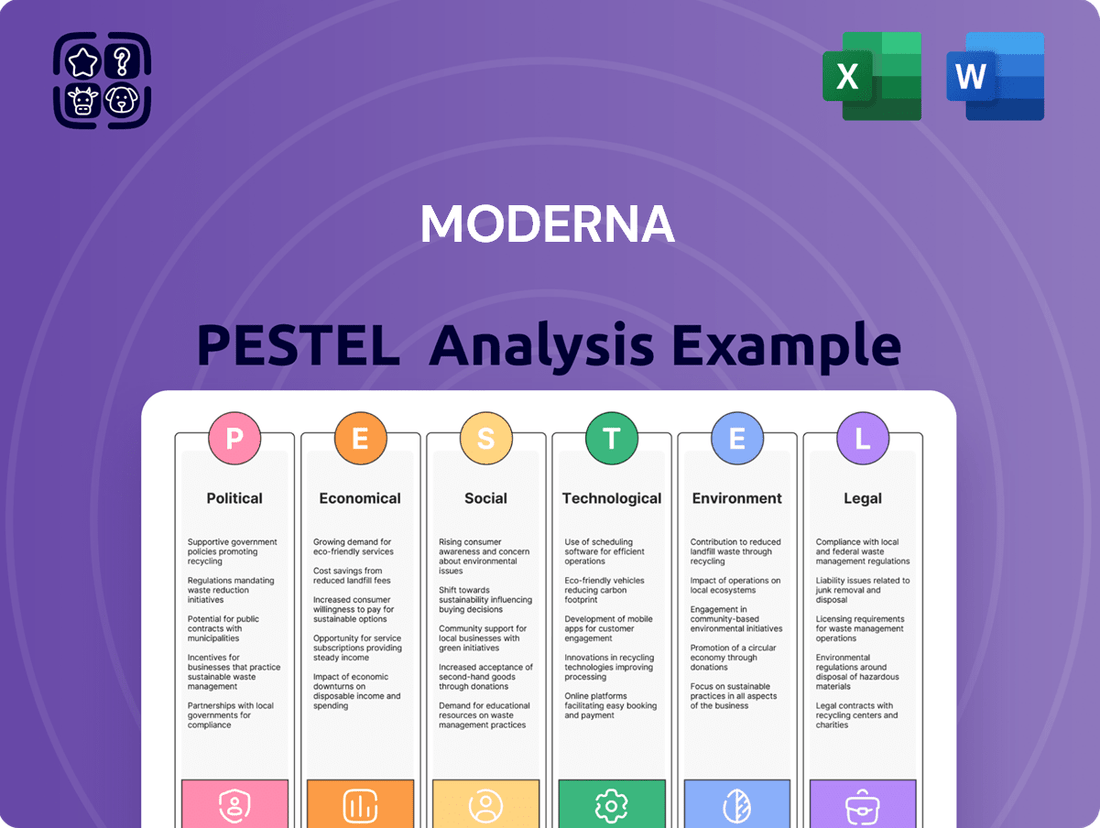
Moderna PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Moderna Bundle
Curious about the external forces shaping Moderna's groundbreaking advancements? Our PESTLE analysis delves into the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that are critically influencing the mRNA giant's trajectory. Understand the regulatory landscape, economic shifts, and societal acceptance impacting vaccine development and beyond. Gain a competitive edge by anticipating these trends and leveraging them for your own strategic planning. Download the full, expertly crafted Moderna PESTLE analysis now to unlock actionable intelligence and secure your future market position.
Political factors
Government healthcare spending and budget allocations are crucial determinants for Moderna, directly impacting the demand and pricing of its innovative mRNA products. Post-pandemic, shifts in governmental priorities can significantly alter vaccine and therapeutic accessibility, as well as the awarding of government procurement contracts.
The U.S. government's decision to cancel a $766 million contract with Moderna for pandemic flu vaccines in late 2023 underscores the inherent volatility associated with government funding and policy changes. This highlights the need for Moderna to navigate these shifting landscapes.
The regulatory environment is a critical factor for Moderna, with agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) setting the pace for new mRNA product approvals. These evolving global regulations directly influence how quickly and smoothly Moderna can introduce its innovative therapeutics and vaccines to the market.
Changes in regulatory standards, such as the more stringent guidelines implemented for COVID-19 vaccines, can significantly affect the speed and overall ease of commercializing products. This means that adapting to and meeting these requirements is paramount for Moderna's success.
Looking ahead, Moderna has projected up to three potential product approvals in 2025. This includes their updated next-generation COVID-19 vaccine, designed to address emerging variants, and an expanded approval for their Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) vaccine, broadening its accessibility.
Trade agreements and market access policies are fundamental to Moderna's ability to distribute its innovative mRNA vaccines and therapeutics worldwide. These agreements directly influence how easily Moderna can enter new markets, the tariffs it faces, and the regulatory pathways for its products.
Strong intellectual property (IP) protection is paramount for Moderna, safeguarding its significant investments in research and development. Without robust patent laws and enforcement in key global markets, the company's ability to recoup its R&D costs and maintain a competitive edge would be severely compromised.
In 2024, international sales represented a substantial component of Moderna's overall revenue, highlighting the critical need for favorable global trade conditions. For instance, the company's COVID-19 vaccine sales in markets outside the United States significantly contributed to its financial performance, underscoring the direct link between trade policies and revenue generation.
Geopolitical Stability and Global Health Initiatives
Geopolitical stability significantly impacts global health initiatives, directly affecting Moderna's ability to distribute its vaccines and tackle health disparities. The World Health Organization's mRNA Technology Transfer Programme, launched in 2021 and expanding its reach into 2024-2025, aims to bolster vaccine manufacturing capabilities in lower-income nations. This initiative could reshape global market competition and influence Moderna's position in safeguarding global health security.
Moderna's commitment to global health equity is evident through its vaccine donation programs. For instance, by the end of 2023, the company had pledged significant doses to COVAX and other initiatives, contributing to broader access. This direct involvement in addressing health inequities underscores its role beyond commercial operations, aligning with international efforts to ensure equitable vaccine distribution in the 2024-2025 period.
- WHO mRNA Technology Transfer Programme: Expanding in 2024-2025 to build local manufacturing capacity in LMICs, potentially altering market dynamics.
- Vaccine Donations: Moderna's continued contributions to programs like COVAX demonstrate a commitment to global health equity, aiming for wider access in the coming years.
- Geopolitical Impact: Stability or instability in various regions can affect supply chains, regulatory approvals, and the willingness of governments to partner on health initiatives.
Public Health Recommendations and Vaccine Mandates
Public health recommendations and the presence or absence of vaccine mandates significantly influence the demand for Moderna's products. For instance, a reduction in routine COVID-19 vaccination guidelines could directly impact sales and require adjustments to commercial strategies. This means Moderna must remain agile, adapting to shifts in public health priorities and navigating a more specialized market landscape.
The market for vaccines is highly sensitive to these public health directives. For example, in early 2024, many countries began to transition COVID-19 vaccines from a public health emergency response to a more routine immunization schedule, similar to the annual flu shot. This shift inherently changes the purchasing patterns and the volume of demand.
- Evolving Recommendations: Public health bodies like the CDC and WHO regularly update their recommendations regarding vaccine timing, target populations, and booster schedules. These updates directly shape demand.
- Mandate Impact: The presence or absence of government mandates for specific vaccines can drastically alter uptake rates. For example, if a mandate for a particular vaccine is lifted, demand may decrease.
- Shift to Routine Care: As COVID-19 transitions to a more endemic state, public health focus shifts towards integrating vaccines into routine healthcare, impacting sales forecasts and marketing approaches.
- Market Segmentation: With changing recommendations, Moderna may need to focus on specific demographic groups or geographic regions where vaccination is still strongly advised or mandated.
Government healthcare spending and budget allocations directly influence demand and pricing for Moderna's mRNA products. Shifts in governmental priorities post-pandemic can alter vaccine accessibility and procurement contracts, as seen with the U.S. government's cancellation of a $766 million flu vaccine contract with Moderna in late 2023, highlighting funding volatility.
The World Health Organization's mRNA Technology Transfer Programme, expanding in 2024-2025 to build local manufacturing in lower-income countries, could reshape global market dynamics. Moderna's continued vaccine donations to programs like COVAX also underscore its commitment to global health equity, aiming for wider access.
Public health recommendations and vaccine mandates significantly impact demand, with shifts from emergency response to routine immunization schedules affecting purchasing patterns. For example, the transition of COVID-19 vaccines to a more endemic state in early 2024 altered sales forecasts and marketing approaches.
Regulatory environments, shaped by agencies like the FDA and EMA, dictate the pace of new mRNA product approvals. Evolving global regulations and stricter standards, such as those for COVID-19 vaccines, directly influence commercialization speed and ease.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing Moderna across Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions. It offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, highlighting how understanding political stability and economic growth can de-risk Moderna's expansion strategies.
Easily shareable summary format ideal for quick alignment across teams or departments, clarifying how technological advancements and regulatory hurdles impact vaccine development timelines and market access.
Economic factors
Global economic growth, alongside persistent inflation and recession risks, directly impacts Moderna's operational expenses and the demand for its healthcare products. Economic slowdowns can pressure healthcare budgets, potentially affecting affordability and the uptake of new therapies.
For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.1% in 2024, a slight uptick from 3.0% in 2023, but still below historical averages, signaling a fragile recovery susceptible to headwinds.
Moderna itself anticipates a substantial revenue decrease in 2025, partly driven by softening demand for its COVID-19 vaccines and evolving market dynamics, underscoring the sensitivity of its business to broader economic conditions and public health trends.
Total healthcare spending, both by governments and individuals, directly influences the market size and pricing flexibility for companies like Moderna. As of 2024, U.S. healthcare spending is projected to surpass $7 trillion by 2028, signaling substantial market potential.
However, national healthcare budgets, often facing constraints, can still impact how much is allocated to purchasing new therapeutics and vaccines. This dynamic means that even with a growing overall market, budget limitations can affect procurement volumes.
Moderna's own financial outlook reflects this evolving landscape, with revenue projections for 2025 indicating a recalibration compared to earlier, higher figures. This adjustment acknowledges the current market realities and budget considerations faced by healthcare systems globally.
Moderna's long-term success hinges on consistent and significant investment in Research and Development. This commitment fuels the innovation pipeline for its mRNA technology, aiming to broaden its impact beyond infectious diseases.
Despite ongoing efforts to optimize expenses, R&D remains a critical pillar for Moderna's future. The company has projected its full-year 2025 R&D expenditure to be around $4.1 billion, underscoring its dedication to scientific advancement.
This substantial R&D outlay is strategically geared towards achieving ambitious growth targets. Moderna aims to secure up to 10 new product approvals between now and 2027, signaling a robust pipeline expansion into therapeutic areas such as oncology and rare diseases.
Competition and Market Share
Moderna faces a dynamic competitive landscape in the mRNA vaccine and therapeutics sector. Established pharmaceutical giants and emerging biotech firms are increasingly entering the mRNA space, directly challenging Moderna's market share and influencing its pricing power. This heightened competition is particularly evident as the market for mRNA therapeutics is anticipated to expand substantially in the coming years.
The competitive pressures have already impacted Moderna's performance, notably in the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine market. Despite its pioneering work, Moderna has encountered difficulties in capturing significant market share against rivals who have introduced bundled product offerings or employed aggressive pricing strategies.
- Market Share Challenges: Moderna's ability to secure and grow its market share is directly influenced by the number and strength of competitors in the mRNA space.
- Pricing Pressures: Increased competition can lead to downward pressure on vaccine and therapeutic prices, affecting Moderna's revenue and profit margins.
- RSV Vaccine Competition: In the RSV vaccine segment, Moderna has seen its market share impacted by competitors' strategies, highlighting the intensity of market battles.
- Future Market Growth: While the mRNA therapeutics market is projected for strong growth, the competitive environment will be a critical factor in determining how much of that growth Moderna can capture.
Currency Fluctuations and Global Supply Chains
Currency fluctuations present a significant economic factor for Moderna, impacting its international revenue streams and the cost of imported components for its mRNA vaccines. For instance, a stronger US dollar in 2024 could reduce the value of sales made in weaker foreign currencies, directly affecting reported profits. Moderna's extensive global supply chain, sourcing materials and manufacturing in various regions, means that movements in exchange rates can substantially alter its cost of goods sold.
Disruptions within these global supply chains, as experienced in recent years, can lead to increased production costs and delays in product delivery. The company's reliance on specialized raw materials and manufacturing partners worldwide means that geopolitical events or logistical bottlenecks can drive up expenses and potentially impact the availability of its vaccines. For example, increased shipping costs in 2024, averaging 15-20% higher than pre-pandemic levels for certain routes, directly add to Moderna's operational expenditures.
To navigate these economic headwinds, Moderna must employ agile financial management and develop resilient supply chain strategies. This includes hedging against currency volatility and diversifying its supplier base to mitigate risks. The company's ability to adapt to these changing economic conditions is crucial for maintaining profitability and ensuring the consistent supply of its life-saving products. In 2024, the company announced investments in expanding its US-based manufacturing capabilities to reduce reliance on overseas suppliers.
- Currency Exchange Rate Impact: Fluctuations in major currencies against the US dollar directly affect Moderna's reported earnings from international sales.
- Supply Chain Cost Increases: Global logistical challenges and raw material price volatility, seen in 2023-2024, have added to Moderna's cost of goods sold.
- Mitigation Strategies: Financial hedging and supply chain diversification are key to managing economic risks associated with global operations.
- Manufacturing Investments: Moderna's strategic investments in domestic production facilities aim to buffer against international supply chain disruptions and currency risks.
Global economic conditions significantly influence Moderna's revenue streams and operational costs. While the IMF projected global growth to be 3.1% in 2024, this fragile recovery means that economic slowdowns can dampen healthcare spending, affecting vaccine and therapeutic demand. Moderna itself anticipates a revenue recalibration in 2025, reflecting these broader economic sensitivities and evolving market dynamics.
The company's substantial investment in research and development, projected at around $4.1 billion for 2025, is crucial for its future growth, aiming for up to 10 new product approvals by 2027. However, this continued R&D expenditure, coupled with increasing competition in the mRNA space, places pressure on profit margins.
Currency fluctuations and supply chain disruptions are also key economic factors. A stronger US dollar can reduce international revenue, while increased shipping costs and raw material prices, which saw 15-20% hikes on certain routes in 2024, directly impact the cost of goods sold. Moderna's strategic investments in US-based manufacturing aim to mitigate these risks.
| Economic Factor | Impact on Moderna | Supporting Data/Trend (2024-2025) |
| Global Economic Growth | Affects demand for healthcare products; potential pressure on healthcare budgets. | IMF projected 3.1% global growth in 2024. |
| Inflation & Interest Rates | Increases operational expenses; impacts cost of capital for R&D. | Inflationary pressures persisted globally in early 2024. |
| Currency Exchange Rates | Reduces value of international sales when USD strengthens. | USD strength in 2024 impacting foreign earnings. |
| Supply Chain Costs | Increases cost of goods sold due to shipping and raw material prices. | Shipping costs up 15-20% on some routes vs. pre-pandemic. |
| Healthcare Spending | Determines market size and pricing flexibility for products. | US healthcare spending projected to exceed $7 trillion by 2028. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Moderna PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use.
This comprehensive PESTLE analysis for Moderna covers all critical aspects, providing a robust understanding of its operating environment.
You'll gain insights into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors influencing Moderna's strategic decisions.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same document you’ll download after payment, enabling immediate application.
Sociological factors
Public perception of mRNA technology and vaccine hesitancy are critical factors influencing Moderna's product adoption. Concerns about the novelty of mRNA vaccines and widespread misinformation can erode public trust in their safety and effectiveness. For instance, studies in late 2023 and early 2024 continued to show pockets of significant vaccine hesitancy, particularly concerning new vaccine formulations.
Negative public sentiment, often amplified by online misinformation campaigns, directly impacts uptake rates for Moderna's COVID-19 vaccines and future mRNA-based therapies. This hesitancy can lead to lower demand, affecting revenue projections and market penetration for new products. Surveys from 2024 indicated that while general acceptance of mRNA vaccines had increased, specific concerns about long-term effects persisted among certain demographics.
To counteract these challenges, Moderna, like other vaccine developers, prioritizes educational initiatives and transparent communication. Building and maintaining public trust in mRNA technology is paramount, requiring clear, evidence-based information to address public concerns and combat misinformation effectively. These efforts are vital for ensuring widespread acceptance of their existing and pipeline products.
Global demographic shifts, notably the increasing proportion of older adults, are a significant driver for Moderna. This aging trend directly fuels demand for vaccines and advanced therapies targeting conditions common in later life, such as respiratory illnesses. For instance, the World Health Organization projects that by 2050, one in six people globally will be over 65, a substantial increase from one in ten in 2020.
Moderna's strategic focus on respiratory viruses like Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) perfectly aligns with this demographic reality. RSV can cause severe illness, particularly in infants and older adults. The company's development and recent approvals of RSV vaccines are therefore positioned to capture a growing market segment.
Further demonstrating this alignment, Moderna's RSV vaccine, which received FDA approval for older adults, has seen its indication expanded to include younger adults at higher risk. This broadened approval in 2024 taps into a wider demographic need, enhancing the vaccine's market potential and reflecting the company's adaptability to evolving public health priorities and population health trends.
Shifting lifestyle factors, like increased sedentary habits and dietary changes, are contributing to a rise in chronic diseases, creating a larger market for preventative and therapeutic solutions. For instance, the World Health Organization reported in 2024 that non-communicable diseases account for an estimated 74% of all deaths globally, a trend that fuels demand for advanced medical interventions. This growing health consciousness directly impacts Moderna's product pipeline, particularly for mRNA-based treatments targeting conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which are often linked to lifestyle choices.
Healthcare Access and Equity
Societal pressure for fair healthcare access significantly shapes Moderna's approach to pricing and how it distributes its products, particularly in developing nations. The company's commitment to global availability of its vaccines and therapies is a direct response to this societal expectation. As of late 2024, discussions around tiered pricing models for advanced therapies are ongoing, reflecting the tension between recouping R&D costs and ensuring broad accessibility.
Moderna actively participates in programs designed to bridge the global health equity gap. A prime example is its collaboration with initiatives like the World Health Organization's (WHO) mRNA Technology Transfer Programme. This program, which aims to bolster vaccine manufacturing capabilities in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), underscores the growing demand for self-sufficiency in critical medical technologies.
The impact of these sociological factors is evident in Moderna's strategic partnerships. For instance, the company's work with the African Vaccine Manufacturing Accelerator is a tangible effort to address historical inequities in global vaccine production. By empowering LMICs with the technology to produce mRNA vaccines, Moderna contributes to a more resilient and equitable global health infrastructure. This focus is crucial as global health organizations continue to advocate for a more balanced distribution of life-saving medical innovations.
Ethical Considerations and Public Trust
Ethical considerations surrounding the novelty of mRNA technology, including potential long-term effects, significantly shape public acceptance and the intensity of regulatory oversight. Moderna's commitment to transparent research, open communication about its vaccine development, and robust safety data are crucial for sustaining public trust and ensuring continued market access.
Maintaining public confidence is paramount for Moderna, especially as discussions around vaccine efficacy and potential side effects continue. For instance, as of early 2024, ongoing research is still exploring the full spectrum of long-term impacts of mRNA vaccines, a factor that can influence public perception and regulatory caution.
The scientific community plays a vital role in counteracting misinformation. By clearly communicating the public health benefits derived from mRNA therapies, such as the rapid development and effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines, they can foster a more informed public discourse.
Moderna's ability to navigate these ethical waters directly impacts its long-term viability. Building and preserving trust through clear communication and demonstrable safety protocols is essential for continued adoption and investment in their mRNA platform.
- Public Trust: Continued emphasis on transparent data sharing and clear communication about mRNA technology's safety profile is essential for public confidence.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Novelty of mRNA technology may lead to ongoing and potentially evolving regulatory requirements, necessitating proactive engagement from Moderna.
- Misinformation Management: Collaborative efforts with the scientific community to address and correct misinformation are critical for public understanding and acceptance.
- Long-Term Effects: Ongoing research into the long-term effects of mRNA therapies, a key area of public interest, will continue to inform ethical considerations and regulatory approaches.
Societal pressure for equitable healthcare access significantly influences Moderna's pricing strategies and global distribution efforts, particularly in developing nations. The company's involvement in initiatives like the WHO's mRNA Technology Transfer Programme demonstrates a commitment to addressing health equity gaps and fostering self-sufficiency in critical medical technologies in low- and middle-income countries. This aligns with growing global demands for broader accessibility to advanced therapies, as seen in ongoing discussions around tiered pricing models in 2024.
Technological factors
Moderna's competitive edge is deeply rooted in the continuous evolution of mRNA technology, particularly in enhancing delivery systems and overall stability. These advancements are crucial for expanding their product pipeline.
Innovations like improved lipid nanoparticle platforms and the development of self-amplifying mRNA technologies are key. These breakthroughs aim to boost the effectiveness of vaccines and therapies while potentially lowering the necessary dosage amounts.
This persistent research and development directly translates to Moderna's ability to quickly create novel treatments and vaccines, a critical factor in addressing rapidly emerging health challenges.
Artificial intelligence and bioinformatics are revolutionizing how new drugs are found and developed. By crunching vast amounts of biological data, AI can speed up research, pinpoint promising drug targets, and even help design better therapies. This integration is a cornerstone of the European Union's biotech strategy, highlighting its growing importance.
For a company like Moderna, embracing AI in its biotechnology research is crucial for efficiency. This technology can streamline the complex process of bringing novel mRNA medicines from the lab to patients, potentially reducing timelines and costs. For instance, AI algorithms are being used to predict the efficacy of mRNA sequences, a key step in developing new vaccines and therapeutics.
The financial impact is substantial. Companies investing in AI for drug discovery are seeing significant gains in research productivity. While specific figures for Moderna's AI investment aren't always public, the broader biotech industry saw venture capital funding for AI-driven drug discovery reach billions in 2024, indicating strong market confidence in this technological shift.
Moderna's manufacturing innovation is key to meeting demand and cutting costs. Their rapid scaling for COVID-19 vaccines proved crucial, and they continue to refine processes for greater efficiency. For instance, in 2023, Moderna reported approximately $1.9 billion in revenue, demonstrating their ability to produce and distribute at scale, though this was down from the $20.8 billion in 2022, indicating the dynamic nature of demand and production needs.
The company is actively integrating sustainability into its manufacturing, aiming for eco-friendly operations in new facilities. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also aligns with increasing investor and regulatory focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors, which can influence capital access and long-term valuation.
Pipeline Diversification and Therapeutic Applications
Moderna is actively diversifying its mRNA technology beyond infectious diseases. The company is focusing on therapeutic areas like oncology, rare diseases, and autoimmune conditions, aiming to unlock new growth avenues. This strategic pivot highlights the broad applicability of its mRNA platform.
Significant growth opportunities lie in Moderna's expansion into new therapeutic areas, particularly in oncology. For instance, its work on melanoma and other cancer treatments showcases this commitment. The company has a stated goal of achieving up to five product approvals within the next three years, demonstrating an aggressive development strategy.
- Pipeline Expansion: Moderna is moving beyond infectious diseases into oncology, rare diseases, and autoimmune conditions.
- Growth Opportunities: Expansion into areas like melanoma and other cancer treatments presents significant market potential.
- Development Targets: Moderna aims for up to five product approvals in the near term, reflecting its pipeline advancement.
Data Analytics and Digital Health Integration
Technological advancements in data analytics and digital health integration are significantly reshaping the pharmaceutical landscape, directly impacting companies like Moderna. The ability to harness vast datasets through advanced analytics allows for more efficient clinical trials, improved patient monitoring, and the development of truly personalized medicine. For instance, in 2024, the global big data and analytics market in healthcare was projected to reach over $100 billion, highlighting the increasing reliance on these technologies.
Moderna's strategy heavily emphasizes the digitization of its operations. This digital transformation is crucial for optimizing every stage of their mRNA product lifecycle, from research and development to manufacturing and commercialization. By integrating digital health platforms, Moderna can gain real-time insights into patient outcomes and treatment efficacy, further refining their therapeutic approaches.
- Enhanced Clinical Trials: Data analytics can identify suitable patient cohorts faster and predict trial outcomes, potentially reducing trial durations and costs.
- Personalized Medicine: Integrating genomic data with patient health records through digital platforms allows for tailor-made mRNA therapies.
- Operational Efficiency: Digitizing supply chains and manufacturing processes improves reliability and scalability for mRNA production.
- Real-time Monitoring: Digital health tools enable continuous patient data collection, offering immediate feedback on treatment effectiveness and safety.
Moderna's technological prowess is centered on its mRNA platform, with ongoing advancements in delivery systems and stability critical for pipeline expansion. Innovations such as improved lipid nanoparticle formulations are key to enhancing vaccine and therapeutic efficacy, potentially enabling lower dosages.
The integration of artificial intelligence and bioinformatics is accelerating drug discovery and development, a trend mirrored in the European Union's biotech strategies. AI's ability to analyze vast biological datasets is crucial for streamlining Moderna's R&D processes, as seen in the billions invested by the broader biotech industry in AI-driven drug discovery in 2024.
Manufacturing efficiency is another technological cornerstone, as demonstrated by Moderna's scaled production during the COVID-19 pandemic. The company's ongoing efforts in process refinement and sustainable manufacturing reflect a commitment to operational excellence and ESG alignment, factors increasingly influencing investor confidence and capital access.
Legal factors
Moderna operates in a heavily regulated sector, necessitating strict adherence to international pharmaceutical regulations for gaining product approval and market access. The company is actively seeking various regulatory nods for its upcoming products, including its advanced COVID-19 vaccine and its RSV vaccine, with key target dates in 2025.
Compliance with these stringent standards is paramount for securing market entry and driving product sales. For instance, the PDUFA dates for potential approvals in 2025 highlight the critical timeline for these regulatory processes.
Moderna's business thrives on its robust intellectual property, particularly patents safeguarding its groundbreaking mRNA technology. This strong IP protection is crucial for preventing competitors from copying its innovations. In 2024, the biotechnology sector continues to see intense focus on patent enforcement, as demonstrated by ongoing legal battles. For instance, Moderna's disputes with Pfizer and BioNTech underscore the critical role and intricate nature of IP in this industry.
The company boasts an extensive patent portfolio that covers its core mRNA platform, various vaccine compositions, and novel therapeutic strategies. This significant collection of intellectual property assets is central to maintaining Moderna's competitive edge and securing future revenue streams. As of early 2025, the value of these patents remains a key component of Moderna's overall valuation, influencing investor confidence and strategic partnerships.
Moderna operates under a complex web of clinical trial regulations, demanding rigorous adherence to patient safety protocols, data accuracy, and ethical standards. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees clinical trials within the United States, setting strict guidelines that Moderna must follow to ensure the safety and efficacy of its mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
Data privacy is equally paramount, with laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States dictating how Moderna handles sensitive patient information collected during research and commercialization. Non-compliance with these data privacy mandates can lead to substantial financial penalties, impacting Moderna's financial health and operational continuity.
Maintaining public trust is intrinsically linked to regulatory compliance; failing to uphold these standards can result in significant reputational damage and legal repercussions, potentially hindering future research and market access. For example, in 2023, the pharmaceutical industry faced increased scrutiny over data integrity in clinical trials, highlighting the critical need for robust compliance frameworks.
Product Liability and Safety Regulations
Moderna, as a pharmaceutical innovator, navigates a landscape heavily influenced by product liability and stringent safety regulations. The company's mRNA technology, while groundbreaking, necessitates rigorous adherence to global health authority standards, such as those set by the FDA and EMA, to ensure the safety and efficacy of its vaccines and therapeutics. Failure to meet these benchmarks could expose Moderna to significant product liability claims, impacting its financial stability and market reputation.
The rapid development and deployment of Moderna's COVID-19 vaccines, for instance, underscored the critical importance of maintaining robust safety protocols. Despite the accelerated timelines, scientific bodies like the CDC and WHO affirmed the vaccines' safety profiles, a crucial factor in public trust and regulatory approval. In 2023, pharmaceutical companies globally faced increasing scrutiny regarding drug safety, with the FDA issuing numerous warning letters related to manufacturing and quality control issues, highlighting the ongoing challenges in this sector.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to FDA, EMA, and other global health authority regulations is paramount for Moderna's mRNA products.
- Product Liability Risk: Potential for lawsuits arising from adverse events or product defects poses a significant legal and financial challenge.
- Safety and Efficacy Focus: Maintaining public confidence hinges on demonstrating the consistent safety and efficacy of its vaccine and therapeutic pipeline.
- Evolving Standards: The regulatory environment for novel therapies is dynamic, requiring continuous adaptation to new safety and data reporting requirements.
Anti-Trust and Competition Law
Moderna's significant market share in the COVID-19 vaccine sector, particularly in 2023 and projected into 2024, brings it under the purview of anti-trust and competition laws globally. These regulations aim to prevent monopolistic practices and ensure a level playing field for all market participants. For instance, the European Commission actively monitors mergers and acquisitions, as well as the competitive impact of dominant firms' strategies, to uphold fair competition within the pharmaceutical industry.
The dynamic and rapidly evolving mRNA vaccine market necessitates careful adherence to competition regulations. Moderna's pricing strategies and market entry plans for new vaccine candidates, such as those targeting influenza or RSV, are subject to scrutiny. Ensuring fair pricing, preventing predatory behavior, and facilitating market access for innovative competitors are key considerations for regulators in 2024 and beyond. In 2023, the global vaccine market was valued at approximately $150 billion, with mRNA technology playing an increasingly vital role.
- Regulatory Oversight: Global competition authorities, including the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the European Commission's Directorate-General for Competition, scrutinize Moderna's commercial practices.
- Market Dynamics: The presence of competitors like Pfizer-BioNTech and emerging players in the mRNA space intensifies regulatory focus on preventing anti-competitive behavior.
- Pricing Scrutiny: Pricing of vaccines, especially during public health emergencies and for new product launches, is a critical area of examination to ensure affordability and prevent price gouging.
- Intellectual Property: Licensing agreements and patent strategies are also reviewed to ensure they do not stifle innovation or create undue market barriers.
Moderna's operations are deeply intertwined with a complex legal and regulatory framework. The company must meticulously adhere to global health authority standards, such as those set by the FDA and EMA, to secure approvals for its mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics. Failure to comply with these rigorous requirements can result in significant product liability claims and damage to its reputation, as seen with increased scrutiny on drug safety across the pharmaceutical industry in 2023.
Intellectual property law is another critical legal factor. Moderna's extensive patent portfolio, safeguarding its core mRNA technology and various vaccine compositions, is vital for maintaining its competitive advantage. The ongoing legal disputes with competitors like Pfizer and BioNTech in 2024 highlight the intense focus on patent enforcement within the rapidly evolving biotechnology sector, underscoring the value of these assets in securing future revenue.
Furthermore, Moderna must navigate data privacy regulations, including GDPR and HIPAA, when handling sensitive patient information gathered during research and commercialization. Non-compliance can lead to substantial financial penalties, impacting operational continuity. The company's commitment to patient safety and data integrity in its clinical trials is paramount for maintaining public trust and regulatory approval.
Moderna also faces scrutiny under anti-trust and competition laws due to its significant market presence, particularly in the COVID-19 vaccine sector. Regulators globally monitor its commercial practices, pricing strategies, and licensing agreements to ensure fair competition and prevent monopolistic behavior, a key concern in the dynamic vaccine market valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023.
Environmental factors
Moderna is actively pursuing sustainable manufacturing, aiming to shrink its environmental impact by cutting waste and improving energy efficiency. This commitment is underscored by ambitious targets: net-zero carbon emissions for Scopes 1 and 2 by 2030, and a broader goal for its entire value chain by 2045. For instance, their new Science Center features advanced sustainable design principles, reflecting this dedication.
Moderna, like all biotechnology firms, faces significant environmental considerations regarding waste management, particularly with the hazardous materials involved in vaccine research and production. The company must adhere to stringent regulations for the disposal of chemical byproducts and biological waste. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reported that the chemical manufacturing industry, a sector allied with biotech, generated millions of tons of hazardous waste annually, underscoring the scale of this challenge.
Effective waste reduction and disposal strategies are paramount for Moderna's environmental compliance and corporate responsibility. This includes exploring advanced methods like bioremediation, which uses biological organisms to break down or neutralize hazardous substances. Such approaches are not only environmentally sound but can also offer cost efficiencies compared to traditional disposal methods, aligning with sustainable business practices.
Biotech companies, including Moderna, are under increasing scrutiny to minimize their environmental footprint. Compliance with environmental laws, such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States, dictates how hazardous waste must be handled from cradle to grave. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and reputational damage, making robust waste management systems a core operational necessity.
Climate change is increasingly influencing where and how infectious diseases spread, directly impacting the demand for vaccines. As temperatures shift and weather patterns become more erratic, diseases once confined to specific regions are appearing in new areas, creating a dynamic landscape for public health threats. This environmental shift can lead to the emergence of novel pathogens or alter the prevalence of existing ones, presenting both challenges and opportunities for vaccine developers like Moderna.
For instance, the World Health Organization (WHO) has noted that changing climate conditions can expand the geographic range of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever, potentially increasing the need for preventative vaccines in previously unaffected populations. Moderna's mRNA platform is uniquely positioned to respond to these evolving disease patterns, allowing for swift development and adaptation of vaccines against emerging or changing threats.
The ability to rapidly develop and deploy new vaccines is crucial in a world grappling with climate-induced health crises. The 2024-2025 period will likely see continued focus on preparedness for climate-sensitive diseases, with research and development efforts increasingly driven by these environmental factors. Moderna's agility in vaccine production means it can be a key player in addressing these growing public health needs.
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Sustainability
Moderna is increasingly focused on ethical sourcing and supply chain sustainability, recognizing the growing importance of responsible practices. This commitment involves collaborating with suppliers who meet stringent environmental and social standards, fostering a more conscientious value chain. The company has set an ambitious goal to have 85% of its suppliers adopt science-based targets by 2028, a significant step towards long-term environmental stewardship.
This strategic focus on sustainability is not just about compliance; it's about building resilience and mitigating risks within Moderna's complex global operations. By encouraging suppliers to set science-based targets, Moderna is aligning its supply chain with global climate goals and enhancing its reputation among stakeholders. This proactive approach is crucial in an industry where trust and ethical conduct are paramount.
- Ethical Sourcing: Prioritizing suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Enhancing visibility into the origins and production methods of raw materials.
- Supplier Engagement: Working collaboratively with suppliers to improve their sustainability performance.
- Science-Based Targets: Aiming for 85% of suppliers to have adopted science-based targets by 2028 to align with climate action.
Environmental Regulations and Compliance
Moderna operates within an increasingly stringent environmental regulatory landscape, requiring significant compliance efforts. These regulations span areas critical to biotechnology, such as the handling of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and the management of hazardous waste generated during research and manufacturing. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines and operational disruptions.
Key to Moderna's operations are adherence to national and international environmental laws. This includes compliance with the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) in the United States, which governs the introduction of new chemicals and materials, and the Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, an international treaty that governs the transboundary movement, handling, and use of living modified organisms (LMOs) derived from modern biotechnology. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) actively enforces TSCA, with significant penalties for non-compliance.
The evolution of biotechnology necessitates adaptive regulatory frameworks. In 2024 and continuing into 2025, U.S. commissions are actively focusing on modernizing biotechnology product regulation. This aims to streamline approvals for innovative products while maintaining robust environmental safety standards, a process that could impact the speed and cost of bringing new mRNA-based therapies to market.
- GMO and Hazardous Waste Management: Moderna must navigate complex rules for handling and disposing of biological materials and chemicals.
- TSCA Compliance: Adherence to the Toxic Substances Control Act is mandatory for chemicals used in R&D and production.
- Cartagena Protocol: International shipments of GMOs require strict adherence to biosafety regulations.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Anticipation of updated biotechnology product regulations in the U.S. is critical for future product development.
Moderna is actively pursuing sustainable manufacturing, aiming to shrink its environmental impact by cutting waste and improving energy efficiency. This commitment is underscored by ambitious targets: net-zero carbon emissions for Scopes 1 and 2 by 2030, and a broader goal for its entire value chain by 2045. For instance, their new Science Center features advanced sustainable design principles, reflecting this dedication.
Climate change increasingly influences disease spread, directly impacting vaccine demand. As temperatures shift, diseases once confined to specific regions appear in new areas, creating a dynamic public health landscape. Moderna's mRNA platform is uniquely positioned to respond to these evolving disease patterns, allowing for swift development and adaptation of vaccines against emerging or changing threats.
Moderna operates within an increasingly stringent environmental regulatory landscape, requiring significant compliance efforts. These regulations span areas critical to biotechnology, such as the handling of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and the management of hazardous waste generated during research and manufacturing. Failure to comply can lead to substantial fines and operational disruptions.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Moderna is built on a comprehensive review of data from leading public health organizations, global economic reports, and regulatory bodies. We incorporate insights from scientific journals, market intelligence firms, and government policy updates to ensure a thorough understanding of the macro-environmental factors influencing the pharmaceutical industry.
