IHI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
IHI Bundle
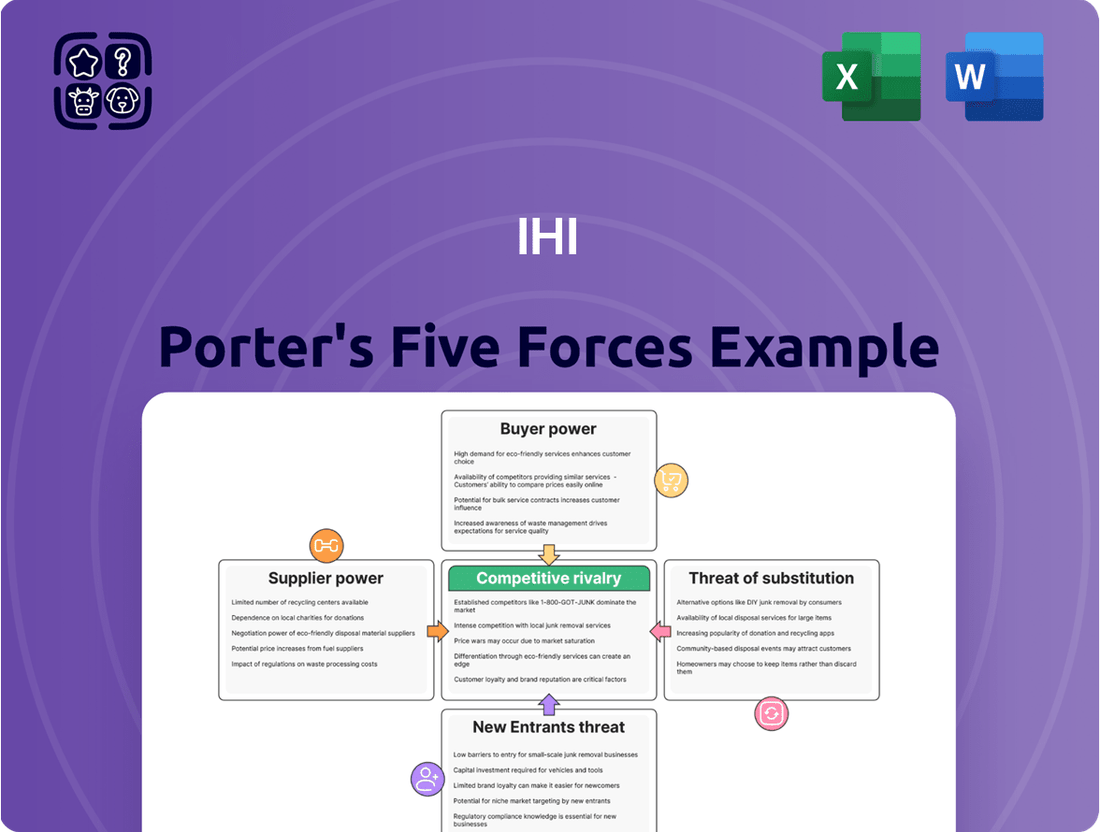
IHI's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces, revealing the intricate dynamics of its industry. Understanding these pressures—rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes—is crucial for strategic positioning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore IHI’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
IHI, a major player in heavy industry, depends on suppliers for specialized components and raw materials. When these are unique or difficult to source, suppliers gain leverage, potentially dictating terms and prices. This is particularly true for precision parts essential for complex machinery.
The global supply chain faced significant disruptions in recent years. For instance, in 2023, the semiconductor shortage, a critical component for many advanced industrial systems, continued to impact lead times and costs across various manufacturing sectors. This volatility means suppliers of essential, specialized materials can exert considerable bargaining power over manufacturers like IHI.
The industrial manufacturing sector, including companies like IHI, is grappling with a significant shortage of skilled labor. This gap is particularly pronounced for critical roles such as welders, machinists, and heavy equipment technicians. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of U.S. manufacturers are experiencing a shortage of skilled production workers.
This scarcity of specialized talent directly amplifies the bargaining power of labor suppliers, which are essentially the skilled workers themselves. As demand for these in-demand skills outstrips supply, workers can command higher wages and better benefits. This can translate into increased labor costs for IHI, potentially impacting its profitability and competitiveness.
Furthermore, these labor shortages can lead to production delays and inefficiencies. When IHI cannot secure enough qualified personnel, it may struggle to meet production targets or fulfill orders on time. This operational disruption can damage customer relationships and reduce overall output, highlighting the substantial impact of skilled labor availability on the company's operations and financial performance.
In specialized markets where IHI operates, such as advanced aerospace components or critical power generation systems, the number of suppliers capable of meeting stringent quality and technical requirements can be very small. This scarcity directly translates into significant bargaining power for these few key suppliers.
For instance, in the aerospace sector, a limited pool of manufacturers for highly specialized engine parts or advanced composite materials can command premium pricing. This concentration means IHI has fewer alternatives, making it harder to negotiate favorable terms or switch suppliers without incurring substantial costs or delays. In 2023, the global aerospace market for engine components alone was valued at over $100 billion, highlighting the scale of these specialized supply chains.
Switching Costs for IHI
Switching suppliers for IHI's critical, custom-engineered components can be a substantial undertaking. These costs can include significant investments in re-tooling existing manufacturing lines, the expense and time associated with re-certifying new suppliers and their processes, and the potential for costly re-design efforts to accommodate alternative materials or specifications.
These high switching costs directly translate into reduced flexibility for IHI, as the financial and operational barriers to changing suppliers are considerable. Consequently, this situation inherently increases the bargaining power of IHI's existing suppliers, allowing them to potentially command higher prices or more favorable terms.
- Re-tooling Costs: For example, a new supplier might require IHI to invest in specialized machinery or adapt existing equipment, potentially costing millions of dollars depending on the component's complexity.
- Certification and Qualification: The process of qualifying a new supplier for critical aerospace or industrial components can take months, involving rigorous testing and audits, which represents a significant time and resource investment.
- Design and Engineering Changes: Adapting IHI's proprietary designs to work with a new supplier's materials or manufacturing capabilities can necessitate extensive engineering work, adding further to the overall switching expense.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Suppliers who possess unique intellectual property or proprietary technology crucial for IHI's manufacturing processes wield significant bargaining power. This is particularly evident in IHI's advanced aerospace and defense sectors, where specialized components and systems are paramount.
IHI's reliance on cutting-edge technologies for its jet engines, for instance, means that suppliers of these critical elements can dictate terms. This dependence limits IHI's ability to switch suppliers easily, thereby strengthening the suppliers' position.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers controlling essential, non-replicable technologies for IHI's core products.
- High Switching Costs: IHI faces substantial costs and disruption if it attempts to change suppliers of proprietary components.
- Market Dominance: Suppliers with unique technology often hold a near-monopoly in their specific niche, enhancing their leverage.
- Innovation Dependence: IHI's own product innovation is often tied to the advancements provided by these specialized suppliers.
When suppliers provide unique or specialized components essential for IHI's complex machinery, their bargaining power increases significantly. This is amplified by high switching costs, including re-tooling and certification, which make it difficult for IHI to find alternatives. Furthermore, the scarcity of skilled labor in the industrial sector, with over 60% of U.S. manufacturers facing shortages in 2024, empowers specialized workers and their supplying agencies.
| Factor | Impact on IHI | Supporting Data/Example |
| Supplier Concentration | Increased leverage for few key suppliers | Limited pool of manufacturers for specialized aerospace engine parts |
| Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility for IHI | Millions in re-tooling, months for certification, potential design changes |
| Labor Scarcity | Higher labor costs and operational disruption | Over 60% of U.S. manufacturers reported skilled labor shortages in 2024 |
| Proprietary Technology | Supplier dictates terms for critical components | Reliance on specialized tech for jet engines |
What is included in the product
IHI's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its operating industries, examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the availability of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats with a clear, actionable overview of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
IHI's customers, often large entities like governments and major corporations, wield considerable bargaining power. These clients engage in substantial, long-term projects such as infrastructure development or defense systems, making contract terms highly significant. For instance, in 2023, IHI secured a major contract for a power plant expansion, where the client's scale allowed for negotiation of highly competitive pricing and extended payment schedules.
IHI Corporation operates across a broad spectrum of industries, including resource, energy, social infrastructure, industrial systems, aero engines, space, and defense. This diversity means that customer bargaining power isn't uniform; it shifts significantly depending on the specific sector and the nature of the client. For example, in 2024, large-scale social infrastructure projects, often funded by public entities, saw government clients wielding substantial influence due to the strategic importance and public accountability tied to these developments.
Customers in IHI's diverse markets, from aerospace to industrial machinery, often demand highly customized solutions. This need for bespoke engineering, designed for specific operational requirements, significantly boosts their bargaining power. For instance, in the heavy industries sector, clients may require unique specifications for turbines or construction equipment, making them less sensitive to standardized offerings and more insistent on tailored performance.
Availability of Alternatives and Project Delay Risks
While IHI operates in highly specialized sectors, customers can still exert significant bargaining power by exploring alternatives from other global heavy industry manufacturers. This is particularly true if IHI's proposed terms, including pricing and delivery schedules, are not competitive. In 2023, for instance, the global industrial machinery market saw robust competition, with numerous players vying for contracts, potentially giving buyers more leverage.
Project delays can also become a potent tool for customers. If IHI faces production or logistical challenges that push back delivery dates for crucial heavy machinery, clients might leverage this to negotiate better terms or even seek alternative suppliers who can commit to more reliable timelines. The inherent long lead times associated with manufacturing complex industrial equipment amplify this risk, as customers may have a greater incentive to switch if IHI's ability to meet demand is questioned.
- Customer Leverage: Buyers can leverage the availability of alternative global heavy industry manufacturers to negotiate terms with IHI.
- Project Delay Impact: If IHI experiences project delays, customers may use this as a bargaining chip for better contract conditions.
- Long Lead Times: The extended production cycles for heavy machinery empower customers to seek alternatives if IHI cannot meet their delivery expectations.
Price Sensitivity in Competitive Bidding
In situations where IHI offers standardized products or services and faces numerous qualified competitors, customers possess considerable leverage to drive down prices. This is particularly evident in competitive bidding scenarios where price becomes a primary differentiator. For instance, in the shipbuilding sector, a core area for IHI, clients often solicit bids from multiple shipyards globally, intensifying price pressure.
Despite IHI's significant investments in research and development to maintain a technological edge, price remains a critical element in winning new contracts. The global nature of many of IHI's markets means that competitors from regions with lower cost structures can often undercut prices, forcing IHI to balance its premium offerings with competitive pricing strategies. In 2023, for example, the shipbuilding industry saw intense competition with average contract values influenced by the cost of raw materials and labor, impacting the bargaining power of major clients.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can significantly influence prices when IHI's offerings are standardized and multiple bidders are available.
- Competitive Bidding: In tenders, especially for large infrastructure or industrial projects, IHI must contend with price-sensitive clients seeking the most cost-effective solutions.
- Technological vs. Price: While IHI's technological advancements are a strength, they don't always negate the impact of price competition, particularly in mature markets.
- Global Market Impact: International competition, often from lower-cost regions, amplifies customer bargaining power by providing readily available alternatives.
Customers in IHI's key markets, such as energy and infrastructure, can exert significant pressure due to the sheer volume of their purchases. For instance, a major utility company contracting for multiple power generation units in 2024 would have substantial leverage to negotiate favorable terms and pricing compared to a smaller, one-off project buyer.
The cost of switching suppliers for complex, integrated systems like aero engines or large-scale industrial plants is often very high for customers. This high switching cost can, paradoxically, give customers more bargaining power if they can demonstrate a willingness to switch, forcing IHI to offer competitive terms to retain them. In 2023, the aerospace sector saw airlines carefully evaluating long-term engine maintenance contracts, where switching providers involved significant retooling and training costs.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Large Infrastructure Clients (e.g., Governments) | Volume of Purchase, Strategic Importance | Secured a major contract for a high-speed rail project, influencing pricing due to the project's scale and long-term commitment. |
| Aerospace Customers (e.g., Airlines) | High Switching Costs, Long-Term Contracts | Airlines negotiating engine supply and maintenance deals, leveraging the significant investment already made in IHI's technology. |
| Industrial Machinery Buyers | Customization Needs, Availability of Alternatives | Clients requiring bespoke solutions for manufacturing plants, potentially switching if IHI's customization doesn't meet specific performance metrics. |
Same Document Delivered
IHI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete IHI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, reflecting the exact document you will receive immediately after purchase. You can be confident that what you see is precisely what you'll download, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces within the healthcare industry. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
IHI operates in a fiercely competitive global landscape, contending with industry giants such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, General Electric, and Larsen & Toubro. These established players boast broad product offerings and significant international footprints, creating direct competition across IHI's diverse business units.
For instance, in the aerospace sector, General Electric's engine division is a dominant force, and in the energy infrastructure space, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries offers a comparable range of solutions. This widespread rivalry intensifies price pressures and necessitates continuous innovation to maintain market share.
Competitive rivalry in IHI's sectors is fierce, fueled by a relentless pursuit of technological advancement. Companies like General Electric and Rolls-Royce are heavily invested in R&D for next-generation aerospace engines, pushing the boundaries of efficiency and performance. This innovation race means IHI must consistently allocate significant resources to research and development to stay competitive and maintain its market position.
The heavy construction equipment market and power generation sectors are booming, fueled by essential infrastructure upgrades and a rising need for electricity. For instance, global infrastructure spending was projected to reach $15 trillion by 2023, with significant portions allocated to modernization projects. This expansion presents a wealth of new projects.
However, this robust growth also sharpens competitive rivalry. As more opportunities emerge, companies like Caterpillar, Komatsu, and Volvo Construction Equipment are aggressively competing for contracts, driving up marketing costs and potentially squeezing profit margins. The intense pursuit of these lucrative projects means rivals are constantly innovating and offering competitive pricing.
Diversified Product Portfolios
Many of IHI's competitors, much like IHI, boast diversified product portfolios spanning various heavy industry segments. This breadth allows rivals to tap into cross-segment synergies, offering customers comprehensive, integrated solutions. For instance, companies like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Hitachi also operate across sectors such as energy, industrial systems, and infrastructure, presenting a united front of capabilities to potential clients.
This diversification intensifies competitive pressure as rivals can bundle services, leverage established relationships across different product lines, and absorb potential downturns in one sector through strength in another. For example, in the shipbuilding sector, where IHI is a significant player, competitors offering related services like engine manufacturing or port equipment can provide more attractive packages.
- Broad Offerings: Competitors often match IHI's extensive product range, making it difficult to gain a distinct advantage based solely on product breadth.
- Integrated Solutions: Diversified rivals can offer customers more complete packages, combining products and services for greater convenience and potential cost savings.
- Cross-Segment Synergies: Competitors can leverage their presence in multiple industries to create internal efficiencies and offer more competitive pricing or innovative solutions.
- Market Resilience: A wide product mix provides competitors with greater stability, allowing them to weather economic fluctuations more effectively than more specialized firms.
Strategic Partnerships and Consolidations
Strategic partnerships and consolidations significantly influence the competitive rivalry within IHI's operating sectors. These collaborations, including joint ventures and mergers, can forge larger entities with enhanced market reach and technological capabilities. For instance, in the heavy industrial equipment sector, a major player might merge with a specialized technology firm to offer integrated solutions, thereby intensifying competition for IHI.
These alliances create more formidable competitors, compelling IHI to constantly reassess and refine its own strategic positioning. The ability of these consolidated entities to leverage combined resources, R&D, and distribution networks presents a substantial challenge. IHI must therefore remain agile, potentially exploring its own strategic alliances to maintain its competitive edge.
The trend towards consolidation is evident across various industries IHI serves. For example, in the shipbuilding sector, there have been notable consolidation activities aimed at achieving greater economies of scale and global competitiveness. In 2023, the global shipbuilding market saw significant M&A activity, with companies seeking to bolster their order books and technological advancements.
- Increased Market Power: Consolidations can lead to fewer, larger players, increasing their bargaining power with suppliers and customers.
- Enhanced Capabilities: Partnerships often combine complementary strengths, such as advanced technology with established market access, creating more competitive offerings.
- Strategic Response: IHI must consider its own strategic alliances or acquisitions to counter the advantages gained by consolidated rivals.
- Market Dynamics Shift: The emergence of larger, more integrated competitors can alter pricing strategies and product development cycles.
Competitive rivalry is a significant force for IHI, facing off against major global players like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, General Electric, and Larsen & Toubro across its diverse business segments. These rivals often possess broad product portfolios and extensive international reach, directly challenging IHI's market presence in areas such as aerospace engines and energy infrastructure.
The intensity of this rivalry is further amplified by a constant drive for technological innovation, with companies like General Electric and Rolls-Royce heavily investing in R&D for next-generation aerospace engines. This necessitates substantial and ongoing resource allocation by IHI to research and development to maintain its competitive edge and market standing.
| Key Competitor | Primary Sectors of Overlap | Key Competitive Strengths |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | Energy, Industrial Systems, Infrastructure, Shipbuilding | Diversified portfolio, integrated solutions, global presence |
| General Electric | Aerospace (engines), Energy (power generation) | Technological leadership, strong R&D, established brand |
| Larsen & Toubro | Infrastructure, Heavy Engineering, Power | Strong project execution, regional dominance, diversified services |
| Caterpillar | Heavy Construction Equipment | Market share, dealer network, product reliability |
| Komatsu | Heavy Construction Equipment | Innovation in automation, global reach |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The global push for decarbonization is a major threat of substitutes for IHI's traditional power generation business. As countries and corporations prioritize sustainability, renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are becoming increasingly competitive and attractive alternatives. For instance, by the end of 2023, global renewable capacity additions reached a record 510 gigawatts, a 50% increase from 2022, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This rapid expansion directly challenges the market share and profitability of fossil fuel-based power generation systems, which IHI has historically relied on.
The increasing sophistication of digitalization and automation presents a significant threat of substitutes for IHI. For instance, advanced robotics and AI-driven systems can increasingly perform tasks traditionally handled by heavy machinery in construction and manufacturing, potentially reducing demand for IHI's core equipment offerings.
In 2024, global spending on industrial automation was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, with significant growth driven by AI integration. This trend suggests that companies may opt for automated solutions over purchasing or leasing new heavy machinery from traditional providers like IHI, impacting their market share.
The threat of substitutes for traditional jet engines, IHI's core business, is growing. While IHI is investing in next-generation jet engine technology, the long-term viability of these engines could be challenged by the emergence of fully electric or hydrogen-powered aircraft. These alternative propulsion systems, still in development, represent a significant shift that could alter demand for conventional engines.
For example, several companies are making strides in electric aviation; in 2024, companies like Eviation are continuing flight tests of their Alice aircraft, powered by advanced battery technology. Similarly, hydrogen fuel cell technology is progressing, with projects aiming for commercial viability in the coming years. IHI's active research into these very areas is a strategic move to address and potentially capitalize on these disruptive substitute technologies.
Modular and Off-site Construction Methods
The increasing adoption of modular and off-site construction methods presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional on-site building. These innovative techniques, which involve prefabricating building components in controlled factory environments, reduce the need for extensive on-site heavy machinery and labor. This shift can lead to faster project completion times and potentially lower overall costs, making them an attractive alternative for developers and clients.
For instance, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately USD 100 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This growth is driven by the efficiency and cost-savings these methods offer.
- Reduced On-Site Equipment Dependency: Modular construction minimizes the requirement for large, expensive on-site equipment like cranes and excavators, lowering capital expenditure for projects.
- Faster Project Delivery: Prefabricated components allow for parallel processing of site preparation and building assembly, often cutting project timelines by 30-50%.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Factory-controlled production leads to less waste and improved quality control, translating into potential cost savings of 10-20% compared to traditional methods.
- Growing Market Acceptance: Major construction firms and developers are increasingly investing in and utilizing modular solutions, indicating a strong market trend away from purely traditional approaches.
Leasing and Rental Models for Heavy Equipment
The increasing popularity of leasing and rental models for heavy equipment presents a significant threat of substitutes for IHI. These flexible arrangements, driven by the substantial capital outlay and extended delivery times for new machinery, offer an alternative to outright ownership. For instance, the global construction equipment rental market was valued at approximately $120 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong preference for rental over purchase for many users.
This trend directly impacts IHI's core business of selling new heavy equipment. Companies can access the machinery they need for specific projects without the long-term commitment and depreciation associated with ownership. This can lead to a reduction in demand for IHI's new unit sales, as customers opt for more adaptable rental solutions.
- Rising Rental Market Share: The construction equipment rental sector is experiencing robust growth, with many regions seeing rental revenue outpace new equipment sales growth.
- Cost and Lead Time Advantages: Rental and leasing offer immediate access to equipment and predictable monthly costs, bypassing the significant upfront investment and lengthy lead times often associated with purchasing new heavy machinery.
- Impact on IHI's Sales: This shift directly substitutes the need for customers to purchase new equipment from manufacturers like IHI, potentially dampening sales volumes for new units.
The growing adoption of alternative energy sources directly substitutes IHI's traditional power generation business. Renewables like solar and wind are becoming more competitive, with global renewable capacity additions reaching a record 510 GW in 2023, a 50% increase from the previous year. This surge in renewable energy deployment challenges the market dominance of fossil fuel-based systems, a sector where IHI has historically held a strong position.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital investment required in industries like aerospace and advanced engineering. For instance, establishing a new commercial aircraft manufacturing facility can easily cost tens of billions of dollars, with a single new plane model development often exceeding $15 billion. This massive upfront expenditure, covering everything from specialized tooling to extensive research and development, acts as a formidable barrier, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to enter and compete effectively.
The sheer scale of research and development (R&D) required to compete in IHI's core markets presents a formidable barrier. Developing advanced technologies, from sophisticated jet engines to intricate power generation systems and novel infrastructure solutions, demands immense and sustained financial commitment. For instance, in 2023, IHI reported significant investments in R&D, a testament to the ongoing need for innovation in these high-tech sectors.
IHI Corporation benefits from decades of accumulated expertise in highly complex engineering and manufacturing. This deep well of knowledge, honed over many years, is a significant barrier for any potential new competitor aiming to enter their specialized markets.
The company's strong brand reputation, forged through consistent reliability and high performance, instills trust among clients, particularly for large-scale, critical projects. New entrants would struggle to replicate this established trust and proven track record, making it challenging to gain a foothold.
Stringent Regulatory and Certification Processes
Stringent regulatory and certification processes act as a significant deterrent to new entrants in many capital-intensive industries. For example, in the aerospace sector, obtaining Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) or European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) certifications for a new aircraft can take years and cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This immense upfront investment and lengthy approval timeline makes it exceptionally difficult for smaller or less capitalized companies to enter and compete.
These hurdles are not unique to aerospace. The power generation industry, particularly nuclear and renewable energy, faces similarly rigorous safety, environmental, and operational standards. In 2024, the average cost to obtain permits for a new utility-scale solar farm in the United States can range from $10,000 to $50,000 per megawatt, with the entire process often extending over several years. Such substantial compliance costs and time commitments effectively raise the barrier to entry.
The complexity and cost associated with navigating these requirements mean that only established players with deep pockets and extensive experience can realistically undertake the process. This creates a formidable moat around existing businesses, protecting them from disruptive newcomers.
- Aerospace: FAA/EASA certification can cost billions and take many years.
- Power Generation: Permitting for utility-scale solar can cost up to $50,000/MW in 2024 and take years.
- High Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment is needed for compliance.
- Time-Consuming Approvals: Lengthy certification processes favor incumbent firms.
Complex Supply Chains and Distribution Networks
IHI's established global supply chains and distribution networks represent a significant barrier to entry. Replicating these complex systems, which are vital for sourcing, manufacturing, and worldwide product delivery, would require substantial investment and time for any new competitor.
For instance, in 2024, the global logistics market was valued at over $9.7 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale and infrastructure required to operate effectively. New entrants would need to build or secure similar extensive networks to match IHI's reach and efficiency.
- Significant Capital Investment: Establishing comparable supply chain and distribution infrastructure demands billions in upfront capital.
- Operational Expertise: Mastering the complexities of global logistics, inventory management, and supplier relationships takes years of experience.
- Established Relationships: IHI benefits from long-standing relationships with suppliers and logistics providers, offering preferential terms and reliability.
- Economies of Scale: IHI's existing scale allows for cost efficiencies in procurement and distribution that new entrants would struggle to achieve initially.
The threat of new entrants for IHI is considerably low due to the immense capital, specialized knowledge, and established infrastructure required in its core industries. For example, the aerospace sector alone demands billions in R&D and manufacturing setup, a barrier few can overcome. Additionally, stringent regulatory approvals, like FAA certification which can cost hundreds of millions, further deter newcomers.
IHI's deep expertise and strong brand reputation, built over decades, also act as significant deterrents. New players would find it extremely challenging to match IHI's proven track record and client trust, especially in critical infrastructure projects. The company's established global supply chains, valued in the trillions, are another formidable obstacle, requiring massive investment and time to replicate.
| Barrier Type | Example | Estimated Cost/Time |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | New aircraft manufacturing facility | Tens of billions of dollars |
| Research & Development | New jet engine development | Over $15 billion |
| Regulatory Approvals | FAA/EASA certification for new aircraft | Hundreds of millions to billions of dollars, years |
| Supply Chain & Distribution | Establishing global logistics network | Billions of dollars, years of development |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from key players, and publicly available company disclosures. We also leverage macroeconomic data and government statistics to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
