Nissha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Nissha Bundle
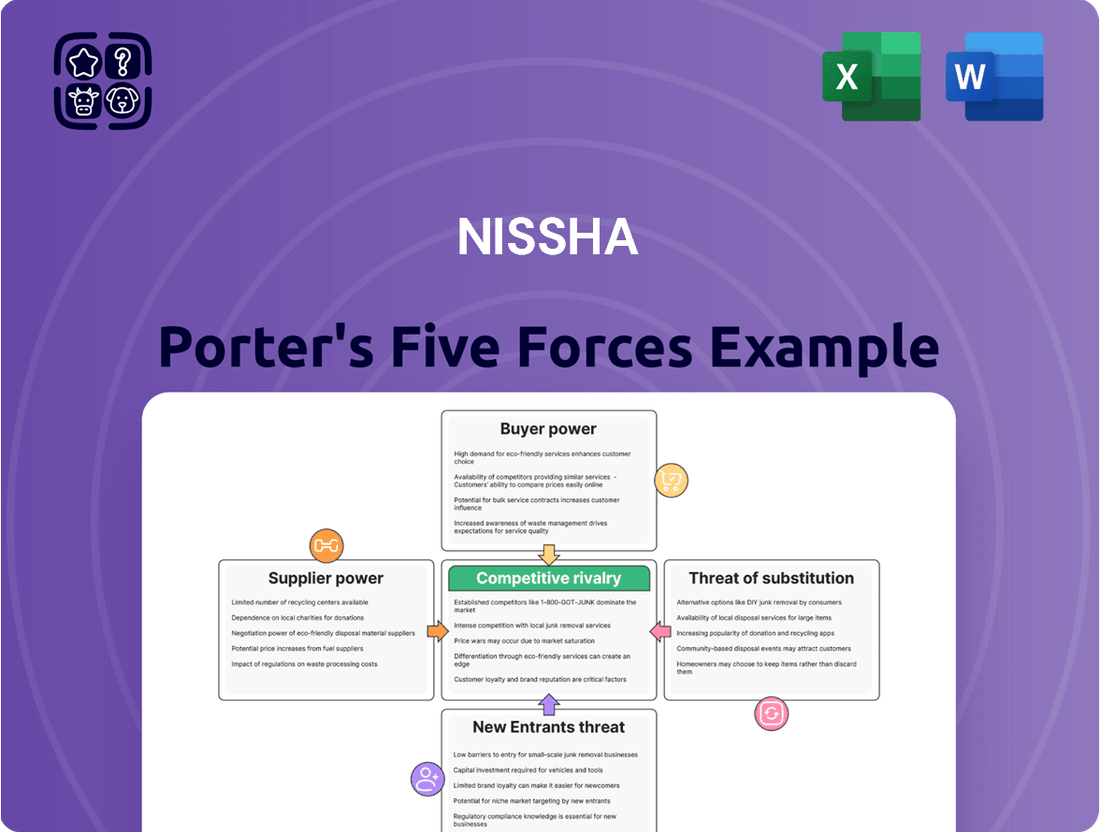
Nissha's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces, revealing the intense pressures and opportunities within its industry. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for strategic planning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these dynamics. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Nissha’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Nissha's reliance on specialized materials, like proprietary films and advanced substrates for its printing and coating technologies, significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. The limited availability of these unique inputs, often developed with specific performance characteristics, means fewer suppliers can meet Nissha's exacting standards.
This specialized nature creates a strong dependency, as finding suitable alternatives is costly and time-consuming, potentially forcing Nissha to accept less favorable terms. For instance, in 2023, the global specialty chemicals market, a key input category, saw price increases averaging 7-10% due to complex manufacturing processes and R&D investment, directly impacting companies like Nissha.
Should critical suppliers experience production issues or market consolidation, Nissha could face significant supply chain disruptions. A hypothetical scenario where a primary supplier of a unique decorative film reduces output by 20% could lead to production delays and increased sourcing costs for Nissha.
In certain advanced technology sectors where Nissha operates, the availability of suppliers for highly specialized materials can be quite restricted. For instance, in the realm of high-performance films for electronics, a handful of companies might dominate the global market, each possessing unique technological expertise. This limited supplier pool inherently diminishes Nissha's negotiation power, as these few key players can exert greater influence over pricing and terms. In 2024, reports indicated that for certain critical components in advanced display manufacturing, only three to four global suppliers met the stringent quality and technological specifications, a situation that can significantly impact input costs.
Nissha faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. Consider the scenario where Nissha relies on specialized, custom-engineered components. Switching to a new supplier for these critical items could necessitate substantial investments in re-tooling manufacturing equipment, a process that might cost hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars depending on the complexity. Furthermore, re-qualifying these new components to meet stringent industry standards and ensuring seamless integration into Nissha's existing product lines can add months of development time and considerable expense, potentially impacting revenue streams.
Differentiation of Supplier Inputs
When suppliers offer highly differentiated or proprietary inputs, they gain significant bargaining power. These unique materials can be crucial for Nissha’s ability to produce products with distinct features or to maintain specific manufacturing efficiencies. For instance, if a supplier provides a specialized coating that is key to Nissha's high-performance films, that supplier can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms.
If these specialized inputs are integral to Nissha's competitive edge, such as enabling unique textures or advanced functionalities in their products, suppliers are in a strong position to demand higher prices. This can directly impact Nissha's cost structure and profitability. Nissha needs to carefully weigh the advantages of using these superior inputs against the premium costs they command.
For example, in 2024, the electronics industry saw continued demand for advanced materials in displays and flexible circuits. Suppliers of specialized polymers and conductive inks, critical for Nissha's printing and decorating technologies, experienced strong pricing power due to the limited availability of comparable alternatives and the essential nature of these components for product differentiation.
- Supplier Differentiation: Nissha's reliance on suppliers for unique inks, films, and processing chemicals directly impacts supplier bargaining power.
- Proprietary Technology: If a supplier's material or process is patented or difficult to replicate, it strengthens their position.
- Cost Impact: The premium pricing for differentiated inputs can significantly affect Nissha's cost of goods sold, potentially reducing profit margins.
- Strategic Sourcing: Nissha must balance the benefits of best-in-class inputs with the financial implications, exploring long-term partnerships or alternative sourcing where feasible.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While less common, some suppliers, particularly those providing highly specialized or intellectual property-rich components, could theoretically consider forward integrating into Nissha's downstream activities. This means they might start producing the final products themselves, bypassing Nissha. For instance, a supplier of advanced display technology might decide to enter the market for electronic devices. Such a move, though unlikely for most raw material suppliers, can subtly influence negotiation dynamics, especially with technology component providers. For example, if a key supplier to the electronics industry in 2024 were to announce plans for forward integration, it could create pressure on companies like Nissha to secure favorable terms or explore alternative sourcing.
This potential for forward integration, however remote, acts as a latent threat. It means suppliers retain a degree of leverage, as they possess the knowledge and capability to enter Nissha's market. This is particularly relevant for suppliers of critical, non-commodity inputs where Nissha has limited alternative options. The bargaining power of such suppliers is thus amplified, as they can credibly threaten to become competitors.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with unique technology or significant R&D investment are more likely to consider forward integration.
- Market Attractiveness: If Nissha's downstream markets are highly profitable, it increases the incentive for suppliers to integrate.
- Dependency: Nissha's reliance on specific suppliers for key components strengthens the suppliers' potential bargaining power.
Nissha's reliance on specialized films and advanced substrates, often proprietary and with limited alternatives, significantly enhances supplier bargaining power. This is further amplified when these inputs are crucial for Nissha's product differentiation and competitive edge.
In 2024, the market for advanced materials in sectors like electronics saw continued price strength for specialized polymers and conductive inks. Suppliers of these critical components, due to limited comparable alternatives and their essential nature for product performance, wielded considerable pricing influence.
High switching costs, including re-tooling and re-qualification, also bolster suppliers' positions, as Nissha faces substantial investments and development time when seeking new sources for custom-engineered components.
The potential for forward integration by suppliers, particularly those providing intellectual property-rich components, acts as a latent threat, subtly influencing negotiation dynamics and strengthening their leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Nissha | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Differentiation | High | Nissha depends on unique inks, films, and chemicals crucial for product features. |
| Switching Costs | High | Significant investment and time required for re-tooling and re-qualification of new suppliers. |
| Proprietary Technology | High | Suppliers with patented or hard-to-replicate materials have stronger negotiation positions. |
| Market Concentration (2024) | Moderate to High | In certain advanced electronics materials, only a few global suppliers met stringent specifications. |
What is included in the product
Nissha's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape impacting the company, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Visually map competitive threats and opportunities, offering a clear, actionable roadmap for strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Nissha's broad reach across sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare is a significant factor in moderating customer bargaining power. By serving numerous industries, the company avoids being overly dependent on any single large buyer. This diversification means that if one customer segment faces economic downturns or demands unfavorable terms, other segments can provide a buffer, thus limiting the leverage any one customer can wield over Nissha's pricing or operational agreements.
While Nissha boasts a diversified customer base across various industries, a key consideration is customer concentration within specific product segments. For example, if a few dominant players in the automotive sector represent a significant portion of Nissha's decorative film sales, these clients gain considerable bargaining power. This can translate into demands for price reductions or preferential treatment, potentially squeezing Nissha's profitability in those niche areas. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry accounted for a substantial percentage of revenue for many advanced materials suppliers, highlighting the potential impact of even a few key relationships.
For standardized products, customers often find it easy and inexpensive to switch to a competitor. This is particularly true when several suppliers offer similar quality and features. For instance, in the general printing materials market, where Nissha also operates, switching costs can be minimal, allowing buyers to prioritize price. In 2024, the global printing ink market, a segment with many commodity-like offerings, saw intense price competition among suppliers, demonstrating this dynamic.
Customers' Potential for Backward Integration
Large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), particularly in sectors like automotive and consumer electronics, often have the substantial financial resources and technical expertise to bring component production in-house. This capability means Nissha's customers could potentially start producing the parts themselves if they feel they are not getting sufficient value or favorable terms. For instance, a major automotive OEM might invest in new manufacturing lines for interior components, directly competing with Nissha's offerings.
This potential for backward integration grants significant bargaining power to Nissha's customers. They can leverage this threat to negotiate better prices, demand higher quality, or push for more advanced technological solutions. Nissha must therefore consistently prove its competitive edge through superior operational efficiency, cost advantages, and ongoing innovation to maintain its position as a valuable and indispensable supplier.
Consider these factors related to customer backward integration:
- Financial Capability: Major OEMs in industries like automotive and electronics often have annual revenues in the tens or hundreds of billions of dollars, providing ample capital for new production investments. For example, in 2023, major automakers reported significant profits, allowing for substantial R&D and capital expenditure.
- Technical Expertise: These large customers typically possess in-house engineering teams and manufacturing know-how, enabling them to develop and operate production processes for components Nissha currently supplies.
- Negotiating Leverage: The credible threat of in-house production empowers customers to demand competitive pricing and terms, forcing Nissha to focus on cost optimization and value-added services.
- Market Dynamics: In highly competitive markets, the pressure to reduce costs and control the supply chain often drives large buyers to explore vertical integration options.
Price Sensitivity in Competitive Markets
Customers in intensely competitive sectors, like the global consumer electronics market which saw sales exceeding $1 trillion in 2023, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This translates directly to suppliers like Nissha, creating pressure to keep component and material prices competitive.
Nissha must therefore prioritize cost leadership, enhanced value-added services, and continuous technological innovation to justify its pricing and sustain profitability when faced with customer demands for reduced costs. For instance, in the smartphone component market, a 1% price reduction by a major OEM can force component suppliers to absorb significant margin compression.
- Price Sensitivity in Consumer Electronics: The consumer electronics sector is characterized by frequent product cycles and intense competition, leading to high customer price sensitivity.
- Upstream Pressure on Suppliers: This customer price pressure forces suppliers like Nissha to maintain competitive pricing for their components and materials.
- Nissha's Strategic Responses: Nissha needs to focus on cost leadership, differentiating through value-added services, and leveraging technological advancements to maintain profitability.
- Market Data Example: In 2024, the average selling price (ASP) for many consumer electronic devices continued its downward trend due to competitive pressures, impacting component supplier margins.
The bargaining power of customers for Nissha is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, and the potential for backward integration. While Nissha's diversified customer base across sectors like automotive and electronics helps mitigate the power of individual buyers, a concentration of sales within specific product lines can empower large clients. For instance, if a few major automotive manufacturers represent a significant portion of Nissha's decorative film revenue, these clients can exert considerable influence on pricing and terms, a dynamic evident in 2024 where automotive was a key revenue driver for advanced materials suppliers.
Low switching costs for standardized products also bolster customer power. When competitors offer similar quality, buyers can easily opt for cheaper alternatives, as seen in the competitive printing materials market where price often dictates choice. In 2024, the printing ink market exemplified this, with intense price competition among suppliers offering commodity-like products.
Furthermore, the capacity of large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to potentially bring production in-house poses a significant threat. Companies with substantial financial resources, such as major automakers with billions in annual revenue as seen in 2023 profit reports, and robust technical expertise, can leverage this capability to negotiate better terms or drive down prices. This threat compels Nissha to continuously demonstrate its value through efficiency and innovation.
| Factor | Impact on Nissha | Example (2024 Data/Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increased bargaining power for key clients | Automotive sector often has few dominant players impacting decorative film suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | Customers can easily switch to competitors | Standardized printing materials have low switching costs, leading to price sensitivity. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Customers can threaten in-house production | Large OEMs in electronics have the financial (e.g., 2023 profit reports) and technical capacity to produce components internally. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on suppliers for lower prices | Consumer electronics market (>$1 trillion sales in 2023) demands competitive pricing, impacting component margins. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Nissha Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Nissha Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, fully formatted document that details Nissha's competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of existing rivalry. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights into Nissha's strategic positioning. What you see here is the complete, ready-to-use file that will be yours upon completion of your purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Nissha operates in a highly competitive global arena, facing a broad spectrum of rivals from massive multinational conglomerates to focused niche specialists. This diverse competitive environment demands constant vigilance regarding market shifts and competitor advancements across all its operational segments.
The intensity of rivalry differs notably between its industrial materials, devices, and medical divisions, compelling Nissha to craft distinct strategic approaches for each market. For instance, in the industrial materials sector, Nissha might compete with established chemical giants, while in medical devices, smaller, highly innovative startups could pose a significant challenge.
In 2023, the global industrial coatings market, a segment where Nissha is active, was valued at approximately $29.3 billion and is projected to grow, indicating robust competition from numerous players offering diverse solutions. Similarly, the global medical device market, exceeding $500 billion in 2023, features intense competition from both large, established firms and agile innovators.
This necessitates continuous innovation and strategic differentiation for Nissha to maintain and expand its market share against a dynamic and varied competitive force. Staying ahead requires understanding the unique competitive dynamics within each of its business areas.
Nissha's competitive rivalry is shaped by the growth dynamics of the industries it operates within. In sectors like printing and packaging, which can experience more moderate growth, competition can be fierce as players fight for existing market share, sometimes leading to price pressures. For instance, the global printing and packaging market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% through 2030, indicating a stable but competitive environment.
However, in areas where Nissha might see higher growth, such as advanced materials for electronics or automotive applications, the landscape shifts. These segments attract significant investment from both established firms and new entrants eager to capitalize on expansion. This dynamic can foster innovation and lead to increased spending on research and development as companies strive to gain a competitive edge.
Nissha's competitive rivalry is heavily influenced by its product differentiation, particularly in printing, coating, and lamination technologies. When products are distinct, competition shifts towards innovation and unique features, moving away from pure price wars. This focus on advanced technology is key to Nissha’s strategy.
The company's commitment to research and development is a critical factor in maintaining its competitive advantage. By investing in proprietary solutions, Nissha aims to reduce the intensity of direct price-based competition. For instance, Nissha reported significant R&D expenditures in its 2023 fiscal year, underscoring this strategic priority.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Industries like advanced manufacturing, where Nissha operates, often demand substantial capital for machinery, research, and specialized facilities. These high fixed costs create significant exit barriers, meaning companies are hesitant to leave the market even when profits are low to avoid abandoning their investments. This can fuel intense competition, as firms may prioritize maintaining operations, potentially leading to overcapacity and aggressive pricing strategies to stay afloat.
For Nissha, managing asset utilization efficiently is crucial to counter the pressures of high fixed costs. Consider the semiconductor industry, a sector with notoriously high upfront capital expenditures, where fab utilization rates are closely watched as a key indicator of profitability and competitive intensity. In 2023, for instance, global semiconductor capital expenditures were projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the immense cost of entry and continued operation.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in specialized equipment and facilities are typical in advanced manufacturing.
- Exit Barriers: The difficulty and cost of leaving the industry often keep companies operating even in challenging economic conditions.
- Intense Rivalry: These factors can lead to aggressive competition, including price wars, as firms strive to cover their fixed costs.
- Asset Utilization: Efficient management of production capacity and resources is vital for Nissha to remain competitive.
Intensity of Competition on Price, Quality, and Service
Competitive rivalry within Nissha's diverse business segments presents a multifaceted challenge. In more standardized markets, price is a primary battleground, forcing Nissha to maintain cost efficiency. However, in critical sectors like automotive and medical, the competition hinges on delivering exceptional quality and unwavering reliability, where even minor deviations can have significant consequences. For instance, the automotive industry demands strict adherence to defect rates, with leading suppliers often aiming for parts-per-million (PPM) levels below 10.
Conversely, the fast-paced consumer electronics sector sees competition driven by rapid innovation, speed-to-market, and the ability to offer flexible design solutions. Nissha must therefore cultivate a strategy that allows it to excel on these distinct competitive factors across its portfolio. This involves a careful balancing act, ensuring cost-effectiveness in some areas while investing heavily in advanced technologies and rigorous quality control for others.
To navigate this landscape effectively, Nissha must strategically align its operations and R&D efforts with the specific demands of each market. This includes:
- Price Optimization: Implementing lean manufacturing and supply chain efficiencies to remain competitive in commoditized product areas.
- Quality and Reliability Enhancement: Investing in advanced testing, process controls, and material science for automotive and medical applications, aiming for industry-leading performance metrics.
- Innovation and Agility: Fostering a culture of rapid prototyping and flexible production to meet the evolving design and speed-to-market requirements of consumer electronics.
- Customer Service Excellence: Differentiating through responsive support and tailored solutions, building strong, long-term relationships across all segments.
Nissha faces intense competition across its diverse business units, with rivalry varying significantly by industry. In mature sectors, price competition is common, while growth industries attract numerous players, intensifying innovation races. High capital expenditures and exit barriers in advanced manufacturing can also fuel aggressive competitive dynamics.
The company's strategy must adapt to these varied competitive pressures, balancing cost efficiency with a strong focus on product differentiation, quality, and rapid innovation. For instance, while the global printing and packaging market, valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023, might see price-driven competition, the medical device market, exceeding $500 billion in 2023, demands superior quality and innovation.
| Competitive Factor | Nissha's Approach | Industry Example | Market Size (2023 est.) | Key Focus Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Cost efficiency, lean operations | Printing & Packaging | $1.1 trillion | Cost leadership |
| Quality & Reliability | Advanced R&D, stringent process controls | Medical Devices, Automotive | $500+ billion (Medical) | Product performance, safety |
| Innovation & Speed | Rapid prototyping, flexible manufacturing | Consumer Electronics | N/A (segment specific) | Time-to-market, design flexibility |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Nissha's touch sensor business, a significant revenue driver, confronts the rising threat of alternative interaction technologies. For instance, advancements in gesture recognition systems and voice command interfaces, gaining traction across consumer electronics and automotive sectors, could reduce reliance on capacitive touch screens. In 2023, the global market for gesture recognition technology was valued at approximately $15 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth.
Similarly, Nissha's decorative films, used in automotive interiors and consumer appliances, face substitution risks from new material science innovations and advanced printing techniques. Emerging trends like sustainable materials, recycled plastics, or direct-to-object printing offer alternative aesthetic solutions that could bypass traditional film applications. The demand for eco-friendly materials in automotive interiors, for example, is a growing trend, impacting the market for conventional decorative films.
The attractiveness of substitutes hinges on their price-performance trade-off. If alternatives offer similar or better functionality at a lower price point, they represent a significant threat to Nissha. For instance, advancements in 3D printing technology have provided more affordable prototyping options for some industries that previously relied on specialized manufacturing processes, potentially impacting demand for Nissha's custom solutions.
Nissha must therefore maintain a keen focus on innovation to ensure its offerings consistently deliver superior value. This means not only enhancing performance and functionality but also optimizing cost structures to remain competitive against these evolving substitute solutions. Demonstrating a clear and compelling value proposition is crucial to counter the allure of cheaper, albeit potentially less capable, alternatives.
Customer willingness to adopt new solutions is a major driver in the threat of substitutes. If customers readily switch to alternatives that offer better value or convenience, Nissha faces a higher threat. For instance, if a new, more cost-effective printing technology emerges that requires minimal retraining for users, adoption rates could be swift.
Factors like perceived benefits, ease of integration, and reliability heavily influence this willingness. If a substitute product is significantly cheaper, simpler to implement, or proven to be as reliable as Nissha's offerings, customers are more likely to switch. This is particularly true for established supply chains where disruption is costly.
Nissha must actively educate its customer base about the unique advantages and long-term value proposition of its proprietary solutions. Highlighting superior performance, lower total cost of ownership, or enhanced functionality can help mitigate the appeal of emerging alternatives. For example, demonstrating how Nissha’s advanced printing solutions in 2024 reduced waste by 15% compared to older methods could sway customer decisions.
The threat is amplified when substitute products meet similar customer needs at a lower price point or with greater convenience. Companies that successfully demonstrate these advantages can quickly capture market share, forcing incumbents like Nissha to innovate or risk losing customers to more agile competitors.
Rapid Innovation in Adjacent Industries
Industries closely related to Nissha's core operations, like advanced materials and digital manufacturing, are seeing swift technological progress. For instance, the global advanced materials market was projected to reach over $237 billion in 2024, indicating significant investment and development. Innovations in these adjacent fields could spawn superior alternatives to Nissha's current offerings, posing a direct threat of substitution.
The pace of change means that solutions developed in areas such as smart sensors, which are expected to see a market value of around $107 billion by 2024, could offer enhanced functionality or cost-effectiveness. Nissha must actively monitor these external technological shifts to identify potential substitutes early.
To counter this, Nissha's strategy must include robust investment in research and development focused on adaptation and foresight. This proactive approach is key to mitigating the risk of its products becoming obsolete due to emerging technologies from these dynamic neighboring sectors.
- Rapid advancements in materials science could yield novel materials with superior properties, directly competing with Nissha's existing product lines.
- Developments in digital manufacturing technologies might enable competitors to produce similar or better-performing goods at a lower cost or with greater customization.
- Emerging smart sensor technologies could offer integrated functionalities that render Nissha's standalone products less attractive or even redundant.
- A significant portion of R&D budgets in the chemical and materials sector, which saw global spending in the hundreds of billions in recent years, is directed towards developing next-generation products, highlighting the competitive pressure.
Regulatory and Environmental Shifts Driving Substitution
Changes in regulations and growing environmental awareness can significantly push consumers towards substitute products or processes. For example, a move towards more eco-friendly or biodegradable materials might lead customers to look for alternatives to existing product formulations.
Nissha needs to actively invest in sustainable innovation. This ensures its products continue to meet market demands and comply with new standards. By 2024, for instance, the European Union's Green Deal initiatives are already impacting material choices across various industries, pushing for circular economy principles.
- Regulatory Push: Policies favoring sustainable materials, like bans on certain plastics, directly increase the threat from alternatives.
- Consumer Demand: A growing segment of consumers, particularly younger demographics, actively seeks out environmentally responsible products, creating a pull for substitutes.
- Innovation in Alternatives: Advancements in biodegradable polymers and recycled materials offer viable, often cost-competitive, alternatives to traditional options.
The threat of substitutes for Nissha's products is a dynamic challenge, influenced by technological progress and evolving consumer preferences. For instance, advancements in areas like smart textiles and flexible electronics could offer new ways for consumers to interact with devices, potentially displacing traditional touch sensor interfaces. The global market for flexible electronics was projected to exceed $40 billion by 2024, indicating a significant area of innovation.
Nissha's decorative film business, particularly in automotive interiors, faces substitution from advancements in direct printing technologies and the use of novel, sustainable materials. As of 2024, the automotive industry's focus on lightweighting and eco-friendly interiors is driving demand for new material solutions, potentially reducing reliance on conventional decorative films.
The cost-performance ratio of substitutes is a critical factor. If alternative technologies can deliver comparable or superior functionality at a more attractive price point, the threat intensifies. For example, the increasing affordability of 3D printing for specialized components can offer a substitute for custom manufacturing processes previously reliant on Nissha’s expertise.
Customer adoption rates, driven by perceived benefits, ease of integration, and reliability, are key. A substitute that is significantly cheaper, simpler to implement, or demonstrably as reliable as Nissha's offerings will likely see faster market penetration. This is particularly relevant in industries where supply chain stability is paramount.
Entrants Threaten
Entering advanced printing, coating, and lamination sectors demands significant capital. Nissha's operations, for instance, necessitate substantial investment in specialized machinery, state-of-the-art facilities, and robust R&D capabilities. In 2024, the cost of acquiring and maintaining cutting-edge industrial printing equipment alone can easily run into millions of dollars.
These considerable upfront expenditures create a formidable barrier for new entrants. Only well-capitalized companies can afford the necessary infrastructure to compete effectively, thereby limiting the pool of potential challengers. This capital intensity inherently shields established firms like Nissha from widespread new competition.
Nissha’s established relationships with key customers and its well-developed global distribution channels across diverse industries present a significant barrier to new entrants. For example, in the automotive sector, securing supply chain integration with major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) often requires years of proven reliability and extensive testing, a hurdle that newcomers would find difficult to overcome quickly.
New companies attempting to enter Nissha's markets would face considerable challenges and substantial costs in replicating these intricate networks. Building trust with major clients and achieving the necessary supply chain integration takes time and significant investment, potentially running into millions of dollars for initial setup and qualification processes.
This existing market access, cultivated over decades, provides Nissha with a strong, defensible competitive advantage. The difficulty and expense associated with replicating Nissha's distribution and customer relationships effectively deter potential new competitors, preserving Nissha's market position.
Nissha's status as a global player grants it substantial economies of scale across manufacturing, purchasing, and research and development. This translates to lower per-unit production costs compared to emerging competitors. For instance, in 2024, Nissha's extensive global supply chain likely allowed for bulk discounts on raw materials, a benefit unavailable to startups.
New entrants would find it exceedingly difficult to replicate Nissha's operational efficiencies without achieving a comparable production volume. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for them to compete on price in the initial stages. A new entrant might face significantly higher material costs per unit, potentially 10-15% more than Nissha in 2024 due to smaller order volumes.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
Nissha's core technologies in printing, coating, and lamination, often backed by patents and trade secrets, represent a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. These proprietary innovations, which have been honed over years of research and development, are not easily replicated. For instance, Nissha's advanced transfer printing technologies for automotive interiors, a key area of their business, are protected, requiring substantial investment and time for competitors to develop comparable capabilities.
The need for new players to either develop their own unique, patent-protected technologies or risk infringement significantly delays their market entry and increases their initial capital expenditure. This intellectual property moat makes it challenging for smaller or less resourced companies to compete effectively. In 2024, the ongoing investment in R&D by established players like Nissha, which often exceeds 5% of sales for specialty materials companies, further widens this gap.
- Proprietary Technology: Nissha possesses specialized printing, coating, and lamination techniques.
- Intellectual Property Protection: These technologies are likely safeguarded by patents and trade secrets.
- Barrier to Entry: New entrants must invest heavily in R&D to develop similar capabilities or face legal challenges.
- Market Penetration Slowdown: The IP protection slows down the ability of new companies to gain market share.
Regulatory Hurdles and Industry Standards
The threat of new entrants for Nissha, particularly in its high-value medical and automotive segments, is significantly mitigated by substantial regulatory hurdles and demanding industry standards. These sectors require extensive compliance with quality certifications and rigorous approval processes that can deter potential competitors. For instance, obtaining certifications like ISO 13485 for medical devices or IATF 16949 for automotive suppliers is a time-consuming and costly endeavor, often taking years and substantial investment. Nissha's established track record and existing certifications act as a formidable barrier, providing a competitive moat against newcomers who lack the necessary experience and resources to navigate these complex requirements.
The threat of new entrants into Nissha's core markets is considerably low due to the immense capital required for advanced printing, coating, and lamination technologies. Acquiring and maintaining state-of-the-art machinery in 2024 can easily cost millions, creating a significant financial barrier. This capital intensity naturally limits the number of companies capable of entering and competing effectively, thereby protecting established players like Nissha.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Nissha leverages data from Nissha's official investor relations website, annual reports, and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and competitor financial statements.
