IIFL Finance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
IIFL Finance Bundle
IIFL Finance operates within a dynamic financial services landscape, facing considerable pressure from established players and nimble new entrants alike. Understanding the intensity of rivalry and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this competitive terrain.
The bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers significantly influences IIFL Finance's operational costs and pricing strategies. Analyzing these forces reveals key leverage points within the industry.
The potential for new companies to enter the market poses a constant challenge, requiring IIFL Finance to maintain innovation and cost efficiency.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore IIFL Finance’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
IIFL Finance relies heavily on banks and financial institutions as its primary capital suppliers for lending operations. The cost of these funds directly dictates the company's net interest margins and overall profitability. For instance, in early 2024, tighter liquidity conditions or increased repo rates from the RBI could elevate borrowing costs for NBFCs like IIFL Finance. A slowdown in bank lending to the NBFC sector, perhaps due to risk aversion, can significantly squeeze margins and limit growth, making suppliers' bargaining power substantial.
IIFL Finance heavily relies on specialized fintech providers for its core banking software and crucial IT infrastructure. The market for these sophisticated financial technology services is often concentrated, granting a few key suppliers significant pricing power. High switching costs, estimated to be substantial for core system changes, further entrench this dependency. For instance, upgrading or replacing a primary loan management system can involve multi-year projects and significant capital expenditure, reinforcing supplier leverage.
IIFL Finance's ability to raise funds through non-convertible debentures and commercial papers significantly influences supplier power.
Investor confidence, despite 2024 regulatory actions, and strong credit ratings like CRISIL A+/Stable are crucial for accessing these markets at favorable rates.
As the RBI maintained the repo rate at 6.50% through 2024, a favorable outlook on potential interest rate cuts in 2025 could make the bond market more attractive for fresh capital raises, reducing the bargaining power of debt providers.
Regulatory Bodies as Suppliers of License
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulatory bodies act as critical suppliers of the license for IIFL Finance to operate in India's financial sector. Compliance with stringent regulations, including capital adequacy norms and reporting requirements, is a mandatory and significant cost of this supply. Changes in regulations can profoundly impact operational freedom and increase costs, as seen with the RBI's March 2024 directive on IIFL Finance's gold loan portfolio. This highlights the substantial bargaining power regulators wield over financial institutions.
- RBI's March 2024 directive on IIFL Finance's gold loan business underscored its significant regulatory power.
- Compliance costs, including capital adequacy ratios, are non-negotiable elements of the licensing "supply."
- Regulatory shifts, like new reporting standards for NBFCs in 2024, directly influence operational frameworks.
- The ability to issue or withdraw licenses provides regulators with immense leverage over market participants.
Human Capital and Talent
Skilled financial professionals, including loan officers, risk analysts, and technology experts, act as critical suppliers of labor for IIFL Finance. Intense competition for top talent in the financial services industry, especially for roles in digital transformation, can drive up wage costs significantly. Strengthening this human capital base remains a significant challenge for financial institutions like IIFL Finance.
- In 2024, the demand for specialized talent in areas like AI/ML and data analytics within India's financial sector has led to an estimated 15-20% increase in average compensation for these roles.
- Attracting and retaining experienced risk analysts is crucial, with their bargaining power strengthened by regulatory demands and complex market conditions.
- The competitive landscape for loan officers, particularly in microfinance and gold loans, necessitates attractive incentive structures to ensure high performance and low attrition.
IIFL Finance confronts significant supplier power from capital providers, with bank lending and debt market access directly impacting its profitability; for instance, the RBI maintained the repo rate at 6.50% through 2024. Critical fintech providers and regulators like the RBI also wield considerable influence, as evidenced by the March 2024 directive on gold loans. The increasing demand for specialized talent, with a 15-20% rise in compensation for AI/ML roles in 2024, further strengthens labor's bargaining position.
| Supplier Type | Key Factor | 2024 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Providers | RBI Repo Rate | 6.50% (maintained) |
| Regulators | RBI Directive | Gold Loan Business |
| Labor | Specialized Talent | 15-20% Wage Rise |
What is included in the product
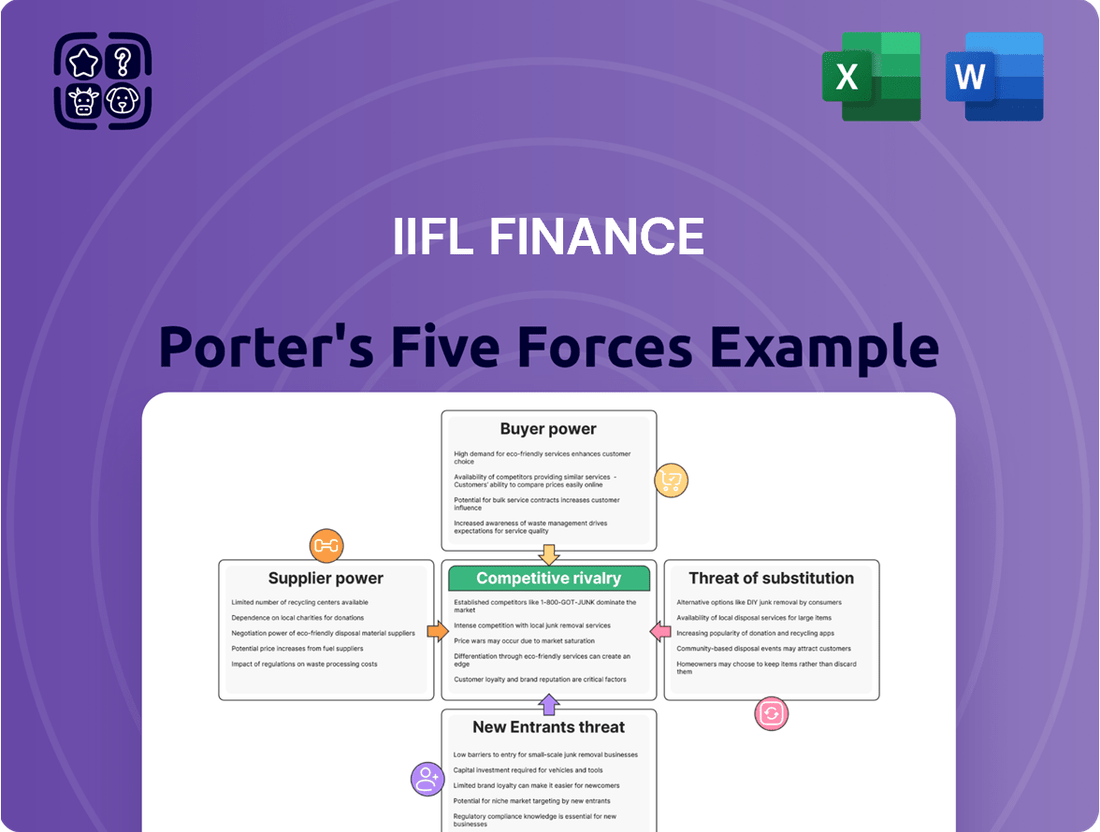
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for IIFL Finance, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products/services.
Understand competitive intensity with a clear visualization of each force, transforming complex analysis into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of IIFL Finance benefit from a high availability of alternatives in the Indian financial landscape. With over 9,500 RBI-licensed Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and numerous traditional banks operating in India as of early 2024, customers have extensive options for financial products. This abundance allows individuals and businesses to easily compare loan offerings and services, significantly increasing their bargaining power. Furthermore, the relatively low switching costs for customers, particularly for unsecured loans, further amplifies their ability to seek better terms, impacting IIFL Finance's pricing strategies.
Borrowers in retail segments, like personal and gold loans, show high sensitivity to interest rates and associated fees. The widespread availability of digital platforms in 2024 empowers customers to easily compare loan terms from various lenders. This ease of comparison drives borrowers to seek out the most favorable rates, increasing their bargaining power. Consequently, IIFL Finance faces significant pressure to offer competitive pricing to attract and retain its customer base.
Customers now have unprecedented access to information on financial products through the internet and digital platforms. This empowers them to make more informed decisions and potentially negotiate better terms with lenders like IIFL Finance. Online searches for financial products in India continue to surge, demonstrating a more empowered customer base. For instance, digital financial transactions in India are projected to reach 87 billion in 2024, reflecting high digital engagement. This increased transparency enhances customer bargaining power significantly.
Focus on Underserved Segments
IIFL Finance strategically focuses on India's underserved and low-income customer segments, a substantial market. While individual customers within this segment may possess limited bargaining power due to smaller loan sizes and varying financial literacy, their collective influence significantly shapes product design and pricing. As of fiscal year 2024, the demand from these segments continues to drive growth in non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) like IIFL, with tailored offerings becoming crucial.
- IIFL targets a vast underserved market.
- Individual customers often have low bargaining power.
- Collectively, this segment dictates product and pricing.
- Their needs drive tailored financial solutions in 2024.
Digital Tools and Platforms
The rise of mobile banking and digital lending platforms has profoundly shifted power towards customers. These tools enable easy application, quick comparison of offerings, and faster loan disbursements, enhancing a customer's ability to choose and negotiate. This increased digital access makes it easier for borrowers to find the best terms from various lenders. For example, India's digital payment ecosystem, including mobile banking, continued its strong growth in 2024, facilitating this shift in bargaining power.
- Mobile banking penetration in India's urban areas remained high in 2024, allowing customers unprecedented access to financial services.
- Digital platforms enable easy comparison of loan interest rates and terms from multiple providers, pressuring lenders to offer competitive deals.
- Customers can now experience quicker loan application processes and faster disbursement times, reducing their reliance on any single financial institution.
Customers wield substantial bargaining power over IIFL Finance due to over 9,500 NBFCs and banks offering alternatives in early 2024. Digital platforms, with 87 billion projected digital transactions in 2024, empower easy rate comparison and lower switching costs. This forces IIFL to offer competitive pricing and tailored solutions, even for its targeted underserved segments.
| Factor | 2024 Data | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| NBFCs in India | >9,500 | High Alternatives |
| Digital Transactions | 87 Billion (Proj.) | Easy Comparison |
Full Version Awaits
IIFL Finance Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of IIFL Finance. Understand the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the financial services sector. This detailed report provides actionable insights for strategic decision-making, ensuring you get a fully formatted and ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian non-banking financial sector faces intense competitive rivalry, stemming from its highly fragmented nature. Numerous players, including large NBFCs like Bajaj Finance and Cholamandalam Investment, along with traditional banks such as SBI and HDFC Bank, and emerging small finance banks, all vie for market share. This competition is particularly fierce across core product segments, including home loans, gold loans, and business loans. For instance, the gold loan market saw significant competitive activity in 2024, impacting margins. This persistent rivalry places considerable pressure on the profitability of entities like IIFL Finance as they navigate dynamic market conditions.
Aggressive competition stems from traditional banks expanding their footprint into rural and semi-urban areas, historically key markets for NBFCs like IIFL Finance. Banks, benefiting from access to low-cost deposits, can offer more attractive lending rates, for instance, with many large banks maintaining a cost of funds below 5% in 2024. This structural advantage allows them to offer housing loans or gold loans at rates NBFCs find hard to match. Such competitive pricing directly pressures IIFL Finance's margins and market share, forcing adaptation in product offerings and service delivery. This intensifies the rivalry, as banks leverage their extensive branch networks and lower capital costs.
Fintech companies represent a significant disruptive force, offering innovative, technology-driven financial products, especially in digital lending and payments. Their agile, digital-first models directly challenge traditional NBFCs like IIFL Finance, pushing for greater technological adoption. This competition is particularly fierce for attracting tech-savvy urban customers, with India's digital payments market volume projected to reach 150 billion transactions in 2024. These new entrants leverage data analytics and AI, making access to credit faster and more convenient. This forces established players to innovate or risk losing market share.
Product and Service Differentiation
IIFL Finance, despite its diversified portfolio, faces significant competitive rivalry due to the largely undifferentiated nature of core products like gold loans and home loans. Competition often centers on factors such as interest rates, loan-to-value ratios, and processing speed, with the gold loan segment, for example, seeing intense rate competition in early 2024. Building strong brand equity and fostering customer loyalty through trust and transparency becomes paramount for differentiation in this crowded market. Service quality, including efficient digital onboarding, also plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining customers.
- IIFL’s gold loan portfolio, a significant segment, faces direct competition from both banks and other NBFCs.
- Interest rates and processing efficiency are key battlegrounds, with customers often comparing offers across platforms.
- Customer service and digital experience are emerging as critical differentiators in 2024, beyond just pricing.
- Brand reputation for reliability and clear terms helps IIFL stand out amidst numerous similar offerings.
Price-Based Competition
The financial services sector, including NBFCs like IIFL Finance, faces intense price-based rivalry due to customer price sensitivity and abundant choices. Competitors, spanning traditional banks and other non-banking financial companies, frequently lower interest rates and processing fees to attract borrowers. This aggressive pricing pressure directly impacts net interest margins for all players. For instance, the average lending rate in India saw fluctuations in early 2024, reflecting this competitive environment.
- In Q4 FY2024, many Indian NBFCs reported tightened net interest margins (NIMs) compared to previous quarters, underscoring the fierce competition.
- Some banks offered home loan rates as low as 8.35% in early 2024, forcing NBFCs to match or offer competitive alternatives.
- Processing fees on personal loans and business loans were also frequently discounted by various lenders in the first half of 2024.
The Indian financial sector presents high competitive rivalry for IIFL Finance, driven by numerous NBFCs, traditional banks, and agile fintechs. This intense competition is particularly evident in core segments like gold and home loans, where pricing and digital experience are key battlegrounds. Banks, leveraging lower cost of funds, offered home loan rates as low as 8.35% in early 2024, while fintechs introduced disruptive digital-first models. This pressure tightened NBFC net interest margins in Q4 FY2024, demanding strong differentiation beyond price.
| Competitive Factor | 2024 Market Data | Impact on IIFL Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Cost of Funds | Many large banks below 5% | Enables lower lending rates, pressuring IIFL's margins. |
| Home Loan Rates | Banks offered as low as 8.35% (early 2024) | Forces competitive pricing and margin compression. |
| Digital Payments Volume | Projected 150 billion transactions | Highlights fintech disruption and demand for digital services. |
| NBFC Net Interest Margins | Tightened in Q4 FY2024 | Directly reflects intense price-based competition. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional commercial banks are a primary substitute for IIFL Finance, offering a similar range of loan products. These banks often provide a wider array of financial services, including savings and checking accounts, which can foster deeper customer relationships. The widespread branch network and established trust of major banks, like State Bank of India's market share in 2024, amplify this competitive pressure. Consequently, the threat posed by traditional banks is considered high for IIFL Finance.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending platforms present a growing threat of substitution to traditional non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) like IIFL Finance. These digital platforms offer an alternative source of credit for both individuals and businesses, directly connecting borrowers with a pool of lenders. They often boast faster loan approvals and potentially more competitive interest rates compared to conventional offerings. For instance, the Indian P2P lending market is projected to continue its strong growth trajectory through 2024, providing a compelling option for borrowers seeking efficient and flexible financing solutions.
Fintech companies and digital-only lenders pose a significant threat, leveraging technology for quick, convenient credit access. Services like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) are rapidly substituting traditional consumer loans, with India's BNPL market projected to reach $20 billion by 2024. These digital platforms are particularly appealing to India's vast younger, tech-savvy population, driving a shift from conventional financing. Digital lending volumes in India are expected to continue their robust growth trajectory through 2024, challenging established players like IIFL Finance.
Informal and Unorganized Lenders
Informal money lenders and unorganized financial entities in India, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, represent a significant substitute for formal credit channels like IIFL Finance. Despite often charging significantly higher interest rates, their ease of access and minimal documentation requirements make them a viable option for certain borrowers, especially those excluded from formal banking. This poses a competitive threat in the underserved markets that IIFL targets, as many prefer immediate, albeit costly, informal credit. In 2024, a notable portion of rural credit demand, estimated by some reports to be over 30%, continues to be met by these unorganized sources.
- Accessibility and quick disbursal often outweigh higher costs for some borrowers.
- Minimal documentation requirements appeal to those lacking formal credit histories.
- The informal sector remains a competitive force in India's vast underserved markets.
- This substitution impacts formal lenders' market penetration and growth in certain segments.
Capital Markets and Other Investment Avenues
The availability of capital markets presents a significant substitute threat for IIFL Finance, as businesses can opt for direct equity or debt issuances instead of non-banking financial company (NBFC) loans. For instance, Indian companies raised over INR 1.2 trillion through public equity issues and qualified institutional placements in fiscal year 2024. Individual investors also have numerous alternatives for their savings, including mutual funds, direct stock investments, and government securities like sovereign gold bonds.
- Alternative financing through public debt issues by Indian companies reached approximately INR 7.5 trillion in 2024.
- Retail participation in Indian equity markets remained robust in 2024, with demat accounts surpassing 150 million.
- Mutual fund assets under management (AUM) in India crossed INR 55 trillion in early 2024, offering diverse investment avenues.
- Government securities provide a low-risk alternative, attracting risk-averse individual investors.
IIFL Finance faces a high threat from diverse substitutes, including traditional banks offering broader services and established trust, with major Indian banks maintaining significant market presence in 2024.
Digital lenders like P2P and BNPL platforms are rapidly gaining traction due to convenience and speed, with India's BNPL market projected to reach $20 billion by 2024.
Informal lenders persist in underserved markets, appealing with accessibility, while capital markets offer large-scale alternative financing, with Indian companies raising over INR 1.2 trillion through public equity in FY2024.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | 2024 Data Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banks | Trust, Branch Network | Dominant market shares |
| Digital Lenders | Speed, Convenience | BNPL market $20B projected |
| Capital Markets | Large-scale Funding | INR 1.2T+ equity raised |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the financial services industry, especially lending, demands significant capital to both satisfy stringent regulatory requirements and to build a substantial loan portfolio. New entrants face a formidable barrier, as they must secure immense funding to compete effectively with established players. IIFL Finance, for example, boasts an impressive loan book of approximately ₹77,444 crore as of late 2023, showcasing the sheer scale needed. This substantial existing asset base makes it incredibly challenging for new firms to quickly match the operational capacity and market presence required to be a significant threat.
The Indian financial sector operates under stringent oversight from the Reserve Bank of India, which has significantly tightened its regulatory grip. Aspiring new entrants, like fintech firms, face a substantial barrier in obtaining a Certificate of Registration, a process involving intense scrutiny of their business models and financial health. In 2024, the RBI continued its rigorous approach, periodically canceling licenses for entities found non-compliant, reinforcing the high regulatory hurdles. This tough environment makes it exceptionally challenging for newcomers to establish a presence, thereby limiting the threat of new competition for established players such as IIFL Finance.
Existing financial players like IIFL Finance possess extensive distribution networks, posing a significant barrier to new entrants. As of early 2024, IIFL Finance operates over 4,200 branches across India, complemented by robust digital platforms that serve millions of customers. Replicating this widespread physical presence and developing sophisticated digital infrastructure demands substantial capital investment and considerable time. New companies would struggle to match this reach, which is critical for customer acquisition and service delivery in the diverse Indian market.
Brand Equity and Customer Trust
IIFL Finance, a prominent player, benefits from robust brand equity and deep customer trust cultivated over years. New entrants face a significant barrier, needing substantial investment in marketing and proving their reliability to compete. Building this credibility is crucial in financial services, where trust directly correlates with customer acquisition and retention. For instance, IIFL Finance's assets under management (AUM) reached over ₹77,400 crore by Q4 FY2024, reflecting its established market presence and customer confidence.
- IIFL Finance’s brand strength makes customer acquisition difficult for new players.
- New entrants must allocate significant capital to marketing and regulatory compliance.
- Trust is paramount; new entrants lack the proven track record of IIFL Finance.
- IIFL Finance’s established market share, evident in its Q4 FY2024 AUM, deters easy entry.
Access to Funding
New entrants into the NBFC sector face significant hurdles in securing funding at competitive rates. Established players like IIFL Finance, which reported a consolidated loan asset under management of Rs 79,216 crore as of March 31, 2024, benefit from long-standing relationships with banks and robust access to diverse debt markets.
This disparity in the cost of funds creates a substantial barrier, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and achieve profitability. For instance, while larger NBFCs can secure funds at lower interest rates, new firms often pay a premium, impacting their operational margins.
- New entrants struggle to secure competitive funding.
- Established NBFCs like IIFL Finance have preferential access to debt markets.
- Higher cost of funds for newcomers hinders price competitiveness.
- This disparity impacts new entrants' profitability and market entry.
The threat of new entrants for IIFL Finance remains low due to significant capital requirements and stringent RBI regulations, which continued to tighten in 2024. Establishing a competitive loan book, like IIFL's ₹79,216 crore consolidated loan AUM as of March 31, 2024, is a major hurdle. Newcomers also struggle to replicate IIFL's extensive distribution network of over 4,200 branches and its well-established brand trust. Furthermore, securing funding at competitive rates poses a substantial barrier, hindering new firms' ability to compete effectively.
| Barrier | Description | IIFL Finance Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Needs | High investment for loan book and operations | Consolidated loan AUM: ₹79,216 crore (Mar 2024) |
| Regulatory | Stringent RBI licensing and compliance | RBI's continued rigorous approach in 2024 |
| Distribution | Extensive network and digital platforms | Over 4,200 branches (early 2024) |
| Funding Access | Difficulty securing competitive cost of funds | Established relationships, diverse debt markets |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for IIFL Finance is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and investor presentations. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets and industry-specific research reports to capture current market dynamics and competitive pressures.
