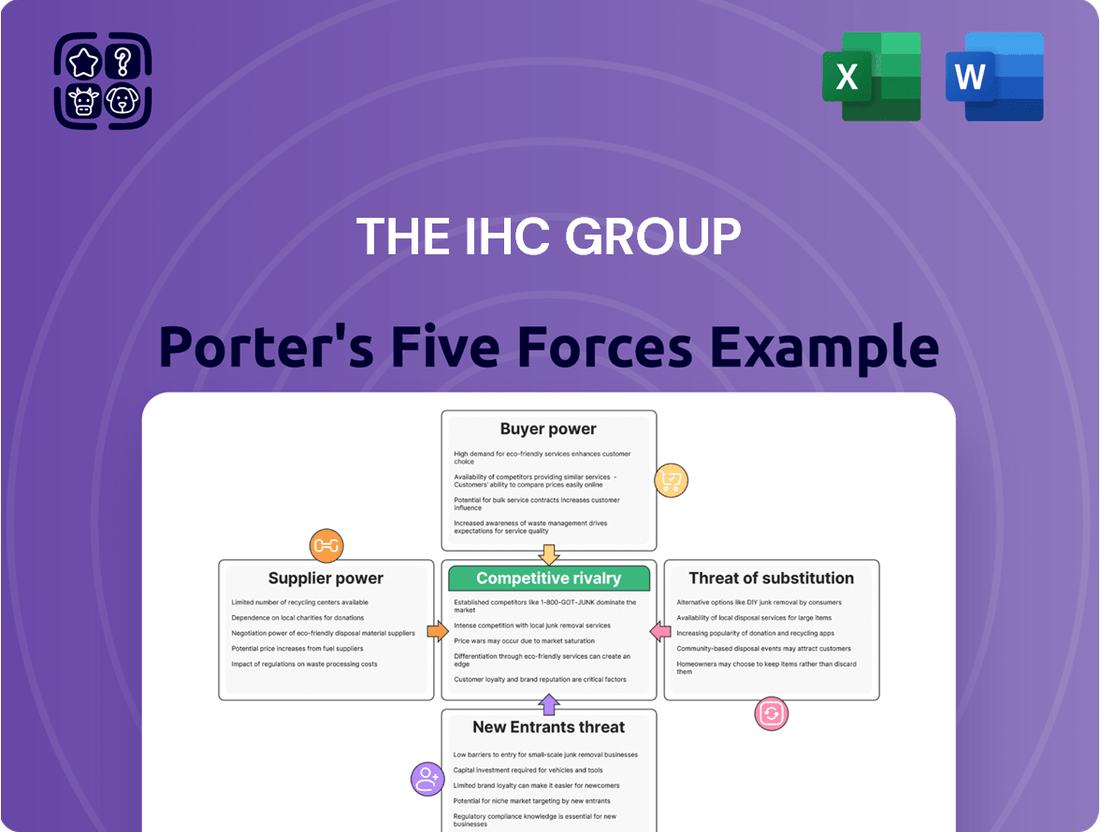
The IHC Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
The IHC Group Bundle
The IHC Group operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping The IHC Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The primary suppliers to IHC's health insurance operations are healthcare providers, such as hospitals, doctors, and pharmaceutical companies. These entities hold significant sway due to the essential nature of their services.
Sustained increases in healthcare costs, fueled by factors like the development of expensive new therapies and a growing elderly population, substantially bolster the bargaining power of these providers. For instance, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family health coverage in the US reached an estimated $24,000 in 2024, a figure heavily influenced by provider pricing.
This elevated supplier power directly translates to increased claims costs for IHC, impacting the profitability of its health and medical stop-loss insurance segments. As providers can command higher prices for their services, IHC faces greater pressure to either absorb these costs or pass them on to consumers, a challenging balancing act in the current market.
The IHC Group, operating within the reinsurance sector, faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers, primarily reinsurers. This dynamic is amplified by the current hardening of the reinsurance market, a trend evident throughout 2023 and continuing into 2024.
Reinsurers are experiencing increased costs and demanding higher premiums, particularly for coverage of high-cost claims, which directly impacts IHC's operational expenses. For instance, global reinsurance premiums saw a notable increase in 2023, with some segments experiencing double-digit percentage rises, reflecting this hardening cycle.
This elevated cost of risk transfer and capital for IHC inherently strengthens the bargaining position of reinsurers. As IHC relies on these suppliers to manage its own risk exposure, especially for products like medical stop-loss, the terms dictated by reinsurers carry substantial weight.
The increasing reliance on digital transformation and artificial intelligence (AI) within the insurance sector significantly bolsters the bargaining power of technology and data providers. Insurers like IHC Group depend heavily on these specialized suppliers for everything from streamlining operations and refining underwriting processes to enhancing customer engagement through advanced analytics.
The specialized nature of cutting-edge AI solutions, coupled with their high demand across the industry, grants these technology vendors considerable leverage. For instance, the global AI in insurance market was projected to reach over $10 billion by 2024, highlighting the critical role and influence of these tech partners.
Specialized Medical Service Providers
Specialized medical service providers, particularly those handling high-cost, complex claims such as advanced cancer treatments or intensive neonatal care, hold significant bargaining power. These niche providers, often specialized networks or facilities, are few in number, limiting options for entities like The IHC Group. This scarcity directly translates into their ability to dictate terms and increase costs for medical stop-loss insurance.
The limited pool of providers capable of managing exceptionally complex medical cases means IHC faces concentrated supplier power. For instance, a single specialized oncology center or a high-risk maternity network might be the only viable option for certain catastrophic claims. This lack of alternatives allows these suppliers to command premium pricing, impacting IHC's overall claims expenditure and profitability.
- Limited Number of Niche Providers: The supply side for highly specialized medical services is concentrated, with few entities possessing the necessary expertise and infrastructure.
- High Cost of Claims: The nature of the services provided (e.g., complex surgeries, long-term critical care) involves substantial costs, amplifying the financial impact of supplier pricing.
- Dependence on Specialized Networks: IHC's ability to offer stop-loss coverage for catastrophic events is contingent on access to these specialized providers, increasing supplier leverage.
Labor and Talent
The availability of skilled professionals in underwriting, actuarial science, claims management, and increasingly, data science and AI, represents a significant supplier of human capital for The IHC Group. A shortage of such talent can drive up labor costs and impact operational efficiency, giving these specialized workers increased bargaining power within the insurance industry. For instance, in 2024, the demand for data scientists in the financial services sector, which includes insurance, continued to outstrip supply, leading to competitive salary offers and enhanced benefits packages. This dynamic directly influences The IHC Group's ability to attract and retain key personnel, potentially increasing operational expenses.
The bargaining power of labor suppliers is amplified when specialized skills are in high demand and short supply. This was evident in 2024, with reports indicating a persistent skills gap in areas like cybersecurity and advanced analytics within financial services. Companies like The IHC Group must therefore invest in competitive compensation and development programs to secure and maintain a skilled workforce, directly impacting their cost structure and operational capabilities.
Key areas where labor bargaining power is most pronounced for The IHC Group include:
- Actuarial and Underwriting Talent: Highly specialized roles requiring advanced quantitative skills.
- Claims Management Experts: Professionals with deep knowledge of claims processing and fraud detection.
- Data Science and AI Specialists: Increasingly critical for innovation and operational efficiency, with high demand across industries.
- IT and Cybersecurity Professionals: Essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity.
The bargaining power of suppliers for The IHC Group is notable, particularly from healthcare providers and reinsurers. Rising healthcare costs, exemplified by the $24,000 average annual premium for employer-sponsored family health coverage in the US in 2024, directly increase IHC's claims expenses.
The reinsurance market hardening in 2023 and 2024 has also driven up premiums for IHC, especially for high-cost claims, impacting its risk transfer costs.
Technology and data providers, crucial for AI and digital transformation, wield significant influence due to the specialized nature of their offerings, with the AI in insurance market projected to exceed $10 billion by 2024.
Furthermore, a shortage of specialized labor, such as data scientists in 2024, strengthens the bargaining power of skilled professionals, increasing operational costs for IHC.
| Supplier Type | Key Influence Factors | Impact on IHC |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Providers | Rising healthcare costs, specialized treatment needs | Increased claims expenses, pressure on profitability |
| Reinsurers | Market hardening, increased demand for capacity | Higher reinsurance premiums, elevated cost of risk transfer |
| Technology/Data Providers | Specialized AI/digital solutions, high industry demand | Leverage in pricing for essential operational tools |
| Skilled Labor (e.g., Data Scientists) | Skills gap, high demand for specialized expertise | Increased labor costs, challenges in talent acquisition/retention |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for The IHC Group dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within its operating industries, examining buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats with a visual, interactive framework.
Gain immediate clarity on market dynamics to proactively address potential disruptions.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual customers, particularly those navigating the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces, now benefit from a wider array of insurer choices and plan options. This increased accessibility directly amplifies their bargaining power, as they can more readily compare offerings and select the most suitable coverage.
The upward trend in health insurance premiums, projected to continue through 2024 and into 2025, significantly heightens price sensitivity among individual consumers. With costs rising, individuals are more inclined to scrutinize their options and are empowered to switch to providers offering better value or more affordable rates, directly impacting insurer competitiveness.
Employers, the primary customers for group insurance, are intensely focused on managing escalating healthcare expenditures. This heightened cost consciousness significantly amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, employer contributions to health insurance premiums continued their upward trend, with the average employer picking up approximately 73% of the total premium for single coverage, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation's Employer Health Benefits Survey. This financial stake drives employers to scrutinize plan offerings, seeking greater value and efficiency.
The drive for cost control compels employers to actively seek out and negotiate for alternative plan designs, such as high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) with health savings accounts (HSAs), and to prioritize high-performance networks that offer better value. They are also demanding greater transparency and accountability from insurers regarding both cost containment and the quality of care delivered. This puts significant pressure on IHC Group to present compelling, cost-effective insurance solutions that align with their clients' budgetary constraints and performance expectations.
A significant trend impacting the bargaining power of customers in the health insurance sector, particularly for groups like those served by The IHC Group, is the increasing shift towards self-funded health plans. Many employers, from small businesses to larger enterprises, are moving away from traditional fully-insured plans. This migration is often coupled with the purchase of medical stop-loss insurance, which protects them from catastrophic claims.
This move to self-funding fundamentally alters the employer's relationship with insurance providers. By taking on more direct responsibility for their healthcare expenditures, employers gain greater control and visibility over costs. This increased control naturally translates into enhanced bargaining power, especially when negotiating terms with stop-loss insurance carriers, a key area for companies like IHC.
For instance, data from the U.S. Department of Labor indicates that as of 2023, a substantial portion of employees in medium and large private industries were covered by self-funded plans. This trend suggests that a growing segment of the customer base for health insurance products is becoming more sophisticated and cost-conscious, directly influencing their negotiation leverage.
Availability of Alternative Health Plans
The availability of alternative health plans (AHPs) significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers, especially employers. These AHPs are gaining traction by offering streamlined designs, enhanced member experiences, and cost savings via incentives for high-value healthcare providers. This trend empowers employers to negotiate more favorable terms and demand greater innovation from established insurers like The IHC Group.
By 2024, the shift towards AHPs is becoming more pronounced. For instance, a significant percentage of employers are actively evaluating or have already implemented self-funded or partially self-funded options, which often incorporate AHP principles. This growing adoption means customers have a wider array of choices, directly increasing their leverage.
- Increased Choice: Employers can select from a growing number of AHPs that may offer better value propositions than traditional fully insured plans.
- Cost Pressure: The competitive landscape created by AHPs forces traditional insurers to offer more cost-efficient solutions to retain business.
- Demand for Innovation: Customers are pushing insurers to develop more flexible, member-centric, and value-based offerings.
Impact of Government Subsidies and Policies
Government policies, particularly those related to healthcare affordability, play a crucial role in shaping customer bargaining power. For instance, subsidies provided under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) directly influence how much individuals can afford to spend on health insurance, thereby impacting their choices and leverage with insurance providers.
Potential shifts in these subsidies or broader reforms in government healthcare strategies, especially with a new administration, could significantly alter the financial landscape for millions of consumers. This, in turn, directly affects their capacity to select insurance plans and their overall bargaining power within the market.
- Government Subsidies: The ACA's premium tax credits, for example, reduce out-of-pocket costs for eligible individuals, directly boosting their purchasing power. In 2024, millions of Americans continued to benefit from these subsidies, making health insurance more accessible.
- Policy Reforms: Discussions around healthcare reform, including potential changes to subsidy levels or the introduction of new public options, can create uncertainty and influence consumer behavior and their perceived bargaining power.
- Impact on Affordability: Any reduction in subsidies could make insurance less affordable for a significant portion of the population, potentially leading to a decrease in demand or a shift towards less comprehensive plans, thereby altering the bargaining dynamic.
Customers, particularly employers, wield significant bargaining power due to the increasing cost-consciousness in healthcare. This is evident as employers continue to bear a substantial portion of premium costs, driving them to seek greater value and efficiency from insurers.
The growing adoption of self-funded health plans and alternative plan designs like AHPs further bolsters customer leverage. By taking on more direct responsibility for healthcare costs and having more plan options, customers can negotiate more effectively.
Government policies, such as ACA subsidies, also directly impact customer affordability and choice, influencing their bargaining power. As of 2024, millions of Americans rely on these subsidies, highlighting their importance in the market dynamic.
| Customer Segment | Key Driver of Bargaining Power | Impact on Insurers |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Consumers (ACA Marketplaces) | Increased choice of insurers and plans; heightened price sensitivity due to rising premiums. | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and diverse plan options. |
| Employers (Group Insurance) | Intense focus on managing escalating healthcare costs; significant financial stake in premiums. | Demand for cost-effective solutions, alternative plan designs (HDHPs, HSAs), and greater transparency. |
| Employers (Self-funded Plans) | Greater control and visibility over healthcare expenditures; negotiation with stop-loss carriers. | Need to provide robust stop-loss coverage and demonstrate cost-containment value. |
Full Version Awaits
The IHC Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details the IHC Group's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
While the broader health insurance landscape sees consolidation, IHC Group strategically targets fragmented niche markets, such as medical stop-loss and supplemental health insurance. Within these specialized segments, competition can be particularly fierce, with numerous smaller, focused providers vying for market share. For instance, the medical stop-loss market, a key area for IHC, is characterized by a multitude of regional and specialty carriers, each emphasizing unique underwriting capabilities and client service. In 2024, the medical stop-loss market continued to see robust growth, with industry reports indicating a compound annual growth rate of over 10% in the preceding years, driven by employers seeking to manage rising healthcare costs.
Insurers like The IHC Group are facing heightened price competition, especially in the individual and small group health insurance sectors. This is driven by escalating healthcare expenses and a growing awareness of costs among consumers, pushing companies to offer more competitive premiums. For instance, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family health coverage in the US reached $24,986 in 2024, a significant jump that makes price a crucial factor for many.
The insurance sector is seeing significant consolidation, with major players actively acquiring smaller competitors or merging to boost their market presence and service portfolios. For instance, in 2024, the global insurance industry witnessed several high-profile mergers and acquisitions, reflecting this ongoing trend of consolidation.
This heightened consolidation intensifies competitive rivalry. Larger, more integrated entities can leverage their expanded scale, broader product lines, and greater financial resources, potentially creating a more challenging environment for companies like IHC Group.
Innovation and Digitalization Race
The insurance industry is locked in an intense innovation and digitalization race, with competitors pouring resources into artificial intelligence, digital tools, and advanced analytics. These investments are aimed at boosting operational efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, and achieving greater pricing accuracy. For instance, by mid-2024, many leading insurers had reported significant increases in their IT budgets, with some dedicating over 15% of their revenue to digital transformation initiatives.
Insurers that fail to keep pace with technological advancements risk falling behind, creating a significant competitive disadvantage. This dynamic intensifies the pressure to innovate rapidly, as companies strive to offer more personalized products, streamlined claims processes, and proactive risk management solutions. The market is increasingly rewarding insurers that demonstrate agility and a forward-thinking approach to technology adoption.
- AI Adoption: Many insurers are exploring AI for fraud detection and underwriting, with some reporting a 5-10% reduction in fraudulent claims.
- Digital Customer Engagement: Investments in mobile apps and online portals are common, aiming to improve customer satisfaction scores by up to 20%.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics are being used to refine pricing models, potentially leading to a 2-5% improvement in loss ratios.
- Efficiency Gains: Automation of back-office processes through digitalization is expected to cut operational costs by 10-15% in the coming years.
Regulatory and Policy Landscape Dynamics
The U.S. health insurance sector, including players like IHC Group, navigates a dynamic regulatory environment. Policy shifts, particularly concerning the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and Medicare Advantage, significantly shape competitive dynamics. For instance, in 2024, legislative proposals aimed at drug price negotiation and benefit expansions for Medicare Advantage plans continued to be debated, creating uncertainty and requiring strategic agility from insurers.
These evolving regulations directly influence competitive rivalry. Companies that can effectively adapt to changes, such as new compliance requirements or altered reimbursement models, can gain or lose market share. For example, a 2024 policy adjustment impacting risk adjustment payments for Medicare Advantage plans could disproportionately affect insurers with specific member demographics, intensifying competition as firms recalibrate their offerings and pricing strategies.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving U.S. health insurance policies, including ACA modifications and Medicare Advantage rule changes, create a fluid competitive landscape.
- Adaptation as Advantage: Insurers' ability to quickly adjust to new regulations, such as those impacting reimbursement or compliance, can foster competitive advantages.
- Intensified Rivalry: Policy shifts can trigger strategic realignments among competitors, leading to heightened competition as companies seek to maintain or improve their market positions.
The competitive rivalry within the health insurance sector, particularly for entities like IHC Group, is shaped by several key factors. While consolidation among larger players is a significant trend, IHC's focus on niche markets means it contends with numerous specialized providers. This creates a dynamic where agility and targeted service offerings are crucial differentiators.
Price competition remains a significant challenge, especially in individual and small group markets, exacerbated by rising healthcare costs that pushed average annual premiums for employer-sponsored family coverage to $24,986 in 2024. Furthermore, an ongoing innovation race, with insurers investing heavily in AI and digital tools, means companies must continuously adapt to technological advancements to avoid falling behind.
| Competitive Factor | Description | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Niche Market Focus | IHC Group targets specific segments like medical stop-loss. | Medical stop-loss market growth exceeds 10% CAGR. |
| Price Sensitivity | Consumers are increasingly cost-aware due to rising premiums. | Average family coverage premium reached $24,986 in 2024. |
| Technological Innovation | Investment in AI, digital tools, and analytics is crucial. | Insurers increased IT budgets, some dedicating >15% of revenue to digital transformation. |
| Consolidation Impact | Mergers and acquisitions increase the scale and resources of larger competitors. | Global insurance industry saw multiple high-profile M&A deals in 2024. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For group health coverage, the most direct substitute for fully insured products like those offered by IHC is employer self-funding. Many employers are increasingly choosing self-funded plans, often combined with medical stop-loss insurance, to gain more control over their healthcare spending.
This trend is particularly noticeable as medical costs continue to climb. Even smaller employers are exploring self-funding options, seeking ways to manage their healthcare expenditures more effectively. This shift presents a significant competitive pressure on traditional fully insured offerings.
Government-sponsored programs like Medicare Advantage and Medicaid represent significant substitutes for private health insurance. For instance, in 2024, Medicare Advantage enrollment reached an estimated 31.7 million beneficiaries, a substantial portion of the Medicare population, demonstrating its appeal as an alternative to traditional Medicare and private plans.
Fluctuations in these government programs, such as changes to eligibility criteria or benefit structures, can directly influence the demand for private insurance. A 2024 policy update that expanded Medicaid eligibility in certain states could potentially divert more individuals from seeking coverage through commercial insurers.
Employers and individuals are actively seeking ways to lower healthcare expenses and enhance care management, leading them to explore direct contracting with healthcare providers. This trend, coupled with the rise of alternative health plans (AHPs), presents a significant threat by offering substitutes that bypass traditional insurance carriers.
These alternative models, focusing on cost reduction and improved care coordination, are gaining traction and directly challenge the market share of conventional insurance products. For instance, by mid-2024, a notable percentage of large employers were reportedly considering or piloting direct contracting arrangements, aiming to capture savings previously retained by insurers.
Wellness and Preventative Care Programs
The growing emphasis on wellness and preventative care programs by employers and healthcare systems presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional health insurance. These initiatives aim to reduce overall healthcare utilization and costs by managing chronic conditions and promoting healthier lifestyles.
For instance, a 2024 report indicated that companies investing in comprehensive wellness programs saw an average reduction of 10% in employee healthcare claims. This shift means individuals and organizations may rely less on insurance to cover routine health needs, as proactive measures become more effective and accessible.
- Reduced Demand for Traditional Insurance: As preventative care becomes more robust, the perceived need for extensive insurance coverage for common health issues diminishes.
- Employer-Sponsored Wellness: Many employers are enhancing their wellness offerings, including health coaching and chronic disease management tools, directly impacting insurance utilization.
- Cost Savings Drive Adoption: The clear cost-saving potential for both individuals and employers encourages the adoption of these substitute programs over solely relying on insurance payouts.
- Focus on Health Outcomes: The shift is towards managing health proactively rather than reactively, making insurance a less central component for everyday health management.
Cash-Pay and Direct Primary Care Models
Cash-pay and direct primary care (DPC) models present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional insurance, particularly for routine medical services. These alternatives allow consumers to pay directly for care, bypassing insurance for predictable, lower-cost needs. For instance, DPC practices often offer monthly membership fees for unlimited primary care visits, with some reporting patient growth in the double digits annually.
While not a complete replacement for comprehensive health insurance, these models can diminish the perceived value of traditional plans for certain segments of the population. This is especially true for individuals seeking straightforward care without complex billing or deductibles. By offering transparent pricing and direct access, these models appeal to consumers looking for simpler healthcare solutions.
The market for these alternative models is expanding. In 2024, estimates suggest the DPC market in the US could reach several billion dollars, driven by patient demand for more accessible and affordable primary care. This trend directly challenges the necessity of traditional insurance for a portion of healthcare expenditures, forcing insurers to adapt their offerings.
- Growing patient adoption: Direct primary care models are seeing increased patient enrollment, with some practices reporting 15-20% annual growth in patient numbers.
- Cost transparency: Cash-pay and DPC models offer clear pricing, often through monthly membership fees, making healthcare costs more predictable for consumers.
- Market expansion: The US DPC market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, potentially reaching several billion dollars in value by 2024, indicating a significant shift in healthcare consumption.
- Reduced reliance on traditional insurance: For routine and predictable medical needs, these alternatives can lessen the perceived value and necessity of traditional insurance plans for a segment of the population.
The threat of substitutes for IHC Group's offerings is substantial, driven by evolving healthcare consumption patterns and a desire for cost control. Employer self-funding, government programs like Medicare Advantage, direct contracting with providers, and direct primary care models all present viable alternatives that can siphon demand from traditional fully insured health plans. These substitutes are gaining traction as individuals and employers seek greater flexibility, transparency, and cost savings in managing healthcare expenses.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on IHC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employer Self-Funding | Employer assumes risk, often with stop-loss insurance. | Increasing adoption by employers of all sizes seeking cost control. | Reduces market share for fully insured products. |
| Government Programs (Medicare Advantage) | Publicly funded health coverage options. | Enrollment reached ~31.7 million beneficiaries in 2024. | Captures a significant portion of the eligible population. |
| Direct Contracting/AHPs | Bypassing traditional insurers for direct provider agreements. | Notable percentage of large employers exploring/piloting in 2024. | Challenges insurer's role and potential revenue streams. |
| Direct Primary Care (DPC) | Membership-based primary care, often cash-pay. | US DPC market projected to reach several billion dollars in 2024. | Diminishes need for insurance for routine primary care. |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector, particularly health and life insurance, demands significant capital reserves to ensure solvency and meet policyholder obligations. For instance, in 2024, many jurisdictions require insurers to maintain capital adequacy ratios well above 100%, with some exceeding 200% depending on the risk profile of their business. This necessitates substantial upfront investment.
Furthermore, new entrants must navigate a labyrinth of complex regulatory frameworks governing licensing, product approval, consumer protection, and financial reporting across various states and countries. Compliance with these intricate rules, which are constantly evolving, adds considerable operational costs and time delays, acting as a formidable barrier.
These high financial and legal barriers significantly limit the threat of new companies easily entering the market. Establishing a reputable and compliant insurance operation requires not only vast financial resources but also deep expertise in regulatory affairs, making it challenging for newcomers to compete effectively with established players like The IHC Group.
Established insurers like IHC Group have cultivated strong brand recognition and deep consumer trust over many years. This is a significant barrier for new entrants, as building that same level of credibility in a sector focused on financial security and health takes considerable time and investment.
For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates for established insurance providers often exceed 85%, demonstrating the loyalty built through consistent service and brand presence. New companies must overcome this inertia, often requiring substantial marketing budgets and a proven track record to even begin to compete for market share.
While the insurance industry traditionally boasts high capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles, the rise of Insurtech presents a significant threat of new entrants. These innovative companies are effectively leveraging advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and sophisticated data analytics to build entirely new business models, optimize operational efficiency, and deliver highly personalized insurance products. For instance, in 2024, Insurtech funding continued to be robust, with significant investments flowing into startups focused on AI-driven underwriting and digital customer acquisition, signaling their growing capacity to challenge established players.
Distribution Channel Access
Gaining access to effective distribution channels presents a significant barrier for new entrants in the insurance industry. Established players have cultivated robust networks of agents, brokers, and direct-to-consumer platforms, creating a formidable hurdle for newcomers seeking market entry and efficient scaling. For instance, in 2023, direct distribution channels accounted for a substantial portion of insurance sales, with digital channels alone seeing a continued rise in adoption, making it harder for new companies without established online presences to compete.
- Established Networks: Incumbents benefit from long-standing relationships with distribution partners, providing them with preferential access and terms.
- Customer Trust: Existing brands often carry greater customer trust, making it easier for them to attract and retain policyholders through their established channels.
- Cost of Entry: Building a comparable distribution infrastructure requires substantial investment in technology, marketing, and personnel, a capital-intensive undertaking for new entrants.
Data and Experience Advantage of Incumbents
Incumbent insurers, like The IHC Group, benefit significantly from a substantial historical data advantage. This vast repository of claims data and actuarial experience is invaluable for precise risk assessment and competitive pricing, a hurdle for newcomers.
New entrants typically lack this deep data pool, making it challenging to develop insurance products that are both profitable and appealing to customers. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continues to rely heavily on sophisticated data analytics, with companies that have decades of data often demonstrating superior underwriting accuracy compared to those with limited historical information.
- Data Depth: Established insurers possess decades of granular claims data, crucial for actuarial modeling.
- Experience Gap: New entrants struggle to replicate the actuarial expertise built over many years.
- Pricing Disadvantage: Incumbents can price more accurately due to their data-rich history, creating a barrier for new, less informed pricing strategies.
- Risk Assessment: The ability to accurately predict and price risk is directly tied to the quality and quantity of historical data available.
The threat of new entrants for The IHC Group is generally moderate due to significant barriers like high capital requirements and complex regulations, demanding substantial upfront investment and regulatory expertise. Established brand loyalty, with customer retention rates often exceeding 85% in 2024, further solidifies the position of incumbents, requiring newcomers to invest heavily in marketing and building trust.
However, the burgeoning Insurtech sector, fueled by robust 2024 funding for AI and data analytics startups, poses a growing challenge by introducing innovative business models and efficient operations. Access to established distribution channels, critical for market penetration as highlighted by the significant role of direct sales in 2023, also presents a considerable hurdle for new companies.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for solvency and regulatory compliance. | Capital adequacy ratios often exceed 100-200%. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, product approval, and consumer protection laws. | Navigating evolving state and country-specific regulations. |
| Brand Recognition & Trust | Difficult to replicate established customer loyalty. | Customer retention rates for incumbents often >85%. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to agent, broker, and digital networks is challenging. | Digital channels saw continued adoption in 2023 insurance sales. |
| Historical Data Advantage | Lack of deep data hinders accurate risk assessment and pricing. | Companies with decades of data show superior underwriting accuracy. |
| Insurtech Innovation | AI and data analytics enable new, efficient business models. | Strong Insurtech funding in AI-driven underwriting. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The IHC Group is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor relations materials. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and data from financial databases to provide a thorough assessment of the competitive landscape.
