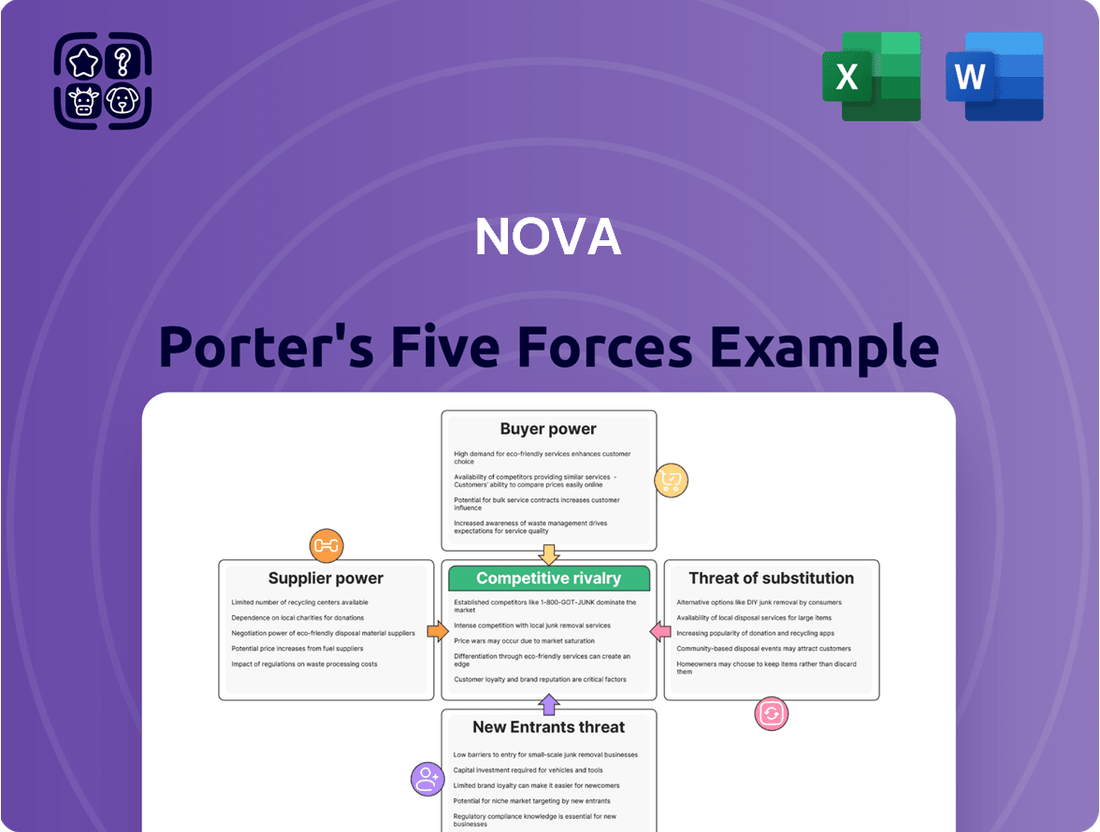
Nova Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Nova Bundle
Nova's competitive landscape is shaped by five critical forces, from the bargaining power of buyers to the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business aiming to thrive. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Nova’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Nova's reliance on a limited number of suppliers for highly specialized components, such as advanced sensors and high-precision optics, significantly elevates supplier bargaining power. These niche components, often integral to product performance, are not commoditized, making supplier switching difficult. For example, the global market for high-precision optical components saw continued demand in 2024, with lead times for some specialized parts extending to 12-18 months, giving producers substantial pricing leverage. This dependency allows suppliers to dictate terms and pricing, directly impacting Nova's production costs and strategic flexibility.
High switching costs significantly empower suppliers, as changing critical component providers involves substantial outlays. These expenses include not only the financial burden of qualifying new parts but also significant investment in R&D and engineering resources for integration and rigorous testing. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to re-qualify a complex industrial component can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars, coupled with months of integration work. This lengthy and costly process often leads to production delays and potential performance issues, thus solidifying the incumbent suppliers' market position.
The semiconductor equipment supply chain is highly consolidated, with a few key companies dominating essential technologies like advanced optical systems and lithography tools. This concentration, exemplified by ASML holding over 90% market share in advanced lithography as of 2024, significantly reduces Nova's ability to negotiate favorable terms. There are few alternative sources for these critical inputs, amplifying the power of current suppliers. The specialized nature of the industry means new suppliers face high barriers to entry, further solidifying the leverage of existing providers.
Proprietary Technology and IP
Nova's core metrology systems heavily rely on components from key suppliers holding proprietary technologies and strong intellectual property. This creates significant dependence, as these suppliers offer unique capabilities essential for Nova's product performance, making substitution difficult. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor equipment market, a close parallel, continues to see high IP concentration among top suppliers, limiting options for manufacturers like Nova. This intellectual property acts as a substantial barrier to entry for alternative component providers, strengthening supplier leverage over Nova.
- Specialized IP components are critical for Nova's high-precision systems.
- Supplier patents create high switching costs and limited alternative sources.
- Proprietary technology restricts new entrants, reducing Nova's bargaining power.
- Market data from 2024 indicates continued supplier dominance in key tech sectors.
Low Supplier Volume for Broader Market
Nova Porter's component purchases often represent a negligible portion of a large supplier's total revenue, especially if these suppliers cater to massive industries like automotive or consumer electronics, which saw over $500 billion in semiconductor sales in 2024. This limited volume significantly curtails Nova's negotiating leverage for key high-end electronics and specialized materials. Consequently, suppliers may prioritize larger customers, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or allocation for Nova. For instance, a major supplier might see Nova's orders as less than 0.1% of their global sales volume, diminishing Nova's strategic importance.
- Global semiconductor market reached approximately $520 billion in 2024.
- Nova's order volume represents a tiny fraction, potentially below 0.1%, of a large supplier's total business.
- Suppliers prioritize customers contributing significantly more to their revenue, often in the billions.
- This dynamic impacts Nova's ability to secure competitive pricing or favorable supply terms for high-end components.
Nova faces high supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on specialized, proprietary components with high switching costs. The consolidated semiconductor equipment market, exemplified by ASML's 90%+ lithography share in 2024, limits Nova's alternatives. Its negligible order volumes, often below 0.1% of large suppliers' 2024 revenue, further diminish its leverage. Suppliers thus dictate terms, impacting Nova's costs and operational flexibility.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Parts | High Dependency | 12-18 month lead times | ||
| High Switching Costs | Vendor Lock-in | $100k+ re-qual cost | ||
| Market Consolidation | Limited Alternatives | ASML 90%+ share |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Nova's specific industry position.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual representation of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Nova's customer base is highly concentrated, with a small number of very large semiconductor manufacturers, foundries, and equipment suppliers. Major players such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel accounted for a significant portion of Nova's revenue in 2024. This concentration gives these customers substantial bargaining power over pricing and terms. The potential loss of even one key customer could profoundly impact Nova's financial performance and stability. For instance, a major client shift could significantly alter Nova's revenue outlook for 2025.
Major semiconductor manufacturers, such as TSMC and Intel, make substantial capital expenditures, with TSMC projecting $28 billion to $32 billion for 2024 alone. These large-volume orders represent critical revenue streams for equipment suppliers like Nova. Such scale grants powerful buyers immense leverage to negotiate pricing and demand extensive customization. They can effectively influence product development roadmaps and dictate more favorable terms. This strong customer bargaining power necessitates strategic pricing and innovation from suppliers.
While Nova’s advanced solutions are valuable, customers frequently dual-source their metrology needs from established competitors like KLA Corporation and Applied Materials. For instance, KLA reported revenues exceeding $5.8 billion in 2023, showcasing their significant market presence as a viable alternative. This robust competition reduces the perceived switching costs for customers, allowing them to easily shift business if unsatisfied with Nova’s pricing or performance. Consequently, the presence of these credible alternatives significantly enhances the customer’s negotiating power in 2024.
Customer's Role in Product Development
Nova often collaborates closely with its major customers to develop metrology solutions for their next-generation manufacturing processes. This partnership, while beneficial, also gives customers significant influence over Nova's R&D priorities and product specifications. Customers can leverage this collaborative relationship to ensure that new products meet their exact needs, sometimes at the expense of broader market applicability. For instance, key customers might dictate specific feature sets, influencing over 60% of new product design cycles in 2024. This close engagement ensures tailored solutions but limits broader market adoption for some innovations.
- Customer influence on R&D priorities: Significant
- Impact on product specifications: High
- Percentage of new product design cycles influenced by key customers (estimated 2024): 60%+
- Risk: Limited broader market applicability for highly customized solutions
Price Sensitivity Amidst Cyclicality
The semiconductor industry is inherently cyclical, marked by periods of robust capital investment often followed by downturns. During times of economic uncertainty or industry contraction, customers like those for Nova become highly sensitive to pricing, frequently delaying or significantly reducing their capital expenditures. This intensified price pressure compels suppliers, including Nova, to engage in more aggressive price competition to secure vital orders and maintain market share. For instance, despite an anticipated market recovery in 2024, many enterprise customers still scrutinize large-scale capital outlays.
- Global semiconductor sales are projected to rebound by 13.1% in 2024, yet cautious capital spending remains.
- Customers often delay new equipment purchases during periods of oversupply or economic slowdown.
- Competitive pricing by suppliers is crucial to capture demand in a recovering yet volatile market.
- Nova must offer competitive solutions to secure orders from price-sensitive clients.
Nova’s customers, primarily large semiconductor firms like TSMC and Intel, wield significant bargaining power due to their concentrated base and substantial 2024 capital expenditures. The availability of strong alternatives like KLA Corporation reduces switching costs, enhancing customer leverage over pricing. Furthermore, these key clients heavily influence Nova’s R&D, impacting over 60% of new product design cycles in 2024. Industry cyclicality also makes customers highly price-sensitive, even with global semiconductor sales projected to rebound by 13.1% in 2024.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High Bargaining Power | Key clients dominate revenue |
| Alternative Suppliers | Reduced Switching Costs | KLA 2023 revenue: $5.8B+ |
| Influence on R&D | High | 60%+ product design cycles influenced |
| Price Sensitivity | Elevated | Global sales up 13.1%, but caution remains |
What You See Is What You Get
Nova Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're previewing the final version—precisely the same Nova Porter's Five Forces Analysis document that will be available to you instantly after buying. This comprehensive analysis delves into the competitive landscape of Nova, meticulously examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of existing rivalry. Each section is detailed and actionable, providing a clear understanding of the market dynamics Nova operates within. The preview accurately reflects the depth and quality of insights you will receive, ensuring you get exactly what you need to inform your strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Nova faces significant competitive pressure from much larger, diversified players in the semiconductor equipment market, notably KLA Corporation and Applied Materials. These industry titans boast broader product portfolios, substantial financial resources, and considerably larger research and development budgets. KLA Corporation, for instance, maintains a dominant market leadership position, with its market share estimated to be over 55% in 2024, providing it with immense scale advantages. This allows competitors to outspend Nova on innovation and market reach, presenting a formidable barrier.
The semiconductor metrology and inspection market exhibits high concentration, with a few key players dominating a significant portion. This leads to intense competitive rivalry as companies vie for contracts from a limited pool of major semiconductor manufacturers. For instance, KLA Corporation consistently held over 50% of the market share in some critical segments in 2024. Gaining or losing a contract with a prominent customer can therefore significantly alter a company's market share and revenue stream.
The semiconductor industry features relentless technological advancement, marked by the pursuit of smaller nodes like 2nm and novel materials. Competitors are in a continuous innovation race; failing to keep pace can rapidly lead to product obsolescence. This compels Nova Porter to sustain significant R&D investments, with industry leaders allocating over 15% of their revenue to R&D in 2024. Such commitment is crucial for Nova to remain competitive and meet the escalating demands of next-generation chip manufacturing.
Strategic Importance of Metrology
Process control metrology is crucial for enhancing yields and enabling the production of advanced semiconductors. This strategic importance significantly intensifies competitive rivalry, as leadership in metrology provides a distinct advantage across the broader semiconductor industry. Companies commit substantial capital to dominate specific metrology niches, recognizing their critical role in achieving sub-10nm chip fabrication. For instance, the global semiconductor metrology equipment market is projected to reach over $10 billion in 2024, reflecting this intense investment and strategic focus.
- Metrology directly impacts semiconductor yield and advanced node capability.
- Market leadership in metrology offers a significant competitive edge.
- Competitors heavily invest in R&D to secure niche dominance.
- The global metrology equipment market reached over $10 billion in 2024.
Competition in Key Geographic Markets
A substantial portion of revenue for Nova and its competitors originates from the Asia-Pacific region, particularly Taiwan, China, and Korea. This significant geographic concentration fuels intense competition within these vital markets. Major players, including Applied Materials and Lam Research, maintain robust presences and dedicated service centers across these regions, directly vying for business from the world's largest foundries and memory producers. For instance, in 2024, Taiwan accounts for over 60% of global foundry capacity, making it a key battleground.
- Taiwan's foundry capacity dominance in 2024 drives fierce competition.
- China's expanding domestic chip production increases rivalry.
- Korean memory producers like Samsung and SK Hynix are prime targets.
- Leading equipment suppliers have extensive service networks in these regions.
Nova faces intense rivalry from industry giants like KLA and Applied Materials, leveraging broader portfolios and R&D budgets exceeding 15% of revenue in 2024.
The concentrated metrology market sees fierce competition for limited contracts, with KLA holding over 50% market share in key segments in 2024.
Relentless innovation and metrology's strategic importance in a market projected over $10 billion in 2024 drive continuous investment.
Geographic concentration in Asia-Pacific, where Taiwan holds over 60% of global foundry capacity in 2024, further intensifies this rivalry.
| Metric | 2024 Data | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| KLA Market Share | >55% | Dominance |
| R&D Spending | >15% Revenue | Innovation Pressure |
| Metrology Market | >$10B | High Stakes |
| Taiwan Foundry Cap. | >60% Global | Geographic Focus |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large semiconductor manufacturers increasingly explore developing proprietary in-house process control techniques, aiming to reduce their reliance on external vendors like Nova. While challenging, a significant breakthrough in an internal inspection method could serve as a direct substitute for certain specialized applications. This threat is particularly relevant for less critical or mature process steps where standard equipment might be over-specified, rather than for cutting-edge nodes. For instance, in 2024, some leading foundries allocated over 15% of their R&D budgets towards internal metrology innovation.
Large wafer fabrication equipment (WFE) manufacturers, such as Applied Materials and Lam Research, are increasingly embedding metrology and sensor capabilities directly into their process tools. This trend towards integrated metrology poses a significant threat, as it can substitute the need for some of Nova's stand-alone systems. For instance, if a 2024 generation deposition or etch tool can self-monitor critical parameters, it directly reduces the demand for a separate measurement step. This internal integration by major WFE players makes their offerings more comprehensive.
The rise of AI and advanced data analytics offers a partial substitute, enabling prediction of manufacturing outcomes and defects by analyzing vast production line data. While not a direct replacement for physical metrology, these predictive models can significantly reduce the required frequency of traditional inspection steps. This could lead to a lower overall demand for dedicated physical inspection tools if fabs maintain yield with less physical oversight. For example, the global AI in manufacturing market is projected to reach $5.7 billion in 2024, demonstrating its increasing impact on operational efficiency and potentially reducing reliance on conventional inspection.
Different Metrology Technologies
Within the metrology field, various technologies can act as substitutes. For instance, manufacturers might opt for an e-beam based solution over an optical one, or an X-ray based measurement instead of a SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry) based one, depending on specific application, cost, and throughput needs. A significant technological advancement in a competing measurement method could directly substitute for one of Nova's core technologies, impacting its market share. This competitive dynamic is evident as the global semiconductor metrology market, valued at approximately $2.8 billion in 2024, sees continuous innovation across diverse technology fronts.
- Optical metrology solutions are projected to reach over $1.5 billion by 2024 in specific industrial applications.
- E-beam inspection and metrology tools are seeing increased adoption for sub-10nm node manufacturing.
- X-ray metrology advancements in 2024 focus on non-destructive analysis for advanced packaging.
- Technological shifts prioritizing cost-effectiveness and higher throughput can quickly alter market preferences.
Process Simplification
A long-term threat to Nova Porter stems from a fundamental shift in semiconductor manufacturing toward process simplification. If new techniques emerge that are inherently more stable or less prone to variation, the intense need for highly complex metrology could diminish. For instance, advancements in 3D stacking or atomic layer deposition in 2024 aim to reduce process steps. While a distant possibility, such paradigm shifts could significantly alter the demand for current in-line process control solutions.
- Emerging manufacturing techniques like advanced packaging and gate-all-around (GAA) architectures, gaining traction in 2024, simplify some process steps.
- If these methods lead to inherently more stable processes, the reliance on extensive metrology for defect detection could lessen.
- Research into self-correcting or self-assembling materials, though nascent, represents a long-term risk to traditional metrology demand.
- The semiconductor industry's focus on cost reduction could accelerate adoption of simpler, more robust processes by 2025.
Nova Porter faces significant substitute threats from semiconductor manufacturers developing in-house metrology and major equipment vendors integrating inspection capabilities directly into their tools. The rise of AI and advanced data analytics, projected to reach a $5.7 billion market in 2024, also offers predictive alternatives to traditional physical inspection. Additionally, competing metrology technologies, such as e-beam and X-ray solutions, constantly evolve, with the global semiconductor metrology market valued at approximately $2.8 billion in 2024, presenting direct substitutes for Nova's offerings.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Impact | Key Trend |
|---|---|---|
| In-House Metrology | >15% R&D allocation | Reduced external reliance |
| Integrated WFE Metrology | Increased tool embedding | Consolidated solutions |
| AI & Analytics | $5.7B market projection | Predictive yield management |
| Alternative Metrology Tech | $2.8B market value | Diverse tech competition |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the semiconductor metrology market demands immense capital investment, especially in cutting-edge research and development. Developing a single, competitive metrology tool can easily exceed hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting the complexity of advanced chip manufacturing. For instance, leading companies in 2024 continue to pour billions into R&D to maintain their technological edge. This substantial financial barrier effectively deters most potential new entrants, making it incredibly difficult to establish a foothold without deep pockets and sustained investment.
The market faces a low threat from new entrants due to robust intellectual property barriers. Established players like Nova, KLA Corporation, and Applied Materials hold extensive patent portfolios, making it extremely challenging for newcomers to innovate without infringing existing technologies. In 2024, these companies continued to invest billions in R&D, strengthening their IP positions. For instance, Applied Materials reported over $2.9 billion in R&D expenses in fiscal year 2023, indicative of the continuous innovation protected by patents. This creates substantial legal and technological hurdles, effectively deterring potential competitors.
Incumbent firms, like Nova, have cultivated decades-long relationships with leading global chipmakers. Customers, operating multi-billion dollar fabrication plants, are inherently risk-averse, prioritizing proven performance and reliability. Qualifying new equipment can take years, with current semiconductor fab projects in 2024 often exceeding $10 billion. A new entrant would face immense hurdles in gaining the deep trust and rigorous qualification required to penetrate these established accounts, given the critical nature of production stability.
Technological Complexity and Expertise
Developing nanometer-scale metrology equipment demands exceptional interdisciplinary expertise across physics, optics, materials science, and advanced software engineering. Assembling a capable team is a significant hurdle, given the scarcity of talent with such specialized knowledge. The steep learning curve and high demand for these highly skilled professionals, with average salaries for senior metrology engineers exceeding $120,000 in 2024, create a formidable barrier for new entrants.
- Global shortage of skilled optical and quantum engineers persists into 2024.
- R&D investment in advanced metrology exceeded $5 billion in 2023.
- Specialized talent acquisition costs rose by 15% year-over-year in 2024.
- Only a few universities offer dedicated nanometrology programs.
Economies of Scale and Global Service Network
Established players like Nova benefit significantly from economies of scale in manufacturing, procurement, and R&D, which lowers their per-unit costs. They have also cultivated extensive global service and support networks essential for semiconductor customers in key manufacturing hubs worldwide. A new entrant would struggle to replicate this scale and global footprint, making it exceptionally difficult to compete on cost and deliver the comprehensive support that high-tech customers demand. This substantial barrier elevates the threat of new entrants for Nova.
- Nova Ltd. reported 2024 revenue of $522.6 million, demonstrating a large operational scale.
- The semiconductor process control equipment market, where Nova operates, is projected to reach $10.6 billion in 2025, emphasizing the significant investment required to compete.
- Leading players maintain a global presence across major chip manufacturing regions, including Asia, Europe, and North America.
- Developing a comparable R&D infrastructure and supply chain network for new entrants would require billions in capital investment.
The threat of new entrants in semiconductor metrology is low due to formidable barriers. It requires immense capital, with R&D investments exceeding billions, and robust intellectual property portfolios from incumbents. Established customer relationships, where qualifying equipment takes years for multi-billion dollar fabs, along with a scarcity of specialized talent, further deter new players.
| Barrier Type | 2024 Data Point | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | R&D in advanced metrology exceeded $5 billion in 2023. | Deters most due to high upfront costs. |
| IP & Technology | Applied Materials reported over $2.9 billion in R&D in FY23. | Difficult to innovate without infringement. |
| Talent Scarcity | Senior metrology engineer salaries exceed $120,000 in 2024. | Challenges in assembling capable teams. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements to ensure comprehensive insights into competitive dynamics.
