Johnson Electric Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Johnson Electric Holdings Bundle
Johnson Electric Holdings navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the constant pressure of substitute products, particularly in the electronics components sector. The bargaining power of buyers, especially large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), significantly influences pricing and product specifications. While the threat of new entrants can be moderate due to capital requirements, established players must remain vigilant.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Johnson Electric Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Johnson Electric's reliance on specialized components like rare earth magnets and advanced electronic controls highlights the potential for supplier concentration to influence its bargaining power. Suppliers with proprietary technologies or exclusive access to critical raw materials can command higher prices, directly impacting Johnson Electric's cost structure.
For instance, the market for certain rare earth magnets, crucial for the efficiency of Johnson Electric's motors, has seen significant price volatility. In 2023, prices for Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets, a key component, experienced fluctuations driven by geopolitical factors and production capacities in major supplying nations, which directly translates to increased input costs for manufacturers like Johnson Electric.
This concentration means fewer suppliers have substantial leverage. If a small number of firms dominate the supply of these niche materials, they can dictate terms, potentially leading to increased procurement costs and disruptions if supply is constrained.
The complexity and customization inherent in electro-mechanical components significantly elevate switching costs for Johnson Electric. When Johnson Electric needs to change suppliers, it often faces substantial expenses related to redesigning its products, retooling its manufacturing facilities, and conducting rigorous testing and re-qualification with its own customers. These high barriers to switching suppliers directly translate to increased leverage for those suppliers.
Suppliers offering unique, patented components essential for Johnson Electric's advanced product lines wield significant bargaining power. For instance, a supplier of a highly specialized micro-motor for a cutting-edge medical device, with no readily available alternatives, can command higher prices. This uniqueness directly impacts Johnson Electric's ability to maintain its competitive edge in demanding sectors like automotive and healthcare.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into manufacturing motion products presents a significant challenge to Johnson Electric. If suppliers, particularly those providing key components, decide to produce complete motor systems, they would directly compete with Johnson Electric, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
This scenario is more plausible for component manufacturers than for highly specialized raw material providers. For instance, a supplier of advanced motor controllers or specialized windings might possess the technical expertise to assemble these into finished motor units.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Suppliers developing their own motor systems directly challenges Johnson Electric's market position.
- Component Manufacturers: This threat is more pronounced for suppliers of integrated components rather than basic raw materials.
- Increased Competition: Successful forward integration by suppliers would introduce new, vertically integrated competitors into the market.
Importance of Johnson Electric to Suppliers
The bargaining power of Johnson Electric's suppliers is significantly influenced by how crucial Johnson Electric is as a customer to them. If a supplier relies heavily on Johnson Electric for a substantial portion of its sales, that supplier will likely be more amenable to negotiating favorable pricing and terms. This dependence gives Johnson Electric leverage to secure better deals.
Conversely, if Johnson Electric is a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, its influence wanes. In such scenarios, the supplier has less incentive to compromise, as losing Johnson Electric's business would have a minimal impact on its overall revenue. This asymmetry in dependence shifts the bargaining power towards the supplier.
- Customer Dependence: Johnson Electric's sales volume relative to a supplier's total revenue is a key determinant of supplier bargaining power.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base are less affected by losing Johnson Electric, thus reducing Johnson Electric's negotiating strength.
- Market Position of Suppliers: If suppliers are dominant in their respective markets and have few alternatives, their bargaining power increases.
Suppliers of highly specialized or proprietary components, such as advanced rare earth magnets or unique electronic control units, hold considerable sway over Johnson Electric. This is amplified when these suppliers control critical raw materials or possess patented technologies, limiting Johnson Electric's options and potentially driving up costs. For example, the global market for Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) magnets, vital for Johnson Electric's high-performance motors, saw price increases in 2023 due to supply chain constraints and demand from the electric vehicle sector, impacting Johnson Electric's procurement expenses.
The high cost and complexity associated with switching suppliers, due to product redesign and retooling, further solidify supplier leverage. If Johnson Electric is a small client for a supplier, or if the supplier is a dominant player in its niche, the supplier's bargaining power increases significantly, as demonstrated by the dependence of many component manufacturers on securing large contracts from key players like Johnson Electric to maintain their own production volumes.
The potential for suppliers to engage in forward integration, moving from component manufacturing to producing finished motor systems, poses a direct competitive threat and enhances their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant for suppliers of integrated components rather than basic raw materials, as they possess the technical capability to assemble complete units, thereby directly challenging Johnson Electric's market position.
What is included in the product
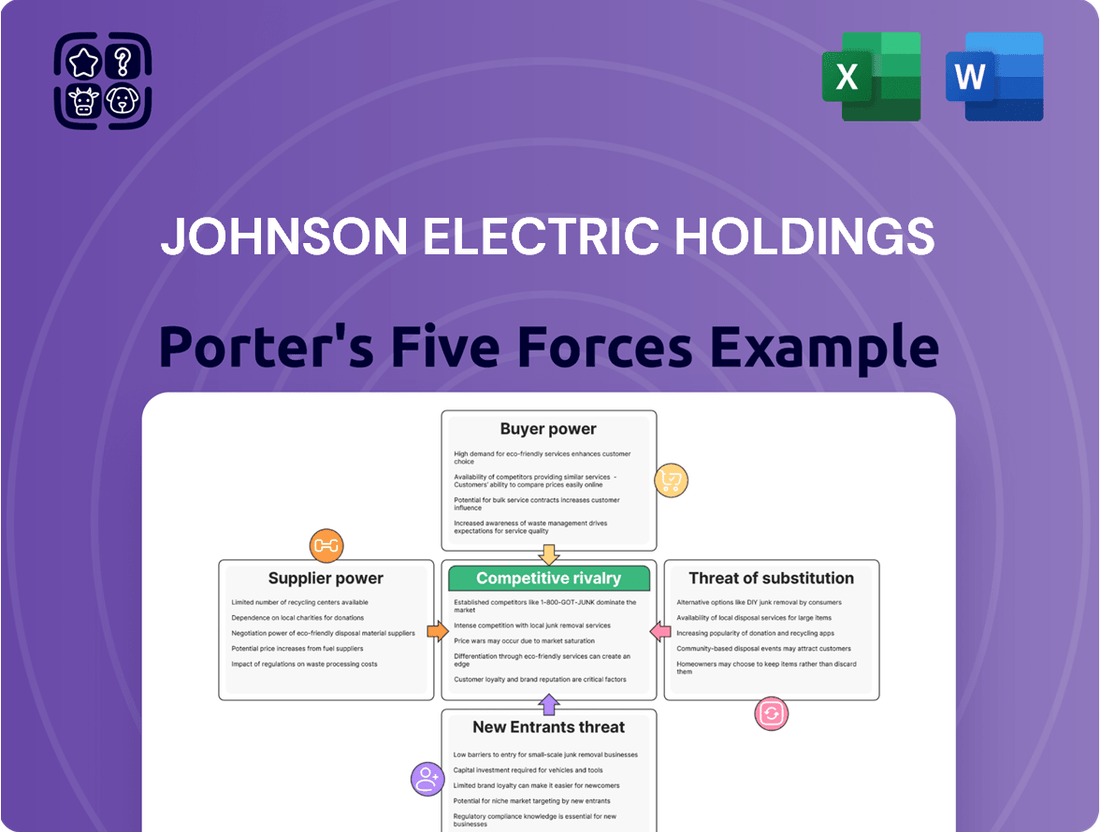
This analysis assesses Johnson Electric Holdings' competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Effortlessly identify competitive pressures with a visual representation of Johnson Electric's industry landscape, aiding in strategic response.
Customers Bargaining Power
Johnson Electric serves large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in sectors like automotive, smart home, and medical devices. These major customers represent concentrated demand and significant purchase volumes.
The sheer scale of their orders gives these OEMs considerable leverage. They can negotiate aggressively on pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Johnson Electric's profitability.
For instance, a single automotive OEM might account for a substantial portion of Johnson Electric's revenue, making that customer's demands particularly impactful. This concentration amplifies their bargaining power.
This power is further enhanced by the customers' ability to switch suppliers if terms are not met. The threat of losing a large, consistent order is a key factor in these negotiations.
Customers face substantial switching costs with Johnson Electric due to the highly specialized nature of its electro-mechanical solutions. For instance, integrating new motors or actuators into a vehicle's intricate electronic architecture or a medical device's critical systems demands extensive redesign, rigorous testing, and often complex regulatory re-approvals. This process is both time-consuming and financially burdensome, effectively locking customers into existing supplier relationships.
Customers in sectors such as automotive and smart home appliances, which often have tight profit margins, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are keenly focused on minimizing component costs to safeguard their own profitability.
This heightened sensitivity exerts considerable pressure on Johnson Electric to offer competitive pricing, even for highly specialized or customized products. For example, in the automotive sector, where component costs can represent a substantial portion of a vehicle's manufacturing expense, buyers frequently seek the lowest possible prices.
In 2024, the global automotive industry, a key market for Johnson Electric, continued to navigate economic uncertainties, including fluctuating raw material costs and evolving consumer demand for electric vehicles, further amplifying the need for cost efficiency at every supply chain level.
As a result, Johnson Electric must constantly balance the need for innovation and quality with the imperative to provide cost-effective solutions, as customers will readily explore alternative suppliers if price points are not met.
Product Differentiation and Importance to Customer's End Product
Johnson Electric's extensive engineering capabilities and diverse product range enable significant differentiation through tailored solutions. These customized motion products often serve as critical, high-value components, directly impacting the performance and brand image of their customers' end products. This inherent criticality can limit a customer's bargaining power.
When Johnson Electric's motors and motion systems are integral to a client's product, particularly in high-performance applications like automotive or advanced medical devices, switching costs can be substantial. For example, in the automotive sector, where Johnson Electric supplies components for electric vehicle powertrains and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), the deep integration and rigorous testing required make finding and qualifying alternative suppliers a lengthy and costly process.
- Customized Solutions: Johnson Electric's ability to engineer bespoke motion solutions reduces the commoditization of its offerings.
- Critical Component Integration: For clients in sectors like automotive and medical, where product failure is not an option, Johnson Electric's reliable and precisely engineered components are indispensable.
- High Switching Costs: The deep integration of Johnson Electric's products into customer systems, particularly those requiring specialized performance and regulatory compliance, creates significant barriers to switching suppliers.
- Brand Reputation Impact: The quality and performance of Johnson Electric's motion systems directly affect their customers' brand reputation, making performance and reliability paramount over price alone.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large automotive and industrial clients, such as major car manufacturers or industrial equipment producers, often possess the substantial financial resources and advanced technical expertise necessary to consider producing certain motion components themselves. This capability, even if not fully realized, acts as a potent lever in negotiations.
The mere credible threat of backward integration by these significant customers can significantly enhance their bargaining power. This compels Johnson Electric to be more competitive on pricing and contract terms to secure and retain these vital relationships.
Consider the automotive sector, where major OEMs often have R&D departments and manufacturing capabilities that could, in theory, be redirected to component production. For instance, a leading automotive manufacturer might spend billions annually on components, making even a small percentage of in-house production a significant consideration if supplier terms become unfavorable.
- Customer Capability: Major clients in sectors like automotive or industrial machinery often have the financial clout and technical know-how to explore in-house component production.
- Negotiating Leverage: The potential for customers to backward integrate provides them with increased bargaining power, influencing pricing and terms offered by suppliers like Johnson Electric.
- Market Dynamics: This threat is particularly relevant when dealing with large-volume buyers who represent a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue.
Johnson Electric's large Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) clients, particularly in the automotive sector, wield significant bargaining power due to their concentrated demand and substantial purchase volumes. This leverage allows them to negotiate aggressively on pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Johnson Electric's profitability.
Customers in price-sensitive markets like automotive, where component costs are critical, exert considerable pressure for competitive pricing. For example, in 2024, the automotive industry's focus on cost efficiency due to economic uncertainties meant buyers were keenly seeking the lowest possible prices for essential components.
The threat of customers switching suppliers, though mitigated by Johnson Electric's specialized solutions and high switching costs, remains a potent negotiation tool. The potential for major clients to bring production in-house also adds to their leverage.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Impact on Johnson Electric |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive OEMs | High purchase volume, price sensitivity, potential for backward integration | Pressure on pricing, demand for cost-effective solutions |
| Smart Home OEMs | Standardized product needs, focus on Bill of Materials (BOM) cost | Negotiation on volume discounts, potential for supplier competition |
| Medical Device OEMs | Critical component integration, regulatory compliance, high switching costs | Reduced price pressure due to product criticality and integration complexity |
What You See Is What You Get
Johnson Electric Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Johnson Electric Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The electric motor and motion subsystem market boasts a robust and varied competitive field. Major global players like Nidec and Mabuchi Motor compete fiercely with specialized manufacturers. This diverse group, including names such as Panasonic Industry Europe, Mitsubishi Electric, Regal Rexnord, and ABB, creates a dynamic environment where each company strives to capture market share across a wide array of applications.
The electric motor and motion control sectors are seeing consistent expansion. The global electric motor market is anticipated to grow from $155.40 billion in 2025 to $258.17 billion by 2032. Similarly, the motion control market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of around 5.9% between 2025 and 2034.
While this overall market growth can sometimes temper competitive pressures, certain key segments, particularly automotive and smart home components, remain intensely competitive for companies like Johnson Electric. These growth areas, despite their overall market expansion, are characterized by significant rivalry.
Johnson Electric leverages its strong engineering capabilities to offer highly customized electro-mechanical solutions. This focus on tailored products sets them apart and reduces direct competition based purely on price.
While Johnson Electric excels in differentiation, rivals are also investing in their own unique product offerings and service enhancements. For instance, many competitors in the automotive and industrial sectors are also pushing for advanced, integrated solutions, necessitating ongoing R&D for Johnson Electric.
The drive for innovation is critical; in 2023, the global electric motor market, a key area for Johnson Electric, saw significant growth driven by demand for energy-efficient and specialized motors, indicating the competitive landscape's focus on technological advancement.
This constant need to innovate and differentiate means Johnson Electric must continually invest in research and development to avoid its offerings becoming standardized, which would then invite more intense price wars.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Johnson Electric operates in an industry characterized by significant fixed costs. Think of the massive investments needed for advanced manufacturing plants, cutting-edge research and development, and highly specialized machinery. These aren't small, easily recouped expenses.
These substantial upfront investments, combined with assets that are difficult to repurpose and deep-seated, long-term relationships with clients, erect formidable exit barriers. It becomes incredibly challenging and costly for companies to simply walk away from the market.
As a result, even when the industry faces economic downturns or reduced demand, companies are often compelled to remain active and continue competing fiercely to cover their fixed overheads. This persistence intensifies the rivalry among existing players, as everyone fights to maintain market share and operational viability.
- High Capital Intensity: The automotive components sector, where Johnson Electric is a key player, demands substantial capital for R&D and production facilities. For instance, establishing a new advanced motor manufacturing line can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
- Specialized Assets: Many of Johnson Electric's production assets are highly specialized for specific product lines, making them difficult to sell or redeploy if a business unit is divested. This lack of flexibility increases the cost of exiting.
- Customer Lock-in: Long-term supply agreements and the integration of Johnson Electric's components into customers' product designs create switching costs for buyers, reinforcing existing relationships and making it harder for new entrants or exiting firms to disrupt the status quo.
- Intensified Competition: In 2023, the global automotive market experienced fluctuations. Companies like Johnson Electric, facing high fixed costs, were incentivized to maintain production levels, leading to aggressive pricing strategies in certain segments to offset overheads.
Strategic Stakes and Market Dominance
Key players in the motion products industry, like Johnson Electric, have significant strategic stakes in sectors such as automotive and smart home. For instance, the automotive sector relies heavily on electric motors for everything from power windows to advanced driver-assistance systems. In 2024, the global automotive market is projected to see continued growth in electric vehicle (EV) production, a segment where reliable and efficient motion control is paramount.
This intense focus on market share fuels aggressive competition. Companies frequently engage in price wars to capture market segments, a strategy that can compress profit margins. Furthermore, substantial investments in research and development are a constant necessity to innovate and stay ahead, particularly in areas like miniaturization and energy efficiency. Strategic alliances and mergers are also common tactics to consolidate market position and gain access to new technologies or customer bases.
- Automotive Sector Growth: The global automotive market is expected to reach over 90 million units in 2024, with EVs comprising a significant and growing portion, increasing demand for sophisticated motion control systems.
- R&D Investment: Leading motion control manufacturers allocate a substantial percentage of revenue, often between 5-10%, to R&D to drive innovation in areas like brushless DC motors and smart actuators.
- Market Dominance Drive: Companies aim to secure dominant positions in high-volume applications, recognizing that scale provides significant cost advantages and pricing power.
The competitive rivalry within the electric motor and motion subsystem market is intense, driven by a large number of global and specialized players. Johnson Electric faces significant competition, particularly in high-growth segments like automotive and smart home components. Companies are actively investing in R&D to differentiate their offerings, leading to a constant need for innovation to maintain market position.
High capital intensity and specialized assets create substantial exit barriers, compelling companies to remain competitive even during downturns. This persistence intensifies rivalry, as firms fight to cover fixed overheads and maintain market share, often resorting to aggressive pricing strategies.
The automotive sector's reliance on advanced motion control, especially with the rise of EVs, fuels this rivalry. Companies strive for market dominance, recognizing the cost advantages of scale and investing heavily in R&D to develop next-generation technologies.
| Competitor | Key Market Focus | 2024 Market Share Estimate (Global Electric Motor) |
| Nidec | Automotive, Industrial, Home Appliances | 15-20% |
| Mabuchi Motor | Automotive, Consumer Electronics | 10-15% |
| Regal Rexnord | Industrial, Commercial | 5-7% |
| ABB | Industrial Automation, Power Generation | 4-6% |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While electric motors are the backbone of motion control, certain industrial applications can utilize alternative technologies such as advanced pneumatics and hydraulics. These systems, though generally not direct competitors in Johnson Electric's primary sectors like smart home and medical devices, could emerge as a threat if they demonstrate superior cost-effectiveness or performance in niche applications. For instance, in heavy-duty manufacturing where robust, high-force actuation is paramount, advancements in hydraulic systems might offer a more compelling solution than electric motors, potentially impacting specific segments of the industrial automation market.
Large automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), a key customer base for Johnson Electric, possess the financial clout and technical expertise to bring certain electro-mechanical component production in-house. For instance, in 2024, major automotive players continued to invest heavily in their own manufacturing capabilities, with some exploring vertical integration for critical components to gain greater control over supply chains and costs. This backward integration poses a significant threat, particularly for standardized or less technologically intensive parts, directly impacting Johnson Electric's market share in those segments.
The threat of substitutes for Johnson Electric’s motion products is present when end-user needs can be fulfilled without traditional motors. For example, in smart home technology, the desire for a comfortable temperature might be achieved through advanced natural ventilation systems, lessening the demand for sophisticated HVAC motor solutions. This shift can indirectly shrink the market for motion components.
In 2024, the smart home market alone was valued at over $115 billion, with significant growth projected in energy efficiency solutions. This indicates a growing segment where non-motion alternatives, such as smart airflow management, could directly compete with motor-driven climate control systems, impacting Johnson Electric's potential market share in this sector.
Emerging Digital and Software-Based Solutions
The increasing sophistication of digital and software-based solutions presents a potential threat to Johnson Electric Holdings. Advanced software, artificial intelligence, and digital control systems are starting to perform functions previously requiring intricate electro-mechanical components. For instance, in certain specialized applications, intelligent software managing simpler mechanical actuators might reduce the need for Johnson Electric's more complex motion control subsystems.
This trend could impact demand, particularly in areas where software can effectively replicate or bypass the need for advanced physical motion. While a direct replacement for electric motors is unlikely across the board, the substitution effect is growing in specific niches. For example, the automotive industry's push towards software-defined vehicles could see certain integrated motor functions being managed by central computing units, potentially altering the demand for specialized, standalone motor modules.
- Software as a Controller: AI and advanced algorithms can optimize and control simpler mechanical systems, potentially reducing the demand for highly sophisticated electro-mechanical subsystems that Johnson Electric offers.
- Niche Application Impact: In specific, high-tech sectors, software solutions could emerge that offer comparable functionality to certain Johnson Electric products, albeit through different technological means.
- Digitalization Trend: The broader industry trend toward digitalization means that more functionalities are being integrated into software, which could diminish the necessity of specialized hardware components in some applications.
Cost-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Johnson Electric Holdings is significantly influenced by the cost-performance trade-off of alternative solutions. If other products or technologies can deliver similar or better functionality, reliability, and efficiency at a more attractive price point, or even a higher performance level that justifies a premium, the pressure from substitutes intensifies across Johnson Electric’s various markets.
For instance, in the automotive sector, electric vehicle powertrain components are facing competition from advancements in hybrid technology and even more efficient internal combustion engines, especially as regulations evolve. Similarly, in the industrial automation space, while Johnson Electric offers robust motor and control solutions, lower-cost, less sophisticated alternatives may suffice for less demanding applications, particularly in emerging markets where cost sensitivity is high.
- Automotive Powertrain: While Johnson Electric is a key player in electric vehicle motors, advancements in hybrid systems and highly efficient ICEs represent potential substitutes, especially in segments prioritizing lower upfront costs.
- Industrial Automation: For less critical industrial applications, lower-cost motor and control solutions from regional competitors can serve as viable substitutes, impacting market share in price-sensitive segments.
- Consumer Electronics: In consumer electronics, the rapid pace of technological development means that emerging miniaturization and power efficiency breakthroughs in alternative component designs could pose a substitution threat, particularly in high-volume, lower-margin products.
- Medical Devices: While reliability is paramount, the development of highly specialized, lower-power-consumption micro-actuators from niche providers could offer a compelling cost-performance alternative for certain medical device applications.
The threat of substitutes for Johnson Electric is moderate, primarily stemming from alternative technologies in specific applications and the increasing sophistication of software. While direct replacements for electric motors are rare across its core markets, functionalities can sometimes be achieved through other means.
For instance, in industrial automation, advanced pneumatic and hydraulic systems can handle certain high-force actuation tasks, offering a substitute in niche areas. Similarly, the smart home sector, valued over $115 billion in 2024, sees potential substitution from advanced natural ventilation systems that reduce reliance on motor-driven HVAC. Furthermore, the automotive industry’s drive towards software-defined vehicles could see certain integrated motor functions managed by central computing units, altering demand for specialized modules.
| Industry Segment | Potential Substitute | Impact on Johnson Electric |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Automation | Advanced Pneumatics & Hydraulics | Niche competition for high-force applications |
| Smart Home | Natural Ventilation Systems | Reduced demand for HVAC motors |
| Automotive | Software-managed Actuators | Potential shift in demand for specialized modules |
Entrants Threaten
Johnson Electric's industry, the manufacturing of electric motors and motion subsystems, demands a significant outlay of capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in cutting-edge research and development to innovate, alongside establishing sophisticated production facilities equipped with specialized machinery. For example, setting up a modern manufacturing plant for electric motors can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, depending on the scale and technological sophistication.
Beyond physical assets, building a global distribution and sales network is crucial for reaching diverse markets, adding another layer of substantial investment. This high barrier to entry, driven by the sheer financial commitment required, naturally curtails the number of new companies that can realistically enter the market and compete with established players like Johnson Electric.
Johnson Electric's deep well of engineering expertise, honed over decades, forms a significant barrier to new entrants. Their extensive product portfolio is a testament to this accumulated knowledge and a substantial base of intellectual property. For instance, the company holds a vast number of patents globally, protecting their innovations in motor technology and actuation systems.
Launching a competitive offering would necessitate massive upfront investment in replicating this proprietary technology, securing equivalent patent protection, and cultivating a highly skilled engineering talent pool. This makes it incredibly challenging and costly for newcomers to match Johnson Electric's technological capabilities and market presence.
Johnson Electric, a leader in motion systems, benefits immensely from established economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, the company reported revenues of HK$17.6 billion, indicating a substantial operational footprint. This scale allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers and spread R&D costs over a larger production volume, resulting in lower per-unit costs compared to any nascent competitor.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating Johnson Electric's cost advantages. Without matching their production volume, new players cannot achieve the same procurement efficiencies or amortize R&D investments as effectively. This inherent cost disadvantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and profitability from the very beginning.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New companies entering the motor and motion control sector face substantial hurdles in securing access to established distribution networks and cultivating enduring relationships with key Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in sectors like automotive, smart home, and medical devices. These established players often have deeply ingrained supplier agreements and rigorous vetting procedures that new entrants find difficult to navigate. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to consolidate its supplier base, with major manufacturers prioritizing suppliers with a proven track record of reliability and scale, making it harder for unproven entities to break in.
Johnson Electric, as a long-standing supplier, benefits from these existing relationships. New entrants would need to invest heavily in building trust and demonstrating consistent quality and supply chain efficiency to even be considered by major OEMs.
- Established OEM Relationships: Johnson Electric has cultivated decades-long partnerships with leading automotive, smart home, and medical device manufacturers, providing them with reliable access to their products.
- Rigorous Qualification Processes: The automotive and medical device industries, in particular, have stringent qualification protocols for new suppliers, demanding extensive testing and validation of components and manufacturing processes.
- Distribution Channel Control: Existing players often control significant portions of the distribution channels, making it challenging for newcomers to reach end customers efficiently.
- Supplier Loyalty and Scale: Major OEMs tend to favor suppliers who can demonstrate consistent volume production and a commitment to long-term partnership, a barrier for smaller, newer companies.
Regulatory Hurdles and Product Qualification
For Johnson Electric Holdings, the threat of new entrants is significantly moderated by the substantial regulatory hurdles and lengthy product qualification processes inherent in key sectors like automotive and medical devices. For instance, obtaining certifications such as ISO 13485 for medical device components can take years and involve rigorous testing and documentation, demanding significant upfront investment.
New players entering these markets must navigate complex compliance landscapes, including automotive safety standards like those set by the NHTSA or medical device regulations from bodies like the FDA. These requirements translate into considerable time and financial commitments, acting as a substantial barrier. For example, the average cost for a new medical device company to bring a product to market can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the device's complexity and classification.
- Automotive Sector: Compliance with standards like IATF 16949 is mandatory for automotive suppliers, involving extensive quality management system audits and continuous improvement processes.
- Medical Device Sector: Adherence to stringent FDA regulations or European CE marking requires thorough validation, risk management, and quality control, often involving lengthy clinical trials.
- Cost of Compliance: The financial burden of meeting these regulatory demands, including testing, documentation, and specialized personnel, can deter potential new entrants.
- Time to Market: The extended timelines for product approval and certification directly impact a new entrant's ability to quickly gain market share and achieve profitability.
The threat of new entrants for Johnson Electric is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish a competitive presence. Setting up advanced manufacturing facilities and global distribution networks demands hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant deterrent for newcomers. Furthermore, the substantial investment in research and development to innovate and protect intellectual property, evidenced by Johnson Electric's numerous patents, creates a high financial barrier.
Established brand loyalty and deep-rooted relationships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) also pose a significant challenge. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to favor suppliers with proven reliability and scale, making it difficult for new entities to secure contracts. Navigating these complex supplier qualification processes requires time and resources that new entrants may lack.
Regulatory compliance, particularly in the automotive and medical device sectors, further limits new entrants. Obtaining certifications like ISO 13485 or adhering to FDA regulations can take years and cost millions, as seen in the medical device industry where bringing a product to market can incur substantial expenses. These stringent requirements act as a powerful protective shield for incumbent firms like Johnson Electric.
Johnson Electric's established economies of scale, reflected in their 2024 revenue of HK$17.6 billion, provide a distinct cost advantage. This scale allows for more favorable supplier negotiations and efficient R&D cost allocation, making it difficult for new, smaller players to compete on price. Replicating this cost efficiency without matching Johnson Electric's production volume is a near-insurmountable hurdle.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Johnson Electric Holdings is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry research firms and market intelligence databases to capture the broader competitive landscape.
