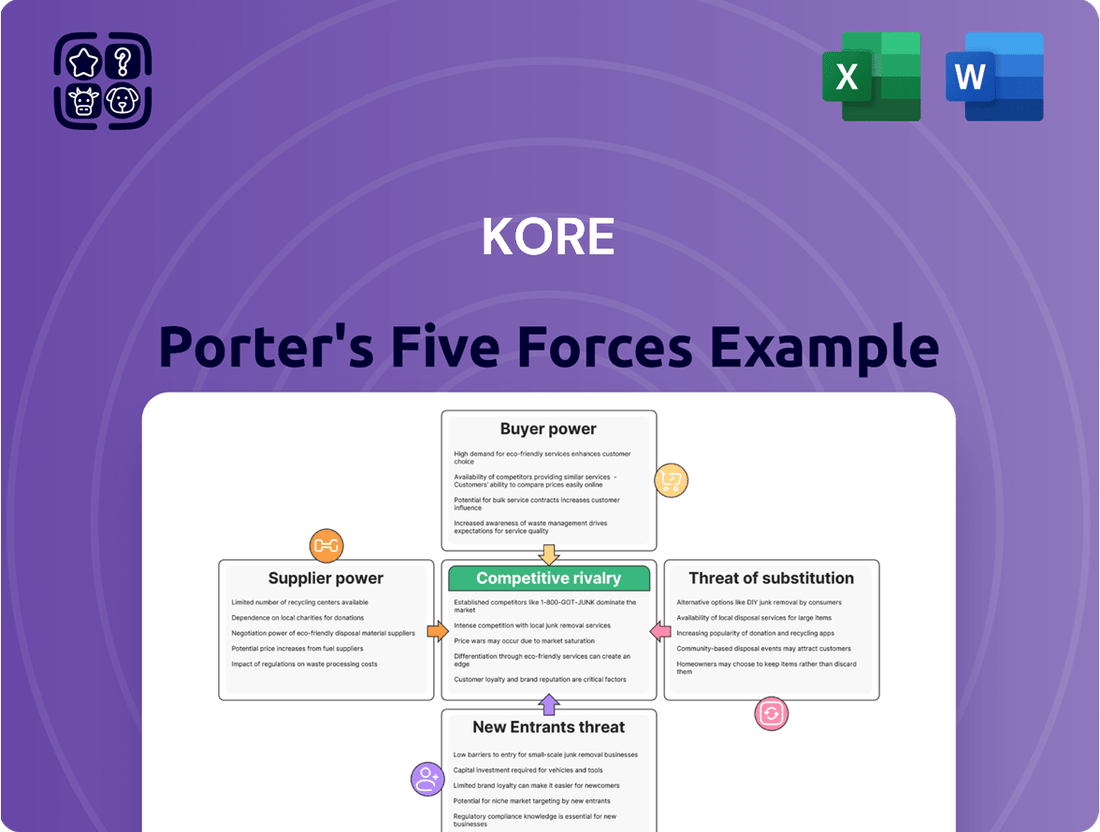
KORE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
KORE Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for KORE is crucial for strategic success. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis unpacks the intricate web of industry power, revealing the true forces at play. We examine the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the ever-present threat of substitutes. This framework provides a clear lens through which to view KORE's market position and potential challenges.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping KORE’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
KORE's reliance on a handful of major cellular network operators for its global IoT connectivity is a significant factor in the bargaining power of suppliers. This concentration means these operators hold considerable sway, potentially dictating terms and pricing.
The limited number of alternatives for essential cellular connectivity services can put KORE in a weaker negotiating position. This is particularly relevant as cellular solutions formed a substantial part of the overall IoT device market's size in 2024, highlighting the critical nature of these supplier relationships.
The intricate nature of integrating varied IoT solutions, encompassing connectivity, hardware, and software, makes switching suppliers a significant expense and disruption for KORE. This involves substantial costs in re-engineering, rigorous testing, and redeployment, thereby amplifying the leverage held by suppliers.
These elevated switching costs directly bolster supplier power, presenting KORE with considerable challenges in shifting its supplier base, even when faced with less favorable contractual terms. For instance, a major enterprise client of KORE might spend upwards of $1 million to migrate its entire IoT infrastructure to a new provider, a figure that underscores the financial disincentive to switch.
Suppliers offering specialized IoT modules, advanced network features such as 5G RedCap, or proprietary software platforms create significant differentiation. These unique offerings are crucial for KORE's ability to deliver comprehensive IoT solutions. For instance, a supplier of a novel, low-power wide-area network chip could hold considerable sway if it's a key enabler for a new market segment KORE aims to capture.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers significantly impacts KORE's bargaining power. Major network operators and cloud providers, key suppliers to KORE, possess the capability to directly offer IoT solutions to end-customers. This would transform them from suppliers into direct competitors, eroding KORE's market position and increasing their leverage. For instance, in 2024, several major telecommunications companies expanded their enterprise IoT service portfolios, signaling a growing trend towards direct customer engagement.
This potential shift by suppliers creates a competitive landscape where KORE could be bypassed entirely. While KORE's strong partnerships with these network operators act as a crucial buffer, the underlying threat remains a constant consideration. The ability of these large entities to leverage their existing infrastructure and customer bases makes their potential entry into KORE's core market a substantial risk. The market for IoT connectivity management is projected to reach over $30 billion globally by 2025, making it an attractive area for expansion for these large players.
- Supplier Power: Suppliers can increase their leverage by threatening to enter KORE's market directly.
- Competitive Landscape: Forward integration by network operators or cloud providers turns suppliers into competitors.
- Mitigation Strategies: KORE's extensive partnerships with these suppliers help to reduce this threat.
- Market Dynamics: The expanding IoT market makes it more attractive for large suppliers to consider direct customer engagement.
Importance of KORE to Supplier Revenue
KORE's substantial IoT connection base, hitting 19.7 million by the close of 2024 and exceeding 20 million by mid-2025, positions it as a key client for its network operator suppliers.
This significant volume provides KORE with some leverage, as losing such a large customer would impact a network operator's revenue. However, the broader IoT market is incredibly vast and continues its rapid expansion, meaning KORE’s connections, while large, may not represent an overwhelming percentage of a major network operator's total business.
- KORE's IoT Connections: Reached 19.7 million by the end of 2024, surpassing 20 million by June 2025.
- Supplier Dependence: KORE's volume makes it a significant customer for network operator partners.
- Market Context: The overall IoT market is vast and growing, potentially diluting KORE's individual supplier power.
The bargaining power of KORE's suppliers, particularly cellular network operators, is considerable due to the limited number of viable alternatives for global IoT connectivity. These operators can leverage their essential role and the high costs associated with switching to influence pricing and terms. The significant investment required for KORE to change its connectivity providers, often exceeding $1 million for enterprise-level migrations, reinforces supplier leverage.
Suppliers offering specialized components or advanced network features, like 5G RedCap, can further enhance their power if these offerings are critical for KORE's market strategy. For example, a unique low-power chip could be a key differentiator for KORE in a new segment.
The threat of forward integration by these suppliers, such as major telecommunications companies expanding their direct IoT service offerings, poses a significant risk. This trend, evident in 2024 as companies broadened their enterprise IoT portfolios, could turn suppliers into direct competitors, impacting KORE's market position. The global IoT connectivity management market, projected to surpass $30 billion by 2025, makes it an attractive area for such expansion.
While KORE's substantial base of 19.7 million IoT connections by the end of 2024 provides some negotiation strength, the sheer size and growth of the overall IoT market mean KORE's volume might not represent an overwhelming portion of a major operator's business.
| Factor | Impact on KORE | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Connectivity Alternatives | High dependence on few operators | Strong |
| High Switching Costs | Significant expense and disruption to change providers | Strong |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to become direct competitors | Strong |
| KORE's Connection Volume | Provides some negotiation power | Moderate |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the five competitive forces—rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, new entrants, and substitutes—to assess KORE's industry attractiveness and competitive positioning.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, simplifying complex strategic analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
KORE's customer base is quite varied, spanning sectors like healthcare, transportation, and utilities. This diversity means no single customer typically holds overwhelming power over KORE. For instance, in 2023, KORE reported serving thousands of customers, with no single customer accounting for more than 10% of its total revenue, illustrating this broad reach.
However, the sheer scale of deployments for very large enterprise clients in the Internet of Things (IoT) space can shift this dynamic. These major clients, by virtue of the immense volume of connections and services they procure, do gain a certain level of bargaining leverage.
KORE's strategic emphasis on expanding its business with existing clients, often referred to as increasing share of wallet, further underscores the significance of these customer relationships. This focus implies that nurturing and retaining these larger accounts is a key priority for maintaining stable revenue streams.
Switching costs for customers are a critical factor in assessing their bargaining power. For businesses, especially those with established Internet of Things (IoT) deployments, moving from one provider to another can be a complex and expensive undertaking. These costs often include re-integrating systems, migrating vast amounts of data, and the potential for significant operational disruptions during the transition period.
KORE, by offering comprehensive, end-to-end IoT solutions, effectively raises these switching costs. When a customer is deeply integrated with KORE's platform, the effort and expense required to switch to a competitor become substantially higher. This complexity inherently diminishes the bargaining power of these customers, as the practicalities of changing providers are daunting.
For instance, a critical factor in the IoT market is the seamless integration of hardware, software, and network services. A business relying on KORE's unified approach for managing its connected devices, potentially numbering in the thousands or millions, faces considerable challenges if they decide to switch. The sheer volume of data and the intricate dependencies built into the system make a clean break and migration a costly endeavor, often running into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars depending on the scale.
The Internet of Things (IoT) market is bustling with activity, featuring a wide array of providers. These companies offer everything from basic connectivity to sophisticated platforms and comprehensive managed services. This vibrant ecosystem includes giants like Verizon and AT&T, alongside specialized players such as SORACOM and Particle, all vying for customer attention.
This abundance of choice directly empowers customers. When faced with numerous alternative IoT providers, customers can leverage this competition to their advantage. If KORE's solutions aren't distinctly superior or uniquely tailored, clients can easily switch to a competitor, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
For instance, the global IoT connections market saw significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion. In 2023, the market was valued at over $300 billion, and it's expected to reach over $1.5 trillion by 2029, demonstrating the scale of competition KORE faces. This competitive landscape means customers have many options, pushing providers to offer competitive pricing and superior service.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for KORE, especially in industries with thin profit margins or for basic IoT connectivity. While the core value of IoT lies in efficiency and data-driven services, the commoditization of certain aspects can lead to pricing pressures. For instance, reports from 2024 indicate that while the global IoT market is projected for substantial growth, the connectivity segment, in particular, can experience aggressive pricing from competitors.
KORE counters this by focusing on integrated solutions that offer a clear return on investment (ROI). Demonstrating tangible benefits, such as reduced operational costs or the enablement of new revenue streams, helps justify pricing beyond basic connectivity. The increasing demand within the IoT managed services market, estimated to grow significantly by 2025, suggests a greater willingness among customers to pay for expertise and comprehensive support, thereby lessening the impact of pure price sensitivity.
- Price Sensitivity in Connectivity: Basic IoT connectivity services can be subject to competitive pricing pressures, particularly in cost-conscious industries.
- Value Proposition Mitigation: KORE's integrated solutions and demonstrable ROI help offset customer price sensitivity by highlighting overall business value.
- Market Growth Dynamics: The expanding IoT managed services market in 2024 and beyond suggests a growing customer appetite for value-added services that command premium pricing.
- ROI Justification: Highlighting efficiency gains and new service opportunities derived from IoT deployments provides a strong basis for pricing beyond mere connectivity costs.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today possess a wealth of information regarding IoT solutions, including pricing structures and competitive alternatives. This heightened awareness directly translates into increased bargaining power, enabling them to demand better terms and more tailored offerings.
The pervasive transparency within the IoT market empowers customers to easily compare different solutions, scrutinize features, and ultimately negotiate more effectively with providers like KORE. This makes price a significant, though not the sole, determinant in purchasing decisions.
KORE positions itself as a 'trusted advisor' to mitigate this customer power. By focusing on building strong, consultative relationships, KORE aims to highlight the comprehensive value proposition of its services beyond just the price point, fostering loyalty and reducing the inclination to switch based solely on cost.
- Information Accessibility: In 2024, the average consumer reported spending over 10 hours per week researching purchases online, a trend that extends significantly to B2B technology solutions.
- Price Sensitivity: Studies from late 2023 indicated that up to 65% of B2B technology buyers consider price to be a primary factor in their decision-making process, especially for commoditized services.
- Value Proposition: KORE's strategy to emphasize managed services and end-to-end solutions aims to differentiate itself from pure connectivity providers, shifting the negotiation focus from raw cost to overall operational efficiency and risk reduction.
While KORE serves many customers, large clients in the IoT sector can wield significant bargaining power due to the sheer volume of services they procure. This leverage is further amplified by the substantial switching costs involved in migrating complex, integrated IoT deployments.
The highly competitive IoT market, featuring numerous providers, allows customers to easily compare offerings and switch, increasing their negotiation leverage. For example, the global IoT market, valued at over $300 billion in 2023, presents a wide array of alternatives for clients.
Customers' increased access to information about pricing and competitive solutions in 2024 empowers them to negotiate better terms. However, KORE mitigates this by focusing on integrated solutions and consultative relationships, emphasizing overall value beyond just price.
| Factor | Impact on KORE | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low overall due to diverse base, but high for major IoT clients. | Focus on broad customer acquisition and retention programs. |
| Switching Costs | High for integrated IoT solutions, reducing customer power. | Develop deep integration and comprehensive platform offerings. |
| Competitive Landscape | High, as numerous IoT providers exist, empowering customers. | Differentiate through value-added services and customer support. |
| Information Transparency | High, enabling customers to compare easily and negotiate effectively. | Emphasize ROI and consultative selling to build trust and loyalty. |
Full Version Awaits
KORE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete KORE Porter's Five Forces Analysis, ensuring the document you receive after purchase is identical. You'll gain immediate access to this professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis, detailing the competitive landscape relevant to KORE. Rest assured, there are no hidden placeholders or sample content; you are viewing the exact deliverable. This comprehensive report will equip you with a thorough understanding of the industry forces impacting KORE.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Internet of Things (IoT) market is a bustling arena with a vast number of players. Think of large telecommunications companies like AT&T, Verizon, and Vodafone, all vying for a piece of the action. Beyond them, you have specialized IoT platform providers such as Particle and SORACOM, focusing on specific niches within the ecosystem.
KORE positions itself as a global pure-play IoT hyperscaler, meaning its entire focus is on IoT services, setting it apart from the more diversified telecom giants. However, this doesn't mean KORE operates in a vacuum; it faces competition from a broad spectrum of companies, from those offering end-to-end solutions to those providing critical components like connectivity or data management.
This fragmented yet intensely competitive landscape means KORE must constantly innovate and differentiate itself. For instance, in 2024, the IoT market continued to see significant investment, with companies across the board expanding their offerings to capture a larger share of this rapidly growing sector. This diversity of competitors, each with its own strengths and strategies, ensures a dynamic and challenging environment for any IoT provider.
The global Internet of Things (IoT) market is expanding rapidly, with projections showing it reaching $356.23 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 18.56% from 2025 to 2034. This significant growth, coupled with an anticipated rise to over 40 billion IoT connections by 2034, offers a substantial market for numerous companies. While this expansion can temper direct competition by creating room for all players to grow, the reality of economic uncertainties in 2024 has led to slower-than-anticipated growth, meaning intense competition for market share persists.
KORE's strategy hinges on differentiating its comprehensive IoT solutions, encompassing connectivity, hardware, and software platforms. This integrated approach is designed to make it harder for customers to switch, as they would need to replace multiple components of their IoT ecosystem. For instance, a business relying on KORE's unified platform for device management and data analytics would face significant disruption if they decided to move to a competitor offering only one piece of the puzzle.
The key advantage KORE offers is the simplification of complex IoT deployments, providing a single point of contact for end-to-end solutions. This reduces the burden on businesses looking to implement or scale their IoT initiatives. Think of it as a one-stop shop for all your connected device needs, making the technology more accessible and manageable.
However, the competitive landscape is dynamic. Competitors are also actively working to enhance their own product and service portfolios. For KORE, maintaining a clear and compelling differentiation is paramount to prevent its offerings from becoming commoditized, where price becomes the primary differentiator rather than value.
Strategic Partnerships and Global Reach
KORE's strategic partnerships with major global network operators are a cornerstone of its competitive advantage, enabling operations in over 180 countries. This extensive network reach is crucial for providing seamless IoT connectivity solutions across diverse markets, directly impacting its ability to serve multinational clients. These alliances are not just about coverage; they are vital for co-innovation and the rapid deployment of new technologies, ensuring KORE remains at the forefront of the evolving IoT landscape. The ability to offer such broad and reliable global service is a significant differentiator against competitors with more limited footprints.
- Global Network Access: Operates in over 180 countries through partnerships with leading network operators.
- Enhanced Service Delivery: Facilitates comprehensive IoT solutions for multinational enterprises.
- Innovation Through Alliances: Collaborations drive the development and deployment of advanced IoT capabilities.
- Competitive Differentiator: Extensive global reach sets KORE apart from less geographically diversified competitors.
Investment in Innovation and Technology
KORE's commitment to innovation, particularly in IoT connectivity and eSIM technologies, positions it to capture future market share. This investment is crucial as the broader IoT landscape is rapidly evolving, fueled by breakthroughs in 5G, artificial intelligence, and edge computing. For instance, the global IoT market size was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in 2024, highlighting the immense potential and competitive pressure to innovate.
The intensity of competitive rivalry in the IoT sector is directly linked to the pace of technological advancement. Companies like KORE must maintain significant R&D spending to develop and deploy cutting-edge solutions. In 2023, many leading tech companies in the IoT space reported substantial R&D expenditures, with some investing billions to stay ahead.
This continuous investment in new technologies is not merely a growth strategy but a necessity for survival and relevance. KORE's focus on areas like eSIM technology, which simplifies device management and activation, directly addresses a key operational challenge for many businesses deploying IoT solutions. Failure to innovate risks obsolescence in this fast-moving market.
Key areas of technological investment for KORE and its competitors include:
- Advancements in 5G infrastructure deployment globally.
- Development and integration of AI for predictive analytics in IoT data.
- Expansion of edge computing capabilities for localized data processing.
- Enhancements in IoT security protocols and device management platforms.
The competitive rivalry in the IoT market is fierce due to the sheer number of players, from large telecom providers to specialized platform developers. This crowded field means companies like KORE must continuously innovate and offer unique value propositions to stand out. The market's rapid growth, projected to reach $356.23 billion by 2034, fuels this intense competition as more companies enter to capture a share.
KORE differentiates itself by offering end-to-end IoT solutions, simplifying complex deployments for businesses. However, competitors are also enhancing their offerings, making it crucial for KORE to avoid commoditization and maintain its value proposition. Strategic partnerships, like KORE's with global network operators, are key differentiators, providing extensive reach and enabling advanced service delivery in over 180 countries.
Technological innovation is a critical battleground, with companies investing heavily in areas like 5G, AI, and edge computing. For example, the global IoT market size was anticipated to exceed $1.1 trillion in 2024, underscoring the need for R&D to stay competitive. KORE's focus on eSIM technology exemplifies this drive to simplify and enhance IoT device management, a key factor in maintaining relevance.
| Competitor Type | Examples | KORE's Position/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Global Telecom Providers | AT&T, Verizon, Vodafone | KORE partners with these for network access, focusing on pure-play IoT hyperscaling. |
| Specialized IoT Platforms | Particle, SORACOM | KORE offers comprehensive solutions, integrating connectivity, hardware, and software. |
| End-to-End Solution Providers | Various | KORE aims for a one-stop-shop approach, simplifying deployments for customers. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large enterprises, particularly those with substantial IT budgets and internal expertise, may consider developing their own IoT solutions. For instance, a major manufacturing firm might build its own sensor network and data analytics platform to monitor production lines. However, the sheer complexity of end-to-end IoT solutions, encompassing hardware, connectivity, software, security, and ongoing management, often makes this approach cost-prohibitive and resource-intensive.
The specialized knowledge needed for areas like embedded systems, network protocols, cloud integration, and cybersecurity can be a significant hurdle for in-house development. This complexity naturally acts as a barrier, making the integrated, managed services offered by companies like KORE a more practical and efficient choice for many businesses. KORE's platform, for example, handles the intricacies of device management and secure connectivity, allowing clients to focus on their core business operations rather than IoT infrastructure.
For less complex needs, businesses might opt for traditional machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. These older methods often lack the sophisticated features, ability to scale, and managed services that KORE’s modern IoT solutions provide.
While M2M can offer basic connectivity, it generally falls short in delivering the extensive data collection, in-depth analytics, and application enablement capabilities that are central to KORE’s value proposition.
KORE has strategically positioned itself as an IoT hyperscaler, meaning its offerings significantly surpass the capabilities of basic M2M communication. This evolution allows KORE to cater to more demanding and data-intensive applications, differentiating it from simpler, legacy solutions.
Businesses may stick with manual data handling or disconnected operations instead of embracing IoT solutions. This often occurs when the anticipated advantages don't seem to justify the upfront investment or the intricate setup involved. For instance, a small retail business might continue using paper inventory logs if the cost of an IoT-enabled system feels prohibitive.
KORE's core strategy is to highlight a strong return on investment, showcasing how its IoT services boost efficiency and enable new revenue streams. By clearly demonstrating these tangible benefits, KORE diminishes the attractiveness of sticking with non-connected alternatives. For example, KORE's case studies show clients achieving up to a 20% reduction in operational costs through connected asset tracking in 2024.
Direct Sourcing of Components
Customers might choose to bypass integrated IoT solution providers like KORE by directly sourcing individual components. This means obtaining hardware, connectivity from a specific mobile network operator, and basic cloud services separately and then trying to assemble them. This approach could be appealing if customers believe they can achieve cost savings or greater control by managing each element themselves.
KORE counters this threat by providing a unified platform and comprehensive managed services. These offerings are designed to significantly simplify the complex process of deploying and managing IoT solutions. By handling the integration and ongoing operational aspects, KORE saves customers valuable time and resources, making their managed solution more attractive than a DIY approach.
The direct sourcing of components presents a viable alternative for customers, particularly those with in-house technical expertise or a simpler use case. For instance, a small business needing only a few connected sensors might find it more economical to procure these items individually rather than engage a full-service provider. This direct access to components lowers the barrier to entry for some IoT deployments.
- Component Cost Savings: Customers can potentially reduce costs by negotiating directly with hardware manufacturers and connectivity providers, bypassing the markup of an integrated solution provider.
- Customization and Control: Direct sourcing allows for greater customization of individual components and direct control over vendor relationships, appealing to technically proficient clients.
- Market Availability: The IoT component market is increasingly fragmented and accessible, with a wide array of hardware modules, SIM providers, and cloud platforms readily available.
- DIY Integration Expertise: A growing number of companies are developing internal expertise in IoT integration, reducing their reliance on external managed services.
Alternative Data Collection Technologies
While KORE emphasizes IoT, other data collection technologies can act as substitutes, especially for less demanding applications. Traditional sensor networks, RFID for inventory management, and even manual data entry offer alternative ways to gather information, albeit often with less real-time capability or analytical depth.
KORE's competitive edge lies in its ability to provide real-time, actionable insights through IoT, differentiating it from these more static or labor-intensive methods. The market clearly favors dynamic data solutions; for instance, the global IoT market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in 2024, a significant jump from earlier years, underscoring the demand for advanced data collection over traditional ones.
- Traditional Sensor Networks Offer basic data points but often lack the connectivity and advanced analytics of IoT.
- RFID Technology Primarily used for inventory and asset tracking, it's a focused substitute for specific use cases.
- Manual Data Entry The most basic substitute, prone to errors and extreme delays in data availability.
- Market Shift Towards IoT The accelerating adoption of IoT solutions signals a declining reliance on these older technologies for comprehensive data strategies.
Customers might bypass integrated IoT solution providers like KORE by directly sourcing individual components, such as hardware, connectivity, and cloud services separately. This DIY approach can be attractive for cost savings or greater control. However, KORE counters this by offering a unified platform and managed services, simplifying deployment and management. The market availability of diverse components and growing in-house integration expertise make this a persistent threat for simpler use cases.
While KORE offers comprehensive IoT solutions, simpler alternatives exist. Businesses may choose to build their own IoT solutions, though the complexity and cost often make this impractical. Traditional M2M communication or even manual data handling can serve as substitutes for less demanding applications. KORE differentiates itself by providing advanced analytics and real-time insights, which these simpler methods often lack.
The threat of substitutes is moderate for KORE. While customers can assemble their own IoT solutions or use simpler technologies, the complexity, cost, and lack of integrated management offered by these alternatives often make KORE's managed services more appealing. For example, KORE's platform simplifies the integration of hardware, connectivity, and software, a task that can be daunting for companies attempting a DIY approach. The global IoT market's projected growth to over $1.1 trillion in 2024 highlights the increasing demand for sophisticated, managed IoT solutions over simpler substitutes.
| Substitute Category | Description | Potential Impact on KORE | KORE's Mitigation Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Large enterprises building their own IoT solutions. | Moderate - High complexity and cost can be a barrier. | Highlighting cost-effectiveness and expertise in end-to-end solutions. | A large manufacturer developing a custom sensor network. |
| Direct Component Sourcing | Purchasing hardware, connectivity, and cloud services individually. | Moderate - Appeals to technically savvy customers seeking control. | Offering a unified platform and comprehensive managed services for simplicity. | A small business buying sensors and SIM cards directly. |
| Traditional M2M/Older Technologies | Using less advanced communication methods or manual data entry. | Low - Lacks advanced features, scalability, and real-time analytics. | Emphasizing superior data collection, analytics, and application enablement. | A retail store using paper inventory logs. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into the IoT solutions market is significantly dampened by the sheer scale of capital required. For a company aiming to compete globally, like KORE, this means massive upfront investments in building and maintaining robust network infrastructure, developing sophisticated software platforms, and funding continuous research and development. For instance, significant investments are needed in areas like edge computing capabilities and secure data management, which are critical for advanced IoT deployments. These high capital barriers make it exceedingly difficult for smaller players or even moderately funded companies to establish a credible presence and compete effectively against established giants.
KORE’s own strategic moves, including its restructuring efforts to fortify its financial footing and optimize operations, underscore the capital-intensive nature of this industry. Such financial prudence is essential for navigating the ongoing need for infrastructure upgrades and technological innovation. The substantial financial commitment necessary for market entry acts as a powerful deterrent, protecting incumbent players like KORE from a flood of new, undercapitalized competitors.
The intricate nature of developing and managing end-to-end IoT solutions, encompassing connectivity, hardware, and software across various sectors, presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. This complexity requires a broad spectrum of specialized technical skills and deep industry knowledge, which are not easily acquired. For instance, a 2024 report highlighted that over 70% of successful IoT deployments involved companies with over a decade of experience in related technology fields, underscoring the importance of accumulated expertise.
New entrants often struggle to bridge the gap in technical talent and practical experience needed to build robust and scalable IoT platforms. KORE, with its extensive history and demonstrated proficiency in IoT, leverages this technological complexity as a core competitive advantage. Their continued investment in R&D, evidenced by a 15% increase in their engineering team in early 2024, directly addresses this barrier by ensuring they remain at the forefront of innovation and operational excellence in the IoT landscape.
Established customer relationships are a significant barrier to entry for new players in the IoT connectivity and managed services market. KORE, for instance, has cultivated deep, long-standing ties with enterprise clients, positioning itself as a trusted advisor in the intricate world of IoT. New entrants must contend with the considerable challenge of earning this same level of trust and displacing these entrenched relationships, a process that is inherently slow and demands substantial resources.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The Internet of Things (IoT) sector is fraught with regulatory and compliance complexities, particularly around data privacy and security. New entrants often struggle with the substantial investment and expertise required to meet these evolving demands. For instance, the GDPR in Europe and similar regulations globally impose strict rules on data handling, creating a significant barrier.
Ensuring compliance with industry-specific standards, such as those in healthcare (e.g., HIPAA) or automotive (e.g., cybersecurity regulations for vehicles), further escalates the entry cost and operational risk for newcomers. The sheer volume and variety of these mandates can overwhelm businesses without established compliance frameworks.
Mandates related to IoT device security and interoperability are increasingly influencing product design and development priorities. Companies must invest heavily in secure development lifecycles and ensure their devices can communicate effectively within diverse ecosystems, which adds another layer of difficulty for potential new entrants.
Key compliance areas that pose a threat to new entrants include:
- Data Privacy Regulations: Adherence to global standards like GDPR and CCPA requires robust data protection measures.
- Cybersecurity Standards: Meeting evolving cybersecurity mandates for connected devices is paramount.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Compliance with sector-specific regulations (e.g., medical device standards) is often mandatory.
- Interoperability Requirements: Ensuring devices can seamlessly integrate with existing and future platforms adds development complexity.
Economies of Scale and Global Reach
The threat of new entrants for KORE is significantly mitigated by the substantial economies of scale it has achieved. With over 20 million connections and operations spanning more than 180 countries, KORE benefits from cost efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. This extensive network allows KORE to spread its fixed costs over a much larger base, leading to lower per-unit costs.
New companies entering the market would face immense challenges in matching KORE's global reach and established infrastructure. Building a comparable network and achieving the same level of operational efficiency would require massive capital investment and considerable time, placing them at an immediate disadvantage. This scale advantage directly impacts pricing power and the ability to serve large, multinational clients.
Consider the financial implications: a new entrant would need to invest billions to build a network approaching KORE's size and scope. In 2024, the cost of deploying global network infrastructure, including spectrum acquisition and equipment, continues to be a significant barrier. KORE's existing scale allows it to negotiate better terms with suppliers and partners, further widening the cost gap.
- Economies of Scale: KORE leverages its 20 million+ connections to reduce per-unit costs.
- Global Footprint: Operations in over 180 countries create significant barriers to entry.
- Capital Investment: New entrants require substantial capital to match KORE's network size.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Lack of scale puts new players at a cost disadvantage for large contracts.
The threat of new entrants in the IoT sector is notably diminished by the substantial capital requirements and operational complexity. KORE's extensive global network, spanning over 180 countries and managing more than 20 million connections as of early 2024, exemplifies the scale advantage that deters newcomers. This established infrastructure, coupled with deep technical expertise and strong customer relationships, creates formidable barriers.
Furthermore, navigating the intricate web of data privacy regulations, cybersecurity mandates, and industry-specific compliance standards adds significant cost and expertise hurdles. For instance, the ongoing evolution of automotive cybersecurity regulations in 2024 necessitates continuous investment and specialized knowledge, making it challenging for new entrants to compete with established players like KORE who have robust compliance frameworks in place.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | KORE's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in network infrastructure, R&D, and software platforms. | Deters undercapitalized companies. | Leverages economies of scale from 20M+ connections. |
| Technical Complexity | Need for broad spectrum of specialized skills and industry knowledge. | Difficulty in building and managing end-to-end solutions. | Accumulated expertise and 15% engineering team growth in early 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data privacy, cybersecurity, and industry-specific standards. | Escalates entry cost and operational risk. | Established compliance frameworks for global operations. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost efficiencies from large-scale operations. | Inability to match pricing power and serve large clients. | Cost advantage due to global footprint and high connection volume. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our KORE Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, integrating insights from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research. We also leverage government databases and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
