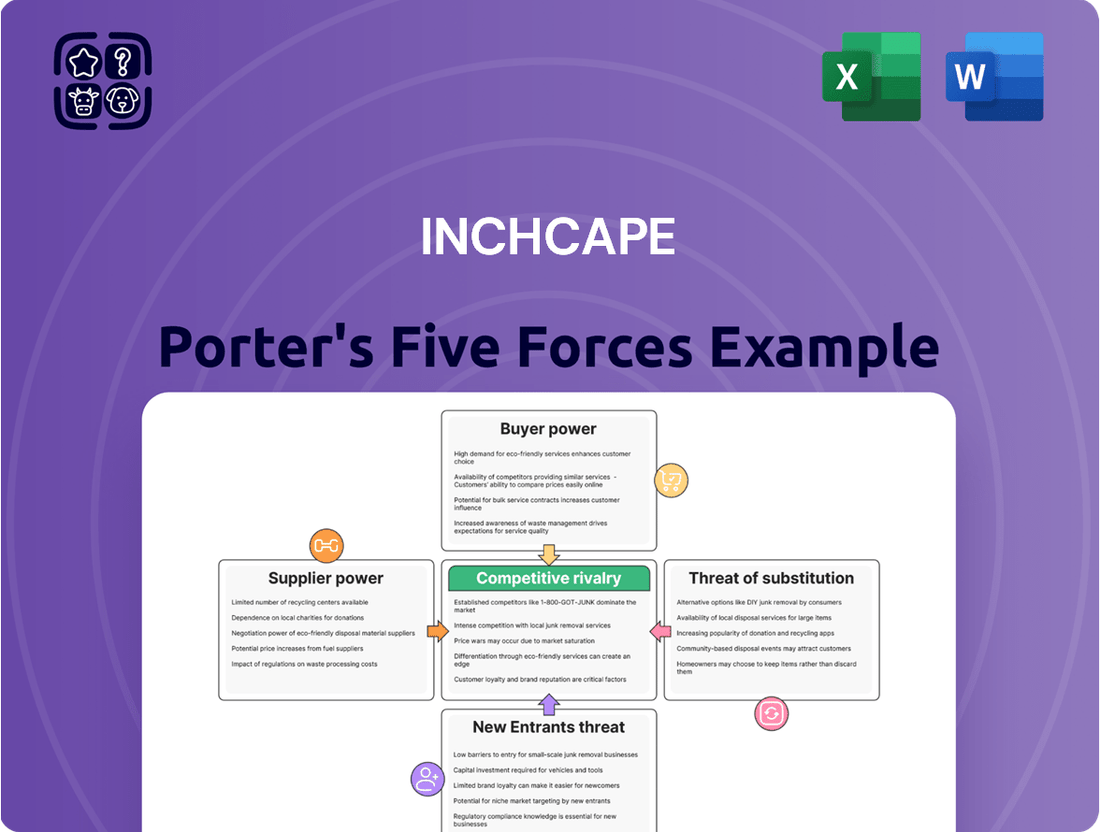
Inchcape Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Inchcape Bundle
Inchcape's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the bargaining power of its buyers and the intensity of rivalry among existing players. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the automotive distribution and retail sector. The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute products also present significant challenges and opportunities for Inchcape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Inchcape’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers in the automotive distribution sector is significantly influenced by the concentration of automotive brands. Inchcape's reliance on a limited number of highly reputable Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like Toyota, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW, which boast substantial brand equity, means these OEMs hold considerable sway. This concentration allows them to dictate terms to distributors, particularly for in-demand models and emerging technologies such as electric vehicles (EVs). For instance, in 2023, Toyota continued its strong global sales performance, and Mercedes-Benz reported significant growth in its EQ electric vehicle line, underscoring the desirability and therefore the supplier power of these brands.
Inchcape faces significant supplier power due to high switching costs for automotive manufacturers. Transitioning from Inchcape to a different distribution partner would necessitate substantial investments in renegotiating agreements, retooling supply chains, retraining personnel, and rebuilding brand awareness, making it an economically burdensome undertaking for OEMs.
These elevated switching costs mean that Inchcape's current brand partners have considerable leverage. For example, in 2023, Inchcape reported revenue of £8.5 billion, indicating the scale of operations dependent on these established brand relationships. This reliance strengthens the bargaining position of the automotive brands Inchcape represents.
Automotive brands Inchcape partners with offer highly differentiated products, from luxury sedans to performance SUVs. This differentiation is crucial as it directly impacts Inchcape's ability to attract and retain customers in a competitive market. For instance, the unique engineering and brand prestige of marques like BMW or Toyota are not easily replicated, giving these manufacturers considerable leverage.
The importance of these specific brands to Inchcape's business model cannot be overstated. Inchcape's revenue and profitability are intrinsically linked to its ability to secure and effectively market vehicles from these sought-after manufacturers. The unique features, advanced technology, and strong consumer demand for particular automotive brands significantly amplify the suppliers' bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration by OEMs
Automotive manufacturers, or OEMs, are increasingly exploring direct-to-consumer sales models. This presents a significant threat of forward integration, potentially allowing them to bypass traditional distributors like Inchcape.
This shift grants OEMs greater leverage in negotiations, as they can theoretically reduce their dependence on existing distribution networks. For example, Tesla's direct sales model has been a key factor in its success and disruption of the traditional automotive retail landscape.
While the full impact of this trend is still unfolding, it’s a critical consideration for distributors. The increasing digital capabilities of OEMs allow them to control the customer experience more directly.
In 2024, many legacy OEMs are investing heavily in their own online sales platforms and company-owned retail outlets. This strategic move aims to capture more of the customer relationship and profit margin traditionally held by dealerships and distributors.
- OEMs are developing direct online sales channels, aiming to control the customer journey from purchase to delivery.
- Investment in company-owned retail and service centers by OEMs is growing, reducing reliance on independent distributors.
- The threat of forward integration increases the bargaining power of OEMs, as they can threaten to disintermediate distributors.
- Customer data ownership shifts to OEMs in direct sales models, providing them with valuable insights for future strategy.
Input Importance and Cost to Suppliers
While Inchcape primarily deals with finished vehicles, its Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) partners are deeply dependent on a wide array of parts manufacturers. The growing complexity and expense of vehicle components, particularly for electric vehicles (EVs), can indirectly affect Inchcape. This is because these rising costs can impact the OEMs' overall profitability and, consequently, their pricing strategies for the vehicles Inchcape distributes.
The increasing reliance on specialized and often proprietary components, especially for advanced automotive technologies, strengthens the bargaining position of these parts suppliers. For instance, the semiconductor shortage experienced globally in 2021 and 2022 significantly highlighted the critical dependence of automakers on chip manufacturers, leading to production delays and increased costs across the industry.
- Input Importance: The value and uniqueness of the components supplied by manufacturers are crucial. Highly specialized or patented parts give suppliers more leverage.
- Cost to Suppliers: The cost incurred by suppliers in producing these inputs is a factor. If suppliers have high fixed costs or limited alternatives, they may be more willing to negotiate.
- Impact on OEMs: For OEMs, the cost and availability of these essential components directly influence their production efficiency and profit margins.
- Indirect Influence on Inchcape: Changes in component costs or supply chain disruptions for OEMs can lead to altered vehicle pricing or availability for Inchcape, impacting its sales and operations.
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), remains a significant force for Inchcape. The concentration of major automotive brands and the high switching costs for OEMs to move away from established distributors like Inchcape grant these suppliers considerable leverage. Furthermore, OEMs exploring direct-to-consumer sales models in 2024 present a credible threat of forward integration, potentially disintermediating distributors and shifting customer data ownership. This strategic shift by OEMs to control the customer journey directly amplifies their bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Inchcape | 2023/2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| OEM Concentration | Increases supplier leverage due to reliance on few key brands. | Inchcape's core business relies on brands like Toyota and Mercedes-Benz, which maintain strong market positions. |
| Switching Costs for OEMs | Deters OEMs from changing distribution partners, strengthening Inchcape's position. | High costs associated with renegotiating, retooling, and retraining make it difficult for OEMs to switch. |
| Direct-to-Consumer Models | Threatens to disintermediate Inchcape, reducing its role. | Many OEMs are investing in online sales platforms and company-owned outlets in 2024. |
| Component Dependency | Indirectly affects Inchcape through OEM production costs and pricing. | Semiconductor shortages in prior years highlighted OEM dependence on component suppliers, impacting vehicle availability and cost. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive landscape for Inchcape by examining the five forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly pinpoint and alleviate competitive pressures by visualizing the impact of each Porter's Five Forces on your industry.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the automotive sector, especially when purchasing new vehicles, are highly attuned to price. This sensitivity is amplified by current economic conditions and the ease with which consumers can access pricing data and available incentives online.
This means distributors like Inchcape face constant pressure to maintain competitive pricing structures and offer attractive discounts to secure sales. For instance, in 2024, many manufacturers rolled out significant cash rebates and low-APR financing deals to stimulate demand amidst fluctuating economic sentiment.
Inchcape's ability to manage its cost of goods sold and operational efficiencies directly impacts its capacity to absorb or pass on price changes without eroding its profit margins, given this customer behavior.
For many end-consumers, switching between car brands or dealerships is a straightforward process with minimal financial or logistical hurdles. This ease of transition allows customers to readily explore alternative options, driving down the bargaining power of individual buyers as they can easily find comparable products or services elsewhere.
With a vast array of car manufacturers and dealerships readily available, and readily accessible online information, customers are well-equipped to compare prices, features, and service quality. This transparency and abundance of choice naturally puts pressure on Inchcape to consistently offer competitive pricing and superior customer experiences to retain its customer base.
In 2024, the automotive market continued to see a high degree of consumer choice, with numerous brands vying for market share. The average consumer typically researches several dealerships and brands before making a purchase, highlighting the low switching costs and the resulting influence customers wield in price negotiations.
The digital age has revolutionized how customers access information, particularly in the automotive sector. With the internet, consumers can easily research vehicle models, compare prices across dealerships, and read countless reviews from other buyers. This wealth of readily available data significantly empowers customers, increasing their bargaining power.
This increased transparency means customers can pinpoint the best deals and understand the true market value of a vehicle. For instance, in 2024, online automotive marketplaces and review sites provide real-time pricing data, allowing consumers to negotiate more effectively. This forces Inchcape to be competitive, as customers can quickly identify and leverage more favorable offers elsewhere.
Customers are no longer reliant on a dealership's provided information; they can independently verify specifications, features, and pricing. This shift means they enter negotiations with a much stronger understanding, demanding better terms and potentially influencing Inchcape's pricing strategies and service offerings to remain attractive in a competitive landscape.
Diverse Customer Segments and Preferences
Inchcape navigates a broad spectrum of customers, from individual car buyers to large fleet operators. This diversity means varying expectations regarding pricing, vehicle features, and after-sales service. For instance, a private buyer might prioritize a specific model's aesthetics and financing options, while a corporate fleet manager will focus on total cost of ownership, bulk discounts, and maintenance efficiency.
The ability of these varied customer groups to influence Inchcape's pricing and terms is a key aspect of their bargaining power. When individual customers have numerous dealership options and access to online price comparisons, their power increases. Similarly, large fleet buyers, by virtue of their volume, can negotiate more substantial discounts and favorable contract terms. For example, in 2024, the automotive retail sector has seen continued pressure on margins, partly due to informed consumers leveraging digital tools to secure better deals, impacting dealership profitability.
- Diverse Customer Needs: Inchcape caters to both individual consumers seeking personal vehicles and businesses requiring fleet solutions, each with distinct purchasing criteria and price sensitivities.
- Information Asymmetry Reduction: The digital age empowers customers with readily available pricing information and competitor analysis, significantly enhancing their ability to negotiate favorable terms.
- Fleet Buyer Leverage: Large corporate clients, placing substantial orders, wield considerable bargaining power, often securing bulk discounts and customized service packages that impact Inchcape's revenue per unit.
- Price Sensitivity: For many customer segments, particularly in competitive markets or during economic downturns, price remains a primary decision factor, amplifying customer bargaining power.
Rise of Online Sales and Mobility Services
The increasing ease of online car purchasing, coupled with the growing appeal of mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) options, particularly among younger demographics, is significantly reshaping the automotive landscape. This trend empowers customers by offering them more choices beyond traditional dealership models. For instance, in 2024, online car retailers have seen substantial growth, with some projecting double-digit increases in sales volume year-over-year, indicating a clear shift in consumer behavior.
Younger generations, like Gen Z and Millennials, are increasingly exploring subscription services and ride-sharing platforms as alternatives to outright vehicle ownership. This growing interest in MaaS directly impacts the bargaining power of customers. In 2023, the global MaaS market was valued at over $70 billion and is projected to expand considerably in the coming years. This signifies a substantial portion of the transportation market now offering alternatives that bypass traditional car buying processes.
- Shift in Acquisition Methods: Online platforms and MaaS offer alternative avenues for vehicle access, reducing reliance on traditional dealerships.
- Customer Empowerment: Increased options allow consumers to negotiate better terms or seek more competitive pricing.
- Demographic Trends: Younger consumers show a higher propensity towards mobility services over traditional ownership.
- Market Evolution: The rise of these new models alters the power dynamic, favoring customers seeking flexibility and convenience.
Customers possess significant bargaining power in the automotive sector due to increased transparency and choice. In 2024, readily available online pricing, competitor analysis, and manufacturer incentives empower consumers to negotiate effectively. This forces distributors like Inchcape to maintain competitive pricing and offer value-added services to retain business.
The ease with which customers can switch brands or dealerships, coupled with the availability of detailed product information, amplifies their leverage. Large fleet buyers, in particular, can negotiate substantial discounts and favorable terms due to their purchasing volume, impacting Inchcape's profit margins on bulk sales.
Furthermore, the growing adoption of mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) and online purchasing platforms offers customers alternatives to traditional dealership models. This diversification of acquisition methods, evident in the projected growth of the MaaS market, further strengthens customer bargaining power by providing more flexible and potentially cost-effective options.
| Factor | Impact on Inchcape | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High pressure on pricing, need for competitive offers. | Significant cash rebates and low-APR financing offered by manufacturers. |
| Information Availability | Empowers customers for negotiation, reduces information asymmetry. | Online marketplaces provide real-time pricing and reviews. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs increase customer ability to explore alternatives. | Consumers research multiple dealerships and brands before purchase. |
| Fleet Buyer Volume | Leverage for bulk discounts and customized terms. | Fleet managers focus on total cost of ownership and efficiency. |
| MaaS Adoption | Potential shift from traditional ownership, impacting sales volume. | Global MaaS market valued over $70 billion, with continued expansion. |
What You See Is What You Get
Inchcape Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The preview you're viewing is the exact, comprehensive Inchcape Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. This detailed document meticulously breaks down the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You can be confident that the insights and strategic frameworks presented here are precisely what you'll be able to download and utilize without any surprises or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
While Inchcape operates as a significant global player, the automotive retail and distribution landscape is often characterized by considerable fragmentation at regional and local levels. This means that even with Inchcape's scale, intense competition exists from a multitude of independent dealerships and smaller, localized groups vying for market share within specific geographic territories. This competitive environment can pressure margins and necessitate agile strategies to maintain dominance.
The automotive distribution and retail sector, including companies like Inchcape, is characterized by substantial fixed costs. These investments span physical assets like showrooms and service centers, significant inventory levels, and the growing need for robust digital infrastructure to support online sales and customer engagement.
These high fixed costs, coupled with significant capital tied up in dealerships and parts, create formidable exit barriers. Companies are compelled to continue operations and vie for market share to cover their overheads, leading to intense competition among existing players to maintain sales volumes and profitability.
For instance, in 2024, the automotive retail sector continues to see players invest heavily in modernizing dealerships and digital platforms, further cementing these high fixed costs. This makes exiting the market a financially challenging prospect, reinforcing the pressure to compete vigorously.
Inchcape's competitive rivalry is shaped by how well it can make its offerings stand out. This goes beyond just selling cars; it includes the quality of aftersales services, the overall customer journey, and the integration of digital tools. For instance, in 2024, Inchcape continued to invest in its digital platforms to enhance customer engagement and streamline service bookings, aiming to create a seamless experience that differentiates it from competitors solely focused on the transaction.
Strong relationships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are also a crucial factor influencing rivalry. Inchcape's ability to secure exclusive or preferred distribution rights for desirable automotive brands provides a significant competitive edge. This access to popular models, often backed by manufacturer marketing support, allows Inchcape to attract and retain customers in a crowded market.
Slow Market Growth in Developed Regions
The automotive distribution sector experiences intensified rivalry when growth in developed markets moderates. While global light vehicle sales might show a slight uptick, countries like the United States and those in Western Europe often see much slower expansion or even contraction. For instance, in 2024, many European markets, including Germany and France, are projected to see only marginal increases in new car registrations, with some potentially declining year-on-year. This subdued growth environment compels distributors like Inchcape to fight harder for a larger slice of a relatively static pie, leading to more aggressive pricing and promotional activities.
This dynamic forces companies to prioritize market share acquisition over capitalizing on broad market expansion. When overall demand isn't significantly increasing, gaining customers from competitors becomes the primary growth lever. This can manifest as increased marketing spend, enhanced customer service initiatives, or the development of more competitive financing and leasing options. The focus shifts internally to operational efficiency and external to outmaneuvering rivals for every available sale.
- Slower Growth in Key Developed Markets: Many established automotive markets, particularly in Europe and North America, are experiencing growth rates below the global average, putting pressure on distributors.
- Focus on Market Share: With limited overall market expansion, competition intensifies as distributors aim to capture a greater percentage of existing sales.
- Increased Promotional Activity: To win customers in a slow-growth environment, expect more aggressive pricing, incentives, and marketing campaigns from distributors.
- Operational Efficiency Becomes Crucial: Companies must streamline operations to maintain profitability when sales growth is hard-won through competitive means.
Strategic Shifts by Competitors and OEMs
Competitors, such as other major automotive dealer groups and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) exploring direct-to-consumer sales models, are actively reshaping their approaches. This includes significant investments in digital platforms, a growing emphasis on electric vehicle (EV) sales and servicing, and the introduction of novel service offerings designed to capture evolving customer preferences. For instance, in 2024, many large dealer groups reported double-digit percentage growth in their EV sales segments, indicating a clear strategic pivot.
Inchcape faces intense pressure to not only match but also anticipate these strategic shifts. The company’s ability to innovate, particularly in areas like online vehicle purchasing experiences and integrated EV charging solutions, is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge. The automotive retail landscape is in constant flux, with early adopters of advanced digital tools and EV infrastructure often gaining substantial market share. In 2023, for example, dealer groups that heavily invested in online configurators and virtual showrooms saw higher customer engagement rates compared to those with traditional digital presences.
- Digital Transformation: Competitors are enhancing online sales platforms and customer service portals.
- New Energy Vehicles (NEVs): A significant focus is being placed on expanding EV and hybrid offerings and related services.
- New Service Models: Innovative subscription services and mobile repair options are gaining traction.
- OEM Direct Sales: The trend of manufacturers bypassing traditional dealerships is an ongoing threat.
Competitive rivalry within the automotive distribution and retail sector is a significant factor impacting Inchcape. The market is populated by numerous established players and emerging entities, all vying for market share and customer loyalty. This intense competition is further amplified by the high fixed costs inherent in the industry, such as investments in dealerships, inventory, and digital infrastructure, which create substantial exit barriers and compel continuous competitive engagement.
Inchcape's competitive landscape is characterized by a diverse range of rivals, including other large global automotive groups, regional dealership networks, and increasingly, manufacturers exploring direct-to-consumer (DTC) sales models. In 2024, the focus on digital transformation and the expansion of electric vehicle (EV) sales and servicing capabilities are key battlegrounds. For example, major competitors are reporting substantial investments in upgrading their online platforms and expanding their EV charging infrastructure to meet evolving consumer demands.
| Competitor Action Area | Inchcape's Response/Challenge | 2024 Market Trend Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Sales Platforms | Enhancing online customer journey and virtual showrooms | Double-digit growth in online inquiries for new vehicles |
| Electric Vehicle (EV) Expansion | Increasing EV model availability and charging solutions | EV market share projected to reach 20% globally in 2024 |
| Aftersales Service Innovation | Focus on mobile servicing and personalized customer care | Customer satisfaction scores linked to service convenience are rising |
| Manufacturer Direct Sales (DTC) | Strengthening brand partnerships and value-added services | Some OEMs increasing DTC pilot programs in key European markets |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Public transportation and ride-sharing services present a significant threat of substitutes for vehicle ownership, particularly in densely populated urban environments. These alternatives offer cost-effective mobility solutions, especially for individuals looking to avoid the expenses associated with purchasing, insuring, and maintaining a personal vehicle. For instance, in 2024, ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft saw continued strong user engagement, with global gross bookings projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating their widespread adoption as a viable transport option.
The rise of long-term vehicle rentals and subscription services presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional car ownership. These models offer consumers flexible access to vehicles, often with all-inclusive packages covering insurance, maintenance, and even roadside assistance. This makes them an attractive alternative for those who prefer not to bear the full burden of ownership.
In 2024, the automotive subscription market continued its growth trajectory, with many manufacturers and third-party providers expanding their offerings. For instance, services like Porsche Drive and Cadillac Live provide convenient digital platforms for users to select and manage vehicle subscriptions. This accessibility directly competes with new and used car sales by offering a different value proposition.
The appeal lies in predictable monthly costs and the ability to switch vehicles as needs change, a stark contrast to the upfront investment and long-term commitment of purchasing a car. This shift in consumer preference, driven by convenience and flexibility, can undoubtedly siphon demand away from traditional sales channels, impacting overall vehicle purchase volumes.
The threat of substitutes in the automotive industry is significantly amplified by a strong used car market and the growing average age of vehicles. Consumers increasingly view pre-owned vehicles as a viable and more budget-friendly alternative to purchasing new cars, directly impacting demand for new models.
This trend extends the typical replacement cycle for new vehicles, as owners can maintain their existing cars for longer periods due to improved reliability and the availability of affordable used options. For instance, in 2024, the average age of vehicles on U.S. roads reached a record 12.6 years, a clear indicator of this substitution effect.
Alternative Mobility Solutions
Beyond traditional cars, alternative mobility solutions are increasingly posing a threat. Electric bikes, scooters, and various micro-mobility options are gaining traction, especially in urban areas for short trips. These alternatives can reduce the perceived need for car ownership, impacting demand for traditional vehicles. For instance, the shared e-scooter market in major cities saw significant growth in 2024, with some regions reporting a 20% increase in usage year-over-year for commutes under 5 miles.
These substitutes offer convenience and can be more cost-effective for certain travel needs. Consider the rise of ride-sharing services combined with these personal mobility devices; they create a compelling package that competes directly with owning and operating a personal vehicle. In 2024, surveys indicated that over 30% of urban dwellers in Europe considered these combined solutions as viable alternatives to a second car.
- Growing adoption of e-bikes and e-scooters for commuting.
- Increased availability and integration of shared mobility services.
- Cost-effectiveness and convenience of micro-mobility for short distances.
- Environmental consciousness driving preference for greener transport options.
OEM Direct Sales and Online Platforms
The increasing capability of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to sell directly to consumers online presents a significant threat. For example, many automotive OEMs have invested heavily in their own digital sales platforms. This bypasses traditional distribution networks like Inchcape, offering an indirect substitute for vehicle transactions. In 2024, direct-to-consumer online sales in the automotive sector continued to grow, with some manufacturers reporting substantial increases in online order volumes. This trend allows OEMs to capture a larger share of the value chain, potentially reducing reliance on intermediaries.
Furthermore, the proliferation of digital marketplaces and other online platforms for vehicle transactions amplifies this threat. These platforms can facilitate the direct buying and selling of vehicles, further disintermediating traditional dealerships and distribution groups. As of early 2024, online car marketplaces continue to gain traction, with significant transaction volumes reported. This signifies a shift in consumer behavior towards digital channels for vehicle acquisition, posing a direct substitute for the services Inchcape historically provides.
- OEM Online Sales Growth: Many automakers saw a notable uptick in online sales inquiries and completed transactions in 2024, indicating a growing consumer comfort with digital purchasing.
- Digital Marketplace Expansion: The number and reach of online platforms dedicated to vehicle sales have expanded, offering consumers more direct alternatives.
- Disintermediation Risk: The ability of OEMs and digital platforms to connect directly with buyers threatens Inchcape's role as a crucial intermediary in the automotive distribution chain.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: A growing segment of consumers now prefers the convenience and transparency offered by online purchasing methods for vehicles.
The automotive industry faces a substantial threat from substitutes beyond traditional vehicle ownership. Ride-sharing, car rentals, and subscription services offer compelling alternatives, especially in urban areas. For instance, in 2024, global ride-sharing bookings were projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, showcasing their widespread acceptance as a mobility solution. This growing adoption directly impacts the demand for new vehicle sales, as consumers opt for more flexible and potentially cost-effective transportation methods.
The increasing popularity of micro-mobility options like e-bikes and e-scooters further diversifies the transportation landscape. These are particularly attractive for short urban commutes, often proving more convenient and economical than car usage. In 2024, shared e-scooter usage saw a notable increase in many cities, with some reporting up to a 20% year-over-year rise for shorter journeys. This trend suggests a diminishing reliance on personal vehicles for everyday travel.
The threat also extends to how vehicles are bought and sold. The rise of direct-to-consumer online sales by manufacturers and expanded digital marketplaces empowers consumers to bypass traditional dealerships. In 2024, many automakers reported significant growth in their online sales channels, indicating a shift in consumer preference towards digital transactions. This disintermediation poses a direct challenge to established distribution networks like Inchcape.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Trend/Data Point | Impact on Traditional Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Ride-Sharing & Car Rentals | Global ride-sharing gross bookings projected in hundreds of billions | Reduces necessity for personal vehicle ownership |
| Vehicle Subscriptions | Continued market growth with expanded OEM offerings | Offers flexible access, competing with purchase models |
| Micro-mobility (e-bikes/scooters) | Up to 20% YoY usage increase in some cities for short trips | Decreases demand for short-distance car use |
| Direct-to-Consumer Online Sales | Significant growth in OEM online order volumes | Bypasses traditional intermediaries, capturing value |
Entrants Threaten
High capital requirements act as a significant barrier to entry in the automotive distribution and retail sector. Establishing a new dealership, for instance, demands substantial upfront investment in real estate, showroom facilities, and service bays. In 2024, the cost to build a new dealership could range from several million to tens of millions of dollars, depending on location and size.
Furthermore, securing and managing a diverse inventory of new vehicles, which can tie up hundreds of millions of dollars, is a critical financial hurdle. Inchcape, for example, invests heavily in its vehicle stock to meet market demand across its various brands and regions. This inventory management, coupled with the need for sophisticated after-sales service infrastructure and increasingly, digital customer engagement platforms, elevates the initial capital outlay considerably.
Established distributors like Inchcape benefit from deep-rooted, often exclusive, partnerships with major automotive Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These enduring relationships are a significant barrier; new market entrants find it exceedingly difficult to secure coveted brand franchises. OEMs typically prioritize established players with a proven track record and robust infrastructure over newcomers.
Incumbent automotive retailers like Inchcape leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This allows them to spread costs across vast networks for logistics, marketing campaigns, and expansive aftersales service centers, creating a cost advantage that new entrants would find difficult to overcome. For instance, in 2024, major automotive groups consistently reported higher operating margins due to their scale, allowing for more competitive pricing and service offerings.
Furthermore, Inchcape and similar established players benefit from the experience curve. Decades of managing intricate global supply chains, navigating complex regulatory environments, and building strong customer loyalty provide invaluable operational efficiencies. This deep-seated expertise in areas like inventory management and customer relationship management translates into smoother operations and cost savings that are not readily replicable by newcomers entering the market in 2024.
Regulatory Hurdles and Licensing
The automotive sector is heavily regulated, with stringent licensing requirements and compliance standards varying significantly by region. For instance, in the European Union, dealerships often require specific authorizations and adherence to consumer protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which impacts how customer data is handled. Navigating this intricate web of regulations presents a substantial challenge for new entrants seeking to establish a foothold.
These regulatory barriers can translate into considerable upfront costs and time investments. New companies must allocate resources to understand and comply with emissions standards, safety regulations, and import/export laws, which can be prohibitive. For example, meeting Euro 7 emissions standards, which are being progressively implemented, requires significant investment in new vehicle technology.
Key regulatory hurdles include:
- Emissions and Safety Standards: Compliance with evolving environmental and safety mandates like WLTP (Worldwide Harmonised Light Vehicles Test Procedure) necessitates substantial R&D and manufacturing adjustments.
- Licensing and Dealership Agreements: Obtaining necessary operating licenses and securing franchise agreements with manufacturers can be a complex and lengthy process, often favoring established players.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Adherence to warranty regulations, return policies, and dispute resolution mechanisms adds layers of operational complexity and potential liability.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Managing customer data in line with regulations such as GDPR or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) requires robust IT infrastructure and compliance protocols.
Brand Loyalty and Network Effects
Inchcape benefits significantly from established brand loyalty and potent network effects. For instance, in 2024, the automotive retail sector continued to see consumers gravitating towards well-known brands with proven track records, making it harder for new entrants to gain traction. These existing relationships translate into repeat business and a reduced need for extensive marketing spend for incumbents.
The network effects are amplified by Inchcape's extensive distribution and service infrastructure. This existing ecosystem, built over years, creates a significant barrier. For a new competitor to replicate this, substantial capital investment would be required, not just in physical locations but also in building trust and brand recognition from scratch.
- Brand Loyalty: Consumers often prioritize brands they trust, leading to repeat purchases and a reduced price sensitivity.
- Network Effects: The value of Inchcape's services increases with its existing customer base and infrastructure, creating a self-reinforcing advantage.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants face substantial hurdles in matching the established brand equity and distribution networks.
- Customer Acquisition Challenge: Entrants need significant investment to attract customers away from loyal, established relationships.
The threat of new entrants for Inchcape is generally moderate due to significant barriers, though specific market conditions can influence this. High capital requirements for dealerships and inventory, coupled with established OEM relationships and brand loyalty, make it challenging for newcomers. For example, in 2024, the cost of establishing a new car dealership could easily run into millions of dollars.
Regulatory hurdles, including emissions standards and licensing, also deter new players. Inchcape's existing economies of scale and experience curve further solidify its position. While brand loyalty and network effects create strong customer retention, the substantial investment required to replicate Inchcape's infrastructure and brand equity limits new competition. The automotive sector's capital intensity and regulatory complexity mean that while the threat exists, it is often mitigated by these substantial entry barriers.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Inchcape Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of publicly available data, including annual reports, financial statements, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also leverage insights from trade journals and regulatory filings to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
