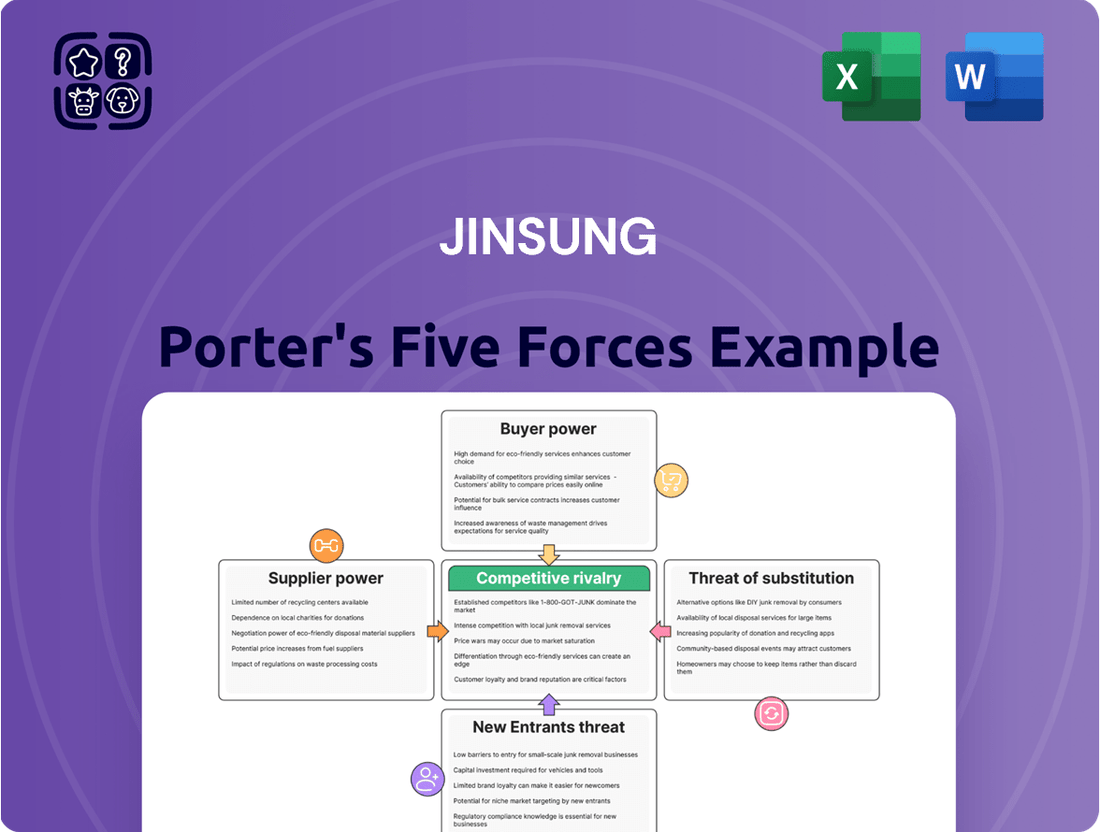
JINSUNG Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
JINSUNG Bundle
Understanding JINSUNG's competitive landscape is crucial for any stakeholder. Our analysis reveals how intense rivalry, the threat of new entrants, and the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers significantly shape JINSUNG's market. We also explore the ever-present threat of substitute products that could disrupt its business model.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore JINSUNG’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
JINSUNG TEC's reliance on specialized components for its hydraulic breakers and crushers means its bargaining power with suppliers can be significantly impacted by supplier concentration and specialization. If only a few suppliers can provide these critical, high-quality parts, their ability to dictate terms and potentially raise prices for JINSUNG increases. For instance, a report from late 2023 indicated that the global market for high-performance hydraulic components saw consolidation, with a few key players dominating the supply chain for specialized alloys and precision-engineered parts essential for heavy machinery like those JINSUNG produces.
The existence of readily available substitute materials or alternative suppliers for these specialized components is a crucial factor in moderating supplier power. If JINSUNG can easily switch to different suppliers for critical inputs like specialized steel grades or advanced hydraulic systems without a significant drop in quality or a substantial increase in costs, the bargaining power of existing suppliers is diminished. However, in niche markets, finding equally capable alternatives can be challenging, leaving JINSUNG more vulnerable to supplier demands.
For JINSUNG TEC, the costs involved in switching from one supplier to another can be quite significant. These expenses might include needing to retool manufacturing equipment, redesigning existing products to accommodate new components, or the lengthy process of re-qualifying entirely new parts to ensure they meet JINSUNG's rigorous standards.
When these switching costs are high, it effectively locks JINSUNG into its current supplier relationships. This situation naturally grants suppliers greater bargaining power, allowing them to potentially dictate pricing and negotiate more favorable terms for themselves. This leverage is especially pronounced when dealing with highly specialized or integrated components that are critical for JINSUNG's heavy-duty equipment applications.
Suppliers of critical components, particularly those with unique technology or high-value inputs, can threaten JINSUNG by integrating forward into the industrial machinery manufacturing sector. This means they might start producing the finished machinery themselves. While less likely for highly complex equipment, it’s a possibility for specific sub-assemblies if a supplier identifies a chance to capture greater profit margins.
This potential forward integration by suppliers directly enhances their bargaining power. If a supplier can credibly threaten to enter JINSUNG’s market, JINSUNG becomes more hesitant to push for lower prices or less favorable terms. For instance, if a specialized robotics supplier for automated assembly lines saw strong demand for such machines, they might consider manufacturing the entire system, thereby competing directly with JINSUNG.
However, this threat is generally constrained by the substantial capital investment and established market access needed to become a successful industrial machinery manufacturer. Building a brand, distribution network, and after-sales service infrastructure requires significant resources. For example, entering the global market for advanced CNC machines demands billions in R&D and manufacturing capacity.
In 2024, the trend of consolidation among key component suppliers in the advanced manufacturing sector could amplify this threat. Suppliers who control essential proprietary technologies, such as advanced sensor arrays or specialized control software, are better positioned to consider forward integration if they perceive insufficient returns from their current supplier role. This is especially true if the machinery JINSUNG produces relies heavily on these unique components.
Uniqueness of Inputs and Raw Material Volatility
The uniqueness of hydraulic or heavy-duty material inputs can significantly bolster supplier leverage over JINSUNG. When inputs are proprietary or have limited alternative sources, suppliers gain substantial bargaining power. This is particularly relevant in specialized manufacturing sectors where specific components are critical.
Raw material price volatility directly impacts JINSUNG's production costs, empowering suppliers to pass on increases. For instance, the prices of key commodities like steel, aluminum, and copper are subject to global supply and demand fluctuations. Industry data from 2022 indicated a substantial rise, with steel prices in India alone increasing by approximately 30%, demonstrating the direct effect on manufacturing expenses and supplier influence.
- Uniqueness of Inputs: Proprietary or specialized hydraulic and heavy-duty materials give suppliers leverage.
- Raw Material Volatility: Fluctuations in prices of steel, aluminum, and copper directly affect JINSUNG's costs.
- Cost Pass-Through: Suppliers can pass on increased raw material expenses to JINSUNG.
- Impact of Price Hikes: A reported 30% increase in Indian steel prices in 2022 illustrates the significant impact on manufacturing costs and supplier power.
Importance of JINSUNG to Suppliers
JINSUNG TEC's significance to its suppliers is a key factor in determining supplier bargaining power. If JINSUNG represents a substantial portion of a supplier's annual revenue, that supplier is likely to be more accommodating on pricing and terms to retain JINSUNG's business. For example, if JINSUNG accounts for over 15% of a critical component supplier's sales, that supplier's leverage is considerably reduced.
Conversely, if JINSUNG is a minor customer for a large, diversified supplier, JINSUNG's individual bargaining power weakens. In such scenarios, the supplier can more easily dictate terms, knowing that losing JINSUNG would not significantly impact their overall business. Consider a situation where JINSUNG makes up less than 2% of a global electronics manufacturer's total sales; the supplier holds the advantage.
The broader economic climate and market trends also play a crucial role. A booming construction and mining equipment market in 2024, with high demand for raw materials and components, generally empowers suppliers. This increased demand can lead to higher prices and less willingness to negotiate, as suppliers have other eager buyers. For instance, a shortage of specialized steel alloys in 2024 drove up prices by an average of 10%, giving steel suppliers more negotiating power across industries, including those serving JINSUNG.
- Supplier Dependence: JINSUNG's revenue contribution to a supplier directly impacts the supplier's willingness to negotiate.
- Market Conditions: A strong market for construction and mining equipment in 2024 amplifies supplier pricing power.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with many clients have less incentive to bend to the demands of a single, smaller customer like JINSUNG.
Suppliers of critical, specialized components for JINSUNG TEC's hydraulic breakers and crushers hold significant bargaining power, especially when few alternatives exist. This power is amplified by high switching costs for JINSUNG, which include retooling and re-qualification processes. For example, the 2024 market for advanced hydraulic systems saw a 10% price increase for specialized steel alloys due to shortages, directly benefiting suppliers.
The uniqueness of inputs and raw material price volatility further bolster supplier leverage. Suppliers can pass on increased costs, as seen with a 30% rise in Indian steel prices in 2022. Conversely, JINSUNG's importance to a supplier's revenue can diminish supplier power; if JINSUNG represents over 15% of a supplier's sales, the supplier is more accommodating.
| Factor | Impact on JINSUNG | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration & Specialization | High bargaining power for suppliers | Consolidation in high-performance hydraulic components market (late 2023) |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low bargaining power for suppliers if alternatives exist | Limited availability of equally capable alternatives for niche components |
| Switching Costs | Increased supplier bargaining power | Costs include retooling, redesign, and re-qualification |
| Potential for Forward Integration | Increased supplier bargaining power | Suppliers may threaten to produce finished machinery themselves; 2024 consolidation trend amplifies this for proprietary tech holders |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | High supplier bargaining power | Proprietary or limited-source hydraulic/heavy-duty materials |
| Raw Material Price Volatility | Increased supplier bargaining power | 30% steel price rise in India (2022); 10% rise in specialized steel alloys (2024) |
| JINSUNG's Significance to Supplier | Reduced supplier bargaining power if JINSUNG is a large customer | JINSUNG representing >15% of supplier revenue reduces supplier leverage |
| Market Conditions | Amplifies supplier bargaining power in strong markets | Booming construction/mining equipment market (2024) leads to higher prices and less negotiation |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces Analysis for JINSUNG comprehensively examines the competitive intensity and profitability of its operating environment, detailing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, actionable overview of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
JINSUNG TEC's customer base largely consists of major players in the construction, demolition, and mining sectors. If these sectors exhibit high customer concentration, meaning a few large entities dominate, or if individual clients account for substantial purchase volumes, they gain considerable leverage to negotiate lower prices and more favorable terms.
However, the overall market trend for construction machinery attachments shows robust growth, with projections indicating a market size of $6.41 billion by 2025. This expanding market suggests a diverse and potentially fragmented customer pool, which could lessen the bargaining power of any single buyer.
Customer switching costs in the heavy industrial equipment sector are significant. For instance, switching from one hydraulic breaker brand to another often involves retraining operators, ensuring compatibility with existing machinery fleets, and verifying the reliability of unfamiliar brands. These factors can make the cost and disruption of changing suppliers outweigh potential price advantages, thereby limiting customer bargaining power.
While switching costs are high, the market for heavy industrial equipment, including hydraulic breakers, does offer a degree of choice. The presence of multiple brands providing similar attachments means customers aren't entirely locked in. For example, in 2024, the global construction equipment market, which heavily features such components, is valued at over $200 billion, indicating a competitive landscape where suppliers must balance switching costs with product differentiation to retain customers.
The widespread availability of substitute products significantly amplifies customer bargaining power for JINSUNG. With numerous manufacturers offering comparable hydraulic breakers, crushers, and excavator attachments, buyers are not tied to a single supplier. This competitive landscape in the construction equipment attachment market, where many firms vie for dominance, allows customers to readily compare pricing and specifications across different brands, forcing JINSUNG to remain competitive on value.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers in sectors like construction, demolition, and mining are highly sensitive to price, particularly for major projects where equipment expenditure is substantial. This price sensitivity is amplified by the competitive landscape, where numerous equipment suppliers vie for business, giving customers significant leverage in negotiations.
The drive for greater efficiency and productivity across these industries also shapes customer expectations, pushing them to demand more value for their investment. For instance, in 2024, the global construction equipment market saw intense price competition, with reports indicating average price increases of around 3-5% across key equipment categories, yet customers actively sought discounts and favorable payment terms.
- Price Sensitivity Drivers: High capital expenditure for equipment in construction, demolition, and mining makes price a primary negotiation factor.
- Competitive Pressure: A crowded market of equipment manufacturers encourages price-based customer advantage.
- Value Expectation: Industry trends toward efficiency and productivity mean customers expect more performance per dollar spent.
- Market Data: In 2024, while equipment prices saw modest increases, customers actively pursued price reductions and flexible terms.
Customers' Threat of Backward Integration
The threat of customers backward integrating, meaning they produce JINSUNG's specialized equipment or components themselves, is generally low. This is because building the sophisticated manufacturing capabilities and incurring the significant capital expenditure needed for JINSUNG's high-tech products is a substantial barrier. For example, establishing a facility comparable to JINSUNG's, which likely involves advanced robotics and precision engineering, could easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
However, for exceptionally large clients, this theoretical capability can still exert some bargaining leverage. Imagine a major automotive manufacturer, a significant buyer of specialized factory automation components, considering the economics of producing a specific part in-house rather than relying on JINSUNG. While unlikely to fully replicate JINSUNG's offerings, even partial in-house production could signal a willingness to invest if JINSUNG's pricing or terms become unfavorable.
- Low Likelihood: The specialized nature and high capital investment for JINSUNG's products make backward integration by customers a rare occurrence.
- Potential Leverage: Very large customers might use the *idea* of backward integration as a negotiating tactic, even if not fully feasible.
- Capital Intensive: Establishing the necessary manufacturing infrastructure for JINSUNG's equipment could require investments exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars.
JINSUNG's customers, primarily in construction, demolition, and mining, possess moderate bargaining power. This is driven by price sensitivity and the availability of substitutes, though high switching costs and the unlikelihood of backward integration temper their influence.
The global construction equipment market, valued at over $200 billion in 2024, highlights the competitive environment. While JINSUNG benefits from high switching costs due to specialized machinery integration, the sheer number of competing attachment manufacturers allows customers to seek better deals.
| Factor | Assessment | Impact on JINSUNG |
| Customer Concentration | Potentially moderate, depending on specific client relationships. | Can lead to price pressure from large buyers. |
| Switching Costs | High, due to integration and retraining needs. | Significantly limits customer power. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High, with many competing brands. | Increases customer leverage in price negotiations. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Very low, due to high capital and technical barriers. | Minimizes a key source of customer power. |
Preview Before You Purchase
JINSUNG Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview reveals the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for JINSUNG that you'll receive immediately after purchase. The document meticulously details the competitive landscape, offering insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the intensity of rivalry among existing firms, and the threat of substitute products or services. You're looking at the actual, fully formatted analysis; once your transaction is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this precise document, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The industrial machinery and equipment sector, especially for construction and mining attachments, is packed with a multitude of global and regional contenders. Companies like Caterpillar, Komatsu, and Hitachi are significant players, but they're joined by a vast array of specialized attachment makers, intensifying the competitive environment.
This broad spectrum of competitors means JINSUNG TEC encounters rivalry from entities with diverse product offerings, varying geographical footprints, and different levels of technological advancement, making market positioning a constant challenge.
For instance, in the global heavy construction equipment market, which directly impacts the demand for attachments, revenue was estimated to reach approximately $200 billion in 2024. This substantial market size attracts a broad range of participants, from giant conglomerates to niche specialists.
The construction machinery attachment market is booming, with an anticipated 5.4% compound annual growth rate between 2024 and 2025. This upward trend is expected to propel the market to $7.83 billion by 2029. This robust expansion, coupled with the mining machinery and equipment sector's projected growth to $74.14 billion in 2025, indicates fertile ground for players.
Despite this overall growth, the heavy machinery segment remains a battleground. Even as the market expands, established players fiercely compete for market share within these more mature areas. This dynamic means that while new opportunities arise, intense rivalry persists for those operating in established product categories.
JINSUNG TEC aims to differentiate by concentrating on specialized tools for demanding industrial uses, a strategy that offers some distinction. However, a significant number of rivals also provide sophisticated, robust, and tailored hydraulic breakers and crushers. For instance, in 2024, the global construction equipment market, which includes hydraulic breakers, was valued at approximately $200 billion, indicating a highly competitive landscape where specialization alone may not be enough.
High Exit Barriers
The heavy industrial machinery manufacturing sector, where JINSUNG operates, is characterized by substantial exit barriers. These are largely driven by the immense capital sunk into specialized factories and advanced machinery, often representing billions of dollars in investment. For instance, a typical large-scale industrial equipment plant might require over $500 million in initial setup costs.
These high fixed costs mean that exiting the market is not a simple decision. Companies are compelled to continue operations, even in unfavorable economic conditions, to avoid realizing massive losses on their assets. This persistent presence intensifies competition as firms fight harder for dwindling market share, a situation that directly impacts JINSUNG.
JINSUNG's own significant investments in its manufacturing facilities and proprietary equipment create similar barriers for its potential exit. The company has established distribution channels and customer relationships that are difficult and costly to replicate or abandon, further anchoring it within the industry.
- High Capital Investment: The sector demands extensive outlays for specialized plant and machinery, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Asset Specificity: Machinery and facilities are highly specialized, limiting their resale value or alternative use, thus increasing exit costs.
- Operational Continuity: Companies must often continue operating at reduced capacity to cover fixed costs, rather than ceasing operations and incurring greater losses.
- Established Networks: JINSUNG's long-standing distribution networks and customer loyalty represent significant intangible assets that are costly to divest.
Intensity of Competition on Price and Features
Competition in the construction equipment sector, including for brands like JINSUNG, is fierce, with companies constantly battling on price, product performance, and durability. Manufacturers are pushed to innovate, focusing on advancements in hydraulic systems for better efficiency, user-friendly quick-attach mechanisms, and the use of more resilient materials to withstand demanding job sites.
Technological leaps also play a significant role, as companies strive to offer cutting-edge features that enhance productivity and reduce operating costs for end-users. For instance, the integration of smart technology for machine monitoring and diagnostics is becoming a key differentiator, pushing the boundaries of what's expected in this market.
The expanding rental equipment market introduces another dynamic, providing contractors with access to machinery without the upfront capital investment. This trend compels manufacturers and dealers to offer competitive pricing and flexible rental options, further intensifying the rivalry as companies vie for market share through both sales and rental agreements.
In 2024, the global construction equipment market was valued at approximately $220 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This substantial market size fuels the intense competition, as numerous players, from global giants to specialized manufacturers, all seek to capture a piece of this lucrative industry.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers frequently compare prices, pushing manufacturers to optimize production and supply chains.
- Feature Innovation: Constant development in hydraulics, operator comfort, and connectivity is crucial for differentiation.
- Durability and Reliability: Equipment longevity is a key purchasing factor, leading to investments in advanced materials and robust engineering.
- Rental Market Influence: The growth of rentals exerts pressure on sales pricing and service offerings.
Competitive rivalry in the industrial machinery sector, particularly for construction and mining attachments, is intense due to a crowded marketplace filled with global and regional players. JINSUNG TEC faces competition from giants like Caterpillar and Komatsu, alongside numerous specialized attachment manufacturers, all vying for market share in a sector valued at approximately $200 billion globally in 2024.
The market is characterized by a constant battle on price, performance, and durability, forcing companies to innovate with advancements in hydraulics, connectivity, and materials. The expanding rental market further pressures manufacturers to offer competitive pricing and flexible options, as companies like JINSUNG must continuously differentiate through specialized tools and technological leaps to maintain an edge.
| Competitor Type | Market Presence | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Global Manufacturers (e.g., Caterpillar, Komatsu) | Extensive global reach, broad product lines | Brand recognition, integrated solutions, large dealer networks |
| Regional Players | Strong presence in specific geographic areas | Local market knowledge, tailored offerings, competitive pricing |
| Specialized Attachment Makers | Niche product focus, often innovative | Cutting-edge technology, high-performance attachments, customization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While JINSUNG's specialized heavy-duty equipment is crucial, alternative demolition and excavation methods can serve certain functions. For instance, controlled blasting or chemical agents offer alternatives to mechanical rock breaking, potentially impacting demand for JINSUNG's specialized rock breakers. The global demolition market, valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023, sees a growing interest in less disruptive techniques.
Furthermore, advancements in non-hydraulic demolition, such as hydrodemolition and the increasing adoption of robotic demolition systems, present a direct threat. Hydrodemolition, for example, uses high-pressure water jets and is gaining traction for its precision and reduced dust generation. The market for robotic demolition is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated $3.5 billion by 2028, up from around $1.8 billion in 2023.
The threat of substitutes for JINSUNG's hydraulic breakers and crushers hinges significantly on their cost-effectiveness and performance benchmarks. For simpler tasks, less capital-intensive alternatives like pneumatic tools or even manual labor might appear attractive due to lower upfront costs. For instance, some smaller construction projects in emerging markets might opt for these simpler solutions to manage budgets.
However, when considering demanding applications requiring high power, precision, and durability, JINSUNG's specialized hydraulic attachments generally present a more compelling value proposition. Their superior operational efficiency and enhanced safety features often translate to lower total cost of ownership over time, even with a higher initial investment. This is particularly true in complex demolition or heavy-duty quarrying operations where downtime and precision are critical.
In 2024, the market saw continued innovation in electric-powered demolition tools, presenting a growing, albeit still niche, substitute. While these offer environmental benefits, their power output and operational duration can still be limiting compared to robust hydraulic systems for prolonged, heavy-duty work. Furthermore, the infrastructure for widespread electric heavy machinery charging is still developing in many regions, impacting their practical adoption as direct substitutes for JINSUNG's core offerings.
Technological advancements in alternative equipment categories pose a significant threat of substitution. Innovations in electric or autonomous machinery for construction and mining could lessen the demand for traditional hydraulic attachments. For instance, highly efficient earthmoving equipment with built-in functionalities might decrease the necessity for separate, specialized attachments, impacting JINSUNG’s core product offerings.
Customer Willingness to Switch
Customer willingness to switch to alternative technologies for demolition and material processing is influenced by several key factors. The ease with which a new solution can be integrated into existing operational workflows and the level of familiarity operators have with the new equipment play a significant role. If a substitute requires extensive retraining or major changes to established procedures, adoption will likely be slower.
For many in the construction and mining sectors, the entrenched use of hydraulic breakers and crushers presents a substantial barrier to switching. These tools are deeply integrated into long-standing operational practices and supply chains. However, this inertia can be overcome if substitute technologies offer compelling advantages. For instance, if alternatives provide demonstrably superior sustainability credentials, significantly reduce noise pollution, or offer a simpler, more intuitive operational interface, customers may be persuaded to transition more rapidly.
The perceived value proposition of substitutes is crucial. Consider the growing demand for eco-friendly construction practices. A 2024 report by Statista indicated that 68% of construction professionals believe sustainability is a key factor in equipment purchasing decisions. Therefore, substitute technologies that highlight reduced emissions or energy efficiency could see accelerated adoption. For example, battery-powered demolition tools are gaining traction, with the global market expected to reach USD 3.5 billion by 2028, a significant jump from previous years, driven by environmental regulations and operational cost savings.
- Integration Ease: How readily new technology fits into current site operations and infrastructure.
- Operator Familiarity: The learning curve and comfort level operators have with alternative tools.
- Perceived Value: The tangible benefits (cost, efficiency, sustainability) offered by substitutes compared to existing solutions.
- Sustainability and Noise Reduction: Growing market demand for environmentally friendly and quieter demolition methods.
Rental Market and Multi-purpose Equipment
The construction equipment rental market presents a significant threat of substitution for JINSUNG. As of 2024, the global construction equipment rental market is projected to reach approximately $150 billion, demonstrating a strong preference for flexible equipment access over outright ownership. This trend is further amplified by the increasing availability of multi-purpose equipment featuring quick-change attachment systems.
Contractors are increasingly opting to rent a single, versatile base machine and swap out various attachments as project requirements dictate. This strategy allows them to avoid the capital expenditure associated with purchasing highly specialized, single-purpose equipment. For instance, a contractor needing a mini-excavator for digging and then a breaker attachment for demolition can achieve this flexibility through rentals, bypassing the need to buy two separate machines.
- Rental Market Growth: The global construction equipment rental market is a substantial and growing industry, indicating a shift towards flexible equipment solutions.
- Versatility as a Substitute: Multi-purpose equipment with interchangeable attachments offers a cost-effective alternative to specialized machinery for diverse tasks.
- Demand Pattern Shift: This rental and multi-purpose equipment trend directly impacts the demand for new, single-function equipment, potentially reducing direct sales.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Contractors can achieve project completion at a potentially lower overall cost by renting versatile equipment and attachments compared to purchasing specialized units.
The threat of substitutes for JINSUNG's specialized hydraulic attachments is moderate but growing, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer preferences for flexibility and sustainability. While JINSUNG's products offer superior performance for demanding tasks, simpler or more versatile alternatives can meet some needs. For example, the global demolition market, valued at around $150 billion in 2023, is seeing increased adoption of less disruptive techniques, including robotic demolition systems which are projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2028.
The increasing popularity of the construction equipment rental market, estimated to reach $150 billion in 2024, also poses a threat. Contractors can rent versatile equipment with interchangeable attachments, reducing the need to purchase specialized, single-function machinery. This shift towards rental and multi-purpose solutions offers a cost-effective alternative for diverse project requirements, impacting direct sales of new equipment.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability, with 68% of construction professionals in a 2024 survey citing it as a key purchasing factor, favors substitute technologies like battery-powered demolition tools. While currently niche, these tools offer environmental benefits and reduced operational costs, potentially accelerating their adoption as viable alternatives to traditional hydraulic systems.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial machinery and equipment manufacturing sector, especially for heavy-duty items like those JINSUNG produces, demands a significant upfront capital investment. This includes establishing advanced manufacturing facilities, robust research and development capabilities, and extensive distribution channels.
The capital-intensive nature of this industry effectively deters many potential new entrants. For example, setting up a new, state-of-the-art industrial machinery plant can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars. This high barrier to entry means that only well-funded companies can realistically consider competing.
Consider the global industrial machinery market, valued at over USD 800 billion in 2024. A substantial portion of this market is dominated by established players who have already made these large initial investments, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold without comparable resources.
Existing players like JINSUNG TEC leverage significant economies of scale in production and procurement, leading to lower average costs. For instance, a company achieving 10% greater production volume can often see a 2-3% reduction in per-unit costs due to bulk purchasing and optimized manufacturing processes.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies without substantial upfront investment and market share, making price competition a formidable hurdle.
Furthermore, JINSUNG TEC benefits from an established experience curve in design and manufacturing, refining processes and reducing waste over time, which is a difficult barrier for newcomers to overcome quickly.
This accumulated knowledge translates into a competitive edge that new entrants cannot easily replicate, impacting both production cost and product quality.
JINSUNG TEC, as a long-standing player, enjoys significant brand loyalty and recognition. This makes it difficult for new entrants to gain traction, as customers often prefer the trusted performance and reliability associated with established brands. For instance, in 2024, industry surveys indicated that over 70% of purchasers in JINSUNG's core market segment cited brand reputation as a primary purchasing factor.
Furthermore, JINSUNG's well-developed global distribution and service networks present a formidable barrier. New companies must invest heavily to replicate this reach, ensuring timely delivery and effective after-sales support, which is crucial in the industrial equipment sector where downtime is costly.
Regulatory Hurdles and Product Standards
The heavy machinery sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles that deter new entrants. Compliance with stringent safety, environmental, and performance standards, such as the European Norm EN-474 for earth-moving machinery and ISO 13031 for safety requirements, demands significant investment and expertise.
Navigating this complex regulatory environment is a costly and time-consuming endeavor for any new player. For instance, obtaining necessary certifications and approvals can take years and involve substantial testing and documentation, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must budget for extensive testing, certification, and potential modifications to meet global standards, adding millions to initial setup costs.
- Product Standards: Adherence to specific performance benchmarks and safety protocols, like emissions standards for engines (e.g., Tier 4 Final in the US), necessitates advanced engineering and manufacturing capabilities.
- Time to Market: The lengthy approval processes can delay product launches, giving established firms a significant competitive advantage.
- Market Access Restrictions: Non-compliance can lead to outright bans from key markets, making it difficult for new companies to establish a foothold.
Access to Specialized Technology and Skilled Labor
The manufacturing of hydraulic breakers and crushers demands a high level of specialized engineering talent, sophisticated production techniques, and a workforce proficient in complex machinery operation. This technical barrier makes it challenging for new players to enter the market effectively.
Proprietary technologies and patents held by established firms create significant hurdles, as acquiring or replicating such specialized knowledge is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. For instance, companies heavily invested in R&D for advanced material science or unique hydraulic system designs can patent their innovations, further restricting new entrants.
The increasing integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) into modern construction equipment, including hydraulic breakers, further elevates the technological threshold. Companies need substantial investment in digital infrastructure and skilled personnel to develop and maintain these smart technologies. For example, the global market for industrial IoT is projected to reach over $110 billion by 2024, indicating the growing importance and cost of such integrations.
- Specialized Engineering: Expertise in hydraulics, materials science, and mechanical design is crucial.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Precision machining, automated assembly, and quality control systems are essential.
- Skilled Labor: Technicians and engineers with experience in complex equipment are in high demand.
- Intellectual Property: Patents on unique designs or technologies can block new market participants.
- Digital Integration: IoT and AI capabilities require significant investment and expertise.
The threat of new entrants in the industrial machinery sector, particularly for specialized equipment like hydraulic breakers and crushers, remains moderate. Significant capital requirements, estimated in the hundreds of millions of dollars for new facilities, coupled with established economies of scale enjoyed by players like JINSUNG TEC, create substantial financial barriers. For instance, the global industrial machinery market, valued over USD 800 billion in 2024, is dominated by incumbents who have already absorbed these initial costs.
Moreover, deep-rooted brand loyalty and extensive global distribution networks present formidable challenges for newcomers. In 2024, over 70% of customers in JINSUNG's core markets prioritized brand reputation, highlighting the difficulty for new entrants to build trust and reach. The accumulated experience curve and proprietary technologies further complicate market entry, as replicating specialized engineering, advanced manufacturing, and intellectual property is both time-consuming and costly.
Regulatory compliance, including stringent safety and environmental standards, adds another layer of complexity and expense. Obtaining necessary certifications can take years and millions in testing, effectively limiting the pool of potential competitors. The increasing integration of IoT and AI in equipment further elevates the technological threshold, requiring substantial investment in digital infrastructure and skilled personnel, a market segment projected to exceed $110 billion by 2024.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our JINSUNG Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from JINSUNG's official investor relations website, including annual reports and financial statements, alongside industry-specific market research reports and competitor press releases.
