was estimated to be in the millions of dollars, making a move to a substitute solution a significant undertaking.
Beyond monetary expenses, operational disruptions during a transition can also deter customers. This includes the time and resources required for data migration, system integration, and employee retraining, all of which impact productivity. For OKI's telecommunications equipment, for example, the need for specialized technical expertise to manage and operate new systems presents a considerable hurdle for potential switchers.
Psychological costs also play a role. Customers may feel comfortable with OKI's established reliability and support networks, leading to a reluctance to adopt unfamiliar technologies or vendors. This inertia, coupled with the perceived risks associated with unproven substitute solutions, reinforces customer loyalty and reduces the immediate threat posed by alternatives, even if those alternatives appear more cost-effective on the surface.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid technological evolution constantly introduces innovative solutions that can bypass traditional hardware offerings. For instance, the rise of cloud computing presents a significant threat to companies like OKI Electric Industry, which traditionally relies on physical infrastructure. As of early 2024, the global cloud computing market continues its robust expansion, with projections indicating continued double-digit growth throughout the year, underscoring the increasing adoption of software-defined solutions over proprietary hardware.
These advancements create entirely new ways for customers to achieve their goals without purchasing or maintaining physical equipment. Consider the shift from on-premise Point of Sale (POS) systems to cloud-based subscription services. This transition means customers no longer need to invest heavily in dedicated hardware, directly impacting demand for traditional POS terminals. The market for cloud-based POS solutions saw significant growth in 2023, with many small and medium-sized businesses opting for these more flexible and cost-effective alternatives.
- Cloud-based services can replace on-premise hardware for functions like network infrastructure and data storage.
- The global cloud computing market is projected for sustained double-digit growth through 2024.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) models offer compelling alternatives to capital expenditure on hardware.
- The increasing affordability and accessibility of cloud solutions lower the barrier for customers to switch from hardware-centric approaches.
Regulatory and Societal Shifts Favoring Substitutes
Regulatory and societal shifts can significantly impact the threat of substitutes for companies like OKI Electric Industry. For example, increased government mandates for energy efficiency and reduced electronic waste could accelerate the adoption of digital communication and cloud-based services, potentially substituting for some of OKI's traditional printing and document management solutions. By 2024, global efforts to reduce carbon footprints are intensifying, with many nations setting ambitious net-zero targets.
New security protocols and data privacy regulations, such as those emphasizing end-to-end encryption or decentralized data storage, might also favor alternative network and communication technologies over established systems. The push for paperless transactions, driven by both environmental concerns and efficiency gains, continues to gain momentum. In 2024, many businesses are actively investing in digital transformation initiatives, further reducing reliance on physical print outputs.
- Accelerated Digital Adoption: Growing regulatory pressure for sustainability and digital transformation can push customers towards paperless solutions, impacting demand for OKI's printing hardware.
- Enhanced Security Preferences: Evolving cybersecurity landscapes and data privacy laws may favor newer, more integrated network solutions over traditional, standalone devices.
- Societal Demand for Greener Solutions: Public and corporate demand for environmentally friendly products and processes can drive the adoption of substitutes that offer lower environmental impact.
The threat of substitutes for OKI Electric Industry's products, particularly in printing and telecommunications, remains a key challenge. Customers can often find alternative solutions that offer similar functionality, sometimes at a lower cost or with added benefits. For instance, the global printer market in 2024 continued to be highly competitive, with major players like HP, Canon, and Epson regularly introducing new models and service bundles that present viable alternatives to OKI's offerings.
The appeal of substitutes is amplified when they offer clear advantages like cost savings or improved performance with minimal switching effort. In the telecommunications sector, cloud-based communication platforms and alternative networking hardware from competitors pose a significant threat if they provide superior value with easy integration. As businesses increasingly focus on digital transformation, they are more open to agile, cost-effective solutions that can replace existing hardware.
Switching costs, both financial and operational, can mitigate the threat of substitutes for OKI. However, rapid technological advancements, such as the continued expansion of cloud computing, which saw robust growth in 2024, create new avenues for customers to achieve their goals without relying on traditional hardware, thereby lowering the barrier to switching.
Regulatory and societal trends also influence substitution. Growing mandates for energy efficiency and digital transformation in 2024 are pushing customers towards paperless and cloud-based solutions, potentially impacting demand for OKI's printing hardware.
| Substitute Category | Example for OKI | 2024 Market Trend | Impact on OKI |
| Cloud Services | Cloud-based communication platforms | Continued double-digit growth in cloud computing market | Potential replacement for on-premise telecommunication hardware |
| Digital Alternatives | Paperless transaction solutions | Increasing investment in digital transformation by businesses | Reduced demand for printing solutions |
| Competitive Hardware | Printers from HP, Canon, Epson | Aggressive pricing and bundled service agreements | Direct competition, requiring OKI to innovate on features and cost |
Entrants Threaten
OKI Electric Industry operates in sectors demanding substantial upfront capital for research, development, and advanced manufacturing, creating a significant barrier to entry. For instance, the semiconductor industry, where OKI has a presence, requires billions in investment for fabrication plants alone. New entrants must overcome these high fixed costs to achieve competitive pricing, a challenge that limits the threat of new companies challenging OKI's market position.
OKI Electric Industry operates in sectors like telecommunications and financial transaction systems, where initial capital requirements are substantial. Establishing a manufacturing facility, investing in cutting-edge research and development, and building a robust distribution network demand significant financial outlays, effectively acting as a barrier to entry for many potential competitors.
For instance, the development and production of advanced telecommunications infrastructure components or sophisticated ATM hardware can easily require hundreds of millions of dollars in upfront investment. This high capital barrier means only well-funded organizations can realistically consider entering these markets, thus limiting the threat of new entrants for established players like OKI.
New entrants often struggle to gain access to established distribution channels, a significant barrier for companies like OKI Electric Industry. Securing shelf space, partnerships with resellers, or even digital storefront visibility can be exceptionally difficult when incumbents have long-standing relationships and exclusive agreements.
For instance, in the highly competitive financial technology sector, where OKI operates, new players face hurdles in integrating with existing payment systems or securing distribution through major financial institutions. These established networks, built over years, represent a formidable advantage.
In 2024, the continued consolidation within retail distribution, particularly for electronics and specialized business equipment, means fewer independent channels are available. New companies must often invest heavily in building their own direct sales forces or forging new, potentially less effective, partnerships.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Switching Costs
Brand loyalty and high customer switching costs present a significant barrier for new entrants looking to challenge OKI Electric Industry. Customers often develop strong allegiances to established brands due to trust in performance and reliability, making them hesitant to switch to unproven alternatives. This inertia means new players must not only offer comparable or superior products but also invest heavily in marketing and incentives to persuade customers to make a change. For example, in the business-to-business sector, the cost of integrating new technology, retraining staff, and potential disruption to operations can be substantial, further solidifying existing relationships. OKI's established reputation means new entrants face an uphill battle convincing clients to abandon a known quantity for the unknown.
The reluctance to switch is amplified by the total cost of ownership, which extends beyond the initial purchase price. Factors like ongoing support, software compatibility, and the perceived risk of failure with a new vendor weigh heavily on decision-makers. In 2024, many industries continue to prioritize stability and proven solutions, especially for critical infrastructure or core business operations. For instance, in the telecommunications sector where OKI operates, the cost of network downtime can run into millions of dollars, making the perceived risk of a new, unproven supplier exceptionally high. This customer behavior directly increases the hurdle for new entrants, requiring them to demonstrate exceptional value and reliability to even be considered.
- Brand Loyalty: Customers often stick with familiar and trusted brands like OKI due to perceived reliability and past positive experiences.
- Switching Costs: For businesses, changing suppliers involves significant costs related to integration, training, and potential operational disruptions.
- Inertia: Overcoming customer inertia requires new entrants to offer compelling advantages that clearly outweigh the risks and costs of switching.
- Risk Aversion: In critical sectors, the fear of failure with a new provider makes customers more inclined to stay with established players like OKI.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
OKI Electric Industry benefits from a strong barrier to entry due to its proprietary technology and extensive patent portfolio, particularly in areas like optical communication devices and printers. For instance, as of their fiscal year 2024 filings, OKI reported significant ongoing R&D investments aimed at developing next-generation technologies, which are protected by numerous patents. This intellectual property makes it exceedingly difficult and costly for new companies to enter the market without substantial investment in their own research and development or licensing agreements, effectively deterring potential competitors.
- Proprietary Innovations: OKI's advanced semiconductor technologies and specialized printing solutions are protected by a robust patent base, limiting direct replication by newcomers.
- High R&D Investment: Continuous significant investment in research and development, as evidenced by their fiscal year 2024 R&D expenditure, reinforces their technological lead and patentable innovations.
- Barriers to Replication: The complexity and originality of OKI's core technologies require substantial time, capital, and expertise to replicate, posing a considerable challenge for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for OKI Electric Industry is generally low due to several significant barriers. High capital requirements for advanced manufacturing and R&D in sectors like semiconductors and telecommunications demand substantial upfront investment, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars. Furthermore, established distribution channels and strong brand loyalty, particularly in business-to-business markets, make it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For example, in 2024, the cost of network downtime in telecommunications discourages switching from proven providers like OKI.
OKI's proprietary technology and extensive patent portfolio also act as a formidable deterrent. Their continuous investment in R&D, as reflected in their fiscal year 2024 expenditures, creates complex innovations that are costly and time-consuming for new companies to replicate. This intellectual property advantage, coupled with the high switching costs for customers who prioritize reliability and integration, significantly limits the potential for new competitors to emerge and challenge OKI's market position.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for OKI Electric Industry leverages a comprehensive dataset including OKI's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and analyses from reputable technology and electronics sector publications to ensure a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape.
