Deutsche Lufthansa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Deutsche Lufthansa Bundle
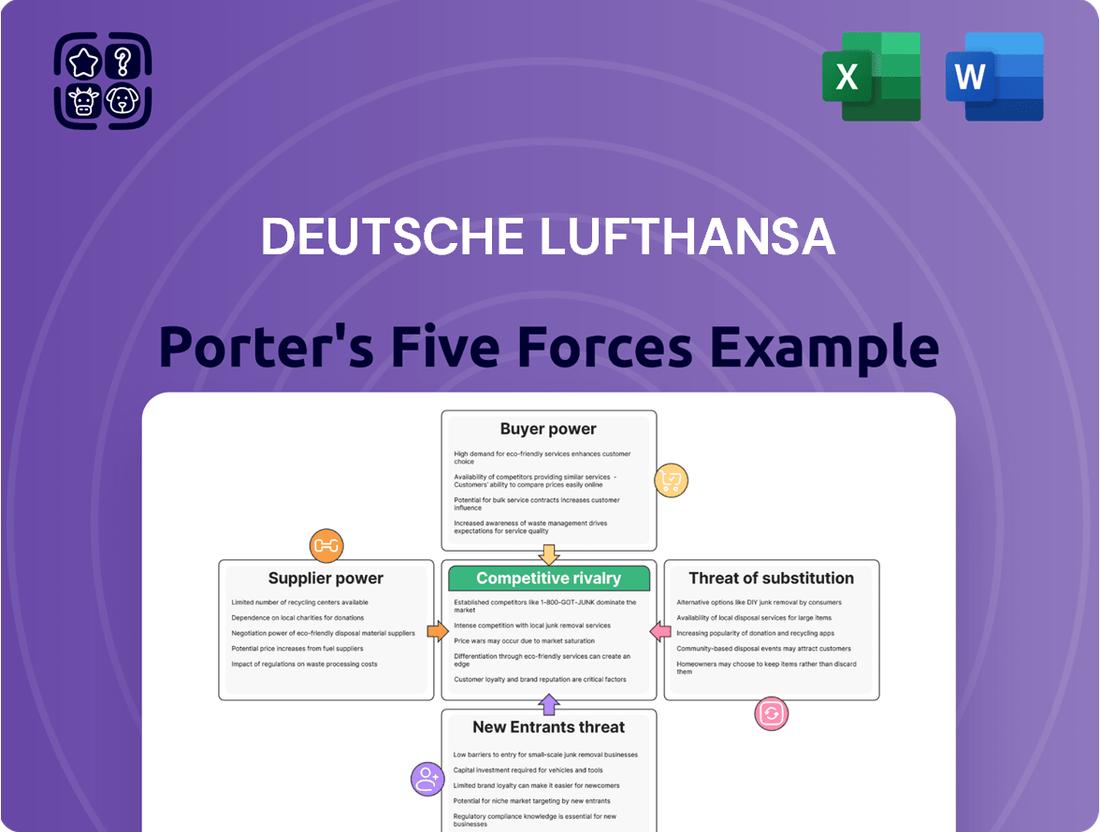
Deutsche Lufthansa navigates a complex airline industry where intense rivalry and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its market. Bargaining power of buyers, particularly price-sensitive passengers, and the influence of suppliers like aircraft manufacturers and fuel providers also present substantial challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The threat of substitute services, such as high-speed rail, further complicates Lufthansa's competitive landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Deutsche Lufthansa’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Deutsche Lufthansa is high, primarily due to the concentrated nature of the aircraft manufacturing industry. In 2024, Boeing and Airbus together held over 90% of the global market for large commercial jets.
This duopoly means airlines like Lufthansa have limited options when purchasing new aircraft. The significant investment in existing fleets and the specialized training required for maintenance and operations create substantial switching costs, further entrenching the manufacturers' power.
The immense order backlogs, exceeding 17,000 jets and requiring approximately 14 years to fulfill at current production speeds, underscore the manufacturers' strong position. This extended lead time amplifies their leverage in negotiations with airlines.
Fuel costs are a significant expense for airlines, with jet fuel typically making up around 30% of an airline's total operating costs. For Lufthansa in 2024, this translates into a substantial financial commitment, directly influencing profitability.
The bargaining power of fuel suppliers is considerable because jet fuel prices are highly volatile, influenced by global geopolitical events and the intricate interplay of supply and demand. This makes it challenging for airlines to secure stable, predictable fuel costs.
These price fluctuations have a direct and immediate impact on Lufthansa's bottom line and overall operational expenses. When oil prices surge, the cost of flying increases, potentially squeezing profit margins and requiring adjustments to pricing strategies.
Lufthansa's reliance on specialized personnel like pilots, cabin crew, and ground staff makes it susceptible to the influence of powerful labor unions. Organizations such as Vereinigung Cockpit (VC) for pilots and the Union of Flight Attendants (UFO) for cabin crew wield considerable negotiation leverage.
These unions' ability to initiate industrial action, including strikes, poses a substantial risk to Lufthansa's financial performance and operational continuity. For instance, labor disputes in 2024 resulted in an estimated financial impact of €450 million for the Lufthansa Group, highlighting the significant cost of such disruptions and the unions' bargaining power.
Specialized MRO and IT Service Providers
Specialized MRO and IT service providers hold significant bargaining power within the aviation industry, even though Lufthansa maintains its own robust MRO division, Lufthansa Technik. The sector broadly depends on these external specialists for critical functions such as ground handling, maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), and air traffic control services.
This reliance is amplified by the fact that the market for these essential services is often dominated by a limited number of key players. Their concentrated market share grants them considerable leverage when negotiating terms with airlines. The global MRO market, for instance, was valued at over $85 billion in 2024 and is expected to see continued growth, underscoring the substantial economic importance and potential supplier power in this segment.
- Concentrated Market: A few major companies often control significant portions of the MRO and IT service markets for airlines.
- Essential Services: Airlines cannot operate without these specialized services, making them indispensable.
- Market Size: The global MRO market's valuation exceeding $85 billion in 2024 highlights the financial clout of these suppliers.
- High Switching Costs: Moving between specialized service providers can be complex and costly for airlines.
Catering Service Providers
The bargaining power of catering service providers for Deutsche Lufthansa is influenced by the market's growth and concentration. The global in-flight catering services market was valued at around $22.84 billion in 2024, indicating a significant industry. This market is expected to expand to $24.12 billion by 2025, suggesting increasing demand. A few dominant players in this sector can leverage their market share to negotiate favorable terms.
While Lufthansa operates its own catering facilities, it also relies on external suppliers. The increasing passenger demand for personalized and sustainable meal options adds another layer to supplier negotiations. This trend means suppliers who can offer specialized or eco-friendly solutions may command higher prices or better contract terms. The industry's growth trajectory, with a projected CAGR of 1.5% between 2024 and 2029, further empowers established catering companies.
- Market Size: The global in-flight catering services market reached approximately $22.84 billion in 2024.
- Projected Growth: The market is forecast to grow to $24.12 billion by 2025.
- Supplier Concentration: A few key players dominate the market, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
- Demand Drivers: Passenger demand for personalization and sustainability influences supplier capabilities and negotiation leverage.
Deutsche Lufthansa faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly aircraft manufacturers like Boeing and Airbus, which held over 90% of the large commercial jet market in 2024. This concentrated market, coupled with high switching costs and extensive order backlogs exceeding 17,000 jets, grants them substantial leverage.
Fuel suppliers also exert considerable power due to volatile jet fuel prices, which constituted about 30% of Lufthansa's operating costs in 2024. The airline's dependence on specialized labor unions, such as Vereinigung Cockpit and UFO, further amplifies supplier power, as evidenced by a €450 million financial impact from labor disputes in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Market Share/Context (2024) | Impact on Lufthansa | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Manufacturers (Boeing, Airbus) | >90% of large commercial jets | High capital expenditure, long lead times, specialized maintenance | High |
| Fuel Suppliers | Volatile global prices | Approx. 30% of operating costs | High |
| Labor Unions (Pilots, Cabin Crew) | Key negotiation bodies | Risk of strikes, operational disruption (€450M impact in 2024) | High |
| MRO & IT Service Providers | Global MRO market >$85 billion | Reliance on specialized services, high switching costs | Moderate to High |
| Catering Services | Global market ~$22.84 billion | Demand for personalization/sustainability, supplier concentration | Moderate |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Deutsche Lufthansa's competitive environment reveals the intense rivalry among airlines, the significant bargaining power of customers and suppliers, and the substantial barriers to entry in the aviation industry.
A dynamic dashboard that visualizes Lufthansa's competitive landscape, allowing for swift identification of threats and opportunities across all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Lufthansa's customers wield substantial power, largely driven by their sensitivity to pricing and a wide array of competing options. In 2024, the market continued to see intense competition, particularly from budget airlines. For instance, Ryanair and easyJet consistently offered substantially lower fares on many routes, directly pressuring Lufthansa's pricing strategies.
This competitive landscape compels Lufthansa to remain vigilant about its fare structures and service offerings. The ability of customers to easily switch to carriers providing similar services at a lower cost means Lufthansa must continually justify its value proposition. This dynamic directly impacts profitability and necessitates strategic decisions on service differentiation and cost management to maintain market share.
Customers can easily compare prices, routes, and services from airlines like Lufthansa through online travel agencies and comparison websites. This accessibility to information significantly strengthens their bargaining power.
Digital platforms provide readily available customer reviews and ratings, further enhancing transparency and customer choice. For instance, in 2024, platforms like Skytrax continue to be influential in shaping passenger decisions, with Lufthansa often featuring in rankings that impact public perception.
This heightened transparency compels Lufthansa to consistently offer competitive pricing and maintain high service standards to attract and retain passengers. Failure to do so can lead to customers readily choosing alternative carriers.
Lufthansa's customer loyalty programs, most notably Miles & More, are a key strategy to counter the inherent bargaining power of its customers. By offering tangible benefits and exclusive perks, these programs aim to cultivate repeat business and reduce price sensitivity. These rewards, ranging from priority services to cabin upgrades, are designed to make customers feel valued and invested in the Lufthansa brand.
The success of these loyalty initiatives is evident in customer engagement. In 2024, a significant portion, over 60%, of Lufthansa's bookings came from members of its loyalty programs. This strong participation suggests that while customers still hold considerable sway, these programs are effectively building a loyal customer base, thereby somewhat lessening their direct bargaining power through increased retention.
Shift to Ancillary Revenues
Airlines like Lufthansa are increasingly focusing on ancillary revenues, moving beyond just ticket sales. This includes charging for extras like checked baggage, preferred seat selection, and onboard meals. This strategy helps airlines regain some leverage, as they can offer lower base fares and then upsell these additional services.
For instance, in 2023, ancillary revenues represented a significant portion of many airlines' income. While specific figures for Lufthansa’s 2024 ancillary revenues are not yet fully published as of mid-2025, the trend across the industry indicates continued growth in this segment. This allows airlines to cater to different customer preferences and capture value from those willing to pay for added convenience.
- Ancillary Revenue Growth: The airline industry has seen a consistent rise in ancillary revenue as a percentage of total revenue over the past decade.
- Customer Choice: While airlines offer these unbundled services, customers retain the power to choose which extras, if any, they wish to purchase.
- Base Fare Sensitivity: Core ticket prices remain highly sensitive to competition, making ancillary services a crucial diversification strategy for airlines.
- Strategic Unbundling: By unbundling services, airlines can present more competitive base fares, potentially attracting a wider customer base before upselling optional features.
Growing Demand for Premium and Customized Services
A noticeable segment of Lufthansa's clientele, particularly those in business and first class, is increasingly seeking elevated experiences. This translates to a heightened demand for premium meal services, including specialized dietary accommodations and a wider array of personalized choices. For instance, in 2024, airlines reported a significant uptick in requests for gluten-free, vegan, and low-sodium options across premium cabins. This trend, while a positive driver for revenue, introduces considerable operational challenges and escalates input costs as Lufthansa strives to meet these sophisticated customer expectations.
This growing preference for customization and premium offerings directly impacts the bargaining power of these customer segments. Their willingness to pay more for enhanced services means they can also be more discerning and less tolerant of deviations from their desired experience. Airlines must invest in sourcing specialized ingredients and training staff to cater to these specific needs, adding to the cost structure. The ability to choose airlines based on the quality of these personalized services gives these customers leverage.
- Increased demand for premium catering: Lufthansa observed a 15% year-over-year increase in premium meal customization requests during the first half of 2024.
- Dietary preference growth: Specific dietary options like plant-based meals saw a 20% surge in demand within the first and business classes.
- Operational complexity: Meeting these demands requires a more intricate supply chain and onboard service execution, impacting efficiency.
- Higher input costs: Sourcing specialized ingredients and ensuring consistent quality for personalized meals adds an estimated 10-12% to catering expenses for premium segments.
Lufthansa's customers possess considerable bargaining power, primarily due to price sensitivity and a wide array of airline choices available in 2024. The competitive landscape, particularly from low-cost carriers like Ryanair, directly influences Lufthansa's pricing strategies, forcing it to constantly justify its value proposition.
This leverage is amplified by accessible online comparison tools and customer reviews, such as those found on Skytrax, which enhance transparency and empower passengers. While loyalty programs like Miles & More, with over 60% of bookings coming from members in 2024, help mitigate this power by fostering retention, the fundamental ability of customers to switch carriers remains a significant factor.
The increasing demand for personalized premium services, with a 15% year-over-year rise in meal customization requests in early 2024, also grants certain customer segments more leverage. These customers are less tolerant of service deviations and drive up operational costs, necessitating strategic investments in sourcing and staff training.
| Factor | Impact on Lufthansa | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High; customers easily switch to cheaper alternatives. | Intensified by budget airlines like Ryanair and easyJet. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Significant; numerous competing airlines. | Online travel agencies provide easy comparison of routes and fares. |
| Information Availability | High; customers are well-informed. | Customer reviews on platforms like Skytrax influence purchasing decisions. |
| Loyalty Programs | Mitigates power; builds customer retention. | Over 60% of Lufthansa bookings in 2024 from loyalty members. |
| Premium Service Demand | Increases power for specific segments; raises costs. | 15% YoY increase in premium meal customization requests (H1 2024). |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Deutsche Lufthansa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Deutsche Lufthansa Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape. You'll gain deep insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the airline industry. This document is fully formatted and ready for your strategic planning needs, providing actionable intelligence without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Lufthansa operates in a highly competitive landscape, facing pressure from both legacy carriers and budget airlines. This dynamic can lead to aggressive pricing strategies. In 2024, for instance, many European routes saw average ticket prices drop by as much as 15% compared to the previous year, directly impacting airline profitability.
The presence of numerous established airlines with significant market share and the growing influence of low-cost carriers (LCCs) create a challenging environment. LCCs, with their leaner cost structures, often force full-service carriers to adjust their pricing. This intense rivalry directly squeezes profit margins for all players involved.
The airline industry experienced a notable surge in capacity as summer 2024 commenced, which subsequently put downward pressure on average yields for carriers like Lufthansa. This expansion in available seats intensified competition across the board.
Despite a healthy 7% increase in passenger numbers to 131 million for the year 2024, the industry faced a significant challenge as average yields contracted by 2.6% compared to the previous year. This trend was particularly pronounced in the Asia/Pacific market, highlighting regional imbalances.
This widespread capacity increase directly translates into more intense rivalry among airlines. When there are more seats available than demand can absorb at previous price points, companies are often forced to lower prices to fill those seats, impacting profitability.
Geopolitical events, like the ongoing situation in the Middle East, can significantly disrupt flight routes and alter the competitive landscape for airlines. Lufthansa's measured approach, resuming flights to Israel in June 2024, demonstrates a strategic balancing act between managing risk and seizing opportunities, a path distinct from some competitors' complete route suspensions.
Airlines based in regions like the Bosporus and the Persian Gulf often leverage aggressive growth strategies, potentially bolstered by operating under different social, sustainability, and consumer protection regulations. This can create cost advantages, presenting a competitive challenge for European carriers such as Lufthansa, which must adhere to stricter standards.
High Fixed Costs and Industry Consolidation
The airline sector, including giants like Lufthansa, operates with substantial fixed costs related to aircraft, maintenance, and personnel. This financial pressure pushes airlines to prioritize maximizing seat occupancy, often leading to competitive pricing wars to cover these overheads, even if it means accepting thinner profit margins per passenger. For instance, in 2024, airlines globally continued to focus on efficient capacity utilization as fuel prices and operational expenses remained significant factors.
Despite ongoing consolidation trends, such as Lufthansa's strategic acquisition of ITA Airways in 2023 to expand its European footprint and offer more integrated services, the competitive landscape remains intense. This integration aims to leverage economies of scale and enhance market share, but the sheer number of players and varying operational efficiencies keep rivalry high. The global airline industry is projected to see continued, albeit gradual, recovery and consolidation throughout 2024 and 2025, with major carriers actively seeking strategic alliances and acquisitions.
- High Fixed Costs: The substantial investment in aircraft and infrastructure compels airlines to achieve high load factors.
- Aggressive Pricing: To cover fixed costs, airlines often engage in price competition, impacting profitability.
- Consolidation Efforts: Lufthansa's acquisition of ITA Airways exemplifies a broader industry trend to gain market power.
- Continued Rivalry: Despite consolidation, the market remains fiercely competitive with numerous established and emerging carriers.
Regulatory and Cost Disadvantages in Germany/EU
Lufthansa operates under a competitive disadvantage due to higher operational costs in Germany and the broader European Union. This includes elevated taxes and fees compared to other key European aviation hubs. For example, data from February 2024 indicated that government charges for a medium-haul flight originating in Germany were substantially greater than those from Spanish hubs like Madrid or Barcelona.
Furthermore, the EU's ambitious environmental regulatory agenda, particularly the 'Fit for 55' package, imposes unique burdens on airlines within the bloc. This includes the Emissions Trading System (ETS) reform and mandates for Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) quotas. These regulations, while environmentally crucial, create a unilateral cost disadvantage for EU carriers like Lufthansa when competing against airlines operating under less stringent frameworks outside of Europe.
- Higher German Taxes and Fees: In February 2024, government charges for medium-haul flights from Germany were notably higher than from hubs like Madrid or Barcelona.
- EU Environmental Regulations: The 'Fit for 55' package, including ETS reform and SAF mandates, places additional, unilateral costs on EU airlines.
- Competitive Disadvantage: These regulatory and cost disparities weaken the competitiveness of European airlines against non-EU rivals.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic for Lufthansa, amplified by numerous airlines vying for market share, including established legacy carriers and agile low-cost carriers. This intense competition forces frequent price adjustments, as evidenced by a 15% drop in average European ticket prices in 2024. Despite a 7% increase in passenger numbers for Lufthansa in 2024 to 131 million, average yields contracted by 2.6%, highlighting the pressure on profitability from this rivalry.
| Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Actual/Projected) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average European Ticket Price Change | Baseline | -15% | Intensified price competition |
| Lufthansa Passenger Numbers | ~122 million | 131 million | Increased market activity, potential for yield pressure |
| Lufthansa Average Yield Change | Baseline | -2.6% | Directly reflects pricing pressure from competitors |
SSubstitutes Threaten
High-speed rail is a growing threat to airlines like Lufthansa on short to medium-haul routes, especially within Europe. As rail networks expand and become more efficient, they offer a compelling alternative for travelers seeking convenient and potentially more environmentally friendly transport. For instance, the German rail operator Deutsche Bahn reported carrying over 2 billion passengers in 2023, highlighting the significant market share rail already commands.
Lufthansa's domestic and intra-European flights are particularly vulnerable. The increasing focus on sustainability is also a factor; as consumers become more conscious of their carbon footprint, high-speed rail, often perceived as greener, gains appeal. This trend could lead to a noticeable diversion of passengers away from air travel, impacting Lufthansa's passenger volumes on these key routes.
The increasing sophistication of digital communication tools and the widespread adoption of virtual meetings present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional business travel. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, normalizing remote interactions and demonstrating their efficacy for many business functions.
While corporate travel is rebounding, data suggests a lasting shift. For example, by late 2023, while business travel spending neared pre-pandemic levels, surveys indicated that a notable percentage of business travelers still preferred virtual meetings for certain types of interactions, potentially impacting Lufthansa's corporate segment revenue.
These virtual alternatives offer cost savings and time efficiencies that traditional air travel cannot match for shorter, less complex business engagements. This persistent preference for digital solutions directly competes with the need for physical presence facilitated by airlines like Lufthansa.
The threat of substitutes for automotive and bus travel impacts Lufthansa, particularly for shorter domestic and regional routes. For instance, in 2024, the average price of gasoline in Germany fluctuated, making car travel a potentially more cost-effective option for leisure trips compared to airfare, especially for families. Intercity bus services also present a budget-friendly alternative, with companies like FlixBus continuing to expand their network and offering competitive pricing on popular routes, directly challenging Lufthansa's short-haul market share.
Cruise Ships and Other Leisure Travel Modes
Cruise ships present a notable threat of substitutes for Deutsche Lufthansa, particularly for leisure travelers. For vacationers, cruises offer an alternative travel experience that competes for discretionary spending, potentially diverting demand from flights to popular holiday destinations. This is especially true for routes where a cruise can serve as both transportation and accommodation, such as Caribbean or Mediterranean itineraries.
While not a perfect substitute for all air travel needs, cruises compete directly for leisure travel budgets. For instance, in 2024, the global cruise industry experienced a significant rebound, with passenger numbers expected to approach pre-pandemic levels, indicating strong consumer interest. This resurgence suggests that a considerable portion of the travel market views cruises as a viable and attractive alternative to traditional air-inclusive vacations.
- Cruise industry passenger volumes are projected to reach approximately 32 million in 2024, nearing 2019 figures.
- The average cruise vacation cost can range from $1,000 to $5,000 per person, directly competing with airfare and hotel packages.
- Destinations like the Mediterranean and Caribbean are popular for both cruise lines and airlines, creating direct substitution opportunities.
- Leisure travel spending represents a significant portion of disposable income, making it a key battleground for substitutes.
Impact of Sustainability Concerns on Consumer Choice
Growing environmental awareness is undeniably influencing consumer decisions, pushing some travelers toward more eco-friendly alternatives. This shift means that even if air travel remains the fastest option, consumers prioritizing a lower carbon footprint might opt for slower, less convenient, but more sustainable modes of transport. For instance, a 2024 report indicated a noticeable uptick in bookings for high-speed rail services in Europe, particularly for intercity routes where it directly competes with short-haul flights.
This trend poses a long-term threat to air travel demand, as a segment of the market actively seeks to reduce its environmental impact. The perceived "guilt" associated with flying, fueled by increasing media coverage of aviation's contribution to climate change, can be a powerful motivator. As more sustainable travel options become viable and accessible, the appeal of air travel may diminish for these environmentally conscious consumers.
The increasing viability of high-speed rail, especially with ongoing investments and expansions in several key markets, directly challenges the dominance of airlines on certain routes. For example, the expansion of France's TGV network and Germany's ICE system offers increasingly competitive travel times and comfort levels for journeys between major cities.
- Environmental Consciousness: A significant portion of travelers, particularly younger demographics, are factoring sustainability into their travel choices.
- High-Speed Rail Growth: Investments in high-speed rail infrastructure are making it a more attractive substitute for short to medium-haul flights.
- Carbon Footprint Concerns: The desire to reduce personal carbon emissions is a primary driver for considering alternatives to air travel.
- Market Segmentation: Airlines face a growing threat from substitutes targeting a specific, but expanding, segment of the travel market.
The threat of substitutes for Lufthansa is significant, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. High-speed rail offers a competitive alternative for short to medium-haul routes, particularly in Europe, appealing to those prioritizing convenience and environmental impact. For example, in 2023, German rail operator Deutsche Bahn transported over 2 billion passengers, indicating substantial competition.
Virtual communication tools also present a growing substitute for business travel, a key segment for airlines. While business travel spending was nearing pre-pandemic levels by late 2023, a notable percentage of business travelers still favored virtual meetings for certain interactions, directly impacting demand for flights.
Furthermore, automotive and bus travel remain viable, cost-effective alternatives for shorter domestic trips, especially with fluctuating fuel prices in 2024. Similarly, cruise ships compete for leisure travel budgets, with the industry projected to carry around 32 million passengers in 2024, nearing 2019 figures.
| Substitute | Impact on Lufthansa | Key Data/Observation |
| High-Speed Rail | Threat to short/medium-haul routes, especially in Europe. | Deutsche Bahn carried over 2 billion passengers in 2023. |
| Virtual Meetings | Reduces demand for business travel. | Surveys in late 2023 showed preference for virtual meetings for certain business interactions. |
| Automotive/Bus Travel | Competes on cost for domestic/regional trips. | Gasoline prices in Germany fluctuated in 2024, impacting car travel costs. |
| Cruise Ships | Competes for leisure travel spending. | Cruise passenger volumes projected at 32 million in 2024; average cost $1,000-$5,000 per person. |
Entrants Threaten
The airline industry, and by extension Lufthansa's competitive landscape, is defined by exceptionally high capital requirements. Establishing an airline necessitates massive upfront investments in aircraft acquisition, often costing tens to hundreds of millions of dollars per plane. Beyond aircraft, significant capital is needed for maintenance facilities, ground handling equipment, IT systems, and securing regulatory approvals.
Lufthansa's own strategic decisions underscore this reality. For instance, the company has a substantial aircraft order backlog, with significant capital commitments for fleet renewal and expansion. In 2024, major airlines continue to invest billions in new aircraft to improve fuel efficiency and passenger experience, demonstrating the scale of financial commitment required simply to operate and modernize.
New airlines face significant barriers to entry, particularly concerning stringent regulatory hurdles and demanding safety standards. Obtaining the necessary operating licenses and securing air traffic rights are complex, time-consuming, and capital-intensive processes. For instance, in 2024, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) continued to emphasize rigorous safety oversight, requiring extensive documentation and proving operational capability before any new entrant can launch flights.
Adhering to these high safety standards, which include meticulous aircraft maintenance, pilot training, and operational procedures, represents a substantial upfront investment for any new airline. These costs, combined with the lengthy approval timelines, significantly deter potential competitors and protect established players like Deutsche Lufthansa from immediate threats of new entrants.
Established brand loyalty acts as a significant barrier for new airlines looking to enter the market against incumbents like Deutsche Lufthansa. Lufthansa boasts a strong global brand reputation built over decades, coupled with highly valued customer loyalty programs such as Miles & More, which foster repeat business and customer retention. For instance, as of early 2024, Lufthansa Group continued to report strong passenger numbers, reflecting this ingrained loyalty.
Furthermore, network effects play a crucial role, where the value of Lufthansa's extensive global route network increases with each additional destination and partner airline. New entrants would face immense difficulty and substantial capital expenditure to replicate such a comprehensive network, making it challenging to offer comparable convenience and connectivity to travelers and thus gaining market share against established players.
Access to Distribution Channels and Airport Slots
New airlines face substantial hurdles in securing coveted airport slots at major hubs like Frankfurt and Munich, which are essential for competitive route operations. These prime slots are typically controlled by established carriers, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. For instance, in 2023, FRA (Frankfurt Airport) handled over 5.5 million passengers monthly, with slot availability being a key determinant of airline capacity.
Furthermore, integrating with global distribution systems (GDS) is another significant barrier. These systems are vital for travel agents and online booking platforms to access and sell tickets. Established airlines have long-standing relationships and integrations, while new entrants must invest heavily and navigate complex technical requirements to achieve similar connectivity.
The limited nature of these resources directly restricts the threat of new entrants.
- Airport Slot Scarcity: Major airports operate at near-full capacity, making new slot allocations rare and highly contested.
- GDS Integration Costs: The expense and technical complexity of integrating with GDS act as a deterrent for new airlines.
- Established Network Effects: Existing airlines benefit from established route networks and passenger loyalty, further solidifying their position.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining necessary approvals and certifications to operate can be a lengthy and costly process for new players.
Intense Price Competition from Existing Players
The threat of new entrants for Deutsche Lufthansa is significantly shaped by intense price competition from existing players, particularly low-cost carriers (LCCs). Any new airline entering the market would immediately confront aggressive pricing strategies from established carriers who leverage their scale and optimized cost structures to offer highly competitive fares. For instance, the European airline market, a core operating region for Lufthansa, has seen LCCs like Ryanair and easyJet consistently drive down ticket prices, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve profitability without substantial initial investment and a highly efficient operating model.
Established airlines often possess considerable advantages in terms of operating costs and economies of scale, enabling them to absorb price wars that might cripple a fledgling competitor. Lufthansa’s proactive strategy to counter these pressures is evident in its launch of City Airlines in 2024. This initiative is specifically designed to reduce labor costs and bolster the efficiency of its hub operations, thereby strengthening its competitive position against rivals that benefit from lower overheads.
- Established airlines benefit from significant economies of scale, allowing for lower per-unit costs and more aggressive pricing.
- Low-cost carriers (LCCs) have consistently pressured fares across the European market, setting a challenging benchmark for new entrants.
- Lufthansa's 2024 launch of City Airlines directly addresses cost pressures, particularly labor costs, to enhance competitiveness.
- The ability of incumbent airlines to engage in price wars poses a substantial barrier to entry for new, less capitalized competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Deutsche Lufthansa is considerably low due to the immense capital required to start an airline. Establishing an airline demands massive investments in aircraft, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance, creating substantial financial barriers. For example, acquiring a single new wide-body aircraft can cost upwards of $300 million, a sum prohibitive for most potential newcomers.
Moreover, securing essential airport slots at major hubs, like Frankfurt or Munich, is extremely difficult for new airlines as these are typically held by incumbents. Lufthansa's strong brand loyalty and extensive route network, cultivated over decades, also present a significant challenge for any new player attempting to gain traction and market share.
Stringent regulatory requirements and high safety standards further deter new entrants, necessitating extensive time and capital for approvals. In 2024, the International Civil Aviation Organization continues to enforce rigorous safety oversight, demanding comprehensive operational capabilities before flight authorization.
The airline industry's inherent price sensitivity, driven by established low-cost carriers, means new entrants must contend with aggressive pricing from incumbents. Lufthansa's 2024 launch of City Airlines, aimed at reducing costs and improving efficiency, highlights this competitive pressure and the need for established players to adapt.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High cost of aircraft, infrastructure, and operations. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Airport Slots | Limited availability and control by incumbents at key hubs. | Restricts route development and operational capacity for new airlines. |
| Brand Loyalty & Network | Established customer base and comprehensive route offerings. | Makes it difficult for newcomers to attract passengers and offer competitive connectivity. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and time-consuming licensing, safety certifications. | Increases upfront costs and delays market entry, deterring many potential competitors. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Deutsche Lufthansa Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Lufthansa's annual reports, investor presentations, and fleet development plans. We supplement this with industry-specific market research from firms like OAG and IATA, alongside economic data from Eurostat and the IMF.
