Infinity Natural Resources Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Infinity Natural Resources Bundle
Infinity Natural Resources operates within a dynamic market, influenced by the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these core forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Infinity Natural Resources’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized oilfield services, particularly those offering advanced drilling and completion technologies crucial for unconventional resource plays, hold considerable bargaining power. This is due to the limited number of firms capable of providing these sophisticated solutions, which Infinity Natural Resources relies on to boost production.
The oilfield services sector is experiencing rapid technological evolution, with AI and big data integration becoming more prevalent. However, this innovation is occurring alongside market consolidation, a trend that is likely to further concentrate power among a smaller group of specialized suppliers.
The availability and cost of critical inputs, such as steel and Oil Country Tubular Goods (OCTG), directly influence the bargaining power of suppliers for companies like Infinity Natural Resources. For instance, in early 2024, global steel prices saw fluctuations, with some benchmarks rising by 5-10% due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand from infrastructure projects.
Furthermore, specialized equipment crucial for resource extraction, if controlled by a limited number of manufacturers, can also tip the scales in favor of suppliers. Potential import restrictions or tariffs imposed on these essential materials in 2024 could significantly increase operational expenses, impacting the economic viability of well projects for Infinity Natural Resources.
The oil and gas sector, including companies like Infinity Natural Resources, relies on a specialized and highly skilled workforce for critical operations such as exploration, drilling, and production. This demand for expertise creates a unique dynamic in the labor market.
A significant factor influencing the bargaining power of suppliers in this industry is the availability of experienced personnel. For instance, in 2024, the global oil and gas industry continued to face challenges in finding enough qualified geoscientists and petroleum engineers, a trend that began to intensify in the preceding years. This scarcity directly translates into increased leverage for these skilled professionals.
When there's a shortage of experienced workers, labor suppliers, meaning the skilled professionals themselves, gain considerable bargaining power. This can lead to upward pressure on wages and benefits, ultimately increasing operational costs for companies like Infinity Natural Resources. For example, reports from industry surveys in early 2024 indicated that average salaries for experienced petroleum engineers saw a notable uptick compared to previous years, reflecting this tight labor market.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Suppliers who possess proprietary technologies or patents for advanced drilling and completion techniques wield significant influence. For instance, companies holding patents on specialized hydraulic fracturing fluids or advanced seismic imaging software can command higher prices. In 2024, the demand for energy independence continued to drive innovation, making access to these cutting-edge technologies a critical factor for oil and gas producers.
New entrants or companies looking to upgrade their operations often find themselves needing to license these patented processes or undertake substantial investment to replicate them. This creates a clear leverage point for established suppliers, who can dictate terms. The global oilfield services market, valued at over $200 billion in 2024, sees a significant portion of its value tied to technological differentiation.
- Proprietary Drilling Technologies: Suppliers with patented drilling equipment or processes can charge premium rates.
- Patent Protection: Patents grant exclusive rights, limiting competition and increasing supplier leverage.
- Licensing Agreements: Companies may be forced into costly licensing deals to access essential technologies.
- High R&D Costs: The significant investment required to develop such technologies justifies higher supplier pricing.
Switching Costs for Services and Equipment
Switching from one service or equipment provider to another in the oil and gas sector often incurs substantial costs for companies like Infinity Natural Resources. These expenses can include the need for retraining personnel on new systems, reconfiguring existing infrastructure to accommodate different equipment, and the potential for costly operational downtime during the transition. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for implementing new upstream software solutions across the industry was estimated to be upwards of $500,000, not including the associated training expenses.
These high switching costs directly bolster the bargaining power of incumbent suppliers. When it’s difficult and expensive for Infinity Natural Resources to move to a different provider, existing suppliers can leverage this situation to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially including higher prices or less flexible contract conditions. This dynamic can limit Infinity Natural Resources' ability to secure more competitive offerings or adapt quickly to changing technological landscapes.
- Significant Retraining: The oil and gas industry requires specialized skills, and retraining staff on new operational software or equipment can take months and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Infrastructure Reconfiguration: Adapting existing rigs, pipelines, or processing facilities to new supplier equipment often involves costly modifications and engineering work.
- Operational Downtime: The period of switching suppliers can lead to production halts, resulting in millions of dollars in lost revenue for exploration and production companies.
- Integration Challenges: Ensuring seamless integration of new equipment or services with existing IT systems and workflows presents a complex and often expensive hurdle.
Suppliers of specialized oilfield services and critical inputs like steel hold significant bargaining power over Infinity Natural Resources. This power is amplified by market consolidation, proprietary technologies, and the high costs associated with switching providers. For example, in 2024, the oilfield services market, valued at over $200 billion, saw a concentration of power among firms with advanced drilling technologies.
The scarcity of skilled labor, particularly experienced geoscientists and petroleum engineers, further empowers suppliers of human capital. In early 2024, industry surveys indicated rising wages for these professionals, reflecting the tight labor market. This directly increases operational costs for Infinity Natural Resources.
Companies that possess patents for essential extraction technologies, such as specialized hydraulic fracturing fluids, can command premium prices. In 2024, the drive for energy independence fueled innovation, making access to these patented processes a critical factor, often necessitating costly licensing agreements for producers.
High switching costs, including retraining staff and reconfiguring infrastructure, solidify the position of incumbent suppliers. For instance, implementing new upstream software in 2024 averaged over $500,000, not including training, giving existing providers leverage to dictate terms and potentially increase prices.
| Factor | Impact on Infinity Natural Resources | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Services & Technology | High bargaining power for suppliers | Market valued at >$200 billion; consolidation increasing supplier leverage. |
| Skilled Labor Shortage | Increased wages and benefits for skilled workers | Notable salary increases for petroleum engineers in early 2024. |
| Proprietary Technology/Patents | Higher prices and licensing fees for essential tech | Demand for energy independence drives innovation, increasing value of patented processes. |
| High Switching Costs | Suppliers can dictate terms due to difficulty in changing providers | New upstream software implementation costs >$500k (excl. training) in 2024. |
What is included in the product
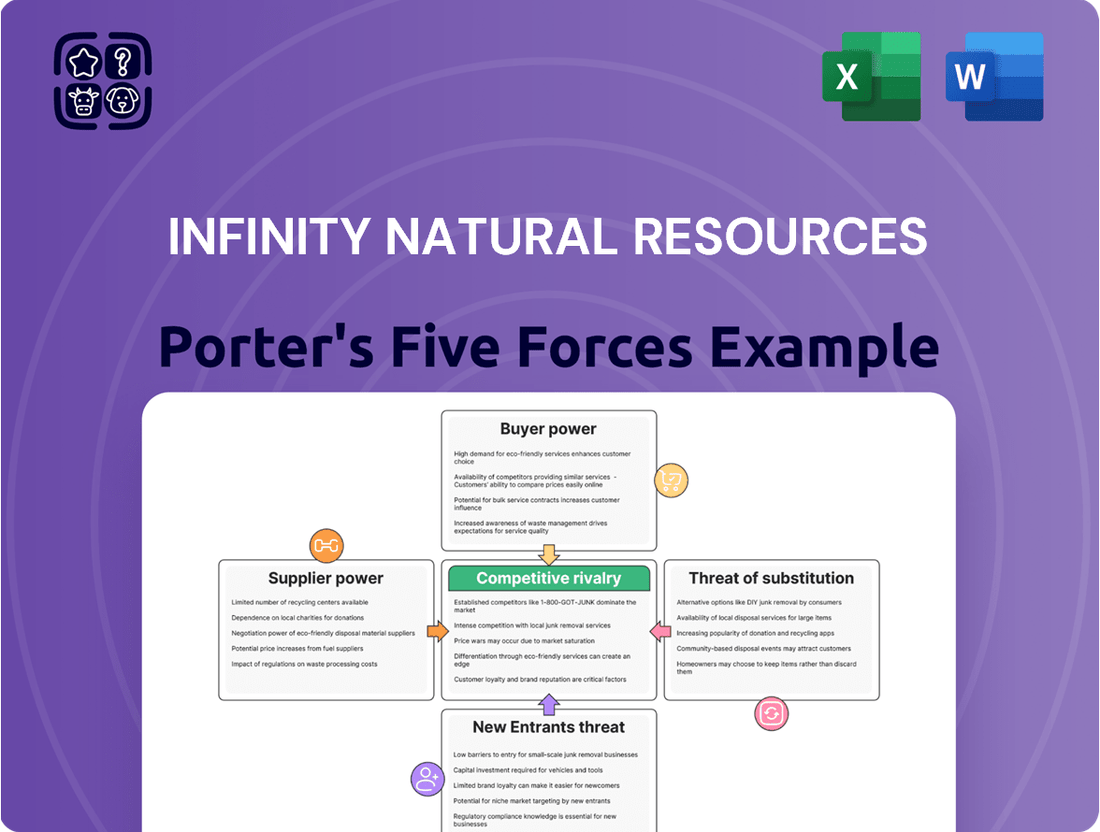
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Infinity Natural Resources examines the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes within the natural resources sector.
Instantly pinpoint competitive pressures and identify strategic vulnerabilities in the natural resources sector with Infinity Natural Resources' Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The commodity nature of oil and natural gas significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Because these resources are largely undifferentiated, buyers can easily switch between suppliers based on price alone, leaving producers with little room to negotiate higher margins.
This price sensitivity is particularly acute when the market is oversupplied. For instance, in early 2024, global oil inventories remained elevated, putting downward pressure on prices and empowering customers to demand the best possible terms from producers like Infinity Natural Resources.
Infinity Natural Resources benefits from a diversified customer base, serving entities like midstream companies, industrial users, and power generators. This broad reach means that the loss of any single customer typically has a minimal impact on the company's overall revenue stream, thereby limiting the bargaining power of individual buyers.
Large industrial customers and utility companies, particularly those with significant natural gas consumption, can exert considerable bargaining power. Their ability to integrate backward into production or secure long-term, fixed-price contracts provides a strong negotiating position, potentially driving down prices for suppliers like Infinity Natural Resources.
For instance, in 2024, major industrial consumers in regions with ample supply may leverage their scale to demand more favorable terms, directly impacting upstream producers. Infinity Natural Resources' strategic focus on the Appalachian Basin, a region with robust regional demand, helps to mitigate some of this pressure by creating a more captive market.
Global and Regional Demand Dynamics
Global and regional demand for oil and natural gas are key drivers of customer bargaining power. Economic growth, particularly in emerging markets, fuels demand, but shifts towards renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures can temper this. For instance, in 2024, global oil demand was projected to increase by around 1.2 million barrels per day according to the IEA, but regional variations and the pace of the energy transition play a crucial role.
Regional oversupply situations can significantly empower buyers. When there's more product available than needed in a specific area, customers can negotiate for better prices or terms. This dynamic is influenced by production levels, transportation infrastructure, and geopolitical factors affecting supply chains. For example, if a particular region experiences a surge in domestic production or a slowdown in economic activity, it can lead to a buyer's market.
The ongoing energy transition introduces another layer of complexity. As countries and corporations commit to decarbonization targets, the demand for fossil fuels may gradually decline, especially in developed economies. This long-term trend can shift leverage towards customers who are increasingly seeking cleaner energy alternatives, potentially impacting the bargaining power of traditional oil and gas suppliers.
- Global Oil Demand Growth (2024 Estimate): Approximately 1.2 million barrels per day (IEA).
- Regional Demand Variability: Influenced by economic growth, weather, and energy policies.
- Energy Transition Impact: Growing adoption of renewables can strengthen buyer positions in the long term.
- Oversupply Dynamics: Regional surpluses increase customer negotiation leverage.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures on Buyers
Customers in sectors like power generation are increasingly driven by regulatory mandates to curb emissions. For instance, by 2024, many regions have tightened emissions standards, directly impacting how much natural gas can be used as a primary fuel source.
These environmental pressures are shifting purchasing strategies, as buyers actively seek alternatives. The global renewable energy market, valued at over $1.5 trillion in 2023, continues its rapid expansion, presenting a compelling alternative to fossil fuels.
This transition influences the bargaining power of customers by creating more options. As clean energy sources become more economically viable and widely adopted, customers can leverage this to negotiate terms or switch suppliers more readily.
- Regulatory Shifts: Increased emissions standards by 2024 are forcing a re-evaluation of fuel choices in power generation.
- Market Alternatives: The robust growth of the renewable energy sector, exceeding $1.5 trillion in 2023, offers viable alternatives to natural gas.
- Customer Leverage: Availability of cleaner energy options strengthens customers' ability to negotiate or switch, impacting demand.
The commodity nature of oil and gas means customers have significant power, especially when supply is abundant. In 2024, elevated global oil inventories put downward pressure on prices, empowering buyers. While Infinity Natural Resources has a diversified customer base, large industrial users can leverage their scale and secure long-term contracts to negotiate favorable terms, potentially impacting prices.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Nature | High; easy switching based on price | Constant pressure on producers |
| Oversupply | Increases buyer leverage | Elevated inventories in early 2024 |
| Customer Scale | Large buyers can negotiate better terms | Major industrial consumers in ample supply regions |
| Energy Transition | Shifts leverage towards buyers seeking alternatives | Growing renewable market ($1.5T+ in 2023) |
Preview Before You Purchase
Infinity Natural Resources Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Infinity Natural Resources meticulously details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Appalachian Basin is a highly competitive arena, populated by a substantial number of independent oil and gas exploration and production companies. This dense ecosystem of players, ranging from smaller, agile operators to larger, established E&P firms, fosters a dynamic and often aggressive competitive landscape.
Infinity Natural Resources faces significant rivalry from these numerous competitors, all vying for prime acreage, essential resources, and a larger slice of market share. This intense competition is a defining characteristic of the basin, impacting everything from lease acquisition costs to the pricing of extracted commodities.
For instance, in 2024, the basin continued to see robust activity, with major players like EQT Corporation and Cabot Oil & Gas (now part of Coterra Energy) leading production. These larger entities, alongside a multitude of smaller independents, collectively drive the competitive pressures that Infinity Natural Resources must navigate.
The oil and gas sector, especially U.S. shale, experienced robust merger and acquisition (M&A) activity throughout 2024. Major deals, like ExxonMobil's acquisition of Pioneer Natural Resources for approximately $60 billion, underscore this trend. This consolidation creates fewer, larger, and more efficient competitors, intensifying the competitive environment for smaller entities such as Infinity Natural Resources.
The intense competition within the energy sector is significantly shaped by the inherent volatility of commodity prices. For instance, Henry Hub natural gas prices experienced considerable fluctuations throughout 2024, impacting drilling decisions and profitability. This volatility necessitates a sharp focus on cost control and operational efficiency to maintain a competitive edge.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Gains
The oil and gas sector, including companies like Infinity Natural Resources, is experiencing intense rivalry driven by technological advancements. The widespread adoption of sophisticated drilling and completion techniques, such as extended reach laterals and automated drilling systems, has dramatically boosted operational efficiency across the industry. For instance, in 2024, the average lateral length for new wells in the Permian Basin continued to increase, leading to higher initial production rates and reduced well-spacing requirements.
Companies that effectively integrate these cutting-edge technologies, like Infinity Natural Resources, gain a significant advantage by lowering their per-unit production costs. This continuous innovation is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in a market where cost leadership is paramount. The pressure to innovate is further amplified by the ongoing pursuit of higher recovery factors and the optimization of reservoir drainage.
- Increased Efficiency: Advanced drilling technologies, such as rig automation and longer laterals, are reducing drilling times and improving well productivity.
- Cost Reduction: Efficiency gains directly translate to lower per-barrel production costs, a key differentiator in competitive markets.
- Innovation Imperative: Companies like Infinity Natural Resources must constantly invest in and adopt new technologies to stay ahead of competitors.
- Market Share: Technological leaders often capture greater market share by offering more competitive pricing and demonstrating superior operational performance.
Access to Midstream Infrastructure and Takeaway Capacity
In key production areas like the Appalachian Basin, having adequate pipeline capacity to move oil and natural gas to market is absolutely vital. For instance, in 2024, the continued build-out of projects like the Mountain Valley Pipeline aimed to alleviate some of these constraints, but demand still often outstripped available takeaway.
When infrastructure is limited, it can lead to significant price differences between regions, directly affecting a company's profitability and its capacity to ramp up production. This bottleneck can intensify competition as companies vie for limited transport options, impacting their ability to realize full market value for their output.
- Limited pipeline takeaway capacity in regions like the Appalachian Basin directly impacts producer revenue.
- Regional price differentials emerge when infrastructure cannot keep pace with production volumes.
- Companies with better access to midstream infrastructure gain a competitive advantage.
- Infrastructure development is a key factor influencing competitive dynamics in the natural resources sector.
Infinity Natural Resources operates in an intensely competitive environment, characterized by a large number of E&P companies vying for resources and market share. This rivalry is amplified by significant M&A activity, as seen in 2024 with major acquisitions like ExxonMobil's $60 billion deal for Pioneer Natural Resources, consolidating the industry and creating larger, more efficient competitors.
Technological advancements further escalate competition, with companies adopting sophisticated drilling techniques to lower production costs. For example, increased lateral lengths in the Permian Basin in 2024 boosted initial production rates. Commodity price volatility, such as fluctuations in Henry Hub natural gas prices throughout 2024, also forces a relentless focus on cost control and operational efficiency to maintain a competitive edge.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristic | Impact on Infinity Natural Resources |
| Large Integrated Majors | Significant capital, advanced technology, economies of scale | Higher production efficiency, potential for lower cost structures |
| Mid-sized E&P Companies | Established acreage, operational expertise | Direct competition for leases and market share |
| Small Independent Operators | Agility, niche acreage focus | Can drive up lease costs in specific areas |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The accelerating growth of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power presents a substantial threat of substitution for fossil fuels, particularly in the electricity generation sector. As global power demand continues to climb, renewables are increasingly positioned to meet a significant portion of this growth. For instance, in 2023, renewable energy sources accounted for a record 83% of new global power capacity additions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
This shift directly impacts the long-term demand for natural gas, a key commodity for Infinity Natural Resources. Projections indicate that renewables will capture an ever-larger share of the energy market, potentially leading to a gradual but persistent decline in the demand for natural gas over the coming decades. This substitution effect is driven by falling renewable technology costs and supportive government policies worldwide.
Advancements in energy efficiency and conservation are significantly impacting the demand for traditional energy sources like oil and natural gas. For instance, by 2024, many countries have seen substantial gains in building insulation and appliance efficiency, directly lowering energy consumption. This trend reduces the reliance on new hydrocarbon extraction, making substitutes more attractive.
The ongoing electrification of transportation, from passenger vehicles to heavy-duty trucks, presents a potent substitute for oil. By the end of 2024, electric vehicle sales are projected to capture a notable percentage of the global automotive market, directly displacing gasoline and diesel demand. Similarly, industrial processes are increasingly adopting electric power, further eroding the market share for natural gas.
While natural gas is often viewed as a bridge fuel away from coal, the broader energy transition is accelerating the development of lower-carbon alternatives. Technologies like green hydrogen production and advanced battery storage are gaining traction, posing a potential long-term threat to demand for traditional oil and gas resources.
These emerging technologies, though currently representing a smaller portion of the global energy mix, are projected to grow significantly. For instance, the global hydrogen market was valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach over $250 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift in energy preferences.
The increasing viability and decreasing costs of renewable energy coupled with storage solutions mean that industries and consumers may increasingly opt for these cleaner substitutes, thereby reducing their reliance on fossil fuels like those produced by Infinity Natural Resources.
Government Policies and Environmental Regulations
Stringent government policies and environmental regulations are increasingly shaping the energy landscape, posing a significant threat of substitution for traditional fossil fuels. Measures focused on decarbonization, such as carbon taxes and emissions standards, directly encourage the adoption of cleaner alternatives. For instance, as of early 2024, many nations have set ambitious net-zero targets, with policies designed to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles and promote electric mobility, thereby reducing demand for oil.
These regulatory shifts can accelerate the market penetration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Government incentives, subsidies, and mandates for renewable energy deployment directly compete with oil and gas in electricity generation and transportation sectors. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in 2024 that renewable energy capacity additions continued to break records, underscoring the tangible impact of supportive policies on the growth of substitutes.
- Accelerated Shift: Government policies aiming for decarbonization are a primary driver for consumers and industries to seek energy alternatives to oil and gas.
- Renewable Energy Growth: Regulations and incentives are fueling significant investment and deployment of renewable energy sources, directly impacting fossil fuel markets.
- Policy Impact on Demand: Environmental regulations, such as those targeting emissions reduction, can curtail demand for oil and gas products in key sectors like transportation and power generation.
- Global Targets: Ambitious national and international climate goals, like achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century, create a long-term imperative for substituting fossil fuels with sustainable options.
Public Perception and ESG Pressures
The increasing focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors significantly impacts the energy sector. Growing public awareness and investor demand for sustainable practices are pushing consumers and corporations to explore alternatives to traditional hydrocarbons. This societal shift creates a strong impetus for substitute energy sources.
In 2024, for instance, global investment in renewable energy is projected to reach new heights, with estimates suggesting it could surpass $2 trillion annually by the end of the decade. This trend directly challenges the dominance of fossil fuels, indicating a tangible threat from substitutes driven by ESG considerations.
- Growing ESG Awareness: Public and investor scrutiny on environmental impact and social responsibility is intensifying.
- Investor Pressure: Funds are increasingly divesting from fossil fuels and channeling capital into green technologies.
- Consumer Preference Shift: Consumers are showing a greater inclination towards products and services with lower carbon footprints.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in renewable energy and energy storage are making substitutes more viable and cost-competitive.
The threat of substitutes for Infinity Natural Resources is substantial, driven by the rapid advancements and increasing adoption of renewable energy technologies. These alternatives are becoming more cost-competitive and widely accepted, directly challenging the market position of natural gas and oil.
The electrification of transportation, coupled with efficiency gains in energy consumption, further diminishes the demand for fossil fuels. For example, by the end of 2024, electric vehicles are expected to capture a significant share of the automotive market, directly impacting gasoline and diesel sales.
Emerging technologies like green hydrogen and advanced battery storage are also gaining momentum, presenting a long-term substitution risk. The global hydrogen market, valued around $130 billion in 2023, is projected to exceed $250 billion by 2030, signaling a clear shift in energy preferences.
Government policies and growing ESG awareness are accelerating this transition. In 2024, renewable energy capacity additions continued to break records, with supportive policies driving this growth. Global investment in renewables is anticipated to surpass $2 trillion annually by the end of the decade, underscoring the tangible impact of these substitutes.
| Key Substitute Trends | 2023 Data/Projection | Impact on Fossil Fuels | Driving Factors |
| Renewable Energy Capacity Additions | Record high in 2023 (IEA) | Direct competition in power generation | Falling costs, government incentives |
| Electric Vehicle Market Share | Notable projected share by end of 2024 | Displacement of gasoline/diesel demand | Technological advancements, policy support |
| Global Hydrogen Market Growth | Valued at ~$130 billion (2023), projected >$250 billion by 2030 | Potential long-term alternative for industrial use | Decarbonization efforts, innovation |
| Global Renewable Energy Investment | Projected to exceed $2 trillion annually by 2030 | Capital diversion from fossil fuels | ESG considerations, climate goals |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the oil and gas exploration and production (E&P) sector, particularly for unconventional resources, demands immense capital. Significant investments are needed for acquiring land rights, drilling wells, and building essential infrastructure like pipelines and processing facilities. For instance, Infinity Natural Resources' projected capital expenditure for drilling and completion (D&C) activities in 2025, estimated at $1.2 billion, underscores the substantial financial commitment required to even begin operations.
Acquiring access to prospective acreage with proven reserves, particularly in mature and productive basins like the Appalachian Basin, presents a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. Established companies, such as Infinity Natural Resources, already possess significant undeveloped locations, creating a considerable advantage in resource ownership and future production potential.
The significant capital investment required for advanced drilling and completion technologies, like those Infinity Natural Resources utilizes, presents a major barrier. For instance, the cost of acquiring and maintaining state-of-the-art hydraulic fracturing equipment can run into tens of millions of dollars, a substantial outlay for any new competitor.
Furthermore, the operational knowledge and proprietary methods developed over years of practice in areas such as reservoir analysis and directional drilling are not easily replicated. New entrants would need to either invest heavily in research and development or acquire existing expertise, both of which are time-consuming and costly endeavors, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
The oil and gas sector faces a formidable barrier to entry due to stringent and ever-changing regulations, especially those focused on environmental stewardship. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to enforce methane emission standards, requiring substantial investments in leak detection and repair technologies. New companies must navigate a complex web of permitting processes and compliance protocols, demanding significant capital and specialized knowledge.
These regulatory hurdles translate into considerable upfront costs for potential new entrants. The need for advanced environmental monitoring systems, specialized waste disposal, and adherence to safety standards can easily run into millions of dollars. For example, meeting the requirements for offshore drilling permits alone can involve extensive environmental impact assessments and mitigation plans, adding significant lead time and expense. This high cost of compliance effectively limits the number of new players who can realistically enter the market.
The evolving nature of environmental legislation, such as potential carbon pricing mechanisms or stricter emissions caps anticipated by 2025, further amplifies the threat. Companies must not only comply with current rules but also anticipate and adapt to future regulatory landscapes. This ongoing uncertainty and the potential for future capital expenditures create a significant deterrent for those considering entry into the oil and gas industry.
- High Capital Investment: Compliance with environmental regulations in 2024, such as methane emission controls, required significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure.
- Navigational Complexity: New entrants must possess deep expertise to understand and adhere to a multifaceted system of local, state, and federal environmental laws.
- Ongoing Adaptation Costs: The dynamic nature of environmental policy necessitates continuous investment to meet evolving standards, posing a long-term financial challenge for new companies.
Established Infrastructure and Supply Chains
Established infrastructure and supply chains present a significant barrier for new entrants in the natural resources sector. Existing players, like Infinity Natural Resources, benefit from long-standing relationships with suppliers, ensuring consistent access to raw materials and preferential pricing. For instance, major oil and gas companies often own or have exclusive access to pipelines, processing facilities, and transportation networks, which are crucial for moving resources from extraction sites to markets. In 2024, the cost of building new midstream infrastructure, such as pipelines, can easily run into billions of dollars, making it economically prohibitive for most newcomers.
Securing reliable and cost-effective supply chains is another hurdle. Companies with established operations have optimized logistics, bulk purchasing power, and deep connections with equipment manufacturers and service providers. A new entrant would need to replicate these complex networks, which requires substantial upfront investment and time to build trust and operational efficiency. The capital expenditure required to establish these foundational elements can deter potential competitors, thereby strengthening the position of incumbents.
- Established Relationships: Existing firms have built deep ties with suppliers, ensuring consistent material flow and favorable terms.
- Infrastructure Access: Incumbents often own or control critical midstream assets like pipelines and processing plants, which are costly for new players to replicate.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Optimized logistics and bulk purchasing power of established companies create cost advantages that are difficult for new entrants to match.
- High Capital Costs: The significant investment needed to build new infrastructure and replicate supply chains acts as a substantial barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants in the oil and gas E&P sector is considerably low due to the immense capital required for operations, access to acreage, and advanced technology adoption. For example, Infinity Natural Resources' 2025 projected capital expenditure of $1.2 billion for drilling and completion highlights the substantial financial commitment needed to even begin. Furthermore, acquiring prime acreage in established basins like the Appalachian presents a significant hurdle, as incumbents already control vast undeveloped resources.
The high cost of proprietary technologies, such as advanced hydraulic fracturing equipment, which can cost tens of millions of dollars, acts as another substantial barrier. New companies must either invest heavily in R&D or acquire existing expertise, both time-consuming and expensive processes, thereby limiting new competition.
Stringent environmental regulations and the need for continuous adaptation to evolving policies, like methane emission controls enforced in 2024, add millions in upfront costs for new entrants. The complexity of navigating permits and compliance, coupled with the anticipation of future regulations such as carbon pricing by 2025, creates a significant deterrent.
Established infrastructure, including pipelines and processing facilities, and optimized supply chains with preferential pricing, present formidable barriers. Replicating these networks requires billions in investment for new midstream infrastructure and significant time to build trust and efficiency, making entry economically prohibitive for most newcomers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Infinity Natural Resources leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and publicly available financial statements to assess competitive pressures.
